Porous Polymer Materials in Triboelectric Nanogenerators: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
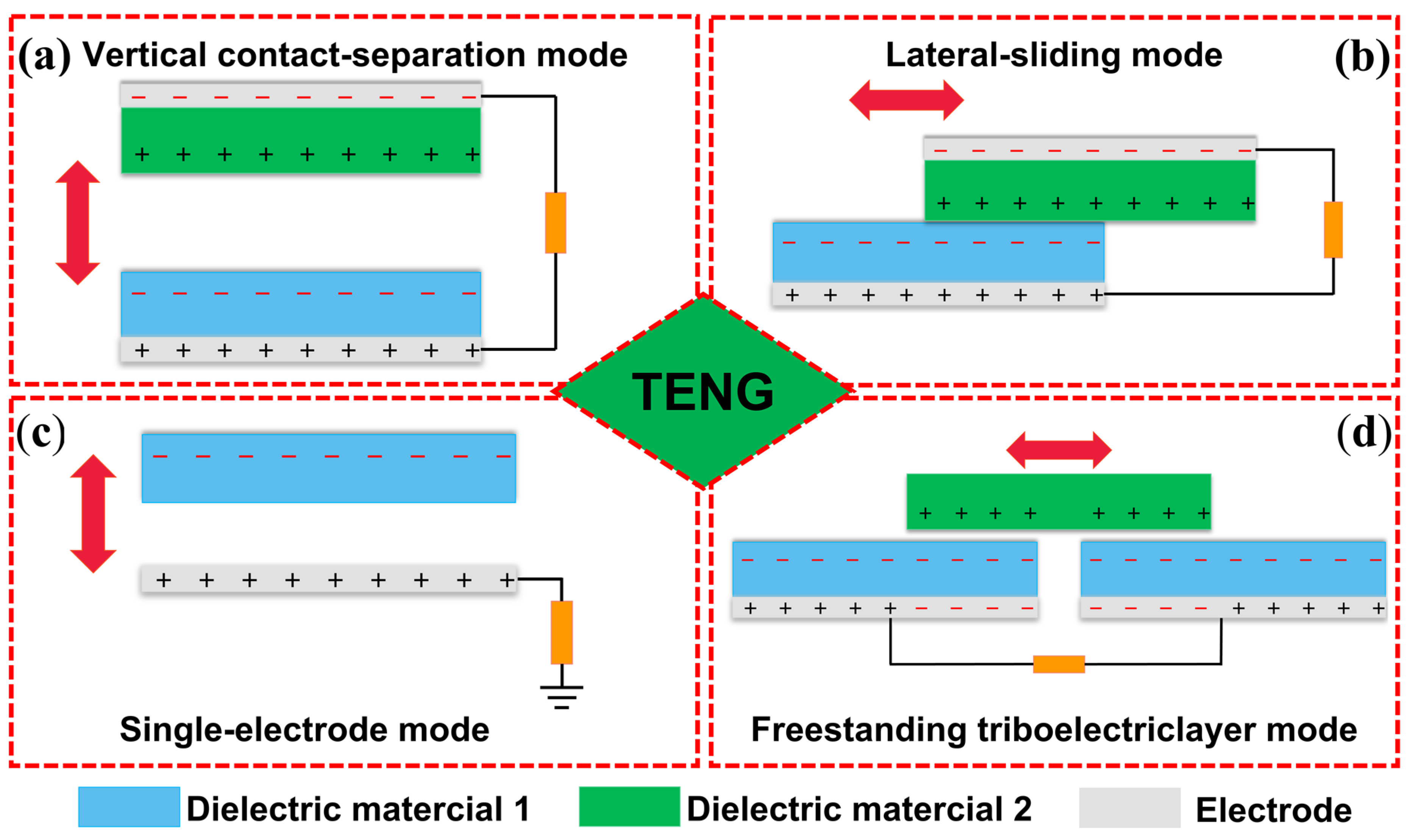
2. Basic Principle and Working Mode of TENG
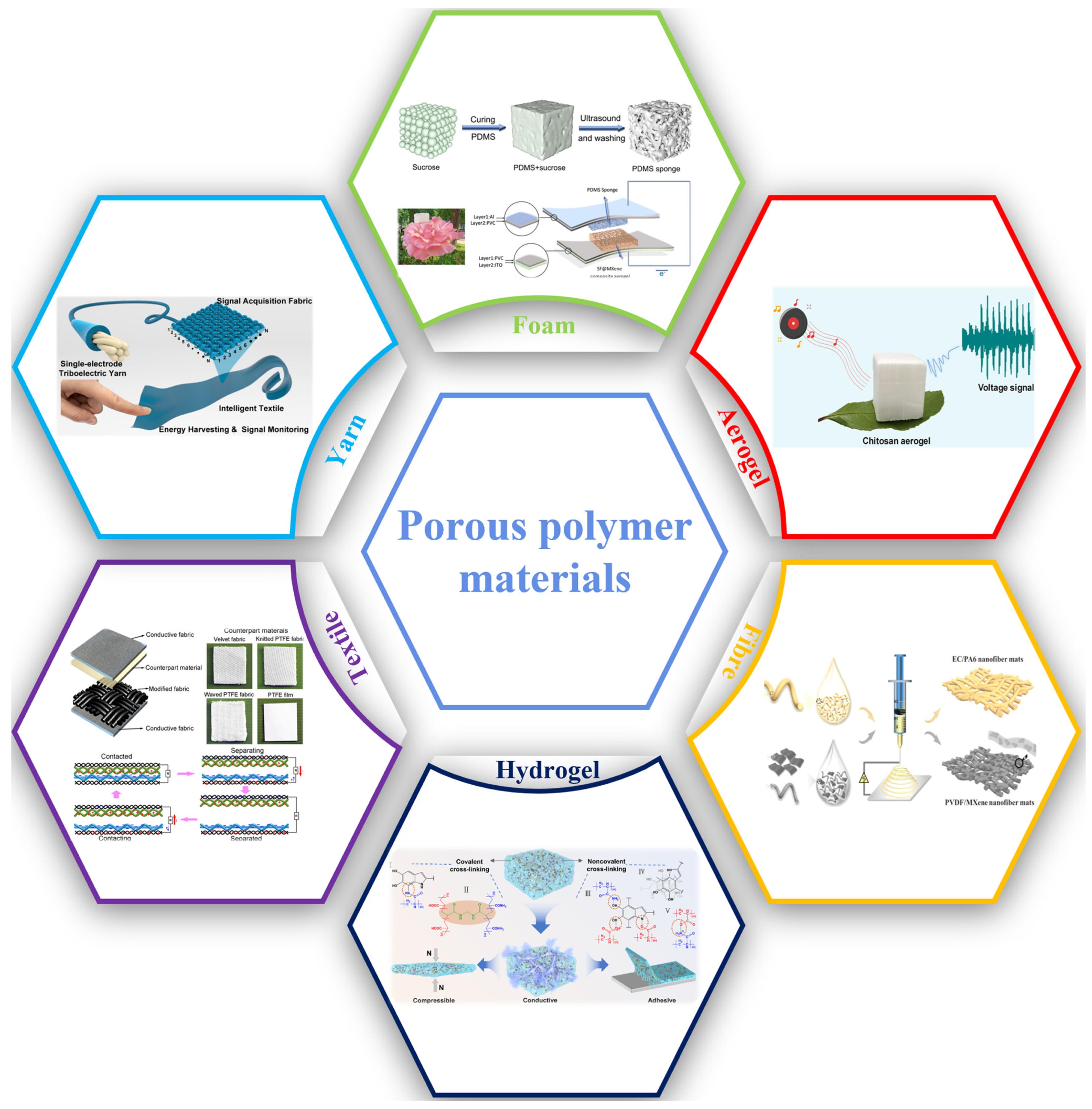
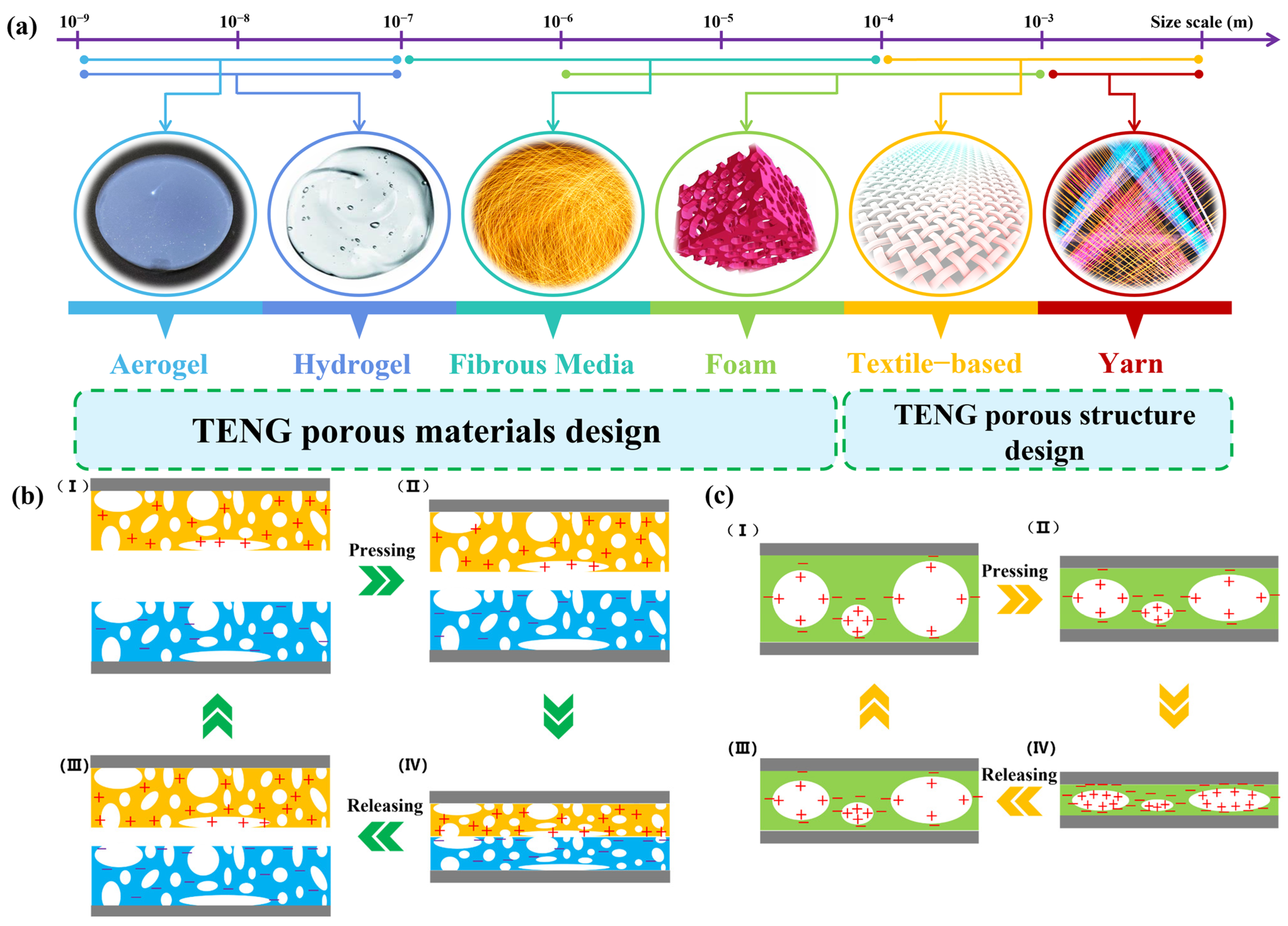
3. Porous Polymer Materials and Structures in TENG Design
3.1. Porous Polymer Dielectric Materials
3.1.1. Foam-Based Polymer Dielectrics
3.1.2. Aerogel-Based Dielectrics
3.1.3. Fiber Dielectric
3.2. Porous Electrode Materials
3.3. Porous Structure Design
3.3.1. Textile-Based TENG Structures
3.3.2. Yarn-Based TENG Structures
4. Application of Porous TENG
4.1. Energy Harvesting
4.2. Intelligent Wearable Devices
4.3. Self-Powering Sensing
4.4. Human–Machine Interface
5. Summary and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, Y.; Wang, W.; Zou, J.; Li, Z.; Cao, X.; Xu, S. Self-powered energy conversion and energy storage system based on triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2020, 76, 105008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, K.; Sharma, S.; Pradhan, G.B.; Bhatta, T.; Maharjan, P.; Rana, S.M.S.; Lee, S.; Seonu, S.; Shin, Y.; Park, J.Y. A Siloxene/Ecoflex nanocomposite-based triboelectric nanogenerator with enhanced charge retention by MoS2/LIG for self-powered touchless sensor applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2113005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Xiao, J.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, J.; Xu, R.; Wen, Z.; Dong, B.; Sun, X. Bamboo-inspired self-powered triboelectric sensor for touch sensing and sitting posture monitoring. Nano Energy 2022, 91, 106670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Pei, Y.; Zhang, C.; Kottapalli, A.G.P. Bioinspired designs and biomimetic applications of triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2021, 84, 105865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ping, J.; Ying, Y. Recent progress in 2D-nanomaterial-based triboelectric nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2009994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.; Uy, C.; Xiao, X.; Chen, J. Self-powered environmental monitoring via a triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2022, 98, 107282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Cao, X.; Wang, N. From Triboelectric nanogenerator to uninterrupted power supply system: The key role of electrochemical batteries and supercapacitors. Batteries 2022, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanani, Z.; Izanzar, I.; Amjoud, M.; Mezzane, D.; Lahcini, M.; Uršič, H.; Prah, U.; Saadoune, I.; Luk’Yanchuk, I.A.; Kutnjak, Z.; et al. Lead-free nanocomposite piezoelectric nanogenerator film for biomechanical energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2021, 81, 105661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, J.; Xiao, H.; Huangfu, G.; Guo, Y. Super flexible and lead-free piezoelectric nanogenerator as a highly sensitive self-powered sensor for human motion monitoring. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.-G.; Kim, D.-W.; Tcho, I.-W.; Kim, J.-K.; Kim, M.-S.; Choi, Y.-K. Triboelectric Nanogenerator: Structure, Mechanism, and Applications. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 258–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parandeh, S.; Etemadi, N.; Kharaziha, M.; Chen, G.; Nashalian, A.; Xiao, X.; Chen, J. Advances in Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Self-Powered Regenerative Medicine. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2105169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Peng, X.; Cheng, R.; Wang, Z.L. Smart textile triboelectric nanogenerators: Prospective strategies for improving electricity output performance. Nanoenergy Adv. 2022, 2, 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Deng, W.; Xu, J.; Chen, J. Engineering materials at the nanoscale for triboelectric nanogenerators. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2020, 1, 100142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Z.L. Reviving vibration energy harvesting and self-powered sensing by a triboelectric nanogenerator. Joule 2017, 1, 480–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yuan, T.; Yao, C. The recent progress in cellulose paper-based triboelectric nanogenerators. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2021, 5, 1904066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Wang, Z.L. Self-charging power textiles integrating energy harvesting triboelectric nanogenerators with energy storage batteries/supercapacitors. J. Semicond. 2021, 42, 101601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, G.; Guo, Q.; Wen, H.; Huang, R.; Meng, X.; Duan, J.; Tang, Q. Triboelectric sensor array for internet of things based smart traffic monitoring and management system. Nano Energy 2022, 92, 106757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lin, X.; Zhang, N.; Lu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Liu, G.; Nie, S. Chemically functionalized cellulose nanofibrils-based gear-like triboelectric nanogenerator for energy harvesting and sensing. Nano Energy 2019, 66, 104126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Zhang, S.L.; Xu, S.; Guo, H.; Yang, W.; Wang, Z.L. Free-fixed rotational triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered real-time wheel monitoring. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2000918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lama, J.; Yau, A.; Chen, G.R.; Sivakumar, A.; Zhao, X.; Chen, J. Textile triboelectric nanogenerators for self-powered biomonitoring. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 19149–19178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Z.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, N.; Cao, X. Thermal-driven soft-contact triboelectric nanogenerator for energy harvesting and industrial cooling water monitoring. Small 2023, 19, e2206269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Zi, Y. Achieving ultrahigh instantaneous power density of 10 MW/m2 by leveraging the oppo-site-charge-enhanced transistor-like triboelectric nanogenerator (OCT-TENG). Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, J.; Ma, Z.; Gong, S. Portable self-charging power system via integration of a flexible paper-based triboelectric nanogenerator and supercapacitor. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 18657–18666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Y.J.; Lu, Y.; Shi, Y.L.