An Eco-Friendly Manner to Prepare Superwetting Melamine Sponges with Switchable Wettability for the Separation of Oil/Water Mixtures and Emulsions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
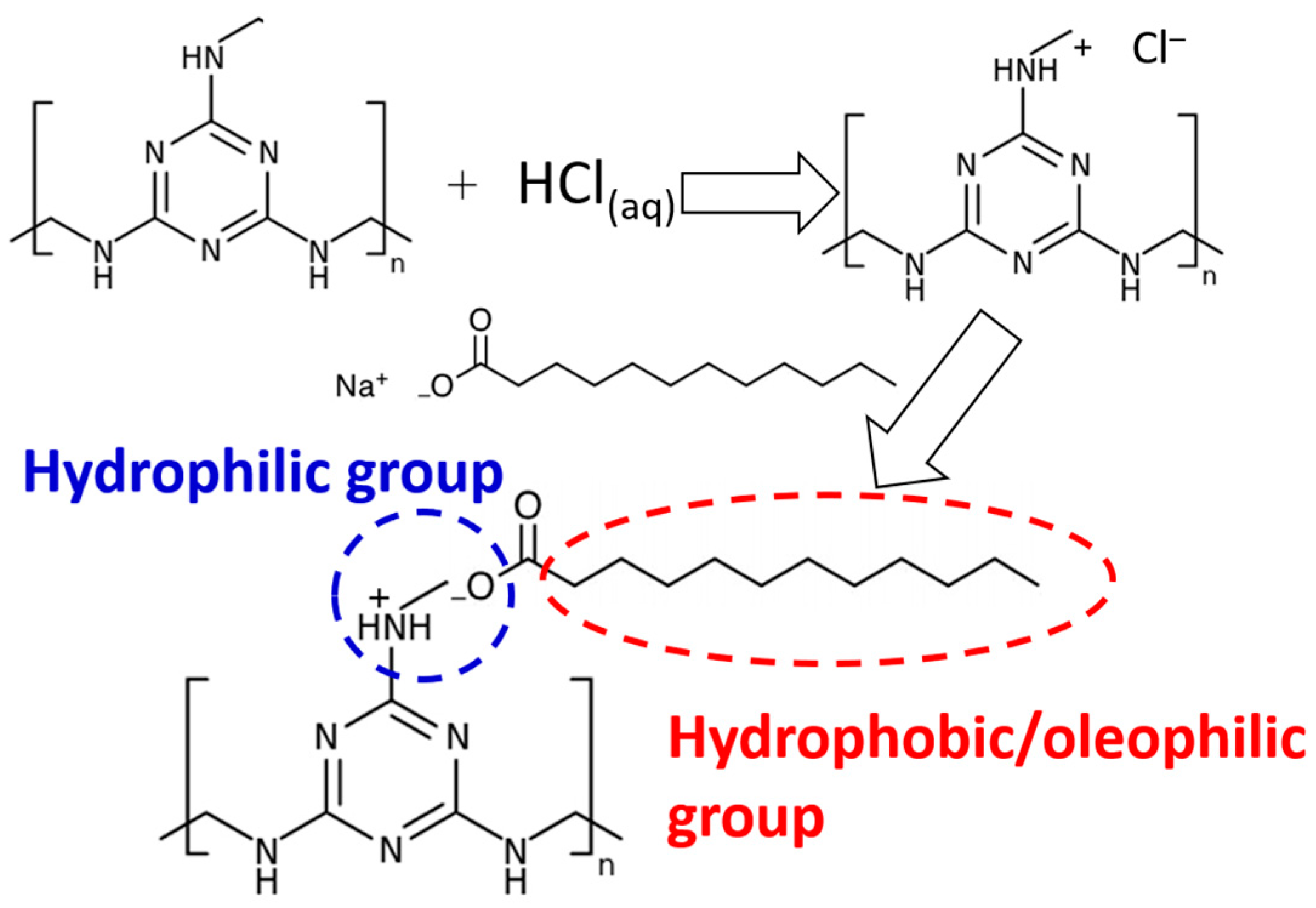
2.2. Preparation of Superwetting Melamine Sponge (SMS) with Switchable Wettability
2.3. Preparation of Various Emulsions
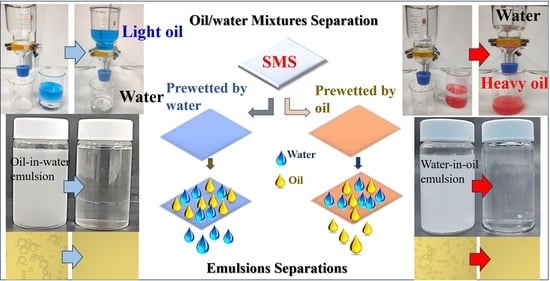
2.4. Oil/Water Mixtures Separation Experiments
2.5. Emulsions Separation Experiments
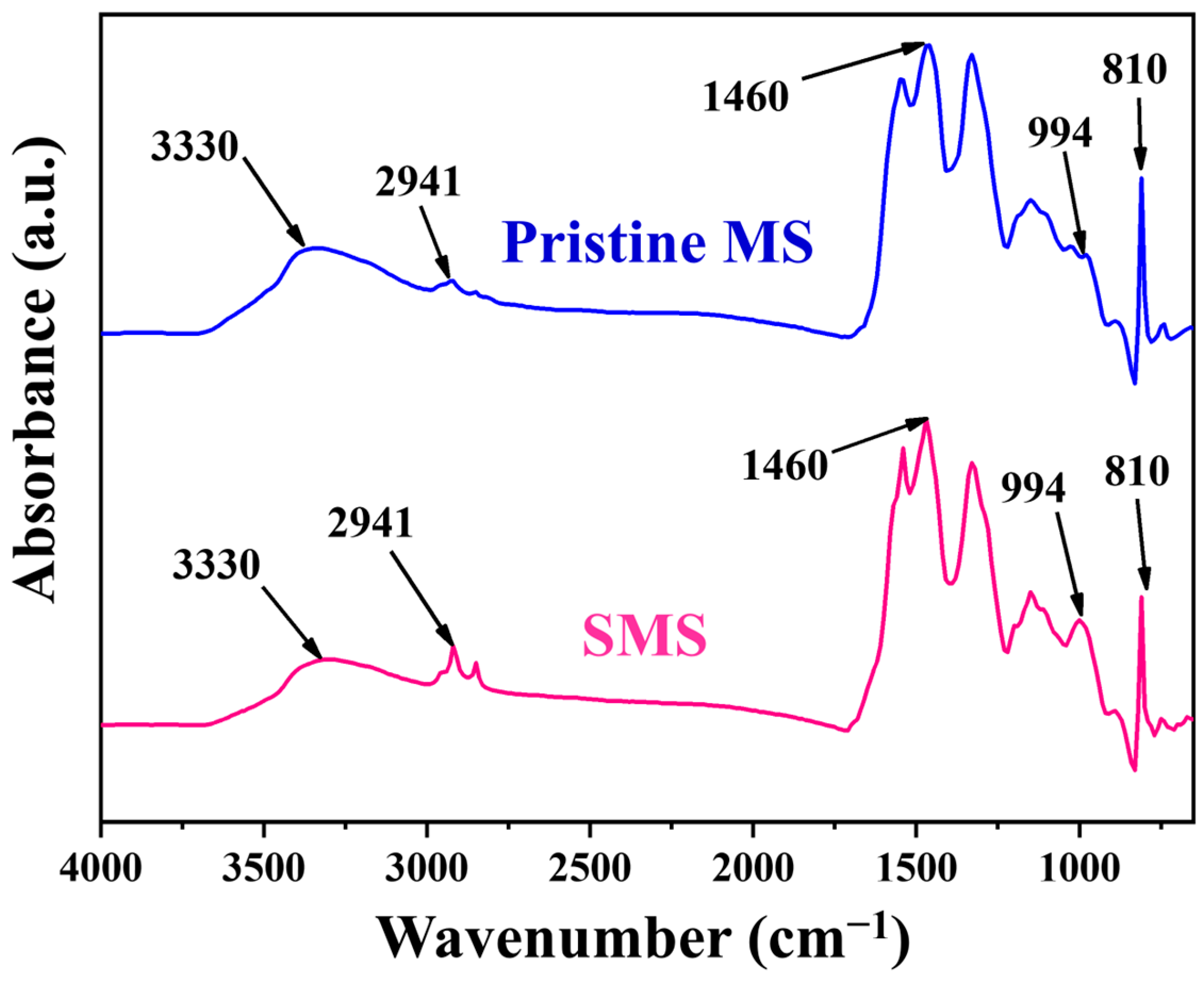
2.6. Instruments and Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Preparation, Morphological Analysis and Surface Chemical Compositions of Melamine Sponges
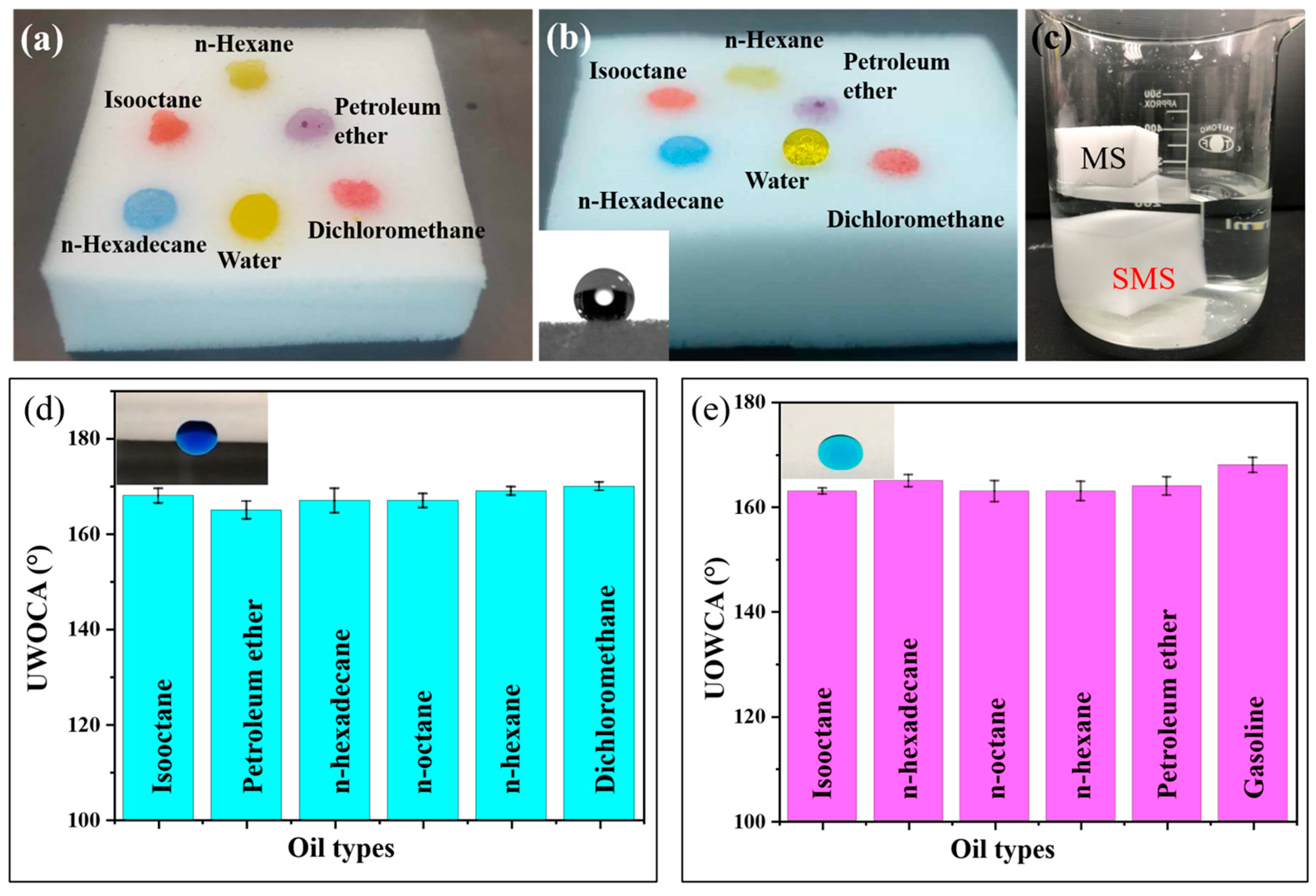
3.2. Wettabilities of Sponges
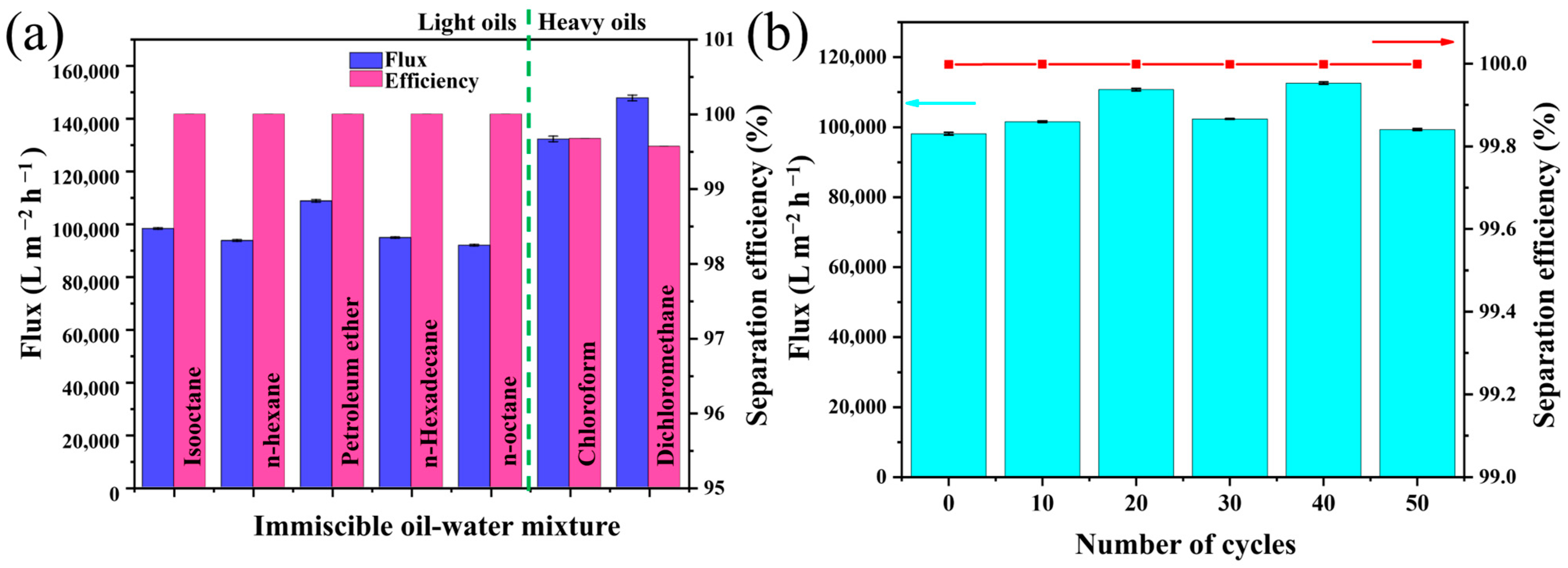
3.3. Oil/Water Mixtures Separation Performance of the SMS
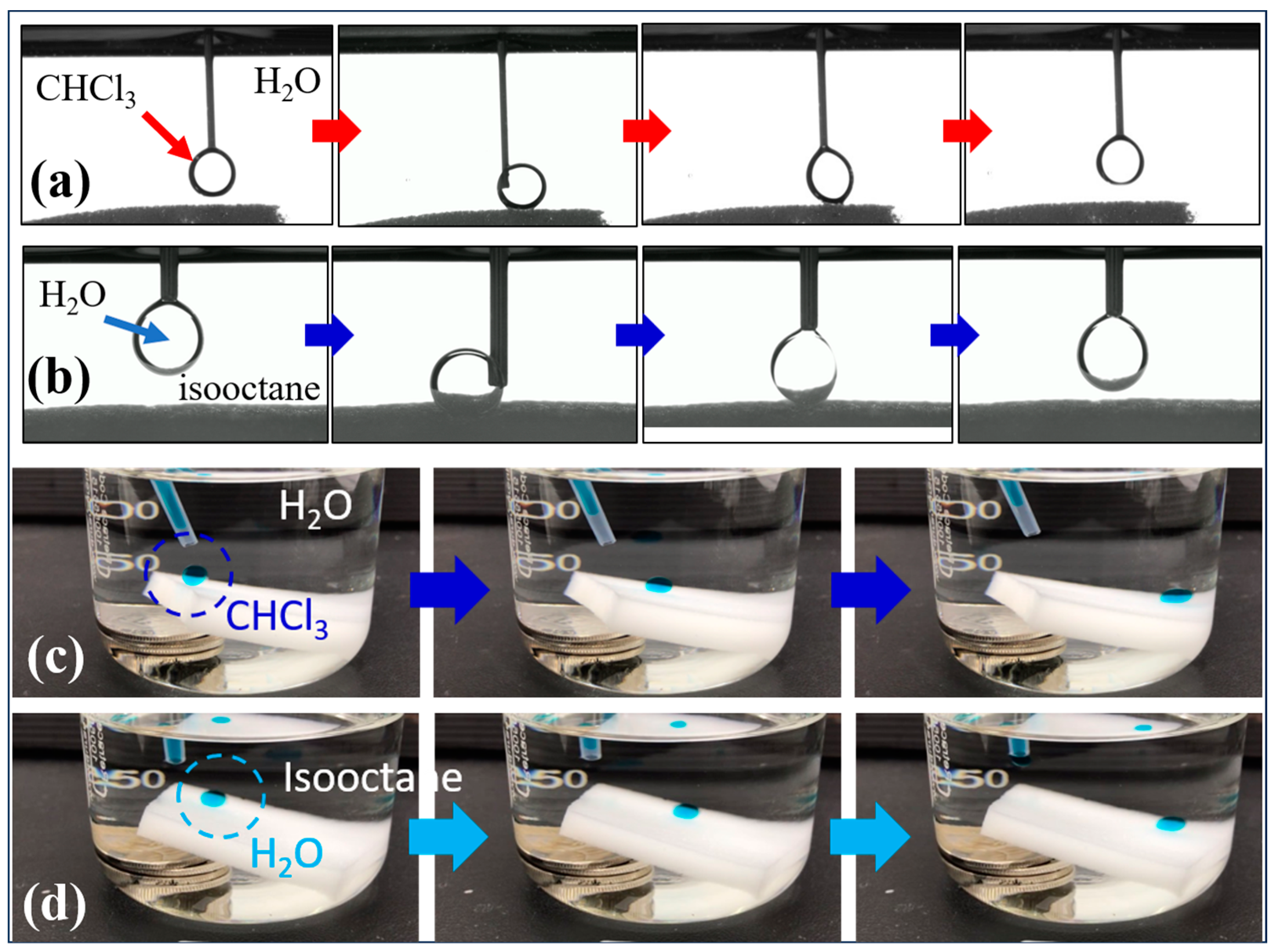
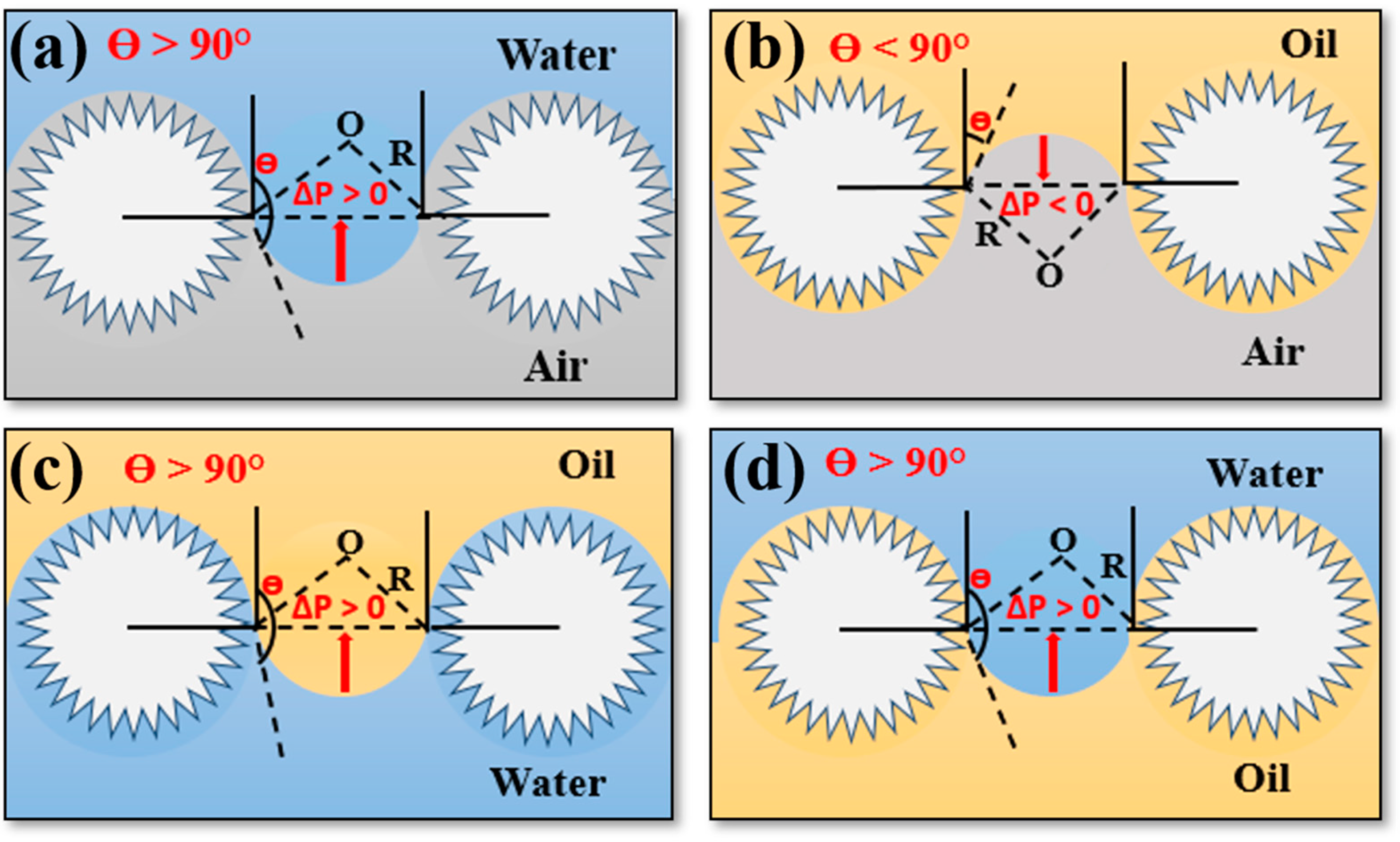
3.4. Oil/Water Mixtures Separation Mechanism
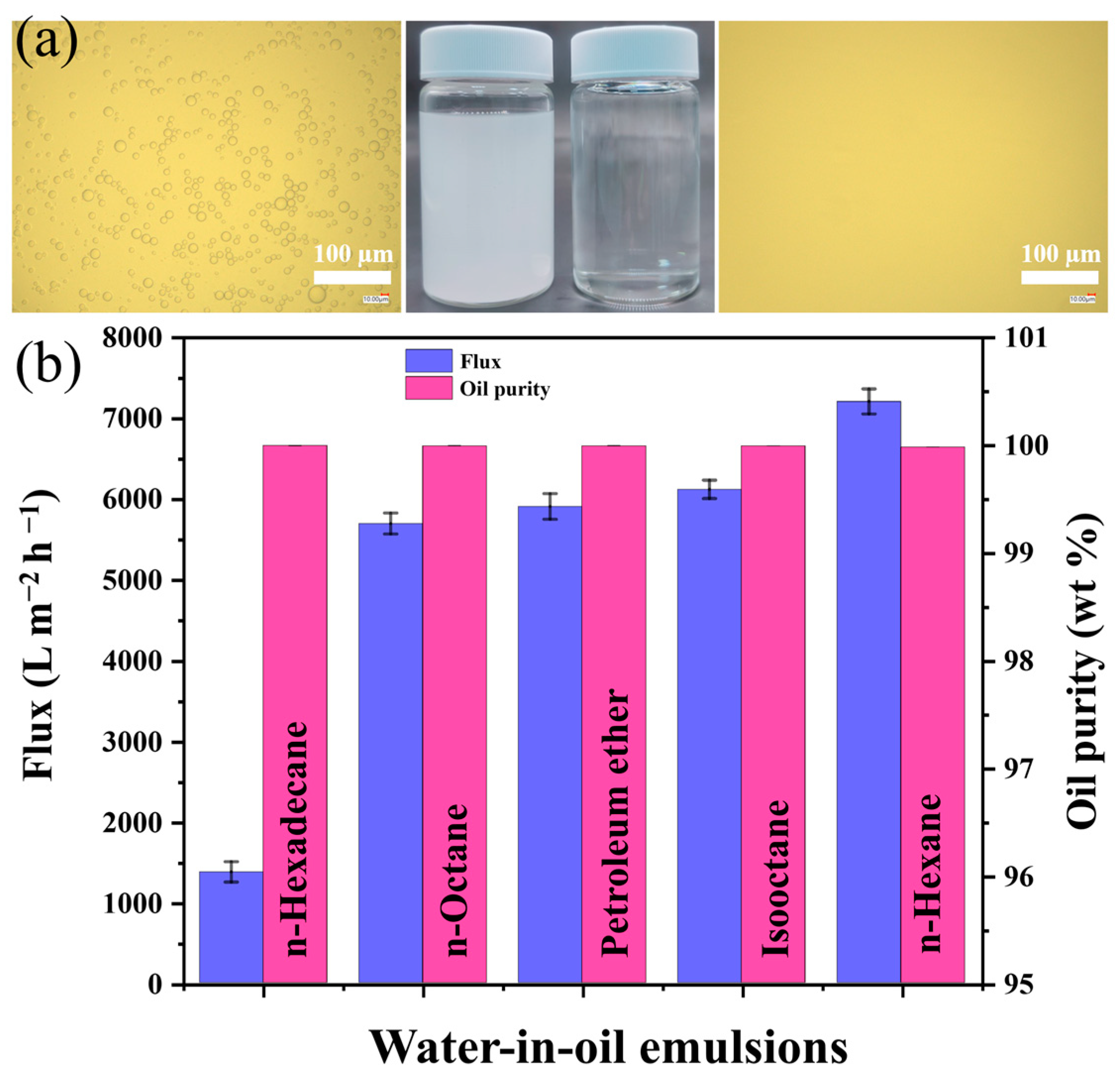
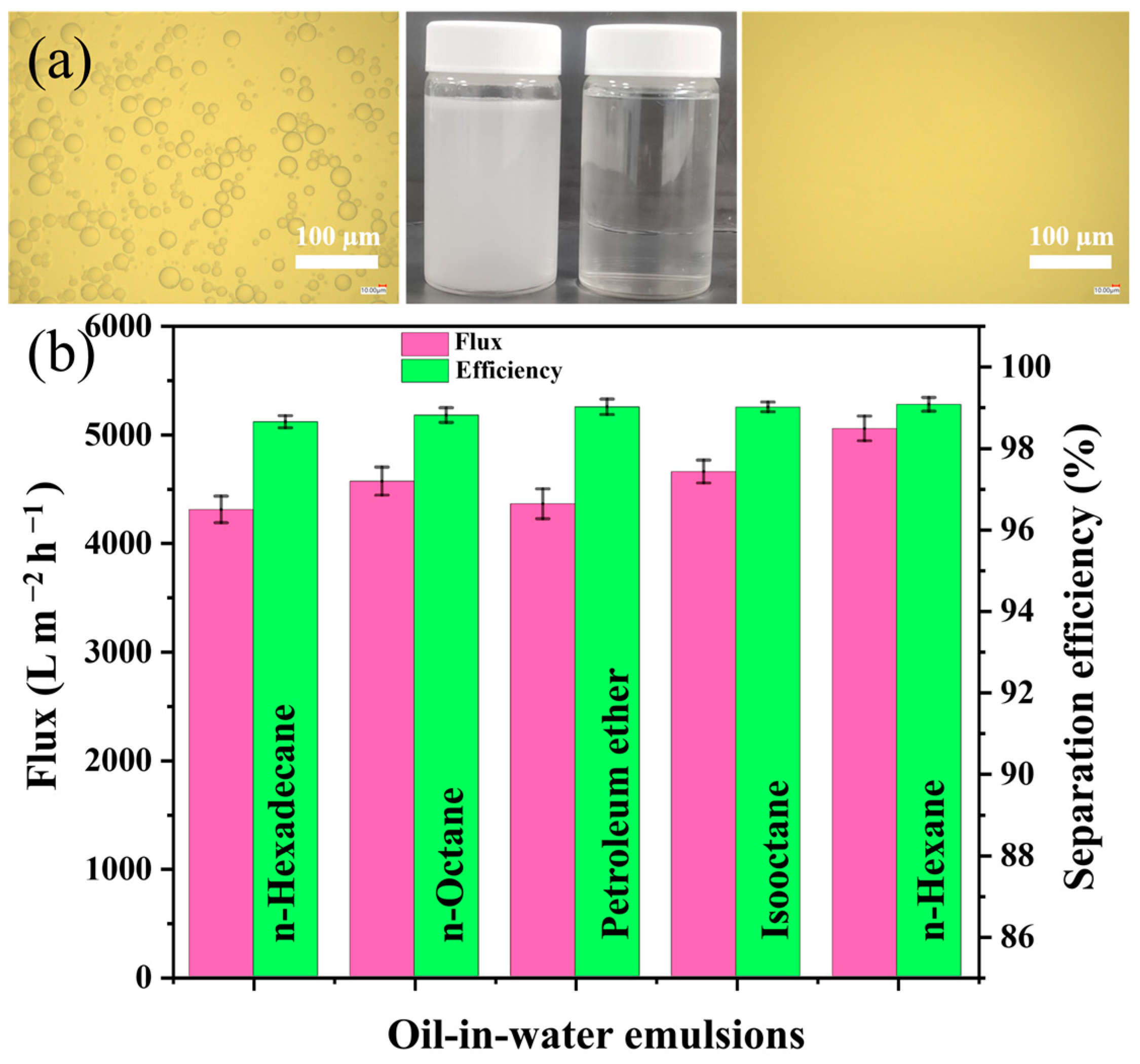
3.5. Emulsions Separation Performance of the SMS
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peterson, C.H.; Rice, S.D.; Short, J.W.; Esler, D.; Bodkin, J.L.; Ballachey, B.E.; Irons, D.B. Long-term ecosystem response to the Exxon Valdez oil spill. Science 2003, 302, 2082–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivshina, I.B.; Kuyukina, M.S.; Krivoruchko, A.V.; Elkin, A.A.; Makarov, S.O.; Cunningham, C.J.; Peshkur, T.A.; Atlas, R.M.; Philp, J.C. Oil spill problems and sustainable response strategies through new technologies. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2015, 17, 1201–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, G.; Kota, A.K.; Li, Y.; Sohani, A.; Mabry, J.M.; Tuteja, A. On-demand separation of oil-water mixtures. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 3666–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, M.A.; Bohn, P.W.; Elimelech, M.; Georgiadis, J.G.; Mariñas, B.J.; Mayes, A.M. Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature 2008, 452, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Cheng, H.; Fane, A.G.; Wang, R.; Zhang, H. Recent development of advanced materials with special wettability for selective oil/water separation. Small 2016, 12, 2186–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, N.; Cao, Y.; Lin, X.; Liu, Y.; Feng, L. Superwetting porous materials for wastewater treatment: From immiscible oil/water mixture to emulsion separation. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1600029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kota, A.K.; Kwon, G.; Choi, W.; Mabry, J.M.; Tuteja, A. Hygro-responsive membranes for effective oil-water separation. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheryan, M.; Rajagopalan, N. Membrane processing of oily streams. Wastewater treatment and waste reduction. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 151, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritt-Rasmussen, J.; Wegeberg, S.; Gustavson, K. Review on burn residues from in situ burning of oil spills in relation to arctic waters. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Sun, Y.; Guo, Z. Designing novel superwetting surfaces for high-efficiency oil–water separation: Design principles, opportunities, trends and challenges. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2020, 8, 16831–16853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Cao, C.; Huang, J.; Zhang, X.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, K.; Chen, Z.; Lai, Y. Rational design of materials interface at nanoscale towards intelligent oil–water separation. Nanoscale Horiz. 2018, 3, 235–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.-L.; Wang, Y.-Z. Novel dual superlyophobic materials in water-oil systems: Under oil magneto-fluid transportation and oil–water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2018, 6, 2935–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Jiang, L. Design and creation of superwetting/antiwetting surfaces. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 3063–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhai, J.; Song, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. Super-hydrophobic surfaces: From natural to artificial. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1857–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, S.; Wei, Z.; Song, Y.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired design of a superoleophobic and low adhesive water/solid interface. