Mechanical, Thermal, and Physicochemical Properties of Filaments of Poly (Lactic Acid), Polyhydroxyalkanoates and Their Blend for Additive Manufacturing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Physicochemical Analysis
2.2.2. Thermal Analysis
2.2.3. Mechanical and Dynamic Mechanical Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical and Structural Composition of the Filaments
3.1.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
3.1.2. Raman Spectroscopy
3.1.3. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy
3.1.4. Wide-Angle X-ray Diffraction
3.2. Thermal Properties and Effect of Melting by Additive Manufacturing
3.2.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry of Filaments
3.2.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis of Filaments
3.2.3. X-ray Diffraction of Polymers after FDM
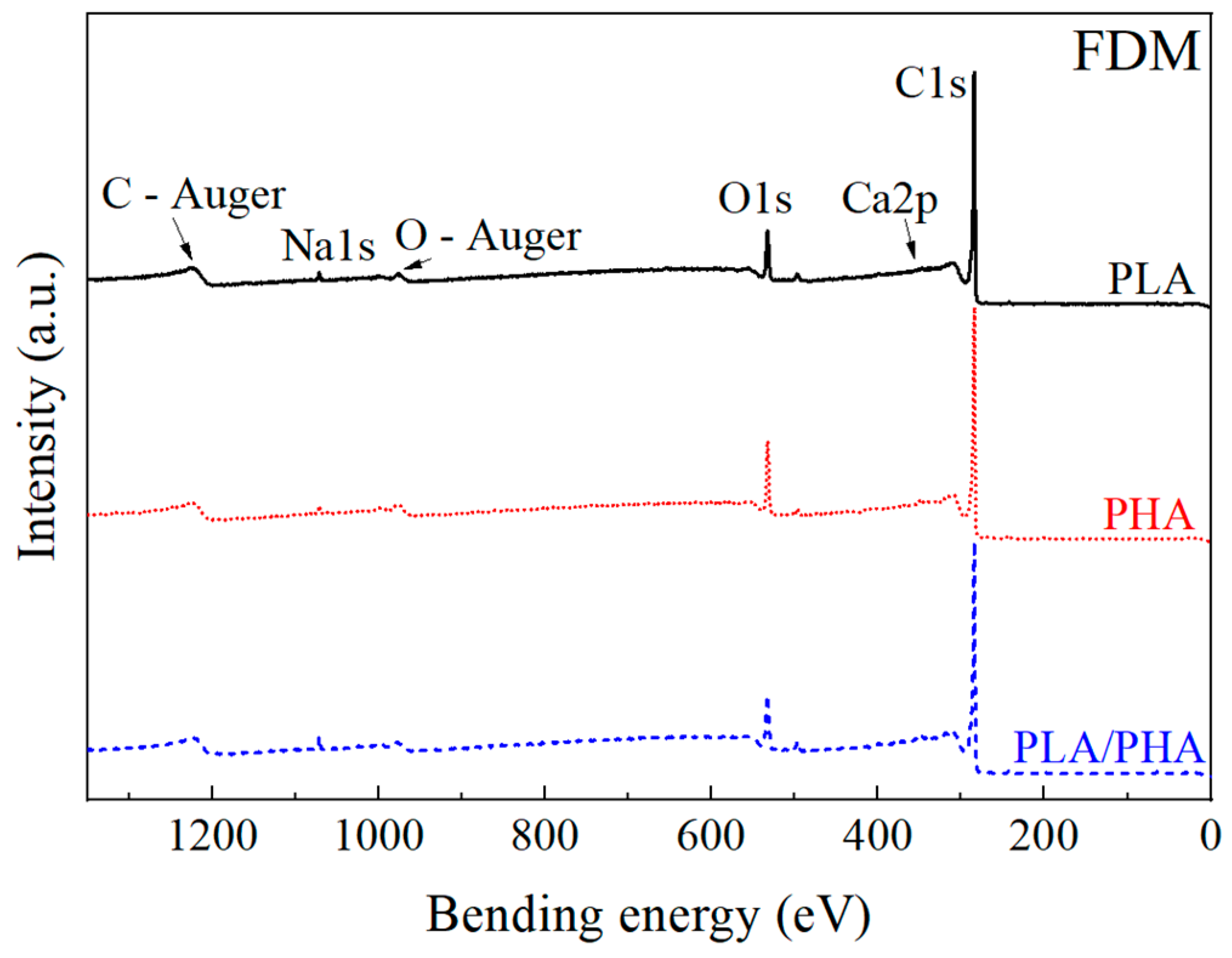
3.2.4. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy
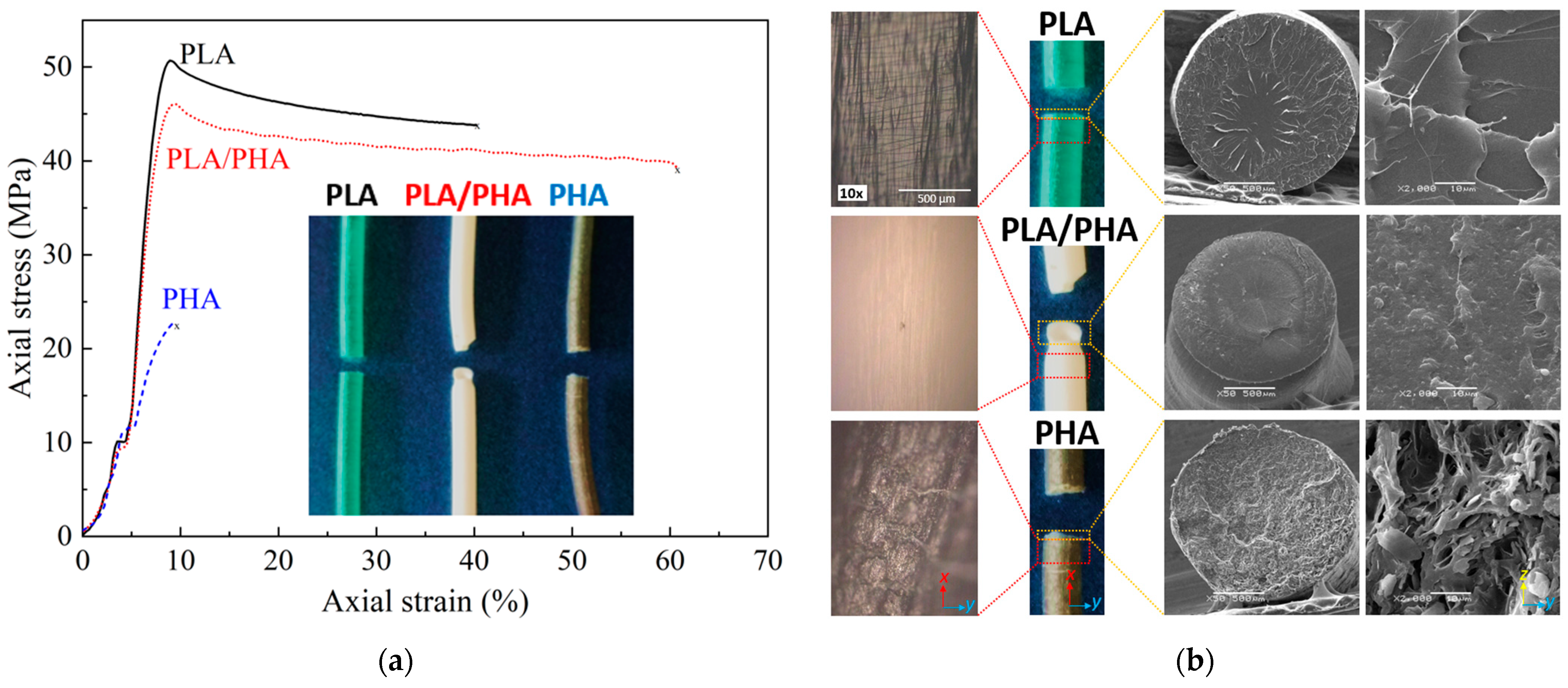
3.3. Quasi-Static Tensile Response of Filaments up to Failure
3.4. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis of Filaments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, L.; Wang, Z.; Ren, L.; Xu, C.; Li, B.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Q. Understanding the role of process parameters in 4D printing: A review. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 265, 110938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawalkar, R.; Dubey, H.K.; Lokhande, S.P. A review for advancements in standardization for additive manufacturing. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 50, 1983–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, N.; Senthil, P.; Vinodh, S.; Jayanth, N. A review on composite materials and process parameters optimization for the fused deposition modelling process. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2017, 12, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aworinde, A.K.; Adeosun, S.O.; Oyawale, F.A.; Akinlabi, E.T.; Akinlabi, S.A. Parametric effects of fused deposition modelling on the mechanical properties of polylactide composites: A review. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1378, 022060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamood, R.M.; Jen, T.C.; Akinlabi, S.A.; Hassan, S.; Abdulrahman, K.O.; Akinlabi, E.T. Role of additive manufacturing in the era of industry 4.0. In Additive Manufacturing: A Tool for Industrial Revolution 4.0; Manjaiah, M., Raghavendra, K., Balashanmugam, N., Davim, J.P., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2021; pp. 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-Calero, M.; Valé, S.C.R.; Marcos-Fernández, A.; Rodríguez-Hernández, J. 3D printing of thermoplastic elastomers: Role of the chemical composition and printing parameters in the production of parts with controlled energy absorption and damping capacity. Polymers 2021, 13, 3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, H.C.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, H. A review on 3D printed smart devices for 4D printing. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2017, 4, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanth, N.; Jaswanthraj, K.; Sandeep, S.; Mallaya, N.H.; Siddharth, S.R. Effect of heat treatment on mechanical properties of 3D printed PLA. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 123, 104764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayrilmis, N.; Kariz, M.; Kwon, J.H.; Kuzman, M.K. Effect of printing layer thickness on water absorption and mechanical properties of 3D-printed wood/PLA composite materials. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 102, 2195–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brütting, C.; Dreier, J.; Bonten, C.; Altstädt, V.; Ruckdäschel, H. Sustainable inmiscible polylactic acid (PLA) and poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) blends: Crystallization and foaming behavior. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 6676–6687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, M.R.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. The effects of process engineering on the performance of PLA and PHBV blends. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2011, 296, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorgan, J.R.; Lehermeier, H.; Mang, M. Thermal and rheological properties of commercial-grade poly(lactic acid)s. J. Polym. Environ. 