MXene/Cellulose Hydrogel Composites: Preparation and Adsorption Properties of Pb2+
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Method
2.1. Materials
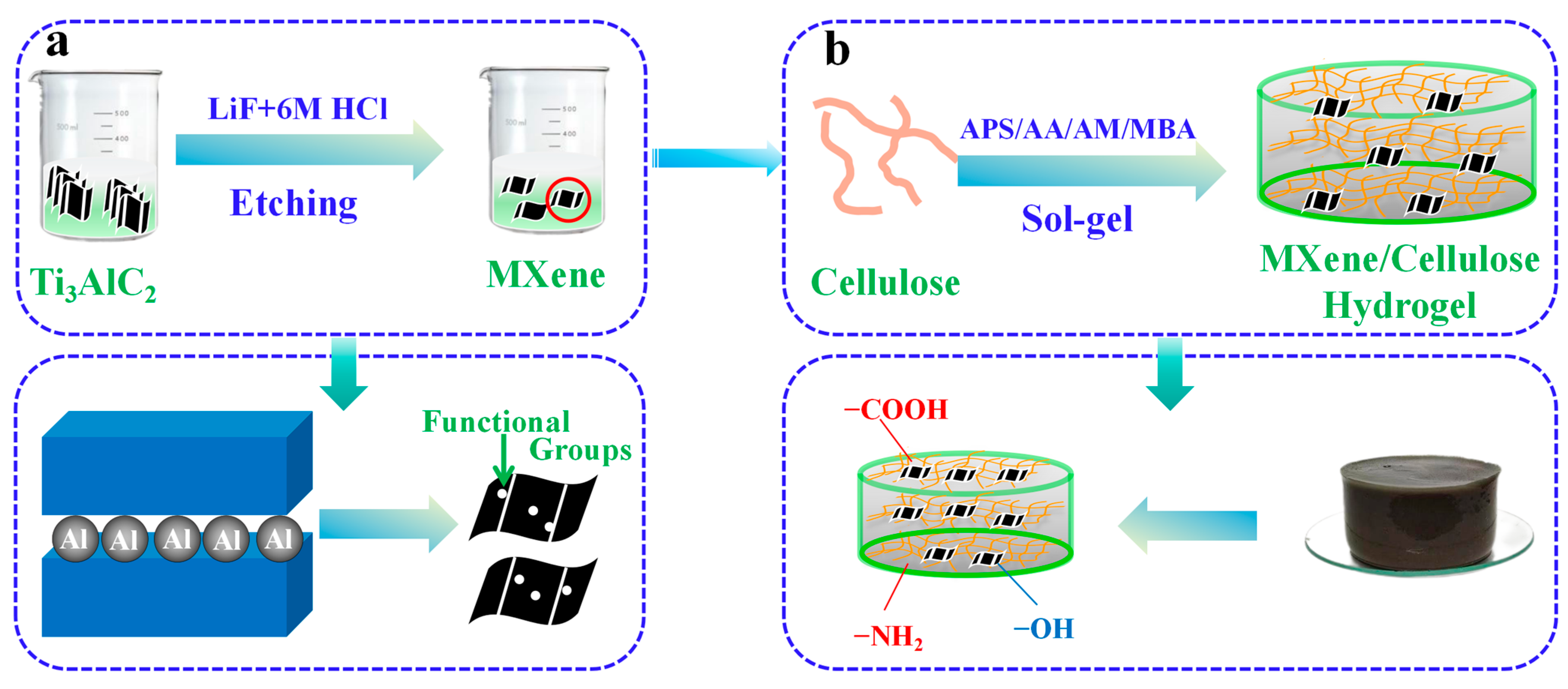
2.2. Stripping Preparation of Single Layer MXene
