Morphology Control of Polymer–Inorganic Hybrid Nanomaterials Prepared in Miniemulsion: From Solid Particles to Capsules
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Strategies type A (both polymer and inorganic components preformed ex situ): they consist of the self-assembly of preformed polymer and inorganic components and involve typical processes of inorganic deposition on functionalized polymers, solvent evaporation, or heterocoagulation techniques.
- Strategies type B (polymer formed in situ): they involve polymerization processes in the presence of preformed inorganic components. This group includes typical miniemulsion polymerization, interfacial polymerization, semi-batch polymerization, seed emulsion polymerization in the presence of inorganic components synthesized ex situ, or Pickering emulsion.
- Strategies type C (inorganic material formed in situ): they use the polymer nanoparticles as supports for inorganic synthesis. In these processes, the in-situ formation of the inorganic species takes place on the preformed polymer by inorganic crystallization, precipitation/mineralization, or interfacial sol–gel processes.
- Strategies type D (both polymer and inorganic components formed in situ): they are “all-in-situ” strategies are challenging syntheses related to the formation of the inorganic nanoparticles via hydrolysis and condensation reactions of inorganic precursors occurring simultaneously to miniemulsion polymerization processes.
- Finally, multistep strategies involve complex cases resulting from the mixture of pure synthetic processes, which occur either simultaneously or consecutively.
2. Preparation of Hybrid Solid Nanoparticles
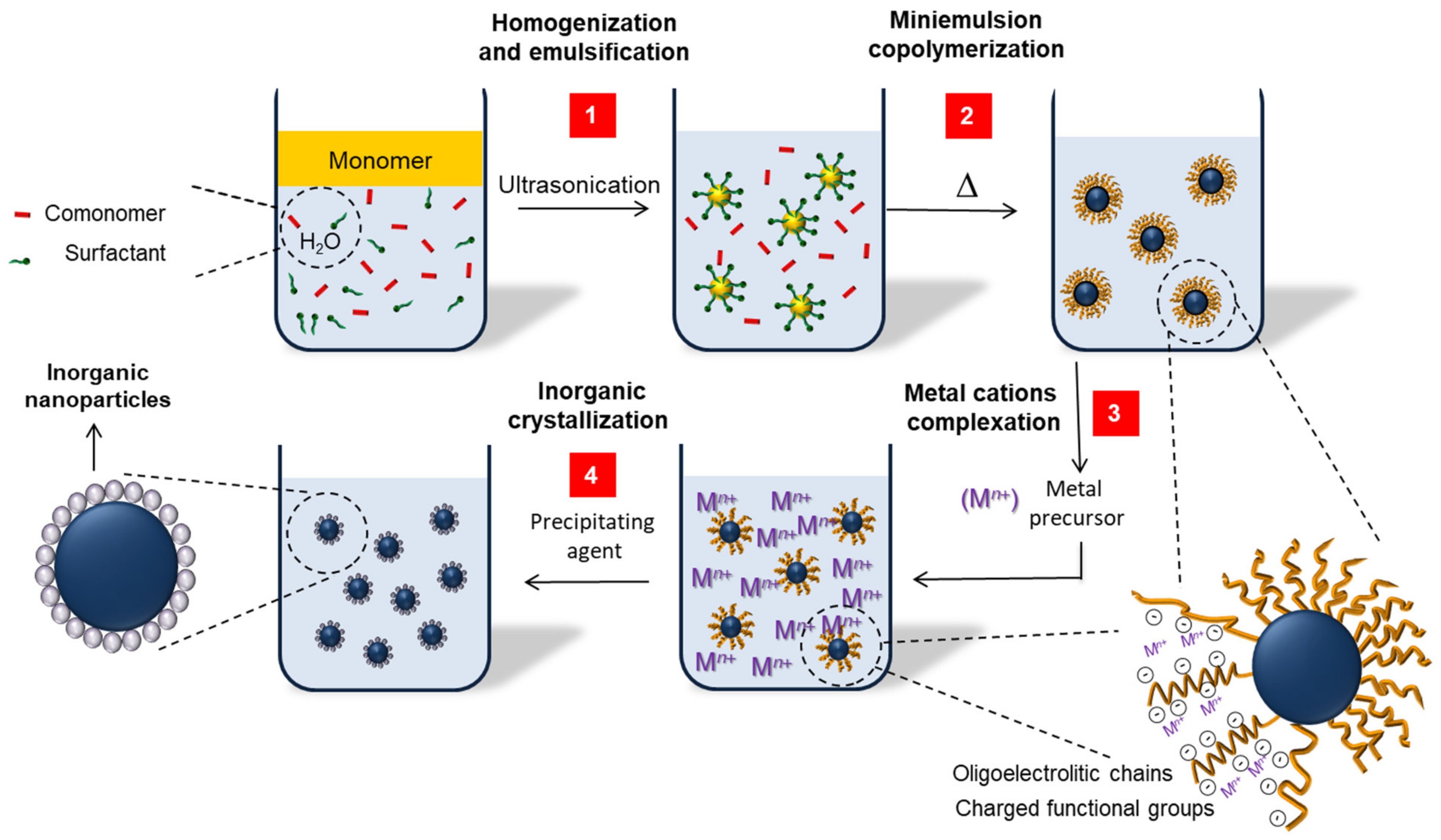
2.1. Basic Principles for Structure Control in Hybrid Nanoparticles
2.2. Preparation Strategies
2.2.1. Hybrid Nanoparticles by Assembly of Preformed Polymer and Inorganic Components (Strategies Type A)
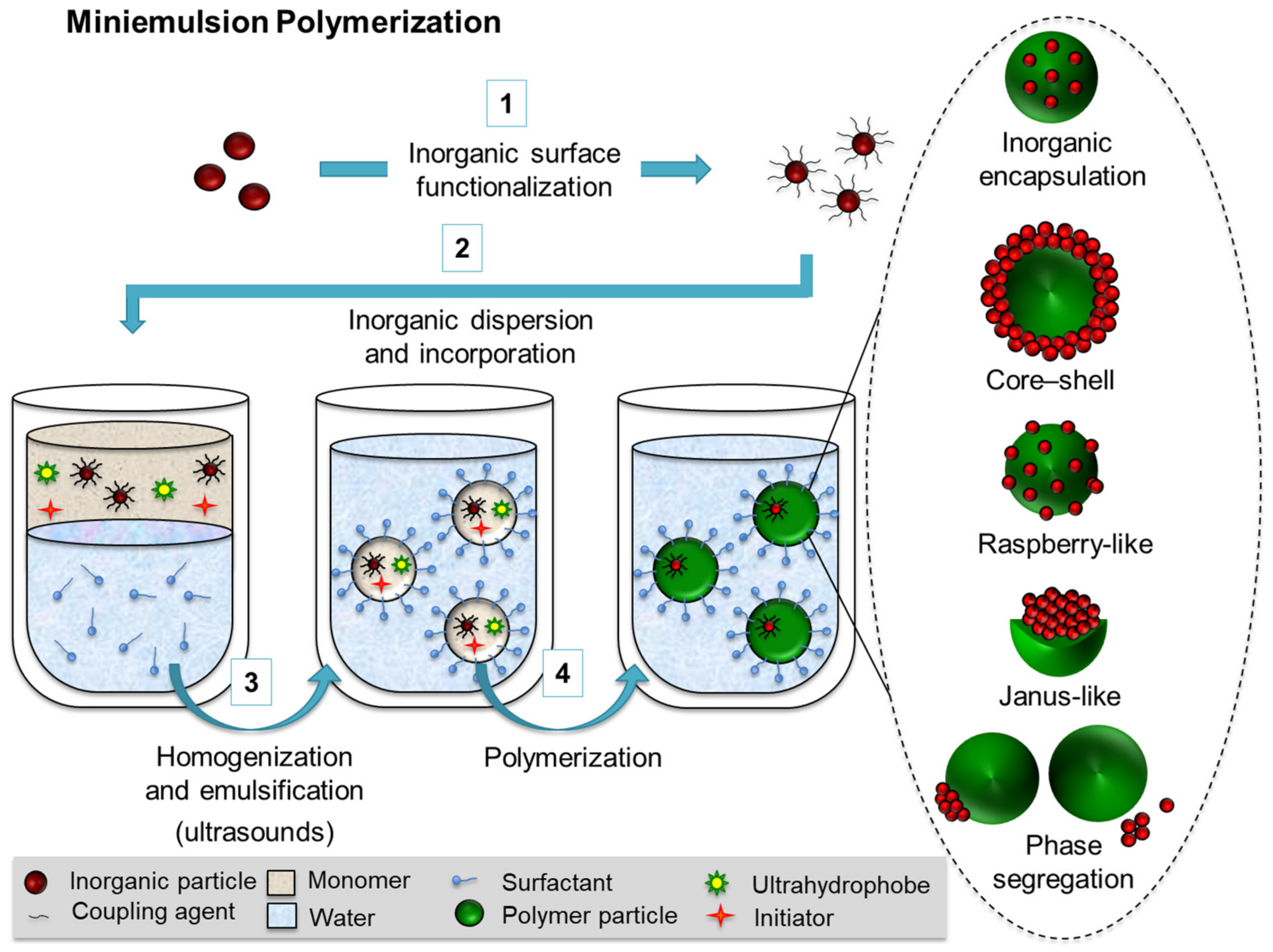
2.2.2. Polymerization Processes in the Presence of Preformed Inorganic Components (Strategies Type B)
2.2.3. Use of Preformed Polymers as Supports for In-Situ Inorganic Precipitation/Crystallization (Strategies Type C)
2.2.4. “All-In-Situ” Formation of Hybrid Nanoparticles (Strategies Type D)
2.2.5. Multistep Preparation of Hybrid Nanoparticles
- Assembly of Preformed Polymer–Inorganic Components Combined with Polymerization Processes (Strategies Type A–B)
- Inorganic Synthesis and Polymerization Processes in the Presence of Preformed Counterpart Species or their Precursors (Strategies B–C)