2000, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naser, A.Z.; Deiab, I.; Darras, B.M. Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), green alternatives to petroleum-based plastics: A review. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 17151–17196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noda, I.; Satkowski, M.M.; Dowrey, A.E.; Marcott, C. Polymer alloys of nodax copolymers and poly (lactic acid). Macromol. Biosci. 2004, 4, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluhm, T.L.; Hamer, G.K.; Marchessault, R.H.; Fyfe, C.A.; Veregin, R.P. Isodimorphism in bacterial poly (β-hydroxybutyrate-co-β-hydroxyvalerate). Macromolecules 1986, 19, 2871–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerard, T.; Budtova, T. Morphology and molten-state rheology of polylactide and polyhydroxyalkanoates blends. Eur. Polym. J. 2012, 48, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, M.L.I.; D’amico, D.A.; Manfredi, L.B.; Cyras, V.P. Effect of natural glyceryl tributyrate as plasticizer and compatibilizer pn the performance of bio-based polylactic acid/poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) blends. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerard, T.; Budtova, T.; Podshivalov, A.; Bronnikov, S. Polylactide/poly (hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) blends: Morphology and mechanical properties. Express Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algarni, M.; Ghazali, S. Comparative study of the sensitive of PLA, ABS, PEEK, and PETG’s mechanical properties to FDM printing process parameters. Crystals 2021, 11, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.; Miri, S.; Cole, R.G.; Postigo, A.A.; Saleh, M.A.; Dondish, A.; Melenka, G.W.; Fayazbakhsh, K. Towards optimization of polymer filament tensile test for material extrusion additive manufacturing process. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 8458–8472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ausejo, J.G.; Rydz, J.; Musiol, M.; Sikorska, W.; Sobota, M.; Wlodarczyk, J.; Adamus, G.; Janeczek, H.; Kwiecien, I.; Hercog, A.; et al. A comparative study of three-dimensional printing directions: The degradation and toxicological profile of PLA/PHA blend. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 152, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frone, A.N.; Nicolae, C.A.; Eremia, M.C.; Tofan, V.; Ghiurea, M.; Chiulan, I.; Radu, E.; Damian, C.M.; Panaitescu, D.M. Low molecular weight and polymeric modifiers as toughening agents in poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) films. Polymers 2020, 12, 2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Cui, Z.; Sun, X.; Turng, L.S.; Peng, X. Morphology and properties of injection molded solid and microcellular polylactic acid / polyhydroxybutyrate-valerate (PLA/PHBV) blends. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidhate, S.; Innocentini-Mei, L.; D’Souza, N.A. Mechanical and electrical multifunctional poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)–multiwall carbon nanotube nanocomposites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2012, 52, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D3379; Standard Test Method for Tensile Strength and Young’s Modulus for High-Modulus Single Filament Fibers. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1975.
- Clyne, T.W.; Hull, D. An Introduction to Composite Materials, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Lv, J.; Feng, J. Spectral characterization of four kinds of biodegradable plastics: Poly (lactic acid), poly (butylenes adipate-co-terepthlate), poly (hydroxybutyrate-cohydroxyvalerate) and poly (butylenes succinate) with FTIR and Raman spectroscopy. J. Polym. Environ. 2013, 21, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, C.M.S.; Temperini, M.L.A. FT-Raman investigation of biodegradable polymers: Poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) and poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate). Vib. Spectrosc. 2010, 54, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.E.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Orts, W.J.; Medeiros, E.S. Structural and morphological characterization of micro and nanofibers produced by electrospinning and solution blow spinning: A comparative study. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 2013, 409572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Anthony, P.; Chowdhury, A. High molecular weight poly (lactic acid) synthesized with apposite catalytic combination and longer time). Orient. J. Chem. 2018, 34, 1984–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.; Dikshit, P.K.; Moholkar, V.S. Production, ultrasonic extraction and characterization of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) using bacillus megaterium and cupriavidus necator. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 2392–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, M.; Sato, H.; Ozaki, Y.; Fischer, D.; Siesler, H.W. Temperature-dependent Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and Raman mapping spectroscopy of phase-separation in a poly (3-hydroxybutyrate)–poly (l-lactic acid) blend. Appl. Spectrosc. 2013, 67, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quynh, T.M.; Mai, H.H.; Lan, P.N. Stereocomplexation of low molecular weight poly (l-lactic acid) and high molecular weight poly (d-lactic acid), radiation crosslinking PLLA/PDLA stereocomplexes and their characterization. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2013, 83, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meaurio, E.; López-Rodríguez, N.; Sarasua, J.E. Infrared spectrum of poly (l-lactide): Application to crystallinity studies. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 9291–9301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kann, Y.; Shurgalin, M.; Krishnaswamy, R.K. FTIR spectroscopy for analysis of crystallinity of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) polymers and its utilization in evaluation of aging, orientation and composition. Polym. Test. 2014, 40, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.; Pokhrel, D.; Coats, E.R.; Guho, N.M.; McDonald, A.G. Effect of 3-hydroxyvalerate content on thermal, mechanical, and rheological properties of poly (3-hydrohybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) biopolymers produced from fermented dairy manure. Polymers 2022, 14, 4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, H.; Ando, Y.; Mitomo, H.; Ozaki, Y. Infrared spectroscopy and x-ray diffraction studies of thermal behavior and lamella structures of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (P(HB-co-HV)) with PHB-type crystal structure and PHV-type crystal structure. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 2829–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.G.; Fernández, N.G.; del Toro, P.O.; Rapado Palenque, M. Raman spectroscopy of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) modified with poly (vinyl acetate) by radiation-induced copolymerization. Nucleus 2007, 42, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, J.P.; Tucker, B.; Moreno, G.H.; Charles, P.; Thomas, V. Low-temperature inductively coupled plasma as a method to promote biomineralization on 3D printed poly (lactic acid) scaffolds. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 14717–14728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crapnell, R.D.; Bernalte, E.; Ferrari, A.G.-M.; Whittingham, M.J.; Williams, R.J.; Hurst, N.J.; Banks, C.E. All-in-one single-print additively manufactures electroanalytical sensing platforms. ACS. Meas. Sci. Au 2022, 2, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelwahab, M.A.; Flynn, A.; Chiou, B.-S.; Imam, S.; Orts, W.; Chiellini, E. Thermal, mechanical and morphological characterization of plasticized PLA-PHB blends. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 1822–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mngomezulu, M.E.; Luyt, A.S.; John, M.J. Morphology, thermal and dynamic mechanical properties of poly (lactic acid)/expandable graphite (PLA/EG) flame retardant composites. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2019, 32, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.X.; Chen, S.H.; Cheng, Y.H.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, M.F. Structural characteristics and enhanced mechanical and thermal properties of full biodegradable tea polyphenol/poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) composite films. Express Polym. Lett. 2013, 7, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunioka, M.; Tamaki, A.; Doi, Y. Crystalline and thermal properties of bacterial copolyesters: Poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and poly (3-hyxroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate). Macromolecules 1989, 22, 694–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.K.; Munir, R.I.; Blunt, W.; Dartiailh, C.; Cheng, J.; Charles, T.C.; Levin, D.B. Synthesis