Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Electrochemical Sensor for the Detection of Azoxystrobin in Aqueous Media
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
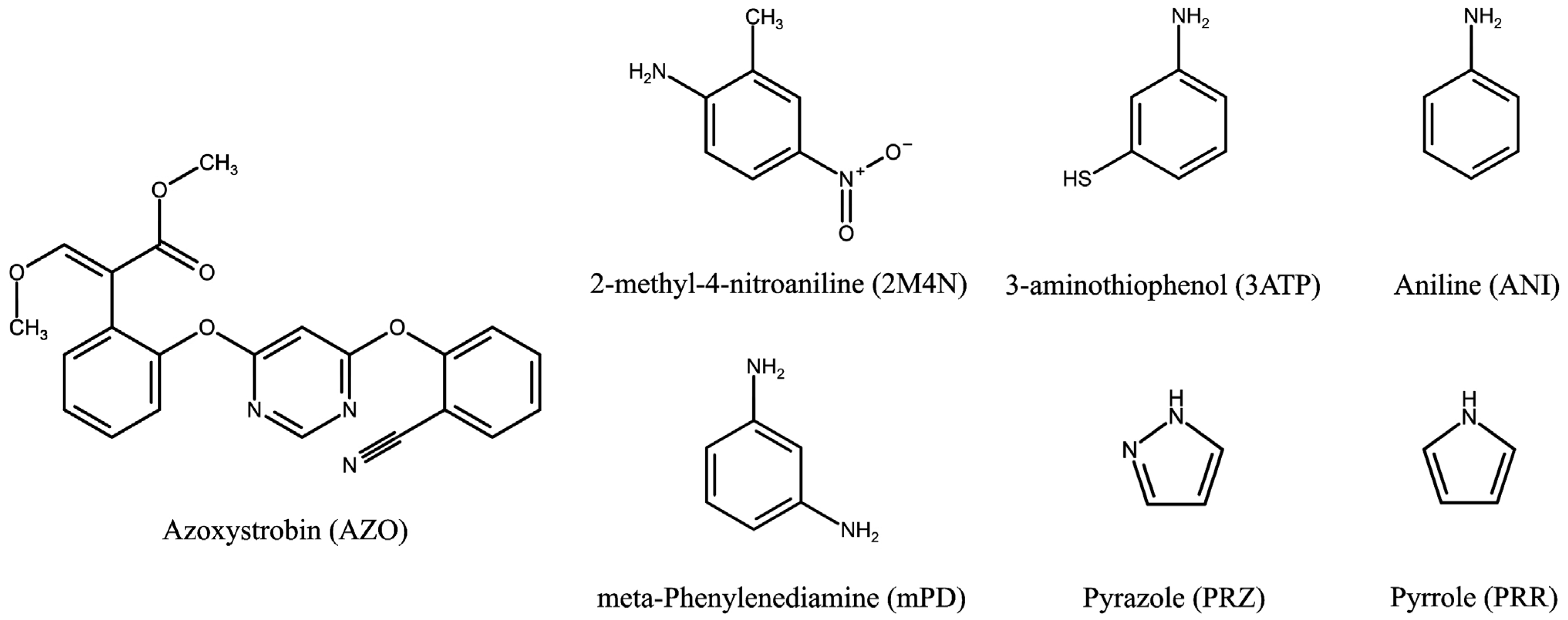
2.2. Functional Monomer Selection
2.3. Sensor Preparation
2.4. Evaluation of Sensor Performance
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Functional Monomers Selection
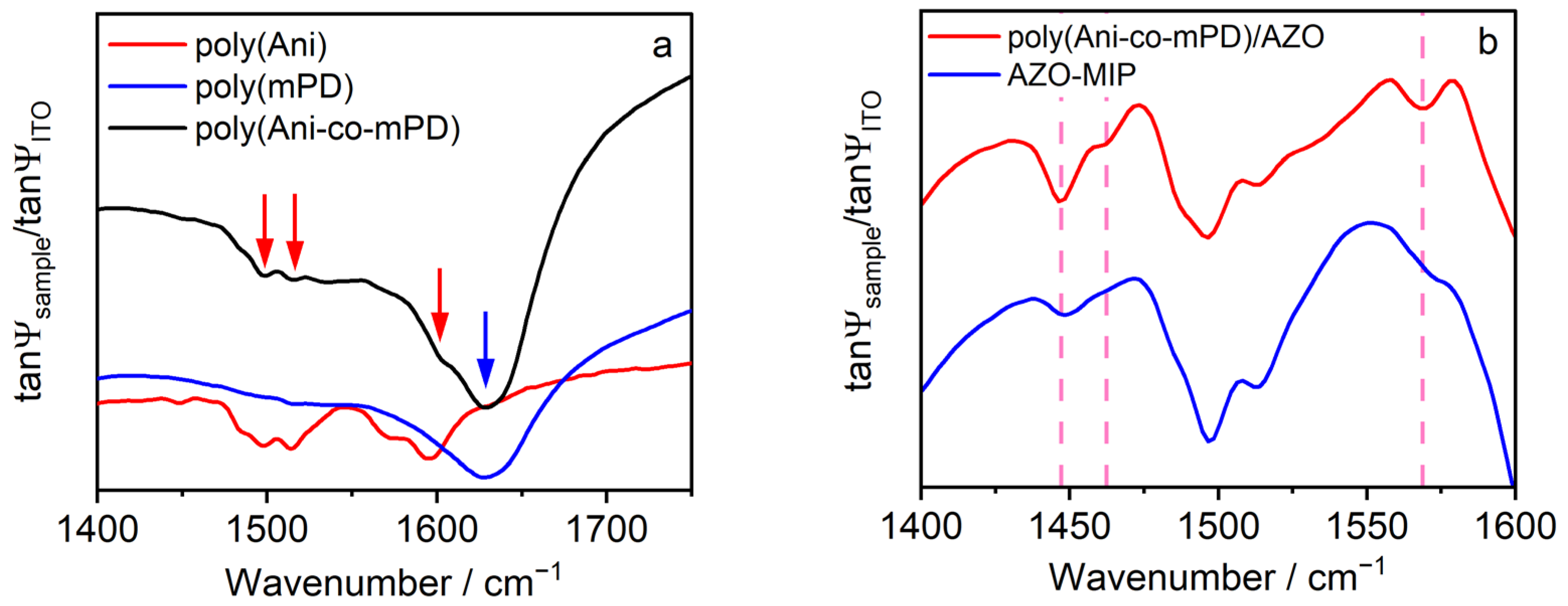
3.2. Synthesis and Characterization of AZO–MIP Film
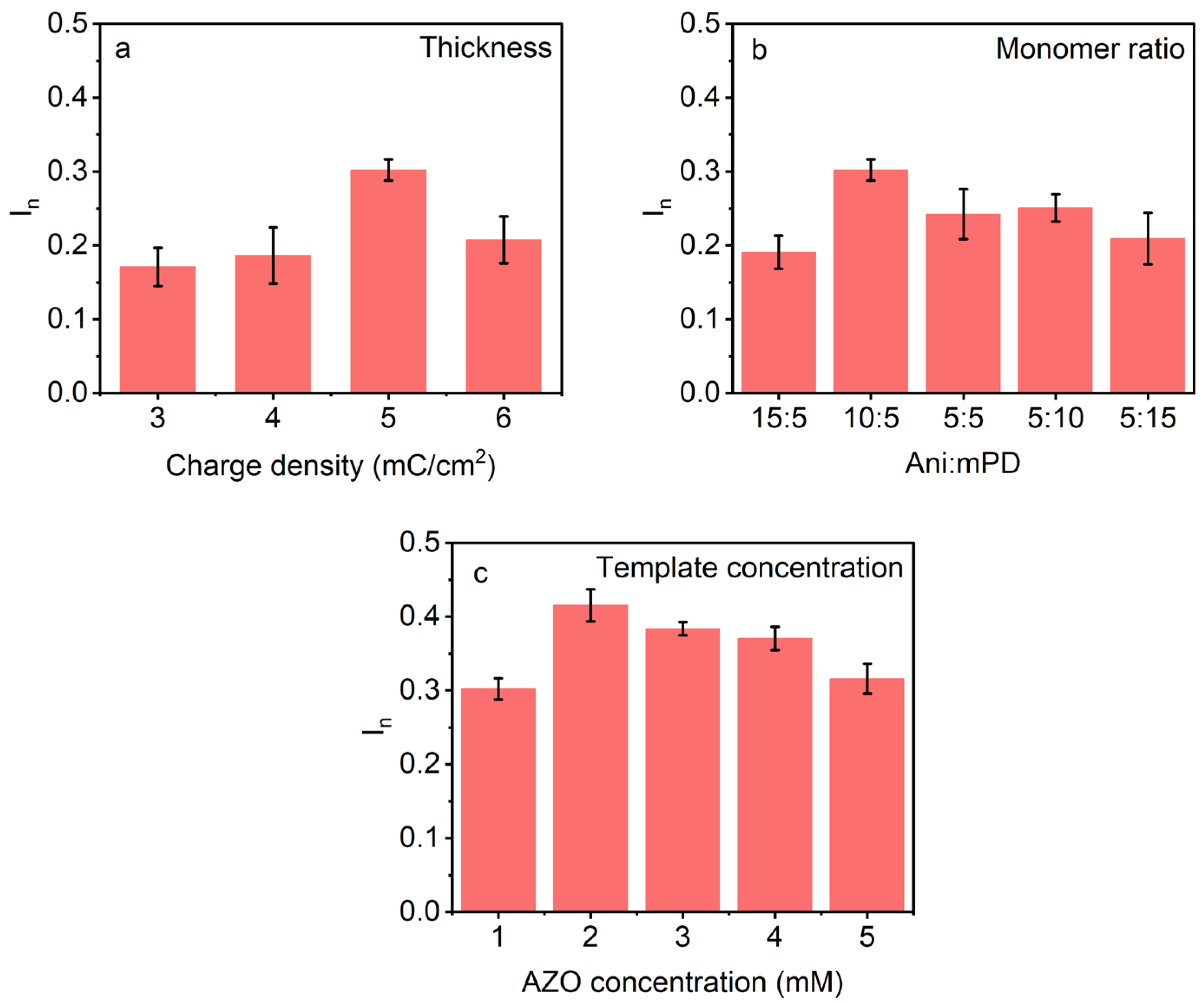
3.2.1. Effect of Thickness
3.2.2. Effect of the Monomer to Template Ratio
3.3. Performance of AZO Sensor
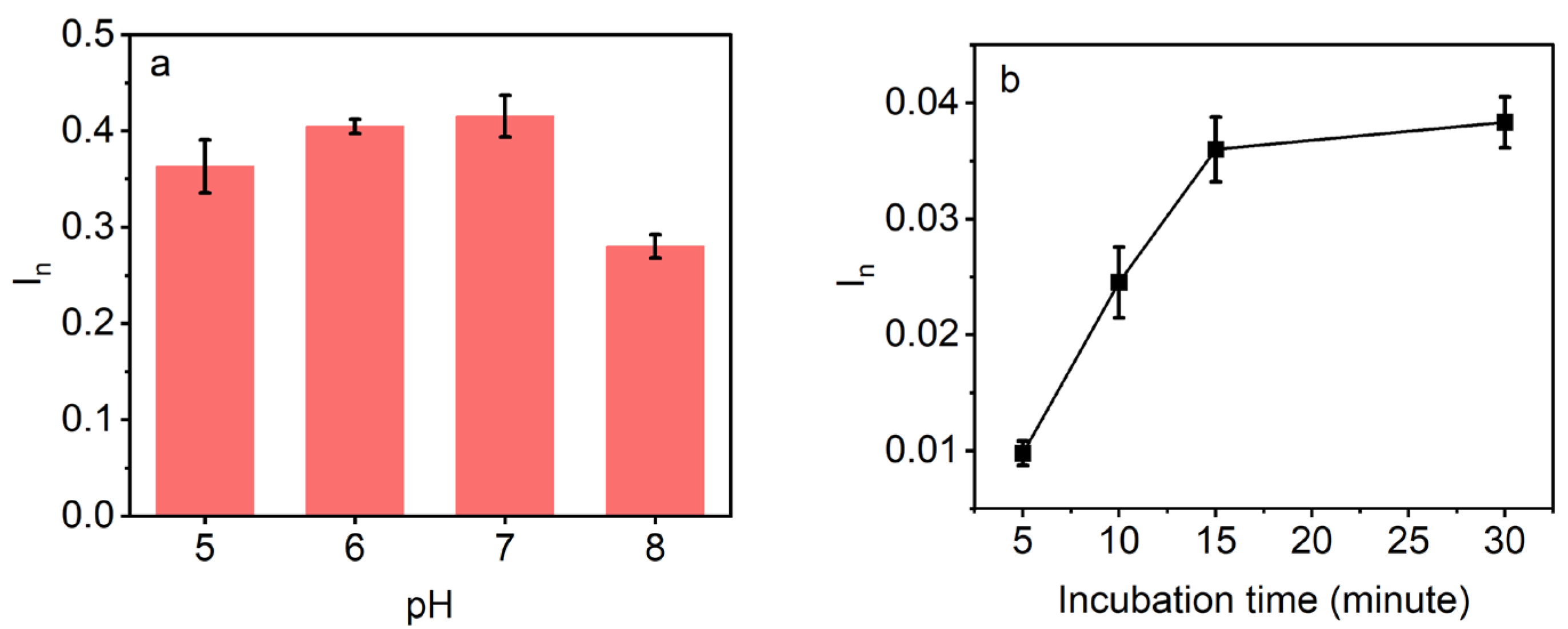
3.3.1. Effect of pH
3.3.2. Effect of Incubation Time
3.3.3. Sensitivity Study
3.3.4. Selectivity Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gikas, G.D.; Parlakidis, P.; Mavropoulos, T.; Vryzas, Z. Particularities of Fungicides and Factors Affecting Their Fate and Removal Efficacy: A Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leadbeater, A.J. Plant Health Management: Fungicides and Antibiotics. In Encyclopedia of Agriculture and Food Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 408–424. ISBN 978-0-08-093139-5. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Campbell, B.C.; Mahoney, N.; Chan, K.L.; Molyneux, R.J.; May, G.S. Enhanced activity of strobilurin and fludioxonil by using berberine and phenolic compounds to target fungal antioxidative stress response. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azoxystrobin Market: Global Industry Analysis And Forecast (2022–2029). 2023. Available online: https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/market-report/global-azoxystrobin-market/107455/ (accessed on 19 October 2023).
- Wu, P.; Wu, W.Z.; Han, Z.H.; Yang, H. Desorption and mobilization of three strobilurin fungicides in three types of soil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnhoorn, I.; Van Dyk, C. The first report of selected herbicides and fungicides in water and fish from a highly utilized and polluted freshwater urban impoundment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 33393–33398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.; Zhang, Q.; Lavoie, M.; Zhu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Yang, J.; Paerl, H.W.; Qian, H.; Zhu, Y.-G. The fungicide azoxystrobin promotes freshwater cyanobacterial dominance through altering competition. Microbiome 2019, 7, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Conclusion on the peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance azoxystrobin. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1542. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, F.; Martyniuk, C.J.; Wu, P.; Zhao, F.; Pang, S.; Wang, C.; Qiu, L. Long-Term Exposure to Environmental Concentrations of Azoxystrobin Delays Sexual Development and Alters Reproduction in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1672–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, F.; Zhu, L.; Li, H.; Yu, S.; Wang, C.; Qiu, L. Reproductive toxicity of azoxystrobin to adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 1109–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsvik, P.A.; Kroglund, F.; Finstad, B.; Kristensen, T. Effects of the fungicide azoxystrobin on Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) smolt. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 1852–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, E.T.; Lopes, I.; Pardal, M.Â. Occurrence, fate and effects of azoxystrobin in aquatic ecosystems: A review. Environ. Int. 2013, 53, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, W.; Qu, Q.; Ke, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Lu, T.; Qian, H. Metabolomic modulations in a freshwater microbial community exposed to the fungicide azoxystrobin. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 97, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, T.; Xu, Y.; Du, Z.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L. Ecotoxicology of strobilurin fungicides. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.; Sanchez, C.L.; Brammer-Robbins, E.; Pena-Delgado, C.; Kroyter, N.; El Ahmadie, N.; Watkins, J.M.; Aristizabal-Henao, J.J.; Bowden, J.A.; Souders, C.L.; et al. Neurotoxicity assessment of QoI strobilurin fungicides azoxystrobin and trifloxystrobin in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells: Insights from lipidomics and mitochondrial bioenergetics. NeuroToxicology 2022, 91, 290–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djangalina, E.; Altynova, N.; Mit, N.; Djansugurova, L. Complex approaches to assessing the pesticides risk on human health and environment. In Pesticides in the Natural Environment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 163–198. ISBN 978-0-323-90489-6. [Google Scholar]
- Polati, S.; Bottaro, M.; Frascarolo, P.; Gosetti, F.; Gianotti, V.; Gennaro, M.C. HPLC-UV and HPLC-MSn multiresidue determination of amidosulfuron, azimsulfuron, nicosulfuron, rimsulfuron, thifensulfuron methyl, tribenuron methyl and azoxystrobin in surface waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 579, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, F.; Portolés, T.; Ibáñez, M.; Bustos-López, M.C.; Díaz, R.; Botero-Coy, A.M.; Fuentes, C.L.; Peñuela, G. Use of time-of-flight mass spectrometry for large screening of organic pollutants in surface waters and soils from a rice production area in Colombia. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 439, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filho, A.M.; Dos Santos, F.N.; Pereira, P.A.D.P. Development, validation and application of a method based on DI-SPME and GC–MS for determination of pesticides of different chemical groups in surface and groundwater samples. Microchem. J. 2010, 96, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasapollo, G.; Sole, R.D.; Mergola, L.; Lazzoi, M.R.; Scardino, A.; Scorrano, S.; Mele, G. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Present and Future Prospective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5908–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Chacón, A.; Cetó, X.; Del Valle, M. Molecularly imprinted polymers—Towards electrochemical sensors and electronic tongues. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 6117–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayankojo, A.G.; Reut, J.; Nguyen, V.B.C.; Boroznjak, R.; Syritski, V. Advances in Detection of Antibiotic Pollutants in Aqueous Media Using Molecular Imprinting Technique—A Review. Biosensors 2022, 12, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebelo, P.; Costa-Rama, E.; Seguro, I.; Pacheco, J.G.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Cordeiro, M.N.D.S.; Delerue-Matos, C. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrochemical sensors for environmental analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 172, 112719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanoun, O.; Lazarević-Pašti, T.; Pašti, I.; Nasraoui, S.; Talbi, M.; Brahem, A.; Adiraju, A.; Sheremet, E.; Rodriguez, R.D.; Ben Ali, M.; et al. A Review of Nanocomposite-Modified Electrochemical Sensors for Water Quality Monitoring. Sensors 2021, 21, 4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umapathi, R.; Ghoreishian, S.M.; Sonwal, S.; Rani, G.M.; Huh, Y.S. Portable electrochemical sensing methodologies for on-site detection of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 453, 214305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinrichs, K.; Eichhorn, K.-J. (Eds.) Ellipsometry of Functional Organic Surfaces and Films; Springer Series in Surface Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 52, ISBN 978-3-642-40127-5. [Google Scholar]