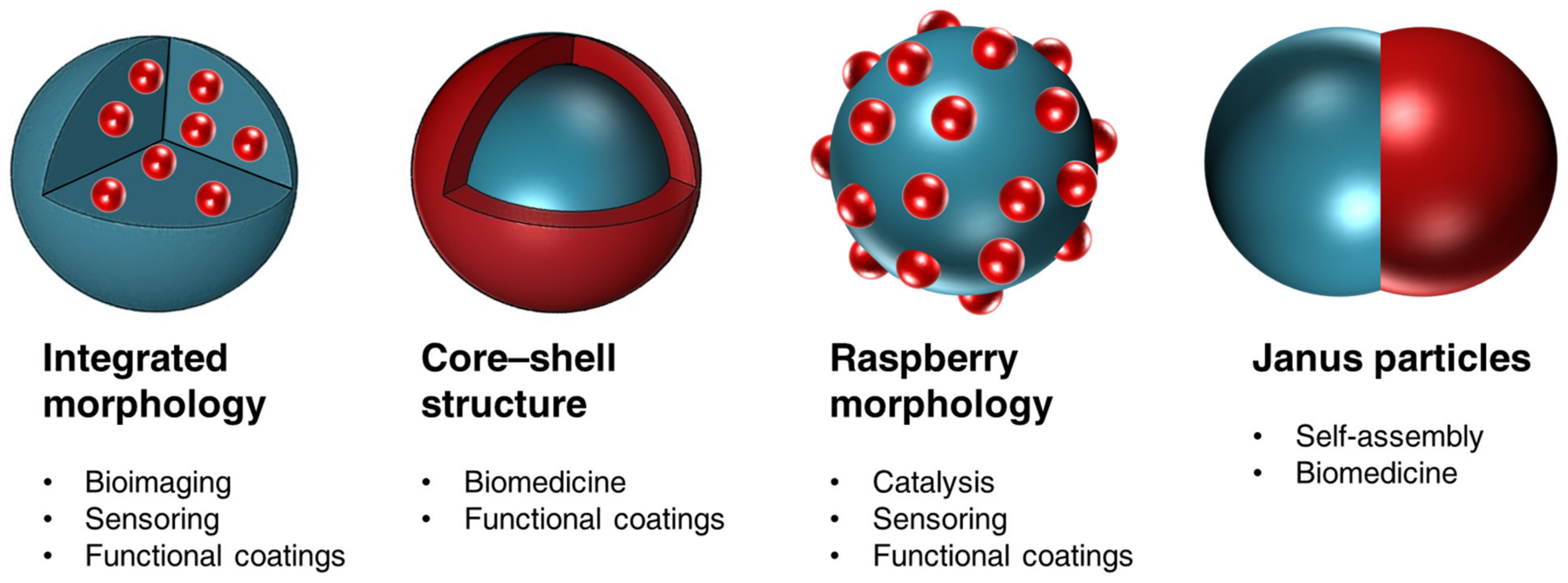
2.3. Applications of Various Nanoparticle Morphologies
3. Preparation of Hybrid Nanocapsules
3.1. General Overview
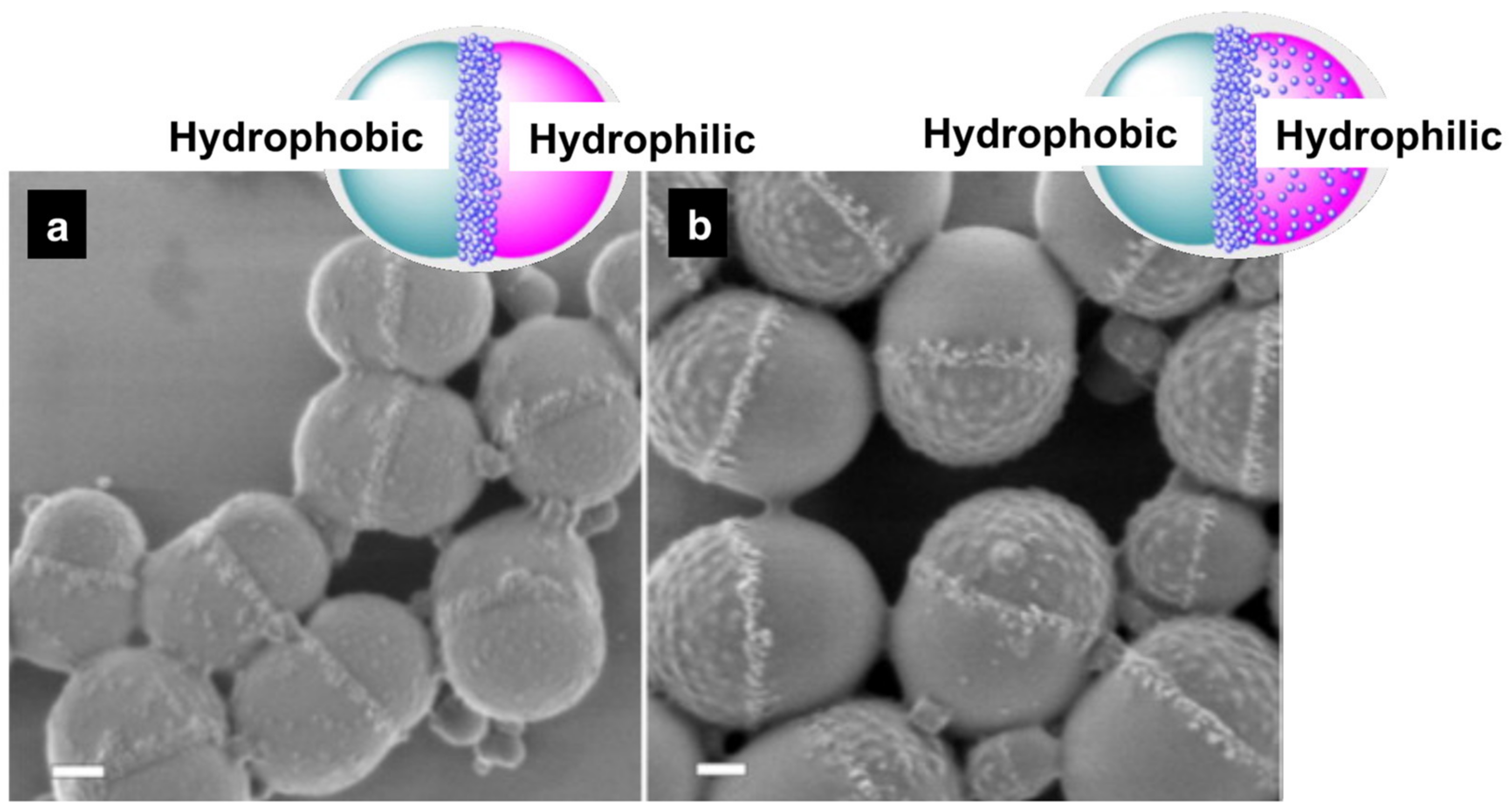
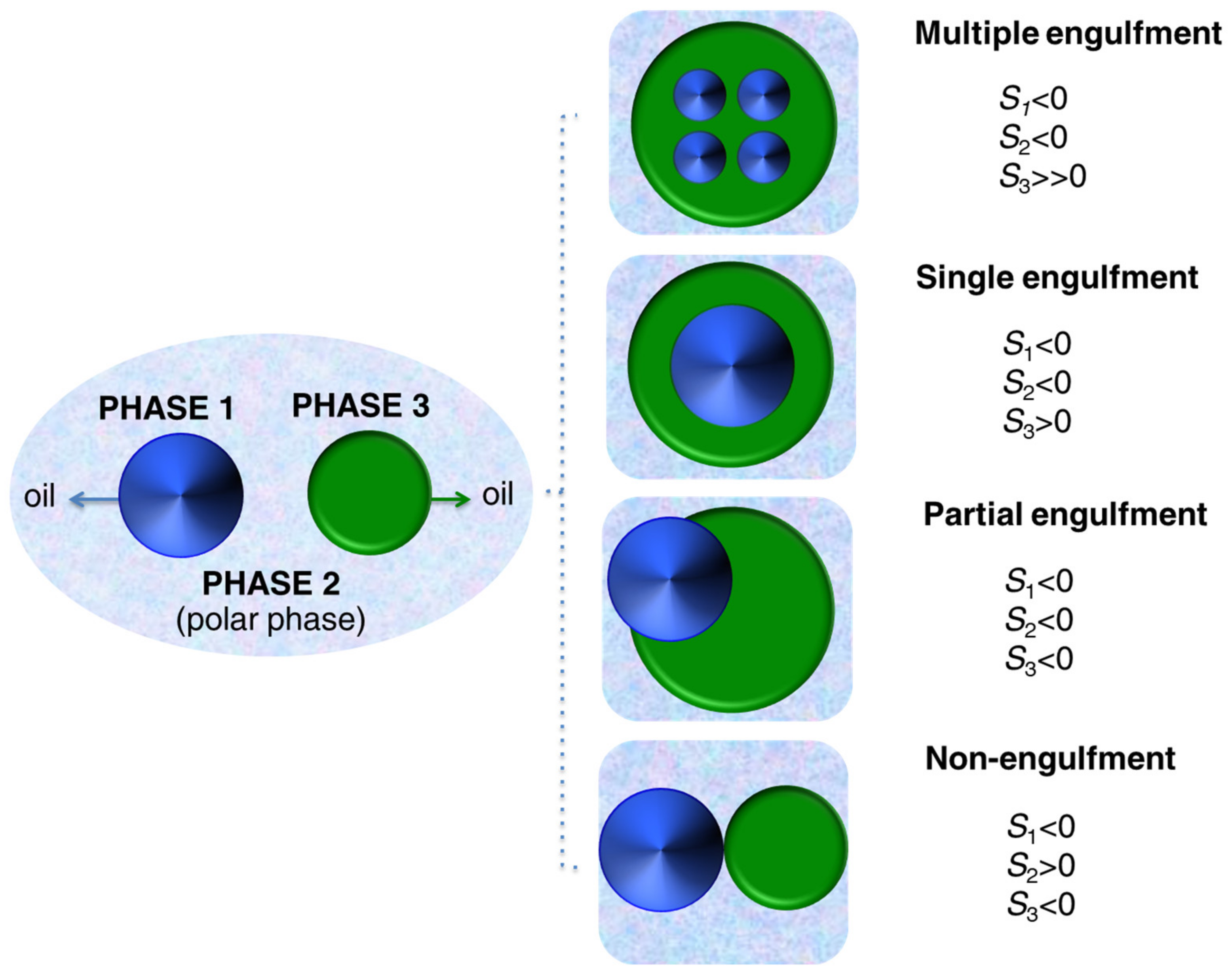
3.1.1. Basic Principles for Structure Control of Hybrid Capsules via Phase Separation
- If the hydrophobicity of phase 3 is much higher than phase 1 (γ12 >> γ23) and the interfacial tension between the oil phases is low (Figure 10), a multiple engulfment of oil 1 in 3 is achieved.
- A core–shell morphology is reached by the single engulfment of the phase 1 into 3 when oil 3 is more hydrophobic than oil 1 (γ12 > γ23) and the interfacial tension between the oil phases is still low.
- If phases 1 and 3 present similar hydrophobicity (γ12 ≈ γ23) and the interfacial tension between them is low, one of the oil phases (1) is partially engulfed by the other one (3) (Figure 10).
- If the interfacial tension between two oil phases (1 and 3) with similar polarity is high, non-engulfment and separation of the droplets as in Figure 10 occur.
3.1.2. Capsule Formation via Chemical Processes at the Interface
3.2. Preparation Strategies
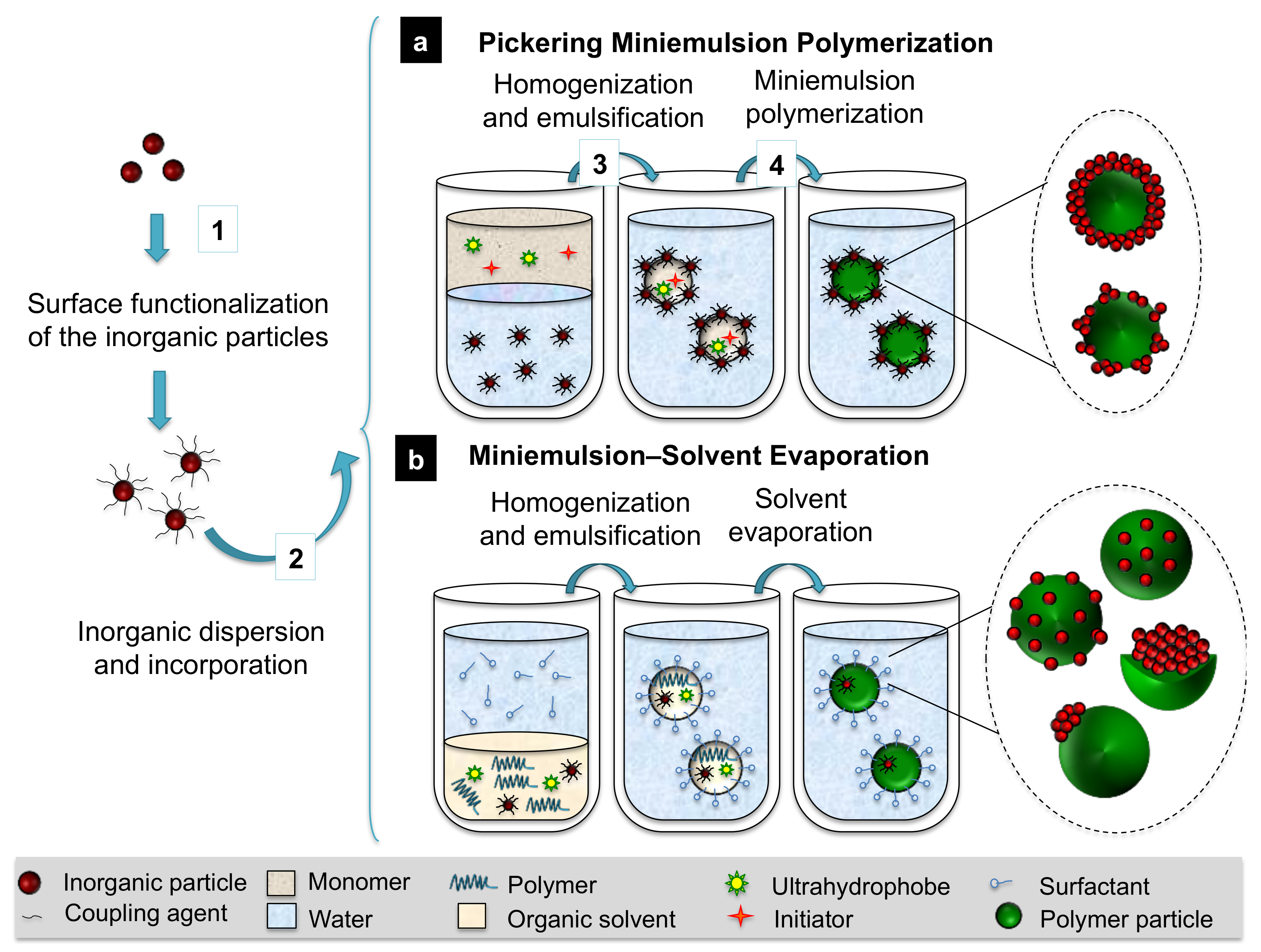
3.2.1. Hybrid Nanocapsules by Assembly of Preformed Polymer and Inorganic Components (Strategies Type A)
3.2.2. Preparation of Hybrid Nanocapsules via Polymerization Processes in the Presence of Preformed Inorganic Components (Strategies Type B)
3.2.3. Use of Preformed Polymers as Supports for the In-Situ Inorganic Precipitation/Crystallization (Strategies Type C)
3.2.4. All-In-Situ Synthesis of Hybrid Nanocapsules (Strategies Type D)
3.2.5. Multistep Synthesis of Hybrid Nanocapsules
- Inorganic Synthesis and Polymerization Processes in the Presence of Preformed Counterparts or their Precursors (Strategies Type B–C)
- Simultaneous Inorganic and Polymer Synthesis, in the Presence of other Preformed Inorganic Species (Strategies Type B–D)
3.3. Applications of Nanocapsule Morphologies
4. Conclusions and Outlook
- Group A involves the self-assembly of preformed polymer and inorganic elements via inorganic complexation and solvent-evaporation techniques in miniemulsion. Complexation, heterocoagulation, or Pickering strategies result in the inorganic coverage of preformed polymer nanoparticles and nanocapsules. The formulation of the polymer matrix allows for the transition between capsule and particle morphologies. The solvent-evaporation method provides different degrees of encapsulation and phase segregation through specific inorganic surface functionalization.
