Recycled Polypropylene/Strontium Ferrite Polymer Composite Materials with Electromagnetic Shielding Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
- SrFe12O19 powder acquired from TODA Ferrite (Korea) with the properties shown in Table 2. One important reason for choosing strontium ferrites is that they are low-cost, widely used for ferrite permanent magnets, and may also become an important source of recycled matter in the near future.
- SrFe12O19 concentrate of F1 type acquired from Mate Co., Ltd. (Wake, Japan) with the trade name HM 1213-PA12 + 85% SrFe12O19 and the properties shown in Table 3.
2.2. Equipment and Methods
2.2.1. Obtaining Polymer Composite Materials
2.2.2. Material Characterization
Density Determination
Mechanical Characterization
SEM Analyses
Thermal Analysis
Dielectric Characterization
Temperature Resistance Testing
Magnetic Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Macrographic Aspect, Density, and Porosity
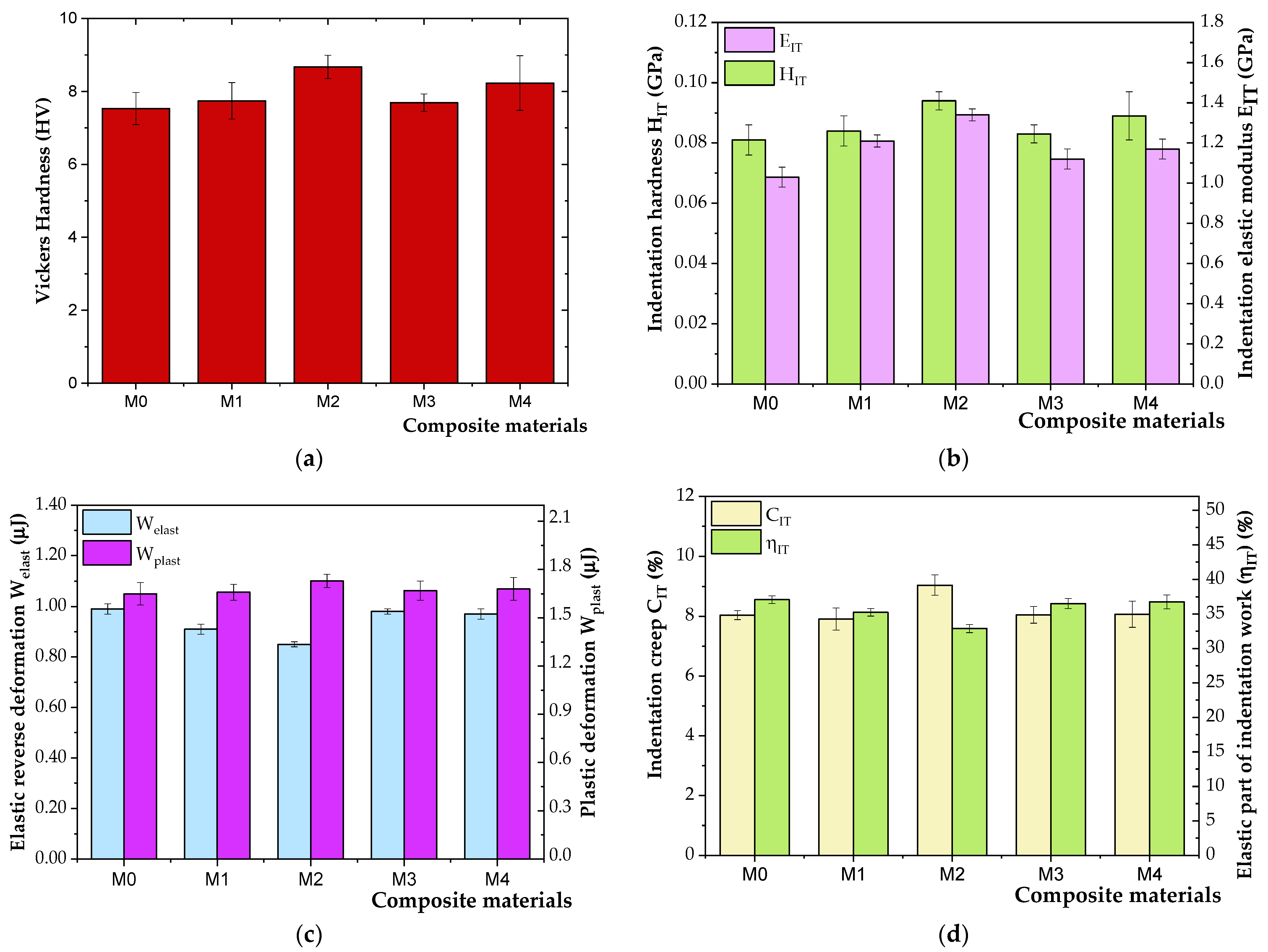
3.2. Mechanical Properties
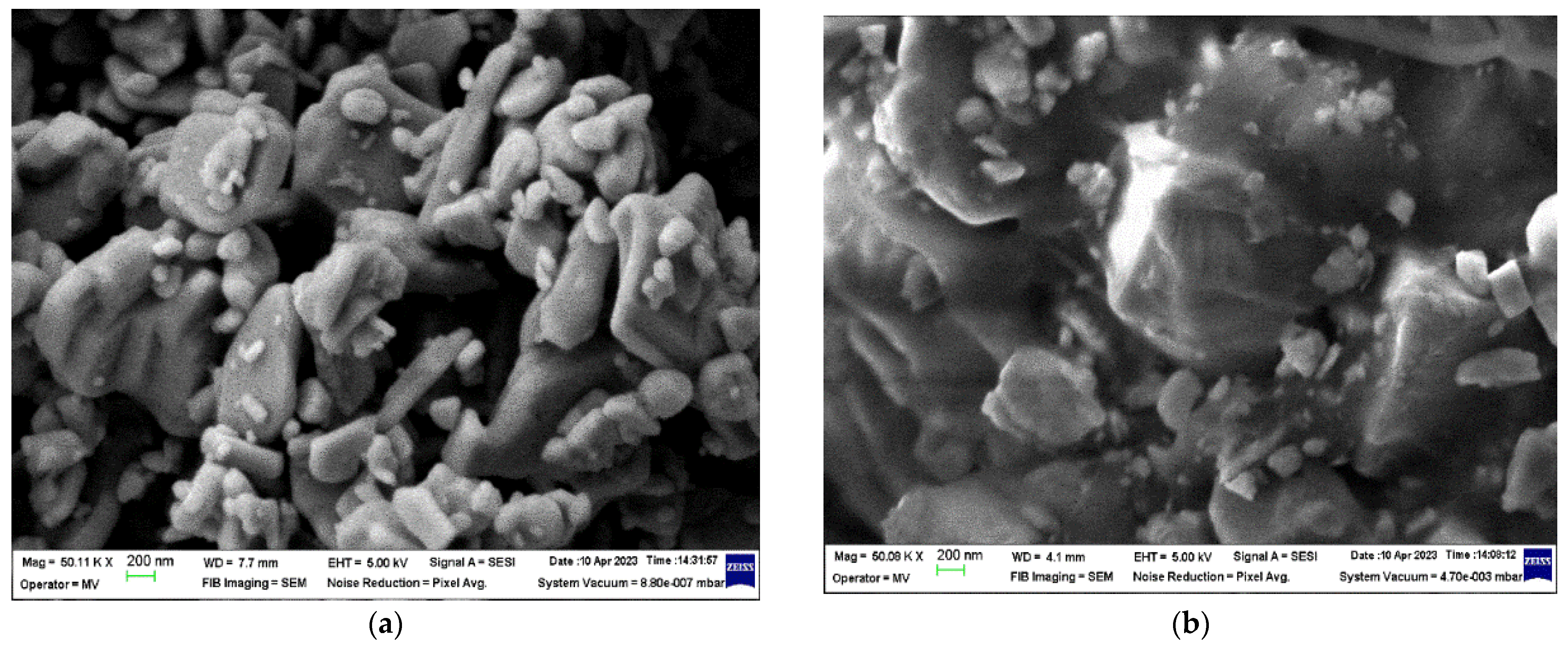
3.3. SEM Analysis
3.4. Thermal Analysis
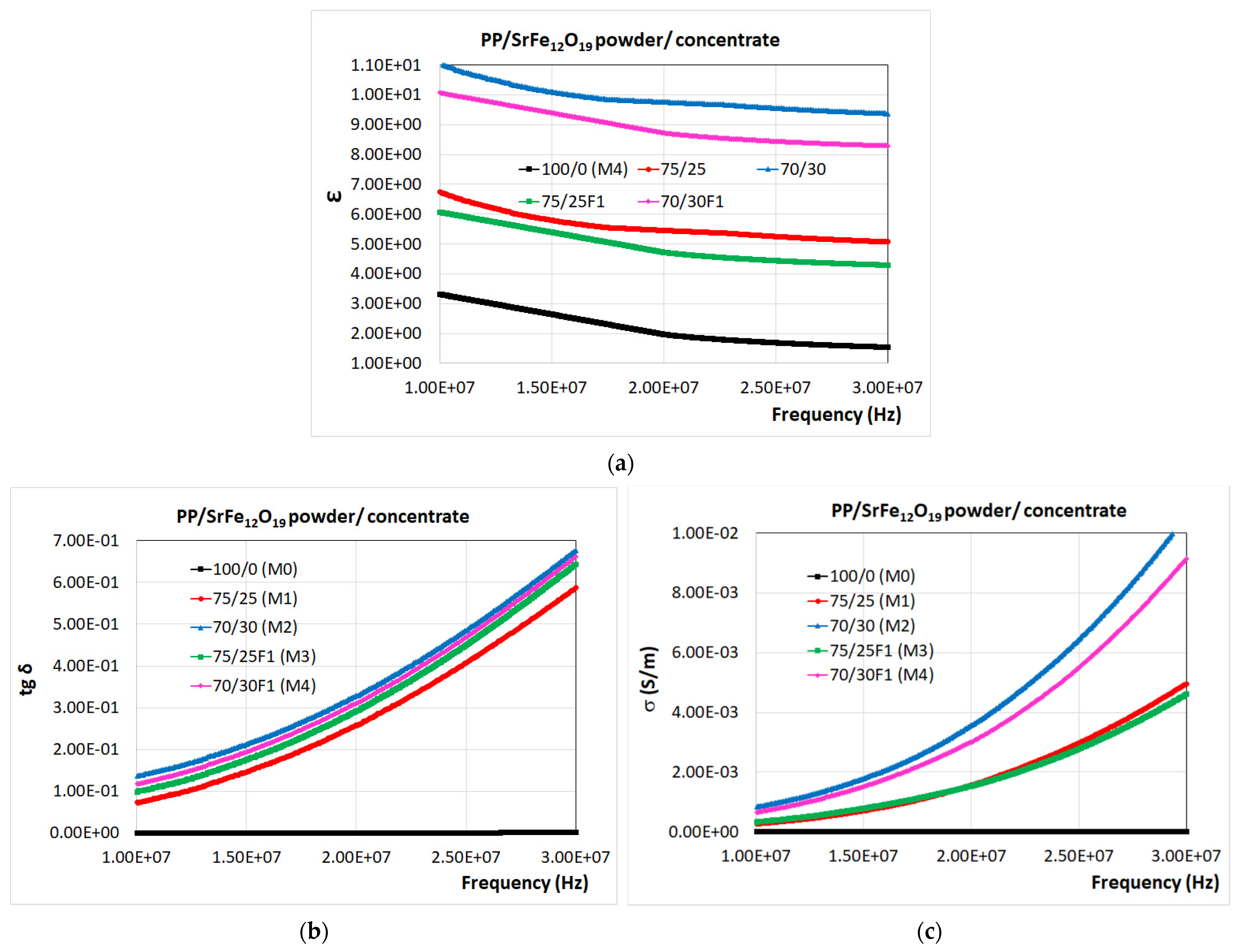
3.5. Dielectric Properties
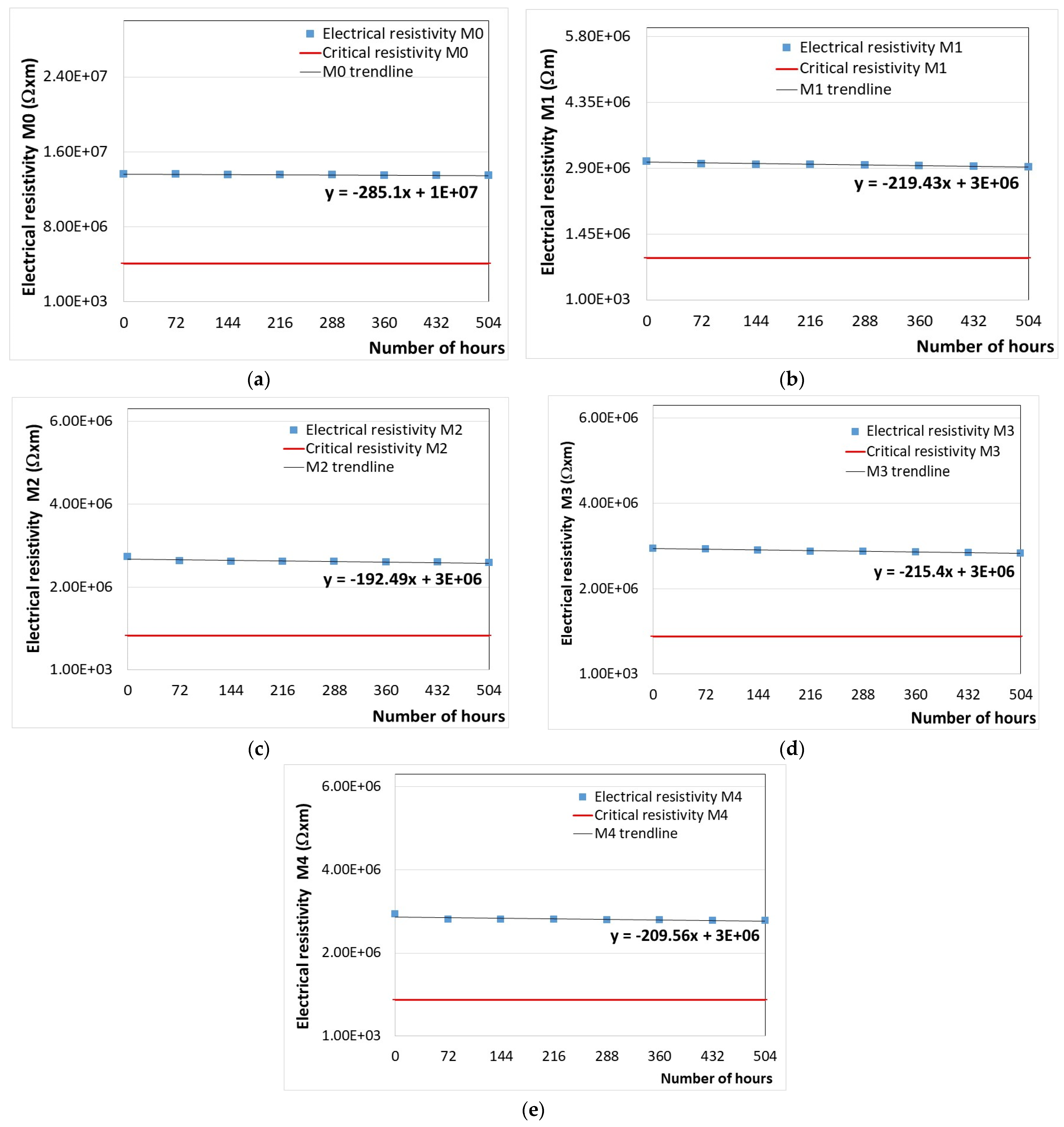
3.6. Temperature Resistance
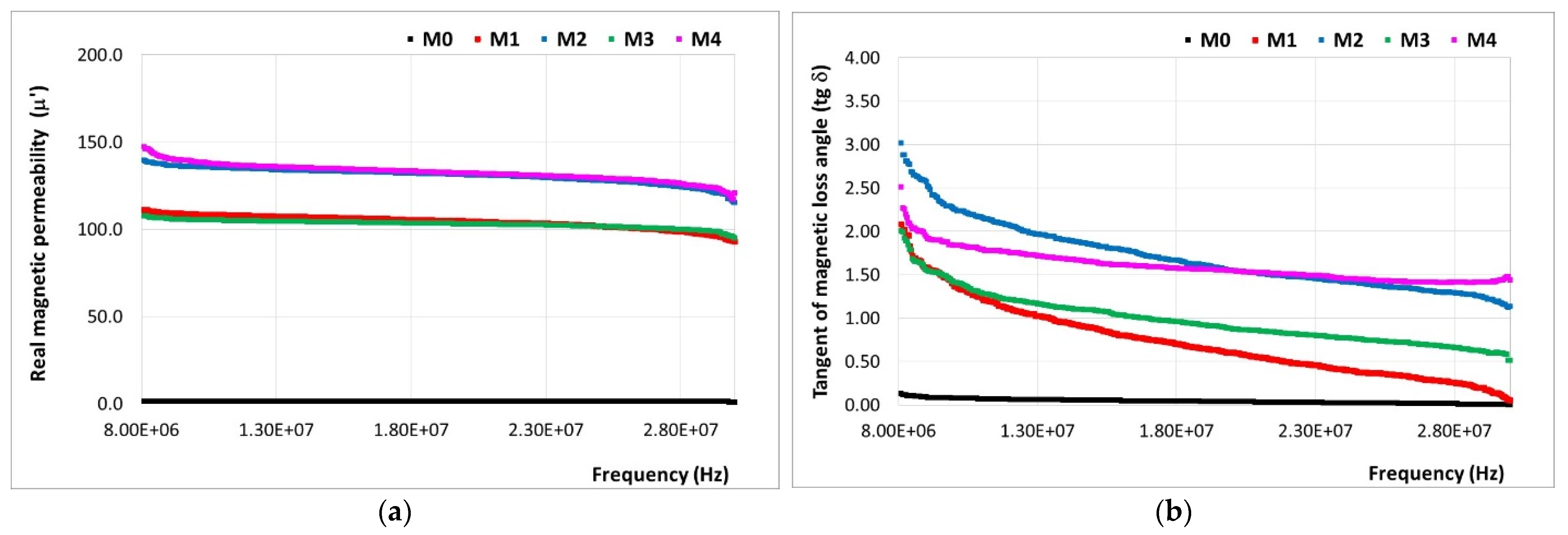
3.7. Magnetic Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, J.K.; Kang, S.-S.; Kim, H.G.; Kwac, L.K. Mechanical Properties and Electromagnetic Interference Shielding of Carbon Composites with Polycarbonate and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene Resins. Polymers 2023, 15, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Hu, D.; Wei, Q.; Fu, Q.; Deng, H. Recent Progress on Multifunctional Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Polymer Composites. J. Mate. Sci. Technol. 2023, 134, 106–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, V. Review of Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Materials Fabricated by Iron Ingredients. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 1640–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed, W.E.; Lezynski, P.; Smolenski, R.; Moonen, N.; Crovetti, P.; Thomas, D.W.P. The Effect of EMI Generated from Spread-Spectrum-Modulated SiC-Based Buck Converter on the G3-PLC Channel. Electronics 2021, 10, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apakuppakul, S.; Methachittiphan, N.; Apiyasawat, S. Effect of ElectroMagnetic Interference from SmartPHone on Cardiac ImplaNtable Electronic Device (EMI-PHONE Study). J. Arrhythm. 