In Situ Thermosensitive Mucoadhesive Nasal Gel Containing Sumatriptan: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Evaluations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Formulation of SMT-Loaded Nasal In Situ Gel Systems
2.2.2. Optimization of SMT In Situ Gel Formulation
2.2.3. Characterization of Gel
Clarity and pH of the Formulations
Gelation Temperature
Gelation Time
Gel Strength
Mucoadhesive Strength
Viscosity
2.2.4. Drug Content
2.2.5. In Vitro Drug Release
2.2.6. Release Kinetics
- (a)
- Zero-order
- (b)
- First-order
- (c)
- Higuchi model
- (d)
- Korsmeyer–Peppas model
2.2.7. DSC Characterization
2.2.8. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.2.9. Ex Vivo Permeation Studies
2.2.10. Stability Study
2.2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Gel Characterization
3.2. Rheological Studies
3.3. Effect of Independent Factors
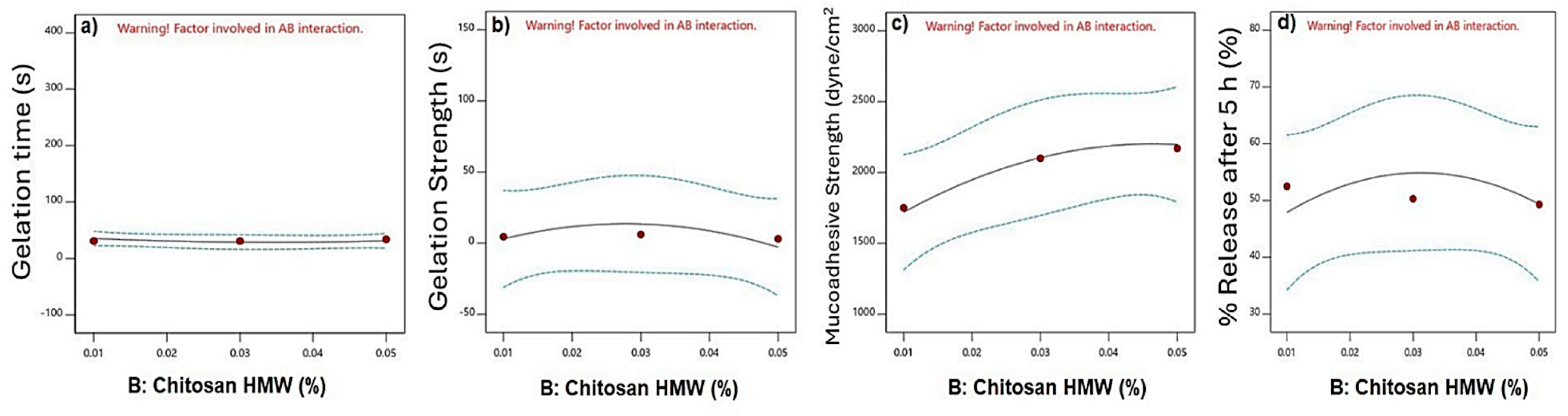
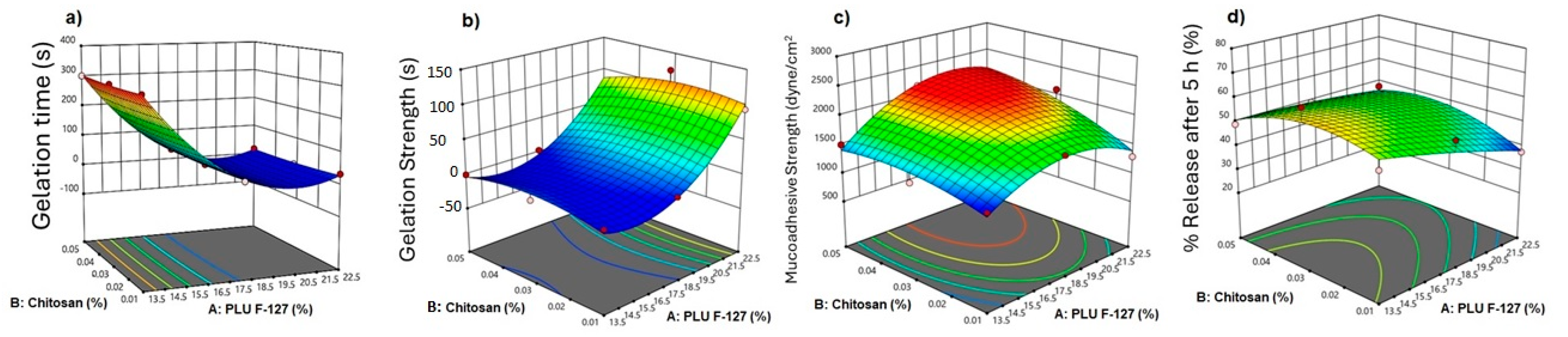
3.3.1. Effect of Independent Factors on Gelation Time
3.3.2. Effect on Gelation Strength
3.3.3. Effect on Mucoadhesive Strength
3.3.4. In Vitro Released
3.3.5. Release Kinetics
3.4. Optimized Formula
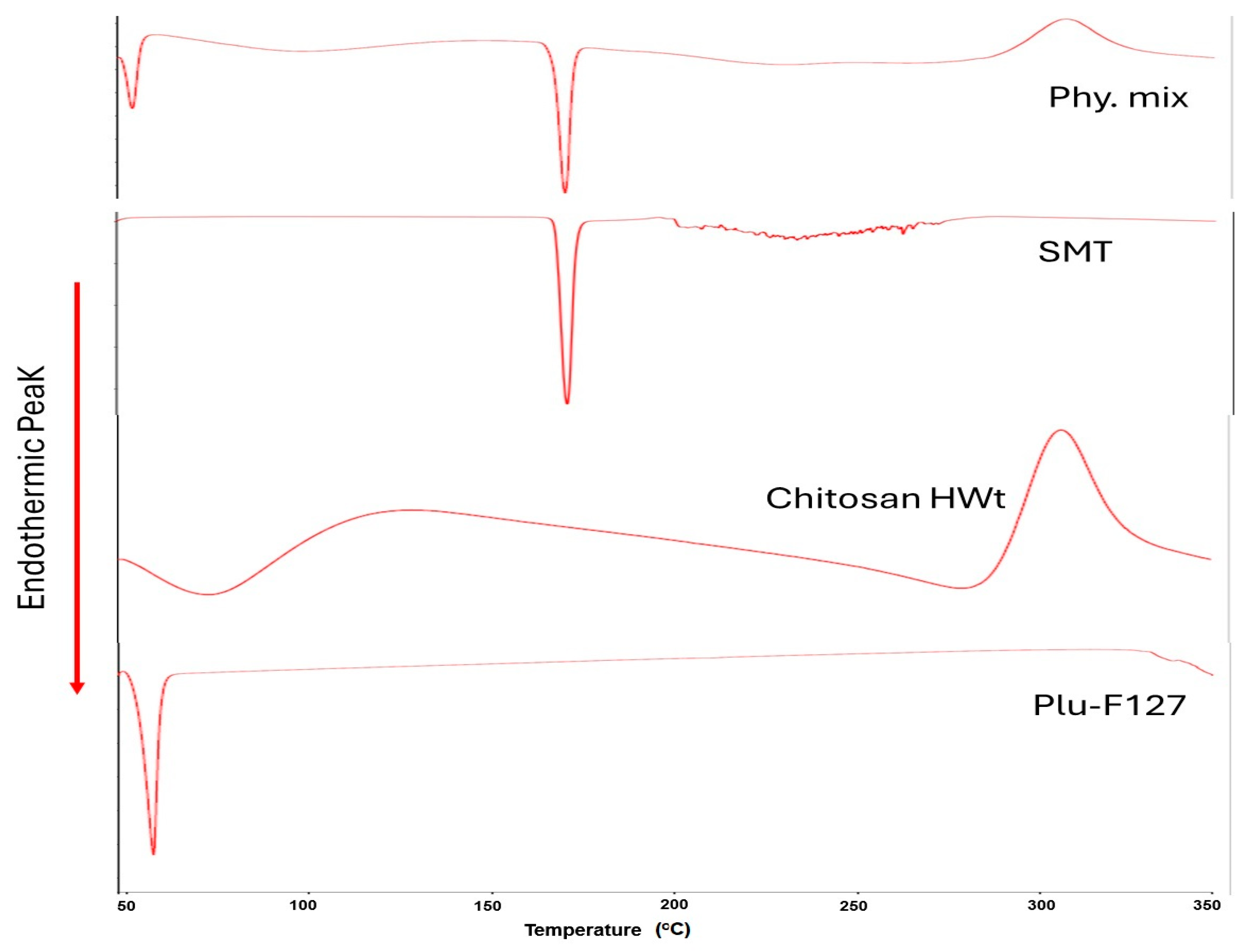
3.5. DSC Characterization
3.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
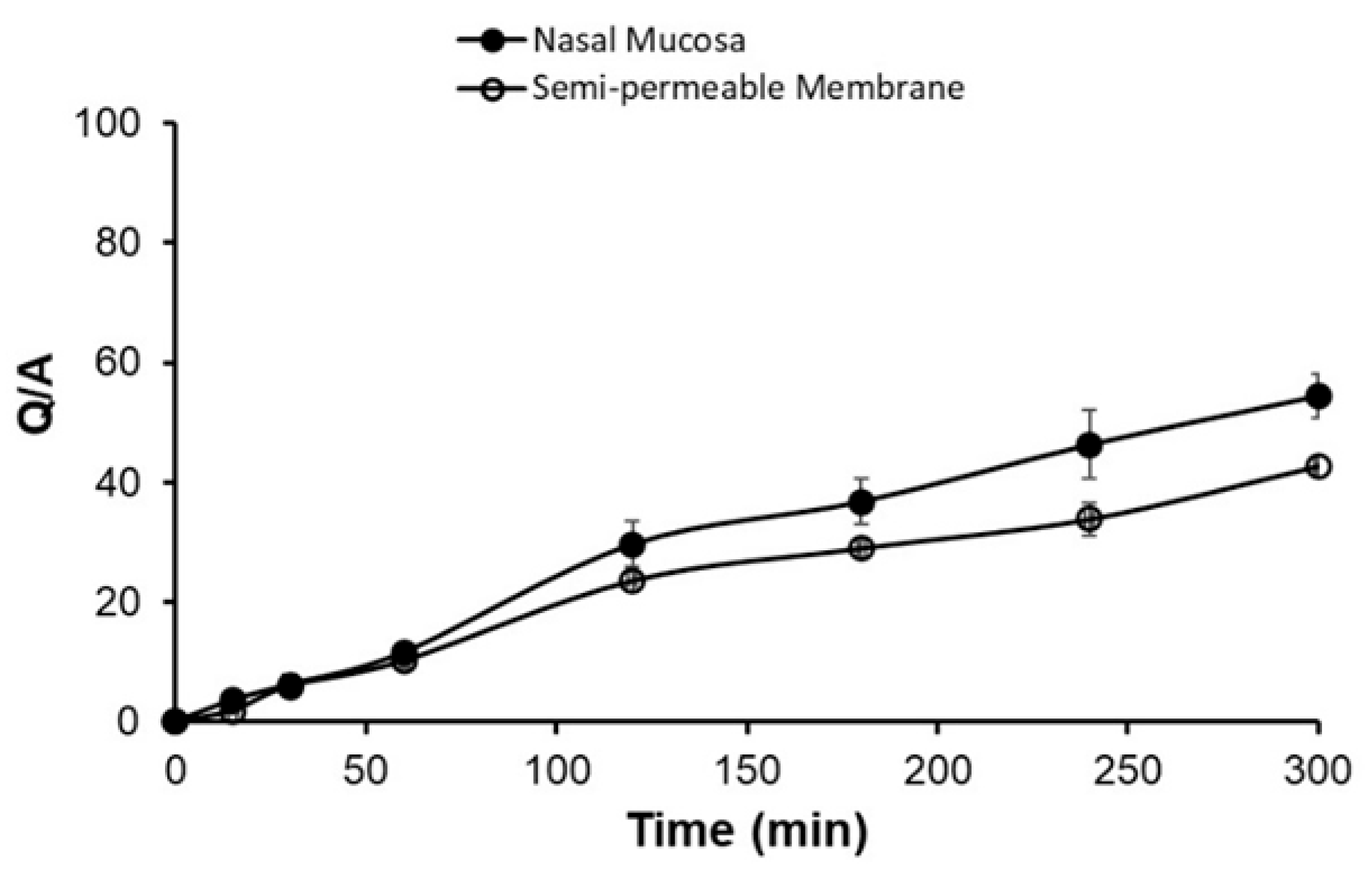
3.7. Ex Vivo: %SMT Permeated
3.8. Stability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeyagurunathan, A.; Abdin, E.; Vaingankar, J.A.; Chua, B.Y.; Shafie, S.; Chang, S.H.S.; James, L.; Tan, K.B.; Basu, S.; Chong, S.A.; et al. Prevalence and comorbidity of migraine headache: Results from the Singapore Mental Health Study 2016. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2020, 55, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menshawy, A.; Ahmed, H.; Ismail, A.; Abushouk, A.I.; Ghanem, E.; Pallanti, R.; Negida, A. Intranasal sumatriptan for acute migraine attacks: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 39, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosymra (Sumatriptan) Nasal Spray Approved for the Acute Treatment of Migraine, with or Without Aura. Available online: https://www.ahdbonline.com/issues/2019/march-2019-vol-12-tenth-annual-payers-guide/tosymra-sumatriptan-nasal-spray-approved-for-the-acute-treatment-of-migraine-with-or-without-aura (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- Imitrex (Sumatriptan Succinate): Side Effects, Uses, Dosage, Interactions, Warnings. Available online: https://www.rxlist.com/imitrex-drug.htm (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- Aderibigbe, B.A. In Situ-Based Gels for Nose to Brain Delivery for the Treatment of Neurological Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majithiya, R.J.; Ghosh, P.K.; Umrethia, M.L.; Murthy, R.S. Thermoreversible-mucoadhesive gel for nasal delivery of sumatriptan. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2006, 7, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, K.C.; Reddy, A.V.; Panda, N.; Reddy, G.N.; Habibuddin, M.D.; Mahapatra, A.P. Formulation and evaluation of thermosensitive intranasal in-situ gel of Sumatriptan succinate by using a blend of polymers. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Aabid, P.K.; Ashwani, M. Formulation and evaluation of nasal in-situ gel of Sumatriptan succinate for the treatment of migraine. J. Drug Delivery Ther. 2019, 9, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkufi, H.K.; Kassab, H.J. Formulation and Evaluation of Sustained Release Sumatriptan Mucoadhesive Intranasal in-Situ Gel. Iraqi J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 28, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Ma, X.; Zong, S.; Su, Y.; Su, R.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, Y. The prescription design and key properties of nasal gel for CNS drug delivery: A review. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 192, 106623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhrushina, E.O.; Mikhel, I.B.; Pyzhov, V.S.; Demina, N.B.; Krasnyuk, I.I. Development of In Situ Intranasal System Based on Chitosan Formate. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2023, 174, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aderibigbe, B.A.; Naki, T. Chitosan-Based Nanocarriers for Nose to Brain Delivery. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaria, V.J.; Saisivam, S.; Alshishani, A.; Aljariri Alhesan, J.S.; Chakraborty, S.; Rahamathulla, M. Design and evaluation of in situ gel eye drops containing nanoparticles of Gemifloxacin Mesylate. Drug Deliv. 2023, 30, 2185180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelke, S.; Shahi, S.; Jalalpure, S.; Dhamecha, D.; Shengule, S. Formulation and evaluation of thermoreversible mucoadhesive in-situ gel for intranasal delivery of naratriptan hydrochloride. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jug, M.; Hafner, A.; Lovrić, J.; Kregar, M.L.; Pepić, I.; Vanić, Ž.; Cetina-Čižmek, B.; Filipović-Grčić, J. An overview of in vitro dissolution/release methods for novel mucosal drug delivery systems. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 147, 350–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, H.; Aqil, M.; Khar, R.K.; Ali, A.; Bhatnagar, A.; Mittal, G. An alternative in situ gel-formulation of levofloxacin eye drops for prolong ocular retention. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2015, 7, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al-Wiswasi, N.N.; Al-Khedairy, E.B.H. Formulation and in vitro evaluation of in-situ gelling liquid suppositories for naproxen. Iraqi J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 17, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, V.M. Formulation and evaluation of In-Situ gel of metoprolol tartrate for nasal delivery. J. Pharm. Res. 2015, 3, 788–793. [Google Scholar]
