Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Embedded in a Polymeric Matrix as a New Material for Thin Film Microextraction (TFME) in Organic Pollutant Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Solutions
2.2. Preparation of the Films
2.3. Thin Film Microextraction Procedure
2.4. Chromatographic Analysis
2.5. Application Studies: River Samples
3. Results
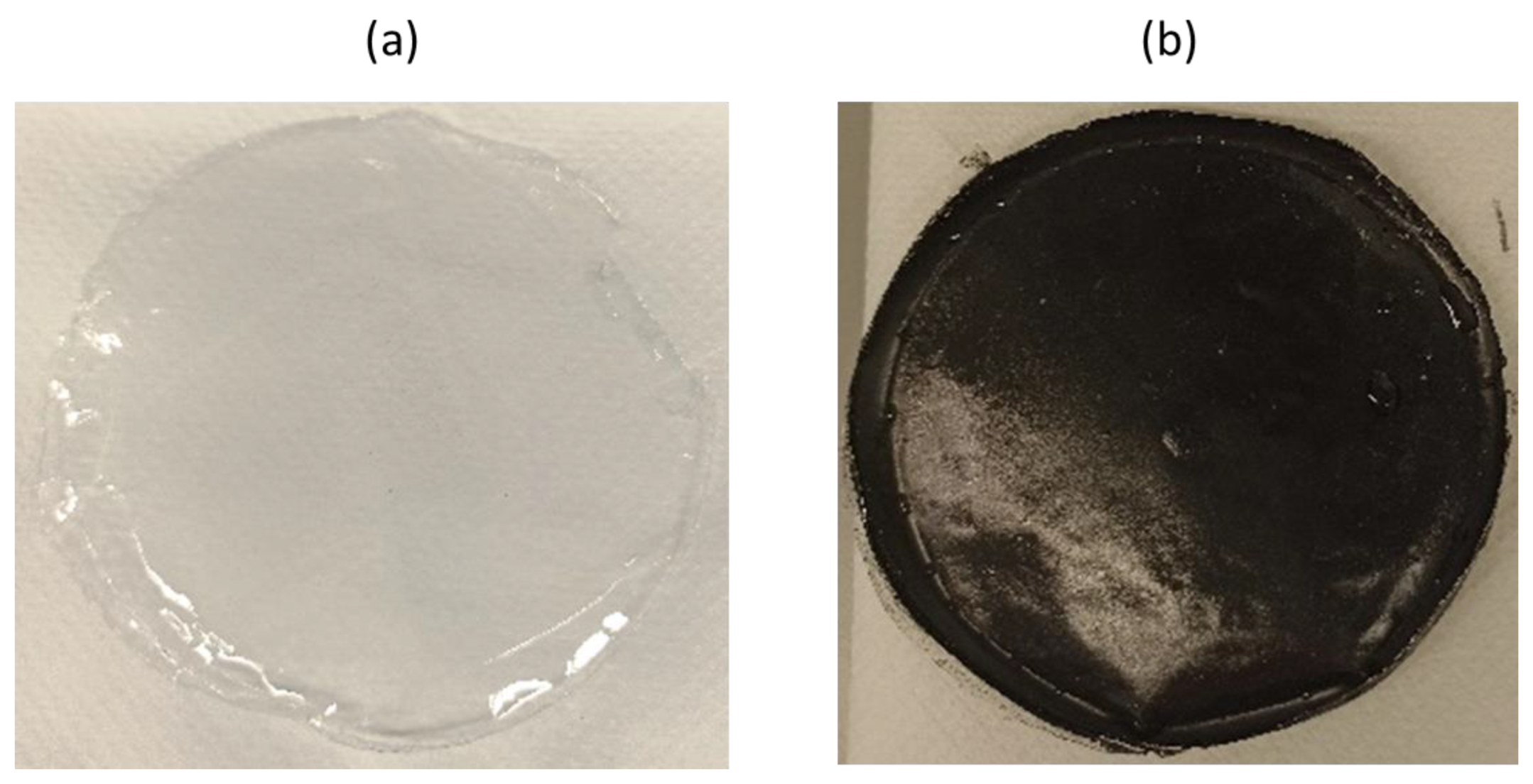
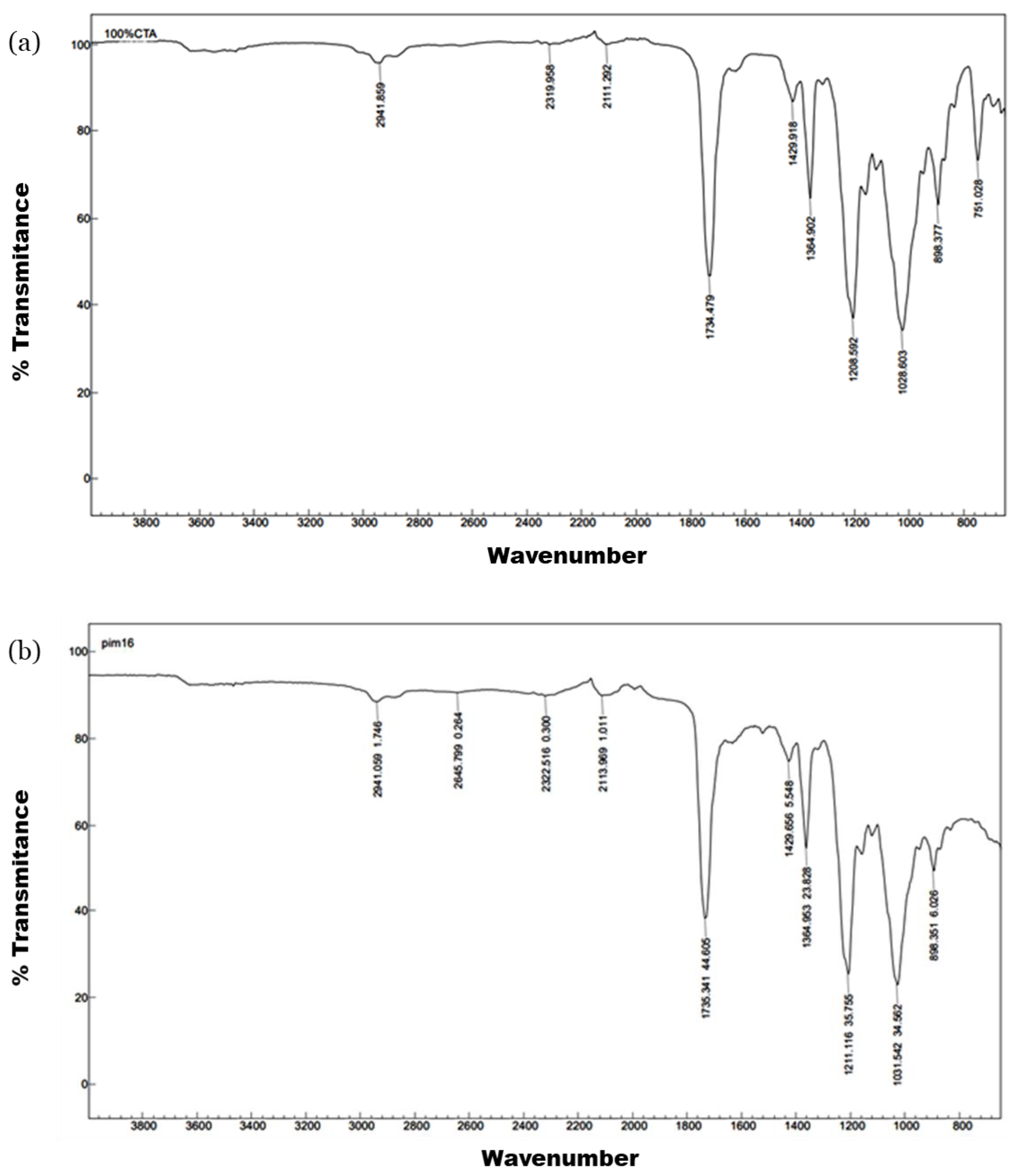
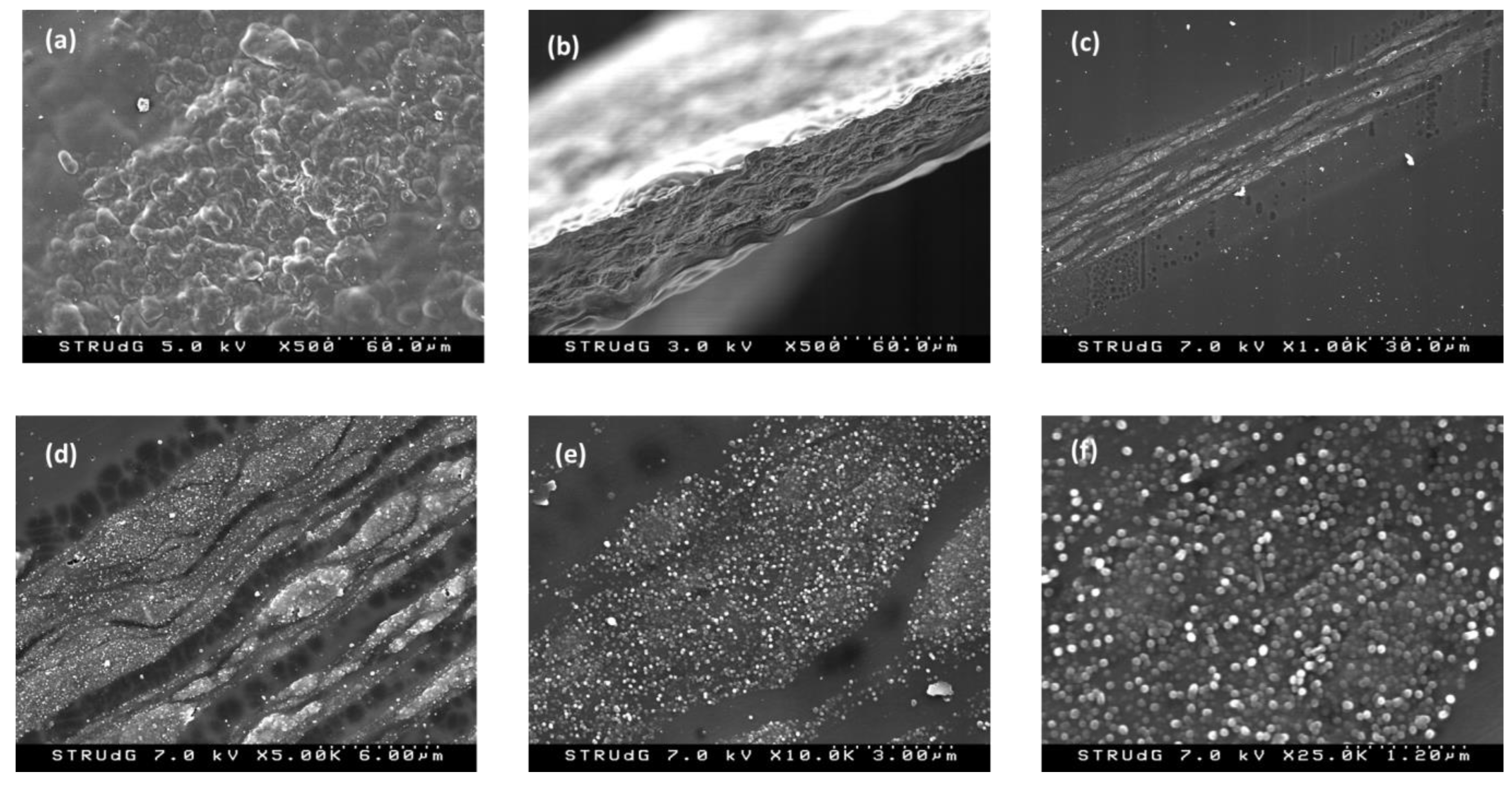
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of the Films
3.2. Interaction of Films with Embedded MWCNTs with the Organic Pollutants
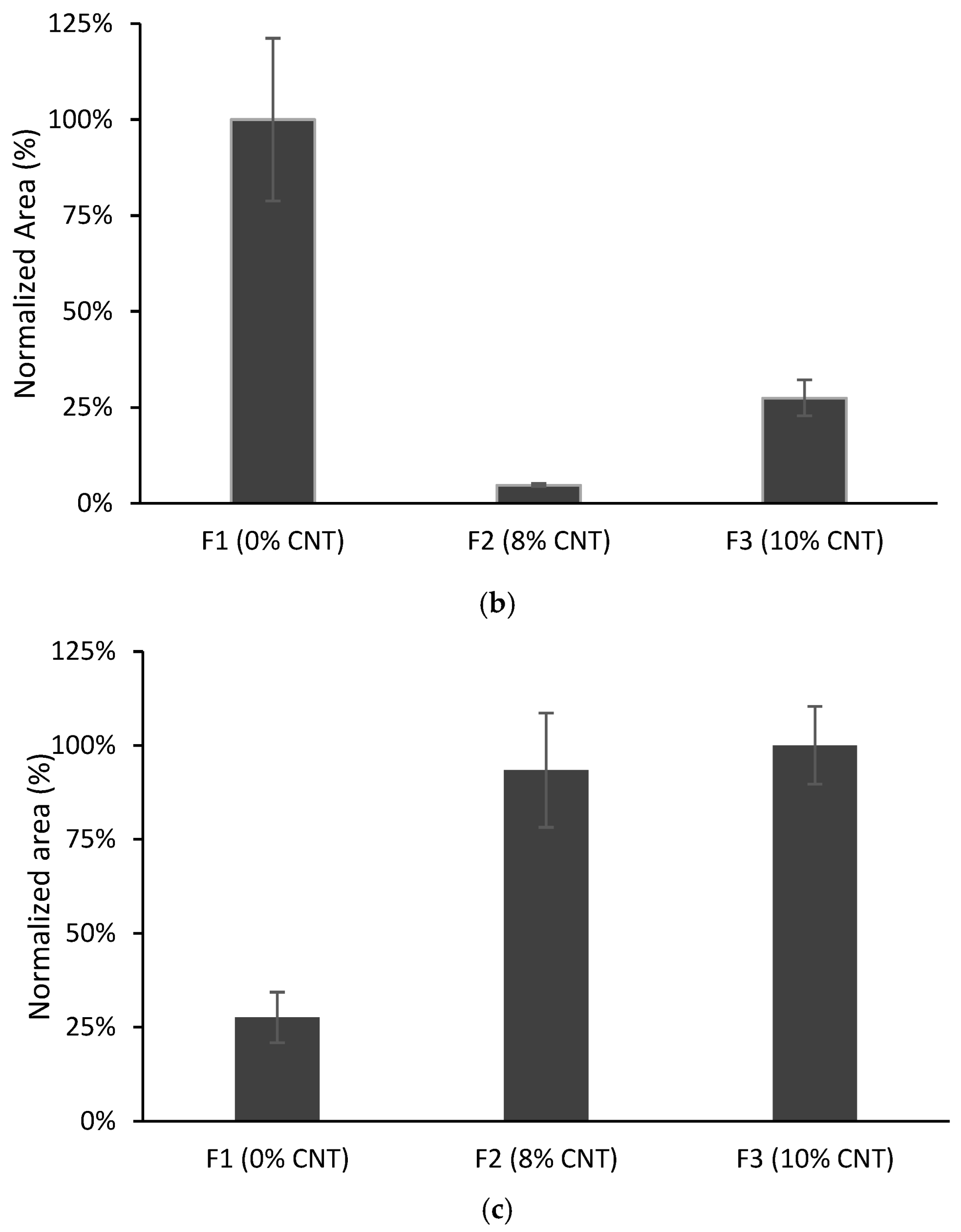
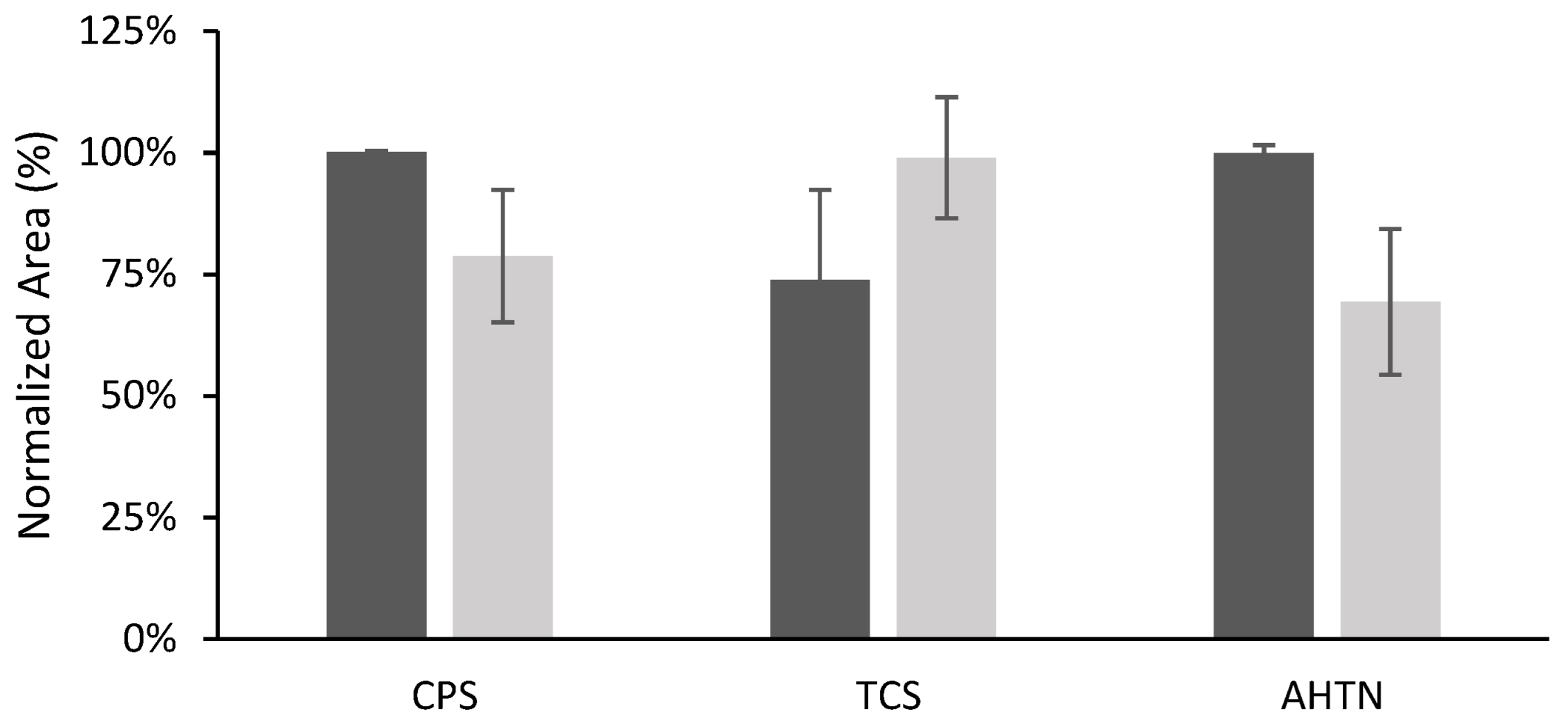
3.3. Effect of Film Composition on TFME
3.4. Elution Conditions
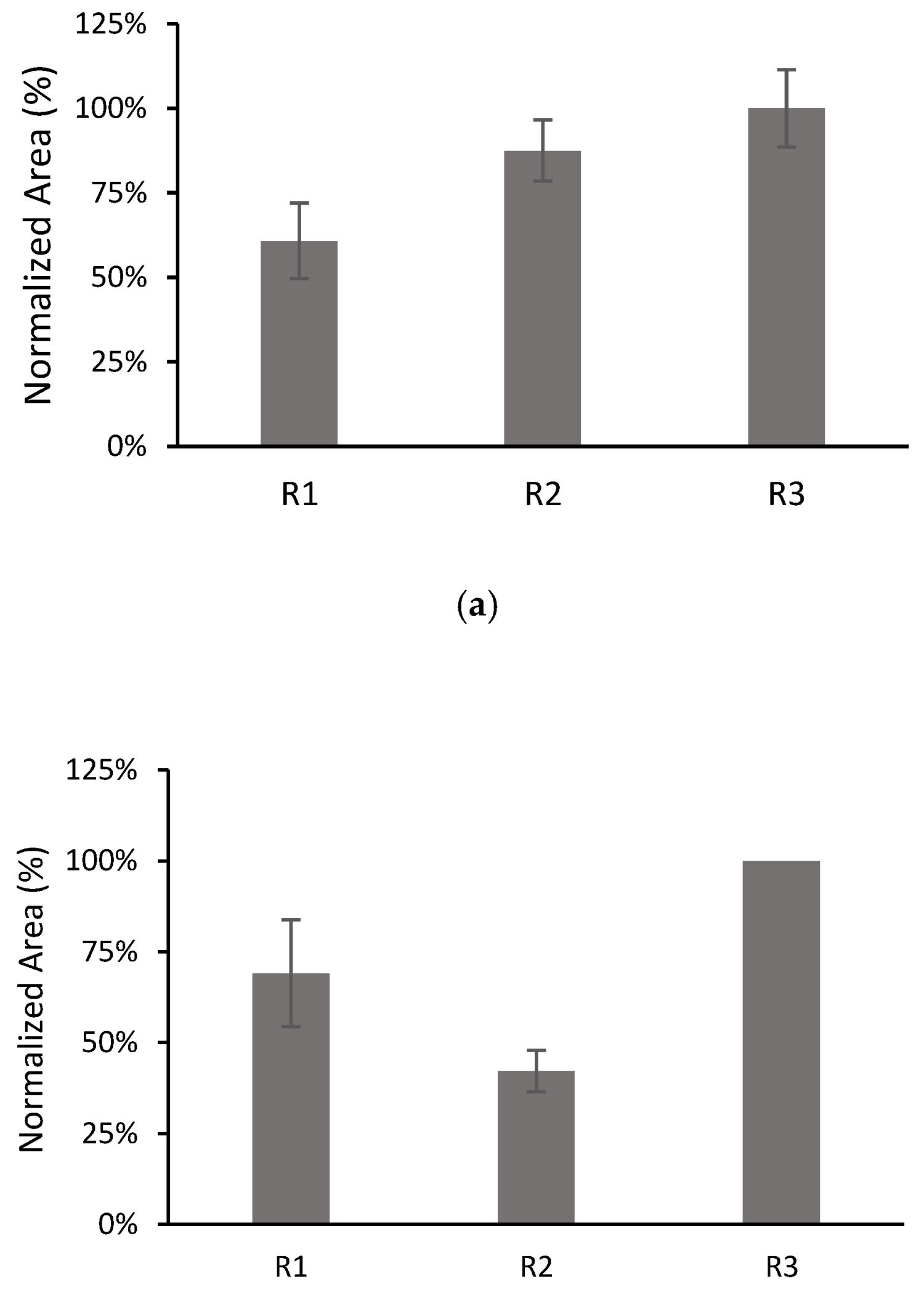
3.5. Repeatability
3.6. Analytical Figures of Merit
3.7. Application to Water Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahugo-Santana, C.; Sosa-Ferrera, Z.; Torres-Padrón, M.E.; Santana-Rodríguez, J.J. Application of new approaches to liquid-phase microextraction for the determination of emerging pollutants. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 731–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, C.L.; Pawliszyn, J. Solid phase microextraction with thermal desorption using fused silica optical fibers. Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 2145–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psillakis, E.; Kalogerakis, N. Developments in liquid-phase microextraction. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2003, 22, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carasek, E.; Merib, J.; Mafra, G.; Spudeit, D. A recent overview of the application of liquid-phase microextraction to the determination of organic-micropollutants. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 108, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidi, S.; Tajik, M.; Baharfar, M.; Rezazadeh, M. Micro solid-phase extraction (pipette tip and spin column) and thin film solid-phase microextraction: Miniaturized concepts for chromatographic analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 810–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Pawliszyn, J. Thin-film microextraction offers another geometry for solid-phase microextraction. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 39, 245–253. [Google Scholar]
- Bruheim, I.; Liu, X.; Pawliszyn, J. Thin-Film Microextraction. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, G. Preparation and application of poly(dimethylsiloxane)/β-cyclodextrin solid-phase microextraction membrane. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 543, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.I.G.S.; Cattrall, R.W.; Kolev, S.D. Recent trends in extraction and transport of metal ions using polymer inclusion membranes (PIMs). J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 415–416, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güell, R.; Anticó, E.; Kolev, S.D.; Benavente, J.; Salvadó, V.; Fontàs, C. Development and characterization of polymer inclusion membranes for the separation and speciation of inorganic As species. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 383, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherasim, C.; Bourceanu, G.; Olariu, R.; Arsene, C. A novel polymer inclusion membrane applied in chromium (VI) separation from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 197, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Khaldoun, I.; Mitiche, L.; Sahmoune, A.; Fontàs, C. An Efficient Polymer Inclusion Membrane-Based Device for Cd Monitoring in Seawater. Membranes 2018, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Rodríguez, A.; Matamoros, V.; Kolev, S.D.; Fontàs, C. Development of a polymer inclusion membrane (PIM) for the preconcentration of antibiotics in environmental water samples. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 492, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anticó, E.; Vera, R.; Vázquez, F.; Fontàs, C.; Lu, C.; Ros, J. Preparation and Characterization of Nanoparticle-Doped Polymer Inclusion Membranes. Application to the Removal of Arsenate and Phosphate from Waters. Materials 2021, 14, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vera, R.; Insa, S.; Fontàs, C.; Anticó, E. A new extraction phase based on a polymer inclusion membrane for the detection of chlorpyrifos, diazinon and cyprodinil in natural water samples. Talanta 2018, 185, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlo, F.; Profumo, A.; Fontàs, C.; Anticó, E. Preparation of new polymeric phases for thin-film liquid phase microextraction (TF-LPME) of selected organic pollutants. Microchem. J. 2022, 175, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojanowicz, M. Analytical applications of carbon