Enhanced Mechanical and Thermal Performance of Sustainable RPET/PA-11/Joncryl® Nanocomposites Reinforced with Halloysite Nanotubes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Extrusion Processing
2.3. Injection Moulding and HNT Nanocomposite Formulations
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FTIR Analysis of Halloysite Nanocomposites
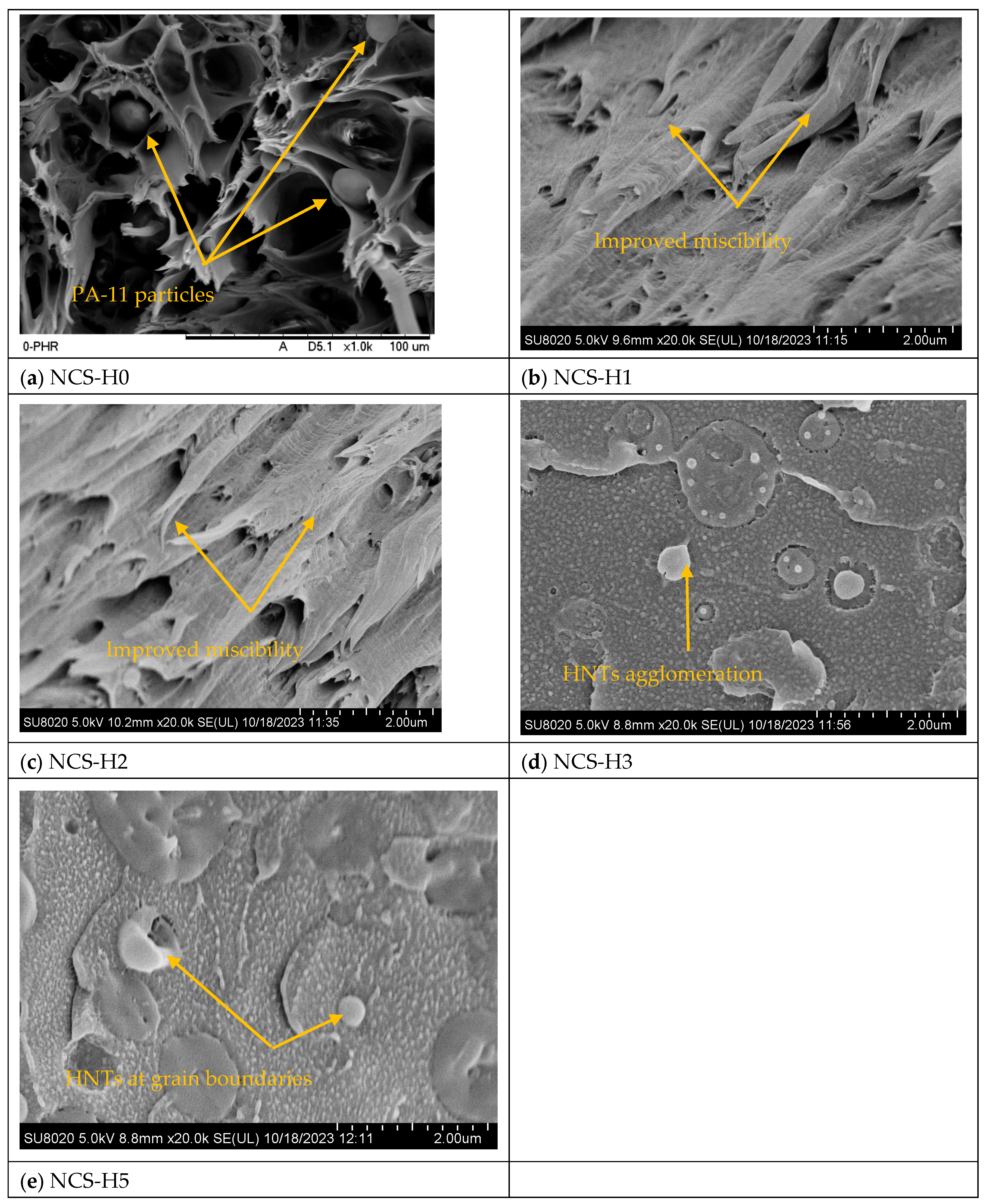
3.2. Morphology of HNT Nanocomposites
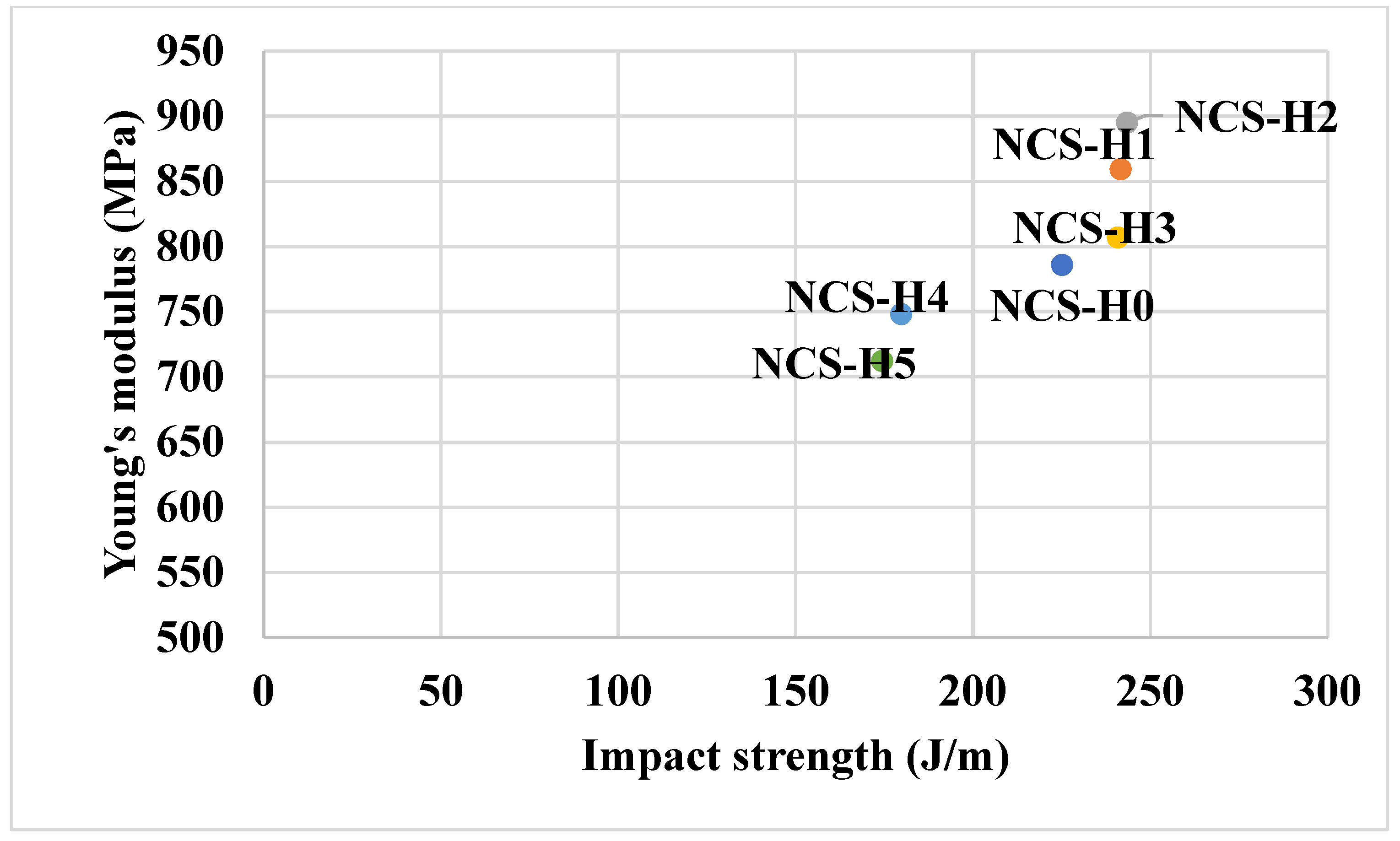
3.3. Tensile Testing of HNT Nanocomposites
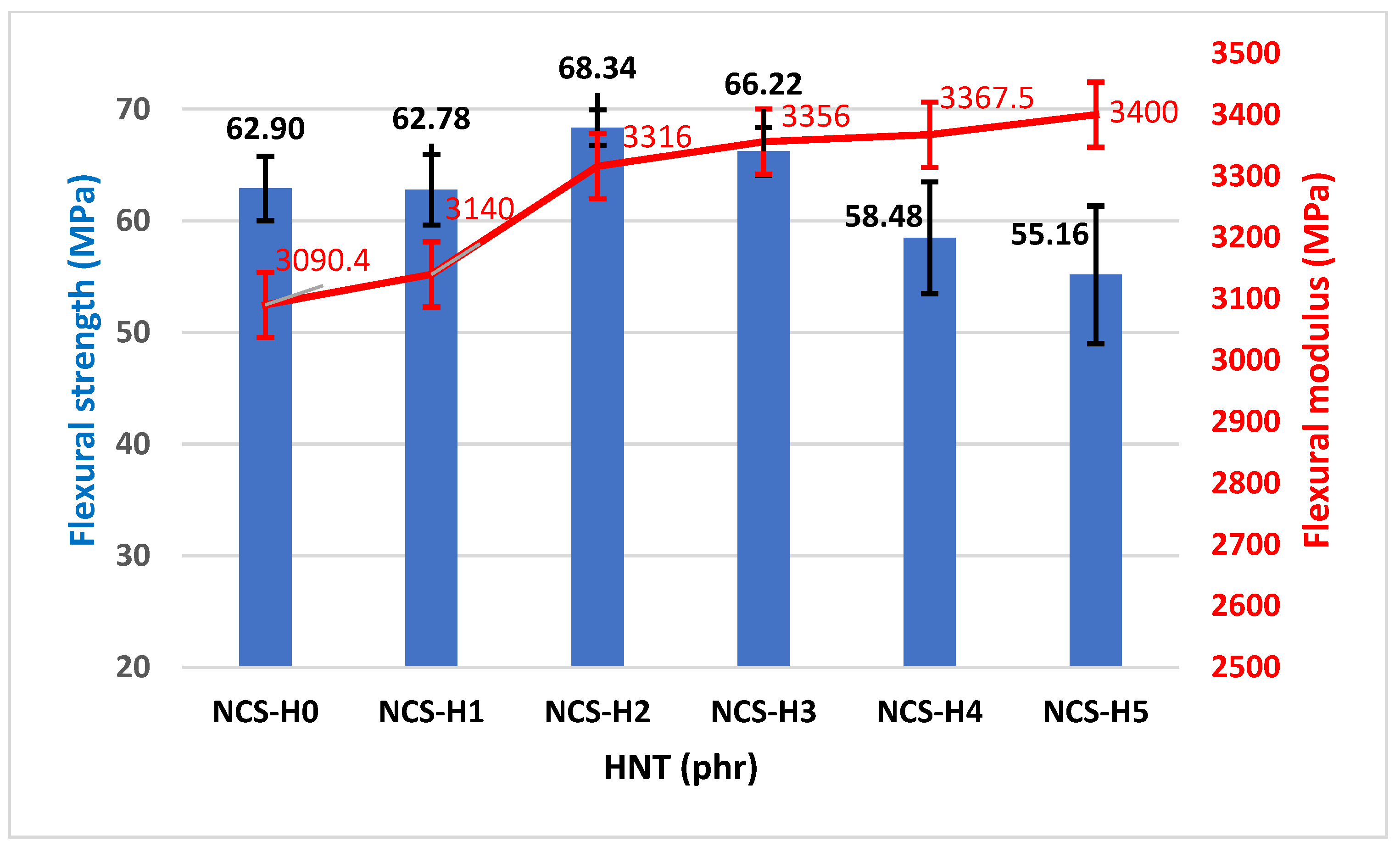
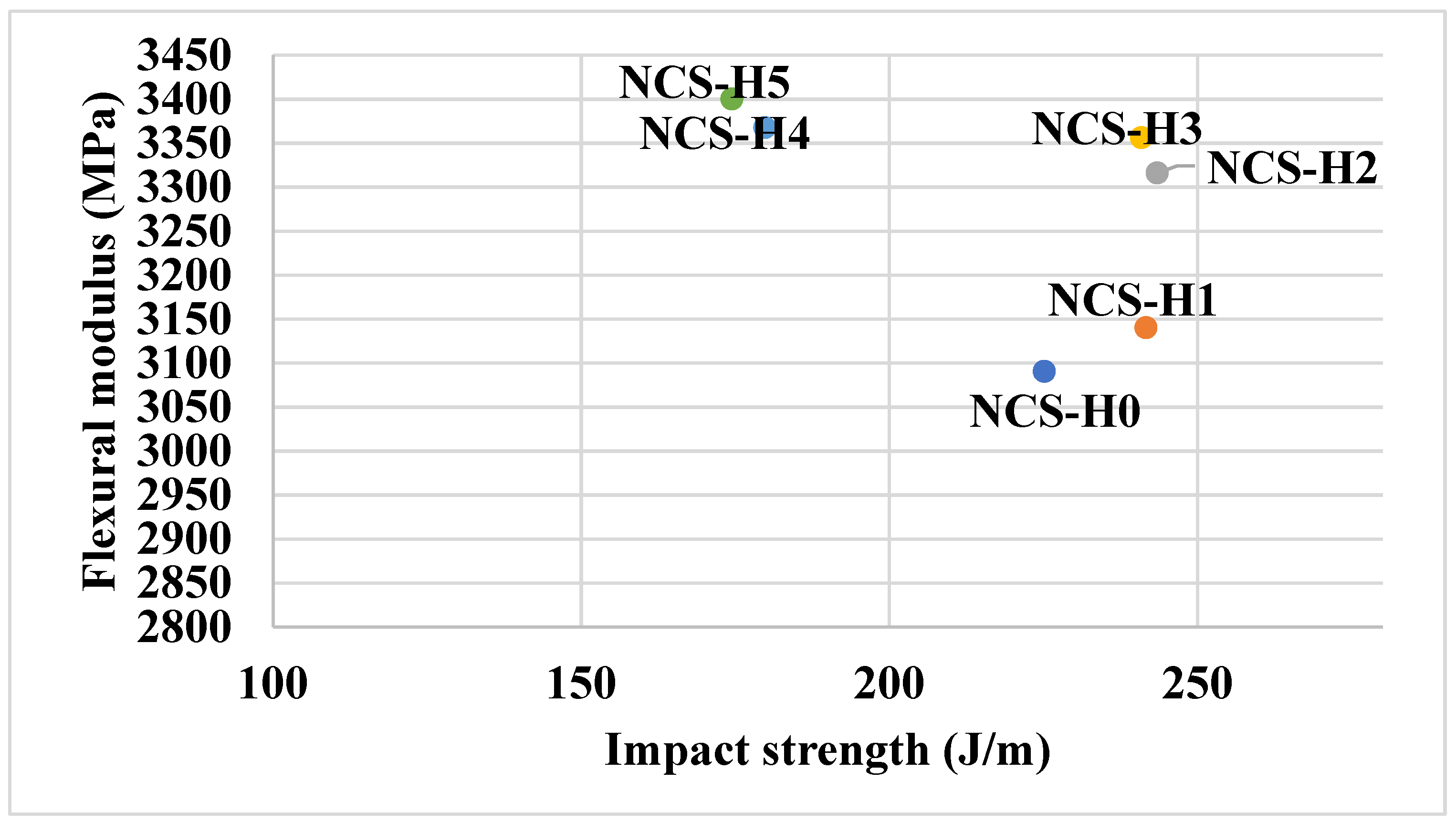
3.4. Flexural Properties of HNT Nanocomposites
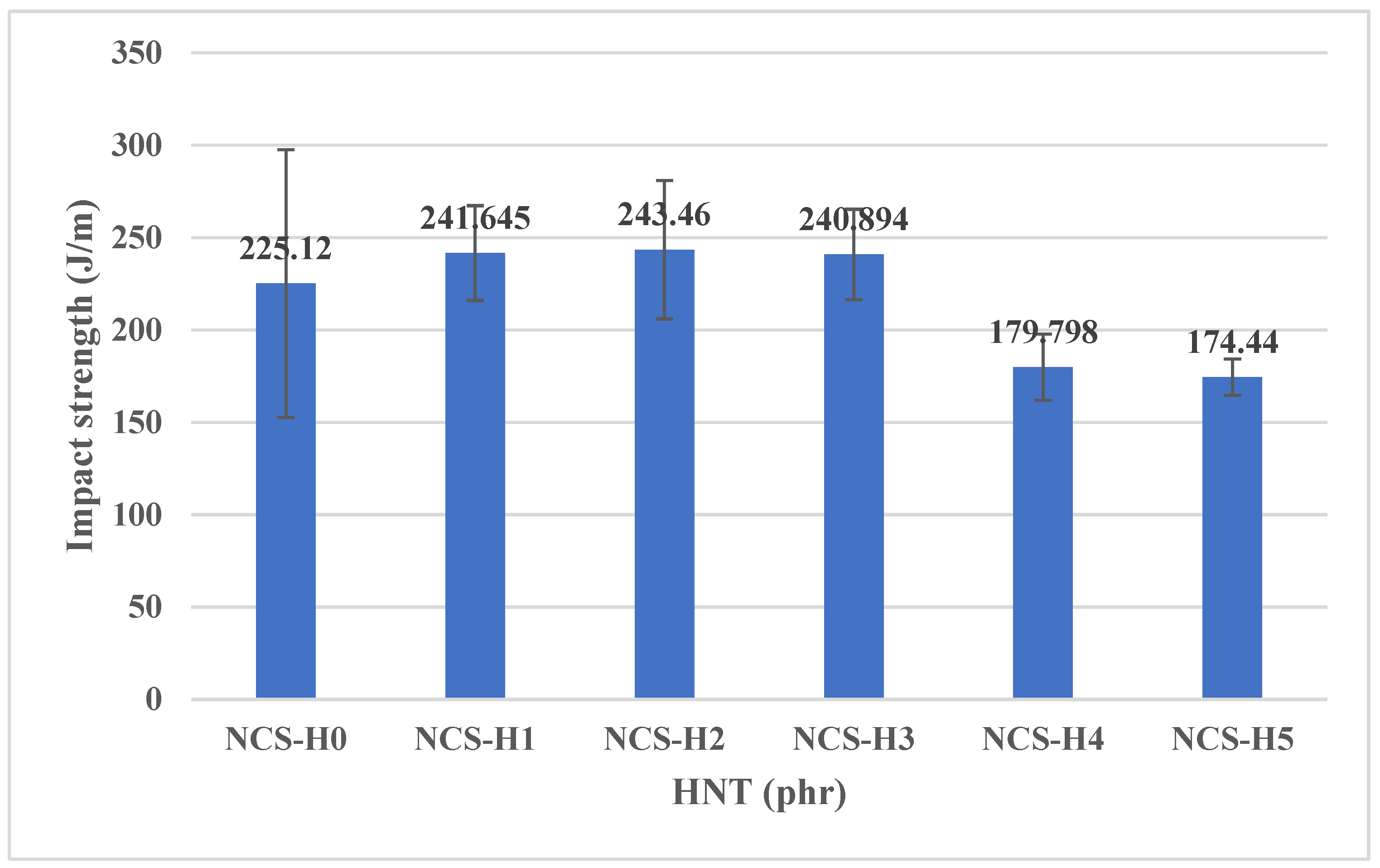
3.5. Impact Strength of HNT Nanocomposites
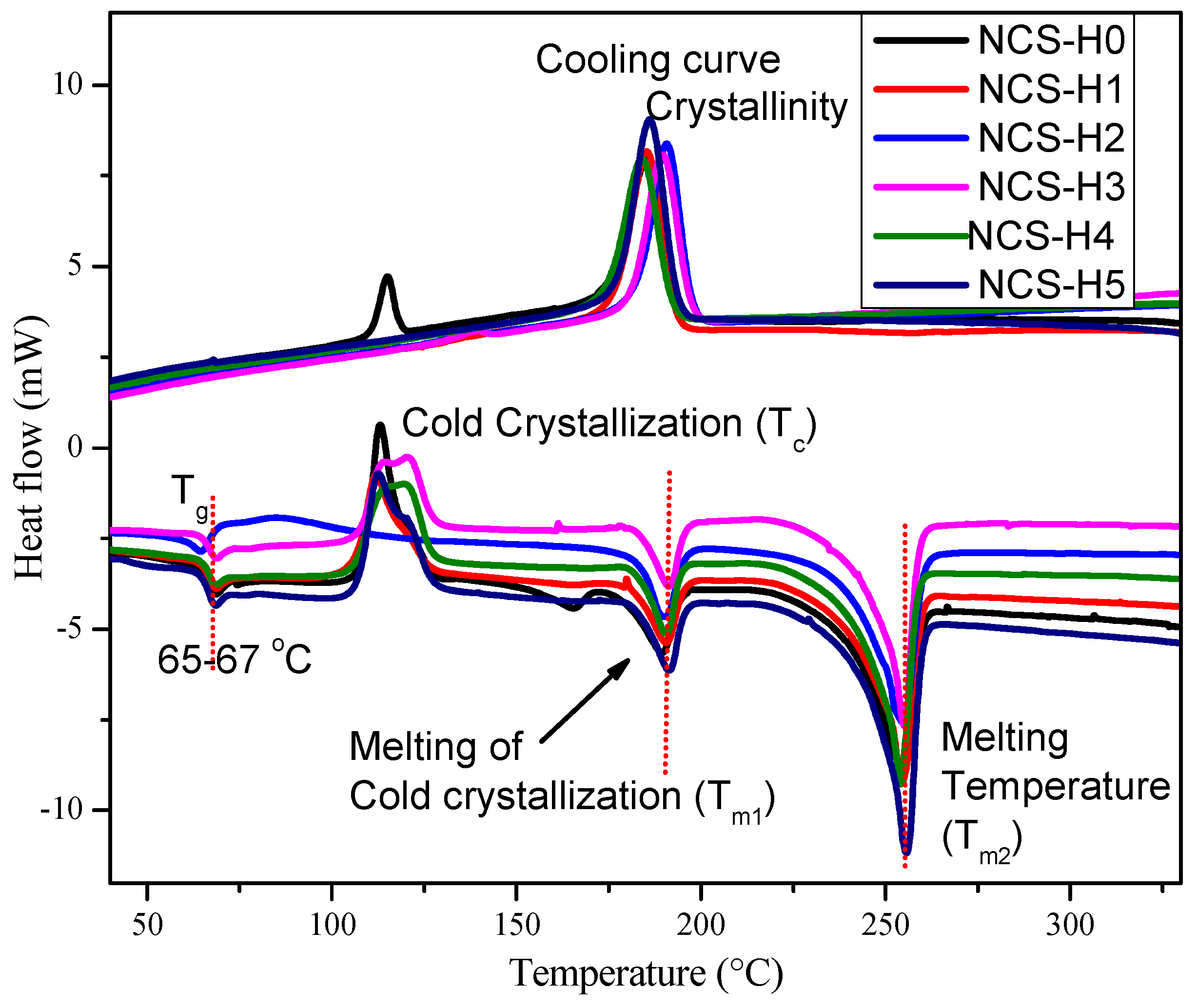
3.6. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
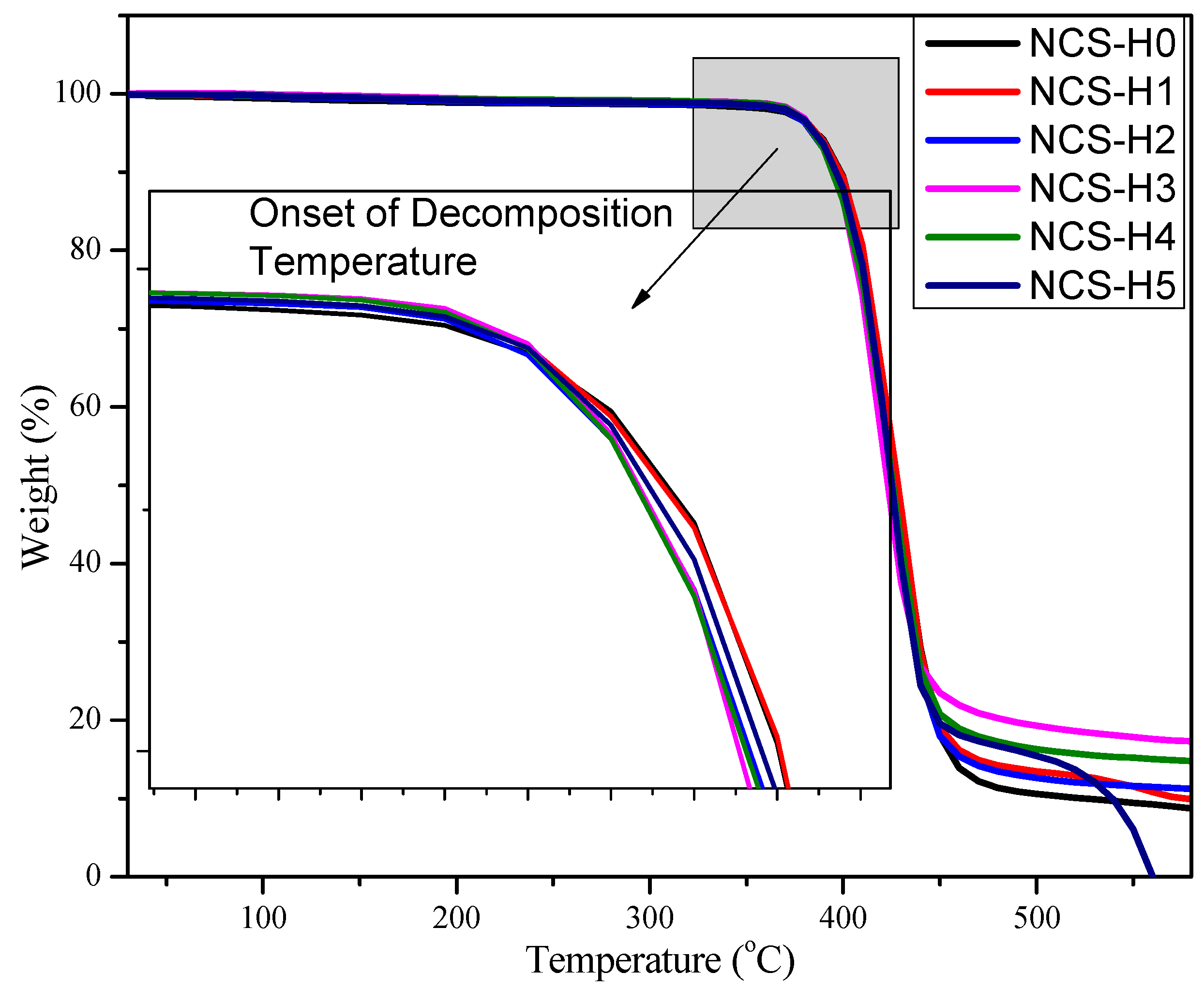
3.7. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
4. Conclusions
5. The Significance of the Study
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clifford, C.A.; Bard, D.; Castro, F.A.; Evans, G.S.; Gee, M.; Hall, S.; Kitchen, S.; Koltsov, D.; Price, A.; Smith, R.; et al. Safe and Sustainable Development of Advanced Materials: UK National Knowledge Sharing Network Workshops. Environ. Sci. Nano 2025, 12, 1858–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, A. Polymer Nanocomposites: A Review on Recent Advances in the Field of Green Polymer Nanocomposites. Curr. Nanosci. 2023, 20, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal Khan, Z.; Habib, U.; Binti Mohamad, Z.; Razak Bin Rahmat, A.; Amira Sahirah Binti Abdullah, N. Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Sepiolite Strengthened Thermoplastic Polymer Nanocomposites: A Comprehensive Review. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 975–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado-Colmenero, J.M.; La Rubia, M.D.; Mata-García, E.; Rodriguez-Santiago, M.; Martin-Doñate, C. Using Numerical-Experimental Analysis to Evaluate RPET Mechanical Behavior under Compressive Stresses and MEX Additive Manufacturing for New Sustainable Designs. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2023, 29, 98–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, M.A.; Ali, I.; Elleithy, R.H.; Al-Zahrani, S.M. Improvements in Barrier Properties of Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) Films Using Commercially Available High Barrier Masterbatch Additives via Melt Blend Technique. J. Plast. Film Sheeting 2013, 29, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, B.; Lorenz, G.; Kandelbauer, A. Recycling of Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate)—A Review Focusing on Chemical Methods. Express Polym. Lett. 2016, 10, 559–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotta, A.; Causa, A.; Salzano de Luna, M.; Ambrogi, V.; Filippone, G. Tuning the Morphology of HDPE/PP/PET Ternary Blends by Nanoparticles: A Simple Way to Improve the Performance of Mixed Recycled Plastics. Polymers 2022, 14, 5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schexnaydre, R.J.; Mitchell, B.S. Solid-State Blending of Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) with Polystyrene: Extent of Compatibilization and Its Dependence on Blend Composition. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2008, 48, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kit, F.M.; Haq, R.H.A.; Manshoor, B.; Ghafir, M.F.A.; Rahman, M.N.A.; Hoffmann, J.; Marwah, O.M.F.; Khirotdin, R.K. Mechanical Properties of Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate/Polycarbonate/Methylene Diphenyl Diisocyanate (r-PET/PC/MDI) Composite. J. Adv. Res. Appl. Mech. 2024, 120, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.