and physical properties of polyhydroxyalkanoates polymers with different monomer compositions by recombinant pseudomonas putida LS46 expressing a novel PHA synthase (PhaC116) enzyme. Appl. Sci 2017, 7, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanheiro, T.L.D.A.; Passador, F.R.; de Oliveira, M.P.; Durán, N.; Lemes, A.P. Preparation and characterization of maleic anhydride grafted poly (hydroxybutirate-co-hydroxyvalerate)-PHBV-g-MA. Mater. Res. 2016, 19, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalcik, A.; Sangroniz, L.; Kalina, M.; Skopalova, K.; Humpolícek, P.; Omastova, M.; Mundingler, N.; Müller, A.J. Properties of scaffols prepared by fused deposition modeling of poly (hydroxyalkanoates). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas, L.F.; Casarin, S.A.; Nepomuceno, N.C.; Alencar, M.I.; Marcondes Angelli, J.A.; Souto de Medeiros, E.; de Oliveira Wanderley Neeto, A.; Pinheiro de Oliveria, M.; de Medeiros, A.M.; Ferreira e Santos, A.S. Reprocessability of PHB in extrusión: ATR-FTIR, tensile tests and thermal studies. Polímeros 2017, 27, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrpouya, M.; Vahabi, H.; Barletta, M.; Laheurte, P.; Langlois, V. Additive Manufacturing of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) biopolymers: Materials, printing, techniques and applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 127, 112216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassie, N.; Murray, E.J.; Holmes, P.A. The thermal degradation of poly (-(D)-βhydroxybutyric acid): Part 1–Identification and quantitative analysis of products. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1984, 6, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Gan, Q.; Liu, X.; Ma, Y.; Hu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, C. Poly(glycerol sebacate)- modified polylactic acid scaffolds with improved hydrophilicity, mechanical strength and bioactivity for bone tissue regeneration. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 79703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stloukal, P.; Novák, I.; Micusik, M.; Procházka, M.; Kurcharczyk, P.; Chodák, I.; Lehocký, M.; Sedlarik, V. Effect of plasma treatment on the release kinetics of a chemotherapy drug from biodegradable polyester films and polyester urethane films. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2017, 67, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vostrejs, P.; Adamcova, D.; Vaverková, M.D.; Enev, V.; Kalina, M.; Machovsky, M.; Sourková, M.; Marova, I. Active biodegradable packaging films modified with grape seeds lignin. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 29202–29213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Pan, Y.T.; Kuehnert, I.; Gehde, M.; Wang, D.Y.; Lauteritz, A. Renewable vanillin-based flame retardant for poly (lactic acid): A way to enhance flame retardancy and toughness simultaneously. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 42189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agaliotis, E.M.; Concha, B.D.A.; May-Pat, A.; Morales, J.P.; Bernal, C.; Valadez-González, A.; Herrera-Franco, P.J.; Proust, G.; Koh-Dzul, J.F.; Carrillo, J.G.; et al. Tensile Behavior of 3D Printed Polylactic Acid (PLA) Based Composites Reinforced with Natural Fiber. Polymers 2022, 14, 3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, S.; Behrooz, R.; Ghasemi, I.; Yassar, R.S.; Long, F. Development of nanocellulose-reinforced PLA nanocomposite by using maleated PLA (PLA–g–MA). J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2017, 31, 1090–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guessasma, S.; Belhabib, S.; Altin, A. On the tensile behavior of bio-sourced 3D-printed structures from a microstructural perspective. Polymers 2020, 12, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santo, J.; Penumakala, P.K.; Adusumalli, R.B. Mechanical and electrical properties of three-dimensional printed polylactic acid-graphene-carbon nanofiber composites. Polym. Compos. 2021, 42, 3231–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argon, A.S.; Cohen, R.E. Mechanisms of toughening brittle polymers. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1994, 176, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datasheet, T. colorFabb Color on Demand; ColorFabb: Belfeld, The Netherlands, 2018; Available online: https://colorfabb.com/media/datasheets/tds/colorfabb/TDS_E%20ColorFabb%20Color%20on%20Demand.pdf (accessed on 8 March 2022).