2022, 38, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Sun, Z. Research on the Effectiveness of Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Electromagnetic Interference Identification Based on I/Q Data. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okechukwu, C. Effects of Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Field Exposure on Neurophysiology. Adv. Hum. Biol. 2020, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razek, A. Biological and Medical Disturbances Due to Exposure to Fields Emitted by Electromagnetic Energy Devices—A Review. Energies 2022, 15, 4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolte, J.F.B.; Baliatsas, C.; Eikelboom, T.; Van Kamp, I. Everyday Exposure to Power Frequency Magnetic Fields and Associations with Non-Specific Physical Symptoms. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 196, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.-H.; Kang, T.-W.; Kwon, J.-H.; Park, S.-O. Effect of Electromagnetic Interference on Human Body Communication. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2017, 59, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliatsas, C.; Van Kamp, I.; Bolte, J.; Schipper, M.; Yzermans, J.; Lebret, E. Non-Specific Physical Symptoms and Electromagnetic Field Exposure in the General Population: Can We Get More Specific? A Systematic Review. Environ. Int. 2012, 41, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szemerszky, R.; Zelena, D.; Barna, I.; Bárdos, G. Stress-Related Endocrinological and Psychopathological Effects of Short- and Long-Term 50Hz Electromagnetic Field Exposure in Rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2010, 81, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, J.; Sahoo, S.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Progress of Novel Techniques for Lightweight Automobile Applications through Innovative Eco-Friendly Composite Materials: A Review. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2020, 33, 978–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, E.; Lipcinski, D.; Tanase, N.; Lingvay, I. The Influence of the 50 Hz Electric Field on the Development and Maturation of Aspergillus Niger. Electroteh. Electron. Autom. 2015, 63, 68–74. [Google Scholar]
