Thermal and Flammability Analysis of Polyurethane Foams with Solid and Liquid Flame Retardants: Comparative Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Production of Rigid Polyurethane Foam
2.2. Flame Retardants Applied to RPUFs
2.3. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Foaming Process of Foams
3.2. Physical and Thermal Properties of Foams
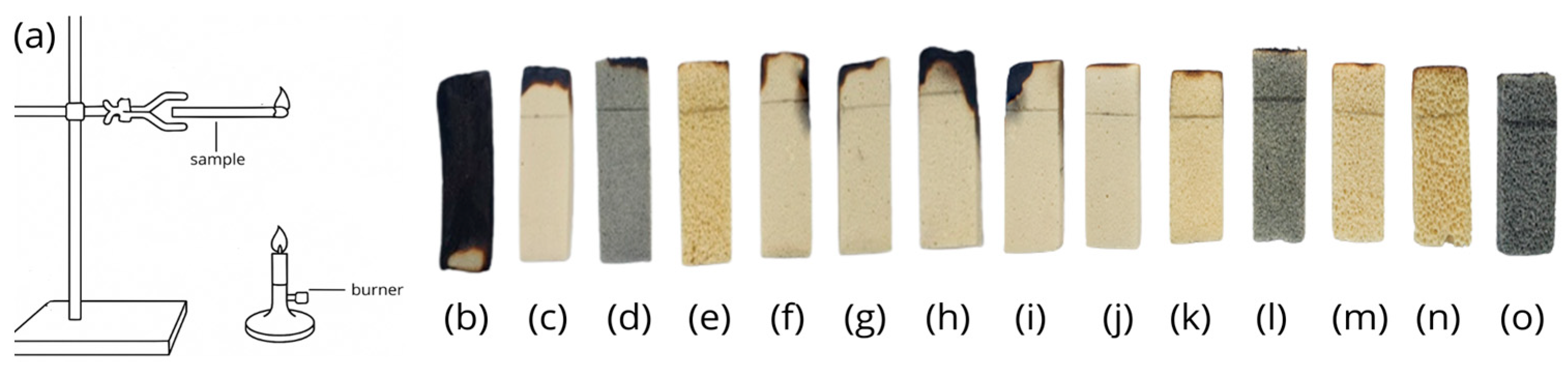
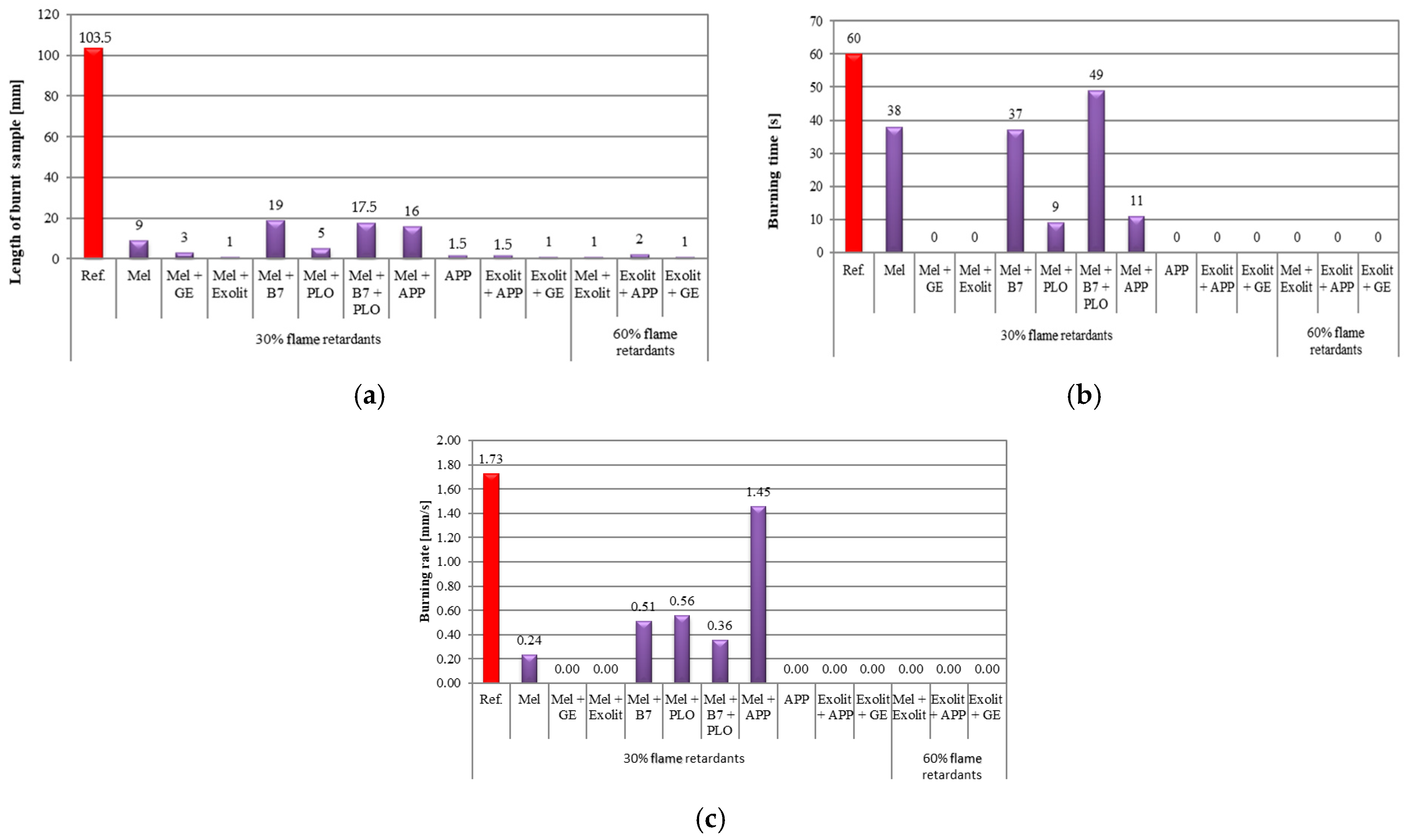
3.3. Foam Flammability Tests
3.4. UL-94 Flammability Test in a Chamber
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RPUF | rigid polyurethane foam |
| REF | reference sample |
| MEL | melamine |
| EG | expanded graphite |
| APP | ammonium polyphosphate |
| TGA | thermogravimetric analysis |
| UL-94 | Underwriters Laboratories 94 |
| LOI | limiting oxygen index |
| FR | flame retardant |
| HRR | heat release rate |
| pHRR | peak heat release rate |
| EHC | effective heat of combustion |
| THR | total heat release |
| TTF | time to flameout |
| TTI | time to ignition |
| PLM | percentage mass loss |
| MLR | mass loss rate |
References
- Zhang, T.; Lin, C.; Li, J.; Li, Y.-J.; Xu, S. Fabricating coconut palm-based rigid polyurethane foam with enhanced compressive strength using biomass waste. Polymer 2024, 310, 127472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.X.; Zhao, H.B.; Rao, W.H.; Huang, S.C.; Wang, T.; Liao, W.; Wang, Y.Z. Inherently flame-retardant rigid polyurethane foams with excellent thermal insulation and mechanical properties. Polymer 2018, 153, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.T.T.; Deshan, A.D.K.; Doherty, W.; Rackemann, D.; Moghaddam, L. Production of rigid bio-based polyurethane foams from sugarcane bagasse. