Characteristics and Models of Moisture Uptake in Fiber-Reinforced Composites: A Topical Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
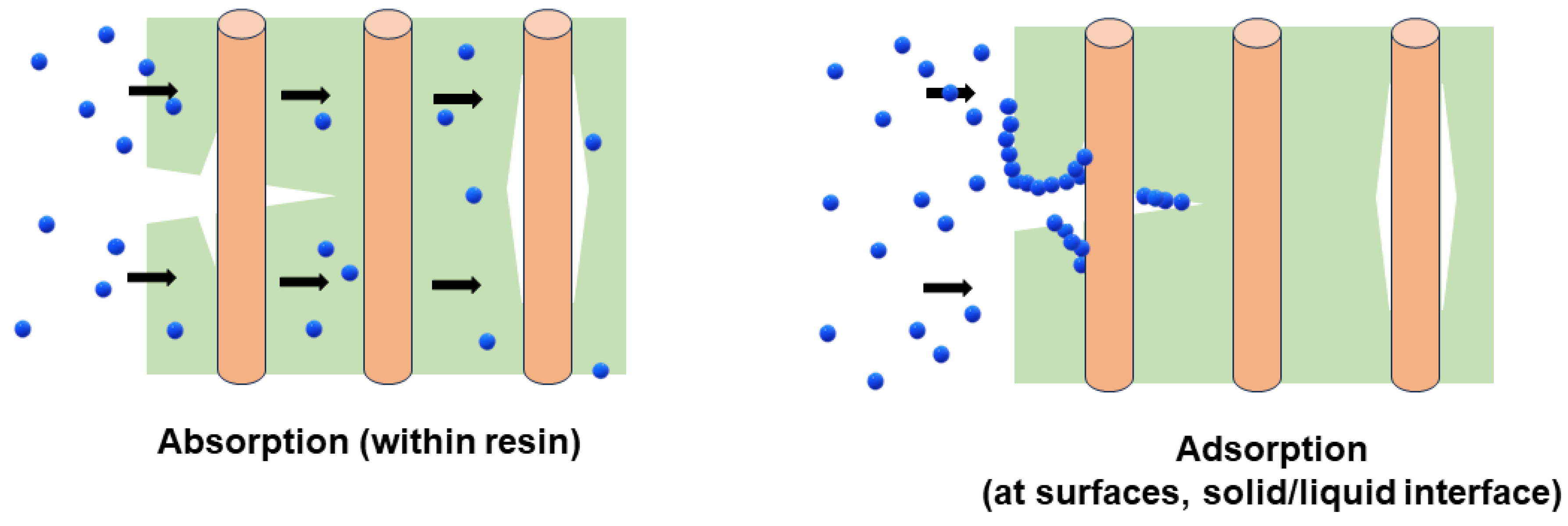
2. Mechanisms and Characteristics Due to Moisture Uptake
3. Moisture Uptake
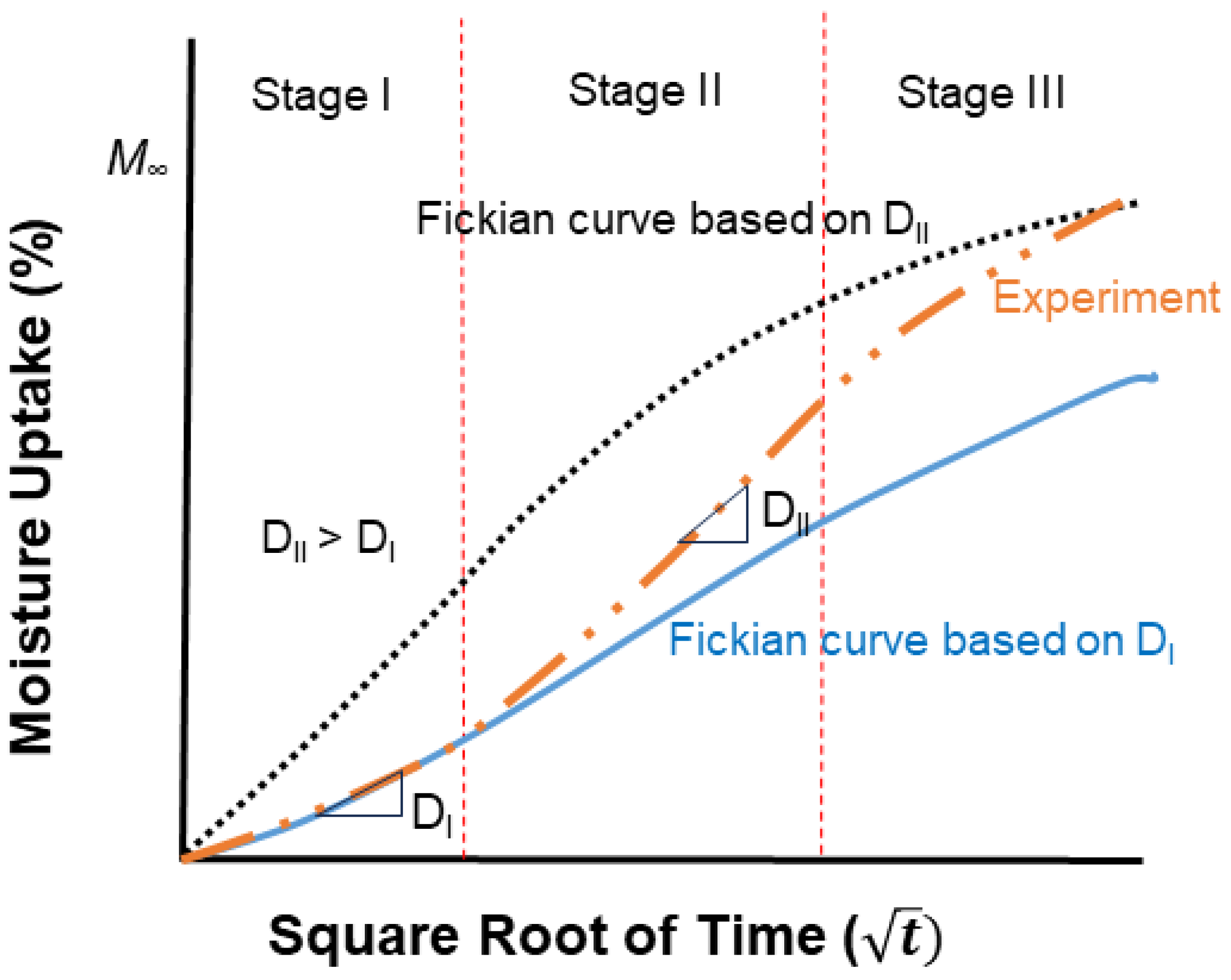
4. Moisture Uptake and Diffusion
5. Diffusion Models
- Case 1: Df = 0 and α = 0
- Case 2: Df = 0 and β = 0
- Case 3: Df = 0 and γ = 0
6. Conclusions
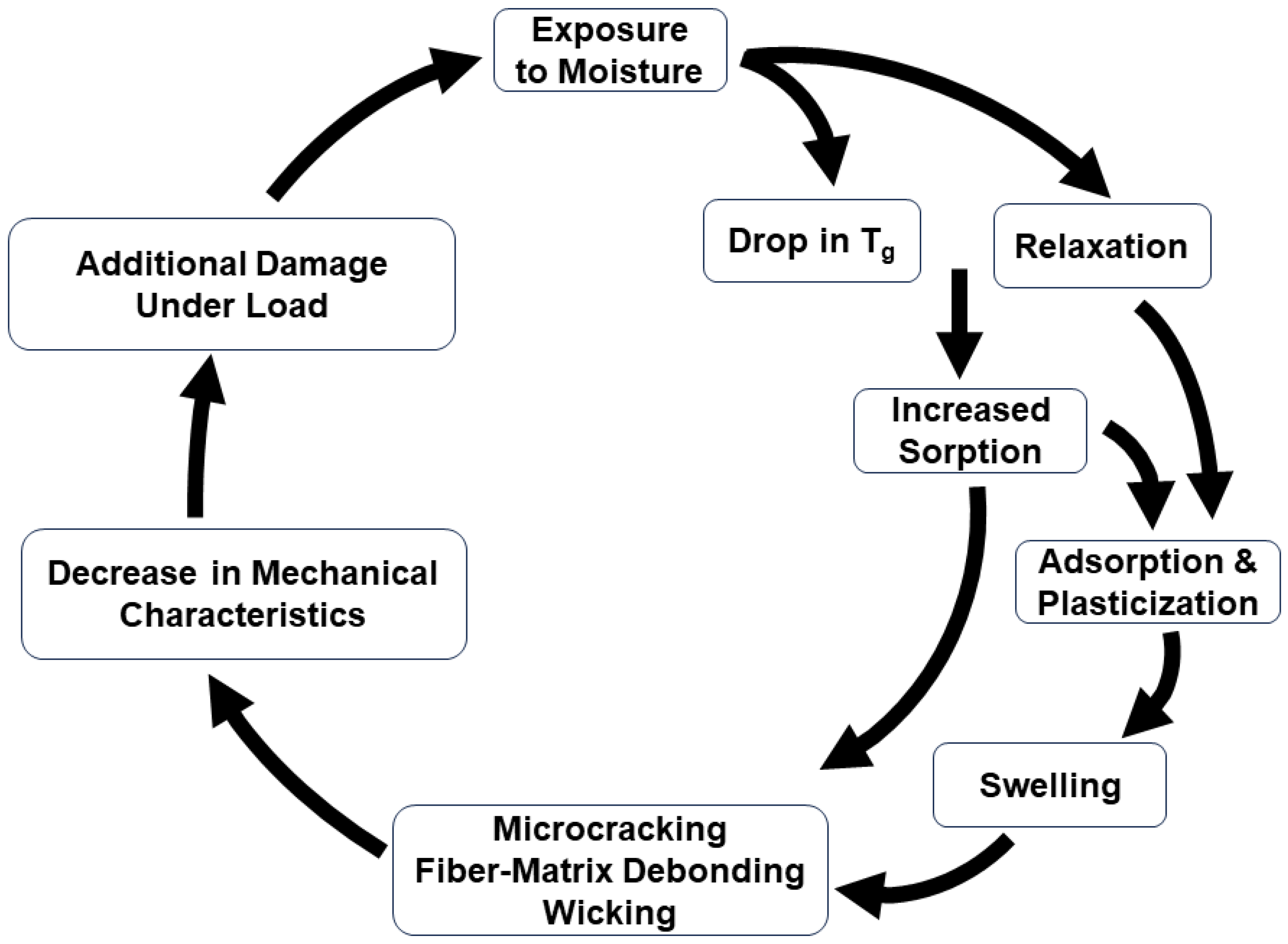
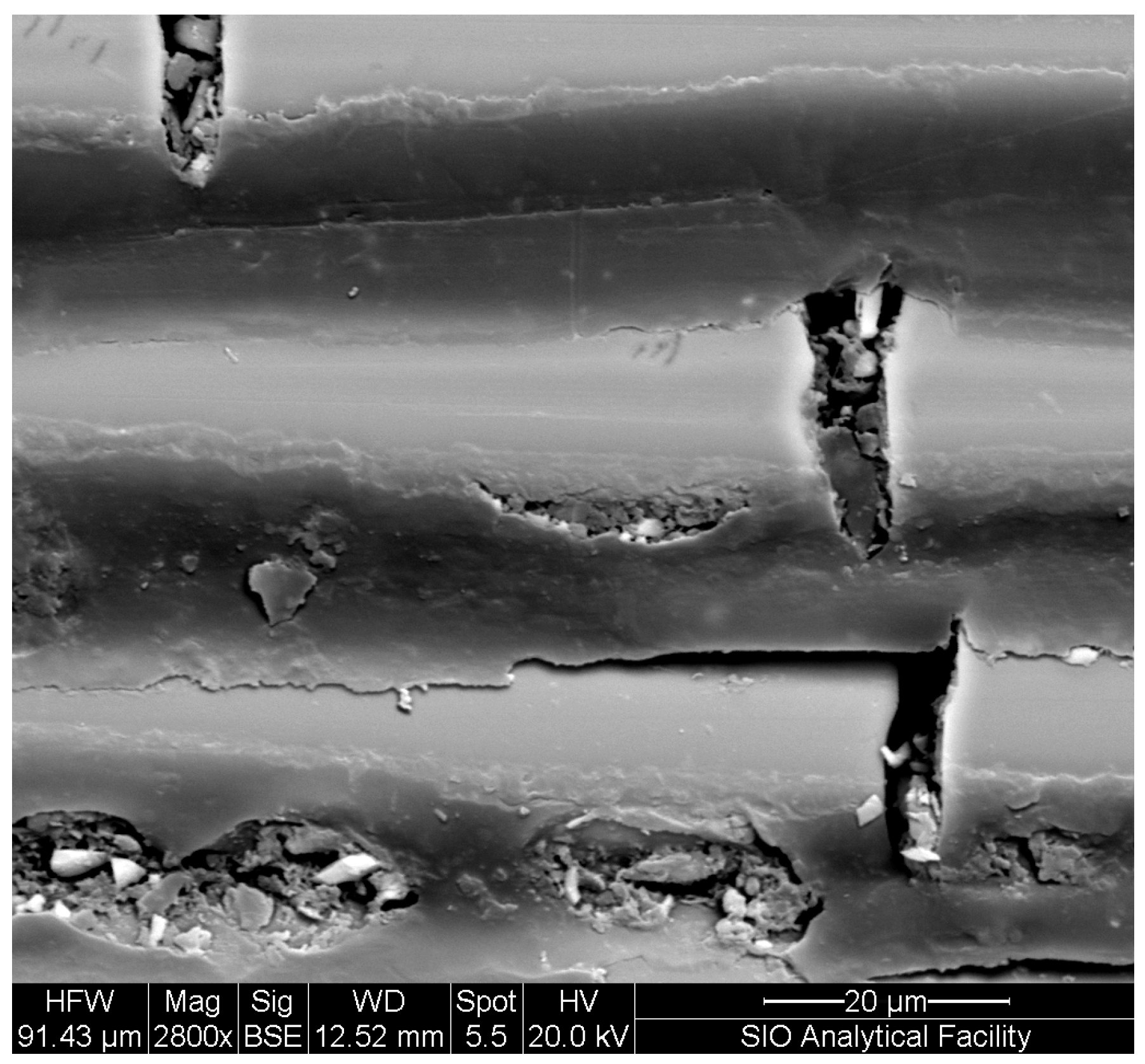
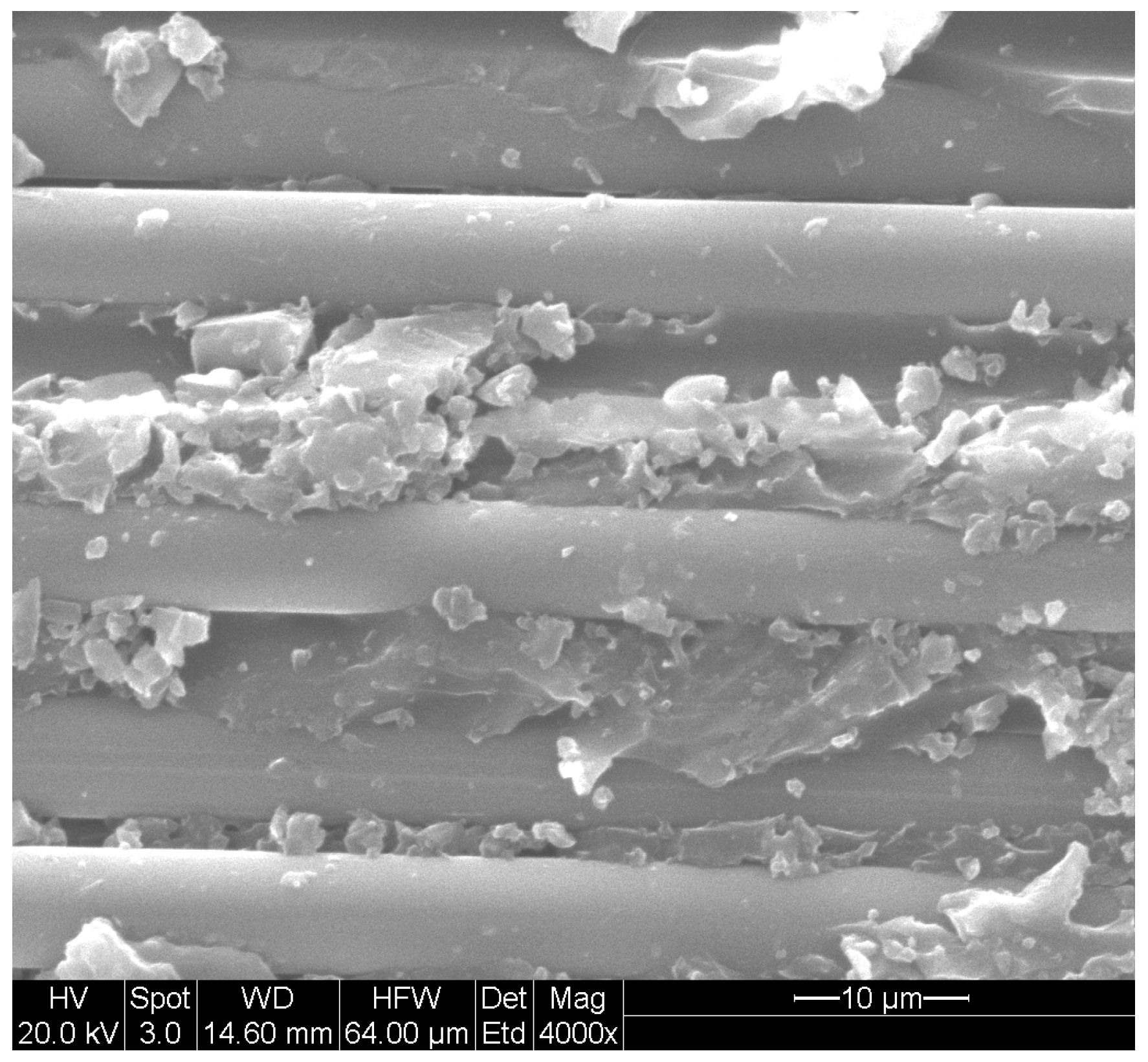
- Transport of moisture into a polymer composite is affected through a range of mechanisms, including through interaction with the polymer chain itself and sorption into the volume. Rates of transport can be accelerated through damage in the composite in the form of microvoids/microcracks and fiber–matrix debonding. The interactions between the sorbed moisture and the constituents of the FRP composite are complex and can change through the service life of the structure.
- Uptake of solution into a composite can result in a range of reversible and irreversible mechanisms, which are affected by factors such as exposure environments, including temperature, constituent materials, extent of cure progression, and pre-existing damage.
- The effect of humidity levels on moisture uptake is dependent not just on the level of the humidity, but also on the temperature of exposure. Although levels of equivalence are often used between saturated humidity and immersion, the effect of both on the rate of uptake and maximum uptake are significantly different.
- Moisture uptake profiles can range from the extremes of linear to exponential with sigmoidal and stepped profiles in between. These can often be characterized by diffusion coefficients and levels of moisture uptake equilibrium, both of which may have multiple phases based on the mechanics of sorption and the resulting shape of the uptake.
- Both rate coefficients and levels of equilibrium (transition, intermediate, and maximum) are affected by the temperature and humidity of exposure, as well as conditions of immersion. Increases in temperature generically increase rates of uptake through increases in molecular mobility. However, temperature increases, as well as initial exposure to moisture, can accelerate cure progression in FRP composites that have not attained complete polymerization prior to exposure, leading to a competition between phenomena that increase performance while decreasing capacity for sorption and those that increase sorption and deterioration.
- The Fickian diffusion model is most commonly used to describe moisture uptake and assumes that the diffusion coefficient is independent of moisture concentration and of its through thickness location, and that an equilibrium level of moisture uptake is attained which is independent of temperature of humidity exposure/immersion. Research has, however, shown that there are significant deviations from Fickian response, resulting in the development and use of stepped and phased models.
- In considering the appropriate model to describe the uptake response of a FRP composite, it is important to consider mechanisms of change in the constituents, as well as effects of aspects such as concentration at saturation and solvent activity. In this regard, the range of responses can be summarized below.
- -
- Henry’s law, where
- -
- Freundlich’s relation (power law), where
- -
- Fick’s law, where
- -
- Langmuir response, where
- -
- Dual phased sorption, where
- The Langmuir model intrinsically relates changes to the probability of conversion between two states of water, free and bound, and thus captures changes in uptake based on the stage of moisture uptake. This addresses some of the deviations from Fickian response but does not address longer-term effects, such as relaxation.
- Phased and stepped models assume that inherent changes in the material are due to the effects of uptake catalyze/initial additional/new mechanisms as the level of uptake increases, representing the changes through steps/phases.
- While the two-phased Fickian and the two-step (structural modification) models share the basic setup characteristics of dividing uptake into three regimes with the initial being diffusion-dominated and the second being a transition, they differ in the consideration of the third, with the former positing diffusion with a contribution to the first stage through two simultaneous mechanisms of diffusion and the latter considering two distinct mechanisms, initially a faster diffusion-dominated regime, and then a slower relaxation/deterioration-dominated regime. The two-step models are thus able to better capture response when there is apparent mass loss due to leaching of lower-molecular-weight species and/or constituents of the FRP composites.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gkikas, G.; Douka, D.D.; Barkoula, N.M.; Paipetis, A.S. Nano-enhanced composite materials under thermal shock and environmental degradation: A durability study. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 70, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machello, C.; Bazli, M.; Rajabipour, A.; Rad, H.M.; Arashpour, M.; Hadigheh, A. Using machine learning to predict the long-term performance of fibre-reinforced polymer structures: A state-of-the-art review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 408, 133692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.Q.; Liu, X.; Feng, P. A comprehensive review on mechanical properties of pultruded FRP composites subjected to long-term environmental effects. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 191, 107958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatar, J.; Milev, S. Durability of externally bonded fiber-reinforced polymer composites in concrete structures: A critical review. Polymers 2021, 13, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsuhaibani, E.; Yazdani, N.; Beneberu, E. Durability and long-term performance prediction of carbon fiber reinforced polymer laminates. Polymers 2022, 14, 3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airale, A.G.; Carello, M.; Ferraris, A.; Sisca, L. Moisture effect on mechanical properties of polymeric composite materials. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Naples, Italy, 2016; Volume 1736, p. 020020. [Google Scholar]
- Khotbehsara, M.M.; Manalo, A.; Aravinthan, T.; Ferdous, W.; Nguyen, K.T.Q.; Hota, G. Ageing of particulate-filled epoxy resin under hygrothermal conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 249, 118846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratasyuk, N.A.; Latyshev, A.V.; Zuev, V.V. Water in epoxy coatings: Basic principles of interaction with polymer matrix and the influence on coating life cycle. Coatings 2023, 14, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, B.C. Effects of crosshead velocity and sub-zero temperature on mechanical behaviour of hygrothermally conditioned glass fibre reinforced epoxy composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 379, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meurs, P.F.; Schreurs, P.J.; Peijs, T.; Meijer, H.E. Characterization of interphase conditions in composite materials. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1996, 27, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Selzer, R.; Friedrich, K. Mechanical properties and failure behaviour of carbon fibre-reinforced polymer composites under the influence of moisture. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1997, 28, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubakri, A.; Elleuch, K.; Guermazi, N.; Ayedi, H.F. Investigations on hygrothermal aging of thermoplastic polyurethane material. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 3958–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammatikos, S.A.; Evernden, M.; Mitchels, J.; Zafari, B.; Mottram, J.T.; Papanicolaou, G.C. On the response to hygrothermal aging of pultruded FRPs used in the civil engineering sector. Mater. Des. 2016, 96, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, T.; Sinmazcelik, T. Effects of hydrothermal aging on glass–fiber/polyetherimide (PEI) composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamson, M.J. Thermal expansion and swelling of cured epoxy resin used in graphite/epoxy composite materials. J. Mater. Sci. 1980, 15, 1736–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbhari, V.M.; Xian, G. Hygrothermal effects on high VF pultruded unidirectional carbon/epoxy composites: Moisture uptake. Compos. Part B Eng. 2009, 40, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidou, S.; Papaspyrides, C.D. The effect of hygrothermal history on water sorption and interlaminar shear strength of glass/polyester composites with different interfacial strength. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2003, 34, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, S.; Zhang, T. Moisture diffusion in carbon/epoxy composite and the effect of cyclic hygrothermal fluctuations: Characterization by dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) and interlaminar shear strength (ILSS). J. Adhes. 2008, 84, 585–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, P.; Ramírez, C.; Torres, A.; Abad, M.J.; Cano, J.; López, J.; López-Bueno, I.; Barral, L. Effect of water sorption on the structure and mechanical properties of an epoxy resin system. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 80, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbhari, V.M.; Chin, J.W.; Hunston, D.; Benmokrane, B.; Juska, T.; Morgan, R.; Lesko, J.J.; Sorathia, U.; Reynaud, A.D. Durability gap analysis for fiber-reinforced polymer composites in civil infrastructure. J. Compos. Constr. 2003, 7, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikols, W.J.; Seferis, J.C.; Apicella, A.; Nicolais, L. Evaluation of structural changes in epoxy systems by moisture sorption-desorption and dynamic mechanical studies. Polym. Compos. 1982, 3, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birger, S.; Moshonov, A.; Kenig, S. The effects of thermal and hygrothermal ageing on the failure mechanisms of graphite-fabric epoxy composites subjected to flexural loading. Composites 1989, 20, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.L.; Fanter, D.L.; Summers, C.J. Spectroscopic evidence for mechanochemical effects of moisture in epoxy resins. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1979, 24, 1643–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.L.; Almeida, S.F.; Rezende, M.C. Hygrothermal effects on dynamic mechanical analysis and fracture behavior of polymeric composites. Mater. Res. 2005, 8, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Lucas, J.P. Hygrothermal effects of epoxy resin. Part I: The nature of water in epoxy. Polymer 1999, 40, 5505–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijović, J.; Lin, K.F. The effect of hygrothermal fatigue on physical/mechanical properties and morphology of neat epoxy resin and graphite/epoxy composite. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1985, 30, 2527–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoon, M.K.; Koenig, J.L. The structure and moisture stability of the matrix phase in glass-reinforced epoxy composites. J. Macromol. Sci.—Rev. Macromol. Chem. 1980, 19, 135–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipes, R.B.; Vinson, J.R.; Chou, T.W. On the hygrothermal response of laminated composite systems. J. Compos. Mater. 1976, 10, 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, H.T. Residual stresses in polymer matrix composite laminates. J. Compos. Mater. 1976, 10, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.M.; Correia, J.R.; Cabral-Fonseca, S. Durability of glass fibre reinforced polymer pultruded profiles: Comparison between QUV accelerated exposure and natural weathering in a mediterranean climate. Exp. Tech. 2016, 40, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral-Fonseca, S.; Correia, J.R.; Rodrigues, M.P.; Branco, F.A. Artificial accelerated ageing of GFRP pultruded profiles made of polyester and vinylester resins: Characterisation of physical–chemical and mechanical damage. Strain 2012, 48, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkova, O.; Buschhorn, S.T.; Mannov, E.; Schulte, K.; Aniskevich, A. Water transport in epoxy/MWCNT composites. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 2138–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammatikos, S.A.; Zafari, B.; Evernden, M.C.; Mottram, J.T.; Mitchels, J.M. Moisture uptake characteristics of a pultruded fibre reinforced polymer flat sheet subjected to hot/wet aging. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 121, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutte, C.L. Environmental durability of glass-fiber composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 1994, 13, 265–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, F.R. Durability of reinforced plastics in liquid environments. In Reinforced Plastics Durability, 1st ed.; Pritchard, G., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 1999; Volume 10, Chapter 3; pp. 70–110. [Google Scholar]
- McKague, E.L., Jr.; Reynolds, J.D.; Halkias, J.E. Swelling and glass transition relations for epoxy matrix material in humid environments. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1978, 22, 1643–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, C.A.; Bradley, W.L. Determination of the effect of seawater on the interfacial strength of an interlayer E-glass/graphite/epoxy composite by in situ observation of transverse cracking in an environmental SEM. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1997, 57, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbel, I.; Valentin, D. Hydrothermal effects on the physico-chemical properties of pure and glass fiber reinforced polyester and vinylester resins. Polym. Compos. 1993, 14, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassila, L.V.; Nohrström, T.; Vallittu, P.K. The influence of short-term water storage on the flexural properties of unidirectional glass fiber-reinforced composites. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 2221–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Morgan, R.J. Synergistic thermal-moisture damage mechanisms of epoxies and their carbon fiber composites. J. Compos. Mater. 1993, 27, 1465–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, H.H.; Kohman, G.T. The mechanism of the absorption of water by rubber. J. Phys. Chem. 1927, 31, 23–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.D.; Singh, M.M. The dynamic properties of fibre-reinforced polymers exposed to hot, wet conditions. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1996, 56, 977–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.C.; Peppas, N.A. Water transport in epoxy resins. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1993, 18, 947–961. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, W.W. The effect of diffusion of water into epoxy resins and their carbon-fibre reinforced composites. Composites 1981, 12, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekatou, A.; Faidi, S.E.; Ghidaoui, D.; Lyon, S.B.; Newman, R.C. Effect of water and its activity on transport properties of glass/epoxy particulate composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1997, 28, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunauer, S. Gases and Vapors, The Adsorption of Gases and Vapors—Physical Adsorption; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1943; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Tvardovskiy, A.V. Sorbent Deformation, 1st ed.; Elsevier, Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 13, Chapter 1; pp. 5–28. [Google Scholar]
- Jost, W. Diffusion in solids, liquids, gases. Z. Für Phys. Chem. 1952, 201, 319–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crank, J. The Mathematics of Diffusion, 2nd ed.; Clarendon press: Oxford, UK, 1975; pp. 104–137. [Google Scholar]
- Karbhari, V.M. E-glass/vinylester composites in aqueous environments: Effects on short-beam shear strength. J. Compos. Constr. 2004, 8, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, J.W.; Nguyen, T.; Aouadi, K. Sorption and diffusion of water, salt water, and concrete pore solution in composite matrices. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 71, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clunie, J.S.; Ingram, B.T. Adsorption of nonionic surfactants. In Adsorption from Solution at the Solid/Liquid Interface; Parfitt, G.D., Rochester, C.H., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 105–152. [Google Scholar]