- In group B, preformed polymers nanoparticles are used as supports for inorganic synthesis. The hybrid morphology is mostly controlled via the complexation chemistry between polymers and inorganic precursors, where the pH and the surfactant have an essential role. Inorganic precipitation and biomimetic mineralization result in “raspberry-like” structures, bulk crystallization, or homogeneous coverage of the polymer surface. Block-copolymers and non-ionic surfactants are also used as soft templates for the preparation of nanocapsules via interfacial sol–gel processes. The transition between capsules and particles is controlled by the inorganic precursor/surfactant ratio and the addition rate of the precipitating agent.
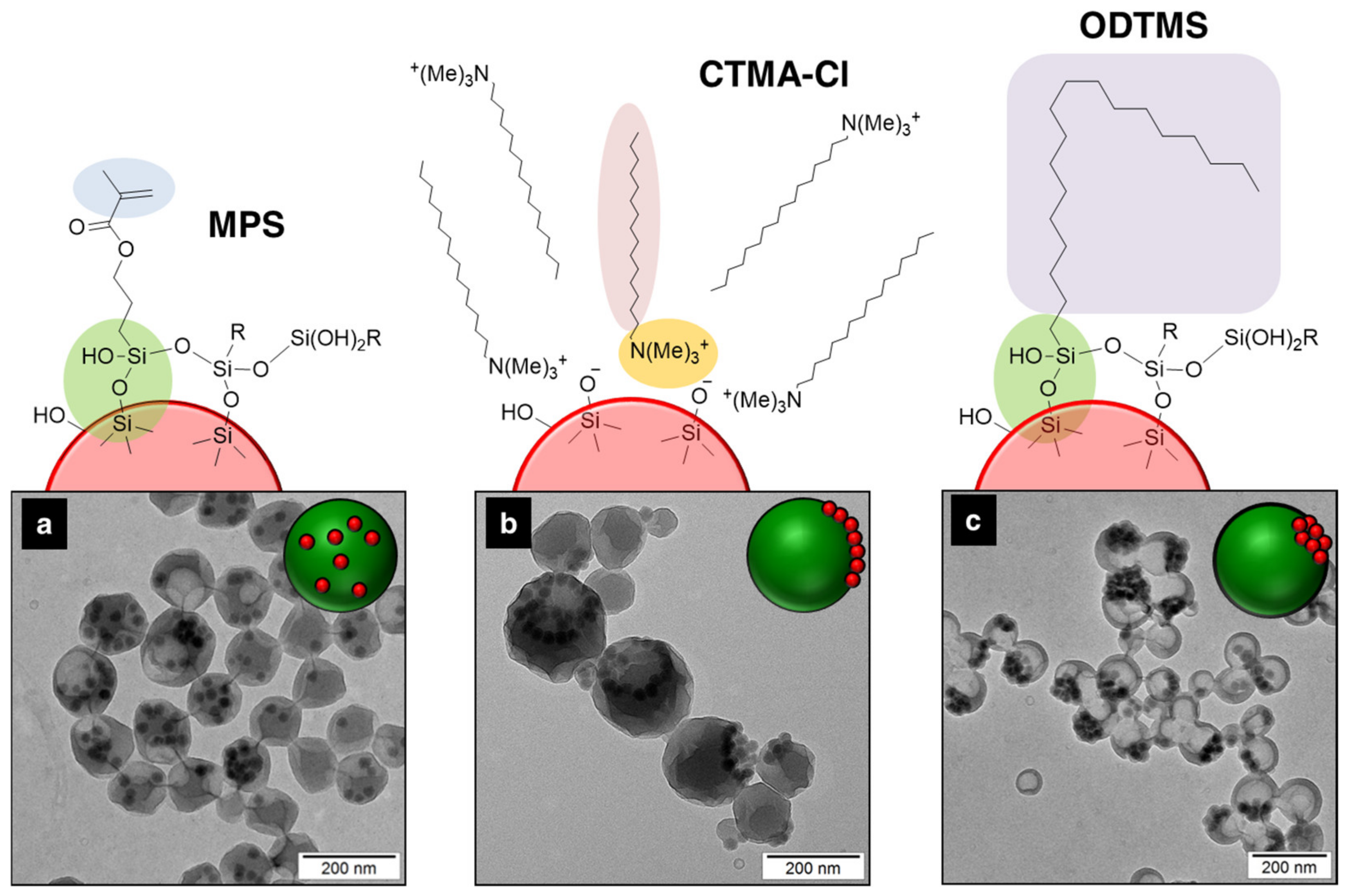
- Group C is based on polymerization processes in the presence of preformed inorganic components. The specific migration of the inorganic functionalities within a forming polymer matrix can be controlled by the nature/type of surfactant and initiator, and the differences of polarity of the monomer/polymer–inorganic system. The inorganic surface functionalization using coupling agents with a specific structure allows for a great variety of hybrid morphologies (e.g., homogeneous inorganic encapsulation, Janus, raspberry, or core–shell structures). Capsule morphologies are reported by an increased content of the hydrophobe in direct miniemulsions or interfacial polymerization and polyaddition processes in inverse miniemulsions.
- Group D comprises the most challenging and less explored strategies comprising quasi/simultaneous polymerization and inorganic synthesis processes taking place in miniemulsion. Miniemulsion polymerization or interfacial polymerization techniques have been combined with the hydrolysis/condensation of metal oxides or the reduction of metal nanoparticles. The morphology development of the nanohybrids follow the principles of reduction of the interfacial energy of the system. The attractiveness of this group relies on the minimization of the synthetic steps and the discovery of organic–inorganic interactions.
- Multistep processes have raised from the combination of individual strategies from the previous groups. The complexity and the potential of those syntheses are high both from the synthetic point of view and the achievable properties and morphologies of the final materials.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hood, M.A.; Mari, M.; Muñoz-Espí, R. Synthetic Strategies in the Preparation of Polymer/Inorganic Hybrid Nanoparticles. Materials 2014, 7, 4057–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asua, J.M. Emulsion polymerization: From fundamental mechanisms to process developments. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2004, 42, 1025–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chern, C.S. Emulsion polymerization mechanisms and kinetics. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 443–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapper, M.; Nenov, S.; Haschick, R.; Müller, K.; Müllen, K. Oil-in-Oil Emulsions: A Unique Tool for the Formation of Polymer Nanoparticles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1190–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, P.A.; Schork, F.J. Fundamentals of Emulsion Polymerization. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 4396–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qun, W.; Shoukuan, F.; Tongyin, Y. Emulsion polymerization. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1994, 19, 703–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thickett, S.C.; Gilbert, R.G. Emulsion polymerization: State of the art in kinetics and mechanisms. Polymer 2007, 48, 6965–6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, B.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, J. Advances in Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Latex Particles via In Situ Emulsion Polymerization. Polymers 2023, 15, 2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Hao, Z.; Wang, C.; Deng, J.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J. In Situ Emulsion Polymerization to Multifunctional Polymer Nanocomposites: A Review. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2023, 224, 2300185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-W.; Suh, K.-D. Monodisperse polymer particles synthesized by seeded polymerization techniques. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2008, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asua, J.M. Miniemulsion polymerization. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2002, 27, 1283–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Ziener, U. Synthesis of nanostructured materials in inverse miniemulsions and their applications. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 10093–10107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, T.G.; Wilking, J.N.; Meleson, K.; Chang, C.B.; Graves, S.M. Nanoemulsions: Formation, structure, and physical properties. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2006, 18, R635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schork, F.J.; Luo, Y.; Smulders, W.; Russum, J.P.; Butté, A.; Fontenot, K. Miniemulsion Polymerization. In Polymer Particles; Okubo, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 129–255. [Google Scholar]
- Solans, C.; Izquierdo, P.; Nolla, J.; Azemar, N.; Garcia-Celma, M.J. Nano-emulsions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 10, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöblom, J.; Lindberg, R.; Friberg, S.E. Microemulsions—Phase equilibria characterization, structures, applications and chemical reactions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 65, 125–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, C.P.; Gan, L.M. Microemulsion Polymerizations and Reactions. In Polymer Particles; Okubo, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 257–298. [Google Scholar]
- Chevalier, Y.; Bolzinger, M.-A. Emulsions stabilized with solid nanoparticles: Pickering emulsions. Colloids Surf. A 2013, 439, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Quinlan, P.J.; Tam, K.C. Stimuli-responsive Pickering emulsions: Recent advances and potential applications. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 3512–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fang, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, W. An Overview of Pickering Emulsions: Solid-Particle Materials, Classification, Morphology, and Applications. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 235054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B. Suspension Polymerization Processes. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2010, 33, 1737–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.; Sharma, S. Suspension polymerization technique: Parameters affecting polymer properties and application in oxidation reactions. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivaldo-Lima, E.; Wood, P.E.; Hamielec, A.E.; Penlidis, A. An Updated Review on Suspension Polymerization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1997, 36, 939–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.G.; Kalfas, G.; Ray, W.H. Suspension Polymerization. J. Macromol. Sci. Part C 1991, 31, 215–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.L.; Möhwald, H.; Shchukin, D.G. Precipitation polymerization for fabrication of complex core–shell hybrid particles and hollow structures. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3628–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Gao, R.; Gou, Q.; Lai, J.; Li, X. Precipitation Polymerization: A Powerful Tool for Preparation of Uniform Polymer Particles. Polymers 2022, 14, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, S.; Ito, K. Dispersion Polymerization. In Polymer Particles; Okubo, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 299–328. [Google Scholar]
- Richez, A.P.; Yow, H.N.; Biggs, S.; Cayre, O.J. Dispersion polymerization in non-polar solvent: Evolution toward emerging applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 897–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Xian, C.; Jia, W. Aqueous dispersion polymerization: An overview of the mechanisms, formulations and applications. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 410, 125557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, F.; Pan, C.-Y. Dispersion Polymerization versus Emulsifier-Free Emulsion Polymerization for Nano-Object Fabrication: A Comprehensive Comparison. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2022, 43, 2100566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganachaud, F.; Katz, J.L. Nanoparticles and Nanocapsules Created Using the Ouzo Effect: Spontaneous Emulsification as an Alternative to Ultrasonic and High-Shear Devices. ChemPhysChem 2005, 6, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, D.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, H.; Hou, J.; Kang, W.; Bai, B. Advances of spontaneous emulsification and its important applications in enhanced oil recovery process. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 277, 102119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchukin, E.D. Conditions of Spontaneous Dispersion and Formation of Thermodynamically Stable Colloid Systems. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2005, 25, 875–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solans, C.; Morales, D.; Homs, M. Spontaneous emulsification. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 22, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, S.; Merkle, H.P.; Gander, B. Microencapsulation by solvent extraction/evaporation: Reviewing the state of the art of microsphere preparation process technology. J. Control. Release 2005, 102, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, P.B.; McGinity, J.W. Preparation of microspheres by the solvent evaporation technique. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 28, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staff, R.H.; Landfester, K.; Crespy, D. Recent Advances in the Emulsion Solvent Evaporation Technique for the Preparation of Nanoparticles and Nanocapsules. In Hierarchical Macromolecular Structures: 60 Years after the Staudinger Nobel Prize II; Percec, V., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 329–344. [Google Scholar]