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 188, 115578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrzewska, P.; Zygmunt-Kowalska, B.; Kuźnia, M.; Głowacz-Czerwonka, D.; Oleksy, M.; Sieradzka, M. Eco-Friendly Polyurethane Foams Enriched with Waste from the Food and Energy Industries. Energies 2024, 17, 3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Michel, F.; Chazeau, L.; Cavaillé, J.Y.; Chabert, E. Mechanical properties of high density polyurethane foams: I. Effect of the density. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 2700–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, K.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, T.; Weng, B.; Wu, S.; Huang, A.; Su, N.; Guo, Y. Properties of two-variety natural luffa sponge columns as potential mattress filling materials. Materials 2018, 11, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, X.; Jiang, H.; Su, X.; Zhang, X.; Zou, M. Study on the Mechanical Properties and Energy Absorbing Capability of Polyurethane Microcellular Elastomers under Different Compressive Strain Rates. Polymers 2023, 15, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Issa, A.; Elshaer, A. A Comprehensive Review and Recent Trends in Thermal Insulation Materials for Energy Conservation in Buildings. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirpluks, M.; Cabulis, U.; Avots, A. Flammability of Bio-Based Rigid Polyurethane Foam as Sustainable Thermal Insulation Material. In Insulation Materials in Context of Sustainability; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, S.T.; Hull, T.R. The fire toxicity of polyurethane foams. Fire Sci. Rev. 2016, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 13501-1; Standard for Fire Classification of Construction Materials: Overview of Performance Classes & Criteria. CEN: Brussels, Belgium, 2018.