- Brunauer, S.; Skalny, J.; Bodor, E.E. Adsorption on nonporous solids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1969, 30, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagymassy, J., Jr.; Brunauer, S.; Mikhail, R.S. Pore structure analysis by water vapor adsorption: I. t-curves for water vapor. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1969, 29, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkees, F. Moisture absorption behavior and diffusion characteristics of continuous carbon fiber reinforced epoxy composites: A review. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Mater. 2023, 62, 1789–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotugno, S.; Larobina, D.; Mensitieri, G.; Musto, P.; Ragosta, G. A novel spectroscopic approach to investigate transport processes in polymers: The case of water–epoxy system. Polymer 2001, 42, 6431–6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Amerongen, G.J. Diffusion in elastomers. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1964, 37, 1065–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinmüller, C.; Langel, C.; Fornasiero, F.; Radke, C.J.; Prausnitz, J.M. Sorption kinetics and equilibrium uptake for water vapor in soft-contact-lens hydrogels. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2006, 77, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Pacheco, E.; Cauich-Cupul, J.I.; Valadez-González, A.; Herrera-Franco, P.J. Effect of moisture absorption on the mechanical behavior of carbon fiber/epoxy matrix composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 1873–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkley, J.A.; Connell, J.W. Resin system and chemistry: Degradation mechanisms and durability. In Long-Term Durability of Polymeric Matrix Composites, 1st ed.; Pochiraju, K.V., Tandon, G.P., Schoeppner, G.A., Eds.; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Chapter 1; pp. 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Hussnain, S.M.; Shah, S.Z.H.; Megat-Yusoff, P.S.M.; Hussain, M.Z. Degradation and mechanical performance of fibre-reinforced polymer composites under marine environments: A review of recent advancements. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2023, 215, 110452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Lucas, J.P. Hygrothermal effects of epoxy resin. Part II: Variations of glass transition temperature. Polymer 1999, 40, 5513–5522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanpour, B.; Karbhari, V.M. Glass transition temperature as a characteristic of the durability of fiber-reinforced polymer composites. In Aging and Durability of FRP Composites and Nanocomposites; Uthaman, A., Thomas, S., Mayookh Lal, H., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing, Elsevier: London, UK, 2024; Chapter 15; pp. 341–362. [Google Scholar]
- Mercier, J.; Bunsell, A.; Castaing, P.; Renard, J. Characterisation and modelling of aging of composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.-R.; Yee, A.F.; Lee, C.Y.-C. Moisture absorption and hygrothermal aging in a bismaleimide resin. Polymer 2001, 42, 7327–7333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léger, R.; Roy, A.; Grandidier, J.C. Non-classical water diffusion in an industrial adhesive. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2010, 30, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, H.; Koenig, J.L. The reinforcement mechanism of fiber-glass reinforced plastics under wet conditions: A review. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1978, 18, 128–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunker, B.C. Molecular mechanisms for corrosion of silica and silicate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1994, 179, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apicella, A.; Nicolais, L.; De Cataldis, C. Characterization of the morphological fine structure of commercial thermosetting resins through hygrothermal experiments. In Characterization of Polymers in the Solid State I: Part A: NMR and Other Spectroscopic Methods Part B: Mechanical Methods, 1st ed.; Kaush, H.H., Zachman, H.G., Eds.; Advances in Polymer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1985; pp. 189–207. [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita, Y.; Becker, E.; Sakata, S.; Miwa, T.; Sawada, T. States of water absorbed in water-borne urethane/epoxy coatings. Polymer 2014, 55, 2505–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijović, J.; Zhang, H. Molecular dynamics simulation study of motions and interactions of water in a polymer network. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 2557–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissan, A.H. H-bond dissociation in hydrogen bond dominated solids. Macromolecules 1976, 9, 840–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwei, T.K. Strength of epoxy polymers. I. Eff. Chem. Struct. Environ. Cond. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1966, 10, 1647–1655. [Google Scholar]
- Wolff, E.G. Environmental effects—Mass Absorption. In Introduction to the Dimensional Stability of Composite Materials; DEStech Publications: Lancaster, PA, USA, 2004; Chapter 5; pp. 155–200. [Google Scholar]
- Abusafieh, A.; Kalidindi, S.R. Effect of water absorption on the izod impact energy of crosslinked poly (methyl methacrylate-acrylic acid) and their composites. Polym. Compos. 1998, 19, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, M.Y.; Fernandez-Garcia, M. Relation of swelling and Tg depression to the apparent free volume of a particle-filled, epoxy-based adhesive. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 87, 1436–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.F. Properties characterization—Mechanical/physical/hygrothermal properties test methods. In Reference Book for Composites Technology; Lee, S.M., Ed.; Technomic Publishing Company: Lancaster, PA, USA, 1989; Volume 2, Chapter 4; pp. 40–78. [Google Scholar]
- Zimm, B.H.; Lundberg, J.L. Sorption of vapors by high polymers. J. Phys. Chem. 1956, 60, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkweather, H.W., Jr. Clustering of water in polymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Lett. 1963, 1, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Wel, G.K.; Adan, O.C.G. Moisture in organic coatings—A review. Prog. Org. Coat. 1999, 37, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karad, S.K.; Jones, F.R. Mechanisms of moisture absorption by cyanate ester modified epoxy resin matrices: The clustering of water molecules. Polymer 2005, 46, 2732–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delasi, R.; Whiteside, J.B. Effect of moisture on epoxy resins and composites. In ASTM STP 658, Advanced Composite Materials—Environmental Effects; Vinson, J.R., Ed.; American Society for Testing and Materials: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1978; pp. 2–20. [Google Scholar]
- Papanicolaou, G.C.; Kosmidou, T.V.; Vatalis, A.S.; Delides, C.G. Water absorption mechanism and some anomalous effects on the mechanical and viscoelastic behavior of an epoxy system. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 99, 1328–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, G.; Karbhari, V.M. Segmental relaxation of water-aged ambient cured epoxy. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedgewood, A.R.; Seferis, J.C.; Beck, T.R. Transport and related properties of paint films. II. Dynamic mechanical properties and humidity effects. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1985, 30, 111–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijovic, J.; Lin, K.F. Time-dependent changes in morphology of neat and reinforced epoxy resins part I. Neat epoxies. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1986, 32, 3211–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, E.S.; Adamson, M.J. Physical ageing and its effect on the moisture sorption of amine-cured epoxies. Polym. Commun. 1983, 24, 171–173. [Google Scholar]
- Le Guen-Geffroy, A.; Le Gac, P.Y.; Habert, B.; Davies, P. Physical ageing of epoxy in a wet environment: Coupling between plasticization and physical ageing. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2019, 168, 108947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leveque, D.; Schieffer, A.; Mavel, A.; Maire, J.F. Analysis of how thermal aging affects the long-term mechanical behavior and strength of polymer–matrix composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravve, A. Degradation of Polymers. In Principles of Polymer Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 581–616. [Google Scholar]