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Wang, X.Q.; Meng, J.J.; Cao, X.; Wang, N. Biodegradable polymers in triboelectric nano-generators. Polymers 2023, 15, 15010222. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Chen, B.; Ma, Z.; Gong, S. A new class of flexible nanogenerators consisting of porous aerogel films driven by mechanoradicals. Nano Energy 2017, 38, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Mun, J.; Kwon, S.Y.; Park, S.; Bao, Z.; Park, S. Electronic skin: Recent progress and future prospects for skin-attachable devices for health monitoring-robotics, and prosthetics. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1904765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, G.; Wang, Z.L. Polymer materials for high-performance triboelectric nanogenerators. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2000186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayababu, N.; Kim, D. ZnO nanorods@conductive carbon black nanocomposite based flexible integrated system for energy conversion and storage through triboelectric nanogenerator and supercapacitor. Nano Energy 2021, 82, 105726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastegardoost, M.M.; Tafreshi, O.A.; Saadatnia, Z.; Ghaffari-Mosanenzadeh, S.; Park, C.B.; Naguib, H.E. Recent advances on porous materials and structures for high-performance triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2023, 111, 108365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Huang, J.; Liu, J.; Gu, J.; Zhu, J.; Huang, B.; Bai, J.; Guo, J.; Yang, X.; Guan, L. High toughness multifunctional organic hydrogels for flexible strain and temperature sensor. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 23243–23255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Yang, F.; Sun, X.; Bai, Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, W.; Wang, R.; He, X. Anti-freezing self-adhesive self-healing degradable touch panel with ultra-stretchable performance based on transparent triboelectric nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2201230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhou, F.; Yan, H.; Gao, G.; Li, H.; Li, R.; Chen, T. Anti-freezing organohydrogel triboelectric nanogenerator toward highly efficient and flexible human-machine interaction at −30 °C. Nano Energy 2021, 90, 106614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Su, B.L.; Xia, H.; Zhao, S.; Gao, C.; Wang, L.; Ogbeide, O.; Feng, J.; Hasan, T. Printed aerogels: Chemistry, processing, and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 3842–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Pang, B.; Xu, W.; Duan, G.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, K. Recent progress on nanocellulose aero-gels-preparation, modification, composite fabrication, applications. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2005569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liang, L.; Lv, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G. Elastic aerogel thermoelectric generator with vertical temperature-difference architecture and compression-induced power enhancement. Nano Energy 2021, 90, 106577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Fu, X.; He, J.; Shi, X.; Chen, T.; Chen, P.; Wang, B.; Peng, H. Application challenges in fiber and textile electronics. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1901971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.; Kim, S.M.; Spinks, G.M.; Kim, S.J. Carbon nanotube yarn for fiber-shaped electrical sensors, actuators, and energy storage for smart systems. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1902670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Feng, Z.; Kim, J.; Robertson, J.L.; Jia, X.; Johnson, B.N. 3D printed stretchable triboelectric nanogenerator fibers and devices. Nano Energy 2020, 75, 104973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiao, S.; Luo, Y.; Tian, S.; Tang, J.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, J. Advances in electrospun nanofibers for triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2022, 104, 107884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yuan, F.; Sang, M.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Xuan, S.; Gong, X. Functional sponge-based triboelectric nan-ogenerators with energy harvesting, oil–water separating and multi-mode sensing performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 6913–6923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, H.; Ding, X.; Lorestani, F.; Huang, C.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, B.; Wang, J.; Cheng, H.; Xu, Y. Human motion-driven self-powered stretchable sensing platform based on laser-induced graphene foams. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2022, 9, 011413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Handschuh-Wang, S.; Zhou, X. Recent progress in fabrication and application of polydimethylsiloxane sponges. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 16467–16497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.Q.; Wang, S.T.; You, Z.Y.; Zheng, J.M.; Liu, Y. High Performance Porous Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Silk Fibroin@MXene Composite Aerogel and PDMS Sponge. ACS Materials Lett. 2023, 5, 1929–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Liu, Z.-J.; Zheng, J.-Q.; Cheng, Q.-K.; Tan, Y.-L.; Huang, S.-L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.-M.; Zhou, H.-M. A Directional Chitosan Sound Sensor Based on Piezoelectric–Triboelectric Sensing. Nano Energy 2023, 12, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.Y.; Hao, Y.; Zhao, M.; Li, W.; Huang, F.L.; Wei, Q.F. All-fiber-structured triboelectric nanogenerator via one-pot electrospinning for self-powered wearable sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2021, 13, 24774–24784. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yao, M.Z.; Luo, Y.-D.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.-L.; Liang, C.; Qin, C.-R.; Huang, C.-X.; Yao, S.-Q. Polydopamine-Reinforced Hemicellulose-Based Multifunctional Flexible Hydrogels for Human Movement Sensing and Self-Powered Transdermal Drug Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 5883–5896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.Y.; Xia, Z.K.; Sun, B.B.; Jing, X.; Li, X.; Tao, X.M.; Mi, H.Y.; Liu, Y.J. Enhancing the Performance of Fabric-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators by Structural and Chemical Modification. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 16916–16927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhou, M.; Wu, R.; Patil, A.; Gong, H.; Zhu, S.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, S.; Dong, K.; et al. Continuous and Scalable Manufacture of Hybridized Nano-Micro Triboelectric Yarns for Energy Harvesting and Signal Sensing. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 4716–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wang, Z.L. Recent advances in triboelectric nanogenerator based self-charging power systems. Energy Storage Mater. 2019, 23, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J.; Kuang, H.; Shen, Q.; Yang, H. High-power triboelectric nanogenerators by using in-situ carbon dispersion method for energy harvesting and self-powered wireless control. Nano Energy 2022, 101, 107561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhou, Y.; Lang, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. Triboelectric nanogenerator and artificial intelligence to promote precision medicine for cancer. Nano Energy 2022, 92, 106783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Cai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z. Electron transfer mechanism of graphene/Cu hetero-structure for improving the stability of triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2020, 70, 104540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Ding, W.; Zi, Y.; Lu, Y.; Ji, L.; Liu, F.; Wu, C.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric microplasma powered by mechanical stimuli. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, S.; Kariper, İ.A. Aerogel based nanogenerators: Production methods, characterizations and applications. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 11088–11110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Luo, C.; Deng, B.W.; Yin, B.; Yang, M.B. Flexible porous silicone rubber-nanofiber nanocomposites generated by supercritical carbon dioxide foaming for harvesting mechanical energy. Nano Energy 2020, 67, 104290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Cui, P.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Parida, K.; Lin, M.F.; Lee, P.S. Skin-touch-actuated textile-based triboelectric nanogenerator with black phosphorus for durable biomechanical energy harvesting. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Dey, M.; Matzke, C.; Ellis, G.; Javaid, S.; Hall, K.; Ji, Y.; Payne, S. Synthesis and characterization of novel foams by pyrolysis of lignin. TAPPI J. 2019, 18, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Li, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Tian, J.; Shi, B.; Zou, Y.; Ouyang, H.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, L.; et al. Fully bioabsorbable natural materials based triboelectric nanogenerators. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1801895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biutty, M.N.; Koo, J.M.; Zakia, M.; Handayani, P.L.; Choi, U.H.; Yoo, S.I. Dielectric control of porous polydimethylsiloxane elastomers with Au nanoparticles for enhancing the output performance of triboelectric nanogenerators. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 21309–21317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.; Kim, J.W.; Jung, W.S.; Kang, C.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Wang, Z.L.; Baik, J.M. Mesoporous pores impregnated with Au nano-particles as effective dielectrics for enhancing triboelectric nanogenerator performance in harsh environments. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 3006–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Choi, H.; Cha, S.; Ahn, D.; Choi, M.; Park, S.; Cho, Y.; Lee, J.; Park, T.; Park, J.J. Highly enhanced triboelectric per-formance from increased dielectric constant induced by ionic and interfacial polarization for chitosan based multi-modal sensing system. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 32, 2109139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannsfeld, S.C.B.; Tee, B.C.-K.; Stoltenberg, R.M.; Chen, C.V.H.-H.; Barman, S.; Muir, B.V.O.; Sokolov, A.N.; Reese, C.; Bao, Z. Highly sensitive flexible pressure sensors with microstructured rubber dielectric layers. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriphan, S.; Pharino, U.; Charoonsuk, T.; Pulphol, P.; Pakawanit, P.; Khamman, O.; Vittayakorn, W.; Vittayakorn, N.; Maluangnont, T. Tailoring charge affinity, dielectric property, and band gap of bacterial cellulose paper by multifunctional Ti2NbO7 nanosheets for improving triboelectric nanogenerator performance. Nano Res. 2022, 16, 3168–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paria, S.; Si, S.K.; Karan, S.K.; Das, A.K.; Maitra, A.; Bera, R.; Halder, L.; Bera, A.; De, A.; Khatua, B.B. A strategy to develop highly efficient TENGs through the dielectric constant, internal resistance optimization, and surface modification. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 3979–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, Z.; Haleem, A.; Ahmad, R.U.S.; Farooq, U.; Shi, L.; Claver, U.P.; Memon, K.; Fareed, A.; Khan, I.; Mbogba, M.K.; et al. Highly porous polymer cryogel based tribopositive material for high performance triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2020, 68, 104294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanbedi, M.; Ardebili, H.; Karim, A. Polymer-based triboelectric nanogenerators: Materials, characterization, and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2023, 144, 101723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhu, W.; Lu, X.; Wang, C. Lightweight and flexible MXene/carboxymethyl cellulose aerogel for electromagnetic shielding, energy harvest and self-powered sensing. Nano Energy 2022, 98, 107229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, F.; Liang, Z.; Yong, Y.; Dai, S.; Li, Z. A stretchable, environmentally stable, and mechanically robust nanocomposite polyurethane organohydrogel with anti-freezing, anti-dehydration, and electromagnetic shielding properties for strain sensors and magnetic actuators. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 6603–6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG)—Sparking an energy and sensor revolution. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2000137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhu, M.; Shi, Q.; Wen, F.; Liu, L.; Dong, B.; Haroun, A.; Yang, Y.; Vachon, P.; Guo, X.; et al. Progress in TENG technology—A journey from energy harvesting to nanoenergy and nanosystem. EcoMat 2020, 2, 12058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Gao, Z.; Yao, K.; Hou, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; He, J.; Huang, X.; Song, E.; Yu, J.; et al. Thin, soft, skin-integrated foam-based triboelectric nanogenerators for tactile sensing and energy harvesting. Mater. Today Energy 2021, 20, 100657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Zhao, P.; McConohy, G.; Yang, H.; Tong, Y.; Wang, X. Sponge-like piezoelectric polymer films for scalable and integratable nanogenerators and self-powered electronic systems. Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1301624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Chen, J.; Guo, H.; Liu, G.; Wei, D.; Xi, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, C. Embedding variable micro-capacitors in polydimethylsiloxane for enhancing output power of triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Res. 2016, 10, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Chun, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.N.; Kang, N.; Kim, J.; Kim, M.H.; Shin, K.; Gupta, M.K.; Baik, J.M.; et al. Hydrophobic sponge structure-based triboelectric nanogenerator. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5037–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, H.; Wang, H.; Cheng, R.; Liao, Y.; Shi, X.; Luo, J.; Li, D.; Wang, Z.L. Smart pillow based on flexible and breathable tribo-electric nanogenerator arrays for head movement monitoring during sleep. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 23998–24007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Park, S.J.; Jeon, S.B.; Seol, M.L.; Choi, Y.K. A triboelectric sponge fabricated from a cube sugar template by 3D soft lithography for super hydrophobicity and elasticity. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2016, 2, 1500331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Qin, Q.; Meng, J.; Mi, Y.; Wang, X.; Cao, X.; Wang, N. Constructing highly flexible dielectric sponge for enhancing triboelectric performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 468, 143802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, N.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ning, C.; Tian, L.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Mao, Y.; Liang, E. Single-electrode triboelectric nanogenerators based on sponge-like porous PTFE thin films for mechanical energy harvesting and self-powered electronics. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 12252–12257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Song, J.; Gao, Y.; Liu, J.; Lee, C.; Chen, G.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Leung, M.K. A fluorinated polymer sponge with superhydrophobicity for high-performance biomechanical energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2021, 85, 106021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.-G.; Kim, J.-K.; Kim, D.-W.; Tcho, I.-W.; Choi, Y.-K. A triboelectric nanogenerator implemented with an acoustic foam for a self-driven silent tire. Nano Energy 2022, 96, 107090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, S.M.; Saha, M.; Sepay, N.; Mallik, A. Energy-from-waste: A triboelectric nanogenerator fabricated from waste poly-styrene for energy harvesting and self-powered sensor. Nano Energy 2022, 104, 107902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Shi, L.; Yang, G.; Zhuang, X.; Cheng, B. 3D fibrous aerogels from 1D polymer nanofibers for energy and environmental applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 11, 512–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Fang, L.; Guo, H.; Yang, K.; Cai, Z.; Meador, M.A.B.; Gong, S. Highly porous polymer aerogel film-based triboelectric nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1706365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yang, W.; Pan, X.; Wang, Z.L. Cellulose II Aerogel-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2001763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Z.; Li, R.; Guo, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Zhao, N.; Xu, J. Triboelectric nanogenerators made of poly benzazole aerogels as fire-resistant negative tribo-materials. Nano Energy 2019, 64, 103900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.-Y.; Jing, X.; Meador, M.A.B.; Guo, H.; Turng, L.-S.; Gong, S. Triboelectric nanogenerators made of porous polyamide nanofiber mats and polyimide aerogel film: Output optimization and performance in circuits. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 30596–30606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, S.; Feng, Y.; He, F.; Zhao, J.; Bai, T.; Lin, H.; Cai, W.; Mao, C.; Chen, Y.; Gan, L.; et al. Biomass-derived, multifunctional and wave-layered carbon aerogels toward wearable pressure sensors, supercapacitors and triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2021, 85, 105973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Ma, H.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, Y.; Yin, B.; Ke, K.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, K.; Yang, M.B. Enhanced triboelectric nanogenerator based on a hybrid cellulose aerogel for energy harvesting and self-powered sensing. ACS Sustain. Chem. 2023, 11, 9424–9432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Li, L.; Gao, M.; Yang, H.; Cai, Z.; Chen, B.; Xiang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Song, Y. All-printed 3D hierarchically structured cellulose aerogel based triboelectric nanogenerator for multi-functional sensors. Nano Energy 2019, 63, 103885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; El-Kady, M.F.; Hassan, I.; Negm, A.; Pourrahimi, A.M.; Muni, M.; Selvaganapathy, P.R.; Kaner, R.B. Fire-retardant, self-extinguishing triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2019, 59, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Wang, W.; He, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, R.; Tao, G.; Hu, B.; Hou, C. High-performance polyimide aerogel film-based triboelectric nanogenerator for trace liquid analyzing. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 5466–5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Tian, E.; Zhang, Y.; Mo, J. Utilizing electrostatic effect in fibrous filters for efficient airborne particles removal: Principles, fabrication, and material properties. Appl. Mater. Today 2022, 26, 101369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastegardoost, M.M.; Tafreshi, O.A.; Saadatnia, Z.; Ghaffari-Mosanenzadeh, S.; Park, C.B.; Naguib, H.E. Porous PVDF mats with significantly enhanced dielectric properties and novel dipole arrangement for high-performance triboelectric nanogenerators. Appl. Mater. Today 2023, 30, 101732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.T.; Rana, S.S.; Abu Zahed, M.; Lee, S.; Yoon, E.