- Sadaoui, A.; Dagenais, C.; Blanchet, P. A Comparative Study of Fire Code Classifications of Building Materials. Fire 2024, 7, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chu, F.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Qian, L.; Hu, Y.; Wang, B.; Hu, W. The improvement of fire safety performance of flexible polyurethane foam by Highly-efficient P-N-S elemental hybrid synergistic flame retardant. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 606, 768–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, L.H.; Nguyen, N.T.; Nguyen, D.M.; Nguyen, T.A.; Nguyen, T.B.; Suhr, J.; Nguyen, T.D.; Rahim, M.; Tran-Le, A.D.; Terrei, L. Effective non-halogen flame-retardants combined with nSiO2 particles to improve thermal stability and fire resistance of high-performance polyurethane nanocomposite foams. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 203, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, W.; Xu, L. Recent Advances in Flame-Retardant Flexible Polyurethane Foams. Fire 2025, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, M.; Lehmann, M.; Meyer, M. Phosphorous-Based, Halogen-Free Flame Retardants for Thin, Flexible Polyurethane Artificial Leathers. Polymers 2025, 17, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, Y.Y.; Schartel, B. It Takes Two to Tango: Synergistic Expandable Graphite—Phosphorus Flame Retardant Combinations in Polyurethane Foams. Polymers 2022, 14, 2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, R.; Qu, B. Expandable graphite systems for halogen-free flame-retarding of polyolefins. I. Flammability characterization and synergistic effect. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 80, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, X.; Liu, D. Physicochemical Mechanism of Flame-Retardant Enhancement for Elastomeric Polyurea: A Mini-Review. J. Polym. Sci. 2025, 63, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Liang, J.; Lin, X.; Lin, H.; Yu, J.; Wang, S. The flame-retardant mechanisms and preparation of polymer composites and their potential application in construction engineering. Polymers 2022, 14, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, F.; Zhang, T.; Deng, J.; Zhang, L.; Bai, Z.; Pan, J. Effect of Melamine-Modified Zinc Phytate on the Flame Retardancy and Smoke Suppression of Silicone Rubber Foams. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2025, 142, e57018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PN EN ISO 845:2010; Cellular Plastics and Rubbers—Determination of Apparent Density. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2013.
- PN-EN ISO 3582:2002; Flexible Cellular Polymeric Materials—Laboratory Assessment of Horizontal Burning Characteristics of Small Specimens Subjected to a Small Flame. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2013.
- ISO 4589-3:2017; Plastics—Determination of Burning Behaviour by Oxygen Index Part 3: Elevated-Temperature Test. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- ISO 13927:2023; Plastics—Simple Heat Release Test Using a Conical Radiant Heater and a Thermopile Detector. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- EN 60695-11-10; Fire Hazard Testing—Part 11-10: Test Flames—50 W Horizontal and Vertical Flame Test Methods. European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2013.