- Apicella, A.; Migliaresi, C.; Nicolais, L.; Iaccarino, L.; Roccotelli, S. The water ageing of unsaturated polyester-based composites: Influence of resin chemical structure. Composites 1983, 14, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Guo, S.; Li, S.; Rahman, M.Z.; Zhou, L.; Shi, C.; Zhu, D. Effect of alkalinity on the shear performance degradation of basalt fiber-reinforced polymer bars in simulated seawater sea sand concrete environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 299, 123957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, J.; Zhi, C.; Meng, J.; Miao, M.; Yu, L. Seawater aging effect on fiber-reinforced polymer composites: Mechanical properties, aging mechanism, and life prediction. Text. Res. J. 2023, 93, 3393–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrololoumi, A.; Morovati, V.; Shaafaey, M.; Dargazany, R. A multi-physics approach on modeling of hygrothermal aging and its effects on constitutive behavior of cross-linked polymers. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2021, 156, 104614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbhari, V.M. Long-term hydrothermal aging of carbon-epoxy materials for rehabilitation of civil infrastructure. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 153, 106705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.Z.; Shanahan, M.E.R. Swelling of DGEBA/DDA epoxy resin during hygrothermal ageing. Polymer 1998, 39, 3253–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boinard, E.; Pethrick, R.A.; Dalzel-Job, J.; Macfarlane, C.J. Influence of resin chemistry on water uptake and environmental ageing in glass fibre reinforced composites-polyester and vinyl ester laminates. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 35, 1931–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouzakis, D.E.; Zoga, H.; Galiotis, C. Accelerated environmental ageing study of polyester/glass fiber reinforced composites (GFRPCs). Compos. Part B Eng. 2008, 39, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, H.; Morovati, V.; Poshtan, E.; Dargazany, R. Understanding decay functions and their contribution in modeling of thermal-induced aging of cross-linked polymers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 175, 109108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.B.; Rockett, T.J.; Hoffman, R.D. Interactions of water with unsaturated polyester, vinyl ester and acrylic resins. Polymer 1992, 33, 3691–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbhari, V.M. Dynamic mechanical analysis of the effect of water on E-glass-vinylester composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2006, 25, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeysinghe, H.P.; Edwards, W.; Pritchard, G.; Swampillai, G.J. Degradation of crosslinked resins in water and electrolyte solutions. Polymer 1982, 23, 1785–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascom, W.D. The surface chemistry of moisture-induced composite failure. In Interfaces Polymer Matrix Composites, 1st ed.; Plueddeman, E.P., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1974; Volume 6, pp. 79–108. [Google Scholar]
- Bascom, W.D. Water at the interface. J. Adhes. 1970, 2, 161–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalske, T.A.; Freiman, S.W. A molecular mechanism for stress corrosion in vitreous silica. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1983, 66, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalske, T.A.; Freiman, S.W. A molecular interpretation of stress corrosion in silica. Nature 1982, 295, 511–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthewson, M.J.; Kurkjian, C.R. Environmental effects on the static fatigue of silica optical fiber. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1988, 71, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kini, M.V.; Pai, D. The ageing effect on static and dynamic mechanical properties of fibre reinforced polymer composites under marine environment-a review. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 52, 689–696. [Google Scholar]
- Mirdehghan, S.A. Fibrous polymeric composites. In Engineered Polymeric Fibrous Materials, 1st ed.; Latifi, M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing, Elsevier: Kidlington, UK, 2021; pp. 1–58. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Fu, Q.; Yan, L.; Kasal, B. Characterization of interfacial properties between fibre and polymer matrix in composite materials–A critical review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 13, 1441–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaw, A.K. Mechanics of Composite Materials, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Browning, C.E. The mechanisms of elevated temperature property losses in high performance structural epoxy resin matrix materials after exposures to high humidity environments. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1978, 18, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.; Tan, Y.M. Influence of moisture-induced stress on in situ fiber strength degradation of unidirectional polymer composite. Compos. Part B Eng. 2001, 32, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, P.C.; Gupta, G.S.; Lyons, D.W. Plastic deformation of fiber coating in polymer matrix composites under hygrothermal loading. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 1999, 18, 985–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, B.C. Temperature effect during humid ageing on interfaces of glass and carbon fibers reinforced epoxy composites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 298, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitsman, Y.J.; Guo, Y.-J. A correlation between fluid-induced damage and anomalous fluid sorption in polymeric composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2002, 62, 889–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Yang, J. Hygrothermal effects in composites. In Comprehensive Composite Materials II; Beaumont, P.W.R., Zweben, C.H., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 1, pp. 502–519. [Google Scholar]
- Gautier, L.; Mortaigne, B.; Bellenger, V. Interface damage study of hydrothermally aged glass-fibre-reinforced polyester composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1999, 59, 2329–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, H.T. Hygrothermal damage in graphite/epoxy laminates. ASME J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 1987, 109, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafodya, I.; Xian, G.; Li, H. Durability study of pultruded CFRP plates immersed in water and seawater under sustained bending: Water uptake and effects on the mechanical properties. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 70, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, J.M.; Browning, C.E. Some anomalies associated with moisture diffusion in epoxy matrix composite materials. In Advanced Composite Materials—Environmental Effects ASTM STP 658; Vinson, J., Ed.; American Society for Testing and Materials: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1978; pp. 43–60. [Google Scholar]
- Pineda, A.F.; Garcia, F.G.; Simoes, A.Z.; da Silva, E.L. Mechanical properties, water absorption and adhesive properties of diepoxy aliphatic diluent-modified DGEBA/Cycloaliphatic amine networks on 316L stainless steel. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2016, 68, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xiao, G.Z.; Delamar, M.A.; Shanahan, M.E.R. Irreversible interactions between water and DGEBA/DDA epoxy resin during hygrothermal aging. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 65, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillet, C.; Tamssaouet, F.; Hassoune-Rhabbour, B.; Tchalla, T.; Nassiet, V. Parameters influencing moisture diffusion in epoxy-based materials during hygrothermal ageing—A review by statistical analysis. Polymers 2022, 14, 2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktas, L.; Hamidi, Y.K.; Altan, M.C. Combined edge and anisotropy effects on Fickian mass diffusion in polymer composites. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 2004, 126, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewimille, B.; Bunsell, A.R. The modelling of hydrothermal aging in glass fibre reinforced epoxy composites. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1982, 15, 2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanitopoulos, C.D.; Koenig, J.L. Infrared spectral imaging of the interphase of epoxy-glass fiber-reinforced composites under wet conditions. Appl. Spectrosc. 1996, 50, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göpferich, A. Mechanisms of polymer degradation and erosion. Biomaterials 1996, 17, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Göpferich, A. Erosion of composite polymer matrices. Biomaterials 1997, 18, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Burkersroda, F.; Schedl, L.; Göpferich, A. Why degradable polymers undergo surface erosion or bulk erosion. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4221–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, S.; Sparer, R.; Untereker, D. Analytical solutions to mathematical models of the surface and bulk erosion of solid polymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2005, 43, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De’Nève, B.; Shanahan, M.E.R. Water absorption by an epoxy resin and its effect on the mechanical properties and infra-red spectra. Polymer 1993, 34, 5099–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.-H.; Springer, G.S. Moisture absorption and desorption of composite materials. J. Compos. Mater. 1976, 10, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, P.V. On the solidification and swelling phenomena of gelatine. J. Phys. Chem. 1903, 45, 75–117. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, P.; Datta, R. Sorption in proton-exchange membranes: An explanation of Schroeder’s paradox. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, E601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Onishi, L.M.; Prausnitz, J.M.; Newman, J. Water−Nafion equilibria. Absence Schroeder’s Parad. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 10166–10173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallieres, C.; Winkelmann, D.; Roizard, D.; Favre, E.; Scharfer, P.; Kind, M. On Schroeder’s paradox. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 278, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, J.F.; Naeem, M. A comparative study of the effect of moisture absorption on the mechanical properties of glass fibre reinforced plastics. In Controlled Interphases in Composite Materials; Ishida, H., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, Netherlands, 1990; pp. 801–808. [Google Scholar]