2.3. The Preparation Process of MXene/Cellulose Hydrogel Composite
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Adsorption Performance
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structure and Morphology Analysis
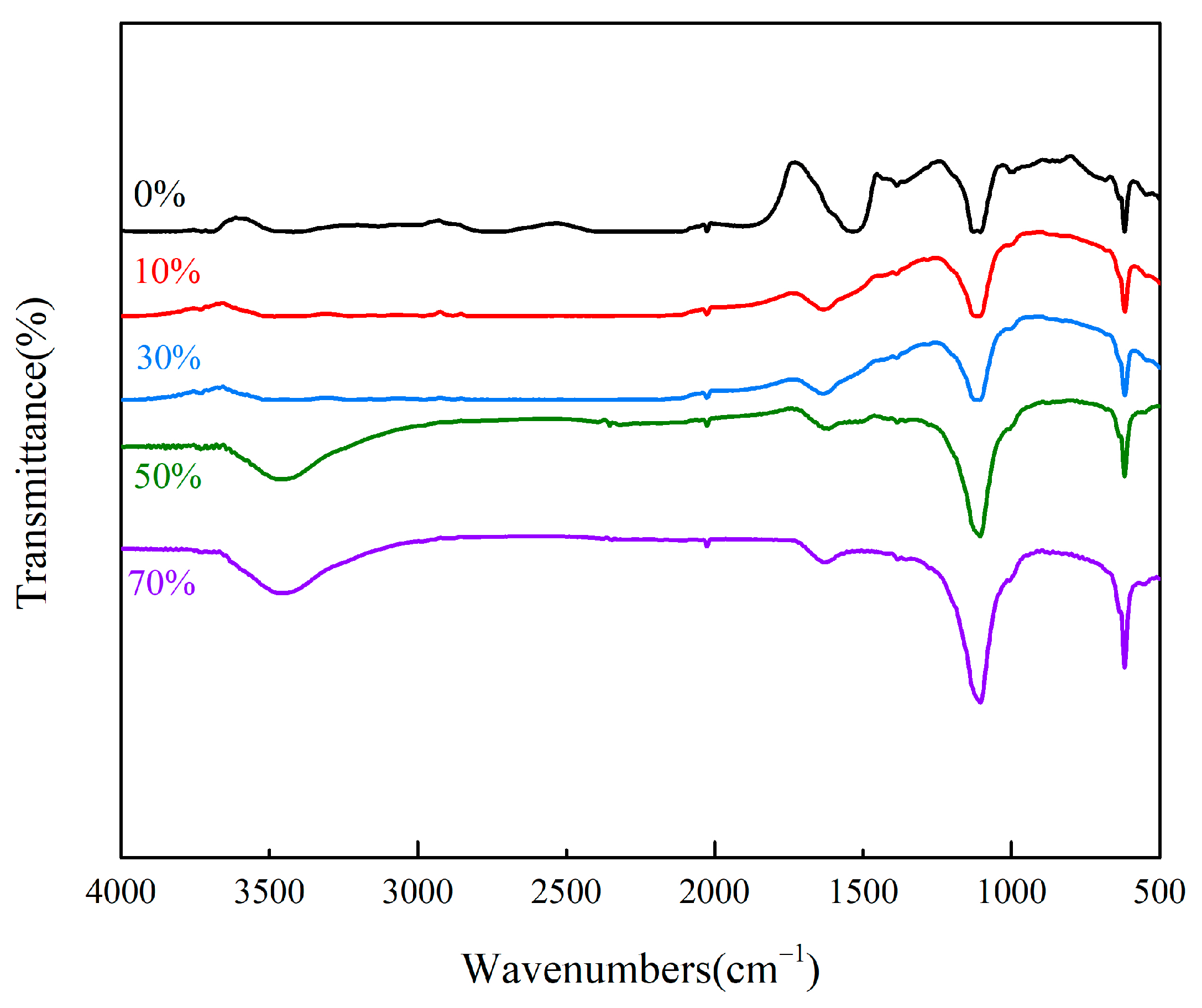
