Properties and Biodegradation of Poly(lactic Acid)/Thermoplastic Alginate Biocomposites Prepared via a Melt Blending Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of TPA
2.3. Preparation of PLA/TPA Biocomposites
2.4. Characterization of TPA and PLA/TPA Biocomposites
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of TPA
3.2. Characterization of PLA/TPA Biocomposites
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, X.; Cornish, K.; Vodovotz, Y. Narrowing the gap for bioplastic use in food packaging: An update. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 4712–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jariyasakoolroj, P.; Leelaphiwat, P.; Harnkarnsujarit, N. Advances in research and development of bioplastic for food packaging. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 5032–5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakadellis, S.; Harris, Z.M. Don’t scrap the waste: The need for broader system boundaries in bioplastic food packaging life cycle assessment-A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 274, 122831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, N.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Durable polylactic acid (PLA)-based sustainable engineered blends and biocomposites: Recent developments, challenges, and opportunities. ACS Eng. Au 2021, 1, 7–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, A.K.; Gupta, M.K.; Singh, H. PLA based biocomposites for sustainable products: A review. Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. Res. 2023, 6, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaaba, N.F.; Jaafar, M. A review on degradation mechanisms of polylactic acid: Hydrolytic, photodegradative, microbial, and enzymatic degradation. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2020, 60, 2061–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, N.; Avhad, M.; Utekar, S.; More, A. Polylactic acid (PLA) membrane—Significance, synthesis, and applications: A review. Polym. Bull. 2023, 80, 1117–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhrib, S.; Djellali, S.; Haddaoui, N.; Karimian, D.; Carraro, M. Biocomposites and poly(lactic acid) in active packaging: A review of current research and future directions. Polymers 2025, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, B.; Török, F.; Tomasek, S.; Miskolczi, N. Vegetable oil based additives to enhance the properties of PLA/starch composites: The effect of reaction parameters. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 191 Pt B, 116025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisuwan, Y.; Baimark, Y. Improvement in thermal stability of flexible poly(L-lactide)-b-poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(L-lactide) bioplastic by blending with native cassava starch. Polymers 2022, 14, 3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Girón, Y.; Fernández-Escamilla, V.V.A.; Martín-del-Campo, A.; González-Nuñez, R.; Canché-Escamilla, G.; Uribe-Calderón, J.; Tepale, N.; Aguilar, J.; Moscoso-Sánchez, F.J. Characterization of polylactic acid biocomposites filled with native starch granules from dioscorea remotiflora tubers. Polymers 2024, 16, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claro, P.I.C.; Neto, A.R.S.; Bibbo, A.C.C.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Bastos, M.S.R.; Marconcini, J.M. Biodegradable blends with potential use in packaging: A comparison of PLA/chitosan and PLA/cellulose acetate films. J. Polym. Environ. 2016, 24, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortalò, C.; Russo, P.; Miorin, E.; Zin, V.; Paradisi, E.; Leonelli, C. Extruded composite films based on polylactic acid and sodium alginate. Polymer 2023, 282, 126162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jullanun, P.; Yoksan, R. Morphological characteristics and properties of TPS/PLA/cassava pulp biocomposites. Polym. Test. 2020, 88, 106522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez Villadiego, K.; Arias Tapia, M.J.; Useche, J.; Escobar Macías, D. Thermoplastic starch (TPS)/polylactic acid (PLA) blending methodologies: A review. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozinovic, A.; Kovac, M.; Ocelic Bulatovic, V.; Kucic Grgic, D.; Miloloža, M.; Subaric, D.; Ackar, Ð. Biopolymeric blends of thermoplastic starch and polylactide as sustainable packaging materials. Polymers 2024, 16, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongsomboon, W.; Srihanam, P.; Baimark, Y. Preparation of flexible poly(L-lactide)-b-poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(L-lactide)/talcum/thermoplastic starch ternary composites for use as heat-resistant and single-use bioplastics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 230, 123172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Shahid, M.A.; Hossain, M.T.; Sheikh, M.S.; Rahman, M.S.; Uddin, N.; Rahim, A.; Khan, R.A.; Hossain, I. Sources, extractions, and applications of alginate: A review. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2024, 6, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Gao, C.; Avérous, L. Alginate-based materials: Enhancing properties through multiphase formulation design and processing innovation. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2024, 159, 100799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Singh, N.; Kumar, P. A review on sources, modification techniques, properties and potential applications of alginate-based modified polymers. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 213, 113078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athamneh, T.; Abuawad, A.; Odat, T.; Alshweiat, A.; Obaidat, R.; Bani Yaseen, F.; Al-Najjar, M.A.; Garafat, R.; Altarabeen, R.; Smirnova, I.; et al. Investigation of the antibacterial activity of ZnO-loaded alginate/hyaluronic acid aerogels for wound dressing applications. Polymers 2025, 17, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouda, K.; Mohamed, R.S. Alginate beads with encapsulated date palm pollen extract: Development, characterization and their potential role in hepato-protection and fertility-stimulating hormones improvement in bisphenol A-treated rats. Polymers 2025, 17, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, N.; Mo, H.; Yang, Z.