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Weng, D.; Mahmood, A.; Chen, S.; Wang, J. Separation mechanism and construction of surfaces with special wettability for oil/water separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 11006–11027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jiang, G.; Gao, S.; Jin, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Jin, J. Cupric phosphate nanosheets-wrapped inorganic membranes with superhydrophilic and outstanding anticrude oil-fouling property for oil/water separation. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ji, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.; He, F.; Peng, S.; Li, Y. Tannic acid encountering ovalbumin: A green mild strategy for superhydrophilic underwater superoleophobic modification of various hydrophobic membranes for oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 13959–13967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondal, M.A.; Sadullah, M.S.; Dastageer, M.A.; McKinley, G.H.; Panchanathan, D.; Varanasi, K.K. Study of factors governing oil–water separation process using TiO2 films prepared by spray deposition of nanoparticle dispersions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 13422–13429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shome, A.; Rather, A.M.; Manna, U. Aloe vera mucilage derived highly tolerant underwater superoleophobic coatings. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 22465–22471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.B.; Song, Y.; Wang, S.; Meng, J.; Yang, G.; Guo, X.; Feng, L.; Jiang, L. Directly coating hydrogel on filter paper for effective oil-water separation in highly acidic, alkaline, and salty environment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 5368–5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Li, J.; Shi, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, Z.; Liu, W. Underwater superoleophobic graphene oxide coated meshes for the separation of oil and water. Chem. Comm. 2014, 50, 5586–5589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, M.; Feng, L.; Jiang, L. A novel superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic hydrogel-coated mesh for oil/water separation. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4270–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Xu, L.; Xue, Z.; Feng, L.; Peng, J.; Wen, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X. Dual-scaled porous nitrocellulose membranes with underwater superoleophobicity for highly efficient oil/water separation. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 1771–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Qi, H.; Gong, X.; Zhao, S. Specially wettable membranes for oil–water separation. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 5, 1800576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Mai, Z.; Ma, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. A super-hydrophobic and super-oleophilic coating mesh film for the separation of oil and water. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 116, 2046–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Guo, F.; Zhu, X.; Men, X.; Ge, B. Robust and durable superhydrophobic cotton fabrics for oil/water separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2013, 5, 7208–7214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejeta, D.D.; Wang, C.-F.; Kuo, S.-W.; Chen, J.-K.; Tsai, H.-C.; Hung, W.-S.; Hu, C.-C.; Lai, J.-Y. Preparation of superhydrophobic and superoleophilic cotton-based material for extremely high flux water-in-oil emulsion separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 402, 126289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, C.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Du, X.; Kong, W.; Pan, D.; Guan, G.; Hao, X. A novel 3D porous modified material with cage-like structure: Fabrication its demulsification effect for efficient oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 5895–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Guo, Z. Nonflammable superhydrophobic paper with biomimetic layered structure exhibiting boiling-water resistance and repairable properties for emulsion separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 7042–7052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Yang, L.; Wang, C.; Lee, E.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S. A multi-functional oil–water separator from a selectively pre-wetted superamphiphobic paper. Chem. Comm. 2015, 51, 6149–6152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, D.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Zha, F.; Lei, Z. A prewetting induced underwater superoleophobic or underoil (super) hydrophobic waste potato residue-coated mesh for selective efficient oil/water separation. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Xue, L.; Liu, F.; Jiang, L. An intelligent superwetting PVDF membrane showing switchable transport performance for oil/water separation. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2943–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Qu, W.; Wang, Z. A facile and mild strategy to fabricate an underwater superoleophobic and underoil superhydrophobic mesh with outstanding anti-viscous oil-fouling properties for switchable high viscosity oil/water separation. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 5080–5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Li, F.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, X. Hygro-Responsive, photo-decomposed superoleophobic/superhydrophilic coating for on-demand oil–water separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 35142–35152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, C.; Wen, X.; Xu, S.; Cheng, J.; Pi, P. A durable underwater superoleophobic and underoil superhydrophobic fabric for versatile oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 370, 1218–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Ho, S.-H. A dually prewetted membrane for continuous filtration of water-in-light oil, oil-in-water, and water-in-heavy oil multiphase emulsion mixtures. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 11305–11313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, J.; Zhou, P.; Zhu, L.; Tang, H. Superhydrophobic copper coating: Switchable wettability, on-demand oil-water separation, and antifouling. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 327, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.D.; Tai, N.-H.; Lee, S.-B.; Kuo, W.-S. Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic properties of graphene-based sponges fabricated using a facile dip coating method. Energy. Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 7908–7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Chu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, N.; Lin, L.; Liu, F.; Pan, Q. Robust superhydrophobic polyurethane sponge as a highly reusable oil-absorption material, J. Mater. Chem. A. 2013, 1, 5386–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Li, L.; Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, A. Magnetic, durable, and