-B.; Chen, R.; Lian, Y.-X.; Wu, W.-J.; Zhang, J.-H.; Fu, C.-X.; Sun, X.-L.; Xiao, L.-R. Recycled PET/PA6 Fibers from Waste Textile with Improved Hydrophilicity by In-Situ Reaction-Induced Capacity Enhancement. Polymers 2024, 16, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosmmi, N.H.; Khan, Z.I.; Mohamad, Z.; Majid, R.A.; Othman, N.; Man, S.H.; Karim, K.J. Impact strength and morphology of sustainably sourced recycling polyethylene terephthalate blends. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2021, 83, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, N.; Mohamad, Z.; Khan, Z.I.; Abdullah, L.C. Rheological Behavior of Recycled Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate)/Poly(Amide) 11 Blends with Chain Extender. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 110, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.I.; Mohamad, Z.B.; Rahmat, A.R.B.; Habib, U.; Abdullah, N.A.S.B. A Novel Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate/Polyamide 11 (RPET/PA11) Thermoplastic Blend. Prog. Rubber Plast. Recycl. Technol. 2021, 37, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeiro, A.; Teixeira, C.; Costa, H.; Coelho, J.F.J.; Serra, A.C. Recycling Polyethylene/Polyamide Multilayer Films with Poly(Isoprene-g-Maleic Anhydride) Compatibilizer. Polymers 2024, 16, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, Z.; Heuzey, M.C.; Randall, J.; Carreau, P.J. Enhanced Properties of Polylactide/Polyamide 11 Blends by Reactive Compatibilization. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 100, 2475–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.I.; Habib, U.; Mohamad, Z.B.; Tufail, A.; Raji, A.M.; Khan, A.U. Innovative Hybrid Nanocomposites of Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate/Polyamide 11 Reinforced with Sepiolite and Graphene Nanoplatelets. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2024, 38, 1063–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.R.d.M.; Henrique, M.A.; Luna, C.B.B.; Carvalho, L.H.d.; Almeida, Y.M.B.d. Influence of a Multifunctional Epoxy Additive on the Performance of Polyamide 6 and PET Post-Consumed Blends during Processing. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, S.; Jin, J.; Li, G. Effect of Copoly(Ester-Amide 6)(Pet-Pa6) on Compatibility of Pet/Pa6 Blended Fibers. Mater. Sci. Forum 2020, 993, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.I.; Habib, U.; Mohamad, Z.B.; Raji, A.M. Enhanced Mechanical Properties of a Novel Compatibilized Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate/Polyamide 11 (RPET/PA11) Blends. Express Polym. Lett. 2021, 15, 1206–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.I.; Habib, U.; Mohamad, Z.B.; Khan, I. Mechanical and Thermal Properties of a Newly Developed Sepiolite Filler-Filled RPET/PA11 Thermoplastic Nanocomposites. Results Eng. 2024, 21, 101731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, U.; Mohsin, M.E.A.; Khan, Z.I.; Mohamad, Z.; Othman, N.; Mousa, S.; Hossain, S.S.; Ali, S.S. Mechanical, Thermal, and Flammability Properties of Eco-Friendly Nanocomposites from Recycled PET/PA-11 Blends Reinforced with Graphene Nanoplatelets. Polymers 2025, 17, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Sun, S.; Liu, J.; Sun, X. Recent Advances of Halloysite Nanotubes in Biomedical Applications. Small 2024, 20, 2306169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Sabatini, C.; Chen, K.; Makowka, S.; Hu, R.; Swihart, M.; Cheng, C. Novel Polymer/Halloysite Composites with High