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Q.; Huang, X.; Han, B. Synthesis of polymer sodium alginate–red mud adsorbent and its application in the removal of low-concentration fluoride. Polymers 2025, 17, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhena, T.; Jacobs, N.; Luyt, A. Nanofibrous alginate membrane coated with cellulose nanowhiskers for water purification. Cellulose 2018, 25, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metha, C.; Pawar, S.; Suvarna, V. Recent advancements in alginate-based films for active food packaging applications. Sustain. Food Technol. 2024, 2, 1246–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Pollet, E.; Avérous, L. Properties of glycerol-plasticized alginate films obtained by thermo-mechanical mixing. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Pollet, E.; Avérous, L. Innovative plasticized alginate obtained by thermo-mechanical mixing: Effect of different biobased polyols systems. Carbohyd. Polym. 2017, 157, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuangchai, A.; Baimark, Y. Improving crystallization properties, thermal stability, and mechanical properties of poly(L-lactide)-b-poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(L-lactide) bioplastic by incorporating cerium lactate. Polymers 2024, 16, 3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baimark, Y.; Srihanam, P.; Srisuwan, Y. Thermal, morphological, mechanical, and biodegradation properties of poly(L-lactide)-b-poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(L-lactide)/high-density polyethylene blends. Polymers 2024, 16, 2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Aziz, M.S.; Salama, H.E.; Sabaa, M.W. Biobased alginate/castor oil edible films for active food packaging. LWT 2018, 96, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-F.; Shankar, S.; Rhim, J.