3.1.1. FT-IR Analysis
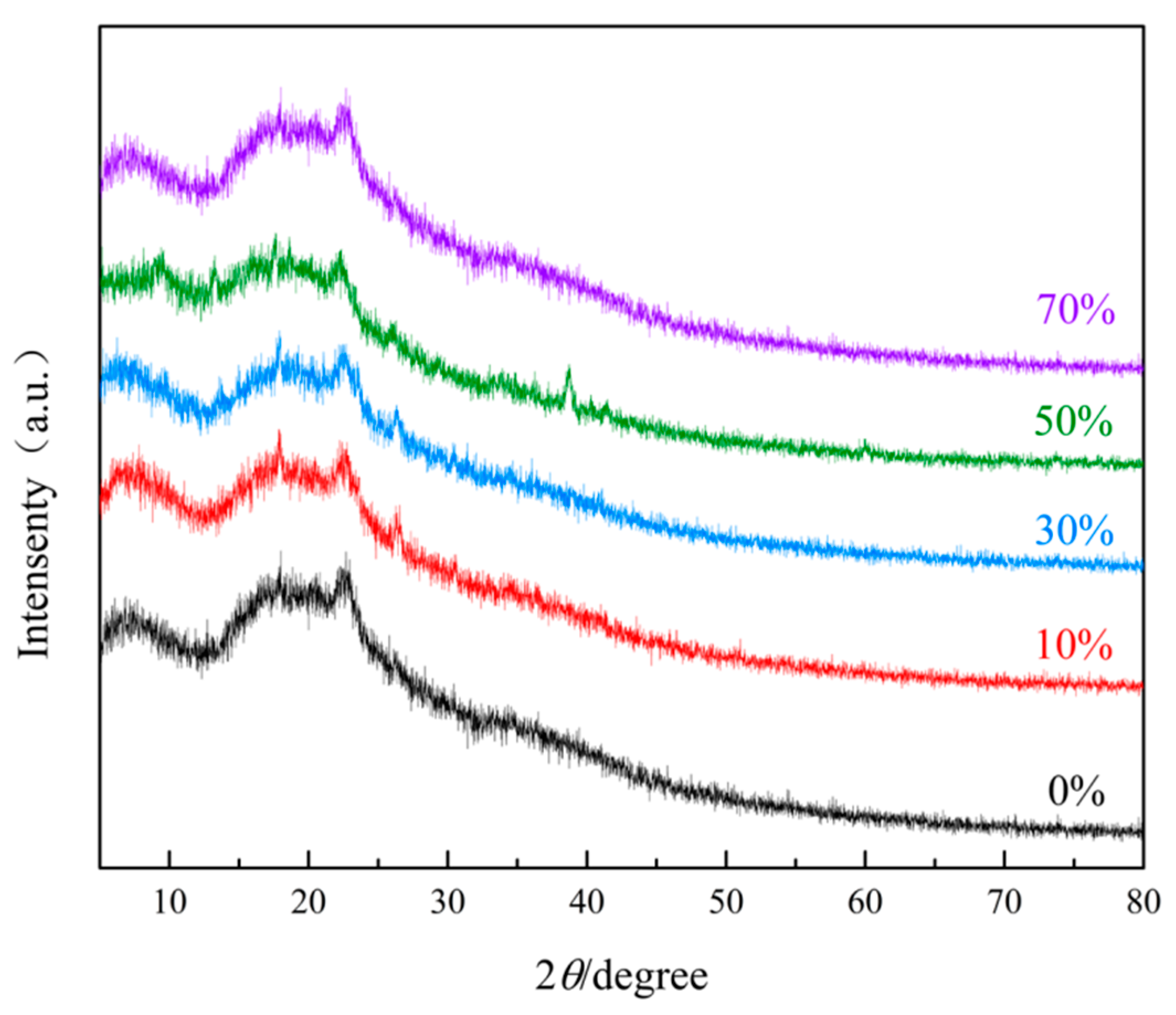
3.1.2. XRD Analysis
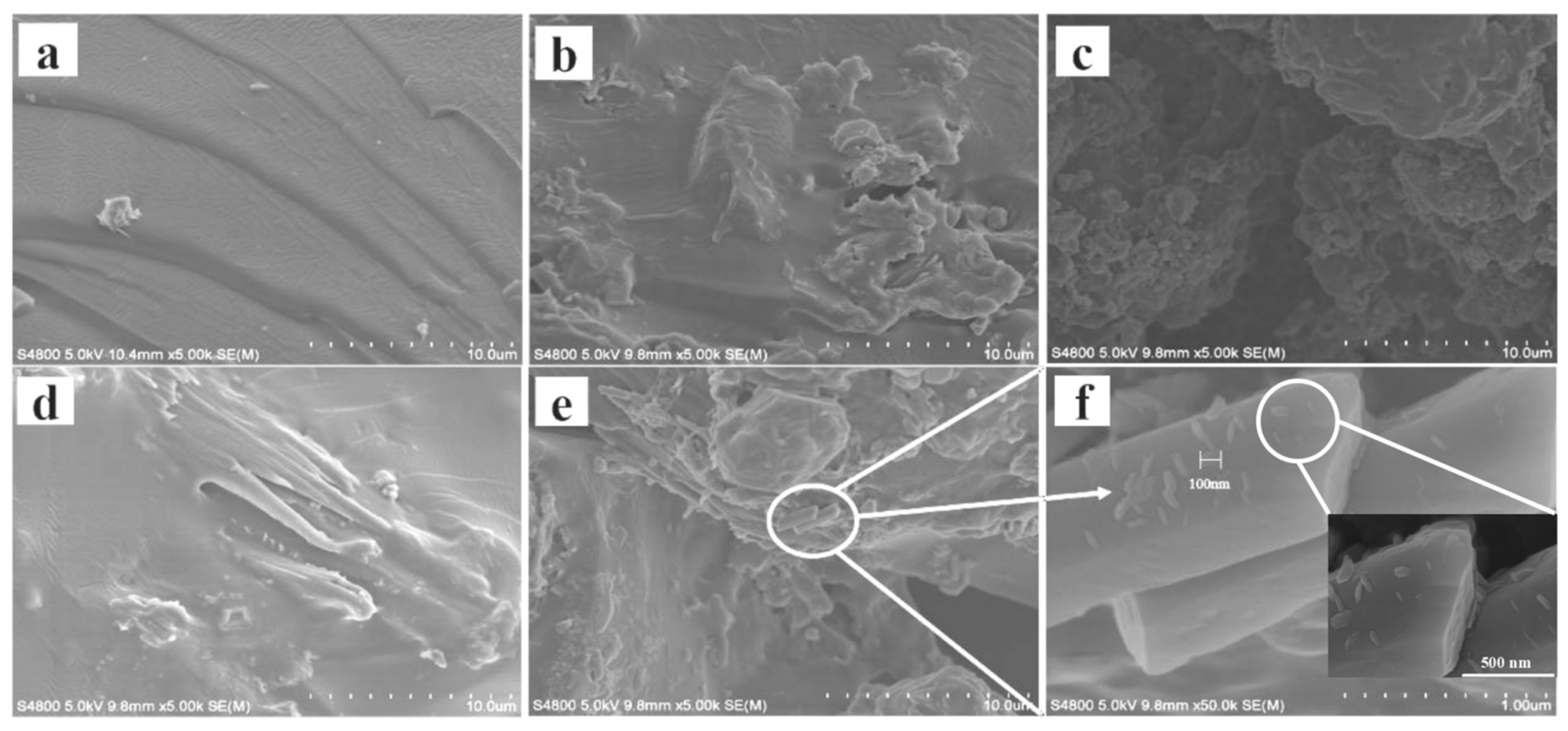
3.1.3. SEM Morphology
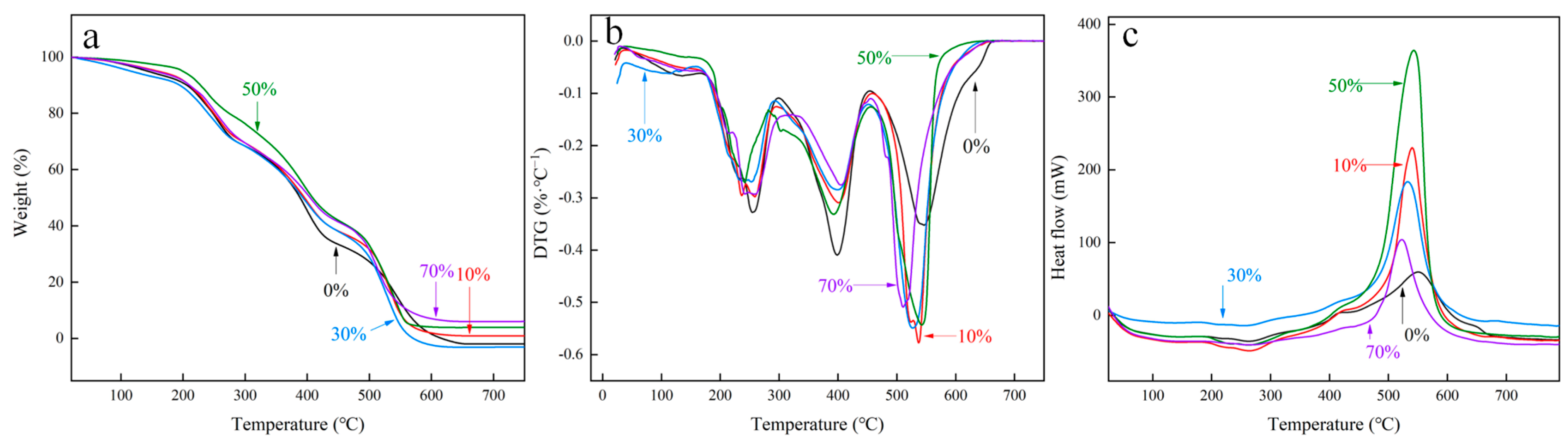
3.1.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3.2. The