- Deshmukh, R.; Wagh, P.; Naik, J. Solvent evaporation and spray drying technique for micro- and nanospheres/particles preparation: A review. Dry. Technol. 2016, 34, 1758–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morteza, E.; Marzieh, S. Recent Advances in Nanoparticle Preparation by Spray and Microemulsion Methods. Recent. Pat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 3, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Zhang, H. Controlled freezing and freeze drying: A versatile route for porous and micro-/nano-structured materials. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2011, 86, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanli, D.; Bozbag, S.E.; Erkey, C. Synthesis of nanostructured materials using supercritical CO2: Part I. Physical transformations. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 2995–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tom, J.W.; Debenedetti, P.G. Particle formation with supercritical fluids—A review. J. Aerosol Sci. 1991, 22, 555–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Erkey, C. Preparation of supported metallic nanoparticles using supercritical fluids: A review. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2006, 38, 252–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Espí, R.; Álvarez-Bermúdez, O. Chapter 15—Application of Nanoemulsions in the Synthesis of Nanoparticles. In Nanoemulsions; Jafari, S.M., McClements, D.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 477–515. [Google Scholar]
- Antonietti, M.; Landfester, K. Polyreactions in miniemulsions. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2002, 27, 689–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Espí, R.; Weiss, C.K.; Landfester, K. Inorganic nanoparticles prepared in miniemulsion. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 17, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Espí, R.; Landfester, K. Low-Temperature Miniemulsion-Based Routes for Synthesis of Metal Oxides. Chem. A Eur. J. 2020, 26, 9304–9313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landfester, K. Miniemulsion Polymerization and the Structure of Polymer and Hybrid Nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 4488–4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elzayat, A.; Adam-Cervera, I.; Álvarez-Bermúdez, O.; Muñoz-Espí, R. Nanoemulsions for synthesis of biomedical nanocarriers. Colloids Surf. B 2021, 203, 111764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Ortiz, L.J.; Asua, J.M. Development of Particle Morphology in Emulsion Polymerization. 1. Cluster Dynamics. Macromolecules 1995, 28, 3135–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asua, J.M. Mapping the Morphology of Polymer–Inorganic Nanocomposites Synthesized by Miniemulsion Polymerization. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2014, 215, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, T.; Yang, D.; Hu, J.; Yang, W.; Wang, C.; Lu, J.Q. Preparation of monodispersed hybrid nanospheres with high magnetite content from uniform Fe3O4 clusters. Colloids Surf. A 2009, 339, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Kawaguchi, H. Impact of initiators in preparing magnetic polymer particles by miniemulsion polymerization. Colloids Surf. B 2007, 56, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudt, T.; Machado, T.O.; Vogel, N.; Weiss, C.K.; Araujo, P.H.H.; Sayer, C.; Landfester, K. Magnetic Polymer/Nickel Hybrid Nanoparticles Via Miniemulsion Polymerization. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2013, 214, 2213–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsden, W. Separation of solids in the surface-layers of solutions and ‘suspensions’ (observations on surface-membranes, bubbles, emulsions, and mechanical coagulation). Proc. R. Soc. Lon. 1904, 72, 156–164. [Google Scholar]
- Pickering, S.U. Emulsions. J. Chem. Soc. Trans. 1907, 91, 2001–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadil, Y.; Jasinski, F.; Wing Guok, T.; Thickett, S.C.; Minami, H.; Zetterlund, P.B. Pickering miniemulsion polymerization using graphene oxide: Effect of addition of a conventional surfactant. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 3368–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Bermúdez, O.; Torres-Suay, A.; Pérez-Pla, F.F.; Landfester, K.; Muñoz-Espí, R. Magnetically enhanced polymer-supported ceria nanocatalysts for the hydration of nitriles. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 405604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinh, L.N.M.; Ramana, L.N.; Agarwal, V.; Zetterlund, P.B. Miniemulsion polymerization of styrene using carboxylated graphene quantum dots as surfactant. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 3217–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- zu Putlitz, B.; Landfester, K.; Fischer, H.; Antonietti, M. The Generation of “Armored Latexes” and Hollow Inorganic Shells Made of Clay Sheets by Templating Cationic Miniemulsions and Latexes. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 500–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, L.N.M.; Tran, B.N.; Agarwal, V.; Zetterlund, P.B. Synthesis of Highly Stretchable and Electrically Conductive Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube/Polymer Nanocomposite Films. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 1867–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, S.; Bannwarth, M.B.; Musyanovych, A.; Landfester, K.; Münnemann, K. How morphology influences relaxivity—Comparative study of superparamagnetic iron oxide-polymer hybrid nanostructures. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2015, 10, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, M.; Musyanovych, A.; Landfester, K. Fluorescent Superparamagnetic Polylactide Nanoparticles by Combination of Miniemulsion and Emulsion/Solvent Evaporation Techniques. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2009, 210, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethirajan, A.; Musyanovych, A.; Chuvilin, A.; Landfester, K. Biodegradable Polymeric Nanoparticles as Templates for Biomimetic Mineralization of Calcium Phosphate. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2011, 212, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.-P.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, H.-X.; Landfester, K.; Crespy, D. From core–shell and Janus structures to tricompartment submicron particles. Polymer 2014, 55, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, M.; Kluge, J.; Mazzotti, M.; Lattuada, M. Preparation of biocompatible magnetite–PLGA composite nanoparticles using supercritical fluid extraction of emulsions. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2010, 54, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuser, P.E.; Bubniak, L.d.S.; Silva, M.C.d.S.; Viegas, A.d.C.; Castilho Fernandes, A.; Ricci-Junior, E.; Nele, M.; Tedesco, A.C.; Sayer, C.; de Araújo, P.H.H. Encapsulation of magnetic nanoparticles in poly(methyl methacrylate) by miniemulsion and evaluation of hyperthermia in U87MG cells. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 68, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuser, P.E.; Jacques, A.V.; Arévalo, J.M.C.; Rocha, M.E.M.; dos Santos-Silva, M.C.; Sayer, C.; de Araújo, P.H.H. Superparamagnetic poly(methyl methacrylate) nanoparticles surface modified with folic acid presenting cell uptake mediated by endocytosis. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2016, 18, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, F.; Liu, K.X.; Jiang, W.; Zeng, X.B.; Wu, Y.; Gu, Z.W. Facile synthesis of monodisperse superparamagnetic Fe3O4/PMMA composite nanospheres with high magnetization. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 225604–225611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Gao, F.; Liang, X.; Li, Y.; Mi, Y.; Qi, Q.; Yao, J.; Cao, Z. Efficient preparation of carboxyl-functionalized magnetic polymer/Fe3O4 nanocomposite particles in one-pot miniemulsion systems. Colloids Surf. A 2019, 570, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Forcada, J. Preparation and characterization of magnetic polymeric composite particles by miniemulsion polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2006, 44, 4187–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.; Forcada, J. Surfactant-free miniemulsion polymerization as a simple synthetic route to a successful encapsulation of magnetite nanoparticles. Langmuir 2011, 27, 7222–7230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Qu, R.; Forcada, J. Preparation of carboxylic magnetic polymeric composite particles by miniemulsion polymerization in the absence of hydrophobe. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 2539–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Ramos, J.; Forcada, J. Self-stabilized magnetic polymeric composite nanoparticles by emulsifier-free miniemulsion polymerization. Langmuir 2007, 23, 12893–12900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lu, Z.; Wu, M.; Wu, Q.; Yang, J. Large-scale synthesis and characterization of magnetic poly(acrylic acid) nanogels via miniemulsion polymerization. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 58889–58894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; He, L.; Wang, Y.-F.; Yu, B.; Cong, H.-L. Magnetic poly(PMMA-EGDMA) nanospheres prepared by miniemulsion polymerization. Ferroelectrics 2018, 529, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Yu, B.; Qi, Q.; Mi, Y.; Cao, Z.; Cui, Q.; Zhao, Z. Construction of magnetic-fluorescent bifunctional nanoparticles via miniemulsion polymerization for cell imaging. Colloids Surf. A 2021, 613, 126062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoth, A.; Keith, A.D.; Landfester, K.; Muñoz-Espí, R. Silanization as a versatile functionalization method for the synthesis of polymer/magnetite hybrid nanoparticles with controlled structure. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 53903–53911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoth, A.; Wagner, C.; Hecht, L.L.; Winzen, S.; Muñoz-Espí, R.; Schuchmann, H.P.; Landfester, K. Structure control in PMMA/silica hybrid nanoparticles by surface functionalization. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2014, 292, 2427–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, T.; Hecht, L.L.; Schoth, A.; Wagner, C.; Muñoz-Espí, R.; Landfester, K.; Schuchmann, H.P. Continuous Preparation of Polymer/Inorganic Composite Nanoparticles via Miniemulsion Polymerization. In Colloid Process Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 345–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoth, A.; Adurahim, E.S.; Bahattab, M.A.; Landfester, K.; Muñoz-Espí, R. Waterborne Polymer/Silica Hybrid Nanoparticles and Their Structure in Coatings. Macromol. React. Eng. 2016, 10, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.-Y.; Käfer, F.; Diaco, N.; Ober, C.K. Silica-PMMA hairy nanoparticles prepared via phase transfer-assisted aqueous miniemulsion atom transfer radical polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 58, 2310–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Zhao, Z.; Lyu, B.; Ma, J. Effect of coated and encapsulated polyacrylate/nano-SiO2 composite emulsions on the finishing performances of leather via miniemulsion polymerization. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 10070–10083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Chen, Q.; Chen, H.; Chen, Z.; Yao, J.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, D. Preparation of polymeric/inorganic nanocomposite particles in miniemulsions: I. Particle formation mechanism in systems stabilized with sodium dodecyl sulfate. Colloids Surf. A 2017, 516, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Cao, Z.; Shang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, D. Preparation of polymeric/inorganic nanocomposite particles in miniemulsions: II. Narrowly size-distributed polymer/SiO2 nanocomposite particles. Colloids Surf. A 2017, 530, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Chen, M.; Zhou, J.; Wu, L. Synthesis of raspberry-like silica/polystyrene/silica multilayer hybrid particles via miniemulsion polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2007, 45, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costoyas, Á.; Ramos, J.; Forcada, J. Encapsulation of silica nanoparticles by miniemulsion polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2009, 47, 935–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailly, B.; Donnenwirth, A.-C.; Bartholome, C.; Beyou, E.; Bourgeat-Lami, E. Silica-Polystyrene Nanocomposite Particles Synthesized by Nitroxide-Mediated Polymerization and Their Encapsulation through Miniemulsion Polymerization. J. Nanomater. 2006, 2006, 076371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeat-Lami, E.; Farzi, G.A.; David, L.; Putaux, J.L.; McKenna, T.F. Silica encapsulation by miniemulsion polymerization: Distribution and localization of the silica particles in droplets and latex particles. Langmuir 2012, 28, 6021–6031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.-W.; Zhou, S.-X.; Weng, Y.-M.; Wu, L.-M. Synthesis of SiO2/Polystyrene Nanocomposite Particles via Miniemulsion Polymerization. Langmuir 2005, 21, 2124–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, S.; Qiao, X.; Li, X.; Wu, L. Synthesis of SiO2/poly(styrene-co-butyl acrylate) nanocomposite microspheres via miniemulsion polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2006, 44, 3202–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Fernández, J.M.; Guillem, C.; Lopez-Buendía, A.; Paulis, M.; Asua, J.M. Synthesis of poly-(BA-co-MMA) latexes filled with SiO2 for coating in construction applications. Prog. Org. Coat. 2011, 72, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metanawin, T.; Panutumrong, P.; Metanawin, S. Synthesis of Polyurethane/TiO2 Hybrid with High Encapsulation Efficiency Using One-Step Miniemulsion Polymerization for Methylene Blue Degradation and its Antibacterial Applications. ChemistrySelect 2023, 8, e202204522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metanawin, T.; Panutumrong, P.; Metanawin, S. Well-defined poly(methyl methacrylate) hybrid titanium dioxide via miniemulsion polymerization: Design and evaluation of methylene blue dye degradation and antibacterial. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2024, 64, 2107–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sheng, X.; Xie, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H. High-performance TiO2/polyacrylate nanocomposites with enhanced thermal and excellent UV-shielding properties. Prog. Org. Coat. 2016, 101, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzehlou, S.; Aguirre, M.; Leiza, J.R.; Asua, J.M. Dynamics of the Particle Morphology during the Synthesis of Waterborne Polymer–Inorganic Hybrids. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 7190–7201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimenti, S.; Vega, J.M.; Aguirre, M.; García-Lecina, E.; Díez, J.A.; Grande, H.-J.; Paulis, M.; Leiza, J.R. Effective incorporation of ZnO nanoparticles by miniemulsion polymerization in waterborne binders for steel corrosion protection. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2017, 14, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delibaş, A. Synthesis of (Sty-co-BA-AA) latexes including ZnO and TiO2 nanoparticle by miniemulsion polymerization. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2021, 18, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, A.M.M.S.; Machado, F.; Bourgeat-Lami, E.; Rubim, J.C.; McKenna, T.F.L. Bio-Based Hybrid Magnetic Latex Particles Containing Encapsulated γ -Fe2O3 by Miniemulsion Copolymerization of Soybean Oil-Acrylated Methyl Ester and Styrene. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2019, 304, 1800449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boivin, G.; Ritcey, A.M.; Landry, V. Silver Nanoparticles as Antifungal Agents in Acrylic Latexes: Influence of the Initiator Type on Nanoparticle Incorporation and Aureobasidium pullulans Resistance. Polymers 2023, 15, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casteleiro, B.; Ribeiro, T.; Mariz, I.; Martinho, J.M.G.; Farinha, J.P.S. Encapsulation of gold nanoclusters by photo-initiated miniemulsion polymerization. Colloids Surf. A 2022, 648, 129410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buruga, K.; Kalathi, J.T. Fabrication of γ-MPS-Modified HNT–PMMA Nanocomposites by Ultrasound-Assisted Miniemulsion Polymerization. JOM 2018, 70, 1307–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslekar, N.; Fadil, Y.; Zetterlund, P.B.; Agarwal, V. Maintaining Colloidal Stability of Polymer/Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite Aqueous Dispersions Produced via In Situ Reduction of Graphene Oxide for the Preparation of Electrically Conductive Coatings. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 5177–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Meng, S.; Lin, H.; Correll, M.; Tong, Z. Nanocomposite of Graphene Oxide Encapsulated in Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA): Pre-Modification, Synthesis, and Latex Stability. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, M.; Fadil, Y.; Tokuda, M.; Zetterlund, P.B.; Minami, H. Preparation of Methacrylate Polymer/Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite Particles Stabilized by Poly(ionic liquid) Block Copolymer via Miniemulsion Polymerization. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2020, 41, 2000141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnefond, A.; Mičušík, M.; Paulis, M.; Leiza, J.R.; Teixeira, R.F.A.; Bon, S.A.F. Morphology and properties of waterborne adhesives made from hybrid polyacrylic/montmorillonite clay colloidal dispersions showing improved tack and shear resistance. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2013, 291, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaconu, G.; Asua, J.M.; Paulis, M.; Leiza, J.R. High-Solids Content Waterborne Polymer-Clay Nanocomposites. Macromol. Symp. 2007, 259, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, C.P.; Jagielski, N.; Heller, J.; Hinderberger, D.; Spiess, H.W.; Lieberwirth, I.; Weiss, C.K.; Landfester, K. Structure formation in metal complex/polymer hybrid nanomaterials prepared by miniemulsion. Langmuir 2011, 27, 12859–12868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
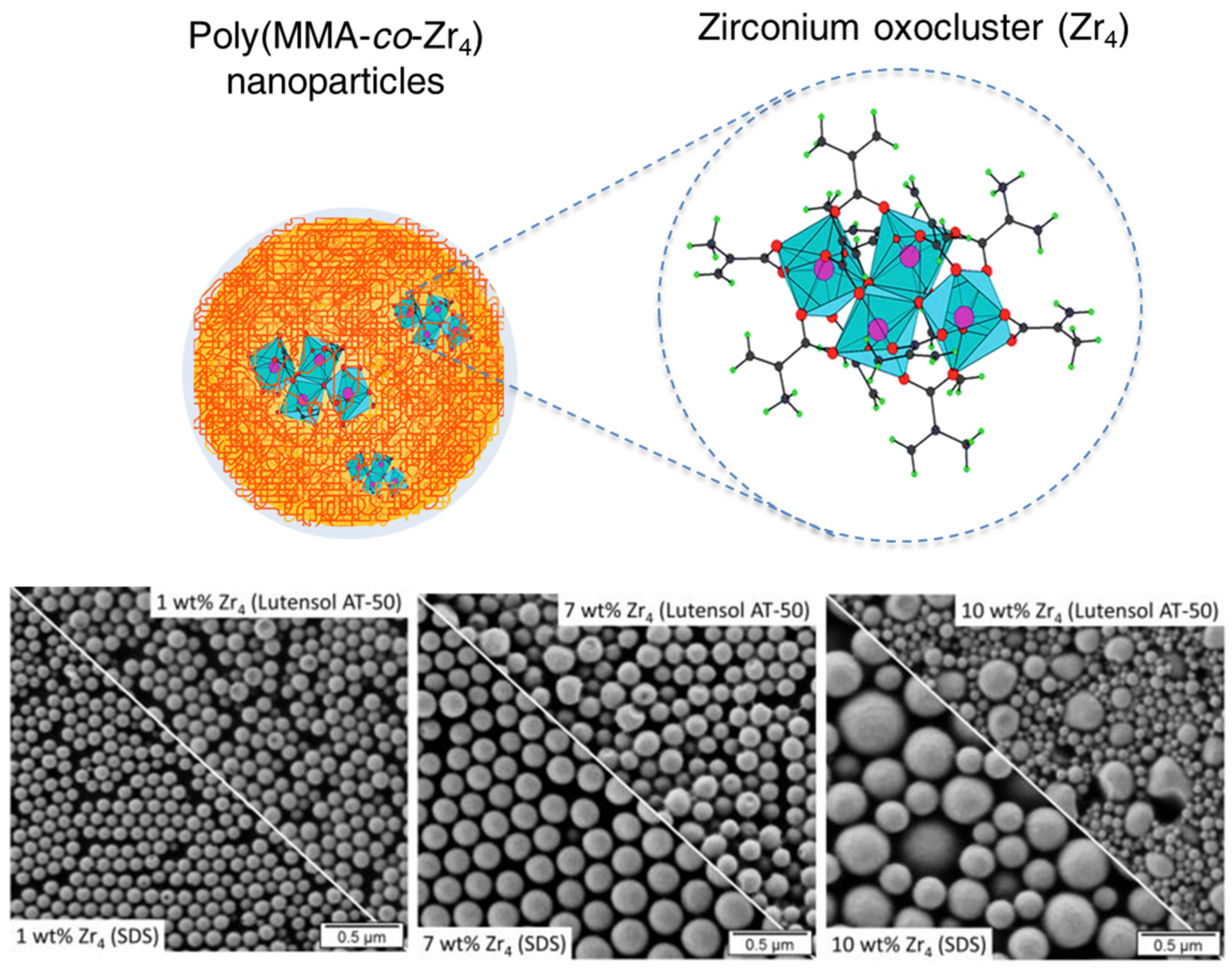
- Pablico, M.H.; Mertzman, J.E.; Japp, E.A.; Boncher, W.L.; Nishida, M.; Van Keuren, E.; Lofland, S.E.; Dollahon, N.; Rubinson, J.F.; Holman, K.T.; et al. Miniemulsion synthesis of metal-oxo cluster containing copolymer nanobeads. Langmuir 2011, 27, 12575–12584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetti, C.; Cazzolaro, A.; Carraro, M.; Graf, R.; Landfester, K.; Gross, S.; Muñoz-Espí, R. Dual Role of Zirconium Oxoclusters in Hybrid Nanoparticles: Cross-Linkers and Catalytic Sites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 26275–26284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, C.; Flouda, P.; Antonello, A.; Rosenauer, C.; Pérez-Pla, F.F.; Landfester, K.; Gross, S.; Muñoz-Espí, R. Zirconium oxocluster/polymer hybrid nanoparticles prepared by photoactivated miniemulsion copolymerization. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 365603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Herrmann, C.; Landfester, K.; Ziener, U. Synthesis of narrowly size-distributed metal salt/poly(HEMA) hybrid particles in inverse miniemulsion: Versatility and mechanism. Langmuir 2010, 26, 18008–18015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrade, A.; Landfester, K.; Ziener, U. Pickering-type stabilized nanoparticles by heterophase polymerization. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6823–6839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnefond, A.; Ibarra, M.; Gonzalez, E.; Barrado, M.; Chuvilin, A.; Maria Asua, J.; Ramon Leiza, J. Photocatalytic and magnetic titanium dioxide/polystyrene/magnetite composite hybrid polymer particles. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2016, 54, 3350–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, E.; Bonnefond, A.; Barrado, M.; Casado Barrasa, A.M.; Asua, J.M.; Leiza, J.R. Photoactive self-cleaning polymer coatings by TiO2 nanoparticle Pickering miniemulsion polymerization. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 281, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgheib, N.; Putaux, J.