-S.; Park, J.Y. Metal-organic framework-derived nanoporous carbon incorporated nanofibers for high-performance triboelectric nanogenerators and self-powered sensors. Nano Energy 2022, 94, 106921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Dong, K.; An, J.; Liang, F.; Yi, J.; Peng, X.; Ning, C.; Ye, C.; Wang, Z.L. UV-Protective, Self-cleaning, and antibacterial nanofiber-based triboelectric nanogenerators for self-powered human motion monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 11205–11214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Hou, X.; He, J.; Xue, F.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L.; Yu, J.; Mu, J.; Geng, W.; Chou, X. Asymmetric permittivity enhanced bilayer polycaprolactone nanofiber with superior inner interfacial polarization and charge retention for high-output and humidi-ty-resistant triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2022, 98, 107289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, X.; Jia, P.; Tian, S.; Pan, C.; Zeng, F.; Chen, D.; Chen, Y.; Tang, J.; et al. Silk inspired in-situ interlocked superelastic microfibers for permeable stretchable triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2022, 98, 107347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Mensah, A.; Liao, S.; Lv, P.; Wei, Q. Scalable, ultra-high stretchable and conductive fiber triboelectric nanogenerator for biomechanical sensing. Nano Energy 2023, 109, 108291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Wang, F.; Cui, X.; Zhu, Y. Recent progress in textile-based triboelectric force sensors for wearable electronics. Adv. Compos. Hybrid. Mater. 2023, 6, 1131–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.S.; Yoon, H.J.; Kim, S.W. Textile-based triboelectric nanogenerators for self-powered wearable electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 29, 1804533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Xiong, Y.; Ma, K.; Liu, S.; Tao, X. Recent advances in wearable textile-based triboelectric generator systems for energy harvesting from human motion. EcoMat 2020, 2, 12054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Wu, H.; Wang, R. Fibrous triboelectric nanogenerators: Fabrication, integration, and application. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 15881–15905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Zhang, K. Recent progress in fibrous high-entropy energy harvesting devices for wearable applications. Nano Energy 2022, 101, 107600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Peng, X.; Wang, Z.L. Fiber/fabric-based piezoelectric and triboelectric nanogenerators for flexible/stretchable and wearable electronics and artificial intelligence. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1902549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Li, Y.; Yang, G.; Hu, S.; Shi, Z.; Yang, G. Fabric-based TENG woven with bio-fabricated superhydrophobic bacterial cellulose fiber for energy harvesting and motion detection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2304809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Cho, C.; Oh, J.H. Highly flexible triboelectric nanogenerators with electrospun PVDF-TrFE nanofibers on MWCNTs/PDMS/AgNWs composite electrodes. Compos. Part. B Eng. 2023, 255, 110622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhong, Y.; Shi, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, P.; Zhao, Y. Triboelectric nanogenerator-based near-field electrospinning system for optimizing PVDF fibers with high piezoelectric performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 5242–5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Dong, B.; He, T.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lee, C. Progress in wearable electronics/photonics—Moving toward the era of artificial intelligence and internet of things. InfoMat 2020, 2, 1131–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parandeh, S.; Kharaziha, M.; Karimzadeh, F.; Hosseinabadi, F. Triboelectric nanogenerators based on graphene oxide coated nanocomposite fibers for biomedical applications. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 385402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Hu, N.; Yan, F.; Wang, Y. Development and applications of electrospun nanofiber-based triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2023, 112, 108444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Cao, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Li, C. Air-Permeable and Washable Paper–Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Highly Flexible and Robust Paper Electrodes. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1800178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.T.; Ouyang, H.; Xin, W.; Chao, S.; Ma, C.; Li, Z.; Chen, F.; Ma, M.G. A stretchable high output triboelectric nanogenerator improved by MXene liquid electrode with high electronegativity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2004181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Huang, F.; Wu, S.; Wang, C.H.; Peng, S. Transparent, stretchable and high-performance triboelectric nano-generator based on dehydration-free ionically conductive solid polymer electrode. Nano Energy 2021, 88, 106289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, C.; Sun, W.; Bai, Y.; Li, Z.; Deng, Y. A Controlled biodegradable triboelectric nanogenerator based on PEGDA/Laponite hydrogels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 12787–12796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, H.; Wang, D.; Xu, Z.; Cai, H.; Xia, H. Triboelectric nanogenerators based on super-stretchable con-ductive hydrogels with the assistance of deep-learning for handwriting recognition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 32993–33002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Wang, Q.; Wan, X.; Yang, M.; Liu, C.; Xu, C.; Hu, B.; Feng, J.; Luo, Z. Wireless electrical stimulation of the vagus nerves by ultrasound-responsive programmable hydrogel nanogenerators for anti-inflammatory therapy in sepsis. Nano Energy 2021, 89, 106327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z.; Xi, G.; Mao, R.; Ma, Y.; Wang, D.; Tang, M.; Xu, Z.; Luan, H. Ultrastretchable, self-healing conductive hydrogel-based triboelectric nanogenerators