Adsorption Performance of MXene/Cellulose Hydrogel for Pb2+
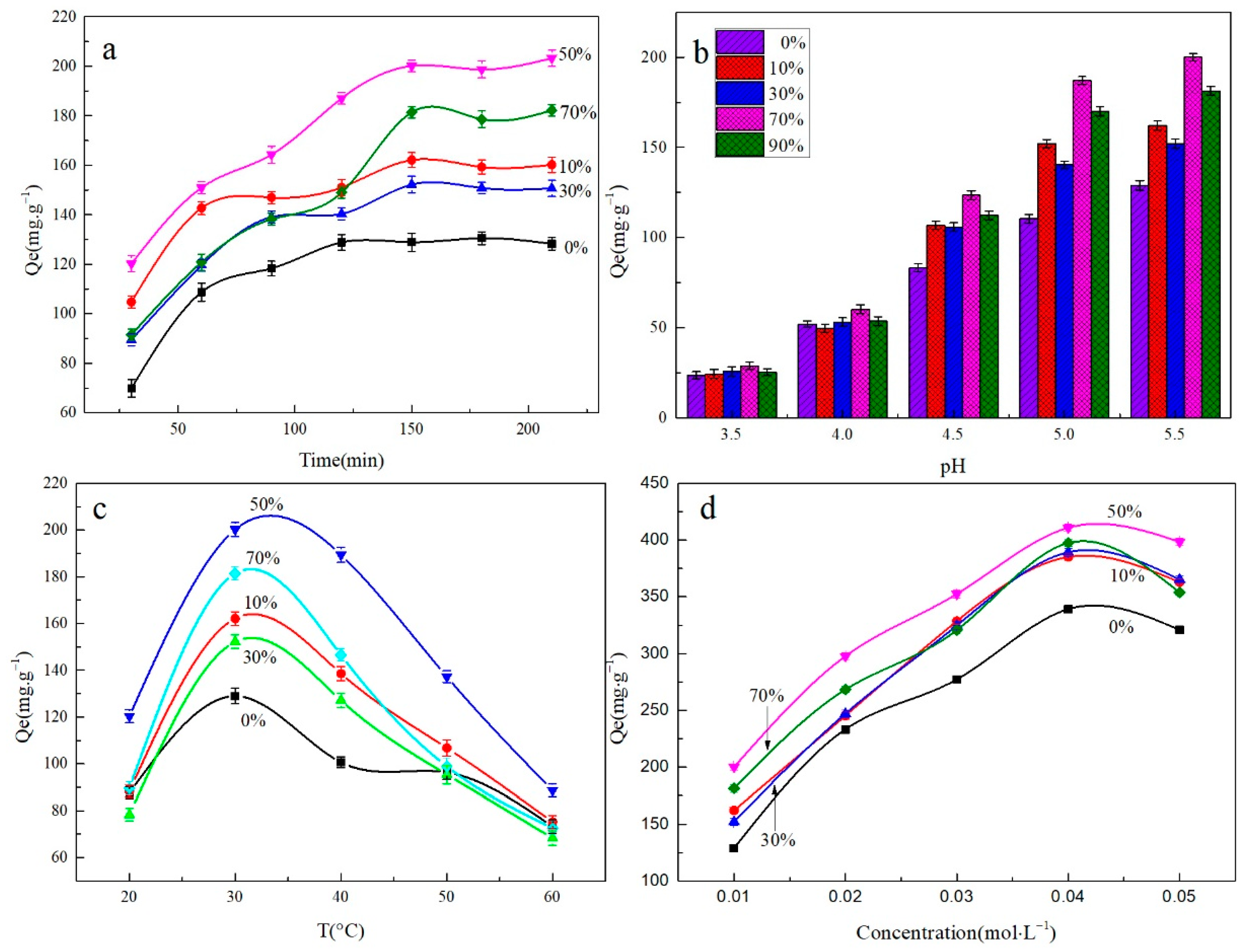
3.2.1. Effect of Adsorption Time
3.2.2. Effect of pH
3.2.3. Effect of Adsorption Temperature
3.2.4. Effect of the Initial Concentration of Pb2+