nanotubes: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2006, 25, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ademyi, A.S.; Conway, J.R.; Garner, K.; Huang, Y.; Su, Y.; Keller, A.A. Engineered nanomaterials for water treatment and remediation: Costs, benefits, and applicability. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 286, 640–662. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Lv, L.; Pan, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Quanzing Zhang, Q. Polymer-supported nanocomposites for environmental applications: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 170, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Duan, C.; Guan, Y. Sorptive extraction techniques in sample preparation for organophosphorus pesticides in complex matrices. J. Chromatogr. B 2010, 878, 1216–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scida, K.; Stege, P.W.; Haby, G.; Messina, G.; García, C.D. Recent Applications of carbon-based nanomaterials in analytical chemistry: Critical review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 691, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socas-Rodríguez, B.; Herrera-Herrera, A.V.; Asensio-Ramos, M.; Hernández-Borges, J. Recent Applications of carbon nanotube sorbents in Analytical Chemistry. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1357, 110–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patiño, Y.; Díaz, E.; Ordóñez, S.; Gallegos-Suarez, E.; Guerrero-Ruiz, A.; Rodríguez-Ramos, I. Adsorption of emerging pollutants on functionalised multiwall carbon nanotubes. Chemosphere 2015, 136, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrzynska, K. Carbon nanotubes as sorbents in the analysis of pesticides. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 1407–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klongklaew, P.; Naksena, T.; Kanatharana, P.; Bunkoed, O. A hierarchically porous composite monolith polypyrrole/octadecyl silica/graphene oxide/chitosan cryogel sorbent for the extraction and pre-concentration of carbamate pesticides in fruit juices. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 7185–7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Gómez, J.; Fresco-Cala, B.; García-Valverde, M.T.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S. Carbon nanohorn suprastructures on a paper support as a sorptive phase. Molecules 2018, 23(6), 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Z. Electrochemically modified carbon fiber bundles as selective sorbent for online solid-phase microextraction of sulfonamides. Michrochim. Acta 2016, 183, 813–820. [Google Scholar]
- Khezeli, T.; Daneshfar, A. Development of dispersive micro-solid phase extraction based on micro and nano sorbents. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.A.; Curbelo, A.; Herrera-Herrera, V.; Hernandez-Borges, J.; Rodríguez Delgado, M.A. Analysis of pesticides residues in environmental water samples using multiwalled carbon nanotubes dispersive solid-phase extraction. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanch, C.; Wu, Q.; Wu, C.; Wang, Z. Determination of some organophosphorus pesticides in water and watermelon samples by microextraction prior to high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 3231–3239. [Google Scholar]
- Sarafraz-Yazdi, A.; Amiri, A.; Rounaghi, G.; Eshtiagh-Hosseini, H. Determination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in urine by hollow-fiber liquid membrane-protected solid-phase microextraction based on sol–gel fiber coating. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Appl. 2012, 908, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celma, A.; Gago-Ferrero, P.; Golovko, O.; Hernández, F.; Yin Lai, F.; Lundqvist, J.; Frank Menger, F.; Juan, V.S.; Wiberg, K.; Ahrens, L.; et al. Are preserved coastal water bodies in Spanish Mediterranean basin impacted by human activity? Water quality evaluation using chemical and biological analyses. Environ. Int. 2022, 165, 107326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arain, M.; Brohi, M.; Channa, A.; Brohi, R.; Mushtaque, S.; Kumar, K.; Ibupoto, A.S. Analysis of Chlorpyrifos Pesticide Residues in Surface Water, Ground Water and Vegetables through Gas Chromatography . Int. J. Appl. Environ. Sci. 2018, 13, 167–173. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, A.H.; Eddleston, M.; Senarathna, L.; Mohamed, F.; Gawarammana, I. Acute Human Lethal Toxicity of Agricultural Pesticides: A Prospective Cohort Study. PLoS Med. 2010, 7, 1000357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission (EC). Directives of 12 August 2013 Amending Directives 2000/60/EC and 2008/105/EC as Regards Priority Substances in the Field of Water Policy. Off. J. Eur. Union 2013, 226, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Weatherly, L.M.; Gosse, J.A. Triclosan Exposure, Transformation, and Human Health Effects. Weatherly L. and Gosse J. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2017, 20, 447–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Shao, Y.; Gao, N.; Deng, J.; Tan, C. Equilibrium, Kinetic and Thermodynamic studies on the Adsorption of Triclosan onto Multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Clean Soil Air Water 2012, 41, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehiguese, F.O.; Alam, M.R.; Pintado-Herrera, M.G.; Araújo, C.V.M.; Martin-Diaz, M.L. Potential of environmental concentrations of the musks galaxolide and tonalide to induce oxidative stress and genotoxicity on the marine environment. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 160, 105019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godayol, A.; Besalú, E.; Antico, E.; Sanchez, J.M. Monitoring of sixteen fragrance allergens and two polycyclic musks in wastewater treatment plants by solid phase microextraction coupled to gas chromatography. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Mubarak, M.; Khalid, M.; Tan, Y.; Abdullah, E.; Rahman, M.; Karri, R. A comprehensive review on micropollutants removal using carbon nanotubes-based adsorbents and membranes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fard, M.; Brian Barkdoll, B. Using recyclable magnetic carbon nanotube to remove micropollutants from aqueous solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 249, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Analytical quality control and method validation procedures for pesticides residues analysis in food and feed. Document No. SANTE/11312/2021.
