Self-Oscillation of Liquid Crystal Elastomer Fiber-Slide System Driven by Self-Flickering Light Source
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Framework
2.1. Self-Oscillating Dynamic of the LCE Fiber-Slide System
2.2. Dynamic LCE Model
2.3. Nondimensionalization
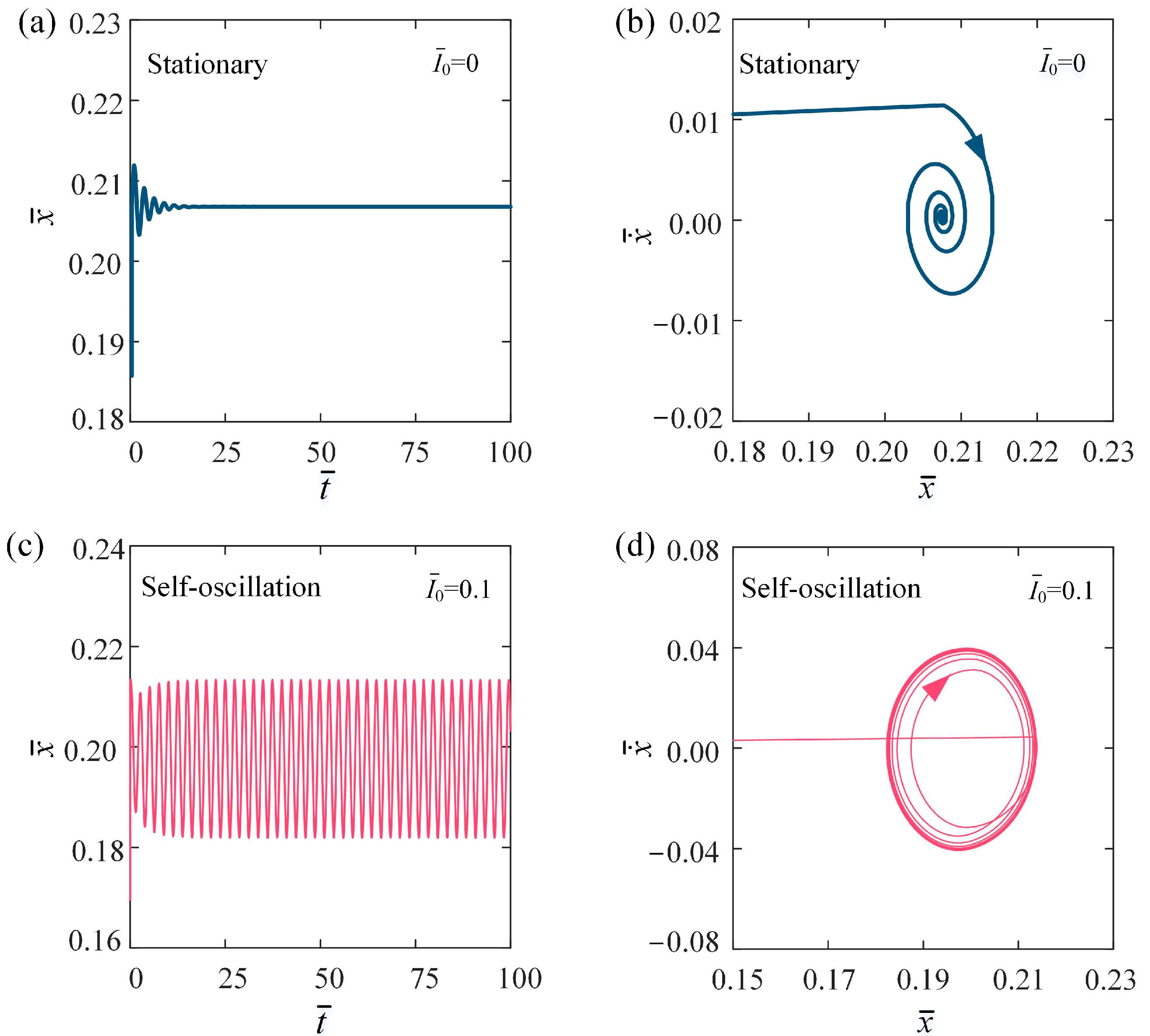
3. Two Motion Phases and Mechanism of Self-Oscillation
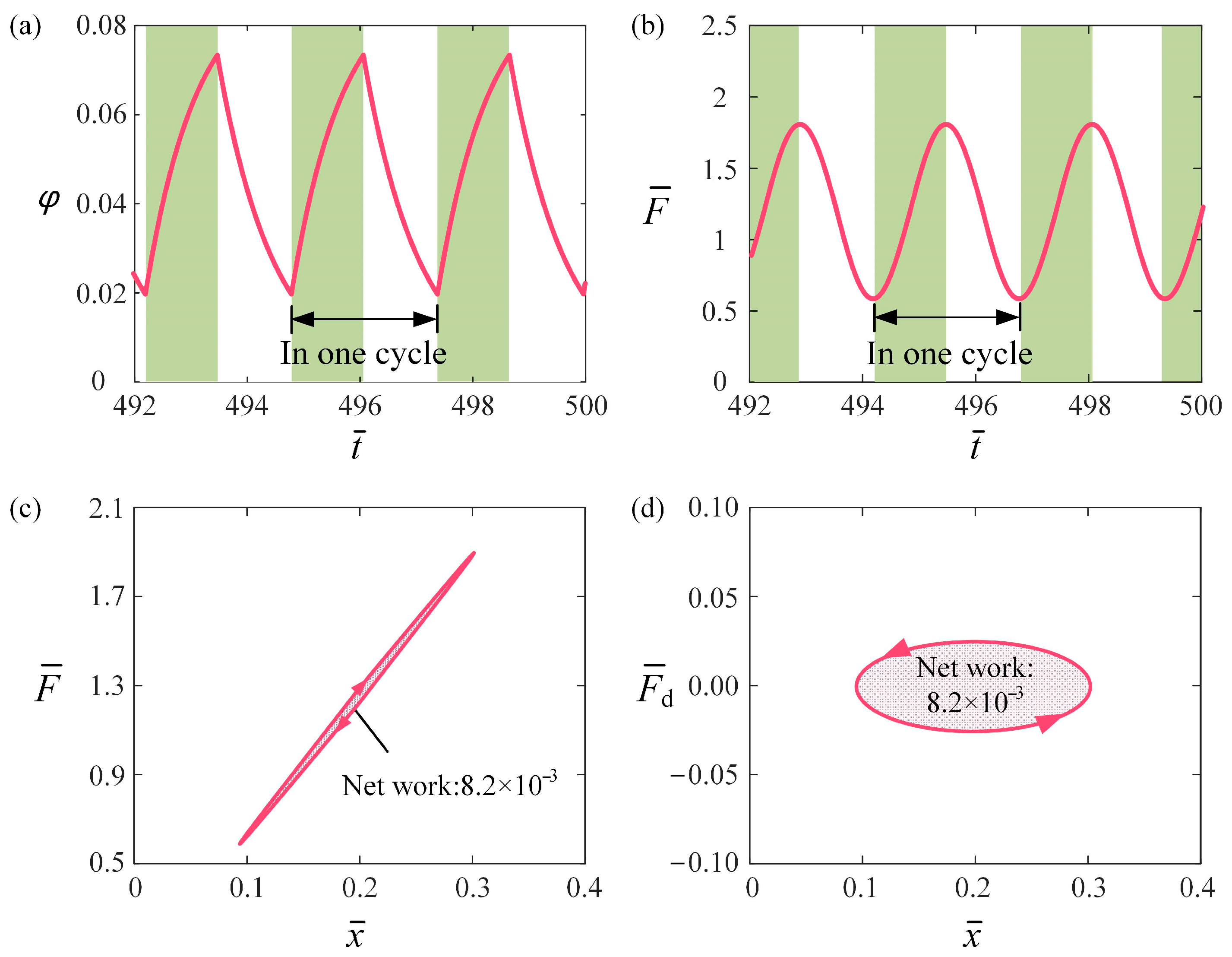
3.1. Two Motion Phases
3.2. Mechanisms of Self-Oscillation
4. Parameter Analysis
4.1. Impact of the Light Intensity
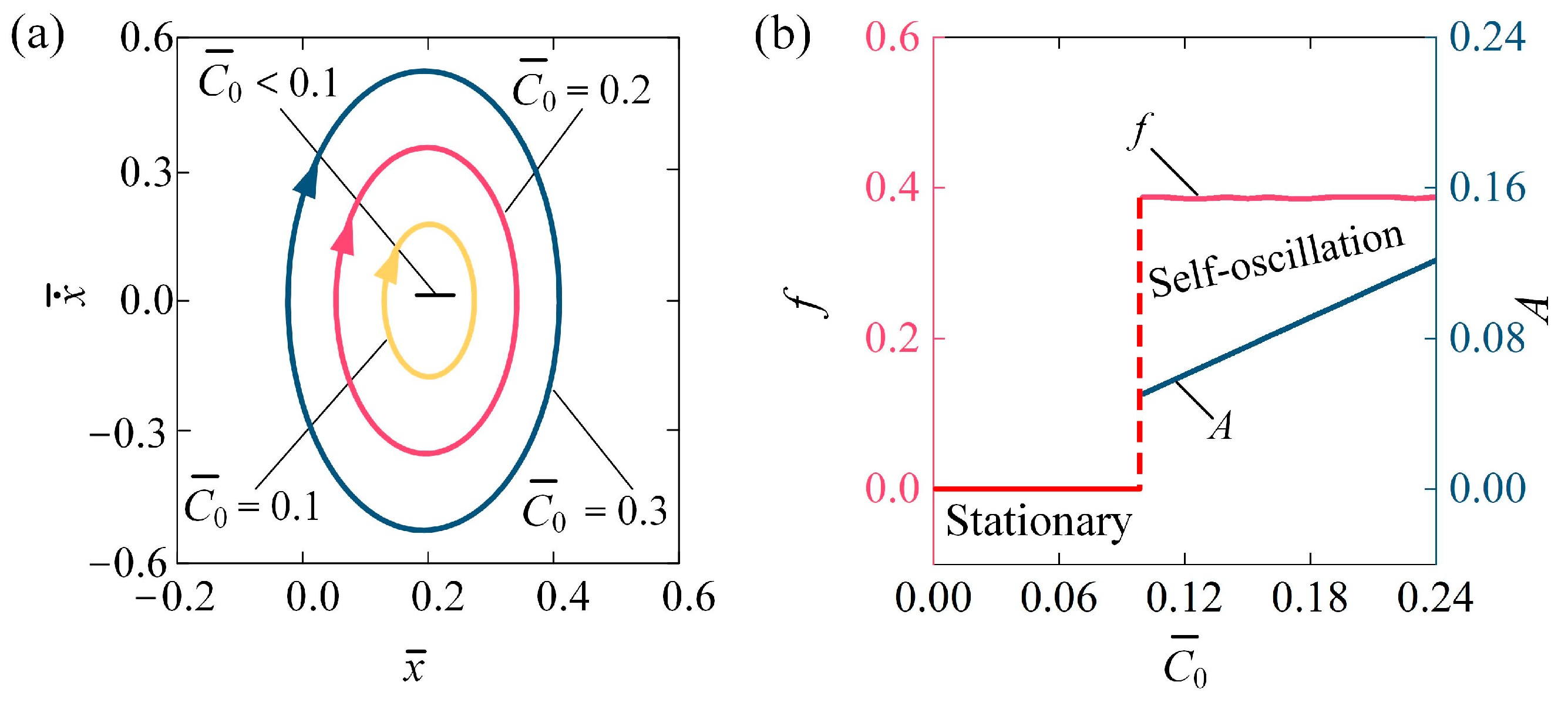
4.2. Impact of the Contraction Coefficient
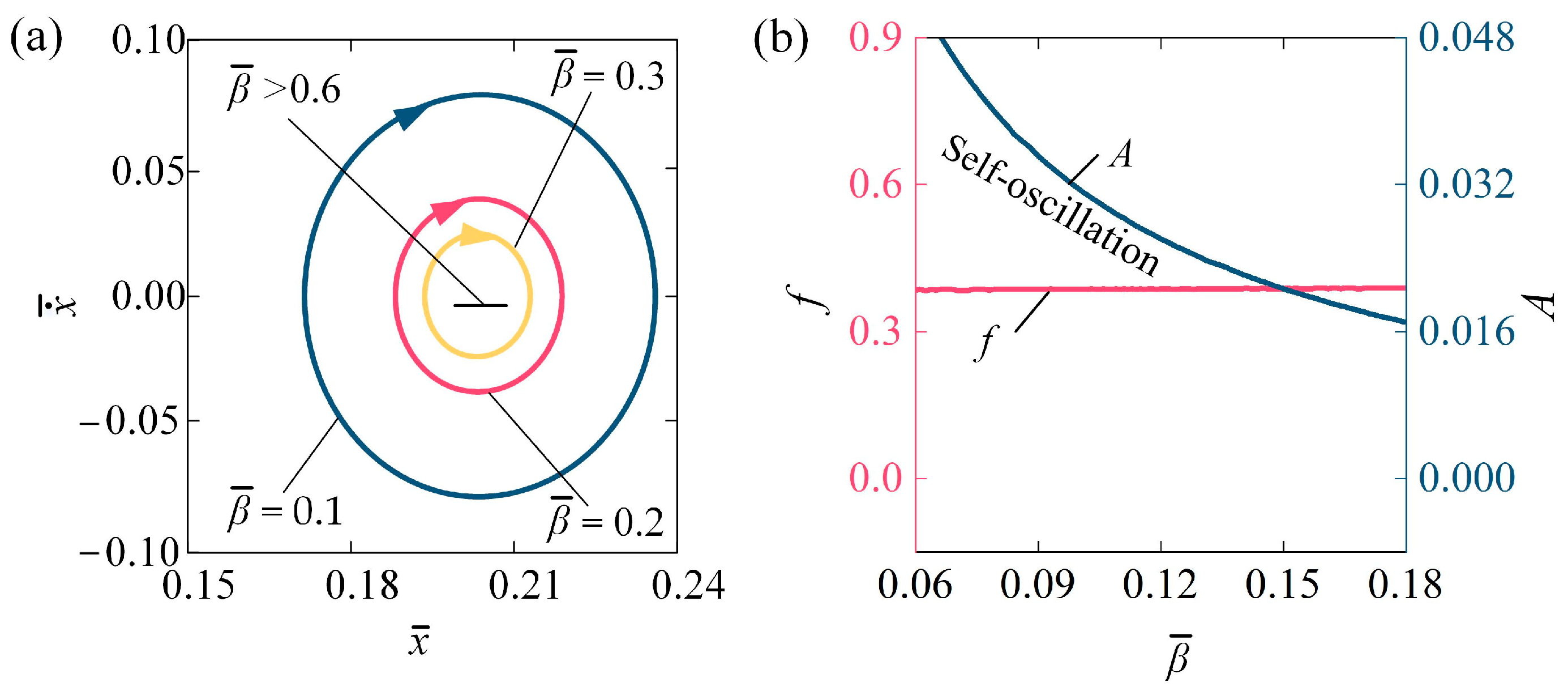
4.3. Impact of the Damping Coefficient
4.4. Impact of the Stiffness Coefficient
4.5. Impact of the Initial Condition
4.6. Impact of the Gravitational Acceleration
4.7. Impact of the Track Position
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Dang, A.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, R.; Gao, Y.; Feng, L.; Yang, S. Repeatable and reprogrammable shape morphing from photo-responsive gold nanorod/liquid crystal elastomers. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2004270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, R.; Jin, L.; Liu, M.; Gao, Y.; Raney, J.; Yang, S. 3D-printed photo-responsive liquid crystal elastomer composites for free-form actuation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2210614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Q.; Tan, C.F.; Chan, K.H. In-built thermomechanical cooperative feedback mechanism for self-propelled multimodal locomotion and electricity generation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Terentjev, E.M.; Zhang, Y. Reprocessable thermoset soft actuators. Angew. Chem. 2019, 58, 17474–17479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Techawanitchai, P.; Ebara, M.; Idota, N.; Asoh, T.A.; Kikuchi, A.; Aoyagi, T. Photo-switchable control of pH-responsive actuators via pH jump reaction. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 2844–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, M.; Kim, C.; Du, Y.; Wu, D.; Bai, R.; He, X. Swaying gel: Chemo-mechanical self-oscillation based on dynamic buckling. Matter 2021, 4, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Sattari, K.; Xie, Y.; Liao, P.; Yan, Z.; Lin, J. Laser reprogramming magnetic anisotropy in soft composites for reconfigurable 3D shaping. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Liao, W.; Yang, Z. Ultrafast, high-contractile electrothermal-driven liquid crystal elastomer fibers towards artificial muscles. Small 2021, 17, 2103700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Yang, Z. The integration of sensing and actuating based on a simple design fiber actuator towards intelligent soft robots. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2101260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, B.; Ha, J.; Lee, M. Hygrobot: A self-locomotive ratcheted actuator powered by environmental humidity. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, eaar2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arazoe, H.; Miyajima, D.; Akaike, K. An autonomous actuator driven by fluctuations in ambient humidity. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, C.; Chen, B.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, R. Bioinspired design of stimuli-responsive artificial muscles with multiple actuation modes. Smart Mater. Struct. 2023, 32, 085023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, B.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, R. Shape memory behaviors of 3D printed liquid crystal elastomers. Soft Sci. 2023, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Yin, R.; Hua, Y.; Jiao, W.; Mo, C.; Shu, H.; Raney, J.R. A modular strategy for distributed, embodied control of electronics-free soft robots. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eade9247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Yamauchi, Y.; Araoka, F. An anisotropic hydrogel actuator enabling earthworm-like directed peristaltic crawling. Angew. Chem. 2018, 57, 15772–15776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, R.; Mou, L. Photothermal bimorph actuators with in-built cooler for light mills, frequency switches, and soft robots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1808995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Iscen, A.; Sai, H. Supramolecular-covalent hybrid polymers for light-activated mechanical actuation. Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kularatne, R.; Kim, H.; Boothby, J.; Ware, T. Liquid crystal elastomer actuators: Synthesis, alignment, and applications. J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Phys. 2017, 55, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Deng, Z.; Fang, B.; Yang, Y.; Sun, F. A review on sensory perception for dexterous robotic manipulation. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2022, 19, 17298806221095974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korner, K.; Kuenstler, A.S.; Hayward, R.C.; Audoly, B.; Bhattacharya, K. A nonlinear beam model of photomotile structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 9762–9770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibaei, R.; Zakerhamidi, M.S.; Korramab, S.; Ranjkesh, A. Effects of polarized light on the optical and self-oscillation behaviors of liquid crystal network polymers. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 14908–14915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, A. Self-oscillation. Phys. Rep. 2013, 525, 167–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, Y.; Deng, Z.; Pi, H.; Guo, H.; Zhang, H. A scalable, incoherent-light-powered, omnidirectional self-oscillator. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2023, 6, 2300054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Bai, C.; Liu, S.; Jia, Y. Light-induced nontethered rolling of liquid crystal elastomer and carbon nanotube composite ring. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 2709–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotikian, A.; McMahan, C.; Davidson, E.C.; Muhammad, J.M.; Weeks, R.D.; Daraio, C.; Lewis, J.A. Untethered soft robotic matter with passive control of shape morphing and propulsion. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4, eaax7044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.L.; Liu, W.; Khoruzhenko, O.; Breu, J.; Hong, W.; Zheng, Q.; Wu, Z.L. Animating hydrogel knotbots with topology-invoked self-regulation. Nat. Commun. 2024, 14, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, X.P.; Wang, T.; Zhang, B.L.; Zhai, Z.Z.; Chen, Y.J.; Pei, D.F.; Ge, A.L.; Li, M.J.; Li, C.X. Two-dimensionally nano-capsulating liquid metal for self-sintering and self-oscillating bimorph composites with persistent energy-harvest property. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 34, 2307830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Q.; Xu, L.L.; Ji, Q.X.; Chang, L.F.; Hu, Y.; Peng, Q.Y.; He, X.D. A MXene-based light-driven actuator and motor with self-sustained oscillation for versatile applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 34, 2310955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.-Z.; Wang, M.; Huang, S.; Liu, Z.; Yang, H. Multimodal self-sustainable autonomous locomotions of light-driven Seifert ribbon actuators based on liquid crystal elastomers. Angew. Chem. 2023, 135, e202304081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Ng, T.N. Self-sustained robots based on functionally graded elastomeric actuators carrying up to 22 times their body weight. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2023, 5, 2100085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helou, C.E.; Hyatta, L.P.; Buskohl, P.R.; Harne, R.L. Intelligent electroactive material systems with self-adaptive mechanical memory and sequential logic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2317340121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayoti, D.; Peeketi, A.R.; Kumbhar, P.Y.; Swaminathan, N.; Annabattula, R.K. Geometry controlled oscillations in liquid crystal polymer films triggered by thermal feedback. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 18362–18371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, R.; Ma, L.; Feng, W.; Pan, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, P.; Bisoyi, H.K.; et al. Autonomous self-sustained liquid crystal actuators enabling active photonic applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2301142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Lahikainen, M.; Liu, L.; Ahmed, Z.; Wani, O.M.; Wang, M.; Yang, H.; Priimagi, A. Light-fuelled freestyle self-oscillators. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Ji, Q.; Huang, M.; Chang, L.; Zhang, C.; Wu, G.; Zi, B.; Bao, N.; Chen, W.; Wu, Y. Light-driven self-oscillating actuators with phototactic locomotion based on black phosphorus heterostructure. Angew. Chem. 2021, 60, 20511–20517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.L.; Chang, L.F.; Hu, Y.; Huang, M.J.; Ji, Q.X.; Lu, P.; Liu, J.Q.; Chen, W.; Wu, Y.C. An autonomous soft actuator with light-driven self-sustained wavelike oscillation for phototactic self-locomotion and power generation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1908842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Mou, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Y. Oscillating light engine realized by photothermal solvent evaporation. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; He, Y.; Wang, B.; Xu, J.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Ren, L.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Q.; et al. 4D printed self-sustained soft crawling machines fueled by constant thermal field. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2400161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Li, K. Self-oscillating buckling and postbuckling of a liquid crystal elastomer disk under steady illumination. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2022, 221, 107233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelebart, G.A.; Mulder, D.J.; Varga, M.; Konya, A.; Vantomme, G.; Meijer, E.W.; Selinger, R.L.B.; Broer, D.J. Making waves in a photoactive polymer film. Nature 2017, 546, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahsavana, H.; Aghakhania, A.; Zeng, H.; Guo, Y.; Davidson, Z.S.; Priimagi, A.; Sitti, M. Bioinspired underwater locomotion of light-driven liquid crystal gels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 117, 5125–5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Fan, Y.; Lv, J. Photomorphogenesis of diverse autonomous traveling waves in a monolithic soft artificial muscle. ACS Appl. Mater. Int. 2022, 14, 23839–23849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Cunha, M.P.; Peeketi, A.R.; Mehta, K.; Broer, D.J.; Annabattula, R.K.; Schenning, A.P.H.J.; Debije, M.G. A self-sustained soft actuator able to rock and roll. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 11029–11032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Cunha, M.P.; Peeketi, A.R.; Ramgopal, A.; Annabattula, R.K.; Schenning, A.P.H.J. Light-driven continual oscillatory rocking of a polymer film. ChemistryOpen 2020, 9, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Cao, R.; Ye, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Tu, Y.; Ge, D.; Yang, X. A bio-inspired homogeneous graphene oxide actuator driven by moisture gradients. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Sun, X.; Dai, Y.; Li, K. Light-powered sustained chaotic jumping of a liquid crystal elastomer balloon. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 266, 108922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebner, T.S.; Korner, K.; Bowman, C.N.; Bhattacharya, K.; White, T.J. Leaping liquid crystal elastomers. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eade1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, G.; Jin, B.; Feng, H.; Chen, Z.; Fang, M.; Yang, B.; Xiao, R.; Xie, T.; Zheng, N. Multimodal autonomous locomotion of liquid crystal elastomer soft robot. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2402358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Jin, B.; Zhao, H.; He, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Jiang, S. Rotini-like MXene@LCE actuator with diverse and programmable actuation based on dual-mode synergy. Small 2024, 20, 2305371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bao, J.; Huang, R.; Song, C.; Shen, C.; Sun, J.; Lan, R.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H. Light- and humidity-driven fluorescence changeable soft robot enabled by water-gated photoinduced electron transfer pathway. Sci. China Mater. 2023, 66, 2445–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ch, Y.; Hong, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Yin, J. Twisting for soft intelligent autonomous robot in unstructured environments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2200265119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, K.; Yang, X.; Zhou, C.; Li, C. Self-regulated reversal deformation and locomotion of structurally homogenous hydrogels subjected to constant light illumination. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Ge, D.; Chen, J.; Xu, P.; Li, K. A light-fueled self-rolling unicycle with a liquid crystal elastomer rod engine. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 186, 115327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Dai, Y.; Liang, H.; Li, K. Self-rolling and circling of a conical liquid crystal elastomer rod on a hot surface. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 263, 108780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Du, C.; Li, K.; Cai, S. Controllable and versatile self-motivated motion of a fiber on a hot surface. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2022, 57, 101918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Qiu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Yu, Y. Modeling the dynamic response of a light-powered self-rotating liquid crystal elastomer-based system. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 263, 108794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Ge, D.; Wu, H.; Li, K.; Xu, P. Self-rotation of a liquid crystal elastomer rod under constant illumination. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 284, 109665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Li, K. Self-rotation-eversion of an anisotropic-friction-surface torus. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 281, 109584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, H.; Li, K. Optically-responsive liquid crystal elastomer thin film motors in linear/nonlinear optical fields. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 202, 112082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Qian, P.; Hu, H.; Dai, Y.; Ge, D. A light-powered liquid crystal elastomer semi-rotary motor. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2023, 284, 112509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Li, K. Self-spinning of liquid crystal elastomer tubes under constant light intensity. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2024, 133, 108296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.L.; Liu, W.; Khoruzhenko, O.; Breu, J.; Bai, H.; Hong, W.; Zheng, Q.; Wu, Z.L. Closed twisted hydrogel ribbons with self-sustained motions under static light irradiation. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2314152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Li, K.; Priimagi, A.; Zeng, H. Light-steerable locomotion using zero-energy modes. Nat. Mater. 2024. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, L.; Li, K. Light-powered self-excited oscillation of a liquid crystal elastomer pendulum. Mech. Syst. Signal. Pro. 2021, 163, 108140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Kang, J.; Wang, Y.Q. Light-induced motion of three-dimensional pendulum with liquid crystal elastomeric fiber. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 266, 108911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Annapooranan, R.; Zeng, J.; Chen, R.; Cai, S. Electrospun liquid crystal elastomer microfiber actuator. Sci. Robot. 2021, 6, eabi9704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhou, K.; Xu, P. Chaotic self-beating of left ventricle modeled by liquid crystal elastomer. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 205, 112540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Li, K. Pulsating self-snapping of a liquid crystal elastomer bilayer spherical shell under steady illumination. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2022, 233, 107646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hong, Y.; Qi, F.; Chi, Y.; Hao, S.; Yin, J. Self-sustained snapping drives autonomous dancing and motion in free-standing wavy rings. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2207372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Li, Y.; Lv, J. Phototunable self-oscillating system driven by a self-winding fiber actuator. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Pei, D.; Yu, S.; Zhang, X.; Yi, M.; Li, C. Design of MXene composites with biomimetic rapid and self-oscillating actuation under ambient circumstances. ACS Appl. Mater. Int. 2021, 13, 31978–31985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Liang, H.; Li, K. Self-oscillation of a liquid crystal elastomer string-mass system under constant gradient temperature. Appl. Mech. 2024, 91, 101001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Du, C.; Zhu, F.; Dai, Y.; Ge, D.; Li, K. Self-galloping of a liquid crystal elastomer catenary cable under a steady temperature field. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 202, 112071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Dai, C.; Dai, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, K. Self-oscillation of cantilevered silicone oil paper sheet system driven by steam. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 203, 112270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantomme, G.; Elands, L.C.M.; Gelebart, A.H.; Meijer, E.W.; Pogromsky, A.Y.; Nijmeijer, H.; Broer, D.J. Coupled liquid crystalline oscillators in Huygens’ synchrony. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 1702–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, B.; Li, K. Synchronous behaviors of three coupled liquid crystal elastomer-based spring oscillators under linear temperature fields. Phys. Rev. E 2024, 109, 024701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Sundaram, S.; Kang, J.; Tanjeem, N.; Emrick, T.; Hayward, R.C. Coupled oscillation and spinning of photothermal particles in Marangoni optical traps. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2024581118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Nakano, M.; Ikeda, T. Photomechanics: Directed bending of a polymer film by light-miniaturizing a simple photomechanical system could expand its range of applications. Nature 2003, 425, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelmann, H.; Nishikawa, E.; Pereira, G.G.; Warner, M. A new opto-mechanical effect in solids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 015501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, D.; Xuan, C.; Warner, M. Deep optical penetration dynamics in photobending. Phys. Rev. 2015, 92, 013206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagele, T.; Hoche, R.; Zinth, W.; Wachtveitl, J. Femtosecond photoisomerization of cis-azobenzene. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1997, 272, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, L.B.; Hessberger, T.; Pütz, E.; Müller, C.; Giesselmann, F.; Serra, C.A.; Zentel, R. Actuating thermo- and photo-responsive tubes from liquid crystalline elastomers. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 9093–9101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Lopez, M.; Finkelmann, H.; Palffy-Muhoray, P.; Shelley, M. Fast liquid-crystal elastomer swims into the dark. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


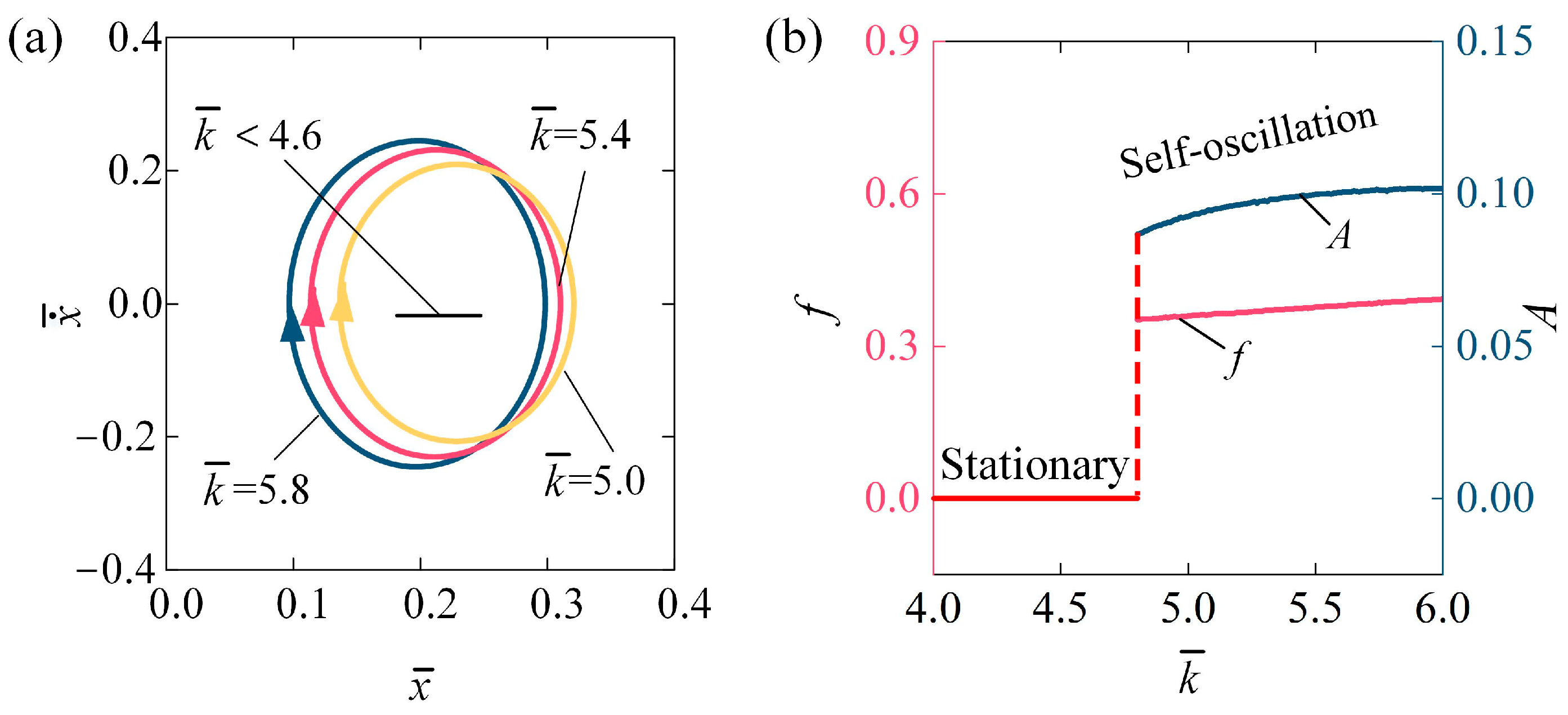
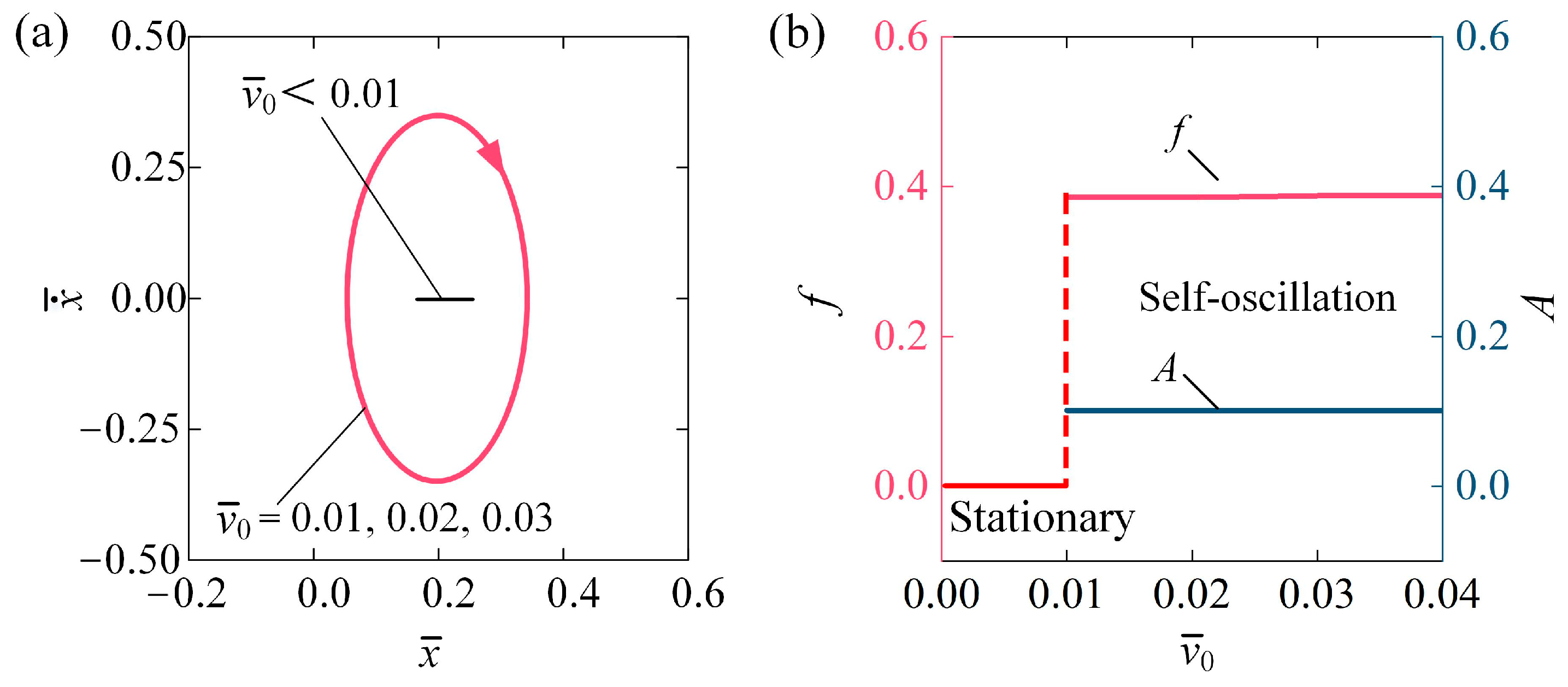
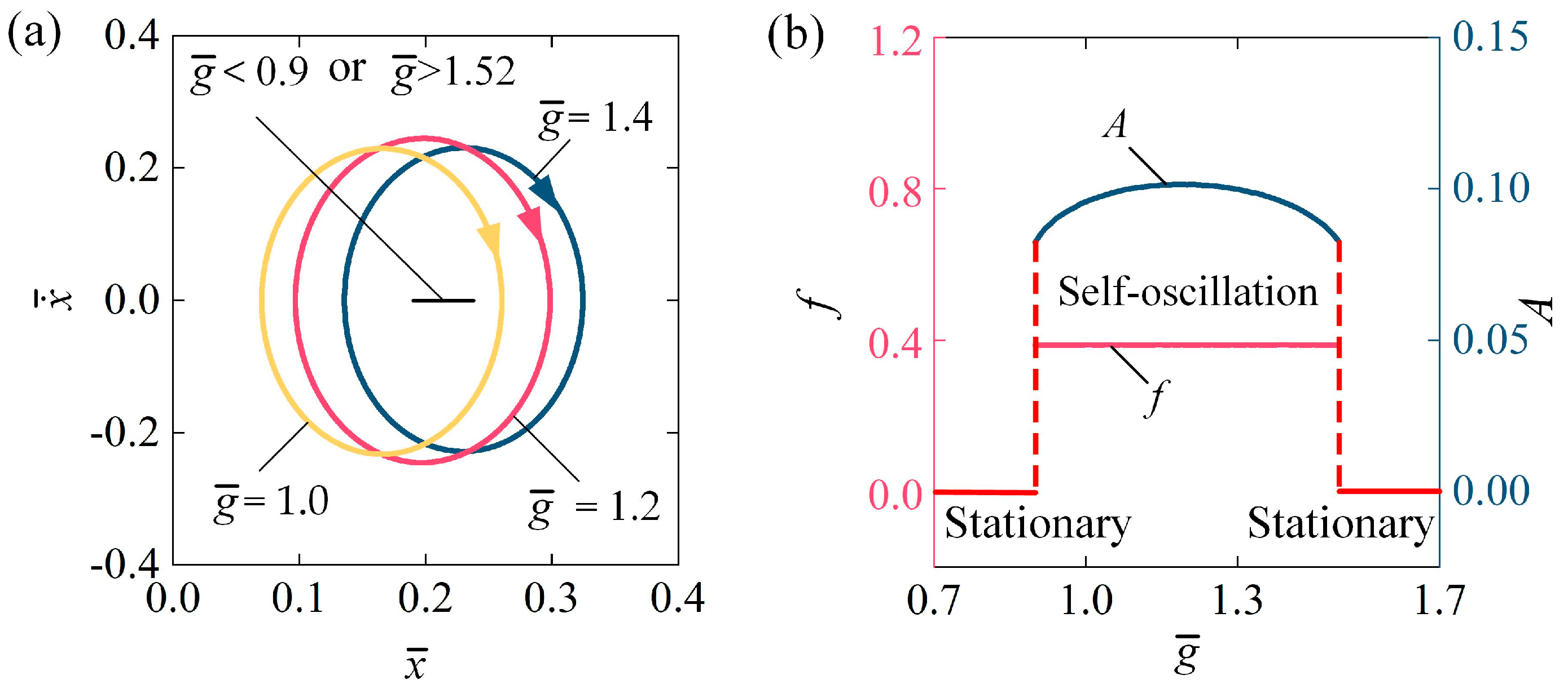
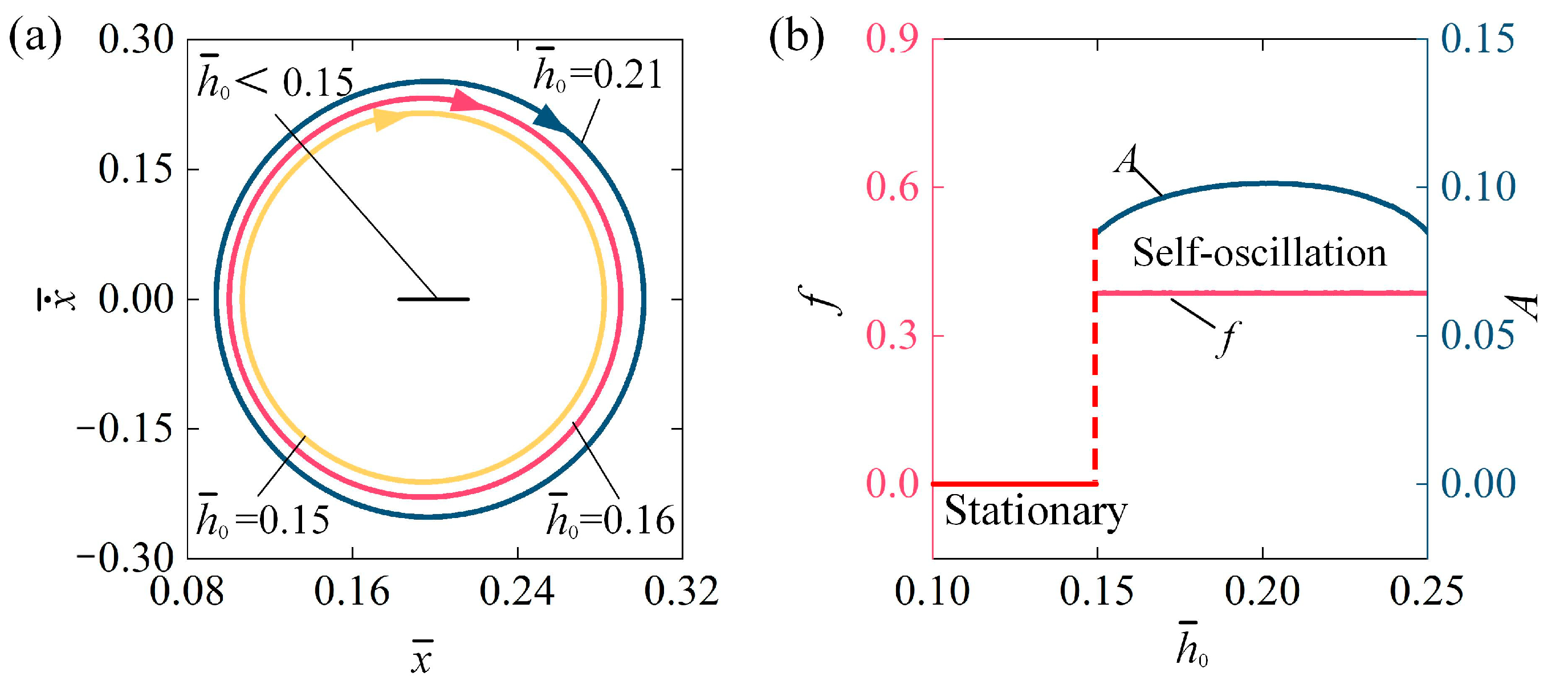
| Parameter | Definition | Value | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contraction coefficient | 0~0.5 | ||
| Light intensity | 0~0.15 | ||
| trans-to-cis thermal relaxation time | 1~100 | ||
| Light absorption constant | 0.0003 | ||
| Original length of LCE fiber | 1~10 | ||
| Stiffness coefficient | 0~20 | ||
| Gravitational acceleration | 10 | ||
| Damping coefficient | 0~0.6 | ||
| Mass of the slider | 0~10 | ||
| Position of the conductive track | 0~0.1 | ||
| Initial velocity | 0~0.1 |
| Parameter | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 0~0.5 | 0~0.5 | 0~10 | 0~0.2 | 0.1~2 | 0~0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, D.; Hong, Q.; Liu, X.; Liang, H. Self-Oscillation of Liquid Crystal Elastomer Fiber-Slide System Driven by Self-Flickering Light Source. Polymers 2024, 16, 3298. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16233298
Ge D, Hong Q, Liu X, Liang H. Self-Oscillation of Liquid Crystal Elastomer Fiber-Slide System Driven by Self-Flickering Light Source. Polymers. 2024; 16(23):3298. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16233298
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Dali, Qingrui Hong, Xin Liu, and Haiyi Liang. 2024. "Self-Oscillation of Liquid Crystal Elastomer Fiber-Slide System Driven by Self-Flickering Light Source" Polymers 16, no. 23: 3298. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16233298
APA StyleGe, D., Hong, Q., Liu, X., & Liang, H. (2024). Self-Oscillation of Liquid Crystal Elastomer Fiber-Slide System Driven by Self-Flickering Light Source. Polymers, 16(23), 3298. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16233298