- Galgatte, U.C.; Kumbhar, A.B.; Chaudhari, P.D. Development of in situ gel for nasal delivery: Design, optimization, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2014, 21, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Murthy, P.N.; Nath, L.; Chowdhury, P. Kinetic modeling on drug release from controlled drug delivery systems. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2010, 67, 217–223. [Google Scholar]
- Mathiowitz, E. Encyclopedia of Controlled Drug Delivery, 2 Volume Set; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999; Volume 2, Available online: http://books.google.ie/books?id=AC5tAAAAMAAJ&q=Encyclopedia+of+Controlled+Drug+Delivery&dq=Encyclopedia+of+Controlled+Drug+Delivery&hl=&cd=2&source=gbs_api (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- Higuchi, T. Physical Chemical analysis of Percutaneous Absorption Process from Creams and Ointments. J. Soc. Cosmet Chem. 1960, 11, 85–97. [Google Scholar]
- Peppas, N.A.; Korsmeyer, R.W. Hydrogels in Medicine and Pharmacy; CRC Press Inc.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1987; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Comyn, J. (Ed.) Introduction to polymer permeability and the mathematics of diffusion. In Polymer Permeability; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1985; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidance for Industry Nasal Spray and Inhalation Solution, Suspension, and Spray Drug Products—Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls Documentation. 2002. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/files/drugs/published/Nasal-Spray-and-Inhalation-Solution--Suspension--and-Drug-Products.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2024).