Halloysite Content and Remarkable Mechanical Strength. RSC Appl. Interfaces 2025, 2, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abotaleb, A.; Gladich, I.; Mroue, K.; Abounahia, N.; Alkhateeb, A.; Al-Shammari, A.; Tong, Y.; Al-Masri, D.; Sinopoli, A. Impact of Thermal Treatment on Halloysite Nanotubes: A Combined Experimental-Computational Approach. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapčík, L.; Sepetcioǧlu, H.; Murtaja, Y.; Lapčíková, B.; Vašina, M.; Ovsík, M.; Staněk, M.; Gautam, S. Study of Mechanical Properties of Epoxy/Graphene and Epoxy/Halloysite Nanocomposites. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2023, 12, 20220520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, Y.; Munir, M.T.; Rhee, K.Y. Tensile Modulus of Polymer Halloysite Nanotubes Nanocomposites Assuming Stress Transferring through an Imperfect Interphase. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D-638; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014. [CrossRef]
- ASTM D790-17; Standard Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2002. [CrossRef]
- ASTM D256-10; Standard Test Methods for Determining the Izod Pendulum Impact Resistance of Plastics. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Habib, U.; Khan, Z.I.; Mohamad, Z.B. Compatibility and Miscibility of Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate/Polyamide 11 Blends with and without Joncryl® Compatibilizer: A Comprehensive Study of Mechanical, Thermal, and Thermomechanical Properties. Iran. Polym. J. 2024, 33, 1313–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, W.; Inoue, K.I.; Nihonyanagi, S.; Tahara, T. Unified Picture of Vibrational Relaxation of OH Stretch at the Air/Water Interface. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.E.; Vakili, M.; Kamounah, F.S.; Spanget-Larsen, J. NH Stretching Frequencies of Intramolecularly Hydrogen-Bonded Systems: An Experimental and Theoretical Study. Molecules 2021, 26, 7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshedi Dehaghi, F.; Aberoumand, M.; Sundararaj, U. A Promising Recycling Strategy via Processing Polypropylene/Recycled Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate): Reactive Extrusion Using Dual Compatibilizers. Polymers 2024, 16, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayeemasae, N.; Waesateh, K.; Masa, A.; Ismail, H. Halloysite Nanotubes Filled Natural Rubber Composites: Functionality, Crystallinity and Thermal Studies. J. Eng. Sci. 2019, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kelani, M.; Buthelezi, N. Advancements in Medical Research: Exploring Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy for Tissue, Cell, and Hair Sample Analysis. Ski. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, e13733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargahi, A.; Duncan, M.; Runka, J.; Hammami, A.; Wen, T.; Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Naguib, H.E. Low-Concentration Graphene Nanoplatelet/HDPE Nanocomposites with Enhanced Dispersion and Interfacial Bonding for Improved CO2 Barrier and Mechanical Performance at Elevated Temperatures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2025, 64, 5359–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Srivastava, A. Determination of Halloysite Reinforced/Epoxy Nanocomposite Impact Strength by Experimental and Computational Procedures. Evergreen 2024, 11, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrajabian, H.; Sadeghian, F. The Investigation of Alumina Nanoparticles’ Effects on the Mechanical and Thermal Properties of HDPE/RPET/MAPE Blends. Int. Nano Lett. 2019, 9, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franciszczak, P.; Taraghi, I.; Paszkiewicz, S.; Meljon, A.; Piesowicz, E.; Burzyński, M. Effect of Halloysite Nanotube on Mechanical Properties, Thermal Stability and Morphology of Polypropylene and Polypropylene/Short Kenaf Fibers Hybrid Biocomposites. Materials 2020, 13, 4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, Y.; Shamsuyeva, M.; Endres, H.J. Thermal and Mechanical Properties of the Recycled and Virgin PET—Part I. Polymers 2022, 14, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, M.; Tatarchuk, T.; Skórczewska, K.; Szulc, J.; Tomaszewska, J. The Effect of Silanized Halloysite Nanotubes on the Structure of Polyethylene–Based Composite. Materials 2024, 17, 3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, A.H.; Zakaria, Z.; Saidi, M.A.A. Azman Hassan Effect of Halloysite Nanotubes on the Mechanical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Impact Modified Poly(Lactic Acid). Perintis eJournal 2020, 10, 50–68. [Google Scholar]




| Properties | Nominal Value Unit |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | 294.19 g/mol |
| Colour | white |
| pH | 4.5–7.0 |
| Length | 1–3 microns |
| Diameter | 30–70 nanometres |
| Pore volume | 1.26–1.34 mL/gm |
| Formulations | RPET (wt%) | PA-11 (wt%) | Joncryl® (phr) | HNT (phr) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCS-H0 | 80 | 20 | 2 | 0 |
| NCS-H1 | 80 | 20 | 2 | 1 |
| NCS-H2 | 80 | 20 | 2 | 2 |
| NCS-H3 | 80 | 20 | 2 | 3 |
| NCS-H4 | 80 | 20 | 2 | 4 |
| NCS-H5 | 80 | 20 | 2 | 5 |
| Formulations | Tg (°C) | Tc (°C) | Tm1 (°C) | Tm2 (°C) | Xc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCS-H0 | 66.72 | 113.19 | 189.24 | 253.53 | 4.19 |
| NCS-H1 | 66.79 | 111.97 | 190.42 | 253.84 | 29.47 |
| NCS-H2 | 63.93 | 86.27 | 189.78 | 254.26 | 29.31 |
