Effect of Discharge Voltage on the Microstructure of Graphene/PEKK Composite Samples by Electromagnetic Powder Molding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment and Method
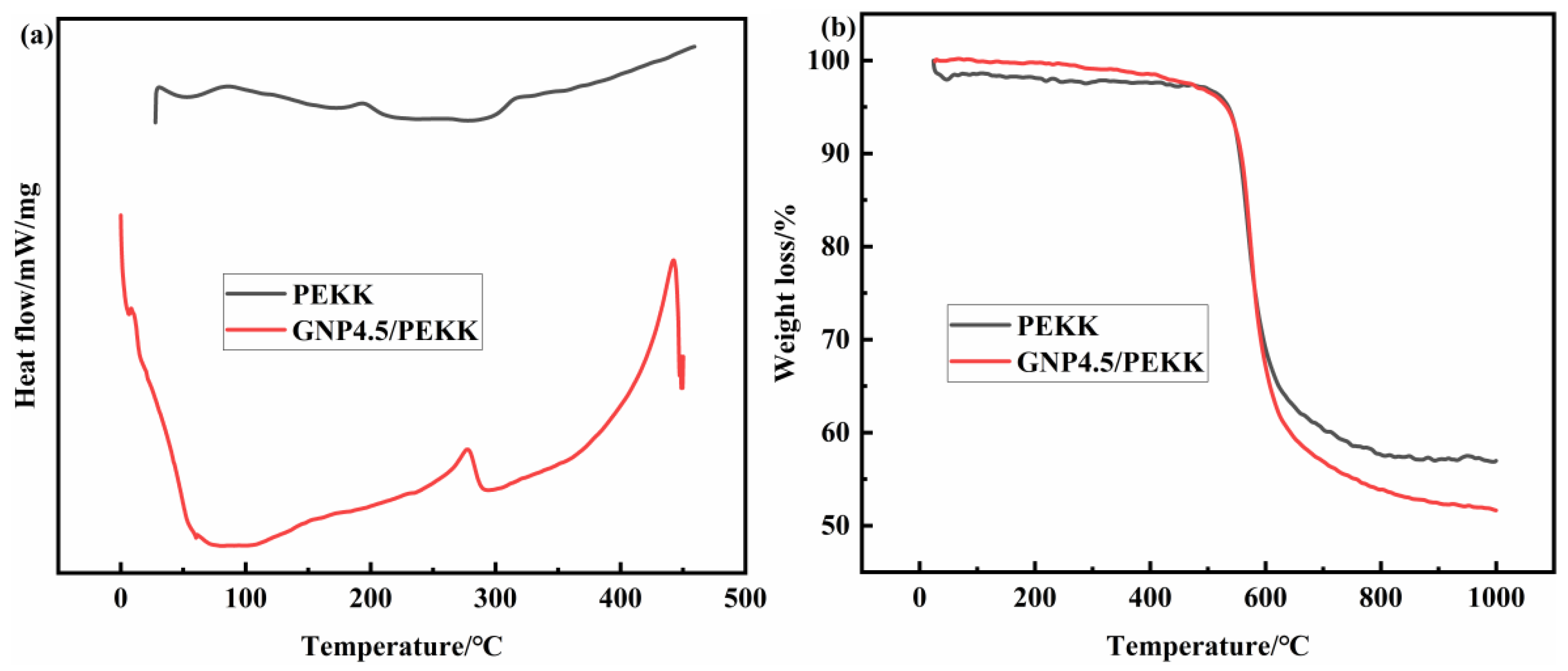
2.1. Material Characterization
2.2. Electromagnetic-Assisted Molding Device
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Discharge Current and Electromagnetic Force
3.2. Microstructure Characteristics
3.3. Conductivity and Mechanical Performance
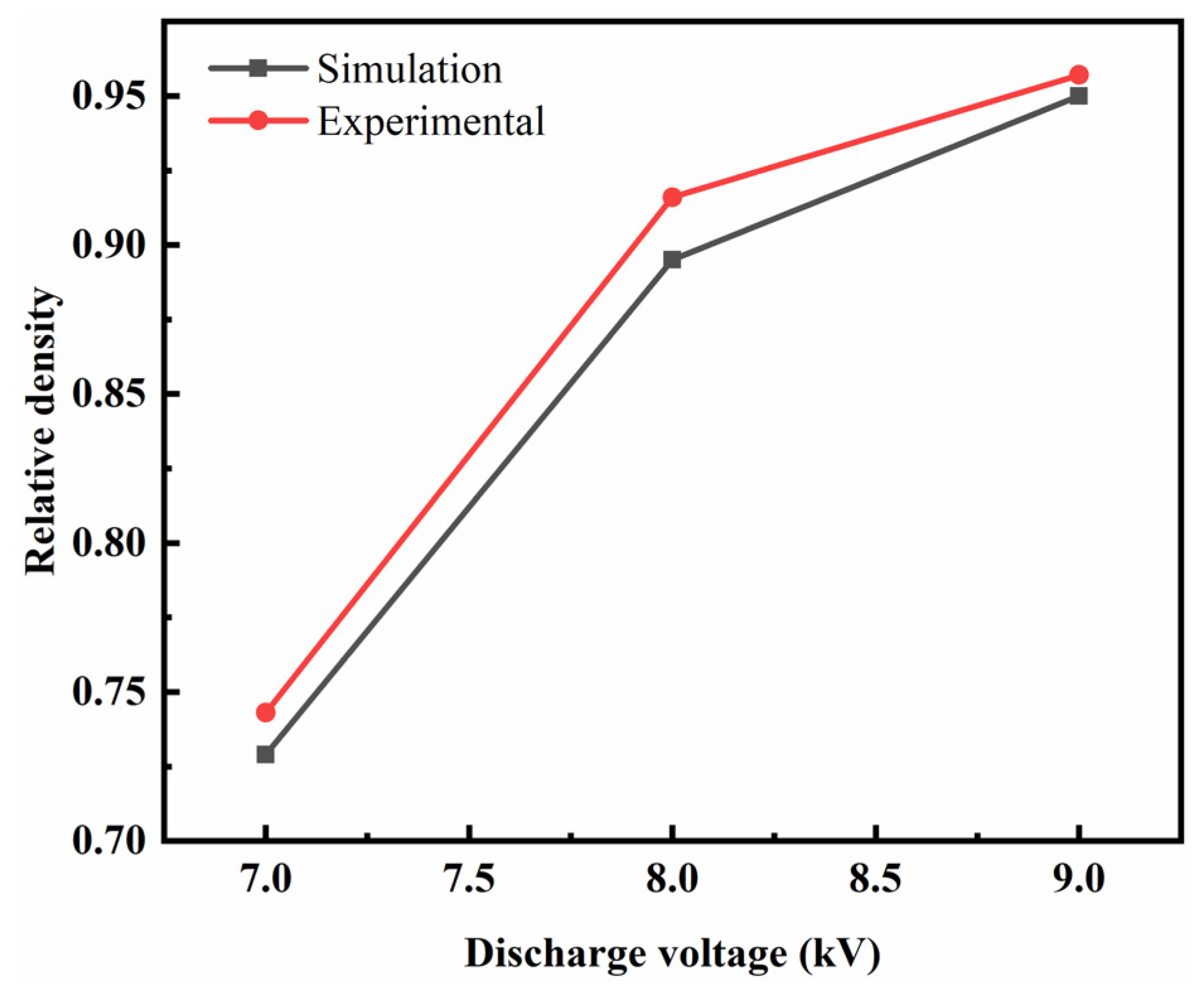
3.4. Numerical Analysis
- (1)
- FE Analysis
- (2)
- Model validation
- (3)
- Stress/strain distribution on the electrode rod
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Electromagnetically assisted powder molding equipment was used to process graphene/PEKK composite electrode rods at different discharge voltages, such as 7 kV, 8 kV, and 9 kV. The discharge voltage was adjusted to improve the compaction density during the powder molding process and to enhance the electrical conductivity and mechanical properties of the electrode rods.