superhydrophobic polyurethane@ Fe3O4@ SiO2@ fluoropolymer sponges for selective oil absorption and oil/water separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 4936–4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, C.; Ai, K.; Li, X.; Lu, L. A superhydrophobic sponge with excellent absorbency and flame retardancy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 126, 5662–5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Tong, Z.; Wang, C. Multifunctional foams derived from poly (melamine formaldehyde) as recyclable oil absorbents. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2014, 2, 9994–9999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, L.; Montiel, G.; Jones, A.; Riel, D.; Abdulaziz, M.; Viva, F.; Bonetta, D.; Vreugdenhil, A.J.; Trevani, L. Melamine adsorption on carbon materials: Impact of carbon texture and surface chemistry. Adv. Mater. 2020, 1, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-F.; Huang, H.-C.; Chen, L.-T. Protonated melamine sponge for effective oil/water separation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhu, X.; Men, X.; Zhou, X. Superhydrophilic–superoleophobic coatings. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 2834–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Su, Z. A surface exhibiting superoleophobicity both in air and in seawater. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 6400–6403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merline, D.J.; Vukusic, S.; Abdala, A.A. Melamine formaldehyde: Curing studies and reaction mechanism. Polym. J. 2013, 45, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Luo, S.; Li, S. Preparation and property analysis of melamine formaldehyde foam. Adv. Mater. Phys. Chem. 2012, 2, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bani-Jaber, A.; Hamdan, I.; Alkawareek, M. The synthesis and characterization of fatty acid salts of chitosan as novel matrices for prolonged intragastric drug delivery. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2012, 35, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Jokinen, V.; Li, J.; Sainio, J.; Ras, R.H. Unusual dual superlyophobic surfaces in oil–water systems: The design principles. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 10652–10658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zheng, Y.; Zhai, J.