- Badia, J.D.; Strömberg, E.; Karlsson, S.; Ribes-Greus, A. Material valorisation of amorphous polylactide. Influence of thermos-mechanical degradation on the morphology, segmental dynamics, thermal and mechanical performance. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofokeng, J.P.; Luyt, A.S.; Tabi, T.; Kovács, J. Comparison of injection moulded, natural fibre-reinforced composites with PP and PLA as matrices. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2011, 25, 927–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Yu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Fu, L. Morphology, crystallization and thermal behaviors of PLA-based composites: Wonderful effects of hybrid GO/PEG via dynamic impregnating. Polymers 2017, 9, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Gupta, N. Determining elastic modulus from dynamic mechanical analysis: A general model based on loss modulus data. Materialia 2018, 4, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
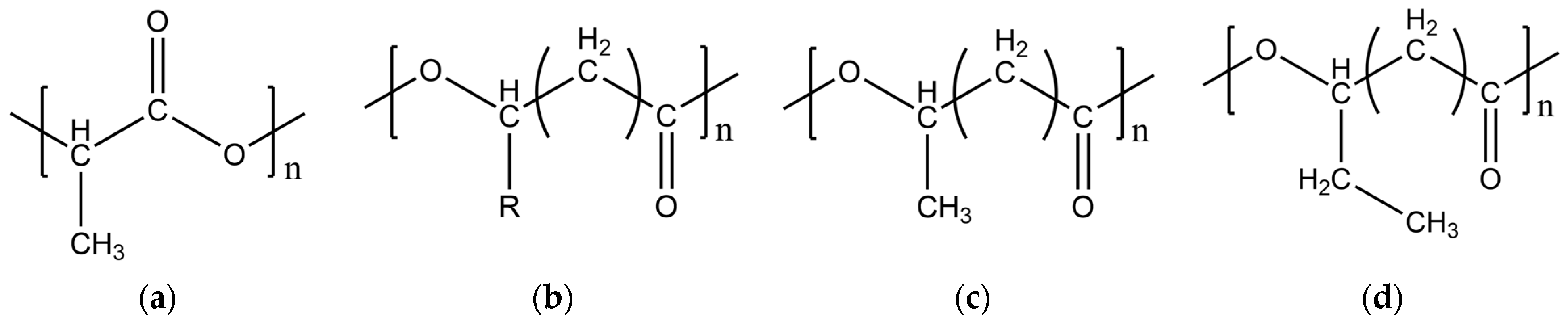
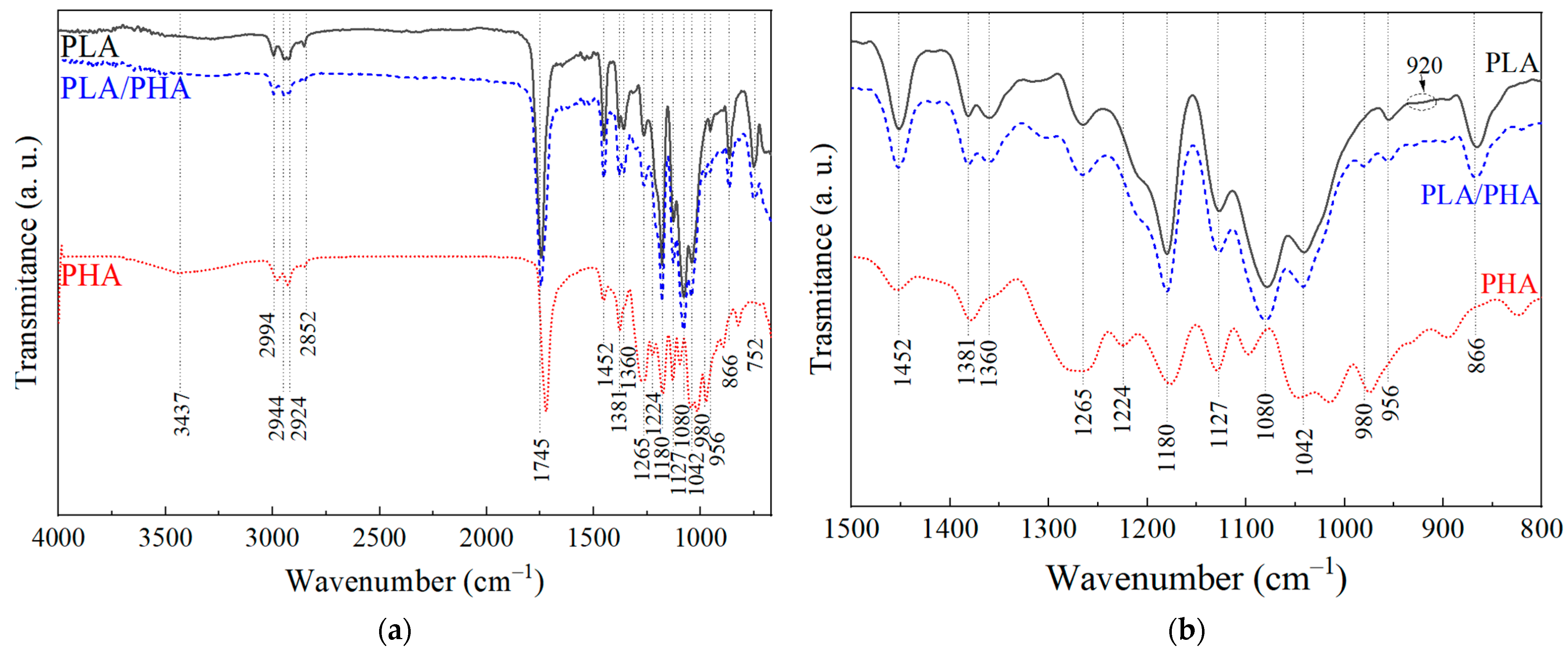

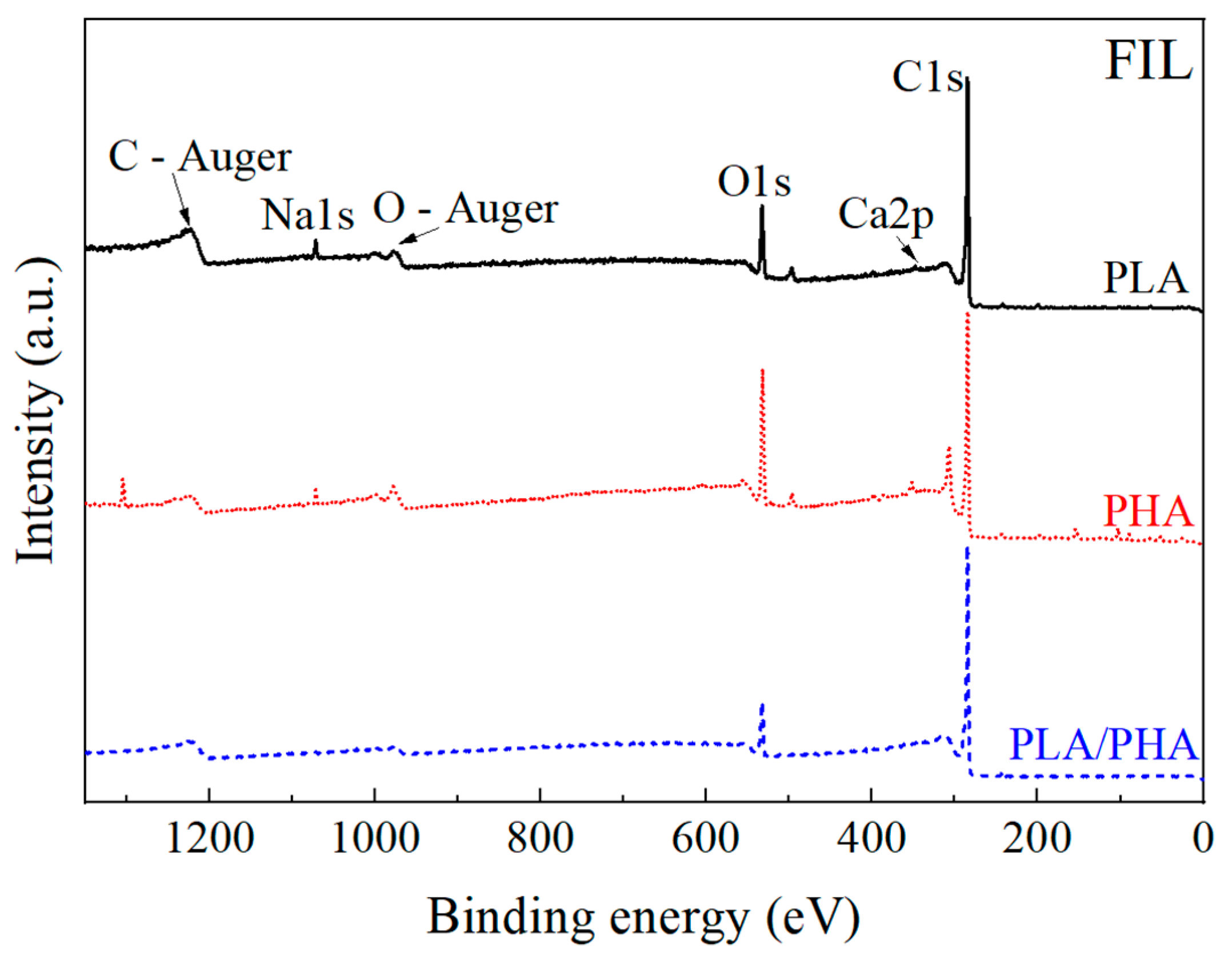



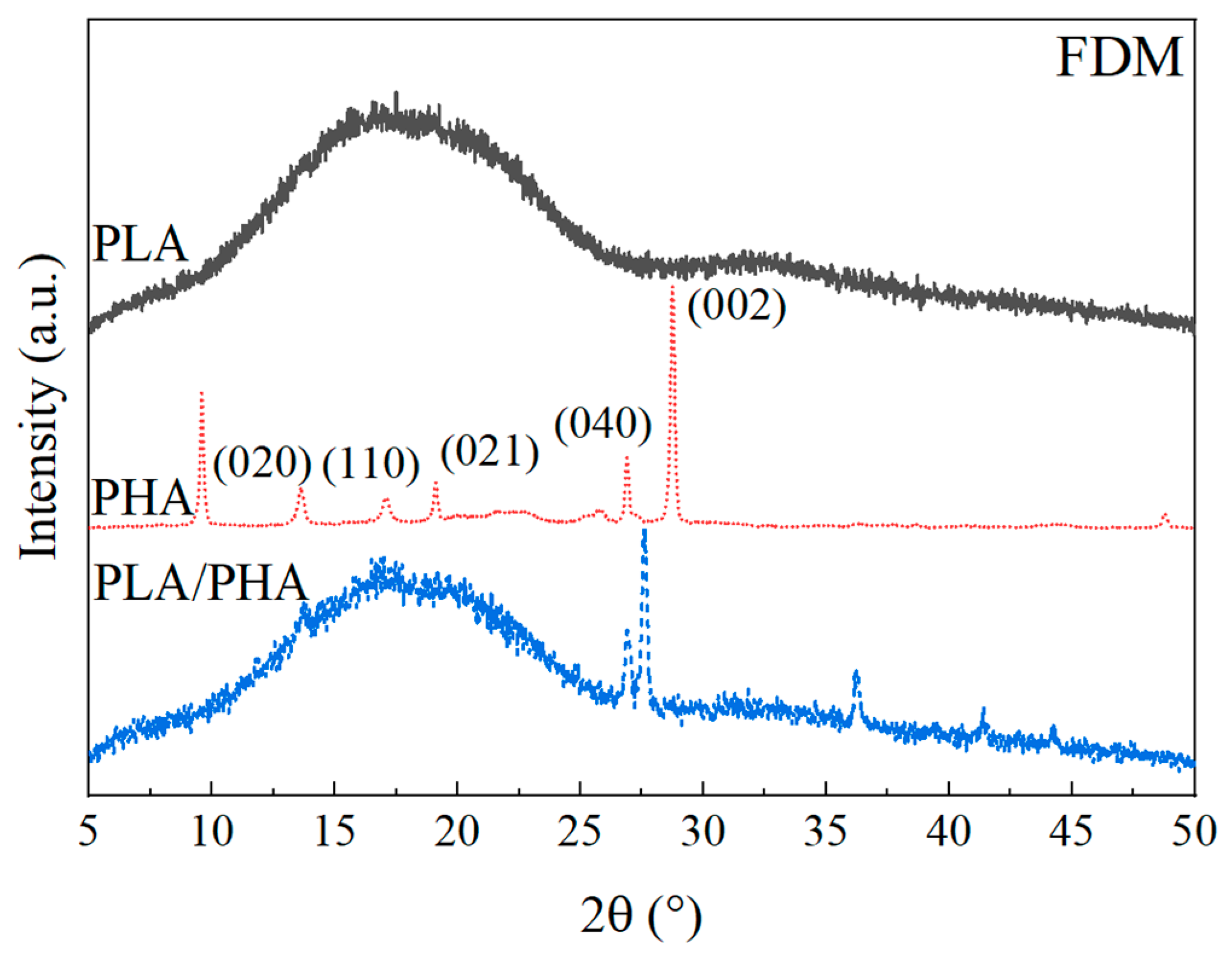

| Matrix | Heating | Tg (°C) | Tcc (°C) | PLA | PHA | (%) Equation (2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tm1 (°C) | Tm2 (°C) | Tm3 (°C) | |||||