- Parcheta-Szwindowska, P.; Habaj, J.; Krzemińska, I.; Datta, J. A Comprehensive Review of Reactive Flame Retardants for Polyurethane Materials: Current Development and Future Opportunities in an Environmentally Friendly Direction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayarama Krishna, J.V.; Srivatsa Kumar, S.; Korobeinichev, O.P.; Vinu, R. Detailed kinetic analysis of slow and fast pyrolysis of poly(methyl methacrylate)-Flame retardant mixtures. Thermochim. Acta 2020, 687, 178545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdu, J.; Zoller, A.; Marcilla, A. Plastisol gelation and fusion rheological aspects. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 2840–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, M.; Wan, C. Density effect on flame retardancy, thermal degradation, and combustibility of rigid polyurethane foam modified by expandable graphite or ammonium polyphosphate. Polymers 2019, 11, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, M.S.; Hussain, S.; Khattri, S.; Usman, K.; Sawlani, K.K. A Comprehensive Guide to the Relationship Between QOL and Socio-Demographic Profile. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2024, 84, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuźnia, M.; Magiera, A.; Pielichowska, K.; Ziąbka, M.; Benko, A.; Szatkowski, P.; Jerzak, W. Fluidized bed combustion fly ash as filler in composite polyurethane materials. Waste Manag. 2019, 92, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Głowacz-Czerwonka, D.; Zakrzewska, P.; Oleksy, M.; Pielichowska, K.; Kuźnia, M.; Telejko, T. The influence of biowaste-based fillers on the mechanical and fire properties of rigid polyurethane foams. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2023, 36, e00610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuźnia, M.; Zakrzewska, P.; Szajding, A.; Zygmunt-Kowalska, B.; Kairytė, A.; Šeputytė-Jucikė, J.; Boris, R.; Balčiūnas, G. Microspheres as a stabilizing element in polyurethane-cork composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 469, 140491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misnon, M.I.; Islam, M.M.; Epaarachchi, J.A.; Chen, H.; Goda, K.; Khan, M.T.I. Flammability characteristics of chemical treated woven hemp fabric reinforced vinyl ester composites. Sci. Technol. Mater. 