- Stancu, C.; Lingvay, M.; Szatmari, I.; Lingvay, I. Influence of 50 Hz Electromagnetic Field on the Yeast (Saccharomyces Cerevisiae) Metabolism. In Proceedings of the 2013 8th International Symposium on Advanced Topics in Electrical Engineering (ATEE), Bucharest, Romania, 23–25 May 2013; IEEE: Bucharest, Romania, 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyza, H.U.; Nejat, S.H.; Fatma, K.Y. Heat-resistant moulds: Assessment, prevention and their consequences for food safety and public health. Czech J. Food Sci. 2022, 40, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Han, C.; Cao, W.-Q.; Cao, M.-S.; Yang, H.-J.; Yuan, J. A Nano-Micro Engineering Nanofiber for Electromagnetic Absorber, Green Shielding and Sensor. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, B.; Shi, W.; Ong, S.J.H.; Lu, X.; Wang, P.L.; Ji, G.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, L.; Xu, Z.J. Defect Engineering in Two Common Types of Dielectric Materials for Electromagnetic Absorption Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1901236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingvay, M.; Caramitu, A.-R.; Borș, A.-M.; Lingvay, I. Dielectric Spectroscopic Evaluation in the Extremely Low Frequency Range of an Aspergillus Niger Culture. Stud. UBB Chem. 2019, 64, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandu, D.; Lingvay, I.; Szabolcs, L.; Micu, D.D.; Popescu, C.; Jurgen, B.; Bartha, C.; Csaba, P. The Effect of Electromagnetic Fields on Baker’s Yeast Population Dynamics, Biocatalytic Activity and Selectivity. Stud. UBB Chem. 2009, LIV, 195–201. [Google Scholar]
- Bors, A.M.; Butoi, N.; Caramitu, A.R.; Marinescu, V.; Lingvay, I. The Thermooxidation and Resistance to Moulds Action of Some Polyethylene Sorts Used at Anticorrosive Insulation of the Underground Pipelines. Mat. Plast. 2017, 54, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartha, C.; Caramitu, A.; Jipa, M.; Ignat, D.M.; Tókos, A. Dielectric Behavior of Sludge from Waste Water Treatment. Stud. UBB Chem. 2020, 65, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokos, A.; Bartha, C.; Jipa, M.; Micu, D.-D.; Caramitu, A.-R.; Lingvay, I. Interactions of Extremely Low-Frequency Electric Field with the Active Sludge Live Materia from Wastewater Treatments. In Proceedings of the 2021 12th International Symposium on Advanced Topics in Electrical Engineering (ATEE), Bucharest, Romania, 25–27 March 2021; IEEE: Bucharest, Romania, 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, S.; Kango, S.; Kumar, A.; Haldorai, Y.; Kumari, B.; Kumar, R. Magnetic Polymer Nanocomposites for Environmental and Biomedical Applications. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2014, 292, 2025–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingvay, I.; Voina, A.; Lingvay, C.; Mateescu, C. The Impact of the Electromagnetic Pollution of the Environment on the Complex Build-up Media. Rev. Roum. Sci. Techn.–Électrotechn. Énerg. 2008, 53, 95–111. [Google Scholar]