-L.; Thill, A.; D’Agosto, F.; Lansalot, M.; Bourgeat-Lami, E. Stabilization of Miniemulsion Droplets by Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles: A Step toward the Elaboration of Armored Composite Latexes. Langmuir 2012, 28, 6163–6174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. Tuning Amphiphilicity of Particles for Controllable Pickering Emulsion. Materials 2016, 9, 903–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Matheus, K.; Leal, G.P.; Asua, J.M. Pickering-Stabilized Latexes with High Silica Incorporation and Improved Salt Stability. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2014, 31, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Matheus, K.; Leal, G.P.; Tollan, C.; Asua, J.M. High solids Pickering miniemulsion polymerization. Polymer 2013, 54, 6314–6320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauvin, S.; Colver, P.J.; Bon, S.A.F. Pickering Stabilized Miniemulsion Polymerization: Preparation of Clay Armored Latexes. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 7887–7889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bon, S.A.F.; Colver, P.J. Pickering Miniemulsion Polymerization Using Laponite Clay as a Stabilizer. Langmuir 2007, 23, 8316–8322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Fadil, Y.; Jasinski, F.; Thickett, S.C.; Agarwal, V.; Zetterlund, P.B. Miniemulsion polymerization using graphene oxide as surfactant: In situ grafting of polymers. Carbon 2019, 149, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.J.; Zhou, S.Z.; Pang, X.C.; Li, K.R.; Qiao, X.G. Preparation of superparamagnetic γ-Fe2O3@LS@PS composite latex particles through pickering miniemulsion polymerization. Colloids Surf. A 2020, 585, 124040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaradia, V.; Valério, A.; Feuser, P.E.; Oliveira, D.d.; Araújo, P.H.H.; Sayer, C. Incorporation of superparamagnetic nanoparticles into poly(urea-urethane) nanoparticles by step growth interfacial polymerization in miniemulsion. Colloids Surf. A 2015, 482, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaradia, V.; Soares, N.S.; Valerio, A.; de Oliveira, D.; Araujo, P.H.; Sayer, C. Immobilization of Candida antarctica Lipase B on Magnetic Poly(Urea-Urethane) Nanoparticles. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 180, 558–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaradia, V.; Valério, A.; de Oliveira, D.; Araújo, P.H.H.; Sayer, C. Simultaneous single-step immobilization of Candida antarctica lipase B and incorporation of magnetic nanoparticles on poly(urea-urethane) nanoparticles by interfacial miniemulsion polymerization. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2016, 131, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, M.; Müller, B.; Landfester, K.; Muñoz-Espí, R. Ceria/Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles as Efficient Catalysts for the Hydration of Nitriles to Amides. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 10727–10733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, V.; Lieberwirth, I.; Jakob, G.; Landfester, K.; Muñoz-Espí, R. Metal Oxide/Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles with Versatile Functionality Prepared by Controlled Surface Crystallization. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, V.; Bannwarth, M.B.; Jakob, G.; Landfester, K.; Muñoz-Espí, R. Luminescent and Magnetoresponsive Multifunctional Chalcogenide/Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 5999–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xie, B.; Li, J.; Fang, B.; Lin, Y. CdS nanodots preparation and crystallization in a polymeric colloidal nanoreactor and their characterizations. Colloids Surf. A 2018, 546, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethirajan, A.; Ziener, U.; Landfester, K. Surface-functionalized polymeric nanoparticles as templates for biomimetic mineralization of hydroxyapatite. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 2218–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöller, K.; Ethirajan, A.; Zeller, A.; Landfester, K. Biomimetic Route to Calcium Phosphate Coated Polymeric Nanoparticles: Influence of Different Functional Groups and pH. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2011, 212, 1165–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Zhao, Z.; Lyu, B.; Ma, J.; Chang, R. Janus composites particles: Prepared via cross-linking driven one-step miniemulsion polymerization and as film-forming material. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 105, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y. Enhanced electrochemical properties of MnO2/PPy nanocomposites by miniemulsion polymerization. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 10603–10610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, Y.; Fujino, K.; Fujimoto, K. One-pot generation of gold-polymer hybrid nanoparticles using a miniemulsion reactor system. Colloids Surf. A 2023, 666, 131319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liang, F.; Zhang, N.; Liu, Y. Preparation of Manganese Dioxide/Polypyrrole Composite by W/O Miniemulsion and Its Electrochemical Performance. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 6584–6597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, F.; Lin, Y. ZnO@PNIPAM nanospheres synthesis from inverse Pickering miniemulsion polymerization. Colloids Surf. A 2020, 603, 125264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, M.; Wu, Q.; Yang, J.; Liu, N.; Jin, Z. Facile Fabrication of Inorganic/Polymer Janus Microspheres by Miniemulsion Polymerization. Chem. Lett. 2010, 39, 206–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, J.; Lin, J.; Wu, B.; Liu, Q.; Yang, W.; Wu, M.; Wu, Q.; Yang, J. Raspberry-like nanocomposite microsphere via Double In situ miniemulsion polymerization using interfacial redox initiator system. Macromol. Res. 2012, 21, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, M.; Wu, L. One-step preparation of PS/TiO2 nanocomposite particles via miniemulsion polymerization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 343, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhou, S.; Wu, L. Preparation of waterborne self-cleaning nanocomposite coatings based on TiO2/PMMA latex. Prog. Org. Coat. 2015, 85, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabih, N.; Herrmann, U.; Glasser, G.; Lieberwirth, I.; Landfester, K.; Taden, A. Water-based hybrid zinc phosphate–polymer miniemulsion as anticorrosive coating. Prog. Org. Coat. 2013, 76, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabih, N.; Landfester, K.; Taden, A. Water-based inorganic/polymer hybrid particles prepared via a multiple miniemulsion process. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2011, 49, 5019–5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarabady, M.M.; Farzi, G.A. Morphology control of silica/poly(methyl methacrylate-co-styrene) hybrid nanoparticles via multiple-miniemulsion approach. e-Polymers 2016, 16, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estupiñán, D.; Bannwarth, M.B.; Landfester, K.; Crespy, D. Size-Dependent Self-Assembly of Anisotropic Silica-Coated Hybrid Nanoparticles. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2015, 216, 2070–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Yang, L.; Yan, Y.; Shang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Qi, D.; Ziener, U.; Shan, G.; Landfester, K. Fabrication of nanogel core-silica shell and hollow silica nanoparticles via an interfacial sol-gel process triggered by transition-metal salt in inverse systems. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 406, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, A.V.; Walter, C.; Landfester, K.; Ziener, U. Biomimetic silver-containing colloids of poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine) and their film-formation properties. Langmuir 2012, 28, 4974–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespy, D.; Landfester, K. Synthesis of polyvinylpyrrolidone/silver nanoparticles hybrid latex in non-aqueous miniemulsion at high temperature. Polymer 2009, 50, 1616–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Deng, H.; Wu, B.; Lin, J.; Wu, M.; Wu, Q.; Yang, J.; He, B. Preparation of magnetic poly(vinyl alcohol) microspheres via inverse miniemulsion technique. Mater. Lett. 2012, 79, 222–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landfester, K.; Musyanovych, A.; Mailänder, V. From polymeric particles to multifunctional nanocapsules for biomedical applications using the miniemulsion process. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2010, 48, 493–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massironi, A. Hybrid Organic Polymer/Inorganic Nano-materials for Biomedical Applications: Where we are and Where to go? Curr. Nanosci. 2024, 20, 188–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, B.; Luo, J.; Gu, Y.; Liu, X. Synthesis of Polyaniline@MnO2/Graphene Ternary Hybrid Hollow Spheres via Pickering Emulsion Polymerization for Electrochemical Supercapacitors. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2021, 4, 7721–7730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kokil, G.R.; He, Y.; Lowe, B.; Salam, A.; Altalhi, T.A.; Ye, Q.; Kumeria, T. Inorganic/organic combination: Inorganic particles/polymer composites for tissue engineering applications. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 24, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvate, S.; Singh, J.; Dixit, P.; Vennapusa, J.R.; Maiti, T.K.; Chattopadhyay, S. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle-Decorated Polymer Microcapsules Enclosing Phase Change Material for Thermal Energy Storage and Photocatalysis. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 1866–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayake, H.; White, J.; Dawood, S. Polysilsesquioxane-based organic-inorganic hybrid nanomaterials and their applications towards organic photovoltaics. Synth. Met. 2021, 273, 116705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Yuan, J.; Dong, S.; Hao, J. Photovoltaic Energy Conversion and Storage of Micro-Supercapacitors Based on Emulsion Self-Assembly of Upconverting Nanoparticles. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 1611–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voisin, H.; Falourd, X.; Rivard, C.; Capron, I. Versatile nanocellulose-anatase TiO2 hybrid nanoparticles in Pickering emulsions for the photocatalytic degradation of organic and aqueous dyes. JCIS Open 2021, 3, 100014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, M.; Barrado, M.; Iturrondobeitia, M.; Okariz, A.; Guraya, T.; Paulis, M.; Leiza, J.R. Film forming hybrid acrylic/ZnO latexes with excellent UV absorption capacity. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Meng Lin, M.; Toprak, M.S.; Kim, D.K.; Muhammed, M. Nanocomposites of polymer and inorganic nanoparticles for optical and magnetic applications. Nano Rev. 2010, 1, 5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keyvan Rad, J.; Alinejad, Z.; Khoei, S.; Mahdavian, A.R. Controlled Release and Photothermal Behavior of Multipurpose Nanocomposite Particles Containing Encapsulated Gold-Decorated Magnetite and 5-FU in Poly(lactide-co-glycolide). ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 4425–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, Y.; Solaimany Nazar, A.R.; Molla-Abbasi, P. Synthesis, characterization and application of a magnetic nanoencapsulated PCM in enhancing the natural convection in a cube cavity. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2024, 47, 102342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Jiang, D.; Li, Q.; Sun, Q.; Mao, X.; Hou, P.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, P. Polymer-modified cement-based coating containing organic-inorganic silicons modified polyacrylate emulsion: Performance and mechanisms. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 421, 135607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privitera, A.; Tuti, S.; Pasqual Laverdura, U.; Duranti, L.; Di Bartolomeo, E.; Taddei, A.R.; Sodo, A. One-step nanoencapsulation of essential oils and their application in hybrid coatings: A sustainable long-lasting treatment of stone materials against biodeterioration. Prog. Org. Coat. 2024, 196, 108759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- wassel, A.R.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Shoueir, K. Recent advances in polymer/metal/metal oxide hybrid nanostructures for catalytic applications: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, A.; Rizwan, K.; Farooq, U.; Iqbal, S.; Altaf, A.A. Advanced polymeric/inorganic nanohybrids: An integrated platform for gas sensing applications. Chemosphere 2022, 294, 133772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Yang, X.-J.; Lu, L. Gelatin-g-poly(methyl methacrylate)/silver nanoparticle hybrid films and the evaluation of their antibacterial activity. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 2617–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, W.; Ding, J.; Li, R.; Ren, X.; Gu, Z.; Sun, Y. Rational design of TiO2 nanomaterials using miniemulsion polymerization: Rapid antimicrobial efficiency and enhanced UV stability. Polym. -Plast. Technol. Mater. 2020, 59, 1585–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Uriostegui, L.; Delgado, E.; Melendez-Ortiz, H.I.; Toriz, G. Synthesis of core-shell hybrid nanoparticles with pH responsive core and silica shell and their surface characterization. Mater. Lett. 2020, 280, 128550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Yu, S.; Ge, Z.; Jiang, J. Temperature-responsive microcapsule hydrogel fabricated by pickering emulsion polymerization for pheromones application. Colloids Surf. A 2024, 684, 133127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshanali, M.; Nodehi, A.; Atai, M. Synthesis and characterization of core-shell nanoparticles and their application in dental resins. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 110, 103926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, W.; Sultana Sarker, M.; Akter, A.; Rahman, A. Synthesis of ZnO/Poly(Styrene-co-Methacrylic Acid) Hybrid Polymer Particles for Enhanced UV-Visible Photodegradation of Methylene Blue. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, e202401456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, K.; Yan, J.; Zhou, T. Synthesis of functionalized janus hybrid nanosheets for one-step construction of Pickering emulsion and selective photodegradation of water-soluble dyes. Colloids Surf. A 2023, 664, 131199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Dugas, P.-Y.; Lansalot, M.; Bourgeat-Lami, E. Synthesis of Iron Oxide-Armored Latex Particles by Pickering Emulsion Polymerization Using 2-Acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propane Sulfonic Acid as an Auxiliary Comonomer. Macromolecules 2022, 55, 4284–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdieh, A.; Mahdavian, A.R.; Salehi-Mobarakeh, H. Chemical modification of magnetite nanoparticles and preparation of acrylic-base magnetic nanocomposite particles via miniemulsion polymerization. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 426, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.; Banerjee, S.L.; Bhattacharya, K.; Singha, N.K. Graphene Quantum Dots-Ornamented Waterborne Epoxy-Based Fluorescent Adhesive via Reversible Addition–Fragmentation Chain Transfer-Mediated Miniemulsion Polymerization: A Potential Material for Art Conservation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 36307–36319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanei, M.; Mahdavian, A.R.; Torabi, S.; Salehi-Mobarakeh, H. Efficient modification of nanosilica particles in preparation of anti-scratch transparent polyacrylic films through miniemulsion polymerization. Polym. Bull. 2017, 74, 1879–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fickert, J. Nanocapsules for Self-Healing Materials. Ph.D. Thesis, Johannes Gutenberg-Universität, Mainz, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fickert, J.; Rupper, P.; Graf, R.; Landfester, K.; Crespy, D. Design and characterization of functionalized silica nanocontainers for self-healing materials. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 2286–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
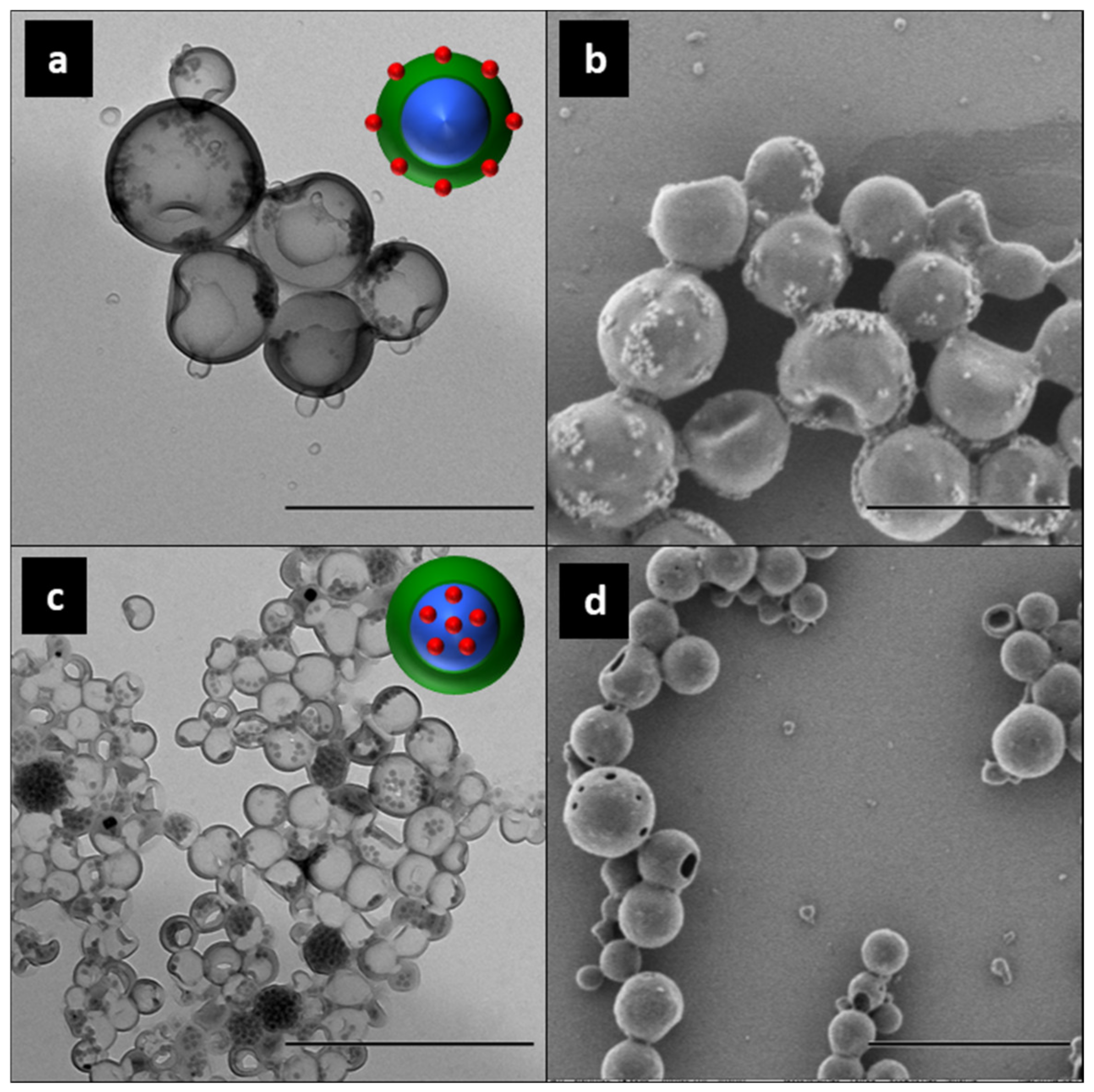
- Schoth, A.; Landfester, K.; Muñoz-Espí, R. Surfactant-free polyurethane nanocapsules via inverse Pickering miniemulsion. Langmuir 2015, 31, 3784–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora-Huertas, C.E.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. Polymer-based nanocapsules for drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 385, 113–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, M.A.; Paiphansiri, U.; Schaeffel, D.; Koynov, K.; Kappl, M.; Landfester, K.; Muñoz-Espí, R. Hybrid Poly(urethane–urea)/Silica Nanocapsules with pH-Sensitive Gateways. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 4311–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torza, S.; Mason, S.G. Three-phase interactions in shear and electrical fields. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1970, 33, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirin-Abadi, A.R.; Khoee, S.; Rahim-Abadi, M.M.; Mahdavian, A.R. Kinetic and thermodynamic correlation for prediction of morphology of nanocapsules with hydrophobic core via miniemulsion polymerization. Colloids Surf. A 2014, 462, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoth, A. Structure Control in Polymer/Inorganic Hybrid Nanomaterials. Ph.D. Thesis, Johannes Gutenberg University of Mainz, Mainz, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundberg, E.J.; Sundberg, D.C. Morphology development for three-component emulsion polymers: Theory and experiments. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1993, 47, 1277–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Liu, F.; Lin, S.; Hu, J.; Liu, G.; Yang, Y.; Tu, Y.; Hou, C.; Li, F.; Hu, M.; et al. Superparamagnetic-Oil-Filled Nanocapsules of a Ternary Graft Copolymer. Langmuir 2014, 30, 3996–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qiu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Yang, B.; Yang, W.; Wu, M.; Wu, Q.; Yang, J. Facile fabrication of Janus magnetic microcapsules via double in situ miniemulsion polymerization. Polym. Chem. 2013, 4, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
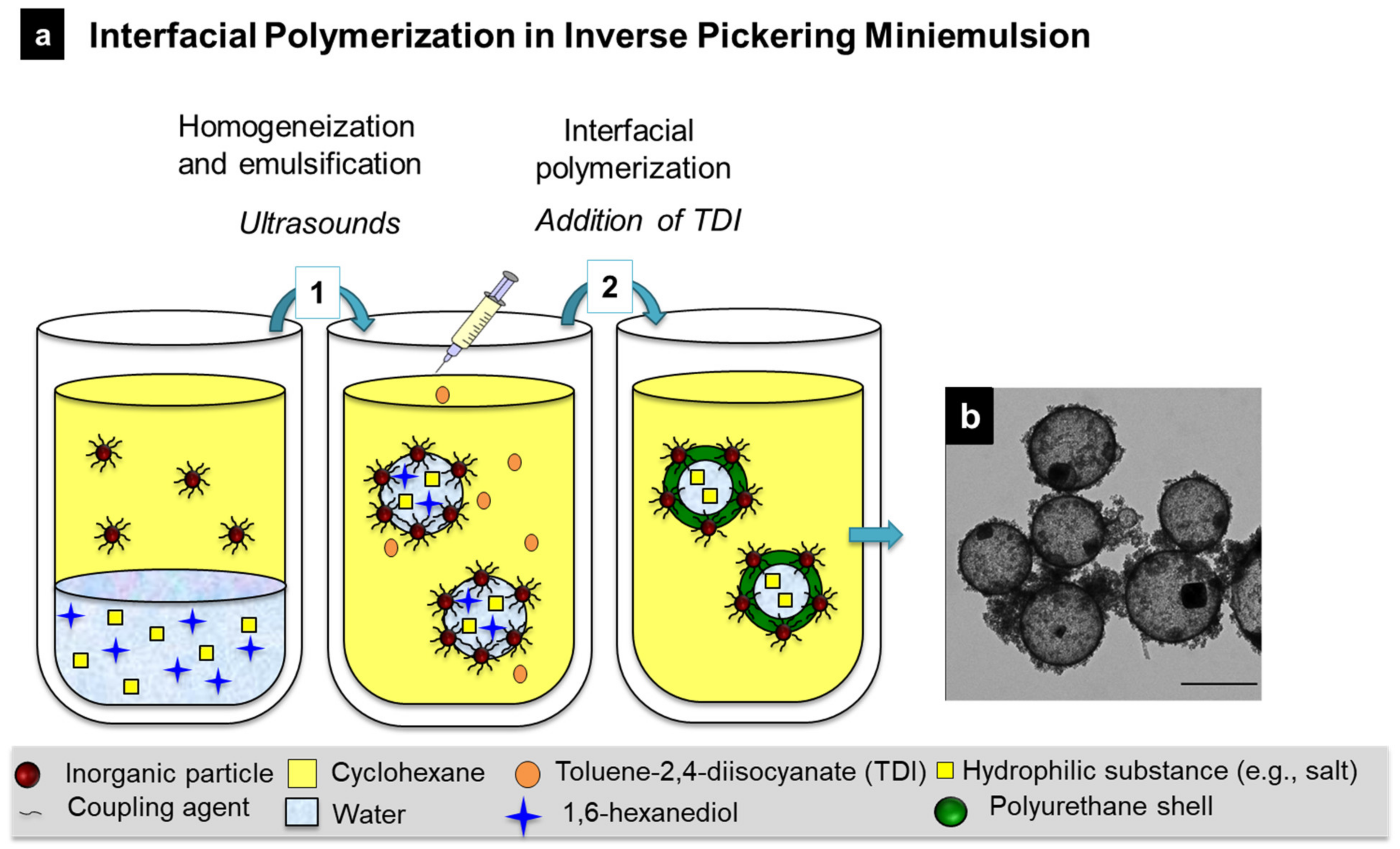
- Rosenbauer, E.M.; Landfester, K.; Musyanovych, A. Surface-active monomer as a stabilizer for polyurea nanocapsules synthesized via interfacial polyaddition in inverse miniemulsion. Langmuir 2009, 25, 12084–12091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
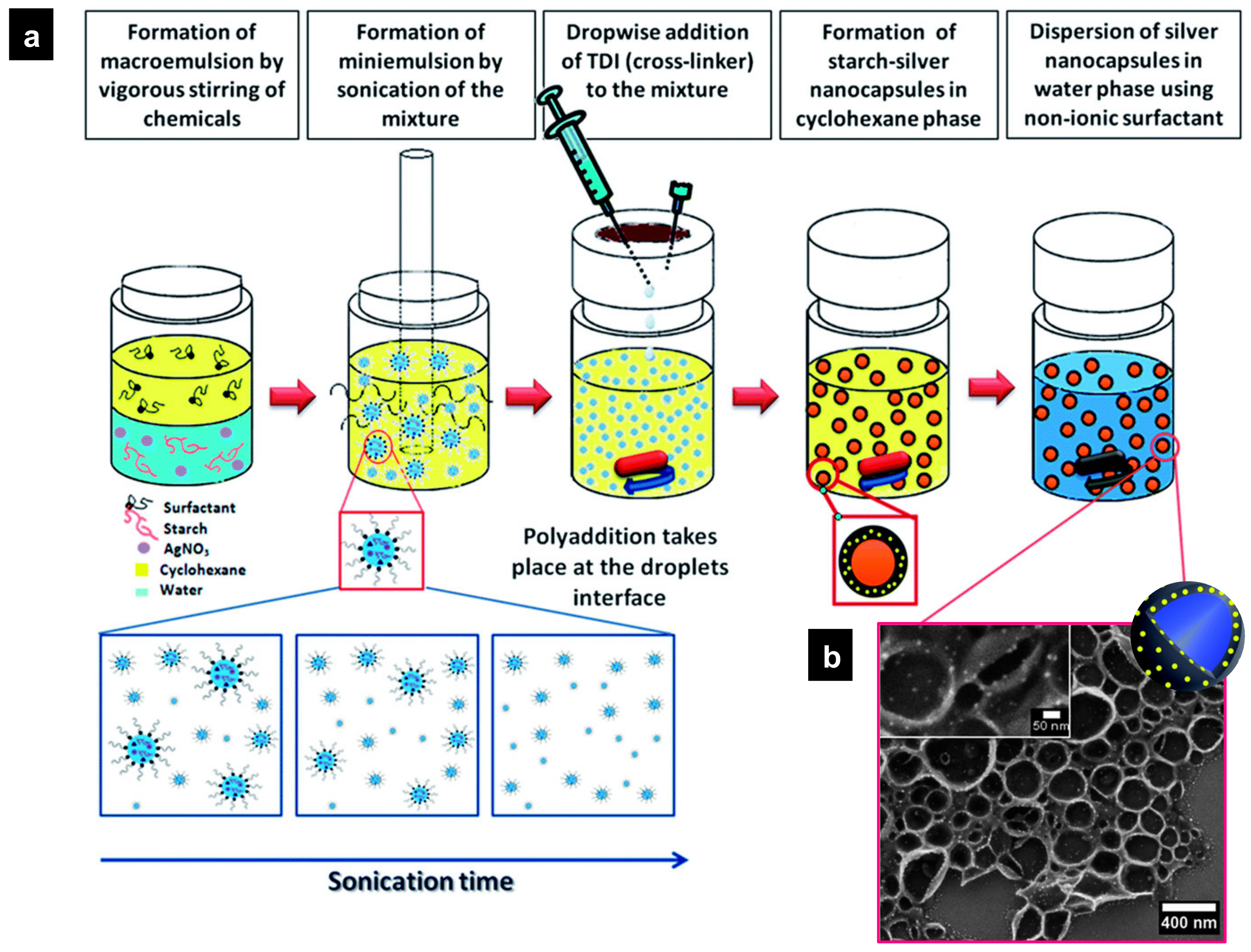
- Taheri, S.; Baier, G.; Majewski, P.; Barton, M.; Förch, R.; Landfester, K.; Vasilev, K. Synthesis and antibacterial properties of a hybrid of silver–potato starch nanocapsules by miniemulsion/polyaddition polymerization. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 1838–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Dong, L.; Li, L.; Shang, Y.; Qi, D.; Lv, Q.; Shan, G.; Ziener, U.; Landfester, K. Preparation of mesoporous submicrometer silica capsules via an interfacial sol-gel process in inverse miniemulsion. Langmuir 2012, 28, 7023–7032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.J.; Yang, L.; Yan, Y.J.; Qi, D.M.; Cao, Z.H. Preparation of silica capsules via an acid-catalyzed sol–gel process in inverse miniemulsions. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2014, 292, 1585–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajir, M.; Dolcet, P.; Fischer, V.; Holzinger, J.; Landfester, K.; Muñoz-Espí, R. Sol–gel processes at the droplet interface: Hydrous zirconia and hafnia nanocapsules by interfacial inorganic polycondensation. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 5622–5628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Landfester, K.; Ziener, U. Preparation of dually, pH- and thermo-responsive nanocapsules in inverse miniemulsion. Langmuir 2012, 28, 1163–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihler, S.; Schrade, A.; Cao, Z.; Ziener, U. Inverse Pickering Emulsions with Droplet Sizes below 500 nm. Langmuir 2015, 31, 10392–10401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Lv, H.; Bi, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhang, H. Research of the synthesis and film performance of silica/poly(St-BA-MPS) core-shell latexes obtained by miniemulsion co-polymerization. Macromol. Res. 2017, 25, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirmohseni, A.; Gharieh, A.; Khorasani, M. Silica encapsulation by miniemulsion polymerization: A novel approach of efficient chemical functionalization on silica nanoparticles. Polymer 2016, 98, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbardella, F.; Bracciale, M.P.; Santarelli, M.L.; Asua, J.M. Waterborne modified-silica/acrylates hybrid nanocomposites as surface protective coatings for stone monuments. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 149, 105897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moarref, P.; Pishvaei, M.; Soleimani-Gorgani, A.; Najafi, F. Synthesis of polypyrrole/indium tin oxide nanocomposites via miniemulsion polymerization. Des. Monomers Polym. 2016, 19, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, N.K.; Gundabala, V. Synthesis and characterization of titanium dioxide encapsulated poly(styrene-co-butyl acrylate-co-acrylic acid) nanocomposite latex. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 111, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronco, L.I.; Feuser, P.E.; da Cas Viegas, A.; Minari, R.J.; Gugliotta, L.M.; Sayer, C.; Araújo, P.H.H. Incorporation of Magnetic Nanoparticles in Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) Nanocapsules. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2018, 219, 1700424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Schrade, A.; Landfester, K.; Ziener, U. Synthesis of raspberry-like organic-inorganic hybrid nanocapsules via pickering miniemulsion polymerization: Colloidal stability and morphology. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2011, 49, 2382–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Bermúdez, O.; Adam-Cervera, I.; Aguado-Hernándiz, A.; Landfester, K.; Muñoz-Espí, R. Magnetic Polyurethane Microcarriers from Nanoparticle-Stabilized Emulsions for Thermal Energy Storage. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 17956–17966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
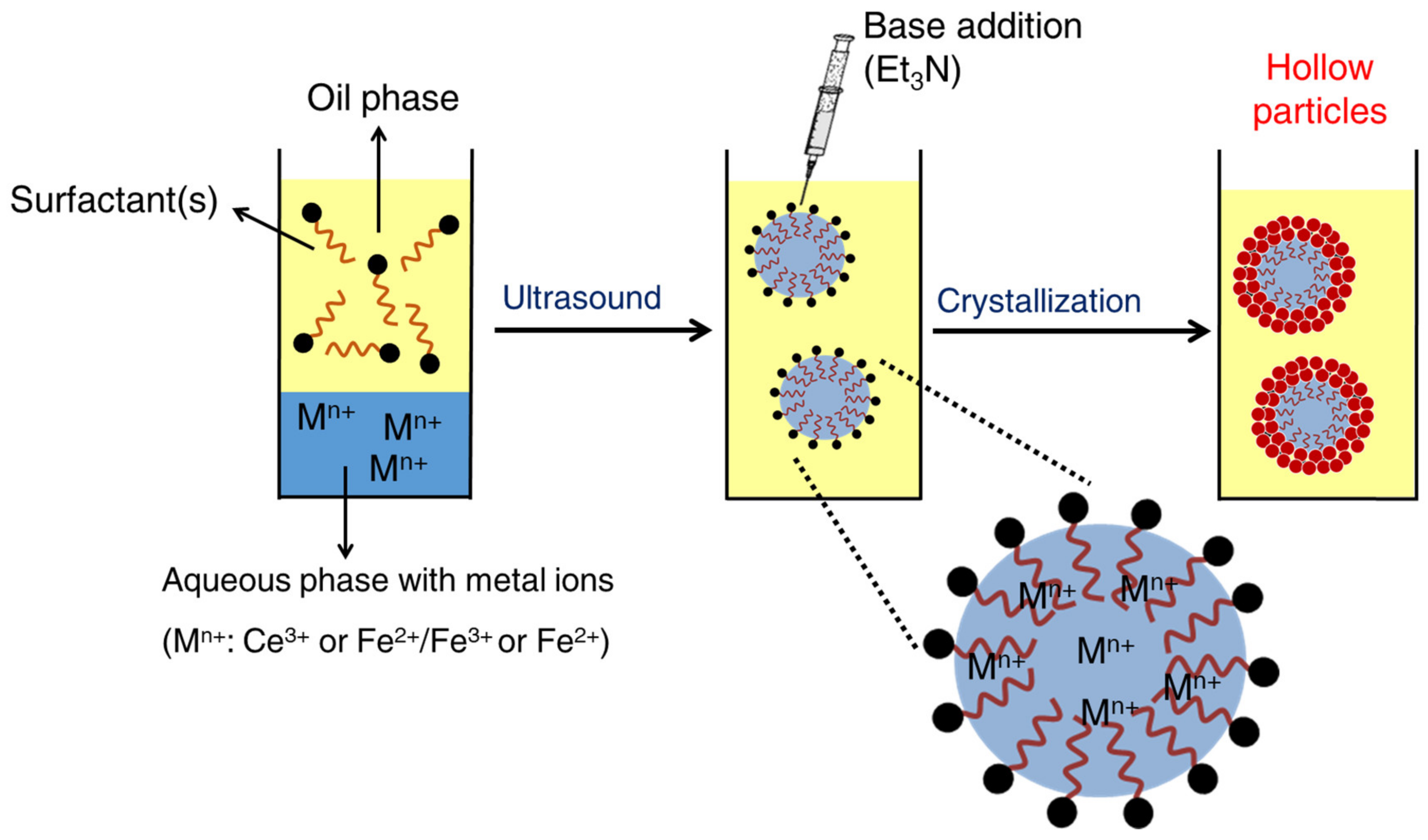
- Varol, H.S.; Álvarez-Bermúdez, O.; Dolcet, P.; Kuerbanjiang, B.; Gross, S.; Landfester, K.; Muñoz-Espí, R. Crystallization at Nanodroplet Interfaces in Emulsion Systems: A Soft-Template Strategy for Preparing Porous and Hollow Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2016, 32, 13116–13123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Landfester, K.; Chandra, A.; Muñoz-Espí, R. A new approach for crystallization of copper(II) oxide hollow nanostructures with superior catalytic and magnetic response. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 19250–19258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Nigam, A.K.; Landfester, K.; Muñoz-Espí, R.; Chandra, A. Anomalous magnetic behavior below 10 K in YCrO3 nanoparticles obtained under droplet confinement. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 182902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan-Nguyen, T.P.; Natsathaporn, P.; Jenjob, R.; Niyom, Y.; Ittisanronnachai, S.; Flood, A.; Crespy, D. Regulating Payload Release from Hybrid Nanocapsules with Dual Silica/Polycaprolactone Shells. Langmuir 2019, 35, 11389–11396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, X.; Möller, M. A Facile One-Step Approach toward Polymer@SiO2 Core–Shell Nanoparticles via a Surfactant-Free Miniemulsion Polymerization Technique. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 1552–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Wu, Q.; Wu, M.; Liu, N.; Jin, Z.; Wang, Y. SiO2/Polymer Hybrid Hollow Microspheres via Double in Situ Miniemulsion Polymerization. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wu, M.; Wu, Q. Facile fabrication of magnetic hybrid-shell microcapsule via miniemulsion polymerization. Mater. Lett. 2014, 114, 60–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, H.; Li, X. Cuprous oxide modified nanoencapsulated phase change materials fabricated by RAFT miniemulsion polymerization for thermal energy storage and photothermal conversion. Powder Technol. 2022, 399, 117189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.-Y.; Johnston, K.P.; Wu, P.-K.; Ahmad, M.; Luo, M.-L.; Zhang, N.; He, J.-T. Facile synthesis of chromium chloride/poly(methyl methacrylate) core/shell nanocapsules by inverse miniemulsion evaporation method and application as delayed crosslinker in secondary oil recovery. Pet. Sci. 2023, 20, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, X.; Möller, M. Hybrid nanostructured particles via surfactant-free double miniemulsion polymerization. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, J.; Wu, B.; Yang, B.; Wu, M.; Yang, W.; Wu, Q.; Yang, J. Facile Fabrication of Hybrid Hollow Microspheres via in Situ Pickering Miniemulsion Polymerization. Chem. Lett. 2012, 41, 970–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ge, X.; Wang, M.; Yang, J.; Wu, Q.; Wu, M.; Liu, N.; Jin, Z. Hybrid hollow microspheres templated from double Pickering emulsions. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 4318–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespy, D.; Stark, M.; Hoffmann-Richter, C.; Ziener, U.; Landfester, K. Polymeric Nanoreactors for Hydrophilic Reagents Synthesized by Interfacial Polycondensation on Miniemulsion Droplets. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 3122–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamberger, A.; Ziener, U.; Landfester, K. Encapsulation of In Situ Nanoprecipitated Inorganic Materials in Confined Geometries Into a Polymer Shell Using Inverse Miniemulsion. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2013, 214, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
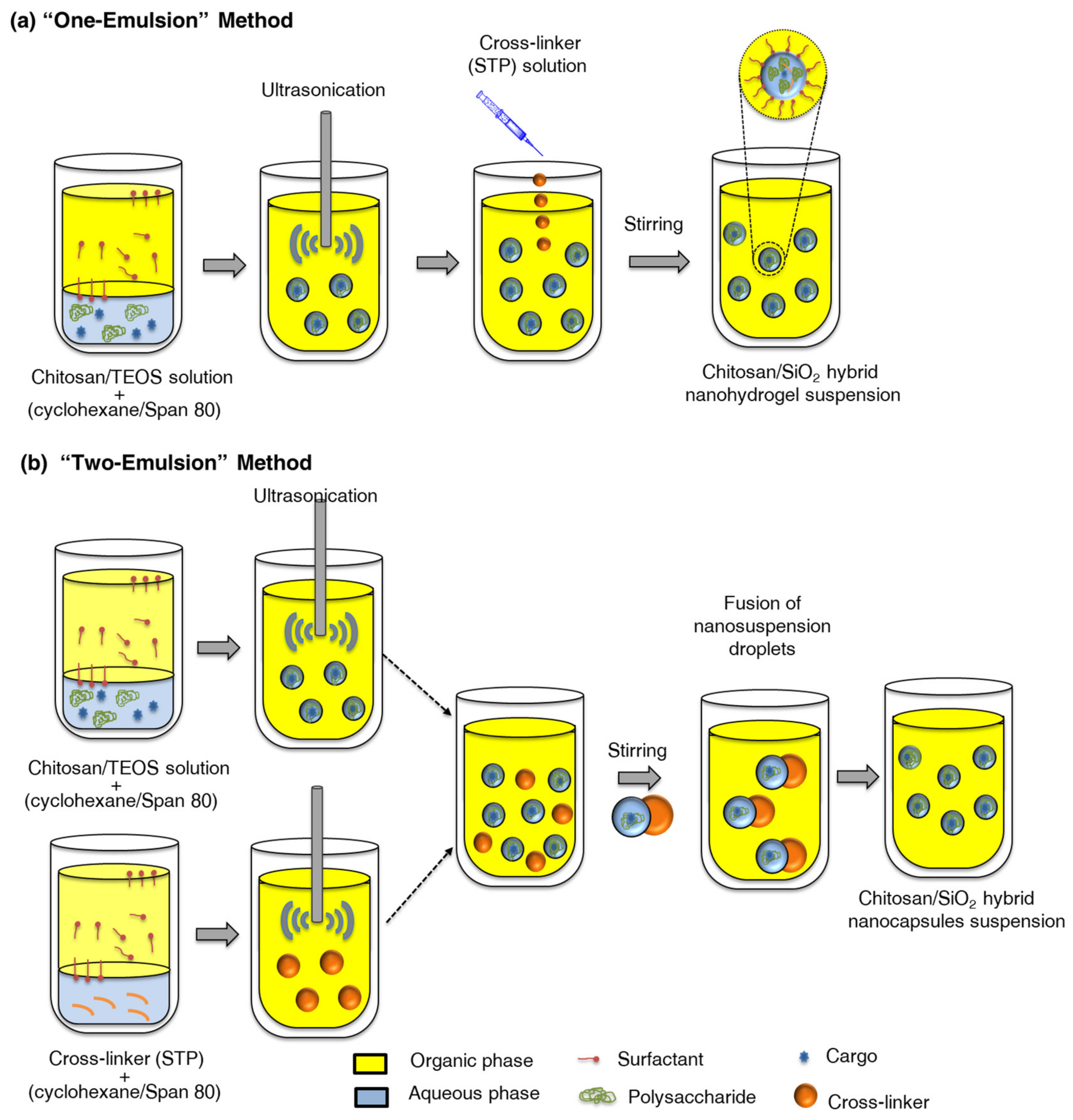
- Elzayat, A.M.; Landfester, K.; Muñoz-Espí, R. Chitosan/Silica Hybrid Nanogels by Inverse Nanoemulsion for Encapsulating Hydrophilic Substances. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2024, 2024, 2400151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Shu, J.; Ge, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, M.; Ge, X. Preparation and performance of magnetic phase change microcapsules with organic-inorganic double shell. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2022, 240, 111716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, X. Bi-Functional Paraffin@Polyaniline/TiO2/PCN-222(Fe) Microcapsules for Solar Thermal Energy Storage and CO2 Photoreduction. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, L.; Song, G.; Tang, G.; Shi, X. Organic-inorganic hybrid shell microencapsulated phase change materials prepared from SiO2/TiC-stabilized pickering emulsion polymerization. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2018, 175, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhao, J.; Cui, Y.; Cheng, W. Synthesis of bifunctional nanoencapsulated phase change materials with nano-TiO2 modified polyacrylate shell for thermal energy storage and ultraviolet absorption. Polym. Int. 2020, 69, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, K.; Liu, R.; Sun, G.; Luo, J. Robust SiO2/polymer hybrid microcapsule synthesized via emulsion photo-polymerization and its application in self-lubricating coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2023, 184, 107856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Zhang, B.; Kou, X.; Niu, Y.; Hong, L.; Zhao, W.; Cai, H.; Lu, X. High-Temperature Aroma Mitigation and Fragrance Analysis of Ethyl Cellulose/Silica Hybrid Microcapsules for Scented Fabrics. Coatings 2022, 12, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wu, W.; Guo, K.; Chen, J.; Zhang, P. Synthesis of Temperature-Responsive Poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide)/Poly(methyl methacrylate)/Silica Hybrid Capsules from Inverse Pickering Emulsion Polymerization and Their Application in Controlled Drug Release. Langmuir 2010, 26, 7971–7980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Hu, J. Interfacial synthesis of magnetic PMMA@Fe3O4/Cu3(BTC)2 hollow microspheres through one-pot Pickering emulsion and their application as drug delivery. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 58511–58515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chen, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, J. Fabrication of zinc–histidine-functionalized graphene quantum dot framework amphiphilic nanoparticles and application in the synthesis of polystyrene microspheres for adsorption of Cu2+ by Pickering emulsion polymerization. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 102534–102541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Refs. | |
| With polymerization | Conventional emulsion polymerization |
|
| [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9] |
| Seeded emulsion polymerization |
|
| [10] | |
| Miniemulsion polymerization |
|
| [11,12,13,14,15] | |
| Microemulsion polymerization |
|
| [16,17] | |
| Pickering emulsions |
|
| [18,19,20] | |
| Suspension polymerization |
|
| [21,22,23,24] | |
| Precipitation polymerization |
|
| [25,26] | |
| Dispersion polymerization |
|
| [27,28,29,30] | |
| Without polymerization | Ouzo effect (spontaneous emulsification) |
|
| [31,32,33,34] |
| Emulsion–solvent evaporation |
|
| [35,36,37] | |
| Spraying techniques (spray drying or freezing) |
|
| [38,39,40] | |
| Supercritical fluid techniques (SAS/RESS) |
|
| [41,42,43] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Álvarez-Bermúdez, O.; Adam-Cervera, I.; Landfester, K.; Muñoz-Espí, R. Morphology Control of Polymer–Inorganic Hybrid Nanomaterials Prepared in Miniemulsion: From Solid Particles to Capsules. Polymers 2024, 16, 2997. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16212997
Álvarez-Bermúdez O, Adam-Cervera I, Landfester K, Muñoz-Espí R. Morphology Control of Polymer–Inorganic Hybrid Nanomaterials Prepared in Miniemulsion: From Solid Particles to Capsules. Polymers. 2024; 16(21):2997. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16212997
Chicago/Turabian StyleÁlvarez-Bermúdez, Olaia, Inés Adam-Cervera, Katharina Landfester, and Rafael Muñoz-Espí. 2024. "Morphology Control of Polymer–Inorganic Hybrid Nanomaterials Prepared in Miniemulsion: From Solid Particles to Capsules" Polymers 16, no. 21: 2997. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16212997
APA StyleÁlvarez-Bermúdez, O., Adam-Cervera, I., Landfester, K., & Muñoz-Espí, R. (2024). Morphology Control of Polymer–Inorganic Hybrid Nanomaterials Prepared in Miniemulsion: From Solid Particles to Capsules. Polymers, 16(21), 2997. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16212997