- Bonniau, P.A.; Bunsell, A.R. A comparative study of water absorption theories applied to glass epoxy composites. J. Compos. Mater. 1981, 15, 272–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.S.; Ahn, K.J.; Nam, J.D.; Chun, H.J. Hygroscopic aspects of epoxy/carbon fiber composite laminates in aircraft environments. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2001, 32, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, L.P. Fundamental concepts and definitions relating to humidity. In Humidity and Moisture, Measurement and Control in Science and Industry; Wexler, A., Ed.; Reinhold Publishing Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 1965; Volume 3, Chapter 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ponec, V.; Knor, Z.; Cerny, S. Adsorption on Solids; Smith, D., Adams, N.G., Eds.; Butterworth: London, UK, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Brunauer, S.; Deming, L.S.; Deming, W.E.; Teller, E. On a theory of the van der Waals adsorption of gases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1940, 62, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieth, W.R.; Howell, J.M.; Hsieh, J.H. Dual sorption theory. J. Membr. Sci. 1976, 1, 177–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, W. Experiments on the quantity of gases absorbed by water, at different temperaturees, and under different pressures. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1803, 93, 29–43. [Google Scholar]
- Loos, A.C.; Springer, G.S. Moisture absorption of graphite-epoxy composites immersed in liquids and in humid air. J. Compos. Mater. 1979, 13, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitsman, Y.J. Moisture in composites: Sorption and damage. In Fatigue of Composite Materials, 1st ed.; Reifsnider, K.L., Ed.; Composite Materials Series; Elsevier Science Publisher B: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 1991; pp. 385–429. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, D.C. LX. A kinetic theory of adsorption. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1922, 44, 689–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flory, P.J. Thermodynamics of high polymer solutions. J. Chem. Phys. 1942, 10, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggins, M.L. Thermodynamic properties of solutions of long-chain compounds. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1942, 43, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I. Solids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1916, 38, 2221–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrer, R.M.; Barrie, J.A.; Slater, J. Sorption and diffusion in ethyl cellulose. Part III. Comparison between ethyl cellulose and rubber. J. Polym. Sci. 1958, 27, 177–197. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, J.M.; Marshall, G.P.; Pinzelli, R.F. The diffusion of liquids into resins and composites. Polym. Compos. 1982, 3, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggana, C.; Pissis, P. Water sorption and diffusion studies in an epoxy resin system. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1999, 37, 1165–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, K.; Li, Y.; Sun, H.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, J. Characteristics of water absorption in amine-cured epoxy networks: A molecular simulation and experimental study. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 8740–8749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Espinel, J.D.; Castro-Fresno, D.; Gayo, P.P.; Ballester-Muñoz, F. Effects of sea water environment on glass fiber reinforced plastic materials used for marine civil engineering constructions. Mater. Des. (1980–2015) 2015, 66, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, F.A.; Richman, D. Concentration gradients for diffusion of vapors in glassy polymers and their relation to time dependent diffusion phenomena. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1960, 82, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-M. Sorption/desorption properties of water vapour in poly (2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate): 2. Two-stage sorption models. Polymer 1996, 37, 3921–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berens, A.R.; Hopfenberg, H.B. Diffusion and relaxation in glassy polymer powders: 2. Separation of diffusion and relaxation parameters. Polymer 1978, 19, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitsman, Y.J. Effects of Fluids on Polymeric Composites—Contract Technical Report, A Review; Prepared for Office of Naval Research, Arlington, Virginia: Knoxville, TN, USA, 1995; Report MAES 95-1.0 CM. [Google Scholar]
- Weitsman, Y.J. Anomalous fluid sorption in polymeric composites and its relation to fluid-induced damage. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2006, 37, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Ma, Y.; Sun, W.; Wang, Z. Effect of hygrothermal aging on moisture diffusion and tensile behavior of CFRP composite laminates. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2023, 36, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, A. Ueber diffusion. Ann. Phys. 1855, 170, 59–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamant, Y.; Marom, G.; Broutman, L.J. The effect of network structure on moisture absorption of epoxy resins. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1981, 26, 3015–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirrell, C.D. Diffusion of water vapor in graphite/epoxy composites. In ASTM STP 658, Advanced Composite Materials—Environmental Effects; Vinson, J.R., Ed.; American Society for Testing and Materials: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1977; pp. 21–42. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, V.B.; Drzal, L.T.; Rich, M.J. The physical basis of moisture transport in a cured epoxy resin system. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1985, 30, 4467–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karad, S.K.; Attwood, D.; Jones, F.R. Moisture absorption by cyanate ester modified epoxy resin matrices. Part IV: Effect of curing schedules. Polym. Compos. 2003, 24, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumosa, L.; Benedikt, B.; Armentrout, D.; Kumosa, M. Moisture absorption properties of unidirectional glass/polymer composites used in composite (non-ceramic) insulators. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2004, 35, 1049–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, L.; Hamidi, Y.; Altan, M.C. Effect of moisture on the mechanical properties of resin transfer molded composites-part I: Absorption. J. Mater. Process. Manuf. Sci. 2002, 10, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronhime, M.T.; Neumann, S.; Marom, G. The anisotropic diffusion of water in Kevlar-epoxy composites. J. Mater. Sci. 1987, 22, 2435–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Xu, W.X.; Park, S.J.; Liechti, K.M. Anomalous moisture diffusion in viscoelastic polymers: Modeling and testing. J. Appl. Mech. 2000, 67, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanicolaou, G.C.; Pappa, A. Water sorption and temperature effects on the dynamic mechanical behaviour of epoxy-matrix particulates. J. Mater. Sci. 1992, 27, 3889–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, L.U.; Bhagawan, S.S.; Nair, K.C.M.; Thomas, S. Water absorption behavior of PALF/GF hybrid polyester composites. Polym. Compos. 2011, 32, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, C.; Alston, S.; Korkees, F.; Dauhoo, S.; Adams, R.; Older, R. Design optimisation of carbon fibre epoxy composites operating in humid atmospheres. In Proceedings of the 10th Annual Conference: Innovation in Composites, Birmingham, UK, 5–6 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle, A.K.; Doolittle, D.B. Studies in Newtonian Flow. V. Further Verification of the Free-Space Viscosity Equation. J. Appl. Phys. 1957, 28, 901–905. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, M.L.; Landel, R.F.; Ferry, J.D. The temperature dependence of relaxation mechanisms in amorphous polymers and other glass-forming liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1955, 77, 3701–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, F.N.; Bueche, F. Viscosity and glass temperature relations for polymer-diluent systems. J. Polym. Sci. 1961, 50, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.-R.; Yee, A.F. Effect of temperature on moisture absorption in a bismaleimide resin and its carbon fiber composites. Polymer 2002, 43, 3987–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celina, M.; Gillen, K.T.; Assink, R.A. Accelerated aging and lifetime prediction: Review of non-Arrhenius behaviour due to two competing processes. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2005, 90, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marru, P.; Latane, V.; Puja, C.; Vikas, K.; Kumar, P.; Neogi, S. Lifetime estimation of glass reinforced epoxy pipes in acidic and alkaline environment using accelerated test methodology. Fibers Polym. 2014, 15, 1935–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, M.; Hosokawa, Y.; Muraoka, Y.; Katayama, T. Life prediction under sulfuric acid environment of FRP using X-ray analysis microscope. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 155, 1558–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, S. Durability and service life prediction of GFRP bars embedded in concrete under acid environment. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2011, 241, 4095–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Dong, Z.-Q.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, Z.-S. Prediction of long-term performance and durability of BFRP bars under the combined effect of sustained load and corrosive solutions. J. Compos. Constr. 2015, 19, 04014058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, H.G.; Kibler, K.G. Langmuir-type model for anomalous moisture diffusion in composite resins. J. Compos. Mater. 1978, 12, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanahan, M.E.; Auriac, Y. Water absorption and leaching effects in cellulose diacetate. Polymer 1998, 39, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Wu, C.; Han, X.; Zhang, W. Effects of moisture ingress on the mesoscale mechanical properties of epoxy adhesives under elevated temperature. Polym. Test. 2021, 94, 107049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starink, M.J.; Starink, L.M.P.; Chambers, A.R. Moisture uptake in monolithic and composite materials: Edge correction for rectanguloid samples. J. Mater. Sci. 2002, 37, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, E.; Long, F.A. Two-stage sorption and desorption of organic vapors in cellulose acetate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1955, 77, 2172–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Adams, R.D.; da Silva, L.F. Absorption and glass transition temperature of adhesives exposed to water and toluene. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2014, 50, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhan, G.; Li, S. Effect of chemical structure on the water sorption of amine-cured epoxy resins. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 3000–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, K.; Childers, C.; Dutta, D.; Gidley, D.; Jackson, M.; Ward, S.; Maskell, R.; Wiggins, J. Fluid uptake behavior of multifunctional epoxy blends. Polymer 2013, 54, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidane, E.H.; Scida, D.; Assarar, M.; Ayad, R. Assessment of 3D moisture diffusion parameters on flax/epoxy composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 80, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, P.; Robert, C.; Brádaigh, C.M. Tidal turbine blade composites—A review on the effects of hygrothermal aging on the properties of CFRP. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 149, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, V.A.; Brøndsted, P. Effects of moisture on glass fiber-reinforced polymer composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2015, 49, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carslaw, H.S.; Jaeger, J.C. Conduction of Heat in Solids, 2nd ed.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, H.; Liu, Y.; Mosallam, A.; Zhang, Y. Moisture diffusion and hygrothermal aging of pultruded glass fiber reinforced polymer laminates in bridge application. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 100, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apeagyei, A.K.; Grenfell, J.R.; Airey, G.D. Application of Fickian and non-Fickian diffusion models to study moisture diffusion in asphalt mastics. Mater. Struct. 2015, 48, 1461–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaPlante, G.; Ouriadov, A.V.; Lee-Sullivan, P.; Balcom, B.J. Anomalous moisture diffusion in an epoxy adhesive detected by magnetic resonance imaging. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 109, 1350–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legghe, E.; Aragon, E.; Bélec, L.; Margaillan, A.; Melot, D. Correlation between water diffusion and adhesion loss: Study of an epoxy primer on steel. Prog. Org. Coat. 2009, 66, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkees, F.; Alston, S.; Arnold, C. Directional diffusion of moisture into unidirectional carbon fiber/epoxy composites: Experiments and modeling. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, E2305–E2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broughton, W.R.; Lodeiro, M.J. Techniques for Monitoring Water Absorption in Fibre-Reinforced Polymer Composites; Report number: NPL Measurement Note CMMT(MN)64; National Physical Laboratory (NPL): Teddington, UK, 2000; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Comyn, J. Introduction to polymer permeability and mathematics of diffusion. In Polymer Permeability, 1st ed.; Comyn, J., Ed.; Springer Nature: Dordrecht, Netherlands, 1985; Chapter 1; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Gurtin, M.E.; Yatomi, C. On a model for two phase diffusion in composite materials. J. Compos. Mater. 1979, 13, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, C.; Korkees, F.; Alston, S. The long-term water absorption and desorption behaviour of carbon-fibre/epoxy composites. In Proceedings of the ECCM-15 Proceedings, ESCM: 15th European Conference on Composite Materials, Venice, Italy, 24–28 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vanlandingham, M.R.; Eduljee, R.F.; Gillespie, J.W., Jr. Moisture diffusion in epoxy systems. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 71, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chateauminois, A.; Vincent, L.; Chabert, B.; Soulier, J.P. Study of the interfacial degradation of a glass-epoxy composite during hygrothermal ageing using water diffusion measurements and dynamic mechanical thermal analysis. Polymer 1994, 35, 4766–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.-R.; Yee, A.F. Moisture diffusion and hygrothermal aging in bismaleimide matrix carbon fiber composites—Part I: Uni-weave composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2002, 62, 2099–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, G.S. Environmental effects. In Engineering Mechanics of Fibre Reinforced Polymers and Composite Structures, 1st ed.; Hult, J., Rammerstorfer, F.G., Eds.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1994; Volume 348, pp. 287–314. [Google Scholar]
- Bone, J.E.; Sims, G.D.; Maxwell, A.S.; Frenz, S.; Ogin, S.L.; Foreman, C.; Dorey, R.A. On the relationship between moisture uptake and mechanical property changes in a carbon fibre/epoxy composite. J. Compos. Mater. 2022, 56, 2189–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, D.; Kamboj, I.; Bera, T.K.; Kang, A.S.; Singla, R.K. Experimental and numerical investigations on the effect of alkaline hornification on the hydrothermal ageing of Agave natural fiber composites. Int. J. Heat Mass. Transf. 2019, 130, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, B. Dimensional stability and mechanical performance evolution of continuous carbon fiber reinforced polyamide 6 composites under hygrothermal environment. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 13, 2126–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.C.; Alston, S.M.; Korkees, F. An assessment of methods to determine the directional moisture diffusion coefficients of composite materials. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2013, 55, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, G.S.; Tsai, S.W. Thermal conductivities of unidirectional materials. J. Compos. Mater. 1967, 1, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbhari, V.M.; Hassanpour, B. Water, saltwater, and concrete leachate solution effects on durability of ambient-temperature cure carbon-epoxy composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e52496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkees, F.; Swart, R.; Barsoum, I. Diffusion mechanism and properties of chemical liquids and their mixtures in 977-2 epoxy resin. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2022, 62, 1582–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrett, W.; Korkees, F. Environmental impact investigation on the interlaminar properties of carbon fibre composites modified with graphene nanoparticles. Polymer 2022, 252, 124921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, B.D.; Staab, G.H.; Chen, R.S. A note on the effects of voids upon the hygral and mechanical properties of AS4/3502 graphite/epoxy. J. Compos. Mater. 1987, 21, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitsman, Y.J. Effects of Fluids on Mechanical Properties and Performance. In Fluid Effects in Polymers and Polymeric Composites; Penumadu, D., Ed.; Mechanical Engineering Series; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 123–144. [Google Scholar]
