Fabrication of Polymeric Hydrogels Containing Esomeprazole for Oral Delivery: In Vitro and In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Characterization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Hydrogels
2.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
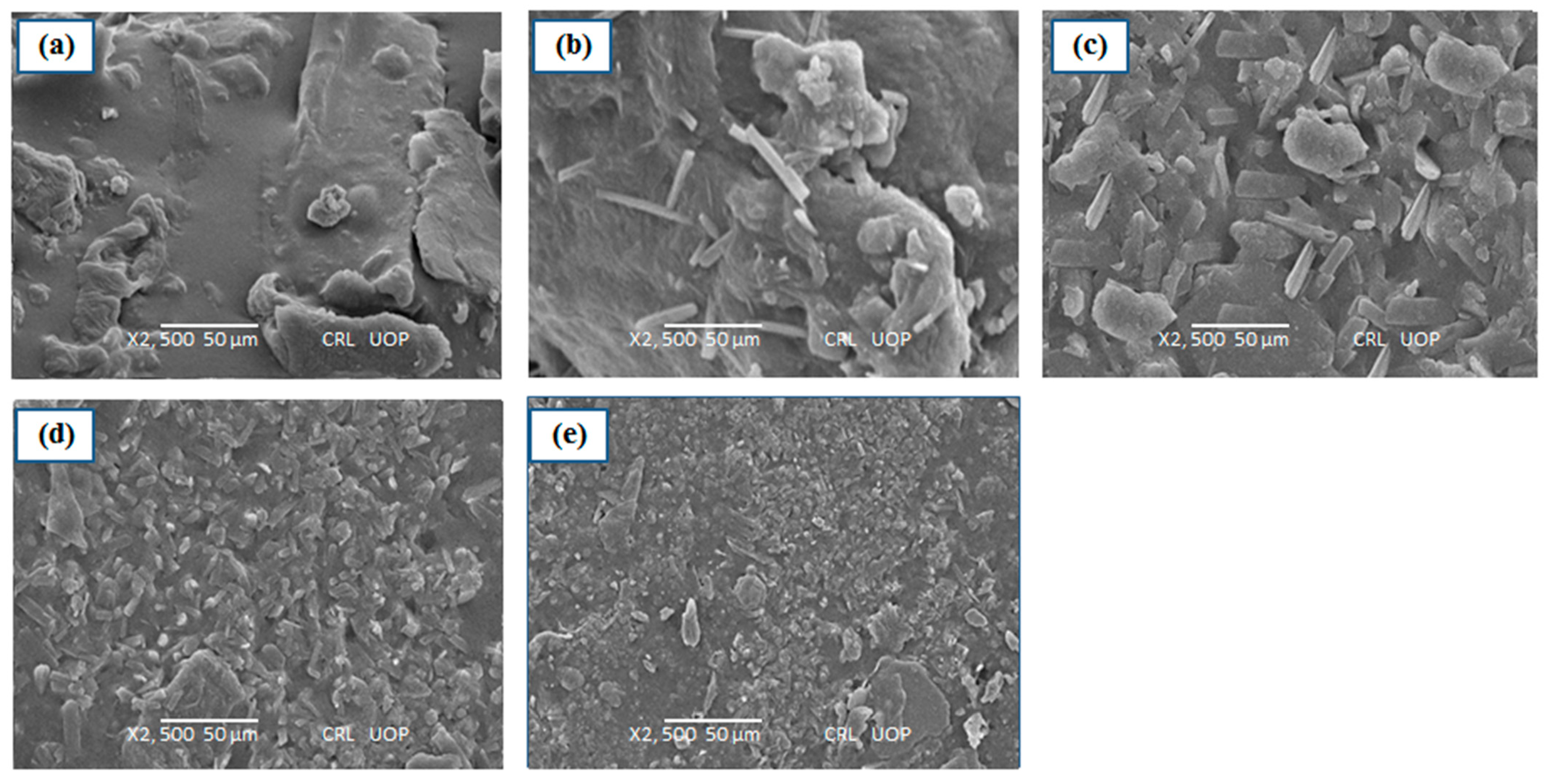
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.5. Swelling Measurements
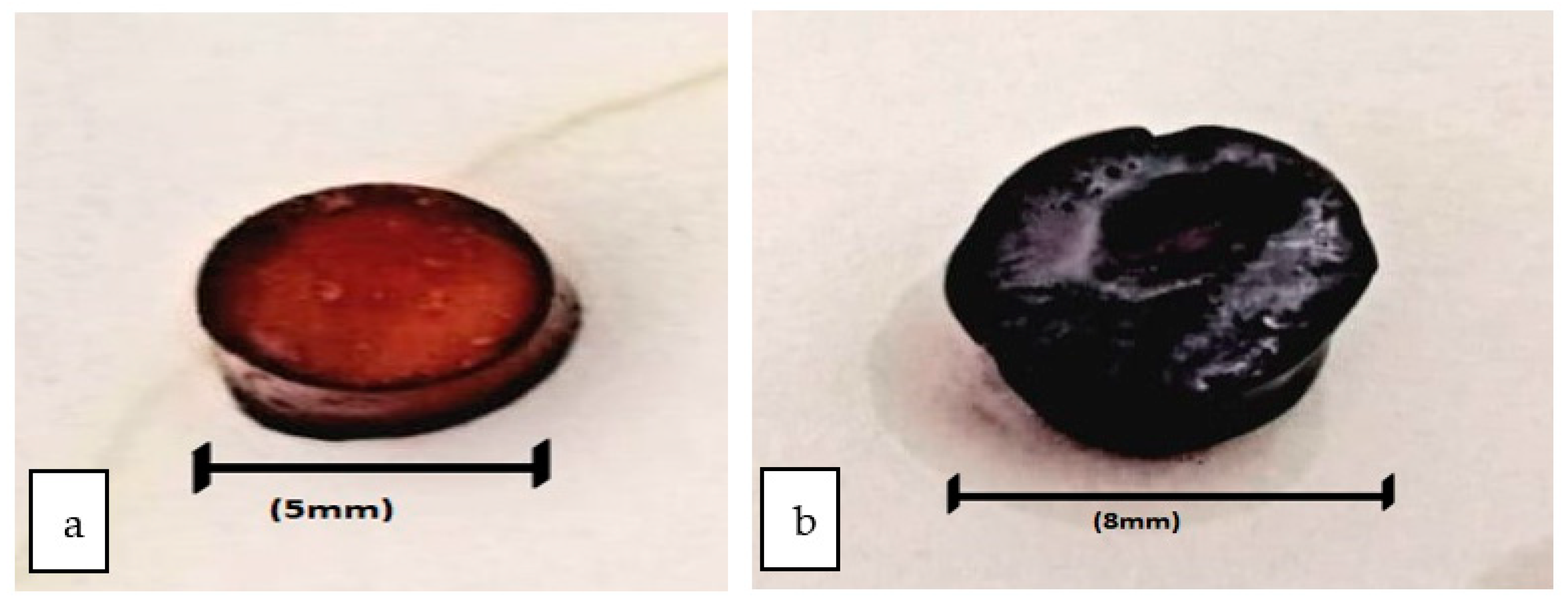
2.6. Surface Roughness of Hydrogel
2.7. Drug Content Analysis
2.8. Encapsulation Efficiency
2.9. In Vitro Release Study
2.10. Drug Release Kinetics
2.10.1. Zero Order Kinetics
2.10.2. First Order Kinetics
2.10.3. Hixon–Crowell Model
2.10.4. Higuchi Model
2.10.5. Power Law Equation
2.11. In Vivo Studies of Prepared Hydrogel
2.12. Stability Study of Prepared Hydrogel Formulations
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
3.2. Swelling Measurements
3.3. Surface Roughness of Hydrogel
3.4. Determination of Encapsulation Efficiency and Drug Content
3.5. SEM Analysis
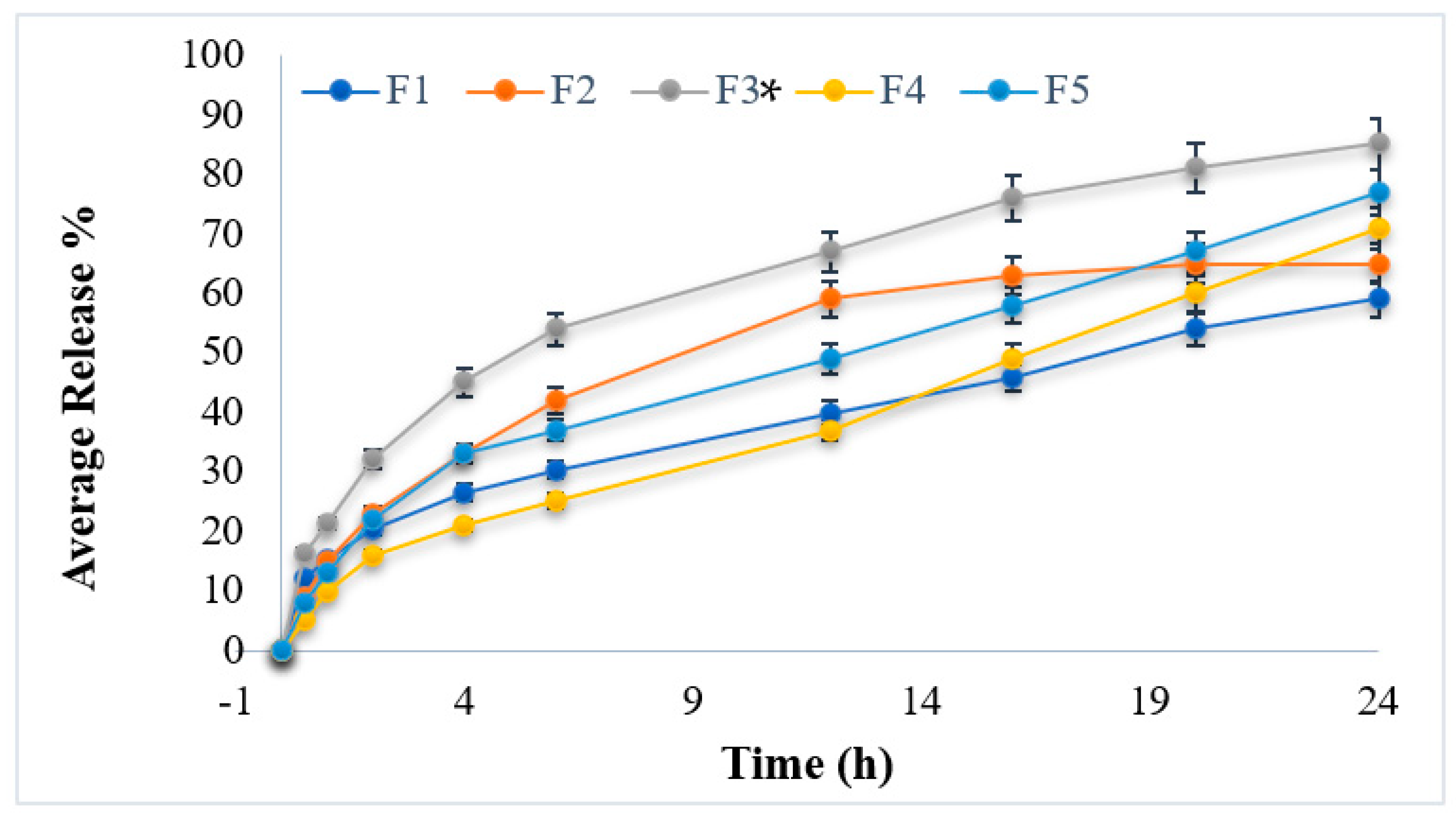
3.6. In Vitro Drug Release Studies
3.7. Kinetic Profiling
3.8. In Vivo Studies
3.9. Stability Study of Prepared Hydrogel Formulations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vilar, G.; Tulla-Puche, J.; Albericio, F. Polymers and drug delivery systems. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2012, 9, 367–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharpe, L.A.; Daily, A.M.; Horava, S.D.; Peppas, N.A. Therapeutic applications of hydrogels in oral drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 901–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahsan, A.; Tian, W.-X.; Farooq, M.A.; Khan, D.H. An overview of hydrogels and their role in transdermal drug delivery. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2021, 70, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeera, M.; Vaidevi, S.; Ruckmani, K. Characterization techniques of hydrogel and its applications. In Cellulose-Based Superabsorbent Hydrogels; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 737–761. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, L.-H.; Qi, C.; Ma, M.-G.; Wan, P. Multifunctional cellulose-based hydrogels for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 1541–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.M. Hydrogel: Preparation, characterization, and applications: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bharskar, G. A review on hydrogel. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 9, 1288–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Calori, I.R.; Braga, G.; de Jesus, P.d.C.C.; Bi, H.; Tedesco, A.C. Polymer scaffolds as drug delivery systems. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 129, 109621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, G.; Wang, Y.; Cai, R.; Chang, H.; Song, K.; Zuo, H.; Zhao, P.; Xia, Q.; He, H. Design and performance of sericin/poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel as a drug delivery carrier for potential wound dressing application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 101, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolarska, O.; Pawlowska-Zygarowicz, A.; Soto, A.; Rodríguez, H.; Smiglak, M. Mixtures of ionic liquids as more efficient media for cellulose dissolution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 178, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Huang, S.; Hu, Z.; Yang, W.; Lan, Y.; Zhu, J.; Hancharou, A.; Guo, R.; Tang, B. In situ formed anti-inflammatory hydrogel loading plasmid DNA encoding VEGF for burn wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2019, 100, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qi, Z.; Zheng, S.; Chang, Y.; Kong, W.; Fu, C.; Yu, Z.; Yang, X.; Pan, S. The application of hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels in bone and cartilage tissue engineering. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 2019, 3027303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nii, T. Strategies using gelatin microparticles for regenerative therapy and drug screening applications. Molecules 2021, 26, 6795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezk, A.I.; Obiweluozor, F.O.; Choukrani, G.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. Drug release and kinetic models of anticancer drug (BTZ) from a pH-responsive alginate polydopamine hydrogel: Towards cancer chemotherapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 141, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laverty, G.; Gorman, S.P.; Gilmore, B.F. Antimicrobial peptide incorporated poly (2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) hydrogels for the prevention of Staphylococcus epidermidis-associated biomaterial infections. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2012, 100, 1803–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhu, T.; Tang, N.; Bai, X.; Zheng, C. Preparation of printable double-network hydrogels with rapid self-healing and high elasticity based on hyaluronic acid for controlled drug release. Polymer 2020, 186, 121994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annuar, A.; Rahman, R.; Munir, A.; Murad, A.; El-enshasy, H.; Illias, R. Assessing the Comperative Effectiveness of Implementation Strategies for Professional Sevices to Community Pharmacy: A Systematic Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 118159. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, C.M.; Lamendola, C.; Holst, J.J.; Deacon, C.F.; McLaughlin, T.L. The use of gastrostomy tube for the long-term remission of hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia after Roux-en-y gastric bypass: A case report. AACE Clin. Case Rep. 2015, 1, e84–e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S.; Sudhakara, P.; Singh, J.; Ilyas, R.; Asyraf, M.; Razman, M. Critical review of biodegradable and bioactive polymer composites for bone tissue engineering and drug delivery applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.H.; Rong, L.H.; Ge, J.; Tiu, B.D.B.; Cao, P.F.; Advincula, R.C. Mussel-inspired hydrogel composite with multi-stimuli responsive behavior. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2019, 304, 1800720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ino, K.; Fukuda, M.T.; Hiramoto, K.; Taira, N.; Nashimoto, Y.; Shiku, H. Fabrication of three-dimensional calcium alginate hydrogels using sacrificial templates of sugar. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2020, 130, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olga, K.; Khalil, A.; Edric, G.; Arousian, A. Review paper: Materials and techniques for in vivo pH monitoring. IEEE Sens. J 2008, 8, 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Cleveland, C.; Yin, X.; Booth, L.; Lin, J.; Lucy Lee, Y.-A.; Mazdiyasni, H.; Saxton, S.; et al. Triggerable tough hydrogels for gastric resident dosage forms. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maeng, J.H.; Bang, B.W.; Lee, E.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.G.; Lee, D.H.; Yang, S.-G. Endoscopic application of EGF-chitosan hydrogel for precipitated healing of GI peptic ulcers and mucosectomy-induced ulcers. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2014, 25, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Si, T.; Kozelskaya, A.I.; Akimchenko, I.O.; Tverdokhlebov, S.I.; Rutkowski, S.; Frueh, J. Biodegradable magnesium fuel-based Janus micromotors with surfactant induced motion direction reversal. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 218, 112780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Wu, Z.; Rutkowski, S.; Tverdokhlebov, S.I.; Frueh, J. Influence of the pH value and the surfactant concentration on the pumping performance of magnesium fuel based Janus micropumps. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 626, 127081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Qing, R.; Hao, S.; Ding, Y.; Yin, H.; Zha, G.; Chen, X.; Ji, J.; Wang, B. Fabrication of ulcer-adhesive oral keratin hydrogel for gastric ulcer healing in a rat. Regen. Biomater. 2021, 8, rbab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, J.; Hochberg, M.; Fort, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hwang, C.; Sostek, M. Clinical trial: The incidence of NSAID-associated endoscopic gastric ulcers in patients treated with PN 400 (naproxen plus esomeprazole magnesium) vs. enteric-coated naproxen alone. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 32, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.K.; Bradshaw, T.D.; Chu, J.; Khoo, T.J.; Wiart, C. In vitro anticancer effect of Artabotrys crassifolius Hook. f. & Thomson against human carcinoma cell lines. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2014, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Pantić, M.; Kravanja, K.A.; Knez, Ž.; Novak, Z. Influence of the Impregnation Technique on the Release of Esomeprazole from Various Bioaerogels. Polymers 2021, 13, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.; Abreu, A.C.; Dias, C.; Saavedra, M.J.; Borges, F.; Simões, M. New perspectives on the use of phytochemicals as an emergent strategy to control bacterial infections including biofilms. Molecules 2016, 21, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhail, M.; Ullah, H.; Vu, Q.L.; Khan, A.; Tsai, M.-J.; Wu, P.-C. Preparation of pH-Responsive Hydrogels Based on Chondroitin Sulfate/Alginate for Oral Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, H.; Ghani, A.; Iqbal, D.N.; Ahmad, N.; Nazir, S.; Muhammad, M.J.; Hussain, E.A.; Nazir, A.; Iqbal, M. Preparation and characterization of guar gum based biopolymeric hydrogels for controlled release of antihypertensive drug. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiya, M.A.M.; Mazumder, K.; Dewan, I.; Al Mamun, M.E. Design and Development of Clarithromycin Floating Pellets Using Sodium Alginate and HPMC. Dhaka Univ. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 21, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, K.; Ray, S.D. Alginate/hydrophobic HPMC (60M) particulate systems: New matrix for site-specific and controlled drug delivery. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 47, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nochos, A.; Douroumis, D.; Bouropoulos, N. In vitro release of bovine serum albumin from alginate/HPMC hydrogel beads. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 74, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthiga, S. Formulation and Characterization of Urapidil Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles for the treatment of Hypertension. Master’s Thesis, College of Pharmacy, Madras Medical College, Chennai, India, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Thai, H.; Nguyen, C.T.; Thach, L.T.; Tran, M.T.; Mai, H.D.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Le, G.D.; Van Can, M.; Tran, L.D.; Bach, G.L.; et al. Characterization of chitosan/alginate/lovastatin nanoparticles and investigation of their toxic effects in vitro and in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forni, F.; Coppi, G.; Vandelli, M.A.; Bernabei, M.T. An interpretation of the diffusion-type mechanism of drug release from microcapsules. Int. J. Pharm. 1990, 60, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritger, P.L.; Peppas, N.A. A simple equation for description of solute release II: Fickian and anomalous release from swellable devices. J. Control. Release 1987, 5, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, M.S.; Al-Harbi, F.F.; Nawaz, A.; Rashid, S.A.; Farid, A.; Mohaini, M.A.; Alsalman, A.J.; Hawaj, M.A.A.; Alhashem, Y.N. Formulation and Evaluation of Hydrophilic Polymer Based Methotrexate Patches: In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization. Polymers 2022, 14, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, M.S.; Nawaz, A.; Rashid, S.A.; Akhlaq, M.; Iqbal, A.; Khan, M.J.; Khan, M.S.; Lim, V.; Alfatama, M. Formulation of Polymers-Based Methotrexate Patches and Investigation of the Effect of Various Penetration Enhancers: In Vitro, Ex Vivo and In Vivo Characterization. Polymers 2022, 14, 2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawłowicz, K.; Paczkowska-Walendowska, M.; Osmałek, T.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Towards the Preparation of a Hydrogel from Lyophilisates of the Aloe arborescens Aqueous Extract. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Ganure, A.L.; Subudhi, B.B.; Shukla, S. Preparation and characterization of pH-sensitive methyl methacrylate-g-starch/hydroxypropylated starch hydrogels: In vitro and in vivo study on release of esomeprazole magnesium. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2015, 5, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizwan, M.; Yahya, R.; Hassan, A.; Yar, M.; Azzahari, A.D.; Selvanathan, V.; Sonsudin, F.; Abouloula, C.N. pH sensitive hydrogels in drug delivery: Brief history, properties, swelling, and release mechanism, material selection and applications. Polymers 2017, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, P.; Ganure, A.L.; Subudhi, B.B.; Shukla, S. Design and Comparative Evaluation of In-Vitro Drug Release, Pharmacokinetics and Gamma Scintigraphic Analysis of Controlled Release Tablets Using Novel pH Sensitive Starch and Modified Starch-acrylate Graft Copolymer Matrices. Int. J. Pharm. Res 2015, 14, 677–691. [Google Scholar]
- Nindiyasari, F.; Ziegler, A.; Griesshaber, E.; Fernandez-Diaz, L.; Huber, J.; Walther, P.; Schmahl, W.W. Effect of hydrogel matrices on calcite crystal growth morphology, aggregate formation, and co-orientation in biomimetic experiments and biomineralization environments. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 2667–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mut, A.M.; Vlaia, L.; Coneac, G.; Olariu, I.; Vlaia, V.; Stănciulescu, C.; Mitu, M.A.; Szabadai, Z.; Lupuleasa, D. Chitosan/HPMC-based hydrogels containing essential oils for topical delivery of fluconazole: Preliminary studies. Farmacia 2018, 66, 248–256. [Google Scholar]
- Gemeinhart, R.A.; Park, H.; Park, K. Pore structure of superporous hydrogels. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2000, 11, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layek, B.; Mandal, S. Natural polysaccharides for controlled delivery of oral therapeutics: A recent update. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 230, 115617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Wong, A.B. Stabilization of ferulic acid in topical gel formulation via nanoencapsulation and pH optimization. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Formulations Code | Esomeprazole (g) | Chondroitin Sulfate (g) | Acrylic Acid (g) | Methylene Bisacrylamide (g) | HPMC (g) | Calcium Alginate (g) | PVA (g) | Distilled Water (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 1 | 0.2 | 5 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 1 | 0.2 | 17.3 |
| F2 | 1 | 0.2 | 5 | 0.05 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 16.55 |
| F3 | 1 | 0.2 | 5 | 0.05 | 1 | 1 | 0.2 | 16.35 |
| F4 | 1 | 0.2 | 5 | 0.05 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 16.55 |
| F5 | 1 | 0.2 | 5 | 0.05 | 2 | 0.25 | 0.2 | 16.3 |
| Characteristics | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Encapsulation efficacy (%) | 81.2 ± 1.27 | 80.4 ± 1.97 | 83.1 ± 2.16 | 79.2 ± 2.41 | 80.9 ± 1.02 |
| Drug Content (%) | 89.3 ± 1.41 | 91.6 ± 1.32 | 92.1 ± 2.31 | 90.8 ± 1.10 | 90.1 ± 1.21 |