- Rus, T.; Bors, A.M.; Caramitu, A.R.; Lingvay, I.; Vaireanu, D.I. Comparative Studies on the Thermal Ageing of Some Painting Materials. Mat. Plast. 2018, 55, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-X.; Zhang, M.; Shu, J.-C.; Wen, B.; Cao, W.-Q.; Cao, M.-S. Thermally-Tailoring Dielectric “Genes” in Graphene-Based Heterostructure to Manipulate Electromagnetic Response. Carbon 2021, 184, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bors, A.-M.; Lingvay, D.; Caramitu, A.-R.; Iordache, I.; Lingvay, I. Comparative Studies on the Electrical and Mechanical Behavior of Some Soldering and/or Impregnation Lacquers. Mat. Plast. 2019, 56, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanida, A.; Stavropoulos, S.G.; Speliotis, T.; Psarras, G.C. Investigating the Effect of Zn Ferrite Nanoparticles on the Thermomechanical, Dielectric and Magnetic Properties of Polymer Nanocomposites. Materials 2019, 12, 3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radoń, A.; Hawełek, Ł.; Łukowiec, D.; Kubacki, J.; Włodarczyk, P. Dielectric and Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Properties of High Entropy (Zn,Fe,Ni,Mg,Cd)Fe2O4 Ferrite. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruželák, J.; Kvasničáková, A.; Hložeková, K.; Dosoudil, R.; Gořalík, M.; Hudec, I. Electromagnetic Interference Shielding and Physical-Mechanical Characteristics of Rubber Composites Filled with Manganese-Zinc Ferrite and Carbon Black. Polymers 2021, 13, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.W.; Yang, Z.H. The Studies of High-Frequency Magnetic Properties and Absorption Characteristics for Amorphous-Filler Composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 391, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakovenko, O.S.; Matzui, L.Y.; Vovchenko, L.L.; Lazarenko, O.A.; Perets, Y.S.; Lozitsky, O.V. Complex Permittivity of Polymer-Based Composites with Carbon Nanotubes in Microwave Band. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 2691–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruželák, J.; Kvasničáková, A.; Hložeková, K.; Hudec, I. Progress in Polymers and Polymer Composites Used as Efficient Materials for EMI Shielding. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 123–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Narayan Maiti, U.; Sikdar, A.; Kumar Das, T.; Kumar, A.; Sudarsan, V. Recent Advances in Polymer and Polymer Composites for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding: Review and Future Prospects. Polym. Rev. 2019, 59, 687–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.-W.; Shen, Y.; Yue, Z.-X.; Nan, C.-W. Enhanced Microwave Absorption in Nickel/Hexagonal-Ferrite/Polymer Composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 132504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchenko, V.A.; Trukhanov, A.; Trukhanov, S.; Damay, F.; Porcher, F.; Balasoiu, M.; Lupu, N.; Chiriac, H.; Bozzo, B.; Fina, I.; et al. Magnetic and Ferroelectric Properties, Crystal and Magnetic Structures of SrFe11.9In0.1O19. Phys. Scr. 2020, 95, 044006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Jeung, W.Y. Anisotropic Injection Molding of Strontium Ferrite Powder Using a PP/PEG Binder System. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2001, 226–230, 1400–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemeda, O.M.; Henaish, A.M.A.; Salem, B.I.; El-Sbakhy, F.S.; Hamad, M.A. The Dielectric and Magnetic Properties of RTV-Silicon Rubber Ni–Cr Ferrite Composites. Appl. Phys. A 2020, 126, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nesraway, S.H.; Al-Maamori, M.H.; Al-Issawe, J.M. Preparation of a Rubber Nanocomposite (Silicone Rubber-Ferrite) for Protect Human from Bioeffects of Microwave Emitted from Mobile Devices. J. Bionanosci. 2018, 12, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruželák, J.; Matvejová, M.; Dosoudil, R.; Hudec, I. Barium and Strontium Ferrite-Filled Composites Based on NBR and SBR. J. Elastomers Plast. 2019, 51, 421–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suprapedi; Muljadi; Ramlan. Effect of Silicon Rubber Composition on Mechanical and Magnetic Properties of Rubber Composite Sr-Ferrite Magnet. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2221, 110005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hema, S.; Sambhudevan, S. Ferrite-Based Polymer Nanocomposites as Shielding Materials: A Review. Chem. Pap. 2021, 75, 3697–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rosa, A.D.; Grammatikos, S.A.; Ursan, G.A.; Aradoaei, S.; Summerscales, J.; Ciobanu, R.C.; Schreiner, C.M. Recovery of Electronic Wastes as Fillers for Electromagnetic Shielding in Building Components: An LCA Study. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 1133. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/83905.html (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- ISO 1183. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/74990.html (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- ISO 306. Available online: https://magazin.asro.ro/ro/standard/280443 (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- ASTM D638. Available online: https://www.astm.org/d0638-14.html (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- ISO 179. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:179:-1:ed-3:v1:en (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- ISO 178. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/70513.html (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- ASTM D792; Standard Test Methods for Density and Specific Gravity (Relative Density) of Plastics by Displacement. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- ISO 14577-1. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/56626.html (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. An Improved Technique for Determining Hardness and Elastic Modulus Using Load and Displacement Sensing Indentation Experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lungu, M.V.; Lucaci, M.; Tsakiris, V.; Brătulescu, A.; Cîrstea, C.D.; Marin, M.; Pătroi, D.; Mitrea, S.; Marinescu, V.; Grigore, F.; et al. Development and Investigation of Tungsten Copper Sintered Parts for Using in Medium and High Voltage Switching Devices. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 209, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lungu, M.V.; Pătroi, D.; Marinescu, V.; Caramitu, A.; Marin, M.; Tălpeanu, D.; Lucaci, M.; Godeanu, P. Preparation and study of the optical, electrical and dielectric characteristics of some disc-shaped tin dioxide-based varistors. Rom. J. Phys. 2022, 67, 610. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, W.; Cao, R.; Mei, C.; Wan, K.; Su, H.; Zhang, X.; Zou, Z.; Wang, J. Reductive Synthesis of Fe@Al2O3 Micro Powders with High Permeability and Low Magnetic Loss in the MHz Range. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2023, 579, 170865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, S.K.; Ohlan, A.; Singh, K. Designing of Nano Composites of Conducting Polymers for EMI Shielding. In Advances in Nanocomposites-Synthesis, Characterization and Industrial Applications; Reddy, B., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhu, J.; Yao, Q.; Wilkie, C.A. A Comparison of Various Methods for the Preparation of Polystyrene and Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) Clay Nanocomposites. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 3837–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidenfeller, B.; Höfer, M.; Schilling, F.R. Cooling Behaviour of Particle Filled Polypropylene during Injection Moulding Process. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2005, 36, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wypych, G. The Effect of Fillers on the Mechanical Properties of Filled Materials. In Handbook of Fillers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 525–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, T.; Kar, S. Nanoindentation of Reinforced Polymer Composites. In Encyclopedia of Materials: Plastics and Polymers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.F. A Review of Recent Research on Nanoindentation of Polymer Composites and Their Constituents. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 105, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Pascual, A.M.; Gómez-Fatou, M.A.; Ania, F.; Flores, A. Nanoindentation in Polymer Nanocomposites. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 67, 1–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. Measurement of Hardness and Elastic Modulus by Instrumented Indentation: Advances in Understanding and Refinements to Methodology. J. Mater. Res. 2004, 19, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovsik, M.; Stanek, M.; Dockal, A. Tribological and Micro-Mechanical Properties of Injected Polypropylene Modified by Electron Radiation. Lubricants 2023, 11, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xiong, Y. Using Nanoindentation to Characterize the Mechanical and Creep Properties of Shale: Load and Loading Strain Rate Effects. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 14317–14331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/B9780128051931000173 (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Available online: https://www.unitest.com/pdf/schwarzbeck/receiver/m1528en.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- IEC 60034-1; Insulation Class and Temperature Rise. IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9214671 (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Available online: https://environment.ec.europa.eu/topics/waste-and-recycling/end-life-vehicles_en (accessed on 10 November 2023).