| NCS-H3 | 66.94 | 120.32 | 191.16 | 254.75 | 28.57 |
| NCS-H4 | 66.79 | 119.30 | 190.43 | 253.67 | 31.83 |
| NCS-H5 | 66.76 | 112.64 | 191.05 | 255.07 | 30.88 |
| Formulation | 10% Loss Temp (°C) | 50% Loss Temp (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| NCS-H0 | ~395 | 428.26 |
| NCS-H1 | ~395 | 428.26 |
| NCS-H2 | ~395 | 426.60 |
| NCS-H3 | ~395 | 425.10 |
| NCS-H4 | ~395 | 426.60 |
| NCS-H5 | ~395 | 436.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, Z.I.; Mohsin, M.E.A.; Habib, U.; Mousa, S.; Hossain, S.S.; Ali, S.S.; Mohamad, Z.; Othman, N. Enhanced Mechanical and Thermal Performance of Sustainable RPET/PA-11/Joncryl® Nanocomposites Reinforced with Halloysite Nanotubes. Polymers 2025, 17, 1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111433
Khan ZI, Mohsin MEA, Habib U, Mousa S, Hossain SS, Ali SS, Mohamad Z, Othman N. Enhanced Mechanical and Thermal Performance of Sustainable RPET/PA-11/Joncryl® Nanocomposites Reinforced with Halloysite Nanotubes. Polymers. 2025; 17(11):1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111433
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Zahid Iqbal, Mohammed E. Ali Mohsin, Unsia Habib, Suleiman Mousa, SK Safdar Hossain, Syed Sadiq Ali, Zurina Mohamad, and Norhayani Othman. 2025. "Enhanced Mechanical and Thermal Performance of Sustainable RPET/PA-11/Joncryl® Nanocomposites Reinforced with Halloysite Nanotubes" Polymers 17, no. 11: 1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111433
APA StyleKhan, Z. I., Mohsin, M. E. A., Habib, U., Mousa, S., Hossain, S. S., Ali, S. S., Mohamad, Z., & Othman, N. (2025). Enhanced Mechanical and Thermal Performance of Sustainable RPET/PA-11/Joncryl® Nanocomposites Reinforced with Halloysite Nanotubes. Polymers, 17(11), 1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111433