| PLA | First | 64.6 | 121.3 | 148.4 | - | - | 1.5 |
| Second | 63.5 | 122.8 | 148.2 | - | - | 1.7 | |
| PHA | First | - | - | - | - | 172.0 | 47.8 |
| Second | - | - | - | 162.4 | 171.2 | 50.1 | |
| PLA/PHA | First | 61.0 | 126.0 | 150.7 | - | - | 0.3 (PLA) |
| Second | 60.5 | 117.0 | 147.8 | - | - | 0.6 (PLA) | |
| Matrix. | PHA | PLA | Tfd (°C) | Residual Mass at 500 °C (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tid1 (°C) | Tdmax1 (°C) | Tid2 (°C) | Tdmax2 (°C) | |||
| PLA | - | - | 319.3 ± 1.2 | 373.7 ± 1.5 | 390.3 ± 1.5 | 0.3 ± 0.1 |
| PHA | 262 ± 1.7 | 296.3 ± 5.5 | - | - | 315.7 ± 5.1 | 11.5 ± 0.1 |
| PLA–PHA | 292.0 ± 1.7 | 315.0 ± 1.0 | 331.0 ± 1.7 | 374.0 ± 1.0 | 394.7 ± 1.5 | 0.3 ± 0.1 |
| Matrix | Type of Sample | C (%) | O (%) | Ca (%) | Na (%) | Cl (%) | N (%) | C/O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | FIL | 83.6 | 11.7 | 0.59 | 1.51 | 0.78 | 1.8 | 7.15 |
| FDM | 89.0 | 9.1 | - | 0.81 | 0.21 | 0.86 | 9.76 | |
| PHA | FIL | 70.2 | 17.6 | 1.48 | 1.03 | 0.98 | 2.11 | 3.99 |
| FDM | 86.9 | 11.8 | - | 0.71 | 0.61 | - | 7.40 | |
| PLA–PHA | FIL | 90.3 | 9.70 | - | - | - | - | 9.31 |
| FDM | 87.1 | 10.5 | 0.78 | 0.92 | 0.48 | 0.3 | 8.32 |
