Ethoxy Acetalated Dextran-Based Biomaterials for Therapeutic Applications
Abstract
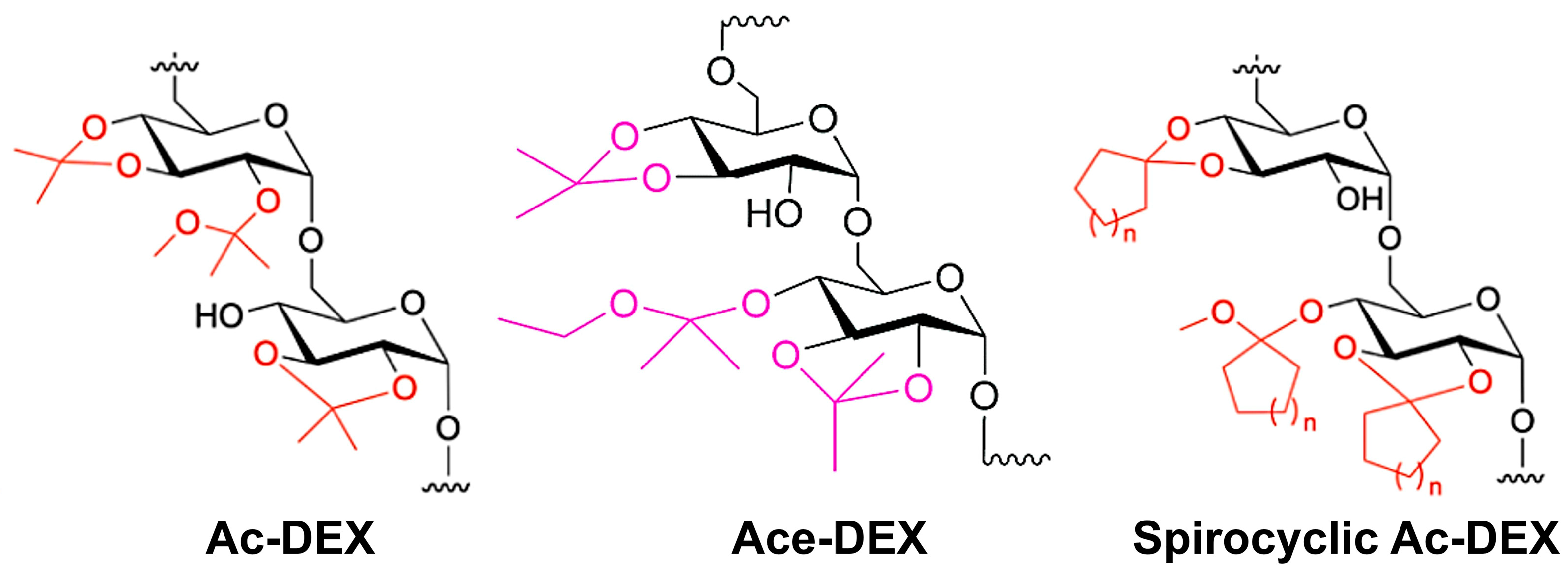
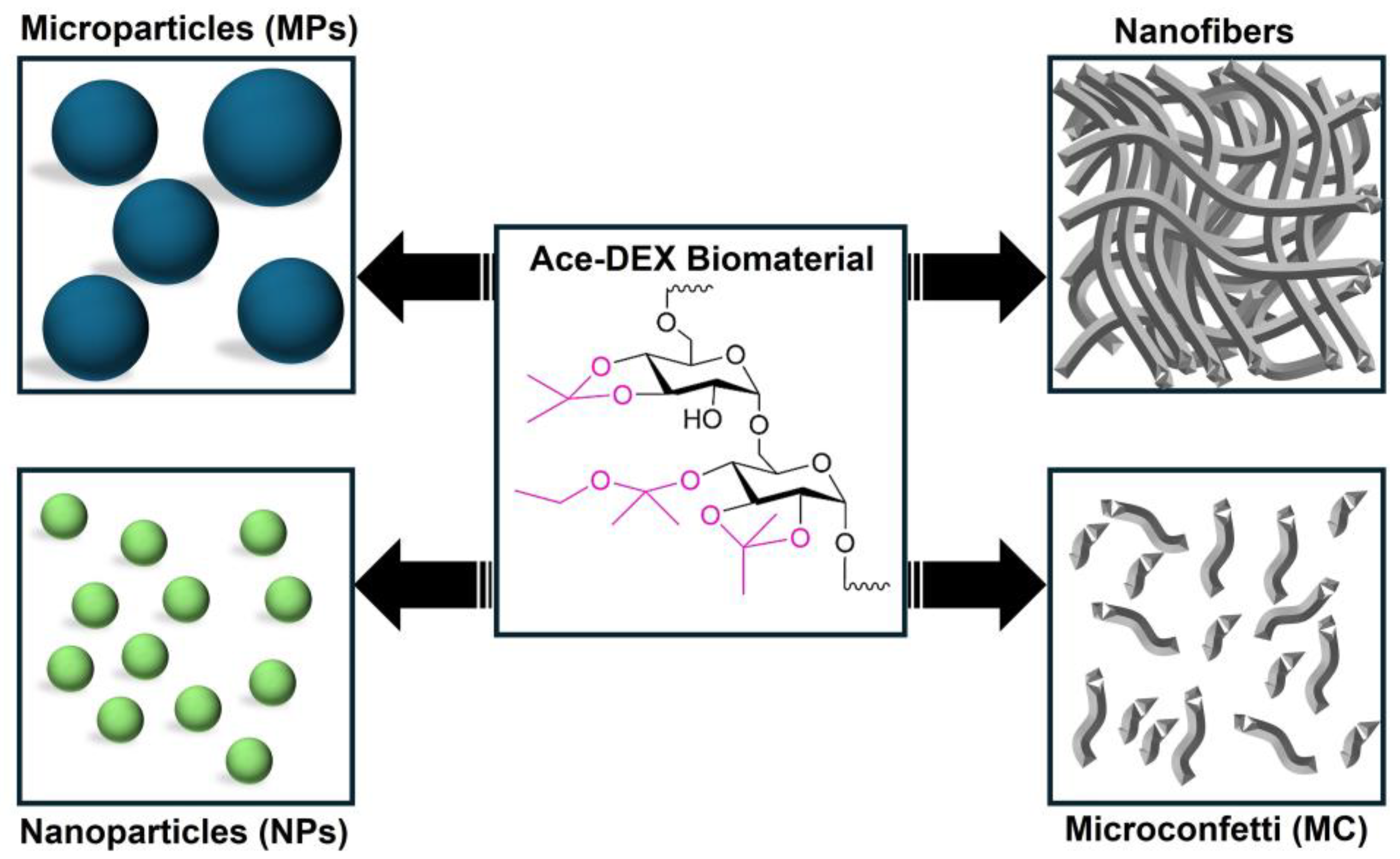
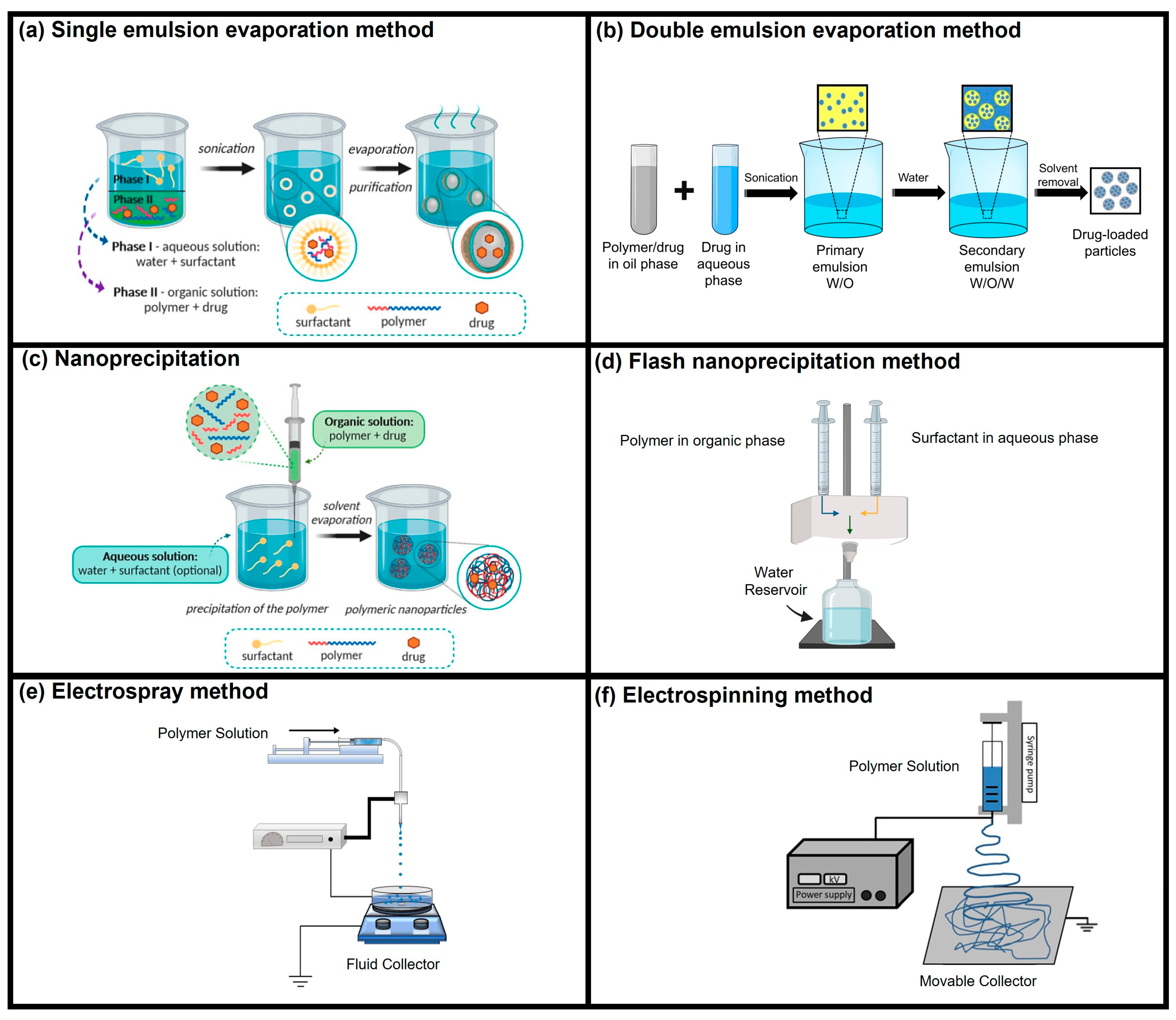
1. Introduction
2. Drug Delivery
2.1. Infectious Disease Treatment
2.2. Cancer Chemotherapy
2.3. Inflammatory Disease Treatment
2.4. HIV-Related Illnesses Treatment
3. Vaccines
3.1. Influenza Vaccines
3.2. Vaccine for Vector-Borne Diseases
3.3. Tolerogenic Vaccines
3.4. Universal SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines
4. Cancer Immunotherapy
5. Tissue Engineering
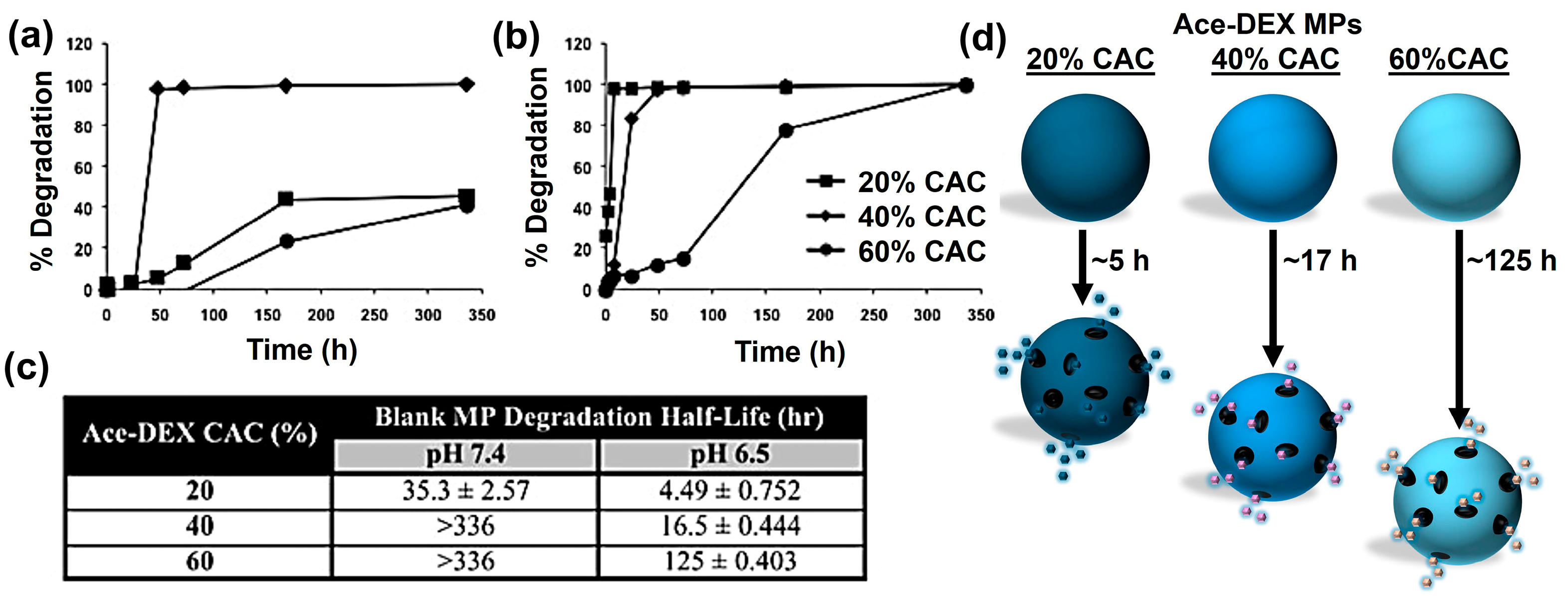
6. Current Limitations
7. Conclusions and Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bachelder, E.M.; Beaudette, T.T.; Broaders, K.E.; Dashe, J.; Fréchet, J.M. Acetal-derivatized dextran: An acid-responsive biodegradable material for therapeutic applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10494–10495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachelder, E.M.; Pino, E.N.; Ainslie, K.M. Acetalated Dextran: A Tunable and Acid-Labile Biopolymer with Facile Synthesis and a Range of Applications. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 1915–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gannimani, R.; Walvekar, P.; Naidu, V.R.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Govender, T. Acetal containing polymers as pH-responsive nano-drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2020, 328, 736–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broaders, K.E.; Cohen, J.A.; Beaudette, T.T.; Bachelder, E.M.; Fréchet, J.M. Acetalated dextran is a chemically and biologically tunable material for particulate immunotherapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5497–5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauffman, K.J.; Do, C.; Sharma, S.; Gallovic, M.D.; Bachelder, E.M.; Ainslie, K.M. Synthesis and characterization of acetalated dextran polymer and microparticles with ethanol as a degradation product. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 4149–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ghassemi, A.H.; Hennink, W.E.; Schwendeman, S.P. The microclimate pH in poly(D, L-lactide-co-hydroxymethyl glycolide) microspheres during biodegradation. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 7584–7593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Pack, D.W.; Klibanov, A.M.; Langer, R. Visual evidence of acidic environment within degrading poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) microspheres. Pharm Res. 2000, 17, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobio, M.; Alonso, M.J. Study of the Inactivation Process of the Tetanus Toxoid in Contact with Poly(lactic/glycolic acid) Degrading Microspheres. STPPharma Sci. 1998, 8, 303–310. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Fontana, F.; Shahbazi, M.A.; Santos, H.A. Acetalated dextran based nano-and microparticles: Synthesis, fabrication, and therapeutic applications. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 4212–4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.M.; Graham-Gurysh, E.G.; Bomba, H.N.; Murthy, A.B.; Bachelder, E.M.; Hingtgen, S.D.; Ainslie, K.M. Impact of composite scaffold degradation rate on neural stem cell persistence in the glioblastoma surgical resection cavity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 111, 110846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham-Gurysh, E.; Moore, K.M.; Satterlee, A.B.; Sheets, K.T.; Lin, F.C.; Bachelder, E.M.; Miller, C.R.; Hingtgen, S.D.; Ainslie, K.M. Sustained delivery of doxorubicin via acetalated dextran scaffold prevents glioblastoma recurrence after surgical resection. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collier, M.A.; Peine, K.J.; Gautam, S.; Oghumu, S.; Varikuti, S.; Borteh, H.; Papenfuss, T.L.; Sataoskar, A.R.; Bachelder, E.M.; Ainslie, K.M. Host-mediated Leishmania donovani treatment using AR-12 encapsulated in acetalated dextran microparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 499, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, K.V.; Borteh, H.M.; Rajaram, M.V.; Peine, K.J.; Curry, H.; Collier, M.A.; Homsy, M.L.; Bachelder, E.M.; Gunn, J.S.; Schlesinger, L.S.; et al. Acetalated dextran encapsulated AR-12 as a host-directed therapy to control Salmonella infection. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 477, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, K.V.; Curry, H.; Collier, M.A.; Borteh, H.; Bachelder, E.M.; Schlesinger, L.S.; Gunn, J.S.; Ainslie, K.M. Needle-free delivery of acetalated dextran-encapsulated AR-12 protects mice from Francisella tularensis lethal challenge. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 2052–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, L.; Feng, J.; Zhou, Z.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, L. Collagenase-loaded pH-sensitive nanocarriers efficiently remodeled tumor stroma matrixes and improved the enrichment of nanomedicines. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 9402–9414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham-Gurysh, E.G.; Moore, K.M.; Schorzman, A.N.; Lee, T.; Zamboni, W.C.; Hingtgen, S.D.; Bachelder, E.M.; Ainslie, K.M. Tumor responsive and tunable polymeric platform for optimized delivery of paclitaxel to treat glioblastoma. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 19345–19356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham-Gurysh, E.G.; Murthy, A.B.; Moore, K.M.; Hingtgen, S.D.; Bachelder, E.M.; Ainslie, K.M. Synergistic drug combinations for a precision medicine approach to interstitial glioblastoma therapy. J. Control. Release 2020, 323, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnke, M.; Klemm, P.; Dahlke, P.; Shkodra, B.; Beringer-Siemers, B.; Czaplewska, J.A.; Stumpf, S.; Jordan, P.M.; Schubert, S.; Hoeppener, S.; et al. Ethoxy acetalated dextran nanoparticles for drug delivery: A comparative study of formulation methods. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 5, 100173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretzer, C.; Shkodra, B.; Klemm, P.; Jordan, P.M.; Schröder, D.; Cinar, G.; Vollrath, A.; Schubert, S.; Nischang, I.; Hoeppener, S.; et al. Ethoxy acetalated dextran-based nanocarriers accomplish efficient inhibition of leukotriene formation by a novel FLAP antagonist in human leukocytes and blood. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, M.A.; Gallovic, M.D.; Bachelder, E.M.; Sykes, C.D.; Kashuba, A.; Ainslie, K.M. Saquinavir Loaded Acetalated Dextran Microconfetti—A Long Acting Protease Inhibitor Injectable. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 1998–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, S.R.; Middleton, D.; Lukesh, N.R.; Islam, M.J.; Bachelder, E.M.; Ainslie, K.M. Microparticles incorporating dual apoptotic factors to inhibit anti-inflammatory effects in macrophages. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batty, C.J.; Amouzougan, E.A.; Carlock, M.A.; Ross, T.M.; Bachelder, E.M.; Ainslie, K.M. Sustained delivery of CpG oligodeoxynucleotide by acetalated dextran microparticles augments effector response to Computationally Optimized Broadly Reactive Antigen (COBRA) influenza hemagglutinin. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 630, 122429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junkins, R.D.; Gallovic, M.D.; Johnson, B.M.; Collier, M.A.; Watkins-Schulz, R.; Cheng, N.; David, C.N.; McGee, C.E.; Sempowski, G.D.; Shterev, I.; et al. A robust microparticle platform for a STING-targeted adjuvant that enhances both humoral and cellular immunity during vaccination. J. Control. Release 2018, 270, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Gallovic, M.D.; Tiet, P.; Ting, J.P.Y.; Ainslie, K.M.; Bachelder, E.M. Investigation of tunable acetalated dextran microparticle platform to optimize M2e-based influenza vaccine efficacy. J. Control. Release 2018, 289, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendy, D.A.; Johnson-Weaver, B.T.; Batty, C.J.; Bachelder, E.M.; Abraham, S.N.; Staats, H.F.; Ainslie, K.M. Delivery