- Röseler, A.; Korte, E. Infrared Spectroscopic Ellipsometry. In Handbook of Vibrational Spectroscopy; Chalmers, J.M., Griffiths, P.R., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001; ISBN 978-0-471-98847-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ayankojo, A.G.; Reut, J.; Öpik, A.; Tretjakov, A.; Syritski, V. Enhancing binding properties of imprinted polymers for the detection of small molecules. Proc. Est. Acad. Sci. 2018, 67, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazeikiene, R.; Malinauskas, A. Electrochemical copolymerization of aniline with m-phenylenediamine. Synth. Met. 1998, 92, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mažeikienė, R.; Niaura, G.; Malinauskas, A. A comparative Raman spectroelectrochemical study of selected polyaniline derivatives in a pH-neutral solution. Synth. Met. 2010, 160, 1060–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, L.; Ho, K.; Shen, S.; Pu, H.; Hsieh, T.; Kuo, C.; Tseng, B. Short polyaniline nanorod prepared in the presence of para-phenylenediamine. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 1853–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Xie, Q.; Hu, J.; Yao, S. Studies on electrochemical copolymerization of aniline with o-phenylenediamine and degradation of the resultant copolymers via electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance and scanning electrochemical microscope. Synth. Met. 2006, 156, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskal, J. Polymers of phenylenediamines. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 41, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskal, J.; Trchová, M. Aniline oligomers versus polyaniline. Polym. Int. 2012, 61, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnu, N.; Kumar, A.S.; Pillai, K.C. Unusual neutral pH assisted electrochemical polymerization of aniline on a MWCNT modified electrode and its enhanced electro-analytical features. Analyst 2013, 138, 6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.B.C.; Ayankojo, A.G.; Reut, J.; Rappich, J.; Furchner, A.; Hinrichs, K.; Syritski, V. Molecularly imprinted co-polymer for class-selective electrochemical detection of macrolide antibiotics in aqueous media. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 374, 132768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayankojo, A.G.; Boroznjak, R.; Reut, J.; Tuvikene, J.; Timmusk, T.; Syritski, V. Electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer for rapid quantitative detection of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 397, 134656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayankojo, A.G.; Reut, J.; Ciocan, V.; Öpik, A.; Syritski, V. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based sensor for electrochemical detection of erythromycin. Talanta 2020, 209, 120502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, M.