2018, 30, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrzewska, P.; Zygmunt-Kowalska, B.; Pielichowska, K.; Nowicka-Dunal, K.; Telejko, T.; Kuźnia, M. Effect of the silanization process on the fire resistance and thermal properties of closed-cell foams with sunflower husk ash. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 218, 118941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zygmunt-Kowalska, B.; Pielichowska, K.; Trestka, P.; Ziąbka, M.; Kuźnia, M. The Effect of Ash Silanization on the Selected Properties of Rigid Polyurethane Foam/Coal Fly Ash Composites. Energies 2022, 15, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Diao, S. Flame retardance of leather with flame retardant added in retanning process. Results Phys. 2019, 15, 102717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Członka, S.; Strąkowska, A.; Strzelec, K.; Kairytė, A.; Kremensas, A. Melamine, silica, and ionic liquid as a novel flame retardant for rigid polyurethane foams with enhanced flame retardancy and mechanical properties. Polym. Test. 2020, 87, 106511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Feng, F.; Tang, S. Bi-phase flame-retardant effect of hexa-phenoxy-cyclotriphosphazene on rigid polyurethane foams containing expandable graphite. Polymer 2014, 55, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Description | Substrates | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rokopol RF 551 | Flame Retardant [g] | TEA [g] | L900 [g] | Water [%] | MDI [g] | ||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |||||||
| Ref | Reference foam | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.66 | 0.14 | 2 | 197 |
| Mel | Foam with 30 wt.% melamine added | 100 | 30 | 0 | 0 | 0.66 | 0.14 | 2 | 197 |
| Mel + GE | Foam containing 15 wt.% melamine and 15 wt.% expanded graphite 290 | 100 | 15 | 15 | 0 | 0.66 | 0.14 | 2 | 197 |
| Mel + Exolit | Foam containing 15 wt.% melamine and 15 wt.% Exolit OP 935 | 100 | 15 | 15 | 0 | 0.66 | 0.14 | 2 | 197 |
| Mel + B7 | Foam containing 15 wt.% melamine and 15 wt.% Roflam B7 | 100 | 15 | 15 | 0 | 0.66 | 0.14 | 2 | 197 |