-W. Properties of alginate-based films reinforced with cellulose fibers and cellulose nanowhiskers isolated from mulberry pulp. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Orozco, R.; Timoteo-Cruz, B.; García-Sánchez, J.J.; Gomez-Espinosa, R.M.; Bernal-Martínez, L.A.; Torres-Blancas, T. Properties of eco-friendly orange peel-alginate-glycerol bioplastic films as potential food packaging applications. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2024, 61, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerapoprasit, C.; Prachayawarakorn, J. Properties of biodegradable thermoplastic cassava starch/sodium alginate composites prepared from injection molding. Polym. Compos. 2016, 37, 3365–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarezi, M.M.F.; de Oliveira Taipina, M.; Escobar da Silva, L.C.; Goncalves, M.C. Poly(ethylene glycol) as a compatibilizer for poly(lactic acid)/thermoplastic starch blends. J. Polym. Environ. 2013, 21, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Carballo, Z.B.; Duarte-Aranda, S.; Canché-Escamilla, G. Properties and biodegradation of thermoplastic starch obtained from grafted starches with poly(lactic acid). J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 2607–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, P.; Imre, B.; Bere, J.; Moczo, J.; Pukanszky, B. Physical ageing and molecular mobility in PLA blends and composites. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 122, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noivoil, N.; Yoksan, R. Oligo(lactic acid)-grafted starch: A compatibilizer for poly(lactic acid)/thermoplastic starch blend. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 160, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, E.M.; Curvelo, A.A.S.; Correa, A.C.; Marconcini, J.M.; Glenn, G.M.