of small molecule mast cell activators for West Nile Virus vaccination using acetalated dextran microparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 634, 122658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiepel, R.T.; Batty, C.J.; MacRaild, C.A.; Norton, R.S.; Bachelder, E.; Ainslie, K.M. Merozoite surface protein 2 adsorbed onto acetalated dextran microparticles for malaria vaccination. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 593, 120168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Peine, K.J.; Collier, M.A.; Gautam, S.; Jablonski, K.A.; Guerau-de-Arellano, M.; Ainslie, K.M.; Bachelder, E.M. Co-Delivery of Disease Associated Peptide and Rapamycin via Acetalated Dextran Microparticles for Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis. Adv. Biosyst. 2017, 1, 1700022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, C.; Jia, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zeng, W.; Huang, X.; et al. Developing Next-Generation Protein-Based Vaccines Using High-Affinity Glycan Ligand-Decorated Glyconanoparticles. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2204598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borteh, H.M.; Gallovic, M.D.; Sharma, S.; Peine, K.J.; Miao, S.; Brackman, D.J.; Gregg, K.; Xu, Y.; Guo, X.; Guan, J.; et al. Electrospun acetalated dextran scaffolds for temporal release of therapeutics. Langmuir 2013, 29, 7957–7965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Johnson, M.M.; Collier, M.A.; Gallovic, M.D.; Bachelder, E.M.; Ainslie, K.M. Tunable degradation of acetalated dextran microparticles enables controlled vaccine adjuvant and antigen delivery to modulate adaptive immune responses. J. Control. Release 2018, 273, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.M.; Collier, M.A.; Hoang, K.V.; Pino, E.N.; Graham-Gurysh, E.G.; Gallovic, M.D.; Zahid, M.S.H.; Chen, N.; Schlesinger, L.; Gunn, J.S.; et al. In vivo and cellular trafficking of acetalated dextran microparticles for delivery of a host-directed therapy for Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi infection. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 5336–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, K.A.; Misra, B.; Maghareh, M.; Samart, P.; Nguyen, E.; Hussain, S.; Geldenhuys, W.J.; Bobbala, S. Flash nanoprecipitation allows easy fabrication of pH-responsive acetalated dextran nanoparticles for intracellular release of payloads. Discov. Nano 2024, 19, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielińska, A.; Carreiró, F.; Oliveira, A.M.; Neves, A.; Pires, B.; Venkatesh, D.N.