| Element | C1s | O1s | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binding | C–C (%) | C–O (%) | C=O (%) | C–O (%) | C=O (%) | |
| PLA | FIL | 66.8 | 29.4 | 3.70 | 81.0 | 19.0 |
| FDM | 77.2 | 15.5 | 7.4 | 93.5 | 6.5 | |
| PHA | FIL | 66.4 | 24.3 | 9.4 | 79.5 | 20.5 |
| FDM | 63.8 | 29.1 | 7.2 | 65.2 | 34.8 | |
| PLA–PHA | FIL | 58.6 | 32.3 | 9.01 | 84.4 | 15.6 |
| FDM | 70.6 | 25.8 | 3.53 | 93.0 | 6.99 | |
| Filament | PLA | PHA | PLA–PHA | PLA–PHA Equation (4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elastic modulus (GPa) | 1.5 ± 0.2 | 0.5 ± 1.6 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 1.4 |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 50.6 ± 0.3 | 21.1 ± 3.8 | 47.4 ± 0.2 | 46.9 |
| Elongation at break (%) | 38.1 ± 3.2 | 16.2 ± 1.8 | 51.4 ± 9.8 | 35.7 |
| Toughness (J/m3) | 16.1 ± 1.5 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 23.8 ± 4.4 | 14.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mondragón-Herrera, L.I.; Vargas-Coronado, R.F.; Carrillo-Escalante, H.; Cauich-Rodríguez, J.V.; Hernández-Sánchez, F.; Velasco-Santos, C.; Avilés, F. Mechanical, Thermal, and Physicochemical Properties of Filaments of Poly (Lactic Acid), Polyhydroxyalkanoates and Their Blend for Additive Manufacturing. Polymers 2024, 16, 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16081062