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Properties of thermoplastic starch from cassava bagasse and cassava starch and their blends with poly(lactic acid). Ind. Crops Prod. 2012, 37, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigo, R.; Bartoli, M.; Malucelli, G. Poly(lactic acid)–biochar biocomposites: Effect of processing and filler content on rheological, thermal, and mechanical properties. Polymers 2020, 12, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, R.; Adhikari, S.; Peng, Y. Properties of polylactic acid and biochar-based composites for environment-friendly plant containers. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2024, 23, 100850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidlou, S.; Huneault, M.A.; Li, H.; Park, C.B. Poly(lactic acid) crystallization. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1657–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Villadiego, K.; Arias-Tapia, M.J.; Jaramillo, A.F. Improving thermal stability of starches native cross-linked with citric acid as a compatibilizer for thermoplastic starch/polylactic acid blends. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 13253–13274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imre, B.; Renner, K.; Pukansky, B. Interactions, structure and properties in poly(lactic acid)/thermoplastic polymer blends. Express Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrami, M.; Ghasemi, I.; Azizi, H.; Karrabi, M.; Seyedabadi, M. A new approach in compatibilization of the poly(lactic acid)/thermoplastic starch (PLA/TPS) blends. Carbohyd. Polym. 2016, 144, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.-Y.; Feng, X.-Q.; Lauke, B.; Mai, Y.-W. Effects of particle size, particle/matrix interface adhesion and particle loading on mechanical properties of particulate–Polymer composites. Compos. B Eng. 2008, 39, 933–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huneault, M.A.; Li, H. Morphology and properties of compatibilized polylactide/thermoplastic starch blends. Polymer 2007, 48, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Li, C.; Ma, S.; Feng, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, J. The properties of poly(lactic acid)/starch blends with a function-alized plant oil: Tung oil anhydride. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 95, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Yu, J.; Chang, P.R.; Ma, X. Influence of formamide and water on the properties of thermoplastic starch/poly(lactic acid) blends. Carbohyd. Polym. 2008, 71, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.; Wahab, M.K.A.; Uylan, D.N.; Ismail, H. Physical and degradation properties of polylactic acid and thermoplastic starch blends—Effect of citric acid treatment on starch structures. Bioresources 2017, 12, 3076–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auras, R.A.; Lim, L.T.; Selke, S.E.; Tsuji, H. (Eds.) Poly(Lactic Acid): Synthesis, Structures, Properties, Processing, and Applications; Wiley-Blackwell, John Wiley & Sons. Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rudnik, E. Biodegradation of Compostable Polymers in Various Environments, in Compostable Polymer Materials, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Chapter 2. [Google Scholar]
- Karamanlioglu, M.; Robson, G.D. The influence of biotic and abiotic factors on the rate of degradation of poly(lactic) acid (PLA) coupons buried in compost and soil. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 2063–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.P.; Pereira, M.d.P.; Passador, F.R.; Montagna, L.S. PLA/coffee grounds composites: A study of photodegradation and biodegradation in soil. Macromol. Symp. 2020, 394, 2000091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
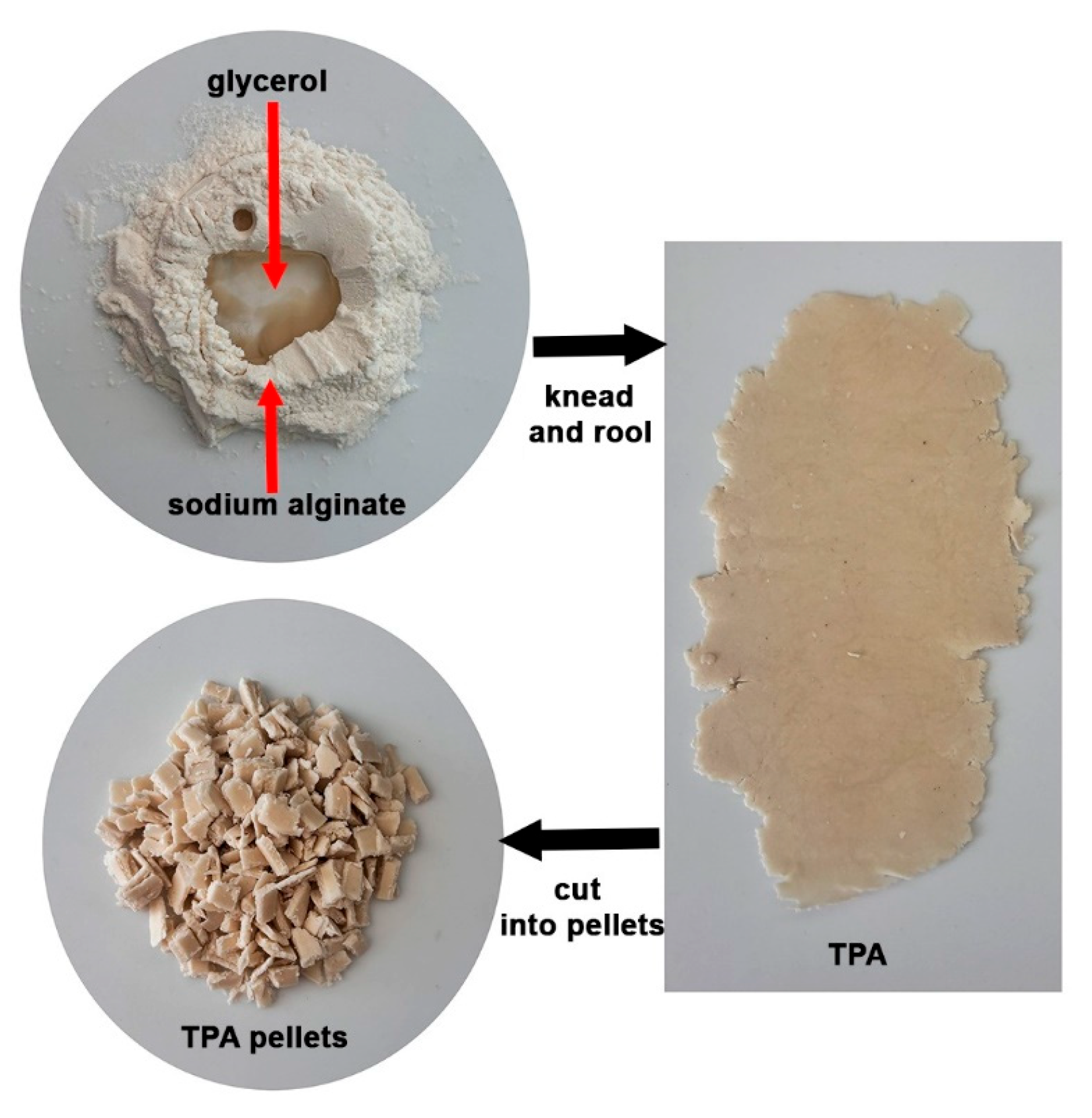
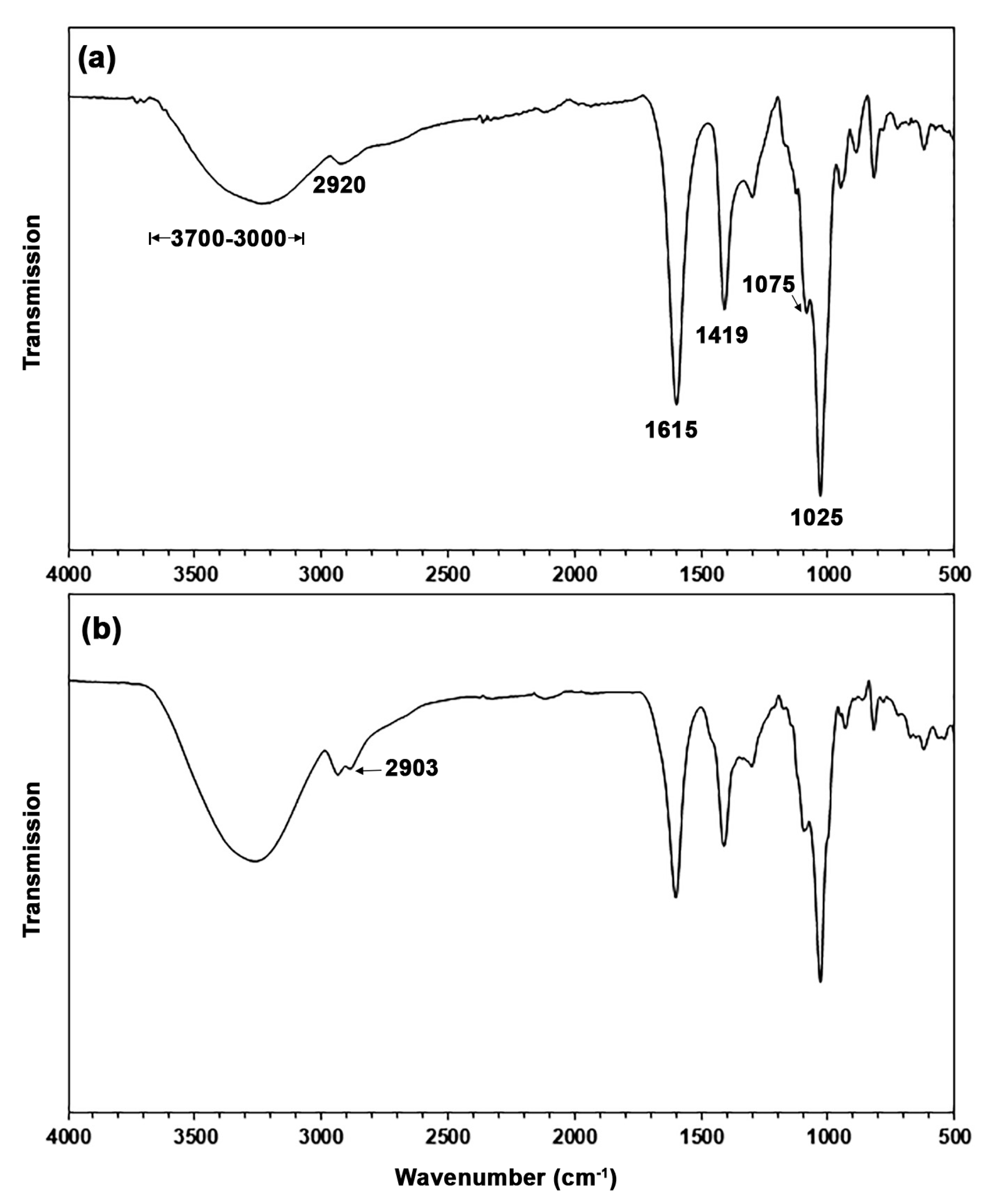

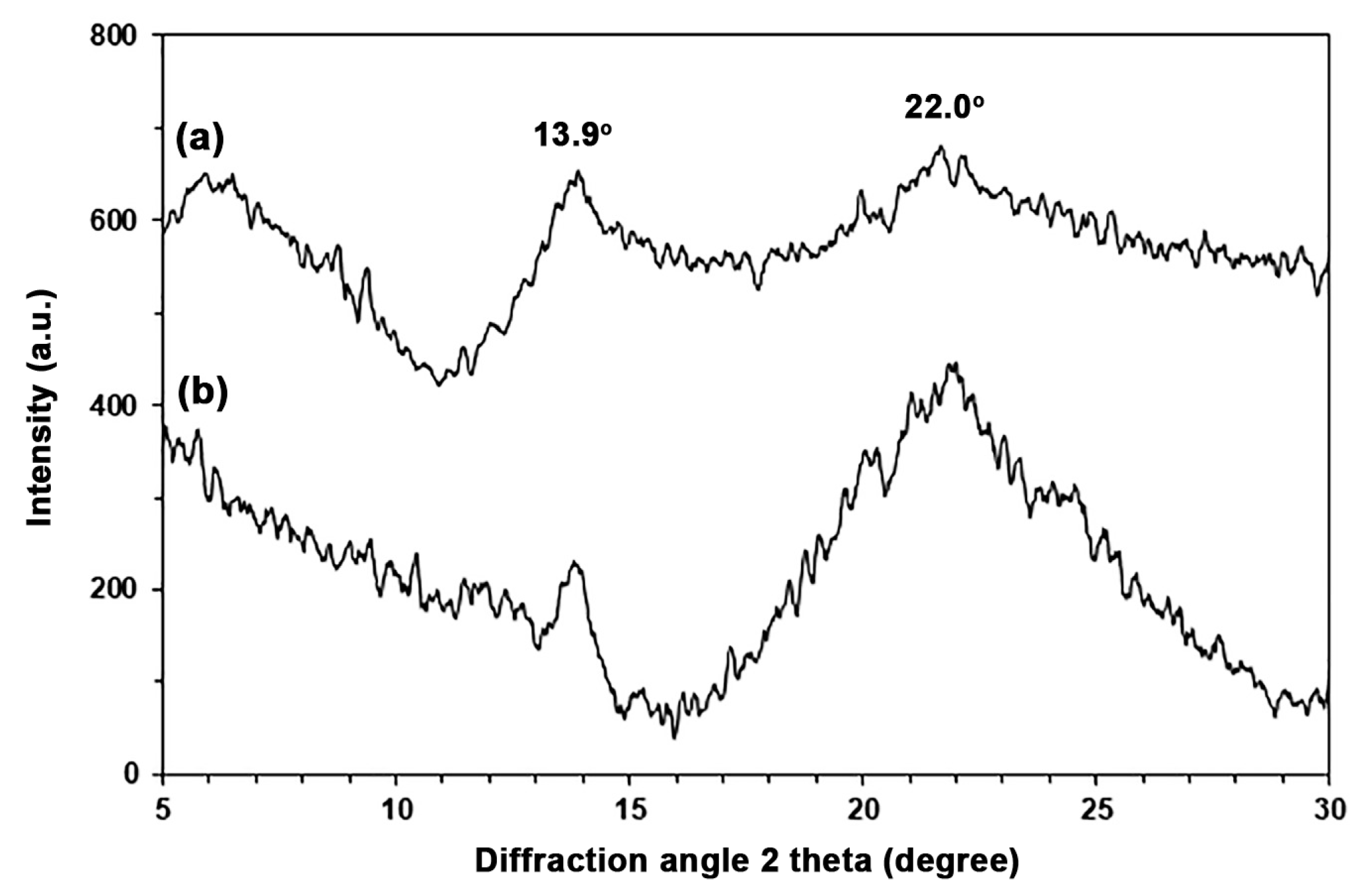
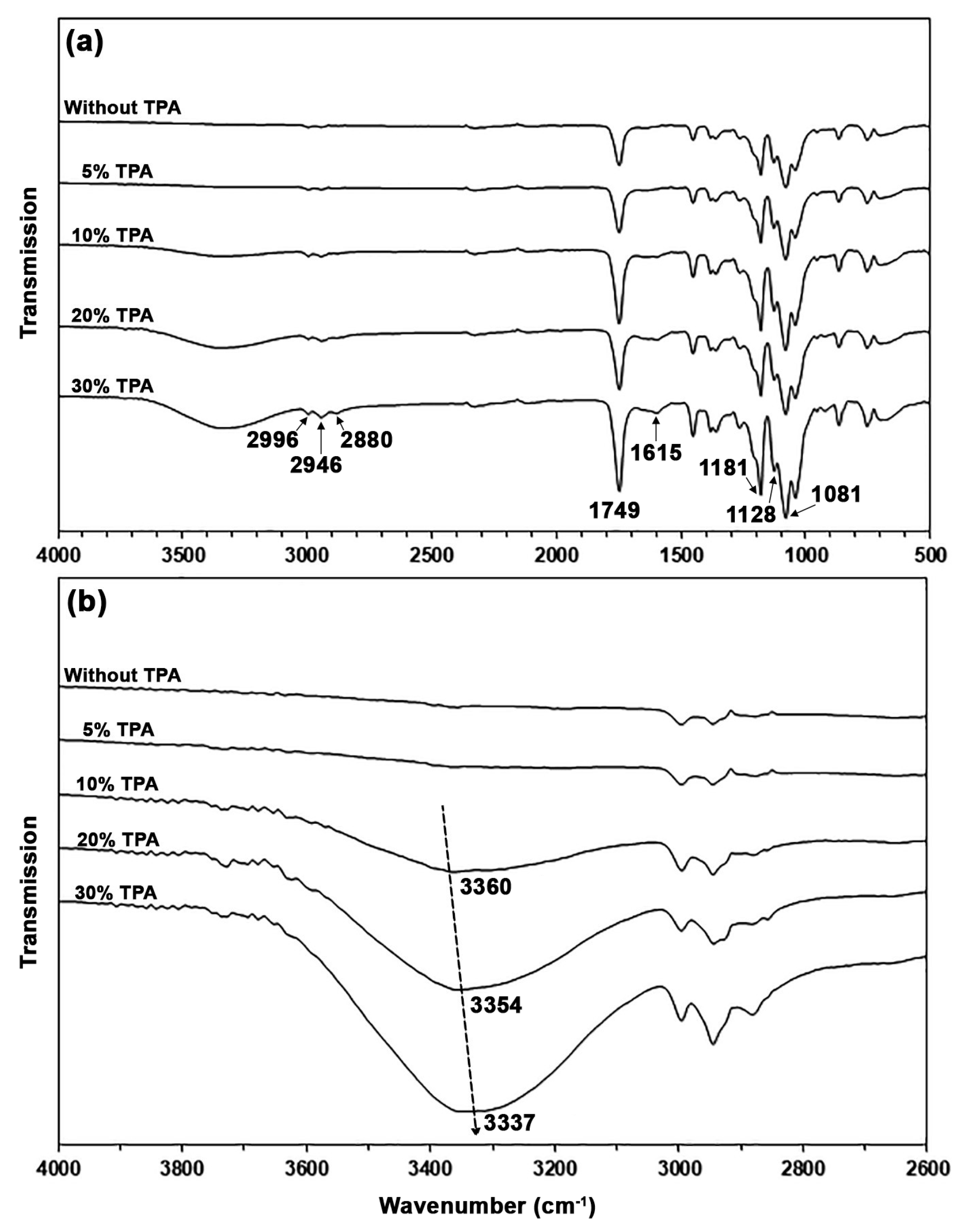

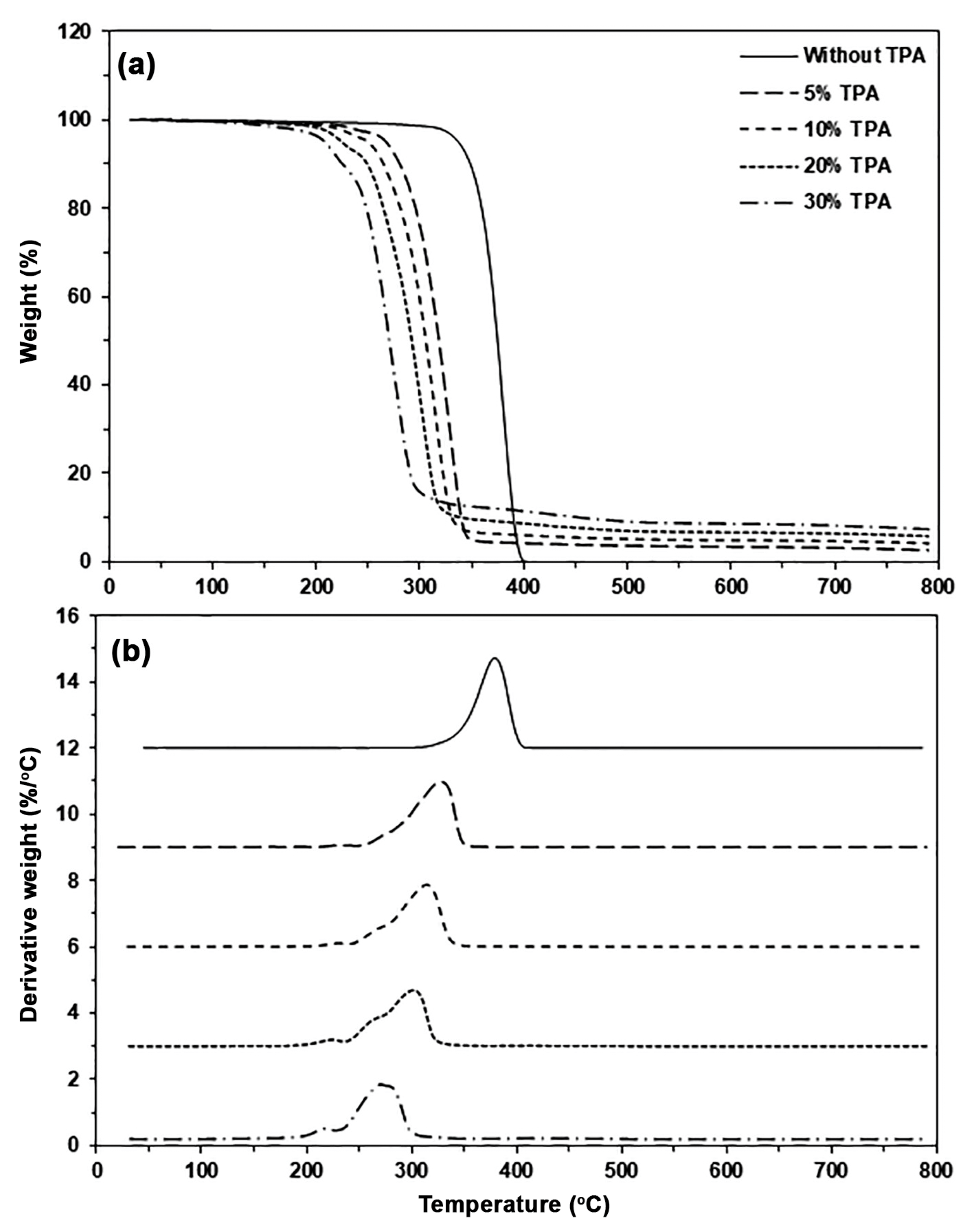
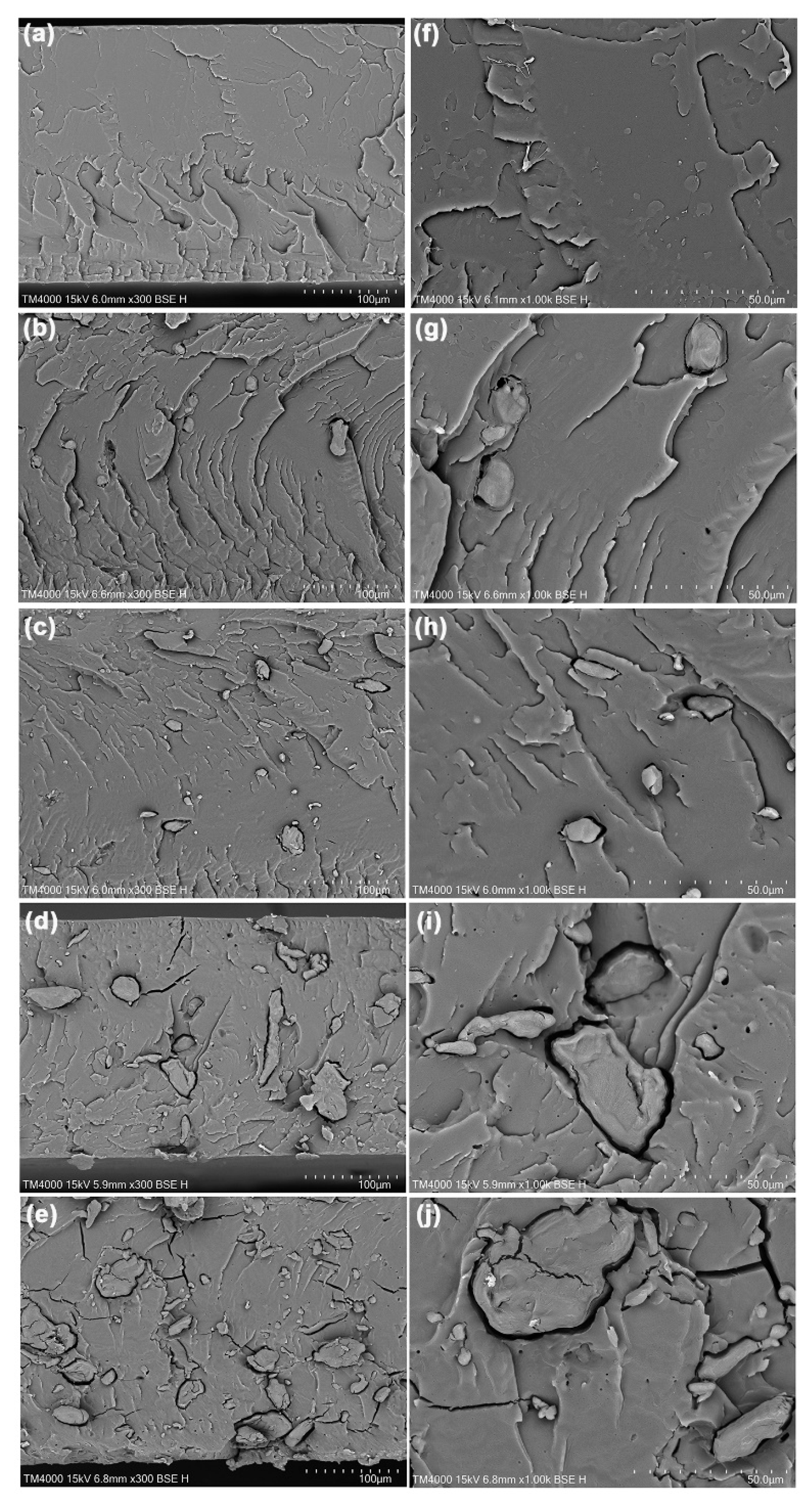
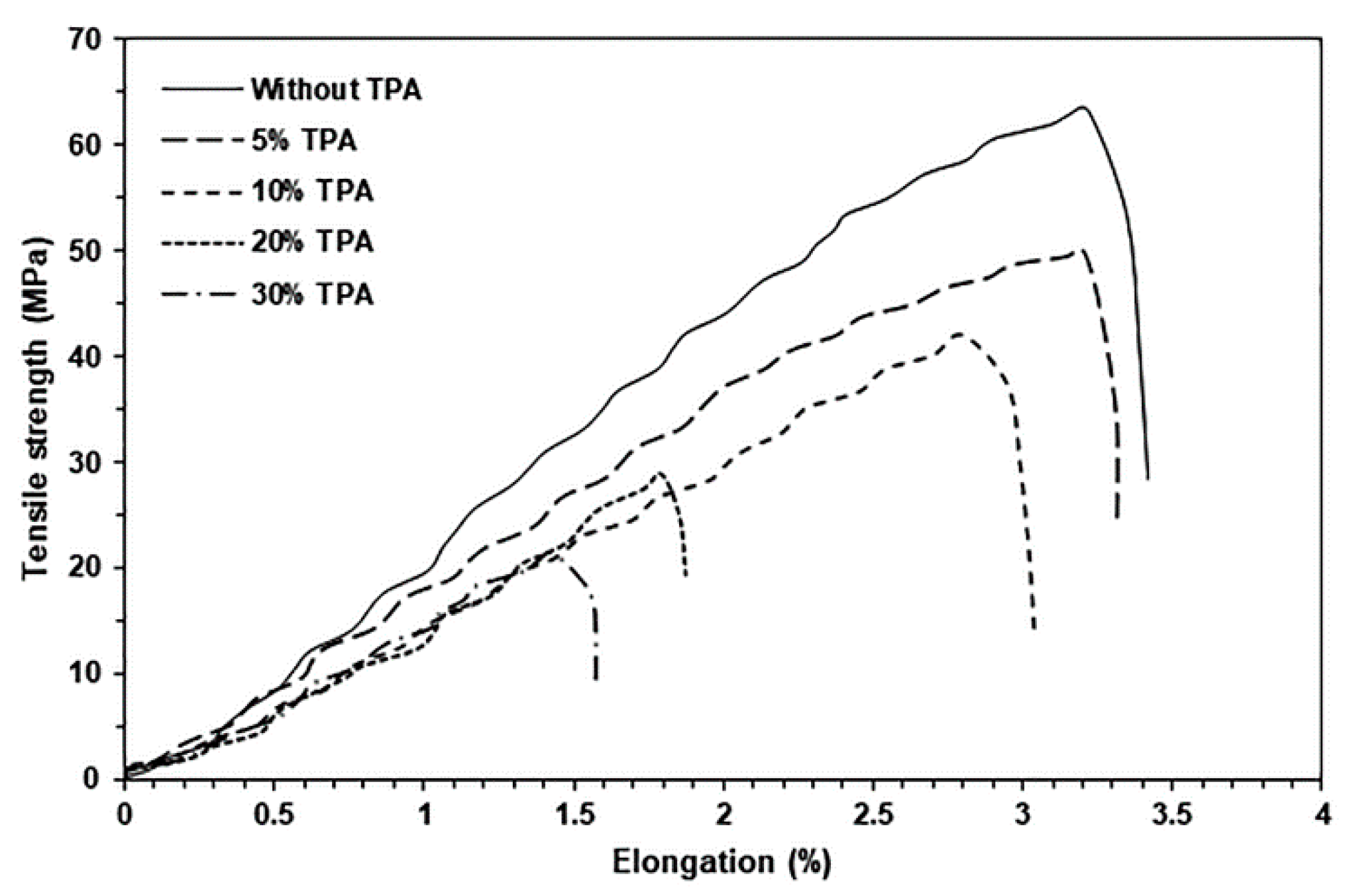
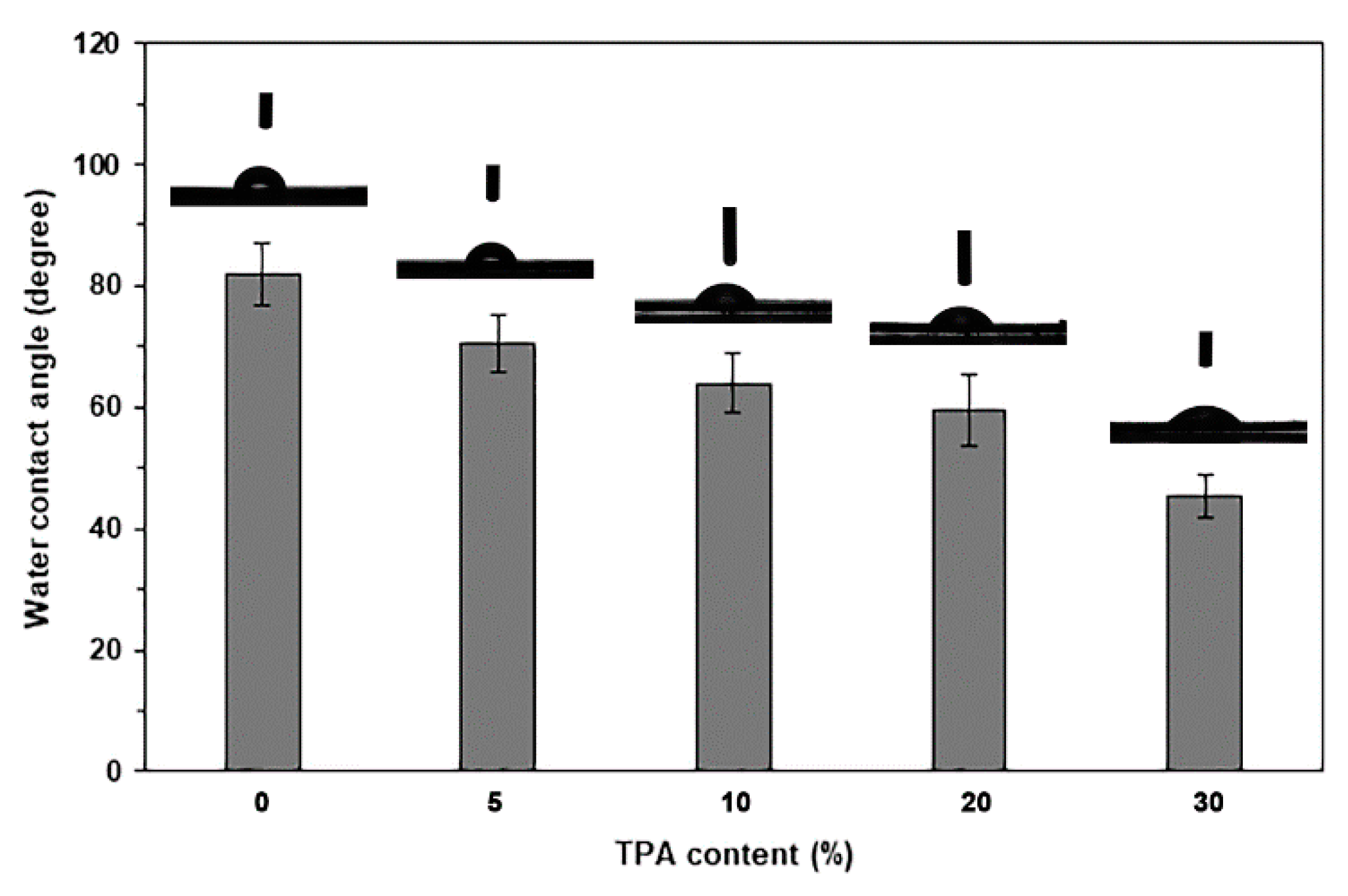


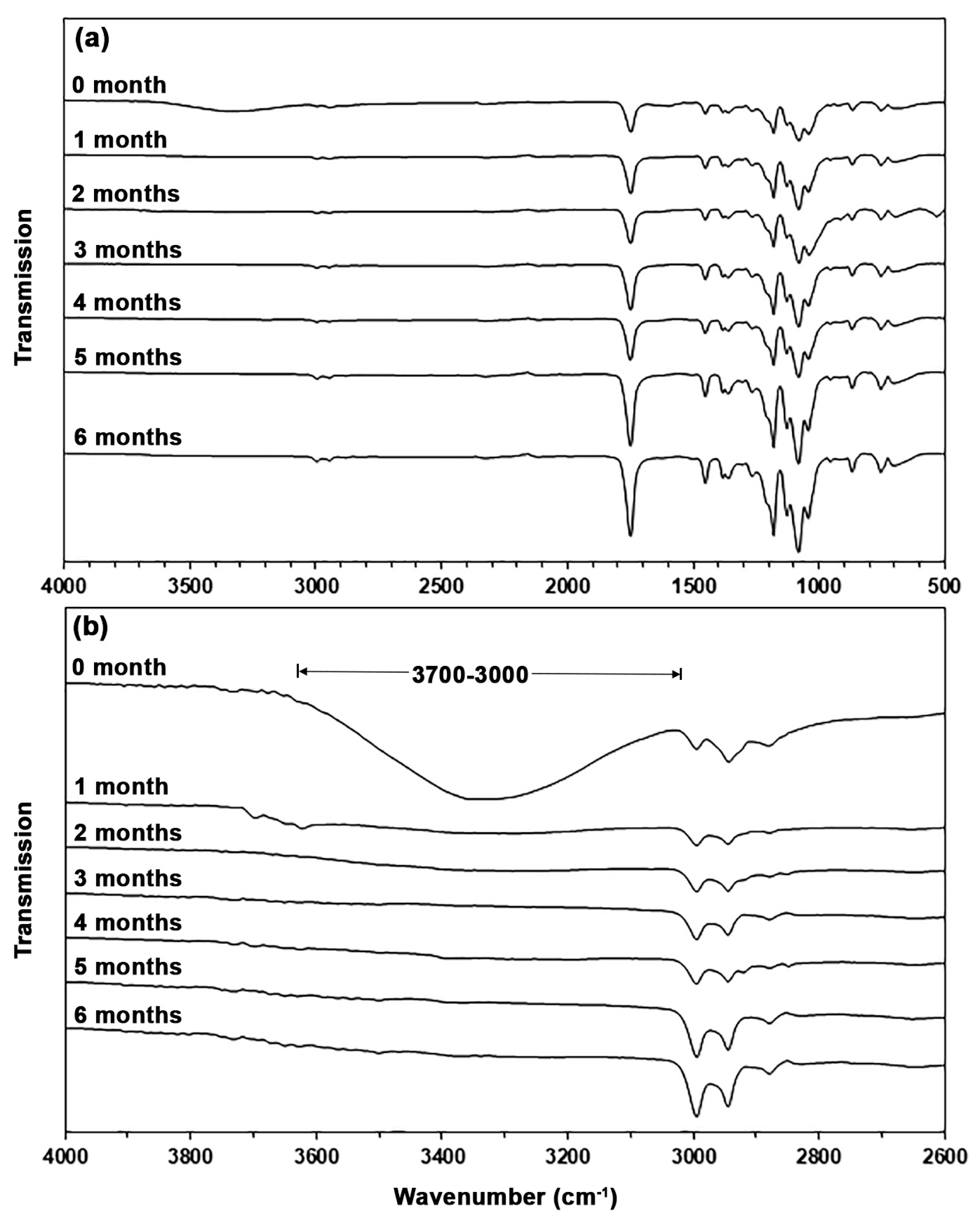
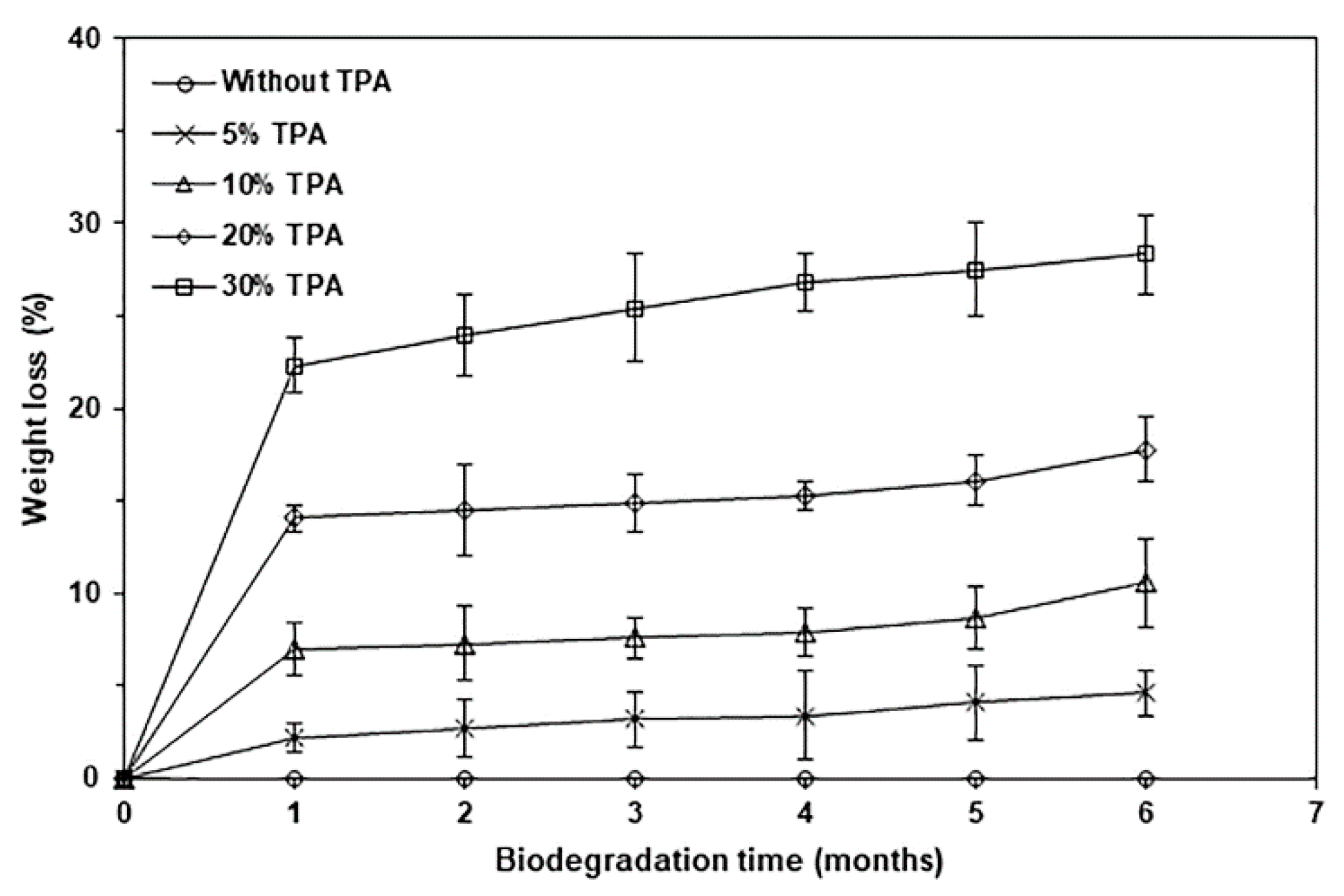