for human-computer interaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 5128–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Cuthbert, T.J.; Shokurov, A.V.; Chu, P.K.; Feng, S.; Menon, C. Hydrogels as Soft Ionic Conductors in Flexible and Wearable Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2106008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, V.; Babu, A.; Sharma, A.; Thomas, J.; Chopra, V.; Malik, P.; Rajput, S.; Mittal, M.; Guha, R.; Chattopadhyay, N.; et al. Tunable, conductive, self-healing, adhesive and injectable hydrogels for bioelectronics and tissue regeneration applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 6260–6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, C.; Zhao, F.; Lan, L.; Yao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Ping, J.; Ying, Y. Fully stretchable triboelectric nanogenerator for energy harvesting and self-powered sensing. Nano Energy 2019, 61, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zhao, T.; Yang, S.; Xie, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sang, S.; Lin, Z.H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H. A spongy electrode-brush-structured dual-mode triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting mechanical energy and self-powered trajectory tracking. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Sun, W.; Li, T.; Wang, D.; Zhou, F. Conductive elastic sponge-based triboelectric nano-generator (TENG) for effective random mechanical energy harvesting and ammonia sensing. Nano Energy 2021, 79, 105422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.G.; Kim, D.; Jeon, S.B.; Park, S.J.; Tcho, I.W.; Jin, I.K.; Han, J.K.; Choi, Y.K. Multidirection and multiamplitude triboelectric nanogenerator composed of porous conductive polymer with prolonged time of current generation. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1800654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, I.; Yun, J.; Kim, D. Liquid-metal embedded sponge-typed triboelectric nanogenerator for omnidirectionally de-tectable self-powered motion sensor. Nano Energy 2021, 89, 106442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; Fang, L.; Cao, B.; Tu, X.; Zhang, R.; Dong, K.; Lai, Y.-C.; Wang, P. Biodegradable, conductive, moisture-proof, and dielectric enhanced cellulose-based triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered human-machine interface sensing. Nano Energy 2023, 107, 108151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hu, K.; Yang, M.; Zou, Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, M.; Wang, H.; Qu, X.; Tan, P.; Wang, C.; et al. Elastic Cu@PPy sponge for hybrid device with energy conversion and storage. Nano Energy 2019, 58, 852–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Dong, K.; Ye, C.; Jiang, Y.; Zhai, S.; Cheng, R.; Liu, D.; Gao, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. A breathable, biodegradable, antibacterial, and self-powered electronic skin based on all-nanofiber triboelectric nanogenerators. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba9624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Li, Y.; Bick, M.; Chen, J. Smart textiles for electricity generation. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 3668–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedin, S.; Uzun, S.; Levitt, A.; Anasori, B.; Dion, G.; Gogotsi, Y.; Razal, J.M. MXene composite and coaxial fibers with high stretchability and conductivity for wearable strain sensing textiles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1910504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, W.; Chen, P.; He, S.; Sun, X.; Peng, H. Smart electronic textiles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 55, 6140–6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Mi, Y.; Lu, Y.; Qin, Q.; Wang, X.; Meng, J.; Liu, F.; Wang, N.; Cao, X. Weaved piezoresistive triboelectric nanogenerator for human motion monitoring and gesture recognition. Nano Energy 2022, 96, 107135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, T.; Cheng, R.; Wei, C.; Su, E.; Jiang, T.; Sheng, F.; Peng, X.; Dong, K.; Wang, Z.L. All-fabric direct-current triboelectric nanogenerators based on the Tribovoltaic effect as power textiles. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2301178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreeja Sadanandan, K.; Saadi, Z.; Murphy, C.; Grikalaite, I.; Craciun, M.F.; Neves, A.I.S. Fabric-based triboelectric nanogenerators with ultrasonic spray coated graphene electrodes. Nano Energy 2023, 116, 108797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xu, B.; Tan, D.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y. Asymmetric-elastic-structure fabric-based triboelectric nanogenerators for wearable energy harvesting and human motion sensing. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 466, 143079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Zhang, J.; Yu, B.; Yu, H.; Long, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, M. Fabric texture design for boosting the performance of a knitted washable textile triboelectric nanogenerator as wearable power. Nano Energy 2019, 58, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Tian, X.; Wen, F.; Shi, Q.; Ho, J.S.; Lee, C. Self-sustainable wearable textile nano-energy nano-system (NENS) for next-generation healthcare applications. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1901437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Padgett, S.; Cai, Z.; Conta, G.; Wu, Y.; He, Q.; Zhang, S.; Sun, C.; Liu, J.; Fan, E.; et al. Single-layered ultra-soft washable smart textiles for all-around ballistocardiograph, respiration, and posture monitoring during sleep. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 155, 112064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, B.; Li, M.; Jiang, C.; Guan, X.; Yang, Y. Scalable core–spun coating yarn-based triboelectric nanogenerators with hierarchical structure for wearable energy harvesting and sensing via continuous manufacturing. Nano Energy 2022, 91, 106672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Wu, Z.; Deng, J.; Wang, A.C.; Zou, H.; Chen, C.; Hu, D.; Gu, B.; Sun, B.; Wang, Z.L. A Stretchable yarn embedded triboelectric nanogenerator as electronic skin for biomechanical energy harvesting and multifunctional pressure sensing. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1804944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Guo, H.