3.3. Adsorption Isotherm Behavior
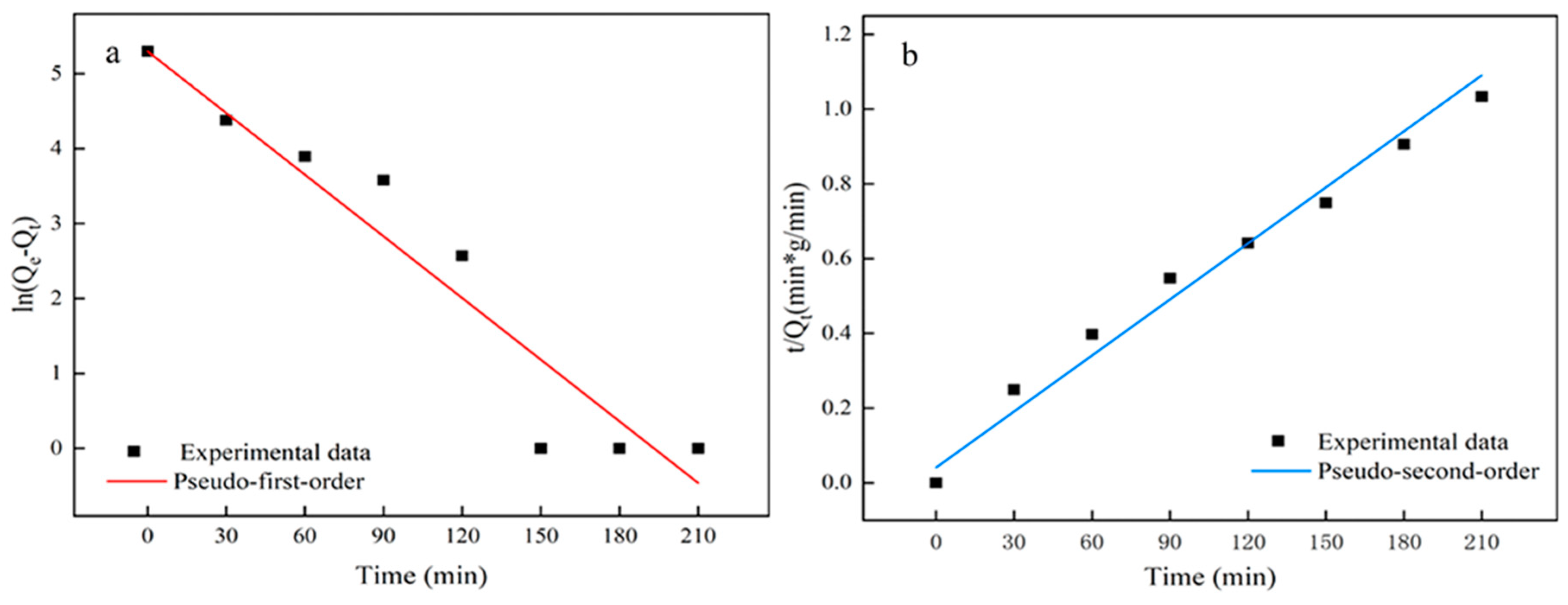
3.4. Kinetics of Adsorption
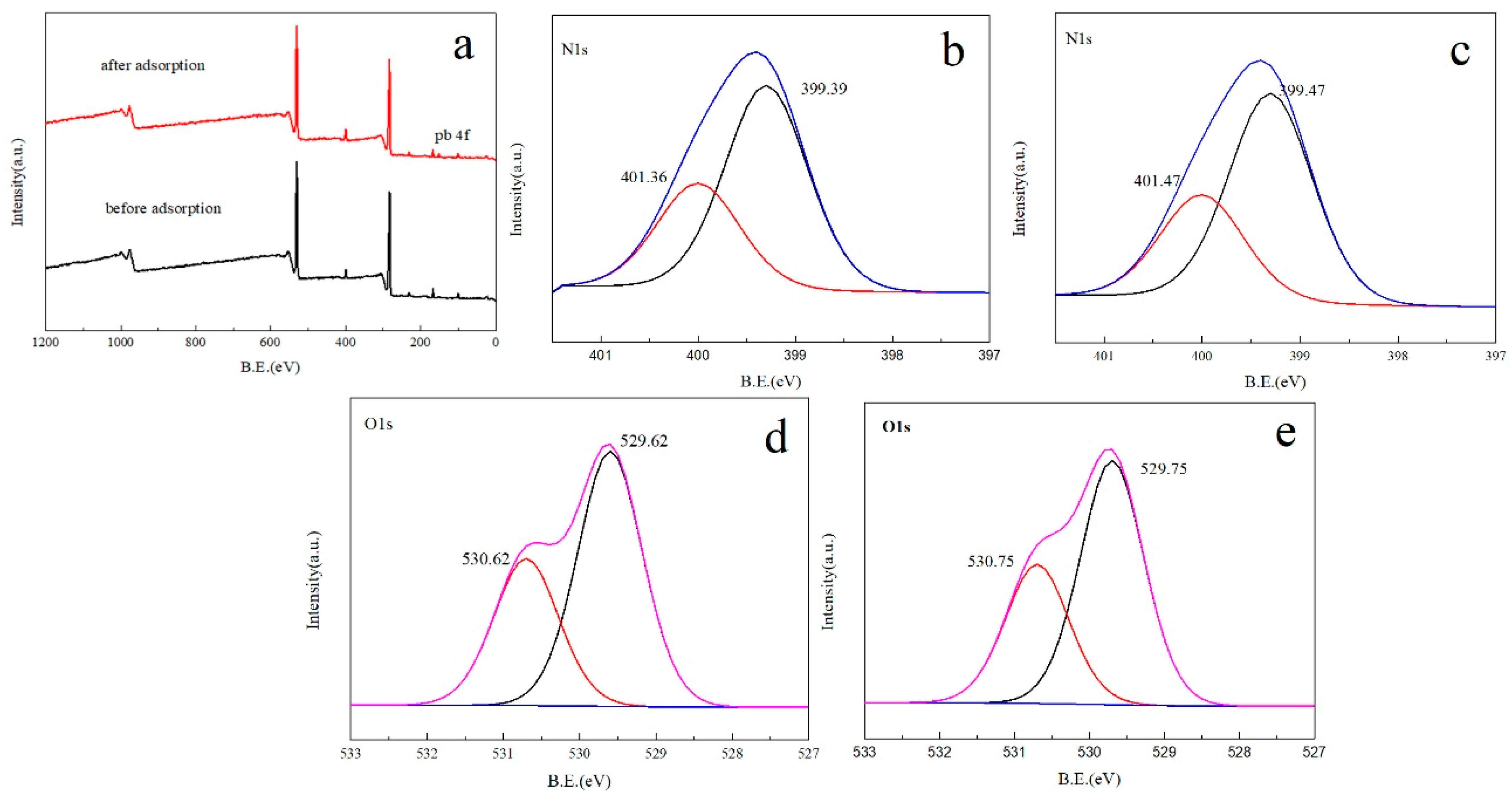
3.5. XPS
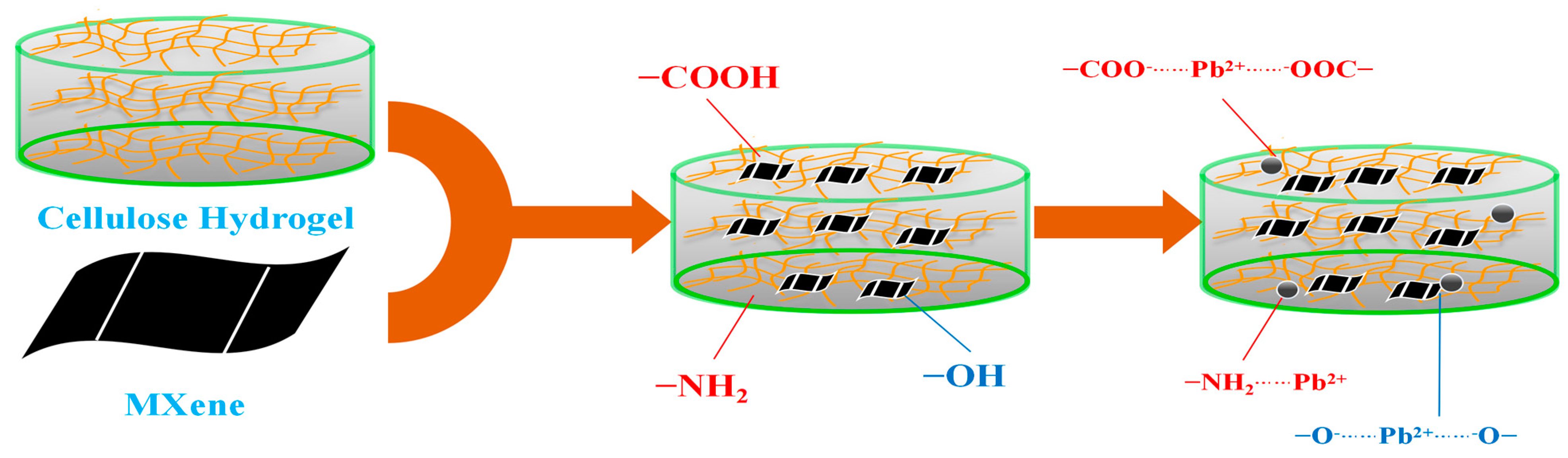
3.6. Suggested Adsorption Mechanism
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The optimized adsorption conditions for MXene/cellulose hydrogel were Pb2+ initial concentration 0.04 mol/L, 150 min, 30 °C, pH = 5.5, and MXene doping content of 50%. Its adsorption capacity attained 410.57 mg/g.