- Lakshmi, P.K.; Harini, K. Design and optimization of thermo-reversible nasal in situ gel of atomoxetine hydrochloride using taguchi orthogonal array design. Dhaka Univ. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 18, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagdale, S.; Shewale, N.; Kuchekar, B.S. Optimization of Thermoreversible In Situ Nasal Gel of Timolol Maleate. Scientifica 2016, 2016, 6401267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morsi, N.; Ghorab, D.; Refai, H.; Teba, H. Ketoroloac tromethamine loaded nanodispersion incorporated into thermosensitive in situ gel for prolonged ocular delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 506, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unal, S.; Tekeli, M.; Dogan, O.; Aktas, Y. Thermosensitive Pluronic® F127-Based in situ gel formulation containing nanoparticles for the sustained delivery of paclitaxel. Med Sci. 2023, 12, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godbole, D.; There, P.W.; Dangre, P.V. Formulation and optimization of prolonged release nasal in situ gel for treatment of migraine. Indo Am. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 4, 1320–1332. [Google Scholar]
- Kakulade, S.; Kulkarni, D.; Moravkar, K.; Zambad, S.; Tekade, A.; Chalikwar, S. Development, characterization and pharmacokinetic evalua-tion of selegiline HCl loaded cubosomal thermoreversible mucoadhesive gel for nose to brain delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 100, 106111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Formula | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F7 | F8 | F9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMT | 5 mg/0.1 mL | ||||||||
| PLU F127 (%) | 13.5 | 18 | 22.5 | 13.5 | 18 | 22.5 | 13.5 | 18 | 22.5 |
| HMW chitosan (%) | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Gelation Temperature (°C) | Gelation Time (s) | Gelation Strength (s) | Mucoadhesive Strength (Dyne/cm2) | % Release After 5 h | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | >70 | >300 | 0.003 ± 1.15 × 104 | 1295 | 57.920 ± 10.862 |
| F2 | 31.667 ± 0.153 | 31 ± 1 | 4.500 ± 0.5 | 1750 | 52.480 ± 2.351 |
| F3 | 24 ± 0.100 | 32 ± 1 | 94 ± 1 | 1295 | 37.508 ± 1.346 |
| F4 | >70 | >300 | 0.003 ± 1.15 × 104 | 1295 | 65.350 ± 5.035 |
| F5 | 31.800 ± 0.100 | 31 ± 1 | 6 ± 1 | 2100 | 50.341 ± 6.454 |
| F6 | 23.900 ± 0.100 | 13 ± 1 | 124 ± 1 | 2100 | 41.107 ± 10.318 |
| F7 | >70 | >300 | 0.003 ± 1.15 × 104 | 1505 | 49.145 ± 2.497 |
| F8 | 31.700 ± 0.200 | 34 ± 1 | 3 ± 1 | 2170 | 49.292 ± 2.708 |
| F9 | 24.033 ± 0.153 | 17 ± 1 | 78 ± 1 | 2100 | 47.731 ± 4.530 |
| Formulations | Eta (mPa∙s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPM | 20 | 50 | 70 | 100 |
| F1 | - | - | - | 4.449 ± 0.665 |
| F2 | 33.418 ± 2.018 | 41.782 ± 0.168 | 44.406 ± 0.100 | 45.788 ± 0.387 |
| F3 | 153.936 ± 17.241 | 142.250 ± 8.603 | 139.474 ± 4.659 | 138.326 ± 4.700 |
| F4 | - | - | 3.772 ± 0 | 3.665 ± 1.149 |
| F5 | 23.390 ± 0.142 | 30.778 ± 1.700 | 33.274 ± 1.092 | 35.25 ± 0.796 |
| F6 | 98.562 ± 0.836 | 105.411 ± 4.976 | 106.553 ± 6.346 | 106.898 ± 7.115 |
| F7 | - | - | 4.267 ± 0.359 | 5.7615 ± 0.128 |