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.C.; Pu, X.; Yu, W.; Wang, F.; Du, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Direct current fabric triboelectric nan-ogenerator for biomotion energy harvesting. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 4585–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, W.B.; Choi, D.S.; Lee, C.H.; Yang, J.Y.; Yoon, G.S.; Hong, J.P. Hierarchically nanostructured 1d conductive bundle yarn-based triboelectric nanogenerators. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1704434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Miao, X.; Yang, H.; Jiang, T.; Yu, A.; Zhai, J. Multiple textile triboelectric nanogenerators based on UV-protective, radiative cooling, and antibacterial composite yarns. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 468, 143800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, F.; Ou, Z.; Gao, X.; Chen, B.; Wang, Z.L. Harvesting Electrical energy from high temperature environment by aerogel nano-covered triboelectric yarns. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2205275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wei, X.; Li, Y.; Dong, W.; Li, X.; Wu, Z.; Wen, J. Stretchable polyurethane composite foam triboelectric nanogenerator with tunable microwave absorption properties at elevated temperature. Nano Energy 2021, 89, 106397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.L.; Song, W.Z.; Sun, D.J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.Q.; Ramakrishna, S.; Long, Y.Z. A self-priming air filtration system based on triboelectric nanogenerator for active air purification. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Song, W.; Liu, M.; Sun, C.; Du, C.; Jiang, C.; Huang, X.; Zou, D.; Hu, W.; Wang, Z.L. Wearable power-textiles by integrating fabric triboelectric nanogenerators and fiber-shaped dye-sensitized solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1601048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doganay, D.; Demircioglu, O.; Cugunlular, M.; Cicek, M.O.; Cakir, O.; Kayaci, H.U.; Aygün, S.; Unalan, H.E. Wet spun core-shell fibers for wearable triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2023, 116, 108823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Fang, H.; Guo, J.; Wu, H. Fully nano/micro-fibrous triboelectric on-skin patch with high breathability and hydrophobicity for physiological status monitoring. Nano Energy 2022, 98, 107311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Dong, K.; Ning, C.; Cheng, R.; Yi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sheng, F.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.L. All-nanofiber self-powered skin-interfaced real-time respiratory monitoring system for obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome diagnosing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2103559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, S.; Zhou, J.; Li, F.; Li, J.; Cao, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; et al. Advanced triboelectric nanogenerator with multi-mode energy harvesting and anti-impact properties for smart glove and wearable e-textile. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.-S.; Wang, Y.; Gong, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Brugger, J. All-fiber hybrid piezoelectric-enhanced triboelectric nanogenerator for wearable gesture monitoring. Nano Energy 2018, 48, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Xu, B.; Gao, Y.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z. Breathable fabric-based triboelectric nanogenerators with open-porous architected polydimethylsiloxane coating for wearable applications. Nano Energy 2022, 104, 107873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Li, G.; Zhang, L.; Sun, W.; Pan, X.; Chen, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Tian, J.; Yang, Y. A waterproof, breathable nitro-cellulose-based triboelectric nanogenerator for human-machine interaction. Nano Energy 2023, 114, 108649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doganay, D.; Cicek, M.O.; Durukan, M.B.; Altuntas, B.; Agbahca, E.; Coskun, S.; Unalan, H.E. Fabric based wearable triboelectric nanogenerators for human machine interface. Nano Energy 2021, 89, 106412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, S.; Shi, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lei, Y.; Han, J.; Xiong, Y.; Sun, J.; Zheng, L.; Sun, Q.; et al. Eco-friendly and recyclable all cellulose triboelectric nanogenerator and self-powered interactive interface. Nano Energy 2021, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Xue, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Mu, L.; Sun, C.L.; Qu, M. Humidity-resistant, conductive fabric-based triboelectric nanogenerator for efficient energy harvesting and human–machine interaction sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 43963–43975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.T.; Rahman, S.; Kumar, H.; Kim, K.; Kim, S. Metal-organic framework reinforced highly stretchable and durable conductive hydrogel-based triboelectric nanogenerator for biomotion sensing and wearable human-machine interfaces. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 2303471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Jo, S.; Kim, I.; Kim, D. Film-Sponge-coupled triboelectric nanogenerator with enhanced contact area based on direct ultraviolet laser ablation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 48281–48291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Song, G.; Park, C.; Yun, K.-S. Multifunctional woven structure operating as triboelectric energy harvester, capacitive tactile sensor array, and piezoresistive strain sensor array. Sensors 2017, 17, 2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Lin, Z.-H.; Cheng, G.; Wen, X.; Liu, Y.; Niu, S.; Wang, Z.L. 3D Fiber-based hybrid nanogenerator for energy harvesting and as a self-powered pressure sensor. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 10674–10681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.; Pu, X.; Wen, R.; Liu, M.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, J.; Hu, W.; Wang, Z.L. Core–shell-yarn-based triboelectric nanogenerator textiles as power cloths. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 12764–12771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, K.; Zhou, J.; Wu, H.; Su, Z. Fibrous self-powered sensor with high stretchability for physiological information monitoring. Nano Energy 2021, 88, 106258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


