Augmenting the Efficacy of a Polyvinyl Alcohol Selective Layer Coated on Polyvinylidene Fluoride Support Membranes with Kaolinite Introduction for Improved Pervaporation Dehydration of Epichlorohydrin/Isopropanol/Water Ternary Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Hydrophilic Kaolinite (HK)
2.3. Preparation of the PVA/HK-PVDF Membrane
2.4. Characterization Techniques for Kaolinite Particles and the PVA Membrane
2.5. Degree of Swelling
2.6. Pervaporation Experiment Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of RK and HK Particles
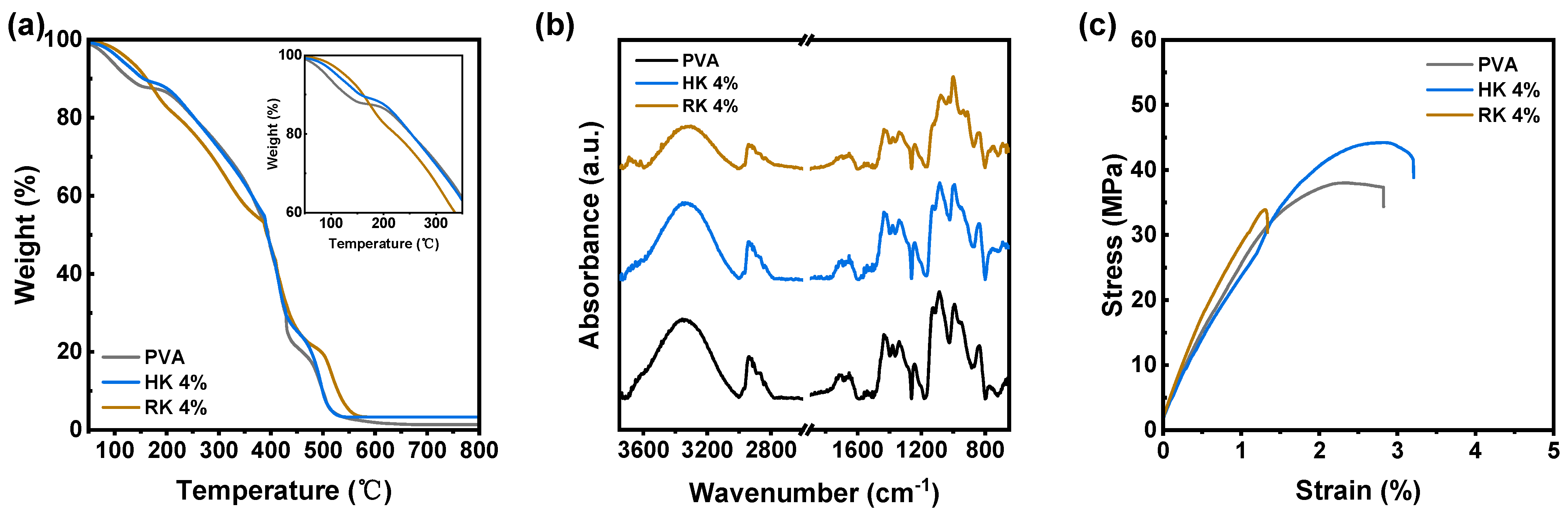
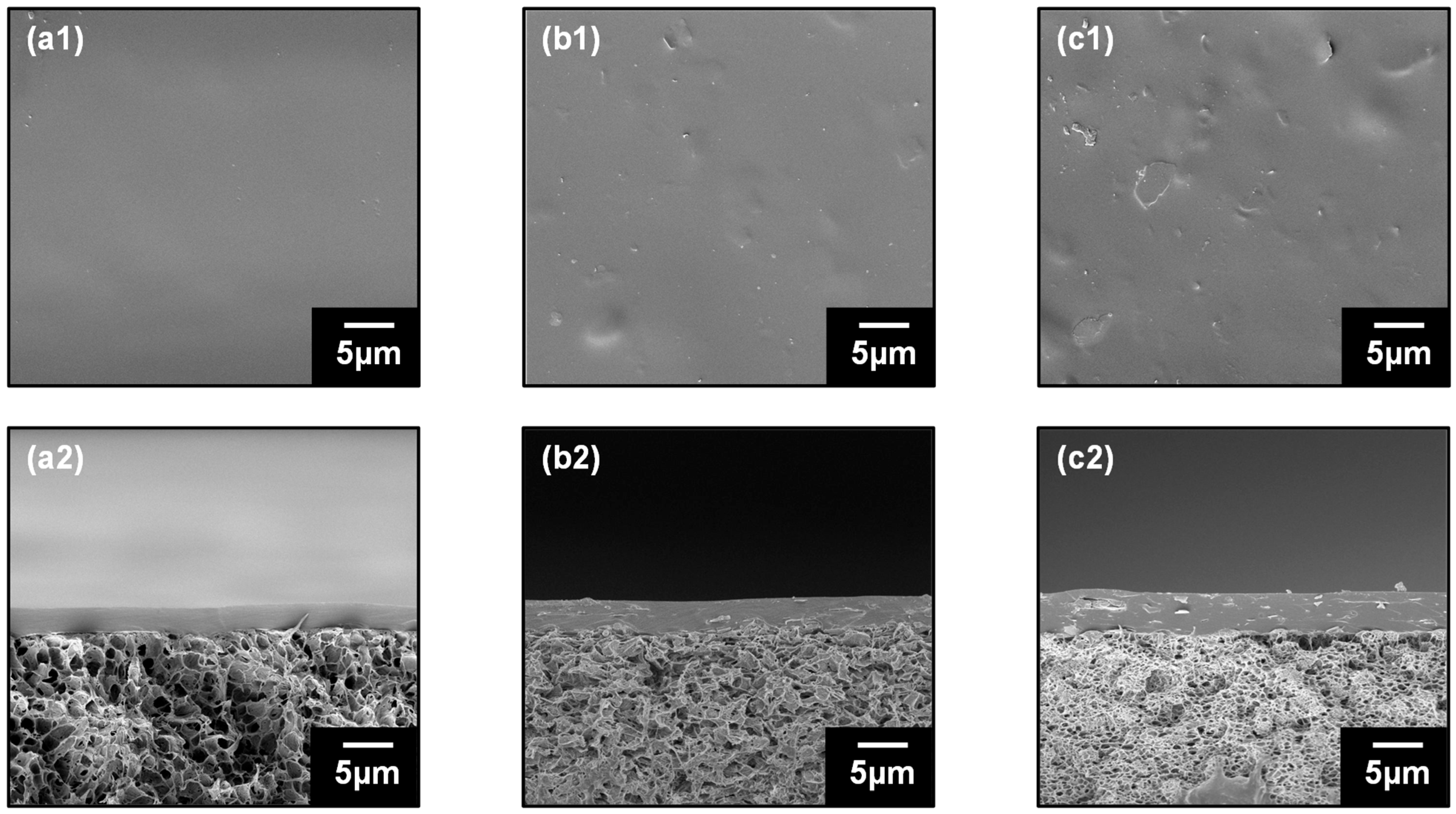
3.2. Characterization of Kaolinite–PVA Composite Membranes
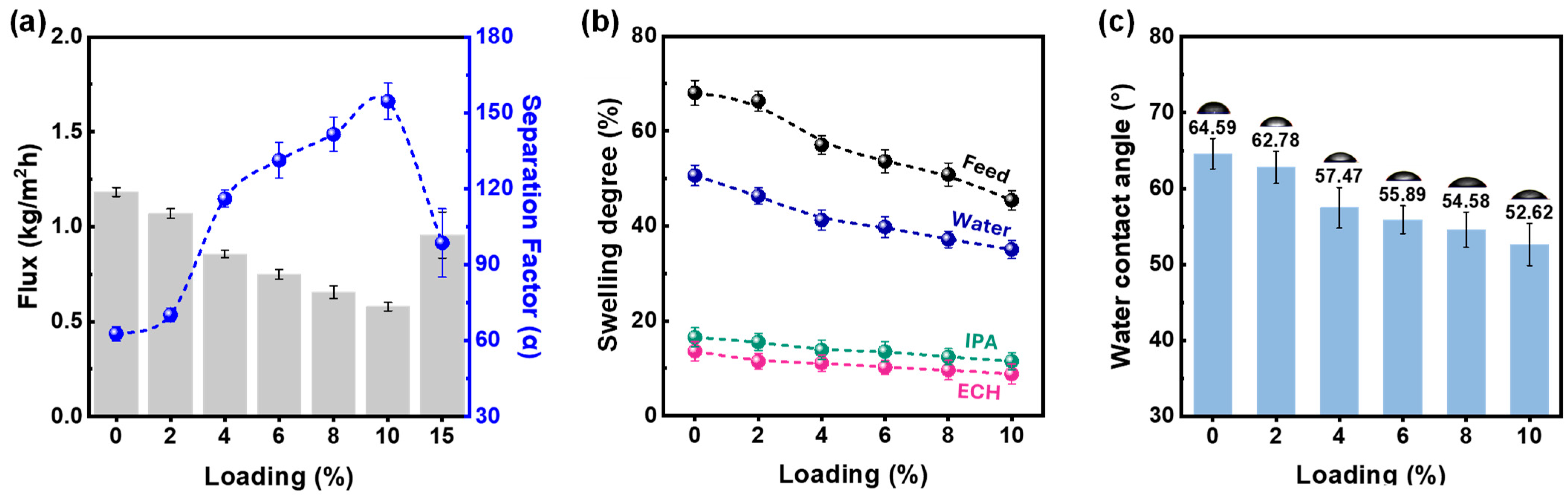
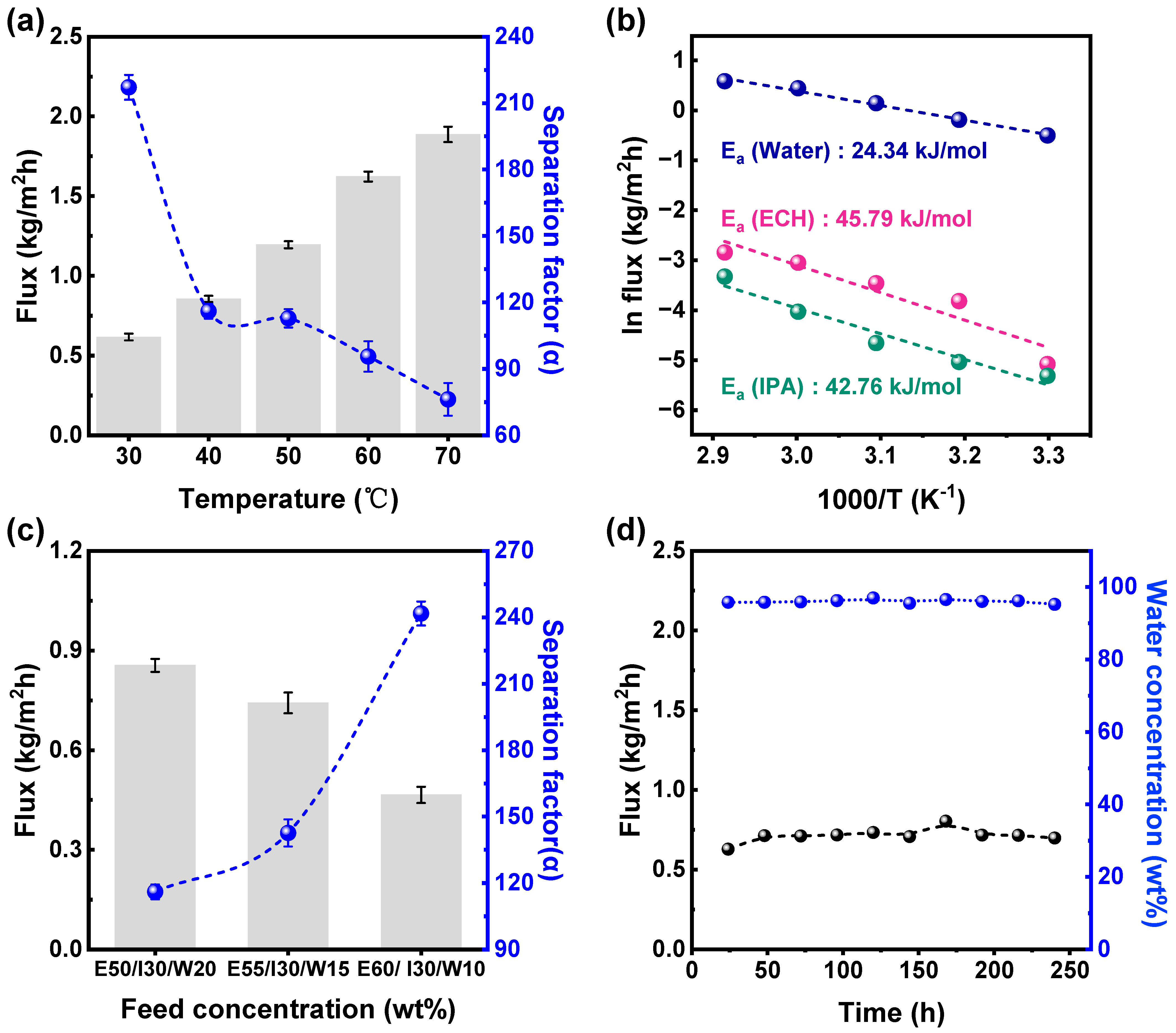
3.3. Pervaporation Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolkowicz, I.; Aronzon, C.; Coll, C. Lethal and sublethal toxicity of the industrial chemical epichlorohydrin on Rhinella arenarum (Anura, Bufonidae) embryos and larvae. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 263, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waidyanatha, S.; Gaudette, N.; Hong, Y.; Fennell, T. Formation of epichlorohydrin, a known rodent carcinogen, following oral administration of 1,3 Dichloro-2-propanol in rats. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2014, 27, 1787–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Na, H.; Lee, H.; Kim, M.; Lim, C.; Lim, C.; Seo, B. Distillation pervaporation membrane hybrid system for epichlorohydrin and isopropyl alcohol recovery in epoxy resin production process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kwon, Y.; Kim, D.; Park, H.; Cho, Y.; Nam, S.; Park, Y. Ultra-dehydration of a reactive epichlorohydrin-containing organic mixture using a defect free thin carbon molecular sieve composite membrane. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 2419–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norkobilov, A.; Gorri, D.; Ortiz, I. Comparative study of conventional, reactive-distillation and pervaporation integrated hybrid process for ethyl tert-butyl ether production. Chem. Eng. Process. Process. Intensif. 2017, 122, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiano, F.; Russo, F.; Ursino, C.; Munoz, R.; Criscuoli, A.; Figoli, A. Pervaporation and membrane distillation technology in biorefinery. In Membrane Engineering in the Circular Economy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 251–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, Y.; Shi, G.; Le, N.; Tang, Y.; Zuo, J.; Nunes, S.; Chung, T. Recent membrane development for pervaporation processes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 57, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, C.; Ying, Y.; Zhang, W. Improve MoF-801 dispersibility in PVA membranes by pre-crosslinking strategy for enhanced pervaporation performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 687, 122043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Cheng, X.; Jiang, G.; Xie, J.; Cai, W.; Li, J.; Wang, Y. Preparation and pervaporation performance of PVA membrane with biomimetic modified silica nanoparticles as coating. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 653, 120535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, H.; Salehian, S.; Amiri, S.; Soltanieh, M.; Musavi, S. UV-cured polyvinyl alcohol-Mxene mixed matrix membranes for enhancing pervaporation performance in dehydration of ethanol. Polym. Test. 2023, 123, 108046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Chen, J.; Chang, C.; Liao, K.; Tung, K.; Price, W.; Yamauchi, Y.; Wu, K. A drying-free, water-based process for fabricating mixed matrix membranes with outstanding pervaporation performance. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 12793–12796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, R.; Gonzalez, J.; Iglesia, O.; Galiano, F.; Fila, V.; Malankowska, M.; Rubio, C.; Figoli, A.; Tellez, C.; Coronas, J. Towards the dehydration of ethanol using pervaporation cross-linked poly (vinyl alcohol)/graphene oxide membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 582, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, M.; Zhou, S.; Xue, A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, Q. Graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets embedded in poly(vinyl alcohol) nanocomposite membranes for ethanol dehydration via pervaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 188, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Gascon, J.; Li, J.; Bruggen, B. Metal-organic frameworks-based membrane for liquid separation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 7124–7144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Ejtemaei, M.; Nguyen, A.; Zhou, C. XPS analysis of the surface chemistry of sulfuric acid-treated kaolinite and diaspore mineral with flotation reagents. Miner. Eng. 2019, 136, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, P.; Pereira, D.; Papini, R.; Magriotis, Z. Effect of dimethyl sulfoxide intercalation in to kaolinite on ether amine adsorption: Experimental and theoretical investigation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, S.; Shin, H.; Cho, K.; Shon, M.; Kwon, H.; Jo, S.; Nam, S.; Park, Y. Highly selective PDMS-PVDF composite membrane with hydrophobic crosslinking series for isopropanol-1,5 pentane diol pervaporation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 114, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, Q. Hierarchical structure Kaolinite Nanospheres with remarkably enhanced adsorption properties for methylene blue. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Abukhadra, M.; Mohamed, A.; Nadeem, A.; Ahmad, S.; Ibrahim, K. Insight into the loading and release properties of an exfoliated kaolinite/cellulose fiber (EXK/CF) composite as carrier for oxaliplatin drugs: Cytotoxicity and release kinetics. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 19165–19173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meskinis, S.; Vasiliauskas, A.; Andrulevicius, M.; Peckus, D.; Tamulevicius, S.; Viskontas, K. Diamond like carbon films containing Si: Structure and nonlinear optical properties. Materials 2020, 13, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Yu, C.; Zhang, B.; Fei, H. Characterization of exfoliated/delaminated kaolinite. Mater. Res. Bull. 2011, 46, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; He, S.; Su, H. Efficient preparation of kaolinite/methanol intercalation composite by using a Soxhlet extractor. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, W.; Deng, Z.; Fan, J.; Lin, Q.; Wu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, Z. Enhanced adsorption performance of La (III) and Y (III) on Kaolinite by oxalic acid intercalation expansion method. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 229, 106693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez, V.; Mantecon, A.; Cadiz, V. Modification of polyvinyl alcohol with acid chlorides and crosslinking with difunctional hardeners. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1996, 34, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamer, T.; Sabet, M.; Omer, A.; Abbas, E.; Eid, A.; Eldin, M.; Hassan, M. Hemostatic and antibacterial PVA/Kaolin composite sponges loaded with penicillin-streptomycin for wound dressing applications. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.; Li, N.; Wang, Q.; Li, S. Chitosan/graphene oxide mixed matrix membrane with enhanced water permeability for high-salinity water desalination by pervaporation. Desalination 2018, 438, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Kulshrestha, V. Synthesis of highly stable and high water retentive functionalized biopolymer-graphene oxide modified cation exchange membranes. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 56498–56506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, Z.; Wang, J.; Ru, X.; Teng, L. PVA/UiO-66 mixed matrix membranes for n-butanol dehydration via pervaporation and effect of ethanol. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 313, 123487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raesi, Z.; Moheb, A.; Sadeghi, M.; Abdolmaleki, A.; Alibouri, M. Titanate nanotube-incorporated poly(vinyl alcohol) mixed matrix membranes for pervaporation separation of water isopropanol mixtures. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2019, 145, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Huang, R. Estimation of activation energy for permeation in pervaporation processes. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 118, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Gu, X. High performance NaY zeolite membranes supported on four channel ceramic hollowfiber for ethanol dehydration. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 95866–95871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baysak, F.; Işıklan, N. Pervaporation performance of poly(vinyl alcohol)-graft-poly(N-hydroxymethyl acrylamide) membranes for dehydration of isopropanol alcohol-water mixture. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 51976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, S.; Chang, D.; Cho, K.; Shon, M.; Kwon, Y.; Nam, S.; Park, Y. Polyvinyl alcohol and graphene oxide blending surface coated alumina hollow fiber (AHF) membrane for pervaporation dehydration of epichlorohydrin (ECH)/isopropanol(IPA)/water ternary feed mixture. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2020, 114, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Chaudhari, S.; Shin, H.; Fitriasari, E.; Shon, M.; Nam, S.; Park, Y. Strategies to overcome the limitations of cross-linked hydrophilic PVA membranes; carboxy methyl cellulose blending for epichlorohydrin-isopropanol-water pervaporation dehydration. J. Water Process. Eng. 2023, 55, 104101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
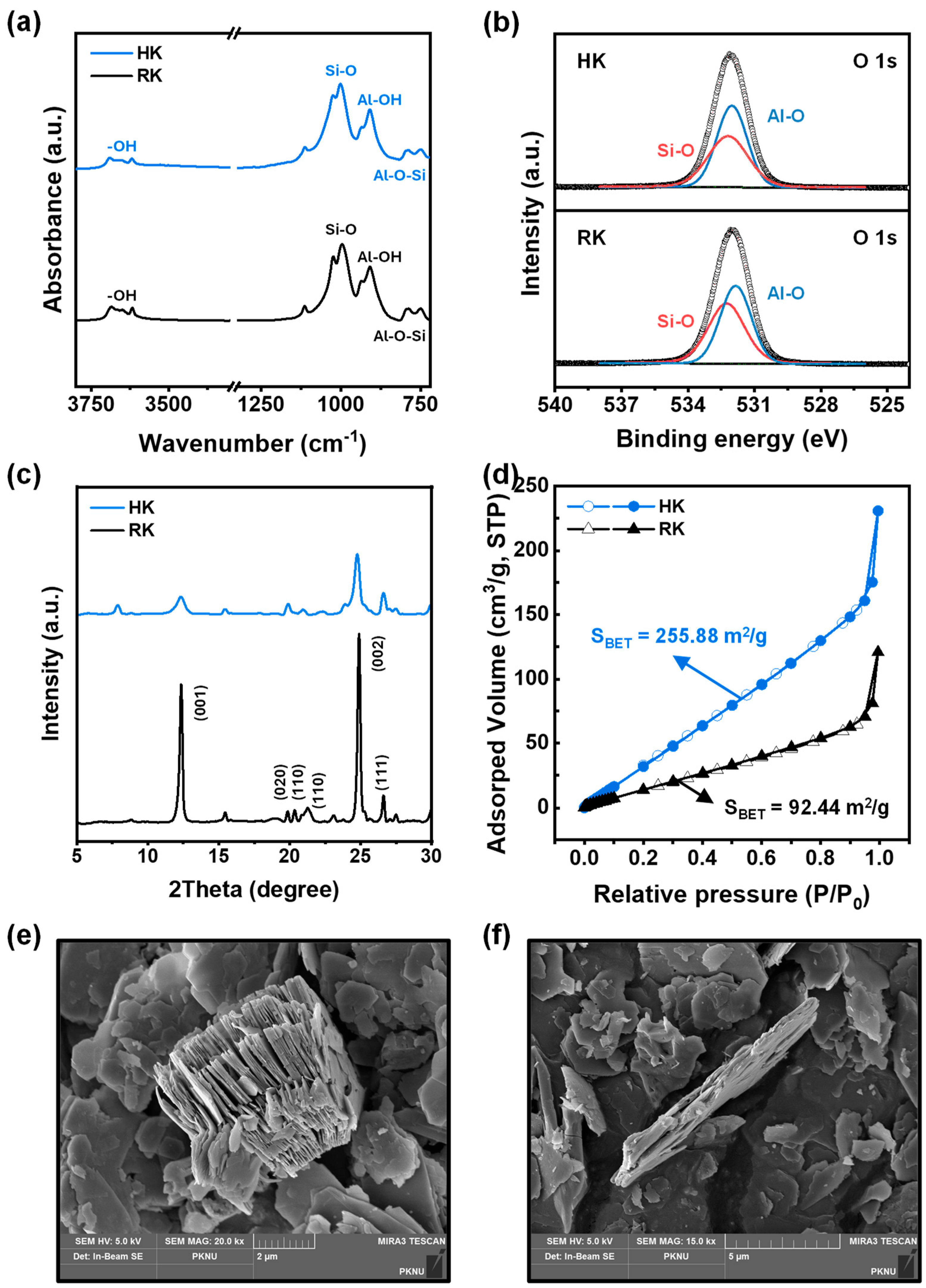
| Particle Type | Elements | Wt.% | Atomic % |
|---|---|---|---|
| RK | O | 54.18 | 67.09 |
| Al | 20.71 | 15.21 | |
| Si | 25.10 | 17.70 | |
| HK | O | 55.24 | 68.03 |
| Al | 20.24 | 14.78 | |
| Si | 24.52 | 17.20 |
| Samples | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|
| PVA | 37.34 | 2.82 |
| HK 4 wt.% | 41.59 | 3.20 |
| RK 4 wt.% | 32.26 | 1.34 |
| Matrix | Nature of the Membrane Preparation Method | Feed (%) Composition, (w/w) | Temperature, (oC) | Flux (J) (kg/m2h) | Separation Factor (∝) | Thickness (µ) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVA | Blending with GO | ECH/IPA/water 50/30/20 | 40 | 0.13 | 4670 | 15 | [33] |
| PVA | CMC40-AHF | ECH/IPA/water 50/30/20 | 40 | 1.214 | 638 | 7.7 | [34] |