| TPA Content (wt%) | Tg (°C) | Tcc (°C) | ΔHcc (J/g) | Tm (°C) | ΔHm (J/g) | Xc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | 58 | 98 | 32.8 | 166 | 40.4 | 8.1 |
| 5 | 54 | 97 | 32.1 | 164 | 40.6 | 9.6 |
| 10 | 54 | 95 | 32.0 | 163 | 40.1 | 9.6 |
| 20 | 50 | 90 | 22.9 | 159 | 29.7 | 9.1 |
| 30 | 46 | 89 | 21.6 | 155 | 26.9 | 8.1 |
| TPA Content (wt%) | Char Residue at 800 °C (%) | Tmax (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| - | - | 378 |
| 5 | 2.65 | 328 |
| 10 | 4.21 | 315 |
| 20 | 5.84 | 302 |
| 30 | 7.43 | 270 |
| TPA Content (wt%) | Maximum Tensile Strength (MPa) * | Elongation at Break (%) * | Young’s Modulus (MPa) * |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | 63.2 ± 3.8 | 3.4 ± 1.2 | 1090 ± 28 |
| 5 | 49.9 ± 4.4 | 3.3 ± 0.8 | 801 ± 37 |
| 10 | 41.8 ± 3.7 | 3.0 ± 0.9 | 692 ± 47 |
| 20 | 28.9 ± 3.5 | 1.9 ± 0.7 | 394 ± 28 |
| 30 | 21.3 ± 2.4 | 1.6 ± 0.4 | 180 ± 19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baimark, Y.; Pakkethati, K.; Srihanam, P. Properties and Biodegradation of Poly(lactic Acid)/Thermoplastic Alginate Biocomposites Prepared via a Melt Blending Technique. Polymers 2025, 17, 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101338
Baimark Y, Pakkethati K, Srihanam P. Properties and Biodegradation of Poly(lactic Acid)/Thermoplastic Alginate Biocomposites Prepared via a Melt Blending Technique. Polymers. 2025; 17(10):1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101338
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaimark, Yodthong, Kansiri Pakkethati, and Prasong Srihanam. 2025. "Properties and Biodegradation of Poly(lactic Acid)/Thermoplastic Alginate Biocomposites Prepared via a Melt Blending Technique" Polymers 17, no. 10: 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101338
APA StyleBaimark, Y., Pakkethati, K., & Srihanam, P. (2025). Properties and Biodegradation of Poly(lactic Acid)/Thermoplastic Alginate Biocomposites Prepared via a Melt Blending Technique. Polymers, 17(10), 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101338