- (2)
- The analysis of adsorption isotherm and kinetics described that the adsorption process of MXene/cellulose hydrogel follows the pseudo-second-order kinetic equation model and is better fitted with the Freundlich model. The experimental data suggest that the MXene/cellulose hydrogel composite has good adsorption capacity for Pb2+ under high concentration and acidic conditions, making it a suitable absorbent material in the field of wastewater treatment of heavy metal ions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berber-Mendoza, M.S.; Leyva-Ramos, R.; Alonso-Davila, P.; Fuentes-Rubio, L.; Guerrero-Coronado, R.M. Comparison of isotherms for the ion exchange of Pb(II) from aqueous solution onto homoionic clinoptilolite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 301, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, G.D.; Cao, Y.M. Development of antifouling reverse osmosis membranes for water treatment: A review. Water Res. 2012, 46, 584–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.F.; Zhang, L.; Wang, R.M.; Li, H.R.; Wang, Y. Loess clay based copolymer for removing Pb(II) ion. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 334, 227–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Yu, Z.; Long, R.; Li, X.; Shao, L.; Zeng, H.; Zeng, G.; Zuo, Y. Self-assembling 2D/2D (MXene/LDH) materials achieve ultra-high adsorption of heavy metals Ni2+ through terminal group modification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 253, 117525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.P.; Wu, J.Z.; Sun, H.W.; Wang, T.; Liu, H.B.; Chang, Y. Adsorption of Pb(II) Ion from Aqueous Solutions by Tourmaline as a Novel Adsorbent. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 8515–8523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Yi, C.; Jiang, H.; Liu, F.; Cheng, G.J. Direct Ink Writing of Hierarchically Porous Cellulose/Alginate Monolithic Hydrogel as a Highly Effective Adsorbent for Environmental Applications. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, C.; Xiong, J.; Tao, J.; Xu, S.; Zhang, D.; Lin, H.; Chen, Y. Sodium alginate/graphene oxide aerogel with enhanced strength-toughness and its heavy metal adsorption study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 83, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Huang, H.; Xu, M.; Chen, Q. Cellulose/poly(ethylene imine) composites as efficient and reusable adsorbents for heavy metal ions. Cellulose 2016, 23, 2527–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Du, X.; Cheng, X.; Du, Z.; Wang, H. Fabrication of MXene/PEI functionalized sodium alginate aerogel and its excellent adsorption behavior for Cr(VI) and Congo Red from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, J.D.; Morales-García, Á.; Vines, F.; Illas, F.; Gomes, J.R. MXenes as promising catalysts for water dissociation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 260, 118191–118197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, B.M.; Kim, S.; Heo, J.; Park, C.M.; Her, N.; Jang, M.; Huang, Y.; Han, J.; Yoon, Y. Review of MXenes as new nanomaterials for energy storage/delivery and selected environmental applications. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 471–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Cheng, R.; Li, Z.; Hu, T.; Zhang, H.; Shi, C.; Yang, J.; Cui, C.; Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; et al. Interlayer engineering of Ti3C2Tx MXenes towards high capacitance supercapacitors. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafiq, S.; Awan, S.; Zheng, R.-K.; Wen, Z.; Rani, M.; Akinwande, D.; Rizwan, S. Novel roomtemperature ferromagnetism in Gd-doped 2-dimensional Ti3C2Tx MXene semiconductor for spintronics. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 497, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, A.; Nawaz, M.; Moztahida, M.; Jang, J.; Tahir, K.; Kim, J.; Lim, Y.; Vassiliadis, V.S.; Woo, S.H.; Lee, D.S. Ti3C2Tx MXene core-shell spheres for ultrahigh removal of mercuric ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 368, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Chen, C.; Zhang, D.; Xue, Y. Kinetics, isotherm and chemical speciation analysis of Hg(Ⅱ) adsorption over oxygencontaining MXene adsorbent. Chemosphere 2021, 278, 130206–130215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, M.Y.; Song, S.X.; Yang, B. Surface modification of PCC filledcellulose paper by Zn-BTC(Zn3(BDC)2) metal-organic frameworks for use as soft gas adsorption composite materials. Cellulose 2017, 24, 3051–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, D.