| PVA | Kaolinite–PVDF support | ECH/IPA/water 50/30/20 | 40 | 0.86 | 166 | 3–4 | [This study] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaudhari, S.; Jeong, Y.; Shin, H.; Jo, S.; Shon, M.; Nam, S.; Park, Y. Augmenting the Efficacy of a Polyvinyl Alcohol Selective Layer Coated on Polyvinylidene Fluoride Support Membranes with Kaolinite Introduction for Improved Pervaporation Dehydration of Epichlorohydrin/Isopropanol/Water Ternary Systems. Polymers 2024, 16, 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16060835
Chaudhari S, Jeong Y, Shin H, Jo S, Shon M, Nam S, Park Y. Augmenting the Efficacy of a Polyvinyl Alcohol Selective Layer Coated on Polyvinylidene Fluoride Support Membranes with Kaolinite Introduction for Improved Pervaporation Dehydration of Epichlorohydrin/Isopropanol/Water Ternary Systems. Polymers. 2024; 16(6):835. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16060835
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaudhari, Shivshankar, YeWon Jeong, HyeonTae Shin, SeWook Jo, MinYoung Shon, SeungEun Nam, and YouIn Park. 2024. "Augmenting the Efficacy of a Polyvinyl Alcohol Selective Layer Coated on Polyvinylidene Fluoride Support Membranes with Kaolinite Introduction for Improved Pervaporation Dehydration of Epichlorohydrin/Isopropanol/Water Ternary Systems" Polymers 16, no. 6: 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16060835
APA StyleChaudhari, S., Jeong, Y., Shin, H., Jo, S., Shon, M., Nam, S., & Park, Y. (2024). Augmenting the Efficacy of a Polyvinyl Alcohol Selective Layer Coated on Polyvinylidene Fluoride Support Membranes with Kaolinite Introduction for Improved Pervaporation Dehydration of Epichlorohydrin/Isopropanol/Water Ternary Systems. Polymers, 16(6), 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16060835