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired super-antiwetting interfaces with special liquid− solid adhesion. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-F.; Lin, S.-J. Robust superhydrophobic/superoleophilic sponge for effective continuous absorption and expulsion of oil pollutants from water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 8861–8864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.-S.; Harriott, P. Critical entry pressure for liquids in hydrophobic membranes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1987, 115, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafuma, A.; Quéré, D. Superhydrophobic states. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Cheng, F.; Pan, Z. Superwetting polymeric three dimensional (3d) porous materials for oil/water separation: A review. Polymers 2019, 11, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Wang, F.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Polybenzoxazine-functionalized melamine sponges with enhanced selective capillarity for efficient oil spill cleanup. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 40274–40285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Liu , Y.; Dai, J.; Cao, L.; Liu, X. A sustainable strategy for remediation of oily sewage: Clean and safe. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 240, 116592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.; Seeger, S. Multifunctional hybrid porous micro-/nanocomposite materials. Adv. Mater 2015, 27, 7775–7781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, W.-T.; Li, S.-Y.; Chen, Z.-B.; Stegmaier, T.; Aliabadi, M.; Han, Z.-W.; Ren, L.-Q. Multifunctional 3D GO/g-C3N4/TiO2 foam for oil-water separation and dye adsorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 541, 148638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Jiang, B.; Sun, Y.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, N.; Hou, S.; Li, J.; Yang, N. Superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic Ti foam with robust nanoarray structures of TiO2 for effective oil-in-water emulsion separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 252, 117437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yan, L.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shao, L. Biomimetic hydrophilization engineering on membrane surface for highly-efficient water purification. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 589, 117223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, J.; Yue, X.; Qiu, F.; Yang, D.; Zhang, T. Study on the application of waste bricks in emulsified oil-water separation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 251, 119609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-C.; Pi, J.-K.; Liao, K.-J.; Huang, H.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Huang, X.-J.; Xu, Z.-K. Silica-decorated polypropylene microfiltration membranes with a mussel-inspired intermediate layer for oil-in-water emulsion separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 12566–12572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Qian, W.; Chen, Y.; Xu, P.; Li, J.; Yang, J. A new treasure in industrial solid waste—Coal fly ash for effective oil/water separation. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2021, 118, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Belachew, G.B.; Hu, C.-C.; Chang, Y.-Y.; Wang, C.-F.; Hung, W.-S.; Chen, J.-K.; Lai, J.-Y. An Eco-Friendly Manner to Prepare Superwetting Melamine Sponges with Switchable Wettability for the Separation of Oil/Water Mixtures and Emulsions. Polymers 2024, 16, 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050693
Belachew GB, Hu C-C, Chang Y-Y, Wang C-F, Hung W-S, Chen J-K, Lai J-Y. An Eco-Friendly Manner to Prepare Superwetting Melamine Sponges with Switchable Wettability for the Separation of Oil/Water Mixtures and Emulsions. Polymers. 2024; 16(5):693. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050693
Chicago/Turabian StyleBelachew, Guyita Berako, Chien-Chieh Hu, Yan-Yu Chang, Chih-Feng Wang, Wei-Song Hung, Jem-Kun Chen, and Juin-Yih Lai. 2024. "An Eco-Friendly Manner to Prepare Superwetting Melamine Sponges with Switchable Wettability for the Separation of Oil/Water Mixtures and Emulsions" Polymers 16, no. 5: 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050693
APA StyleBelachew, G. B., Hu, C.-C., Chang, Y.-Y., Wang, C.-F., Hung, W.-S., Chen, J.-K., & Lai, J.-Y. (2024). An Eco-Friendly Manner to Prepare Superwetting Melamine Sponges with Switchable Wettability for the Separation of Oil/Water Mixtures and Emulsions. Polymers, 16(5), 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050693