- Placette, M.D.; Fan, X.; Zhao, J.-H.; Edwards, D. A dual stage model of anomalous moisture diffusion and desorption in epoxy mold compounds. In Conference on Thermal, Mechanical & Multi-Physics Simulation and Experiments in Microelectronics and Microsystems; IEEE Conference: Linz, Austria, 2011; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Popineau, S.; Rondeau-Mouro, C.; Sulpice-Gaillet, C.; Shanahan, M.E. Free/bound water absorption in an epoxy adhesive. Polymer 2005, 46, 10733–10740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.W.; Weitsman, Y.J. Non-Fickian moisture diffusion in polymeric composites. J. Compos. Mater. 1994, 28, 130–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.Z.; Wang, Y.L.; Cheng, G.X.; Han, K.Y. Three-dimensionally braided carbon fiber–epoxy composites, a new type of material for osteosynthesis devices. I. Mech. Prop. Moisture Absorpt. Behav. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 85, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar]
- Neumann, S.; Marom, G. Free-volume dependent moisture diffusion under stress in composite materials. J. Mater. Sci. 1986, 21, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, S.; Marom, G. Prediction of moisture diffusion parameters in composite materials under stress. J. Compos. Mater. 1987, 21, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, H.N.; Zhang, Z. Polymer matrix composites: Moisture effects and dimensional stability. In Wiley Encyclopedia of Composites, 2nd ed.; Nicolais, L., Borzacchiello, A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; Volume 1, pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, L.L.; Lasky, R.; Seraphim, D.P.; Springer, G.S. Moisture solubility and diffusion in epoxy and epoxy-glass composites. IBM J. Res. Dev. 1984, 28, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, H. Diffusion in polymer-diluent systems. In Fortschritte der Hochpolymeren-Forschung; Jayakumar, R., Ed.; Advanced in Polymer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1961; Volume 3, pp. 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Crank, J.; Park, G.S. Diffusion in Polymers; Academic Press: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1968; p. 452. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.-K.; Hu, C.; Woo, R.S.; Sham, M.-L. Moisture barrier characteristics of organoclay–epoxy nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coniglio, N.; Nguyen, K.; Kurji, R.; Gamboa, E. Characterizing water sorption in 100% solids epoxy coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2013, 76, 1168–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubashar, A.; Ashcroft, I.A.; Critchlow, G.W.; Crocombe, A.D. Modelling cyclic moisture uptake in an epoxy adhesive. J. Adhes. 2009, 85, 711–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Kolstein, H.; Bijlaard, F.S. Moisture diffusion in glass–fiber-reinforced polymer composite bridge under hot/wet environment. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 45, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, M.; Roy, R.; Benmokrane, B. Environmental effects on glass fiber reinforced polypropylene thermoplastic composite laminate for structural applications. Polym. Compos. 2010, 31, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotugno, S.; Mensitieri, G.; Musto, P.; Sanguigno, L. Molecular interactions in and transport properties of densely cross-linked networks: A time-resolved FT-IR spectroscopy investigation of the epoxy/H2O system. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.C.; Broutman, L.J. Moisture diffusion in epoxy resins Part I. Non-Fickian sorption processes. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1985, 25, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, R.-J.; Lin, P.-W.; Lin, K.-F. Two-stage moisture absorption behavior and hydrolysis of cured dicyanate ester resins. J. Polym. Res. 2002, 9, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsikos, G.; Gibson, A.G.; Mawella, J. Assessment of moisture absorption in marine GRP laminates with aid of nuclear magnetic resonance imaging. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2007, 36, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, P.M.; Jones, F.R. Diffusion of moisture into two-phase polymers: Part 3 Clustering of water in polymer resins. J. Mater. Sci. 1990, 25, 2471–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meares, P. The solubilities of gases in polyvinyl acetate. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1958, 54, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.R. Effect of immobilizing adsorption on the diffusion time lag. J. Polym. Sci. Part A-2 Polym. Phys. 1969, 7, 1811–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.R.; Koros, W.J. Effect of partially immobilizing sorption on permeability and the diffusion time lag. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. Ed. 1976, 14, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, N.L.; Riebel, F.; Zhou, A.; Keller, T.; Case, S.W.; Lesko, J.J. Investigation of 3D moisture diffusion coefficients and damage in a pultruded E-glass/polyester structural composite. J. Compos. Mater. 2009, 43, 75–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitsman, Y.J. Diffusion with time-varying diffusivity, with application to moisture-sorption in composites. J. Compos. Mater. 1976, 10, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, L.R.; Altan, M.C. Characterization of anisotropic moisture absorption in polymeric composites using hindered diffusion model. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2012, 43, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guloglu, G.E.; Altan, M.C. Moisture absorption of carbon/epoxy nanocomposites. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.J.; Low, K.O.; Israr, H.A.; Tamin, M.N. Thickness-dependent non-Fickian moisture absorption in epoxy molding compounds. Microelectron. Reliab. 2016, 65, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Boo, W.-J.; Clearfield, A.; Sue, H.-J.; Pham, H.Q. Barrier properties of model epoxy nanocomposites. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 318, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hoa, S.V.; Pugh, M. Water uptake of epoxy–clay nanocomposites: Model development. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 3308–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berens, A.R. Diffusion and relaxation in glassy polymer powders: 1. Fickian diffusion of vinyl chloride in poly (vinyl choride). Polymer 1977, 18, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaskova, T.I.; Guedes, R.M.; Morais, J.J.; Aniskevich, A.N. A comparative analysis of moisture transport models as applied to an epoxy binder. Mech. Compos. Mater. 2007, 43, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensitieri, G.; Lavorgna, M.; Musto, P.; Ragosta, G. Water transport in densely crosslinked networks: A comparison between epoxy systems having different interactive characters. Polymer 2006, 47, 8326–8336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, P.; Lees, J.M. Water, salt water, and alkaline solution uptake in epoxy thin films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 1898–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratasyuk, N.A.; Ostanin, S.A.; Mokeev, M.V.; Zuev, V.V. Water transport in epoxy/polyurethane interpenetrating networks. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2022, 33, 3173–3191. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, R.Q.C.; Santos, W.R.G.; Barbosa de Lima, A.G.; Lima, W.M.P.B.; Silva, J.V.; Farias, R.P. Water absorption process in polymer composites: Theory analysis and applications. In Transport Phenomena in Multiphase Systems; Delgado, J., Barbosa de Lima, A., Eds.; Advanced Structured Materials; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 93, pp. 219–249. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.; Zhou, C. Moisture absorption and cyclic absorption–desorption characters of fibre-reinforced epoxy composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 8289–8301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiman, S.; Salman, S.; Maryudi, M. Effects of volume fraction on water uptake and tensile properties of epoxy filled with inorganic fillers having different reactivity to water. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 24, 101360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suri, C.; Perreux, D. The effects of mechanical damage in a glass fibre/epoxy composite on the absorption rate. Compos. Eng. 1995, 5, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Miranda, J.; Sue, H.-J. Hygrothermal diffusion behavior in bismaleimide resin. Polymer 2001, 42, 7791–7799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Xing, P. Moisture absorption characterization of carbon fiber-reinforced polymer using Fickian and non-Fickian models. Polym. Compos. 2022, 43, 8935–8946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Roy, S. Modeling of anomalous moisture diffusion in nanographene reinforced thermoset polymers. Compos. Struct. 2015, 122, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guloglu, G.E.; Hamidi, Y.K.; Altan, M.C. Moisture absorption of composites with interfacial storage. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 134, 105908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanpour, B.; Karbhari, V.M. Moisture and glass transition temperature kinetics of ambient-cured carbon/epoxy composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connelly, R.W.; McCoy, N.R.; Koros, W.J.; Hopfenberg, H.B.; Stewart, M.E. The effect of sorbed penetrants on the aging of previously dilated glassy polymer powders. I. Low. Alcohol Water Sorpt. Poly (Methyl Methacrylate). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1987, 34, 703–719. [Google Scholar]
- Newns, A.C. The sorption and desorption kinetics of water in a regenerated cellulose. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1956, 52, 1533–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulos, J.H.; Roussis, P.P. Diffusion of penetrants in organic solids accompanied by other rate processes. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1969, 9, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M.E.; Hopfenberg, H.B.; Koros, W.J.; McCoy, N.R. The effect of sorbed penetrants on the aging of previously dilated glassy polymer powders. II. N-Propane Sorpt. Polystyr. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1987, 34, 721–735. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, T.C.; Broutman, L.J. Water in epoxy resins part II. Diffusion mechanism. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1985, 25, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johncock, P.; Tudgey, G.F. Epoxy systems with improved water resistance, and the non-fickian behaviour of epoxy systems during water ageing. Br. Polym. J. 1983, 15, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkova, O.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Schnoor, T.; Sevcenko, J.; Schulte, K. Anomalous water diffusion in epoxy/carbon nanoparticle composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2019, 164, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berens, A.R.; Hopfenberg, H.B. Induction and measurement of glassy-state relaxations by vapor sorption techniques. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. 1979, 17, 1757–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavril’eva, A.A.; Kychkin, A.K.; Sivtseva, A.N.; Vasil’eva, A.A. Moisture absorption by a reinforced polymer composite (BFRP Rebar). Russ. Eng. Res. 2021, 41, 612–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, B.C.; Rathore, D. Environmental damage and degradation of FRP composites: A review report. Polym. Compos. 2015, 36, 410–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, P.C.; Mishra, A. Modified one-dimensional fickian solution for moisture absorption in composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 1990, 9, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, H. Hygrothermal aging on pultruded carbon fiber/vinyl ester resin composite for sucker rod application. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2006, 25, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, K.; Taki, T. Moisture diffusivity of unidirectional composites. J. Compos. Mater. 1982, 16, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.R.; Yee, A.F. Moisture diffusion and hygrothermal aging in bismaleimide matrix carbon fiber composites—Part II: Woven and hybrid composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2002, 62, 2111–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loung, C.L.; Dynes, P.J.; Kaelble, D.H. Moisture diffusion analysis of micro-structure degradation in graphite epoxy composites. In ASTM STP 696, Nondestructive Evaluation and Flaw Criticality for Composite Materials; Pipes, R.B., Ed.; American Society for Testing and Materials: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1979; pp. 298–315. [Google Scholar]
- Arao, Y.; Koyanagi, J.; Hatta, H.; Kawada, H. Analysis of time-dependent deformation of CFRP considering the anisotropy of moisture diffusion. Adv. Compos. Mater. 2008, 17, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana, H.R.; Perronnet, A.; Freour, S.; Casari, P.; Jacquemin, F. Identification of moisture diffusion parameters in organic matrix composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2013, 47, 1081–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allred, R.E.; Lindrose, A.M. The room temperature moisture kinetics of Kevlar 49 fabric/epoxy laminates. In ASTM STP 674. Composite Materials: Testing and Design; Tasai, S.W., Ed.; American Society for testing and Materials: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1979; pp. 313–323. [Google Scholar]
- Cervenka, A.J.; Bannister, D.J.; Young, R.J. Moisture absorption and interfacial failure in aramid/epoxy composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1998, 29, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Yu, T.; Li, Q.; Li, Z. Anisotropic behaviors of moisture absorption and hygroscopic swelling of unidirectional flax fiber reinforced composites. Compos. Struct. 2022, 297, 115941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
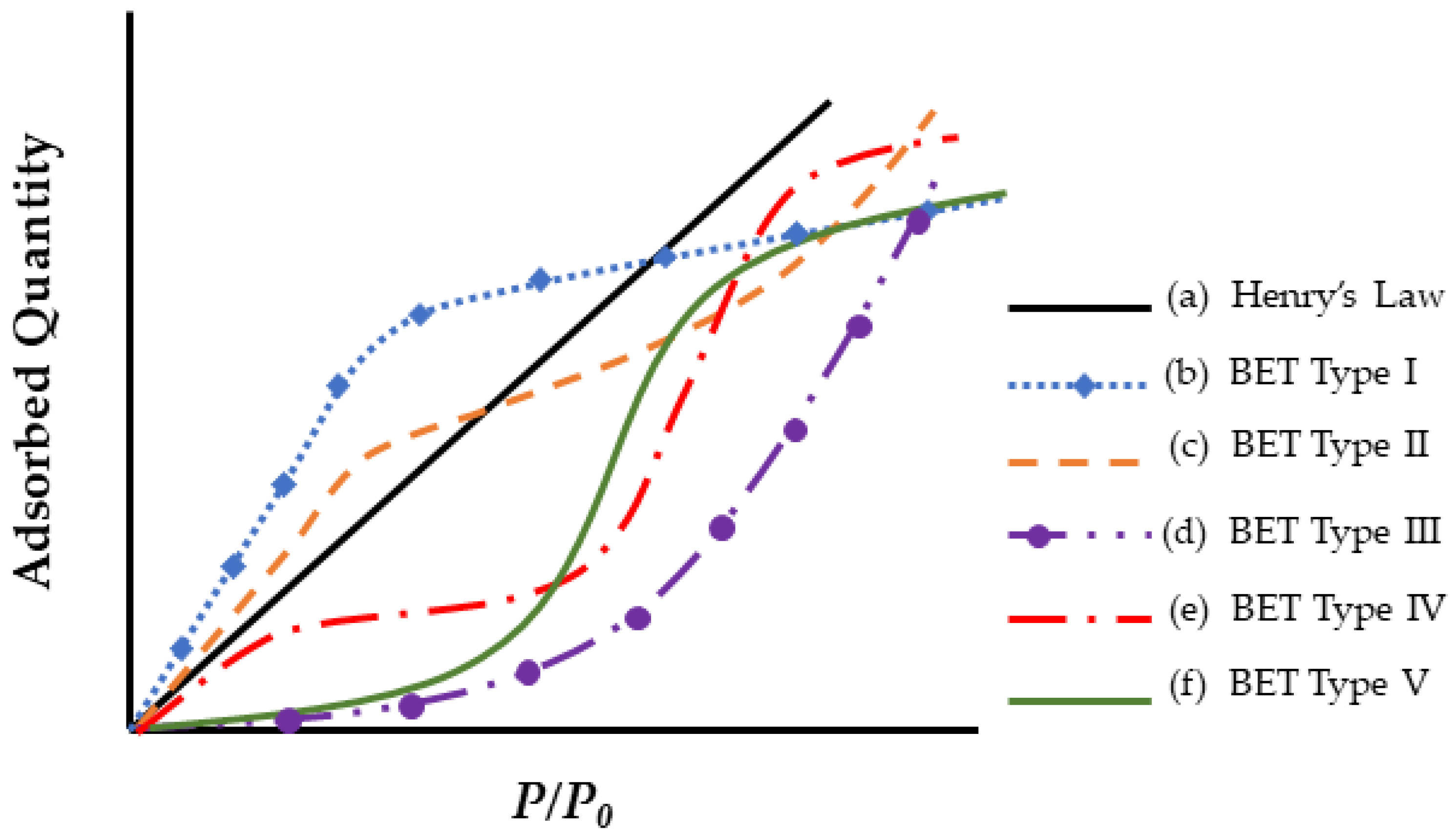
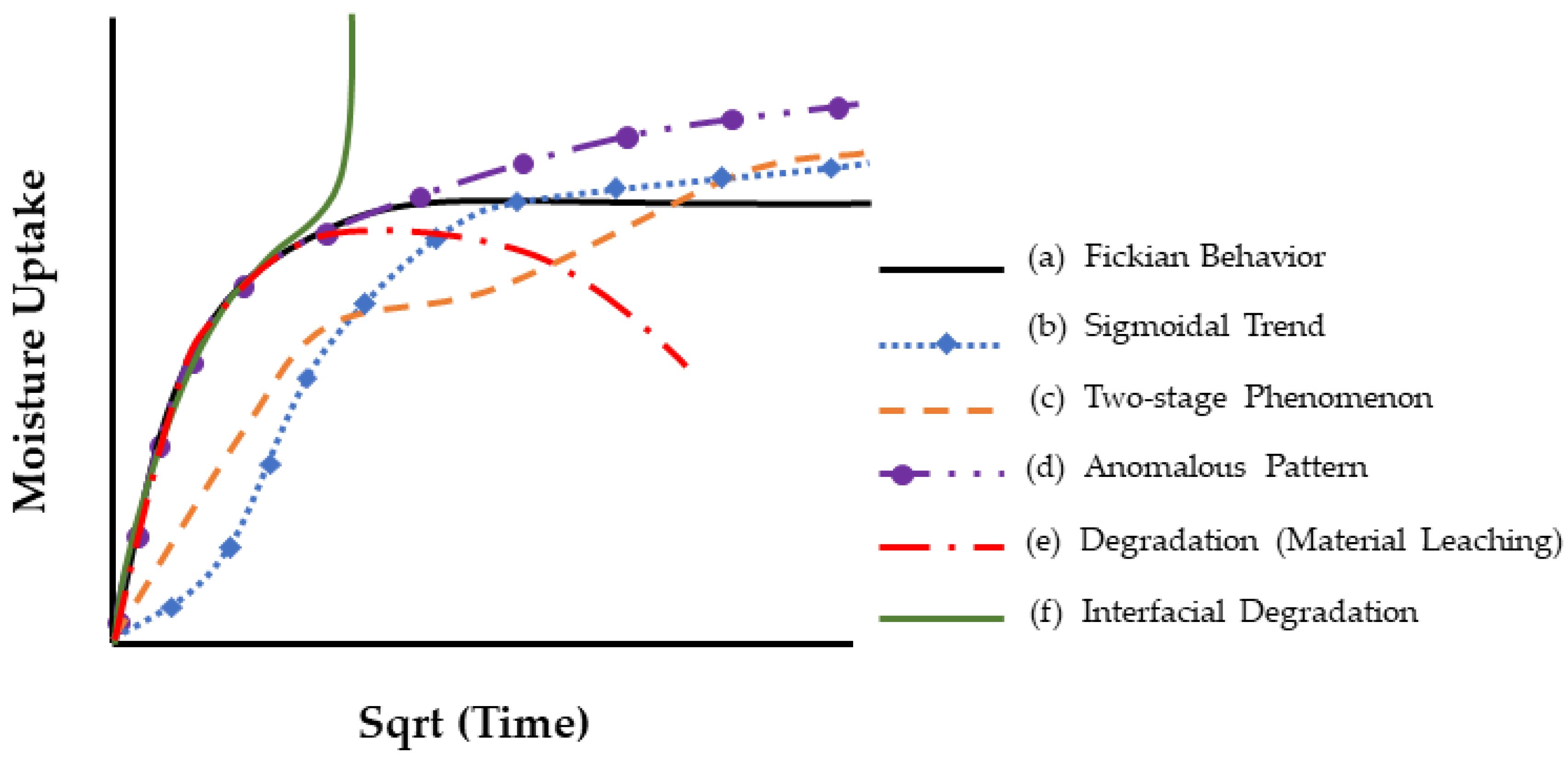
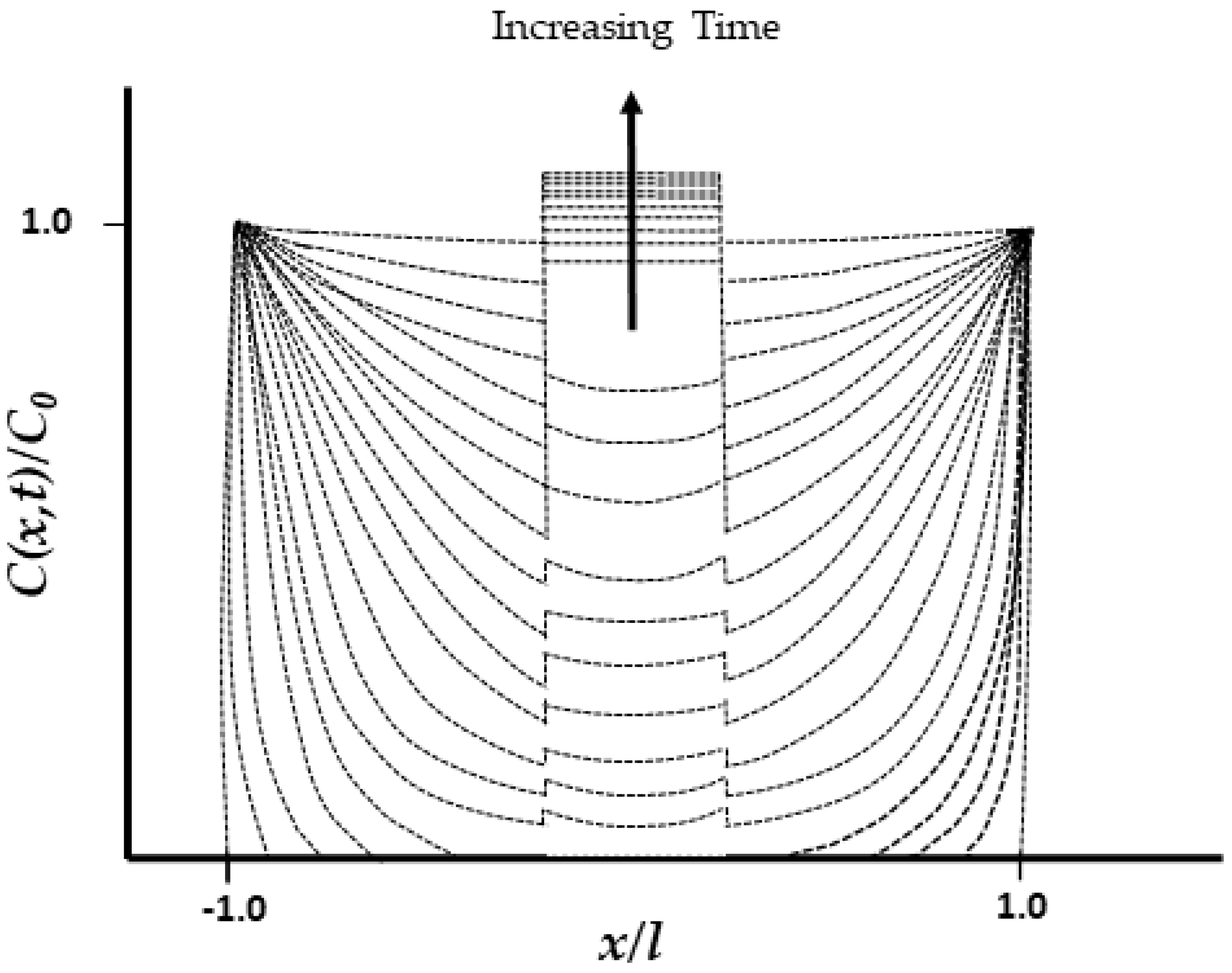
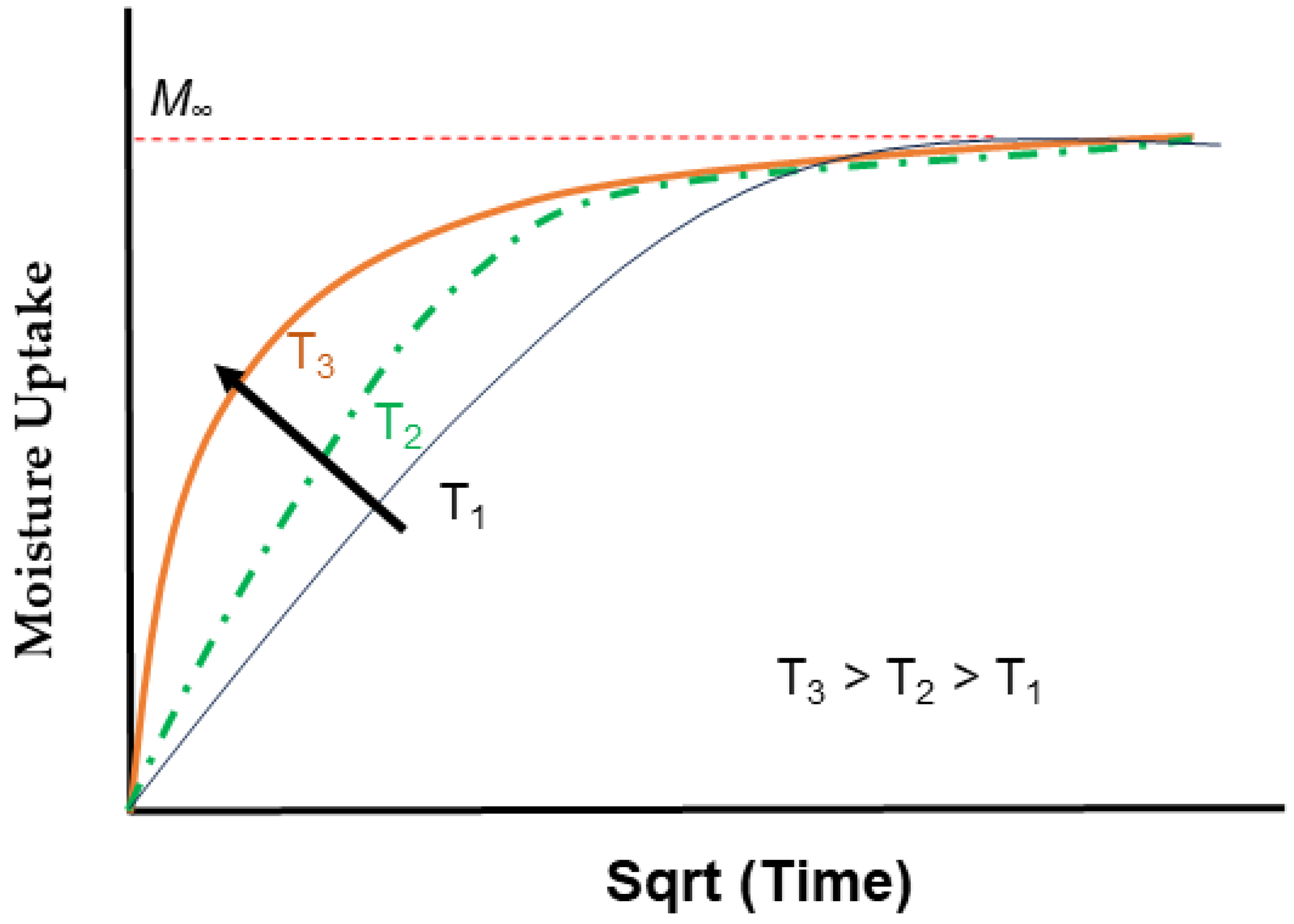
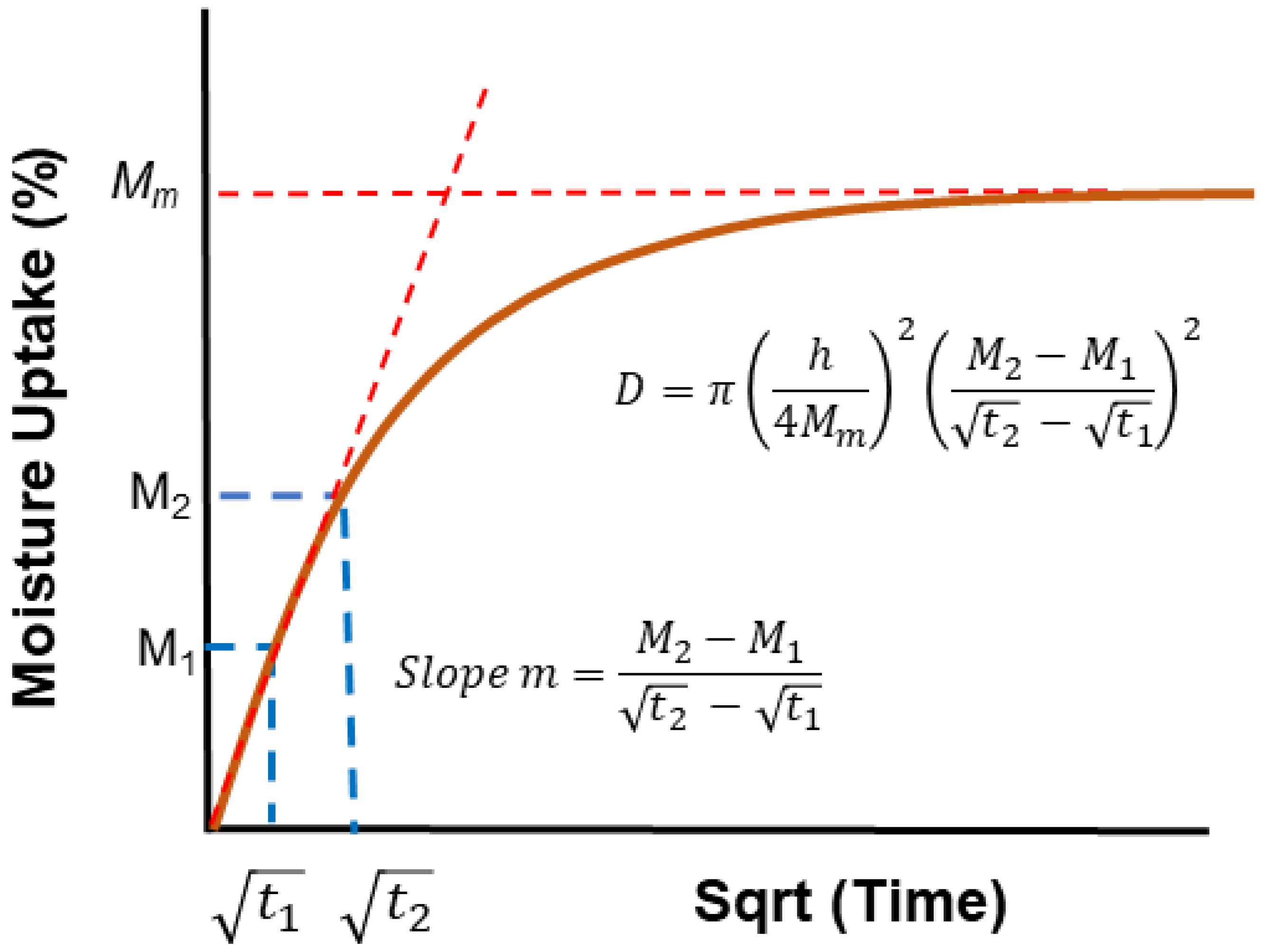
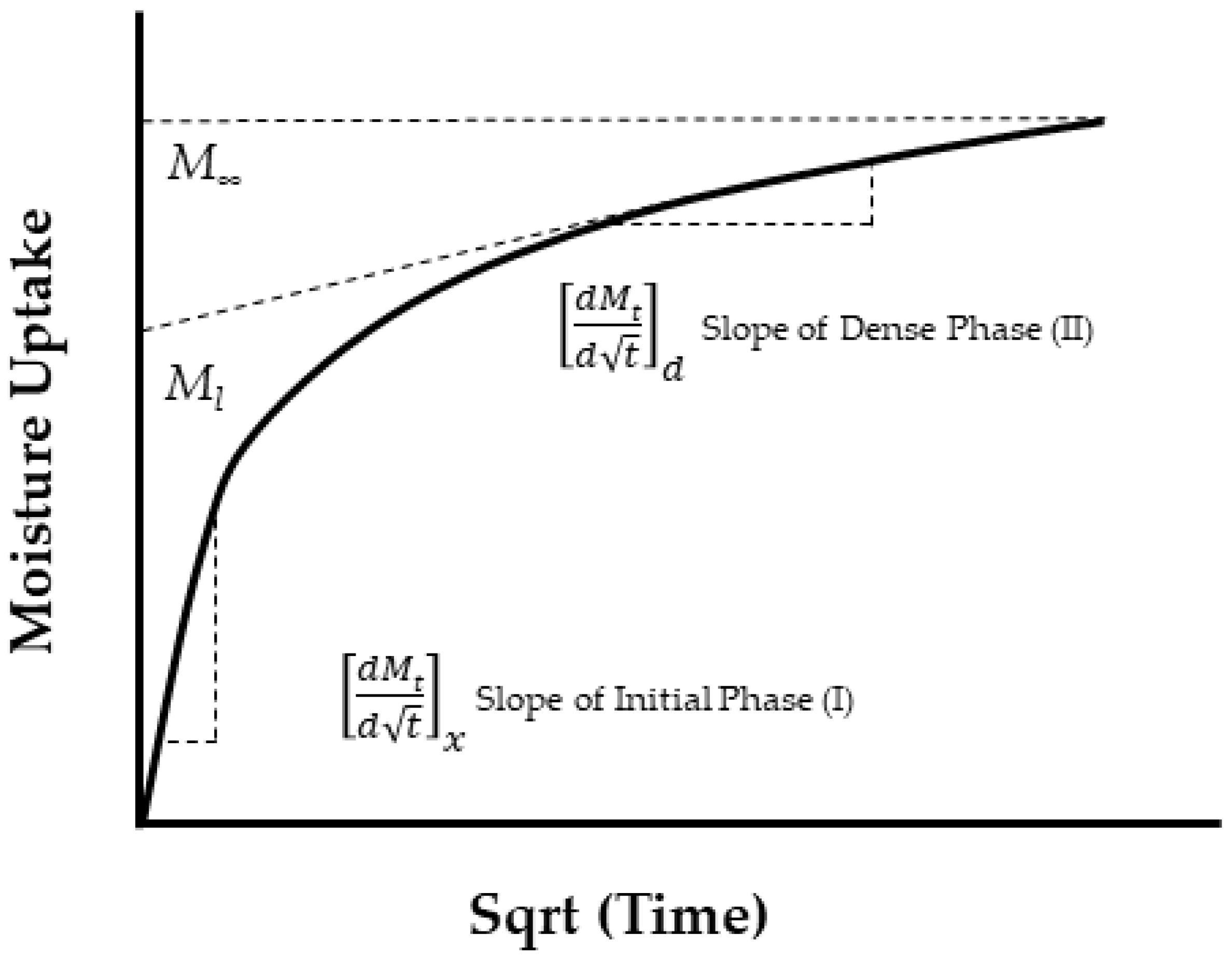
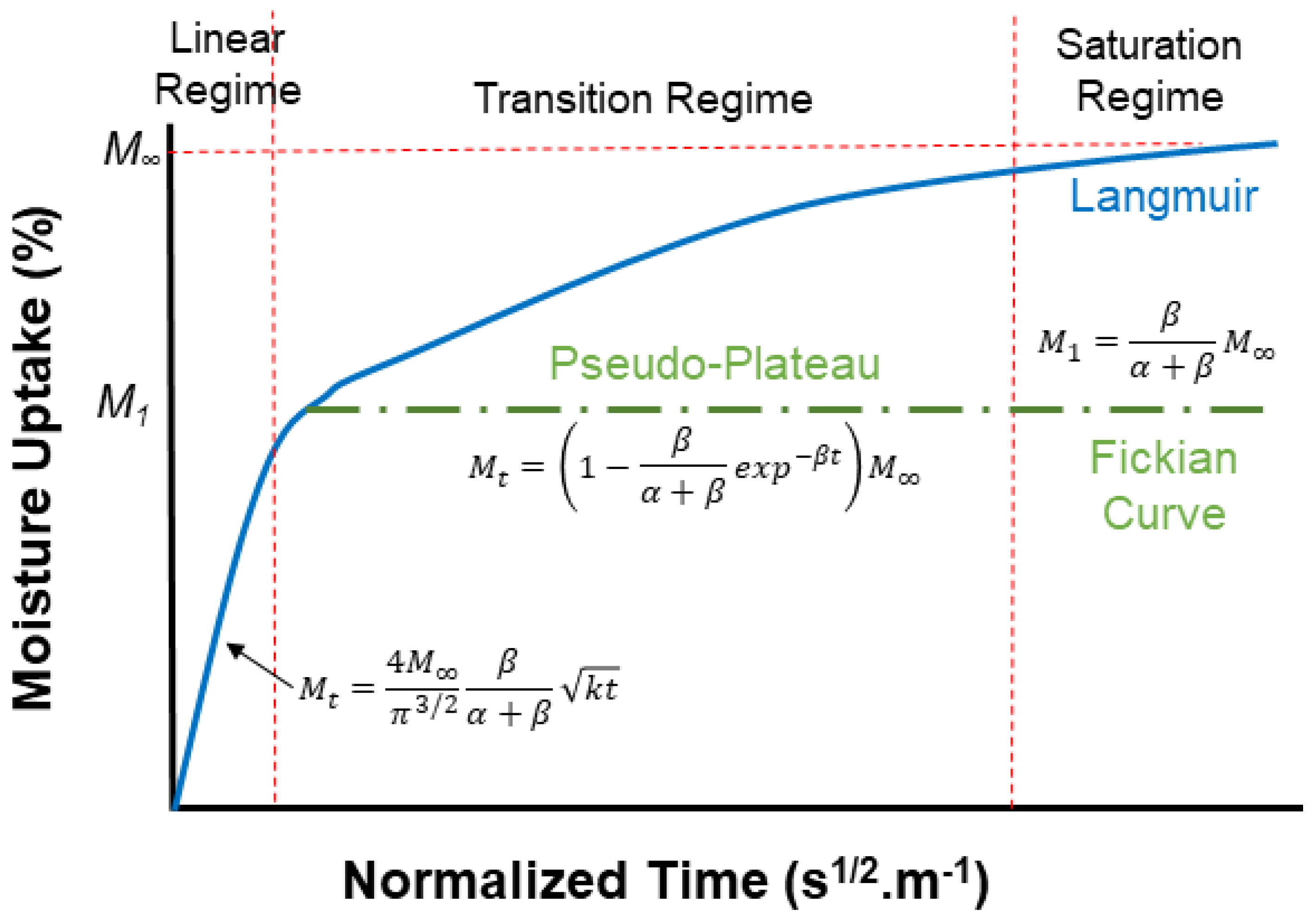
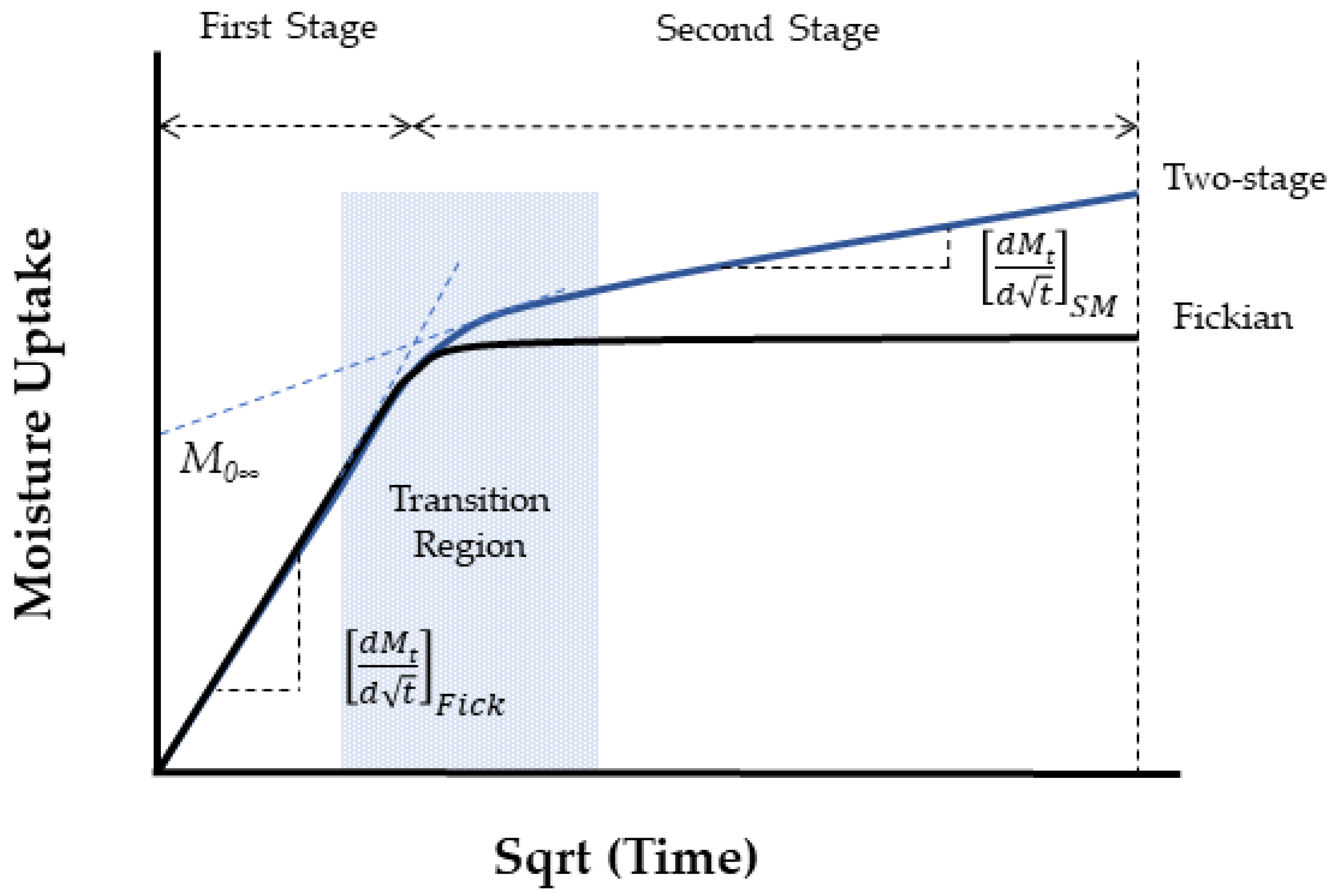
| Classification of Mechanism | Degradation Mechanism | F | Location M | I | Reversible? Y/N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical | Hydrolysis | × | × | N | |
| Pitting | × | N | |||
| Chain Scission | × | N | |||
| Debonding | × | N | |||
| Physical | Plasticization | × | × | Y | |
| Swelling | × | Y | |||
| Leaching | × | × | × | N | |
| Relaxation (Physical Aging) | × | N | |||
| Physio-mechanical | Microcracking | × | × | N | |
| Micro voids | × | × | N |
| Material | a | b | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resin: 3501 | 6.3 | 1.7 | [82] |
| Resin: NMD 2373 | 9.9 | 2.3 | [82] |
| Composite: T300/1034 | 1.4 | 2 | [133] |
| Composite: Glass/Epoxy | 1 | 1 | [139] |
| Composite: T300/1034 | 1.7 | 1 | [146] |
| Composite: AS/3501-5 | 1.9 | 1 | [146] |
| Composite: E-glass/epoxy at 20 °C | 0.216 | 1.188 | |
| Composite: E-glass/epoxy at 40 °C | 0.496 | 1.752 | |
| Composite: E-glass/epoxy at 60 °C | 0.752 | 3.682 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hassanpour, B.; Karbhari, V.M. Characteristics and Models of Moisture Uptake in Fiber-Reinforced Composites: A Topical Review. Polymers 2024, 16, 2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16162265
Hassanpour B, Karbhari VM. Characteristics and Models of Moisture Uptake in Fiber-Reinforced Composites: A Topical Review. Polymers. 2024; 16(16):2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16162265
Chicago/Turabian StyleHassanpour, Behnaz, and Vistasp M. Karbhari. 2024. "Characteristics and Models of Moisture Uptake in Fiber-Reinforced Composites: A Topical Review" Polymers 16, no. 16: 2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16162265
APA StyleHassanpour, B., & Karbhari, V. M. (2024). Characteristics and Models of Moisture Uptake in Fiber-Reinforced Composites: A Topical Review. Polymers, 16(16), 2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16162265