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Eder, P.; Silva, A.M.; et al. Polymeric Nanoparticles: Production, Characterization, Toxicology and Ecotoxicology. Molecules 2020, 25, 3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Huang, C.; Yue, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, P.; Wu, A.; Chen, C.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, C. Application advance of electrosprayed micro/nanoparticles based on natural or synthetic polymers for drug delivery system. Mater. Des. 2022, 220, 110850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luraghi, A.; Peri, F.; Moroni, L. Electrospinning for drug delivery applications: A review. J. Control. Release 2021, 334, 463–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Zafar, N.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. Double emulsion solvent evaporation techniques used for drug encapsulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 496, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, J.H.; Kulp, S.K.; Chen, C.S.; Chiu, H.C. Sensitization of intracellular Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium to aminoglycosides in vitro and in vivo by a host-targeted antimicrobial agent. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 7375–7382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peine, K.J.; Bachelder, E.M.; Vangundy, Z.; Papenfuss, T.; Brackman, D.J.; Gallovic, M.D.; Schully, K.; Pesce, J.; Keane-Myers, A.; Ainslie, K.M. Efficient Delivery of the Toll-like Receptor Agonists Polyinosinic: Polycytidylic Acid and CpG to Macrophages by Acetalated Dextran Microparticles. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 2849–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanthamneni, N.; Sharma, S.; Meenach, S.A.; Billet, B.; Zhao, J.C.; Bachelder, E.M.; Ainslie, K.M. Enhanced stability of horseradish peroxidase encapsulated in acetalated dextran microparticles stored outside cold chain conditions. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 431, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passerini, N.; Craig, D.Q.M. An investigation into the effects of residual water on the glass transition temperature of polylactide microspheres using modulated temperature DSC. J. Control. Release 2001, 73, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.; Kumar, V.; Ratner, B.D. Generation of porous microcellular 85/15 poly (DL-lactide-co-glycolide) foams for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 2611–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batty, C.J.; Pena, E.S.; Amouzougan, E.A.; Moore, K.M.; Ainslie, K.M.; Bachelder, E.M. Humoral response to the acetalated dextran M2e vaccine is enhanced by antigen surface conjugation. Bioconj. Chem. 2023, 34, 1447–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, J.D.; Ross, T.M. Bivalent H1 and H3 cobra recombinant hemagglutinin vaccines elicit seroprotective antibodies against H1n1 and H3n2 influenza viruses from 2009 to 2019. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0165221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sautto, G.A.; Kirchenbaum, G.A.; Abreu, R.B.; Ecker, J.W.; Pierce, S.R.; Kleanthous, H.; Ross, T.M. A computationally optimized broadly reactive antigen subtype-specific influenza vaccine strategy elicits unique potent broadly neutralizing antibodies against hemagglutinin. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varma, D.M.; Batty, C.J.; Stiepel, R.T.; Graham-Gurysh, E.G.; Roque, J.A., III; Pena, E.S.; Hasan Zahid, M.S.; Qiu, K.; Anselmo, A.; Hill, D.B.; et al. Development of an intranasal gel for the delivery of a broadly acting subunit influenza vaccine. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Shi, H.; Hendy, D.A.; Bachelder, E.M.; Ainslie, K.M.; Ross, T.M. Multi-COBRA hemagglutinin formulated with cGAMP microparticles elicit protective immune responses against influenza viruses. mSphere 2024, 9, e00160-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batty, C.J.; Lifshits, L.M.; Hendy, D.A.; Eckshtain-Levi, M.; Ontiveros-Padilla, L.A.; Carlock, M.A.; Ross, T.M.; Bachelder, E.M.; Ainslie, K.M. Vinyl sulfone-functionalized acetalated dextran microparticles as a subunit broadly acting influenza vaccine. AAPS J. 2023, 25, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, M.A.; Junkins, R.D.; Gallovic, M.D.; Johnson, B.M.; Johnson, M.M.; Macintyre, A.N.; Sempowski, G.D.; Bachelder, E.M.; Ting, J.P.Y.; Ainslie, K.M. Acetalated dextran microparticles for codelivery of STING and TLR7/8 agonists. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 4933–4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, E.S.; Batty, C.J.; Hendy, D.A.; Yang, S.; Ontiveros-Padilla, L.; Stiepel, R.T.; Ting, J.P.Y.; Ainslie, K.M.; Bachelder, E.M. Comparative study of acetalated-dextran microparticle fabrication methods for a clinically translatable subunit-based influenza vaccine. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 652, 123836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Kroger, C.J.; Tisch, R.M.; Bachelder, E.M.; Ainslie, K.M. Prevention of type 1 diabetes with acetalated dextran microparticles containing rapamycin and pancreatic peptide P31. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1800341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.M.; Batty, C.J.; Stiepel, R.T.; Genito, C.J.; Bachelder, E.M.; Ainslie, K.M. Injectable, ribbon-like microconfetti biopolymer platform for vaccine applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 38950–38961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Xie, B.; Wang, Q.; Yang, R.; Sun, J.; Hu, C.; Liu, S.; Tao, Y.; Xiao, D. New insights into immune cells in cancer immunotherapy: From epigenetic modification, metabolic modulation to cell communication. MedComm 2024, 5, e551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagher, O.K.; Schwab, R.D.; Brookens, S.K.; Posey, A.D. Advances in cancer immunotherapies. Cell 2023, 186, 1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins-Schulz, R.; Tiet, P.; Gallovic, M.D.; Junkins, R.D.; Batty, C.; Bachelder, E.M.; Ainslie, K.M.; Ting, J.P. A microparticle platform for STING-targeted immunotherapy enhances natural killer cell-and CD8+ T cell-mediated anti-tumor immunity. Biomaterials 2019, 205, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lins, L.C.; Wianny, F.; Livi, S.; Hidalgo, I.A.; Dehay, C.; Duchet-Rumeau, J.; Gerard, J.F. Development of bioresorbable hydrophilic-hydrophobic electrospun scaffolds for neural tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 3172–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Pan, Y.; Liu, R.; Luo, X.; Zeng, X.; Zhi, D.; Li, J.; Cheng, Q.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, H.; et al. Biocompatibility and biodegradation properties of polycaprolactone/polydioxanone composite scaffolds prepared by blend or co-electrospinning. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2019, 34, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Xiao, Z.; Long, H.; Ma, K.; Zhang, J.; Ren, X.; Zhang, J. Assessment of the characteristics and biocompatibility of gelatin sponge scaffolds prepared by various crosslinking methods. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghuman, H.; Mauney, C.; Donnelly, J.; Massensini, A.R.; Badylak, S.F.; Modo, M. Biodegradation of ECM hydrogel promotes endogenous brain tissue restoration in a rat model of stroke. Acta Biomater. 2018, 80, 66–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Rudym, D.D.; Walsh, A.; Abrahamsen, L.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.S.; Kirker-Head, C.; Kaplan, D.L. In vivo degradation of three-dimensional silk fibroin scaffolds. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 3415–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
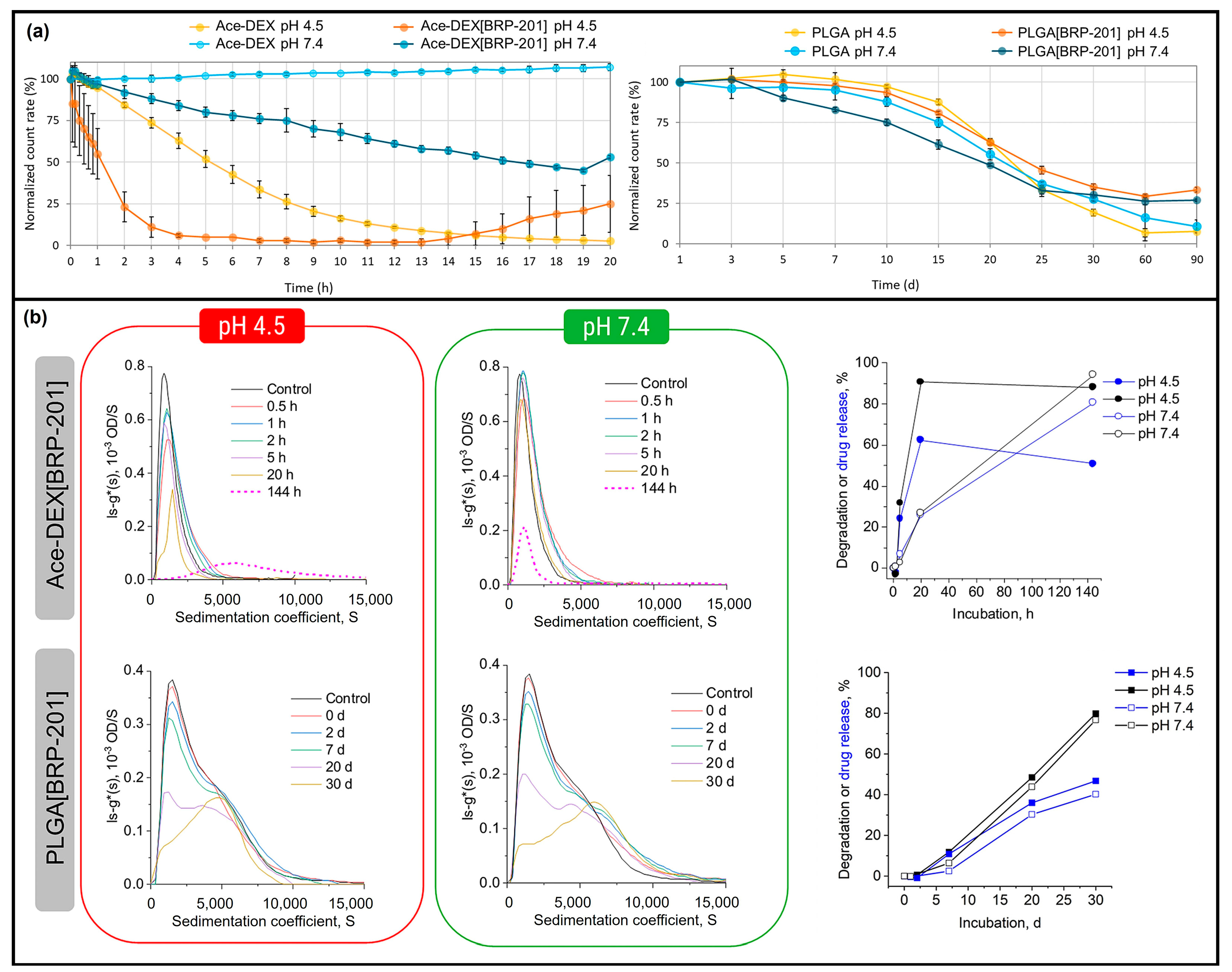
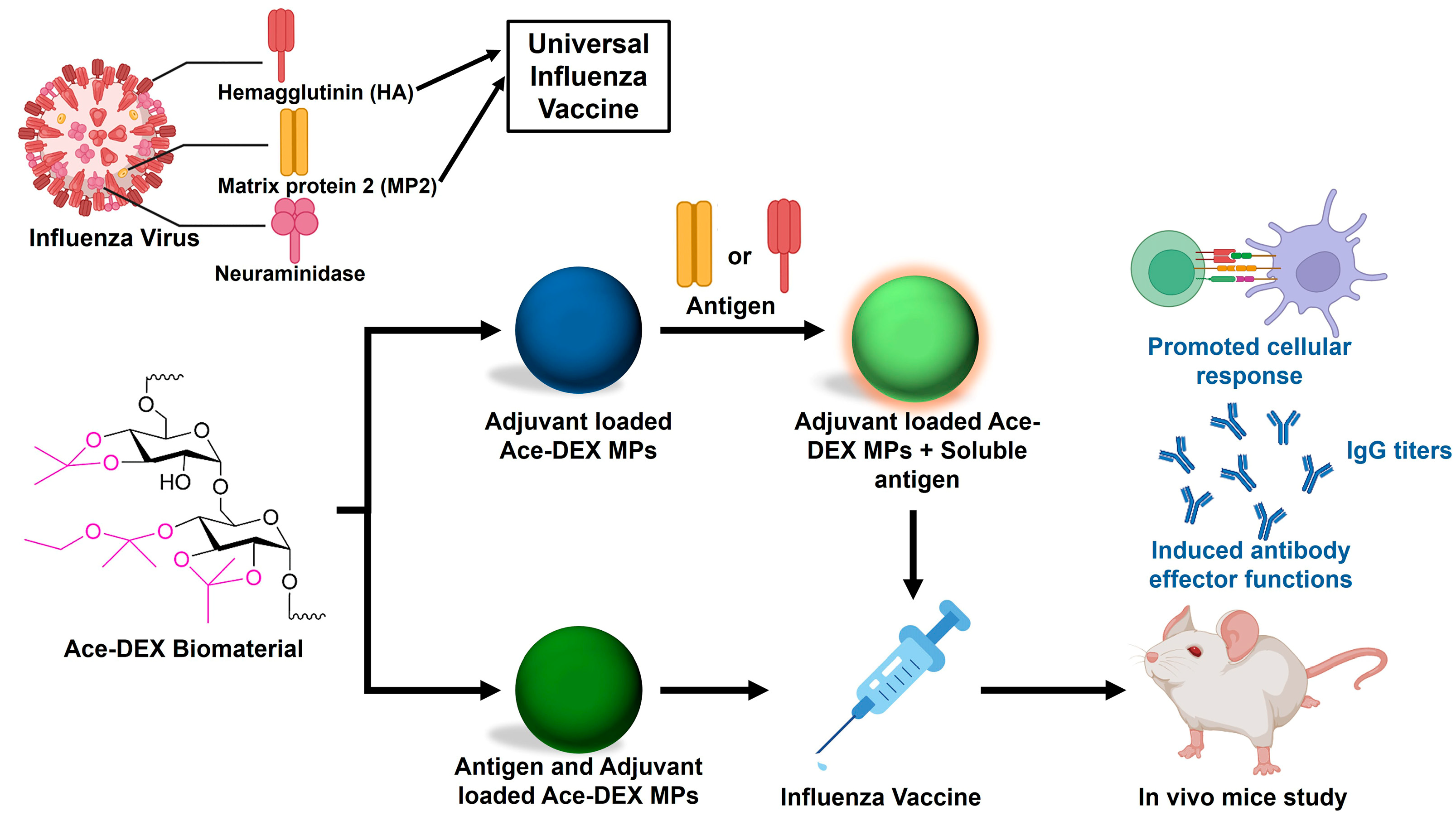
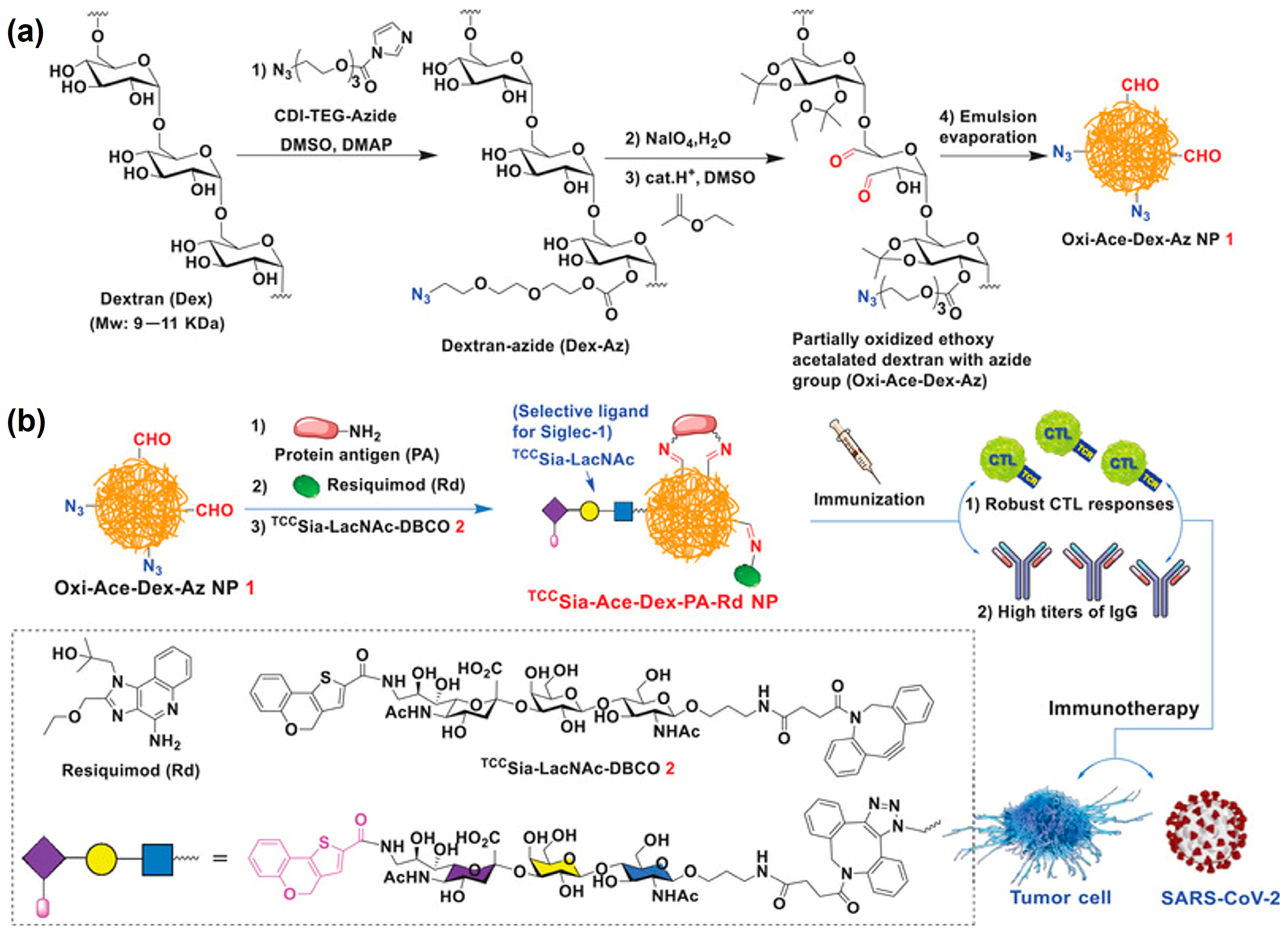
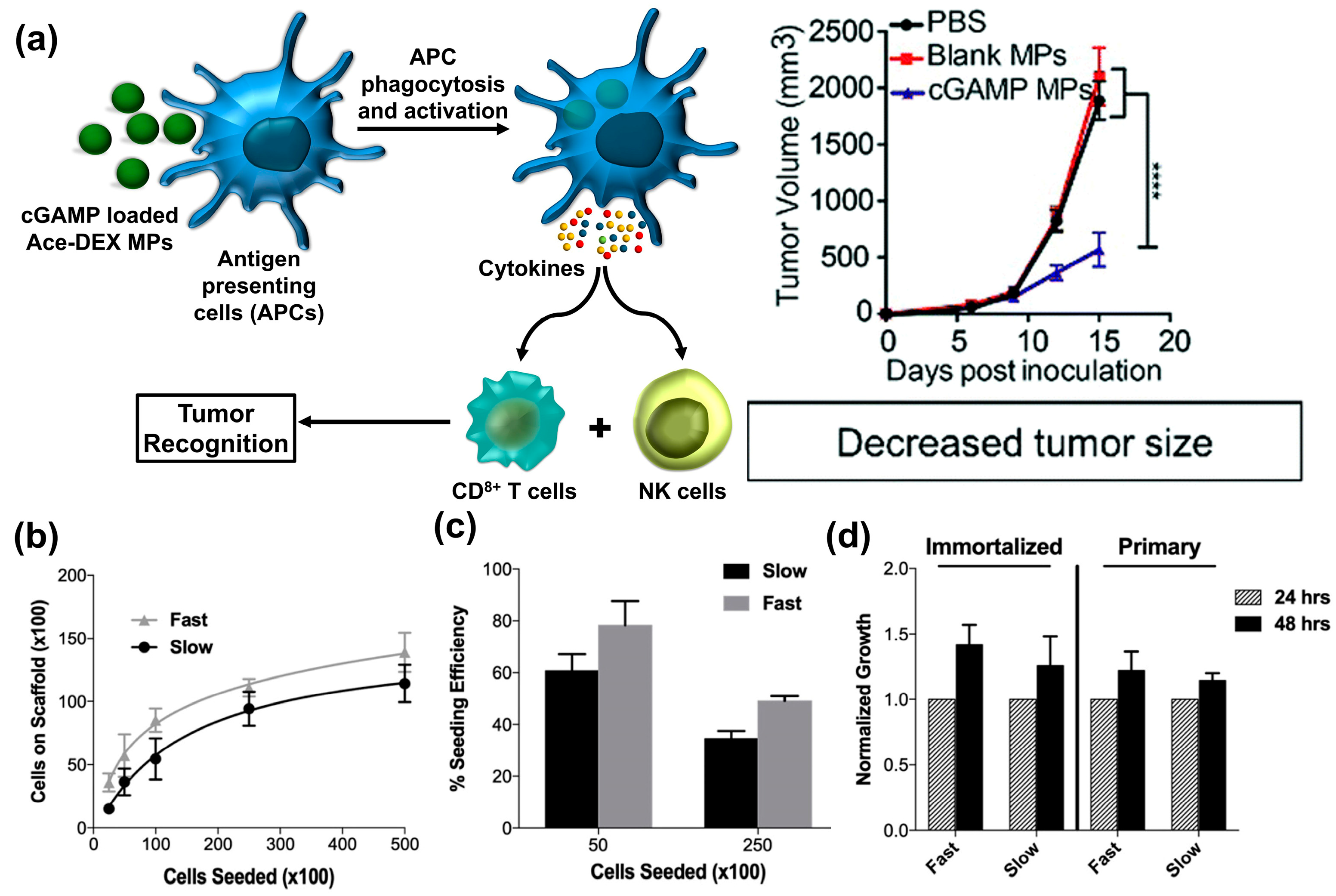
| Drug/Load | Ace-DEX Carrier | Fabrication Method | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gelatin | Nanofiber | Electrospinning | Tissue engineering | [10] |
| Doxorubicin | Nanofiber | Electrospinning | Glioblastoma interstitial therapy | [11] |