-I.; Quillard, S.; Rebourt, E.; Louarn, G.; Buisson, J.P.; Monkman, A.; Lefrant, S. Vibrational Analysis of Polyaniline: A Model Compound Approach. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 7382–7392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-G.; Huang, M.-R.; Duan, W.; Yang, Y.-L. Novel Multifunctional Polymers from Aromatic Diamines by Oxidative Polymerizations. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 2925–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chai, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Yu, W.; Sang, P. pH Manipulation: A Facile Method for Lowering Oxidation State and Keeping Good Yield of Poly (m-phenylenediamine) and Its Powerful Ag+ Adsorption Ability. Langmuir 2011, 27, 13729–13738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Duan, W.; Huang, M.; Yang, Y. Preparation and characterization of soluble terpolymers from m-phenylenediamine, o-anisidine, and 2,3-xylidine. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2001, 39, 3989–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chang, H.; Zhao, W.; Liang, D.; Tang, S.; Jin, R. Theoretical design and preparation of molecularly imprinted polymers of formaldehyde and acrylamide. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, A.; Tiwari, S.K.; Pandey, H.K.; Chaurasia, A.K.; Singh, S.; Singh, Y.V. Groundwater quality assessment using water quality index (WQI) under GIS framework. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan Omer, N. Water Quality Parameters. In Water Quality—Science, Assessments and Policy; Summers, K., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; ISBN 978-1-78985-577-7. [Google Scholar]
- Mattson, M.D. Acid lakes and rivers. In Environmental Geology; Encyclopedia of Earth Science; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 6–9. ISBN 978-0-412-74050-3. [Google Scholar]
- Senapathi, V.; Chung, S.Y.; Lee, S.; Park, N. Assessment of river water quality via environmentric multivariate statistical tools and water quality index: A case study of Nakdong River Basin, Korea. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2014, 9, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Specifications FAO. FAO Specifications and Evaluations for Agricultural Pesticides; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Dinelli, E.; Lima, A.; Albanese, S.; Birke, M.; Cicchella, D.; Giaccio, L.; Valera, P.; De Vivo, B. Major and trace elements in tap water from Italy. J. Geochem. Explor. 2012, 112, 54–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; An, W.