- Guidelines for Standard Method Performance Requirements; 21st Ed. of the Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC INTERNATIONAL. 2019. Available online: http://www.eoma.aoac.org/app_f.pdf (accessed on 29 November 2022).





| Compound Name | IUPAC Name | Molecular Weight (g mol−1) | Classification | CAS Number | Log Kow * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorpyrifos (CPS) | O,O-Diethyl O-(3,5,6- trichloropyridin-2-yl) phosphorothioate | 350.6 | Organophosphorus insecticide | 2921-88-2 | 4.96 |
| Triclosan (TCS) | 5-Chloro-2-(2,4- dichlorophenoxy)phenol | 289.5 | Antibacterial and fungicide | 3380-34-5 | 4.76 |
| Tonalide (AHTN) | 6-Acetyl-1,1,2,4,4,7- hexamethyltetralin | 258.398 | Aroma musk | 21145-77-7 | 5.70 |
| Film | % CTA | % MWCNT | % Plasticizer (NPOE or DBS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 70 (120 mg) | - | 30 (50 mg) |
| F2 | 72 (126 mg) | 8 (14 mg) | 20 (32 mg) |
| F3 | 90 (120 mg) | 10 (14 mg) | - |
| Compounds | Rt | m/z |
|---|---|---|
| CPS | 13.39 | 197,341 |
| TCS | 14.80 | 218,288,290 |
| AHTN | 12.26 | 243,258 |
| CPS | TCS | AHTN | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration Curve | y = 9715.6x – 138,832 | y = 8869.4x + 478,841 | y = 13,362x – 370,528 |
| Determination coefficient (R2) | 0.9991 | 0.9853 | 0.9993 |
| Working range (µg L−1) | 50–200 | 500–4068 | 50–200 |
| LOD (µg L−1) | 1 | 10 | 1 |
| LOQ (µg L−1) | 5 | 50 | 5 |
| AR (%) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Osor River | Llémena River | |
| CPS | 91 (13) | 65 (11) |
| TCS | 70 (7) | 51 (10) |
| AHTN | 100 (11) | 59 (11) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quintanilla, I.; Perelló, C.; Merlo, F.; Profumo, A.; Fontàs, C.; Anticó, E. Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Embedded in a Polymeric Matrix as a New Material for Thin Film Microextraction (TFME) in Organic Pollutant Monitoring. Polymers 2023, 15, 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15020314
Quintanilla I, Perelló C, Merlo F, Profumo A, Fontàs C, Anticó E. Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Embedded in a Polymeric Matrix as a New Material for Thin Film Microextraction (TFME) in Organic Pollutant Monitoring. Polymers. 2023; 15(2):314. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15020314
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuintanilla, Ivonne, Carlos Perelló, Francesca Merlo, Antonella Profumo, Clàudia Fontàs, and Enriqueta Anticó. 2023. "Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Embedded in a Polymeric Matrix as a New Material for Thin Film Microextraction (TFME) in Organic Pollutant Monitoring" Polymers 15, no. 2: 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15020314
APA StyleQuintanilla, I., Perelló, C., Merlo, F., Profumo, A., Fontàs, C., & Anticó, E. (2023). Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Embedded in a Polymeric Matrix as a New Material for Thin Film Microextraction (TFME) in Organic Pollutant Monitoring. Polymers, 15(2), 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15020314