| Characteristics | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Release (%) | 59.21 ± 0.21 | 65.26 ± 0.31 | 85.43 ± 0.32 | 71.63 ± 0.23 | 77.45 ± 0.23 |
| Formulations Code | Zero Order | First Order | Higuchi | Korsemeyer–Peppas | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r2 | K0 | r2 | K1 | r2 | KH | r2 | nP | |
| F1 | 0.935 | 5.12 | 0.932 | 0.023 | 0.912 | 4.115 | 0.934 | 1.12 |
| F2 | 0.923 | 5.32 | 0.916 | 0.042 | 0.932 | 4.121 | 0.943 | 1.34 |
| F3 | 0.939 | 5.41 | 0.927 | 0.054 | 0.942 | 4.154 | 0.954 | 1.54 |
| F4 | 0.919 | 5.65 | 0.917 | 0.017 | 0.946 | 4.112 | 0.923 | 1.23 |
| F5 | 0.917 | 5.15 | 0.920 | 0.085 | 0.965 | 4.165 | 0.965 | 1.56 |
| Formulation Code | Day “0” | Day “30” | Day “60” | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color | Drug Content % | Color | Drug Content % | Color | Drug Content % | |
| F1 | NC | 89.3 ± 1.41 | NC | 89.1 ± 1.32 | NC | 88.8 ± 1.41 |
| F2 | NC | 91.6 ± 1.32 | NC | 90.8 ± 1.45 | NC | 91.1 ± 1.32 |
| F3 | NC | 92.1 ± 2.31 | NC | 91.7 ± 2.65 | NC | 91.7 ± 2.31 |
| F4 | NC | 90.8 ± 1.10 | NC | 90.1 ± 1.38 | NC | 89.1 ± 1.10 |
| F5 | NC | 90.1 ± 1.21 | NC | 89.9 ± 1.65 | NC | 89.8 ± 1.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ullah, I.; Farooq, A.S.; Naz, I.; Ahmad, W.; Ullah, H.; Sehar, S.; Nawaz, A. Fabrication of Polymeric Hydrogels Containing Esomeprazole for Oral Delivery: In Vitro and In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Characterization. Polymers 2023, 15, 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071798
Ullah I, Farooq AS, Naz I, Ahmad W, Ullah H, Sehar S, Nawaz A. Fabrication of Polymeric Hydrogels Containing Esomeprazole for Oral Delivery: In Vitro and In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Characterization. Polymers. 2023; 15(7):1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071798
Chicago/Turabian StyleUllah, Irshad, Ayesha Shuja Farooq, Iffat Naz, Waqar Ahmad, Hidayat Ullah, Shama Sehar, and Asif Nawaz. 2023. "Fabrication of Polymeric Hydrogels Containing Esomeprazole for Oral Delivery: In Vitro and In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Characterization" Polymers 15, no. 7: 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071798
APA StyleUllah, I., Farooq, A. S., Naz, I., Ahmad, W., Ullah, H., Sehar, S., & Nawaz, A. (2023). Fabrication of Polymeric Hydrogels Containing Esomeprazole for Oral Delivery: In Vitro and In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Characterization. Polymers, 15(7), 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071798