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Y. Assessing the impact of source water on tap water bacterial communities in 46 drinking water supply systems in China. Water Res. 2020, 172, 115469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azoulay, A.; Garzon, P.; Eisenberg, M.J. Comparison of the mineral content of tap water and bottled waters. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2001, 16, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berenzen, N.; Lentzen-Godding, A.; Probst, M.; Schulz, H.; Schulz, R.; Liess, M. A comparison of predicted and measured levels of runoff-related pesticide concentrations in small lowland streams on a landscape level. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madej, M.; Kochana, J.; Baś, B. Determination of viloxazine by differential pulse voltammetry with boron-doped diamond electrode. Monatsh Chem. 2019, 150, 1655–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharous, M.; Bounab, L.; Pereira, F.J.; Choukairi, M.; López, R.; Aller, A.J. Electrochemical Kinetics and Detection of Paracetamol by Stevensite-Modified Carbon Paste Electrode in Biological Fluids and Pharmaceutical Formulations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Spiked AZO (nM) | Found AZO (nM) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 15 ± 0.1 | 18 ± 1 | 119 ± 6 |
| 30 ± 0.2 | 29 ± 1 | 95 ± 4 |
| 50 ± 0.4 | 47 ± 3 | 94 ± 7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, V.B.C.; Reut, J.; Rappich, J.; Hinrichs, K.; Syritski, V. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Electrochemical Sensor for the Detection of Azoxystrobin in Aqueous Media. Polymers 2024, 16, 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16101394
Nguyen VBC, Reut J, Rappich J, Hinrichs K, Syritski V. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Electrochemical Sensor for the Detection of Azoxystrobin in Aqueous Media. Polymers. 2024; 16(10):1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16101394
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Vu Bao Chau, Jekaterina Reut, Jörg Rappich, Karsten Hinrichs, and Vitali Syritski. 2024. "Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Electrochemical Sensor for the Detection of Azoxystrobin in Aqueous Media" Polymers 16, no. 10: 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16101394
APA StyleNguyen, V. B. C., Reut, J., Rappich, J., Hinrichs, K., & Syritski, V. (2024). Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Electrochemical Sensor for the Detection of Azoxystrobin in Aqueous Media. Polymers, 16(10), 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16101394