| Mel + PLO | Foam containing 15 wt.% melamine and 15 wt.% Roflam PLO | 100 | 15 | 15 | 0 | 0.66 | 0.14 | 2 | 197 |
| Mel + B7 + PLO | Foam containing 10 wt.% added melamine, 10 wt.% Roflam B7, and 10% Roflam PLO | 100 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 0.66 | 0.14 | 2 | 197 |
| Mel + APP | Foam containing 15 wt.% melamine and 15 wt.% ammonium polyphosphate | 100 | 15 | 15 | 0 | 0.66 | 0.14 | 2 | 197 |
| APP | Foam containing 15 wt.% ammonium polyphosphate | 100 | 30 | 0 | 0 | 0.66 | 0.14 | 2 | 197 |
| Exolit + APP | Foam containing 15 wt.% of Exolit OP 935 and 15 wt.% of ammonium polyphosphate | 100 | 15 | 15 | 0 | 0.66 | 0.14 | 2 | 197 |
| Exolit + GE | Foam containing 15 wt.% Exolit OP 935 and 15 wt.% expanded graphite EG 290 | 100 | 15 | 15 | 0 | 0.66 | 0.14 | 2 | 197 |
| Mel + Exolit (60 wt.%) | Foam with 30 wt.% melamine and 30 wt.% Exolit OP 935 | 100 | 30 | 30 | 0 | 0.66 | 0.14 | 2 | 197 |
| Exolit + APP (60 wt.%) | Foam containing 30 wt.% Exolit OP 935 and 30 wt.% ammonium polyphosphate | 100 | 30 | 30 | 0 | 0.66 | 0.14 | 2 | 197 |
| Exolit + GE (60 wt.%) | Foam containing 30 wt.% Exolit OP 935 and 30 wt.% expanded graphite EG 290 | 100 | 30 | 30 | 0 | 0.66 | 0.14 | 2 | 197 |
| Sample | Apparent Density [kg·m−3] |
|---|---|
| Ref | 64.2 |
| Mel | 65.7 |
| Mel + GE | 67.8 |
| Mel + Exolit | 62.1 |
| Mel + B7 | 65.4 |
| Mel + PLO | 65.9 |
| Mel + B7 + PLO | 64.4 |
| Mel + APP | 73.7 |
| APP | 71.5 |
| Exolit + APP | 69.1 |
| Exolit + GE | 66.8 |
| Mel + Exolit (60%) | 75.3 |
| Exolit + APP (60%) | 75.7 |
| Exolit + GE (60%) | 73.2 |
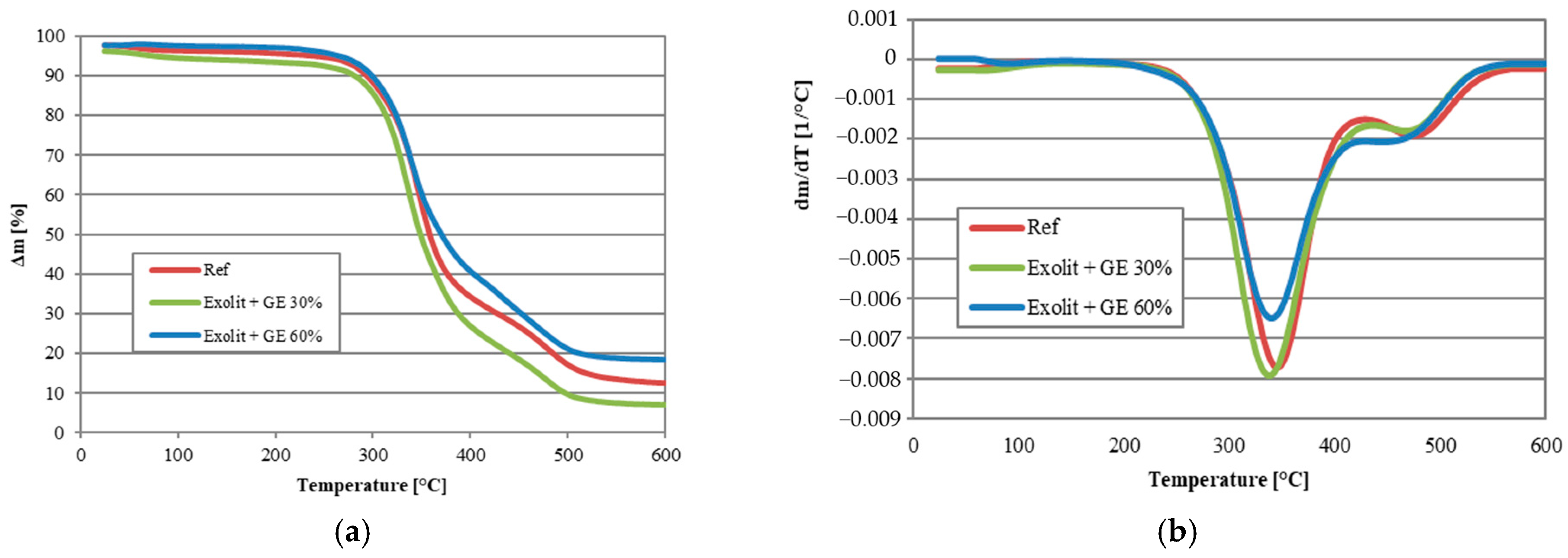
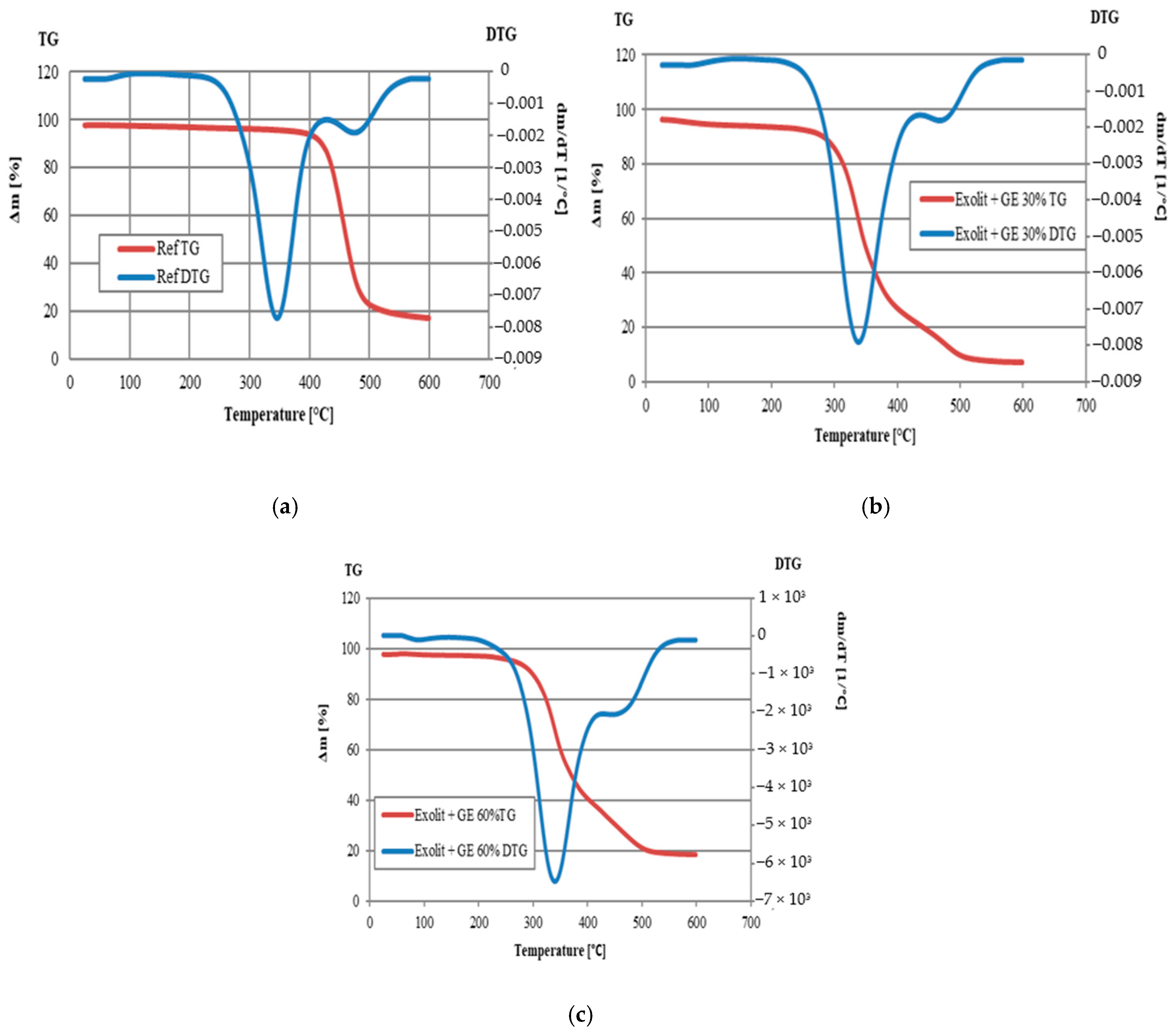
| Sample | T5% [°C] | T10% [°C] | T15% [°C] | T20% [°C] | T50% [°C] | Residue at 600 °C [wt.%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref | 234 | 293 | 310 | 321 | 358 | 12.62 |
| Exolit + GE 30% | 110 | 282 | 302 | 313 | 348 | 7.00 |
| Exolit + GE 60% | 263 | 298 | 313 | 324 | 370 | 18.56 |
| Sample | LOI [vol.%] | |
|---|---|---|
| Ref | 18.70 |  |
| Mel | 21.00 | |
| Mel + GE | 21.50 | |
| Mel + Exolit | 22.40 | |
| Mel + B7 | 20.30 | |
| Mel + PLO | 21.00 | |
| Mel + B7 + PLO | 21.20 | |