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Xiu, H.; Liu, Q. Selective hydrolysis of cellulose for the preparation of Microcrystalline cellulose by pho sphotungstic acid. Cellulose 2016, 23, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Guo, X.; Wan, P.; Yu, G. Conductive MXene Nanocomposite Organohydrogel for Flexible, Healable, Low-Temperature Tolerant Strain Sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1904507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliha, M.; Brammananth, R.; Dyson, J.; Coppel, R.L.; Werrett, M.; Andrews, P.C.; Batchelor, W. Biocompatibility and selective antibacterial activity of a bismuth phosphinato-nanocellulose hydrogel. Cellulose 2021, 28, 4701–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Yin, X.; Wu, H.; Hou, Z.; Song, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, L. Ti3C2 MXenes with modified surface for high-performance electromagnetic absorption and shielding in the X-Band. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 21011–21019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anasori, B.; Lukatskaya, M.R.; Gogotsi, Y. 2D metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) for energy storage. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 16098–16114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Mao, Y.; Cao, W.; Hu, P.; Peng, X. Two-Dimensional Titanium Carbide for Efficiently Reductive Removal of Highly Toxic Chromium(VI) from Water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar]
- Jahan, M.S.; Saeed, A.; He, Z.; Ni, Y. Jute as raw material for the preparation of microcrystalline cellulose. Cellulose 2011, 18, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurgel LV, A.; Júnior, O.K.; de Freitas Gil, R.P.; Gil, L.F. Adsorption of Cu(II), Cd(II), and Pb(II) from aqueous single metal solutions by cellulose and mercerized cellulose Chemically modified with succinic anhydride. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 74, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, W.; Xu, C.; Qian, G.; Huang, G.; Tang, X.; Lin, B. Adsorption of Cu(ii), Zn(ii), and Pb ii) from aqueous single and binary metal solutions by regenerated cellulose and sodium alginate chemically modified with polyethyleneimine. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 18723–18733. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Agarwal, G.P. Interactions of Proteins with Immobilized Metal Ions: A Comparative Analysis Using Various Isotherm Models. Anal. Biochem. 2001, 288, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, K.G.; Sarma, A. Adsorption characteristics of the dye, brilliant green, on neem leaf owder. Dyes Pigment. 2003, 57, 21l–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, C.; Hu, Y. Facile preparation ofmagnetic sodium alginate/carboxymethyl cellulose composite hydrogel for removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 13096–13107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, U.; Kaur, M.P.; Jawa, G.K.; Sud, D.; Garg, V.K. Removal of cadmium (II) from aqueous solutions by adsorption on agricultural waste biomass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Fu, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhan, H.; Levit, M.V. Use of carboxylated cellulose nanofibrils-filled magnetic chitosan hydrogel beads as adsorbents for Pb(II). Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godiya, C.B.; Cheng, X.; Li, D.; Chen, Z.; Lu, X. Carboxymethyl cellulose/polyacrylamide composite hydrogel for cascaded treatment/reuse of heavy metal ions in wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 364, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, N.; Ping, Q. Preparation of Hemicellulose-based Hydrogel and its Application as an Adsorbent Towards Heavy Metal Ions. BioResources 2018, 13, 3208–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Yu, F.; Ma, J. Recent progress on MXene-Derived material and its’ application In energy and environment. J. Power Sources 2021, 490, 229250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
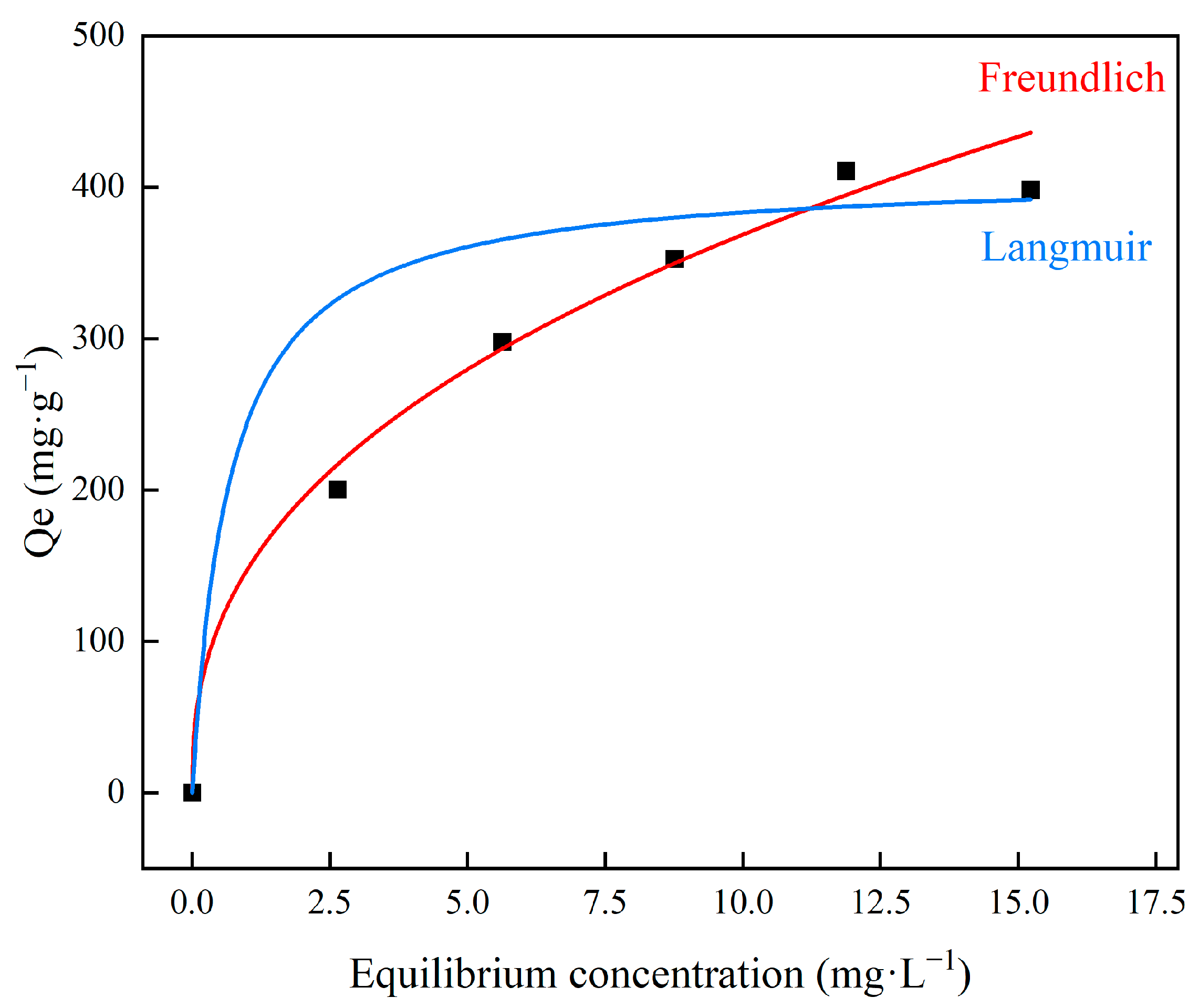
| Isotherms | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Qm | kl | R2 | n | kf | R2 |
| 412 | 1.48598 | 0.51702 | 2.50794 | 147.2 | 0.97093 | |
| Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | k1 (min−1) | Qe (mg/g) | R2 | k2 (g/mg·min) | Qe (mg/g) | R2 |
| 0.0274 | 200.13 | 0.9189 | 0.6146 | 410.57 | 0.9784 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yin, H.; Guo, J.; Lv, S.; Li, Y. MXene/Cellulose Hydrogel Composites: Preparation and Adsorption Properties of Pb2+. Polymers 2024, 16, 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16020189
Yang Q, Zhang J, Yin H, Guo J, Lv S, Li Y. MXene/Cellulose Hydrogel Composites: Preparation and Adsorption Properties of Pb2+. Polymers. 2024; 16(2):189. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16020189
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Qiang, Jia Zhang, Hairong Yin, Junkang Guo, Shenghua Lv, and Yaofeng Li. 2024. "MXene/Cellulose Hydrogel Composites: Preparation and Adsorption Properties of Pb2+" Polymers 16, no. 2: 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16020189
APA StyleYang, Q., Zhang, J., Yin, H., Guo, J., Lv, S., & Li, Y. (2024). MXene/Cellulose Hydrogel Composites: Preparation and Adsorption Properties of Pb2+. Polymers, 16(2), 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16020189