| Property Name | Standard | Property Value |
|---|---|---|
| Melt flow index (230 °C/2.16 kg) | ISO 1133 [45] | 25 g/10 min |
| Density | ISO 1183 [46] | 0.9 g/cm3 |
| Vicat softening temperature (condition A120) | ISO 306 [47] | 150 °C |
| Tensile stress at yield | ASTM D638 [48] | 33 MPa |
| Charpy impact strength (23 °C/notched) | ISO 179 [49] | 2.5 kJ/m2 |
| Flexural modulus | ISO 178 [50] | 1400 MPa |
| Property Name | Property Value |
|---|---|
| Particle diameter | <1.05 μm |
| Molecular weight | 1061.7 g/mol |
| Melting point | >450 °C (mL) |
| Density | 5.18 g/mL at 25 °C (mL) |
| Solubility | Soluble in organic solvents |
| Property Name | Property Value |
|---|---|
| Specific gravity | 3.2 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 190 °C |
| Residual magnetic field strength | 235 mT |
| Coercive force | 177 kA/m |
| Intrinsic coercive force | 251 kA/m |
| Maximum stored energy | 10.9 kJ/m3 |
| Density after ripening | 3.21 g/cm3 |
| Melt flow index (270 °C/10 kg) | 130 g/10 min |
| Bending strength | 125 MPa |
| Impact strength | 28 kJ/m2 |
| Material Code | Composition (wt.%) of PP/SrFe12O19 Powder | Composition (wt.%) of PP/SrFe12O19 Concentrate |
|---|---|---|
| M0 | 100/0 | - |
| M1 | 75/25 | - |
| M2 | 70/30 | - |
| M3 | - | 75/25 |
| M4 | - | 70/30 |
| Material Code | Theoretical Density (g/cm3) | Mean Density ± SD (g/cm3) | Relative Density (%) | Porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0 | 0.900 | 0.894 ± 0.002 | 99.33 | 0.67 |
| M1 | 1.134 | 1.077 ± 0.002 | 94.95 | 5.05 |
| M2 | 1.197 | 1.157 ± 0.002 | 96.69 | 3.31 |
| M3 | 1.097 | 1.068 ± 0.002 | 97.32 | 2.68 |
| M4 | 1.148 | 1.138 ± 0.019 | 99.15 | 0.85 |
| Material Code | HIT (GPa) | Vickers Hardness HV | EIT (GPa) | S (mN/μm) | CIT (%) | Welast (μJ) | Wplast (μJ) | ηIT (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0 | 0.081 ± 0.005 | 7.53 ± 0.44 | 1.03 ± 0.06 | 101.59 ± 3.80 | 8.04 ± 0.15 | 0.99 ± 0.02 | 1.65 ± 0.07 | 37.07 ± 0.57 |
| M1 | 0.084 ± 0.005 | 7.74 ± 0.50 | 1.21 ± 0.05 | 112.51 ± 1.92 | 7.91 ± 0.37 | 0.91 ± 0.02 | 1.66 ± 0.05 | 35.25 ± 0.55 |
| M2 | 0.094 ± 0.003 | 8.67 ± 0.32 | 1.34 ± 0.03 | 118.38 ± 1.83 | 9.04 ± 0.34 | 0.85 ± 0.01 | 1.73 ± 0.04 | 32.89 ± 0.59 |
| M3 | 0.083 ± 0.003 | 7.69 ± 0.24 | 1.12 ± 0.03 | 104.71 ± 5.27 | 8.05 ± 0.28 | 0.98 ± 0.01 | 1.70 ± 0.06 | 36.52 ± 0.71 |
| M4 | 0.089 ± 0.008 | 8.23 ± 0.75 | 1.17 ± 0.05 | 105.43 ± 2.88 | 8.07 ± 0.44 | 0.97 ± 0.02 | 1.66 ± 0.07 | 36.75 ± 1.02 |
| Material Code | Equation | Critical Electrical Resistivity (Ω·m) | Critical Time (h) | Critical Time (days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0 | y = −285.1x + 1 × 107 | 4,084,298 | 20,750 | 865 |
| M1 | y = −219.43x + 3 × 106 | 917,492 | 9491 | 395 |
| M2 | y = −192.49x + 3 × 106 | 820,393 | 11,323 | 472 |
| M3 | y = −215.4x + 3 × 106 | 884,210 | 9823 | 409 |
| M4 | y = −209.56x + 3 × 106 | 879,685 | 10,118 | 422 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caramitu, A.R.; Lungu, M.V.; Ciobanu, R.C.; Ion, I.; Marin, M.; Marinescu, V.; Pintea, J.; Aradoaei, S.; Schreiner, O.D. Recycled Polypropylene/Strontium Ferrite Polymer Composite Materials with Electromagnetic Shielding Properties. Polymers 2024, 16, 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16081129
Caramitu AR, Lungu MV, Ciobanu RC, Ion I, Marin M, Marinescu V, Pintea J, Aradoaei S, Schreiner OD. Recycled Polypropylene/Strontium Ferrite Polymer Composite Materials with Electromagnetic Shielding Properties. Polymers. 2024; 16(8):1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16081129
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaramitu, Alina Ruxandra, Magdalena Valentina Lungu, Romeo Cristian Ciobanu, Ioana Ion, Mihai Marin, Virgil Marinescu, Jana Pintea, Sebastian Aradoaei, and Oliver Daniel Schreiner. 2024. "Recycled Polypropylene/Strontium Ferrite Polymer Composite Materials with Electromagnetic Shielding Properties" Polymers 16, no. 8: 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16081129
APA StyleCaramitu, A. R., Lungu, M. V., Ciobanu, R. C., Ion, I., Marin, M., Marinescu, V., Pintea, J., Aradoaei, S., & Schreiner, O. D. (2024). Recycled Polypropylene/Strontium Ferrite Polymer Composite Materials with Electromagnetic Shielding Properties. Polymers, 16(8), 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16081129