| Mel + APP | 20.70 | |
| APP | 21.20 | |
| Exolit + APP | 21.70 | |
| Exolit + GE | 25.10 | |
| Mel + Exolit (60 wt.%) | 24.20 | |
| Exolit + APP (60 wt.%) | 23.90 | |
| Exolit + GE (60 wt.%) | 29.80 |
| Sample | HRR [kW/m2] | pHRR [kW/m2] | THR [MJ/m2] | EHC [MJ/kg] | TTI [s] | TTF [s] | PLM [wt.%] | MLR [g/s] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref | 95.00 | 90.76 | 13.00 | 8.05 | 13 | 215 | 82.50 | 0.070 |
| Mel | 40.62 | 56.19 | 10.70 | 9.32 | 5 | 261 | 69.50 | 0.038 |
| Mel + GE | 23.34 | 37.27 | 7.70 | 7.57 | 6 | 327 | 5.30 | 0.027 |
| Exolit + APP | 65.14 | 88.81 | 13.50 | 8.77 | 13 | 219 | 81.40 | 0.065 |
| Mel + B7 + PLO | 19.02 | 45.33 | 7.90 | 6.33 | 12 | 400 | 68.30 | 0.026 |
| Exolit + GE | 25.00 | 41.01 | 8.10 | 7.01 | 7 | 322 | 64.80 | 0.031 |
| Mel + Exolit (60%) | 62.20 | 88.53 | 11.0 | 7.52 | 14 | 187 | 74.00 | 0.072 |
| Exolit + APP (60%) | 55.57 | 69.39 | 9.90 | 7.29 | 11 | 186 | 77.20 | 0.067 |
| Exolit + GE (60%) | 13.98 | 35.55 | 4.60 | 5.87 | 8 | 313 | 39.30 | 0.021 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Głowacz-Czerwonka, D.; Zakrzewska, P.; Zygmunt-Kowalska, B.; Zarzyka, I. Thermal and Flammability Analysis of Polyurethane Foams with Solid and Liquid Flame Retardants: Comparative Study. Polymers 2025, 17, 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141977
Głowacz-Czerwonka D, Zakrzewska P, Zygmunt-Kowalska B, Zarzyka I. Thermal and Flammability Analysis of Polyurethane Foams with Solid and Liquid Flame Retardants: Comparative Study. Polymers. 2025; 17(14):1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141977
Chicago/Turabian StyleGłowacz-Czerwonka, Dorota, Patrycja Zakrzewska, Beata Zygmunt-Kowalska, and Iwona Zarzyka. 2025. "Thermal and Flammability Analysis of Polyurethane Foams with Solid and Liquid Flame Retardants: Comparative Study" Polymers 17, no. 14: 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141977
APA StyleGłowacz-Czerwonka, D., Zakrzewska, P., Zygmunt-Kowalska, B., & Zarzyka, I. (2025). Thermal and Flammability Analysis of Polyurethane Foams with Solid and Liquid Flame Retardants: Comparative Study. Polymers, 17(14), 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141977