| F8 | 19.202 ± 3.112 | 26.767 ± 3.120 | 29.332 ± 3.033 | 31.045 ± 3.329 |
| F9 | 114.973 ± 18.975 | 125.417 ± 15.073 | 126.164 ± 15.474 | 126.455 ± 15.605 |
| Zero-Order Model | First-Order Model | Higuchi Diffusion Model | Korsmeyer–Peppas Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | Slope | R | Slope | R | Slope | R | n | |
| F1 | 0.954 | 0.182 | −0.977 | −0.001 | 0.980 | 4.003 | 0.936 | 0.766 |
| F2 | 0.996 | 0.173 | −0.999 | −0.001 | 0.993 | 3.682 | 0.998 | 0.918 |
| F3 | 0.999 | 0.121 | −0.998 | −0.001 | 0.987 | 2.556 | 0.999 | 0.923 |
| F4 | 0.996 | 0.214 | −0.999 | −0.002 | 0.996 | 4.579 | 0.999 | 0.860 |
| F5 | 0.998 | 0.165 | −0.998 | −0.001 | 0.990 | 3.491 | 0.999 | 0.925 |
| F6 | 0.997 | 0.124 | −0.994 | −0.001 | 0.987 | 2.627 | 0.998 | 0.789 |
| F7 | 0.994 | 0.166 | −0.999 | −0.001 | 0.996 | 3.561 | 0.996 | 0.949 |
| F8 | 0.999 | 0.163 | −0.998 | −0.001 | 0.989 | 3.458 | 0.999 | 0.970 |
| F9 | 0.999 | 0.156 | −0.993 | −0.001 | 0.9787 | 3.257 | 0.997 | 0.950 |
| Formulation Composition | Parameters | Predicted Value | Observed Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLU F-127 (17.972%) Chitosan (0.03%) | Gelation temperature (°C) | 31.842 | 33.03 ± 0.115 |
| Gelation time (s) | 30 | 53 ± 1 | |
| Gelation strength (s) | 13.179 | 5.6 ± 0.454 | |
| Mucoadhesive strength (dyne/cm2) | 2099.267 | 1423 ± 0 | |
| % released after 5 h | 54.880 | 42.748 ± 1.436 | |
| pH | 5.5 | ||
| Clarity | Clear | ||
| Drug content % | 102.319 ± 0.764 |
| Membrane Type | Cumulative Amount Permeated (µg/cm2) After 5 h | Flux (µg/cm2/h) | Lag Time (h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal mucosa | 3920.165 ± 171.330 | 90.870 ± 4.790 | 0.83 ± 0.003 |
| Semipermeable membrane | 3080.300 ± 4.990 | 75.553 ± 4.270 | 0.895 ± 0.240 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alshraim, A.; Alshora, D.; Ashri, L.; Alhusaini, A.; Alanazi, N.; Safwan, N.M. In Situ Thermosensitive Mucoadhesive Nasal Gel Containing Sumatriptan: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Evaluations. Polymers 2024, 16, 3422. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16233422
Alshraim A, Alshora D, Ashri L, Alhusaini A, Alanazi N, Safwan NM. In Situ Thermosensitive Mucoadhesive Nasal Gel Containing Sumatriptan: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Evaluations. Polymers. 2024; 16(23):3422. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16233422
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlshraim, Aseel, Doaa Alshora, Lubna Ashri, Ahlam Alhusaini, Nawal Alanazi, and Nisreen M. Safwan. 2024. "In Situ Thermosensitive Mucoadhesive Nasal Gel Containing Sumatriptan: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Evaluations" Polymers 16, no. 23: 3422. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16233422
APA StyleAlshraim, A., Alshora, D., Ashri, L., Alhusaini, A., Alanazi, N., & Safwan, N. M. (2024). In Situ Thermosensitive Mucoadhesive Nasal Gel Containing Sumatriptan: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Evaluations. Polymers, 16(23), 3422. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16233422