Mondragón-Herrera LI, Vargas-Coronado RF, Carrillo-Escalante H, Cauich-Rodríguez JV, Hernández-Sánchez F, Velasco-Santos C, Avilés F. Mechanical, Thermal, and Physicochemical Properties of Filaments of Poly (Lactic Acid), Polyhydroxyalkanoates and Their Blend for Additive Manufacturing. Polymers. 2024; 16(8):1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16081062
Chicago/Turabian StyleMondragón-Herrera, L. Itzkuautli, R. F. Vargas-Coronado, H. Carrillo-Escalante, J. V. Cauich-Rodríguez, F. Hernández-Sánchez, C. Velasco-Santos, and F. Avilés. 2024. "Mechanical, Thermal, and Physicochemical Properties of Filaments of Poly (Lactic Acid), Polyhydroxyalkanoates and Their Blend for Additive Manufacturing" Polymers 16, no. 8: 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16081062
APA StyleMondragón-Herrera, L. I., Vargas-Coronado, R. F., Carrillo-Escalante, H., Cauich-Rodríguez, J. V., Hernández-Sánchez, F., Velasco-Santos, C., & Avilés, F. (2024). Mechanical, Thermal, and Physicochemical Properties of Filaments of Poly (Lactic Acid), Polyhydroxyalkanoates and Their Blend for Additive Manufacturing. Polymers, 16(8), 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16081062