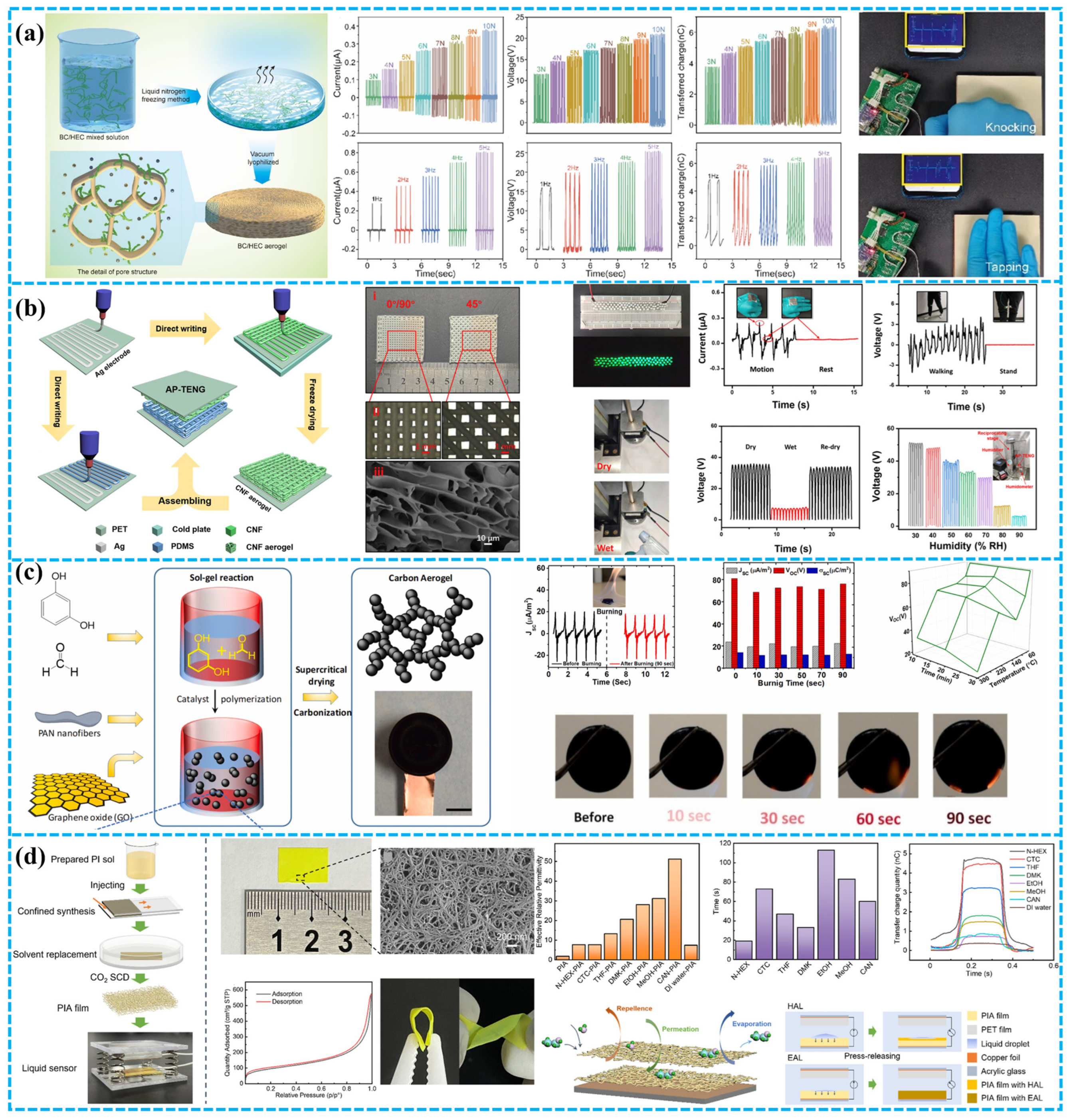

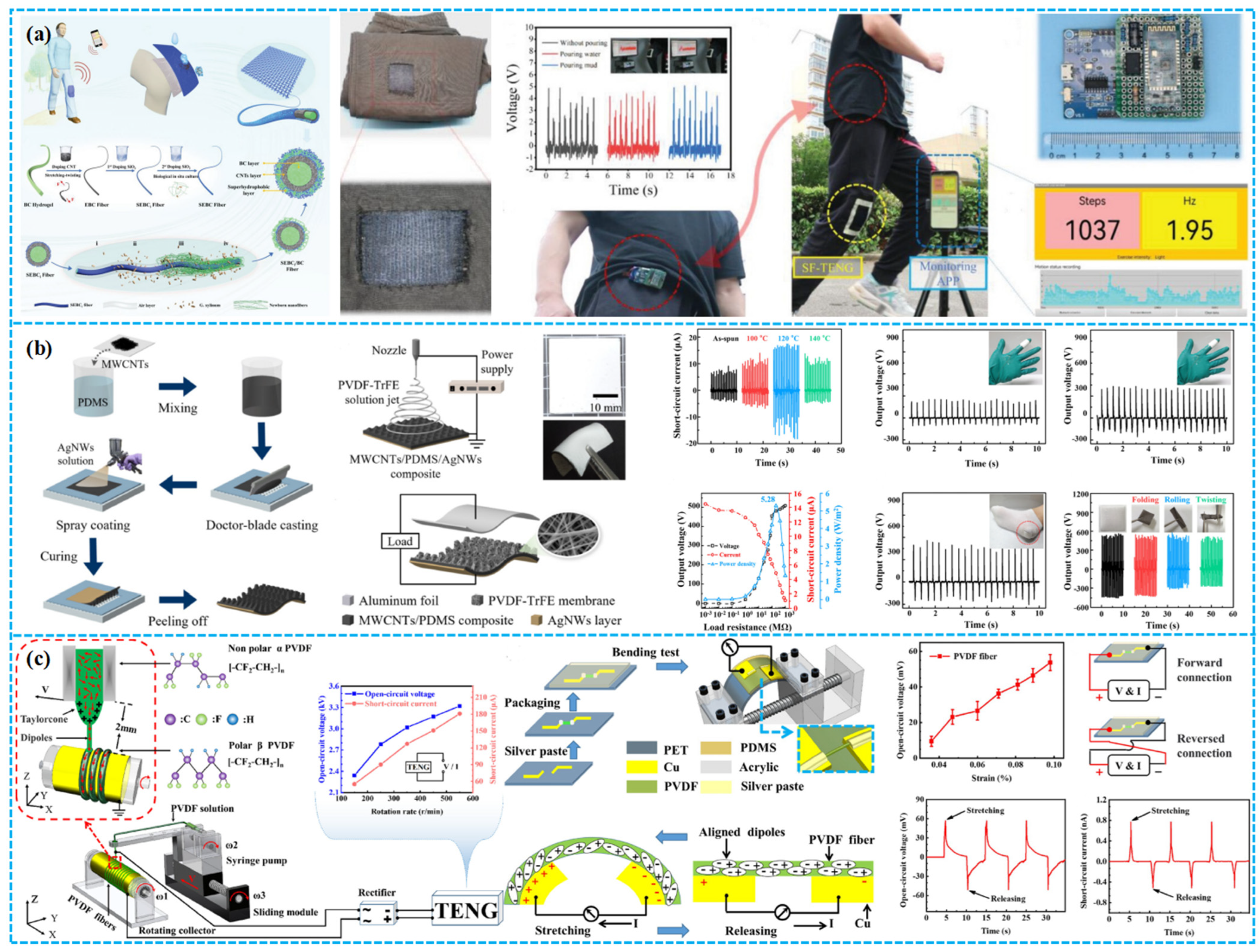



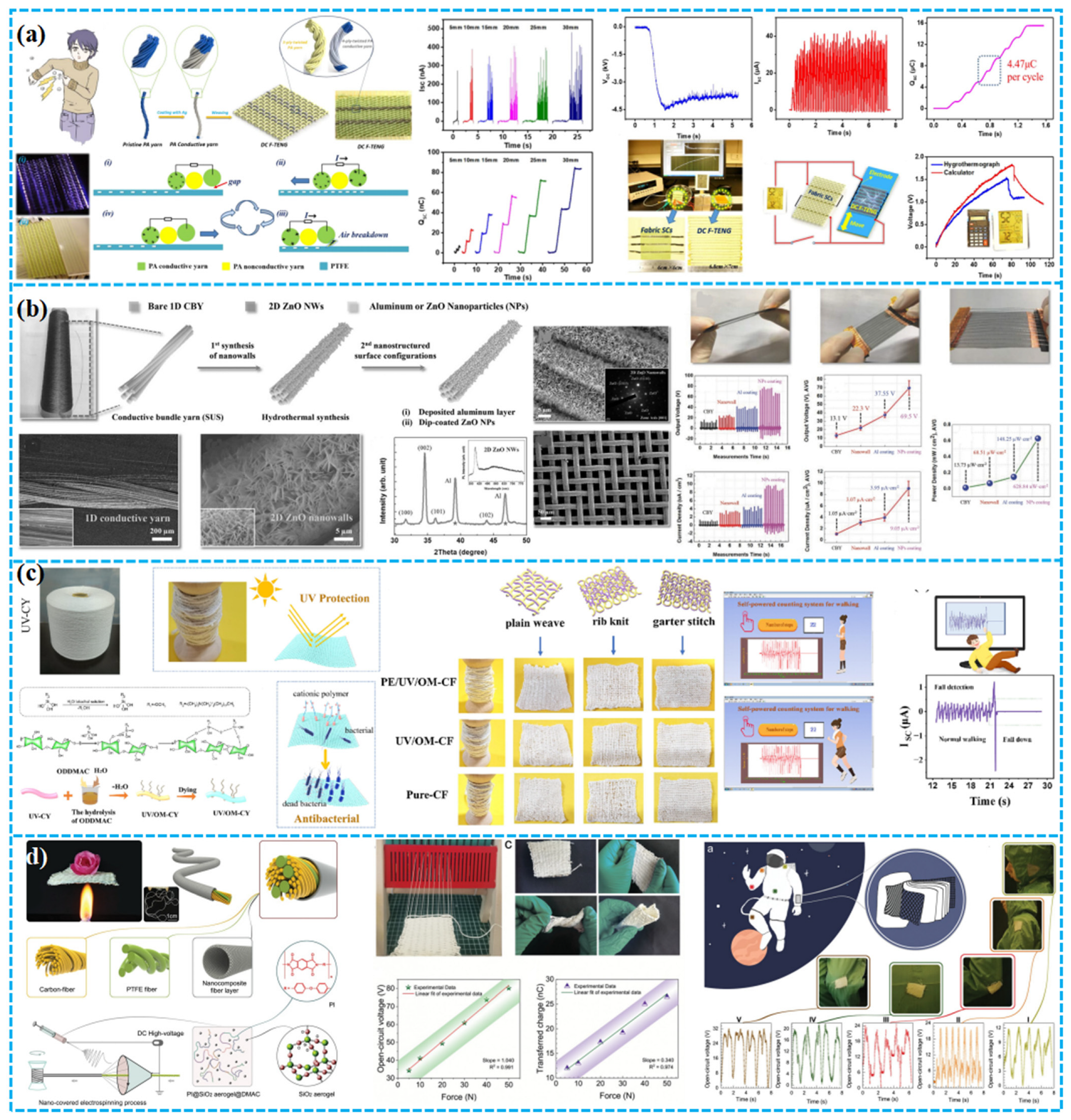
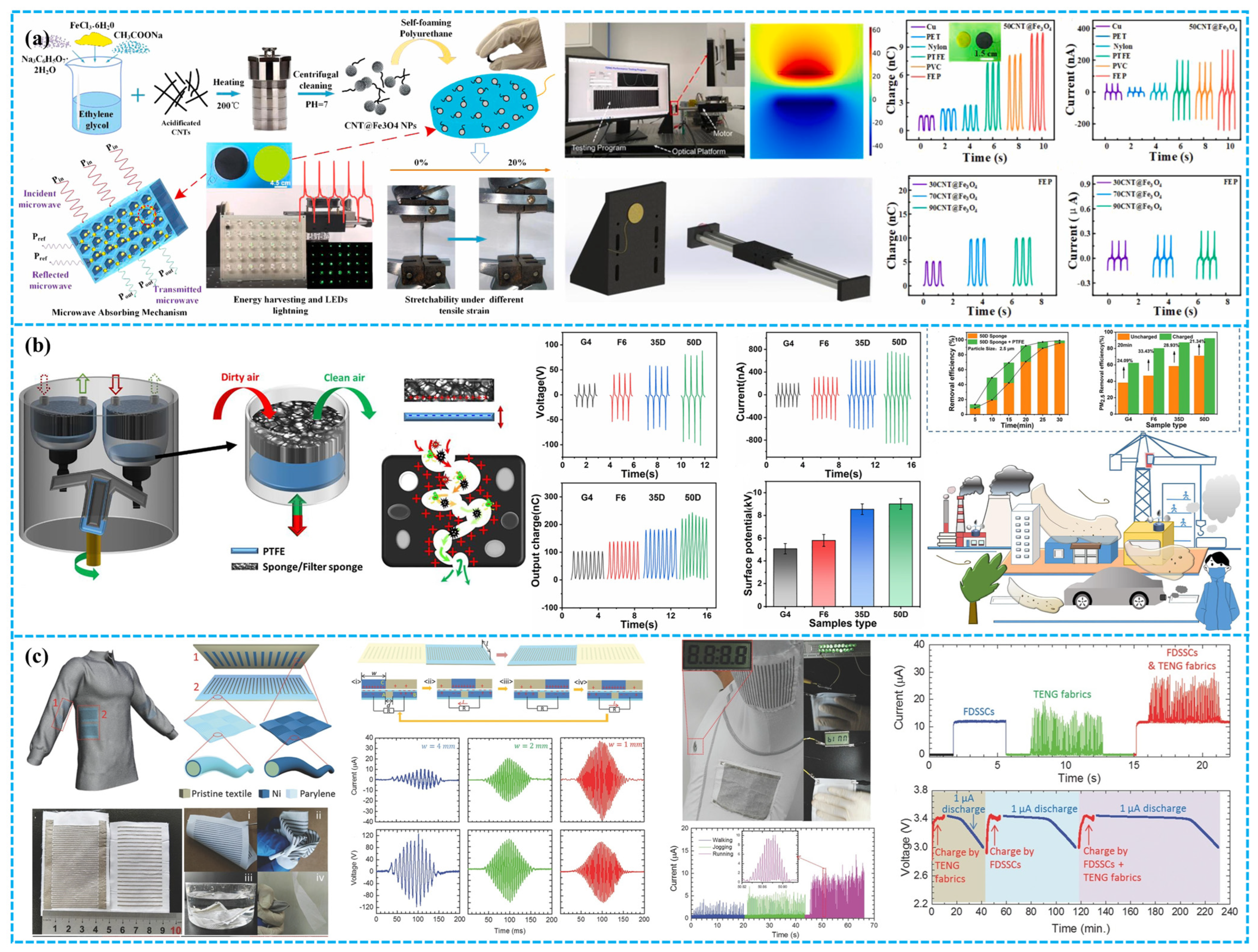
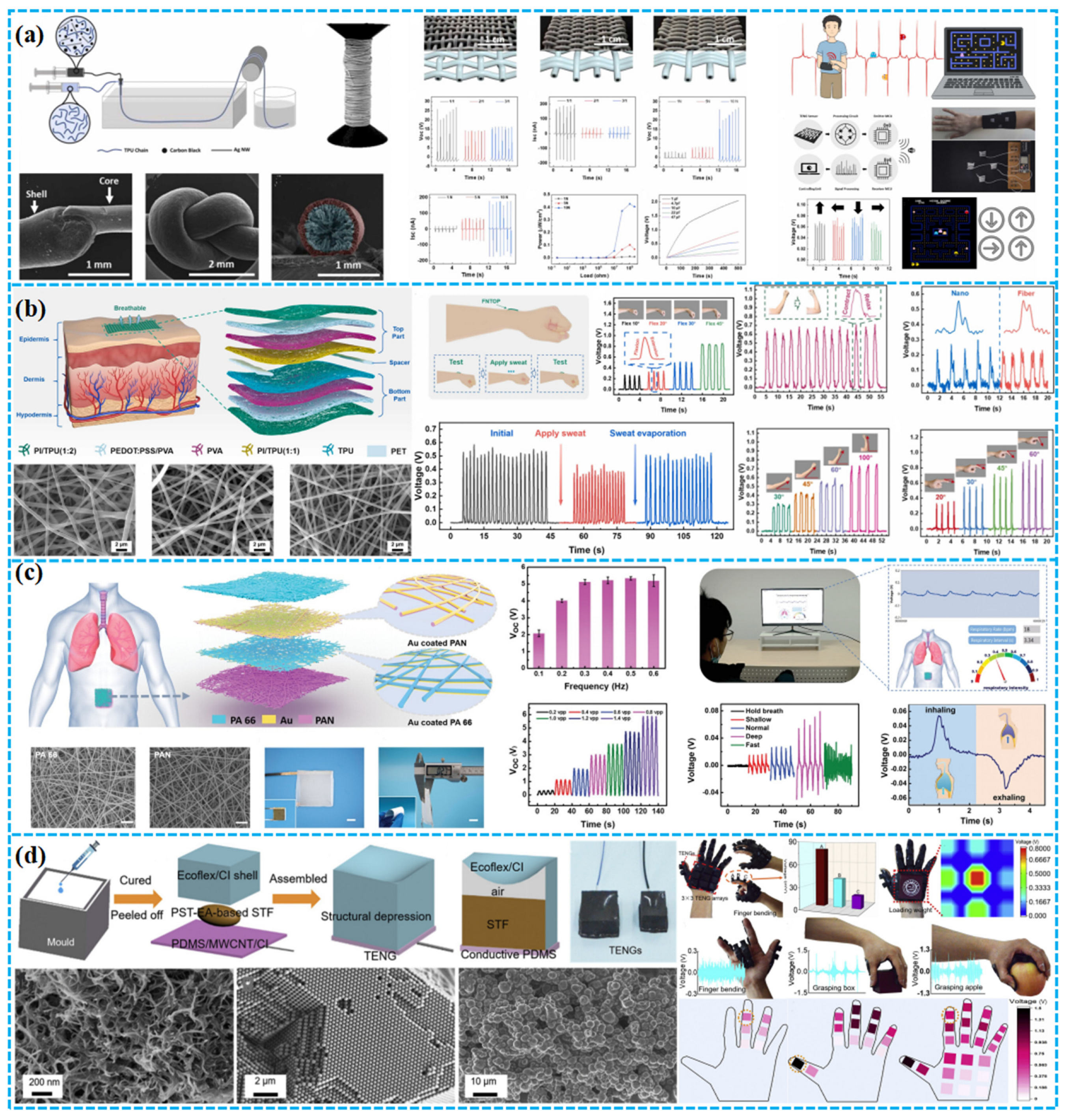


| Porous Materials and Structure | Material | The Other Electrode | Average Pore Size (μm) | Electrical Output | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foam | PDMS | Al | 2 | 130 V/- | Energy harvesting | [74] |
| Foam | PDMS | Kapton | 80 | 65 V/1 μA | Self-powered active sensing system | [75] |
| Foam | PDMS | Au | 1500 | 450 V/0.14 mA cm−2 | Energy harvesting | [76] |
| Foam | PDMS | Cu | - | 291.14 V/35.49 µA | Energy harvesting | [77] |
| Foam | PTFE | Al | - | 5.1 V/6.7 µA | Energy harvesting | [78] |
| Foam | PDMS | Cu | 250 | 184 V/9.5 μA | Energy harvesting | [79] |
| Foam | CNT-PDMS | PFA cloth | 200 | 500 V/40 μA | Energy harvesting | [80] |
| Foam | WPS | PTFE | ~4 | ~250 V/~52 μA | Energy harvesting and self-powered sensor | [81] |
| Foam | PDMS | PU-GR@MCNTs | - | 92 V/- | Energy harvesting and self-powered sensor | [120] |
| Foam | Ni/PU | PP | 300 | 21 V/0.31 μA | Energy harvester and self-powered sensor | [121] |
| Foam | PANI/PU | PTFE | 100 | 520 V/6.3 μA | Energy harvesting and ammonia sensing | [122] |
| Foam | PDMS-CNT/PTFE | Al | 250 | 320 V/13 μA | Energy harvesting | [123] |
| Foam | Silicon rubber | - | 200 | 24 V/188 nA | Energy harvesting and self-powered sensor | [124] |
| Foam | PDMS | Cu | 500 | 50 V/400 nA | Energy harvesting | [126] |
| Foam | CNTs@Fe3O4/PU | FEP | 10 | 34.8 V/267.1 nA | Energy harvesting | [144] |
| Foam | PP/PE | PTFE | 500 | 78 V/750 nA | Energy harvesting | [145] |
| Foam | PI | SRPA | 100 | 48.19 V/1.243 μA | Energy harvesting | [158] |
| Aerogel | CNF | PDMS | 3 | 60.6 V/7.7 μA | Energy harvesting | [83] |
| Aerogel | Cellulose II | PTFE | 0.01–0.025 | 65 V/1.86 μA | Energy harvesting | [84] |
| Aerogel | PBOA | PEO | 0.3 | 40 V | Energy harvesting | [85] |
| Aerogel | PI | PA | 0.686 | 115 V/9.5 μA | Energy harvesting | [86] |
| Aerogel | CGD/CNF | - | - | 38 V/3 μA | Energy harvesting | [87] |
| Aerogel | MXene/CMC | PVDF | - | 54.37 V/1.22 μA | Energy harvest and self-powered sensing | [67] |
| Aerogel | BC/HEC | PVDF | 77.9 | 21 V/0.39 μA | Energy harvest and self-powered sensing | [88] |
| Aerogel | CNF | PDMS | 40 | 75 V/- | Energy harvest and self-powered sensing | [89] |
| Aerogel | CaNC | FEP | - | 80 V/- | Energy harvest and self-powered sensing | [90] |
| Aerogel | PIA | Liquids | 0.2 | 12 V/300 nA | Biochemical sensing | [91] |
| Aerogel | CCA | FEP | 300 | 200.4 V/18.2 μA | Self-powered sensing and human–machine interfaces | [125] |
| Fibrous media | ANF | PVDF | 0.85 | 130 V/12 μA | Energy harvesting | [93] |
| Fibrous media | Co-NPC | PVDF | 0.95 | 710 V/- | Energy harvest and self-powered sensing | [94] |
| Fibrous media | PAN/TiO2 | Nylon | 0.5 | 60 V/0.05 μA | Self-powered sensing and human–machine interfaces | [95] |
| Fibrous media | PCL/CNT | Ecoflex | 0.6 | 2.24 kV/256 μA | Energy harvesting | [96] |
| Fibrous media | SPSM | Al | 10 | 36.8 V/0.91 μA | Energy harvest and self-powered sensing | [97] |
| Fibrous media | MXene/TPU | Al | 0.39 | 20.1 V/0.92 μA | Energy harvest and self-powered sensing | [98] |
| Fibrous media | SEBC | Cu | 200 | 266 V/5.9 μA | Intelligent wearable devices | [105] |
| Fibrous media | PVDF-TrFE | MCNT/PDMS | 2 | 508 V/16.5 μA | Energy harvesting | [106] |
| Fibrous media | PVDF | - | 6 | 54 mV/0.31 nA | Energy harvesting | [107] |
| Fibrous media | PLGA | PTFE | 2 | 95 V/1.7 μA | Energy harvest and self-powered sensing | [127] |
| Fibrous media | CB/Ag NW/TPU | PDMS | 1000 | 2 V/42 nA | Intelligent wearable devices | [147] |
| Fibrous media | PI/TPU | TPU | 2 | 0.92 V/9 nA | Intelligent wearable devices | [148] |
| Fibrous media | PA66 | PAN | 2 | 5.2 V/2 nA | Intelligent wearable devices | [149] |
| Fibrous media | Silk | PVDF | 3 | 500 V/12 μA | Self-powered sensing | [151] |
| Textile-based | Cotton/SCNT | Cu | 200 | 0.2 V/0.29 μA | Energy harvest and self-powered sensing | [132] |
| Textile-based | PDMS | Nitrile | 170 | 397 V/6.8 μA | Energy harvest and self-powered sensing | [133] |
| Textile-based | Nylon | PDMS-BTO | - | 864 V/28.6 μA | Energy harvest and self-powered sensing | [134] |
| Textile-based | Nylon | E-PTFE | 500 | 800 V/15 μA | Energy harvest and self-powered sensing | [135] |
| Textile-based | Nitrile, | Silicone rubber | 300 | -/13 μA | Self-powered sensing and intelligent wearable devices | [136] |
| Textile-based | PA | PTFE | - | 4500 V/40 μA | Energy harvesting | [140] |
| Textile-based | PET | Parylene | 200 | 130 V/37 µA | Energy harvesting | [146] |
| Textile-based | PVDF/PDMS | Nylon | 100 | 600 V/15 μA | Energy harvest and self-powered sensing | [152] |
| Textile-based | TPU | PLA | 250 | 162 V/42 µA | Self-powered sensing and human–machine interfaces | [154] |
| Textile-based | HPC | PTFE | 500 | 180 V/35 μA | Energy harvest and human–machine interfaces | [156] |
| Yarn | SUS | PDMS | 400 | 69.5 V/- | Energy harvesting | [141] |
| Yarn | PE | PDMS | 1000 | 200 V/10 μA | Self-powered sensing and intelligent wearable devices | [142] |
| Yarn | PI | PTFE | 1000 | 8 V/0.08 μA | Self-powered sensing and intelligent wearable devices | [143] |
| Yarn | FOTS | Ag | 10000 | 43 V/9.9 μA | Energy harvesting | [159] |
| Yarn | PDMS | Nylon | 500 | 1.5 V/0.0055 μA | Energy harvest and self-powered sensing | [160] |
| Yarn | Polyester/cotton | Polyurethane | 200 | 75 V/1.2 μA | Energy harvesting | [161] |
| Yarn | Dragon Skin | rGP/PDMS | - | 10 V/0.6 μA | Self-powered sensing | [162] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mi, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, H.; Lu, Y.; Wang, N. Porous Polymer Materials in Triboelectric Nanogenerators: A Review. Polymers 2023, 15, 4383. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15224383
Mi Y, Zhao Z, Wu H, Lu Y, Wang N. Porous Polymer Materials in Triboelectric Nanogenerators: A Review. Polymers. 2023; 15(22):4383. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15224383
Chicago/Turabian StyleMi, Yajun, Zequan Zhao, Han Wu, Yin Lu, and Ning Wang. 2023. "Porous Polymer Materials in Triboelectric Nanogenerators: A Review" Polymers 15, no. 22: 4383. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15224383
APA StyleMi, Y., Zhao, Z., Wu, H., Lu, Y., & Wang, N. (2023). Porous Polymer Materials in Triboelectric Nanogenerators: A Review. Polymers, 15(22), 4383. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15224383