| AR-12 | Microparticles | Emulsion solvent evaporation | Treatment for visceral leishmaniasis | [12] |
| AR-12 | Microparticles | Emulsion solvent evaporation | Treatment for Salmonella infection | [13] |
| AR-12 and gentamicin | Microparticles | Emulsion solvent evaporation | Treatment for Francisella infection (rabbit fever) | [14] |
| Collagenase | Nanoparticles | Emulsion solvent evaporation | Cancer treatment | [15] |
| Paclitaxel | Nanofiber | Electrospinning | Glioblastoma interstitial therapy | [16] |
| Paclitaxel and Everolimus | Nanofiber | Electrospinning | Glioblastoma interstitial therapy | [17] |
| BRP-187 | Nanoparticles | Emulsion solvent evaporation, microfluidics and nanoprecipitation | Anti-inflammatory | [18] |
| BRP-201 | Nanoparticles | Nanoprecipitation | Inhibition of leukotriene formation | [19] |
| Saquinavir | Microconfetti | Electrospinning | HIV treatment | [20] |
| Phosphatidylserine (PS) | Microparticles | Emulsion solvent evaporation | Cancer immunotherapy | [21] |
| Cytosine–phosphate–guanine (CpG) | Microparticles | Electrospray | Influenza vaccine | [22] |
| Cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate cGAMP | Microparticles | Electrospray | Influenza vaccine | [23] |
| Matrix protein 2 (M2e) and cGAMP | Microparticles | Emulsion solvent evaporation | Influenza vaccine | [24] |
| MCA ST101036, R529877, ST048871, and ST027688 | Microparticles | Nanoprecipitation | West Nile Virus (WNV) vaccine | [25] |
| Merozoite surface protein 2 (MSP2) | Microparticles | Electrospray | Malaria Vaccine | [26] |
| Rapamycin and Ovalbumin | Microparticles | Double emulsion method | Multiple sclerosis (encephalomyelitis) vaccine | [27] |
| Resiquimod | Microparticles | Emulsion and evaporation | SARS-CoV-2 vaccines | [28] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Damus, B.J.; Amaeze, N.R.; Yoo, E.; Kaur, G. Ethoxy Acetalated Dextran-Based Biomaterials for Therapeutic Applications. Polymers 2024, 16, 2756. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16192756
Damus BJ, Amaeze NR, Yoo E, Kaur G. Ethoxy Acetalated Dextran-Based Biomaterials for Therapeutic Applications. Polymers. 2024; 16(19):2756. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16192756
Chicago/Turabian StyleDamus, Branden Joshua, Nzube Ruth Amaeze, Eunsoo Yoo, and Gagandeep Kaur. 2024. "Ethoxy Acetalated Dextran-Based Biomaterials for Therapeutic Applications" Polymers 16, no. 19: 2756. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16192756
APA StyleDamus, B. J., Amaeze, N. R., Yoo, E., & Kaur, G. (2024). Ethoxy Acetalated Dextran-Based Biomaterials for Therapeutic Applications. Polymers, 16(19), 2756. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16192756