- (2)
- Under high-speed impact, graphene is uniformly dispersed in the PEKK matrix and along the direction perpendicular to the impact force. The flake graphene structure is relatively compact with increasing discharge voltage (electromagnetic force). The relative density values are 0.957 at 9 kV, 0.916 at 8 kV and 0.734 at 7 kV. Thus, the compaction density increases as the discharge voltage increases, and the flake graphene structure is tight, resulting in an increase in the carrier motion rate.
- (3)
- During the electromagnetically assisted molding of the graphene/PEKK composite powder, the electrical conductivity and hardness increased with increasing discharge voltage, indicating that the compaction density affected the mechanical and electrical properties of the graphene/PEKK composite. When the discharge voltage reached 9 kV, the conductivity of the electrode rod reached 2.65 S/m on the surface.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ge, L.; Chen, J.; Tian, G.; Ahmed, J.; Huang, Q.; Hu, Z. Study on the new electromagnetic flowmeter based on three-value trapezoidal wave excitation. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2021, 78, 101882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Tang, H.; Wu, B.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Luo, W.; Liu, Q. Application status of platinum iridium alloy. J. Funct. Mater. 2020, 51, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Umoren, S.A.; Solomon, M.M. Protective polymeric films for industrial substrates: A critical review on past and recent applications with conducting polymers and polymer composites/nanocomposites. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 104, 380–450. [Google Scholar]
- Akpan, E.I.; Shen, X.; Wetzel, B.; Friedrich, K. 2-Design and Synthesis of Polymer Nanocomposites. In Polymer Composites with Functionalized Nanoparticles; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 47–83. [Google Scholar]
- Mirzaei, M.; Abbasi, M. Dynamic response of moderately thick graphene reinforced composite cylindrical panels under the action of moving load. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2023, 146, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolotin, K.I.; Sikes, K.J.; Jiang, Z.; Klima, M.; Fudenberg, G.; Hone, J.; Kim, P.; Stormer, H.L. Ultrahigh electron mobility in suspended graphene. Solid State Commun. 2008, 146, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phiri, J.; Gane, P.; Maloney, T.C. General overview of graphene: Production, properties and application in polymer composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2017, 215, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balandin, A.A.; Ghosh, S.; Bao, W.; Calizo, I.; Teweldebrhan, D.; Miao, F.; Lau, C.N. Superior thermal conductivity of single-layer graphene. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 902–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Tan, S.T.; Yi, X.; Wang, G.; Sun, X.; Zhu, H.; Demir, H.V. Graphene-based transparent conductive electrodes for GaN-based light emitting diodes: Challenges and countermeasures. Nano Energy 2015, 12, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Martín, H.; Mackenzie, P.; Baidak, A.; Brádaigha Conchúr, M.Ó.; Dipa, R. Crystallinity studies of PEKK and carbon fibre/PEKK composites: A review. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 223, 109127. [Google Scholar]
- Pedoto, G.; Grandidier, J.C.; Gigliotti, M.; Alain, V. Characterization and modelling of the PEKK thermomechanical and creep behavior above the glass transition temperature. Mech. Mater. 2022, 166, 104189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Berretta, S.; Evans, K.; Smith, K.; Ghita, O. A primary study into graphene/polyether ether ketone (PEEK) nanocomposite for laser sintering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 428, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhosale, S.D.; Gaikwad, S.D.; Gadve, R.D.; Goyal, R.K. Synergistic effects of graphene nanoplatelets on X-band electromagnetic interference shielding, thermal expansion and thermal stability of poly(ether–ketone) based nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 265, 115038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Ye, Z. Experimental research on moulding of graphene/PEKK composite powder by spark plasma sintering technology. Appl. Phys. A 2022, s128, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jia, D.; Pei, X.; Wu, X.; Xu, F.; Ye, Z.; Wang, H. Mechanical performance of graphenex/poly (ether ketone ketone) composite sheets by hot pressing. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raps, L.; Chadwick, A.R.; Schiel, I.; Schmidt, I. CF/LM-PAEK: Characterization and sensitivity to critical process parameters for automated fibre placement. Compos. Struct. 2022, 284, 115087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dul, S.; Fambri, L.; Pegoretti, A. Fused deposition modelling with ABS–graphene nanocomposites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 85, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikas, H.; Stavropoulos, P.; Chryssolouris, G. Additive manufacturing methods and modelling approaches: A critical review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 83, 389–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Song, G.; Ma, L.; Feng, P.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Jin, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, X. Evolution of properties and enhancement mechanism of largescale three-dimensional graphene oxide–carbon nanotube aerogel/polystyrene nanocomposites. Polym. Test. 2021, 97, 107158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Z.; Guo, Y.; Luan, J.; Geng, Z.; Wang, G. Design and preparation of graphene/poly(ether ether ketone) composites with excellent electrical conductivity. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 2372–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang-Hwa, Y.; Hee-Tae, J. Grafting polycarbonate onto graphene nanosheets: Synthesis and characterization of high performance polycarbonate–graphene nanocomposites for ESD/EMI applications. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 45902–45910. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, V.; Kim, S.; Neuhofer, S.; Paulik, C. Polyethylene/graphene nanocomposites: Effect of molecular weight on mechanical, thermal, rheological and morphological properties. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2016, 294, 691–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infurna, G.; Teixeira, P.F.; Tz, N.; Hilliou, L.; Mantia, F.P.; Covas, J.A. Taking advantage of the functional synergism between carbon nanotubes and graphene nanoplatelets to obtain polypropylene–based nanocomposites with enhanced oxidative resistance. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 133, 109796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jia, D.; Pei, X.; Wu, X.; Xu, F.; Wang, H.; Cao, M.; Chen, H. Investigation of Electromagnetic Pulse Compaction on Conducting Graphene/PEKK Composite Powder. Materials 2021, 14, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Gao, M.; Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Yan, F.; Zhao, H.; Yao, Q. Polymer-based Graphene Composite Molding: A Review. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 2538–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parandoush, P.; Lin, D. A review on additive manufacturing of polymer-fiber composites. Compos. Struct. 2017, 182, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wang, H.; Wu, X.; Ye, Z. A Density-Dependent Modified Doraivelu Model for the Cold Compaction of Poly (Ether Ketone Ketone) Powders. Polymers 2022, 14, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Suonan, A.; Zhou, J.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhao, X.; Lou, X.; Yang, C.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.-G. PEEK (Polyether-ether-ketone) and its composite materials in orthopedic implantation. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 102977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadimi, N.P.; Grange, K.C.; Gascoin, S.N.; Senave, I.R. Thermal degradation analysis of innovative PEKK-based carbon composites for high-temperature aeronautical components. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2017, 65, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doraivelu, S.M.; Gegel, H.L.; Gunasekera, J.S.; Malas, J.C.; Morgan, J.T.; Thomas, J.F., Jr. A new yield function for compressible PM materials. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 1984, 26, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, F.; Gao, M.; Wang, H.-X.; Wu, X.-L.; Liu, H.; Ma, C.; Yao, Q.-T.; Zhao, H.-Y. Effect of Discharge Voltage on the Microstructure of Graphene/PEKK Composite Samples by Electromagnetic Powder Molding. Polymers 2023, 15, 3256. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153256
Xu F, Gao M, Wang H-X, Wu X-L, Liu H, Ma C, Yao Q-T, Zhao H-Y. Effect of Discharge Voltage on the Microstructure of Graphene/PEKK Composite Samples by Electromagnetic Powder Molding. Polymers. 2023; 15(15):3256. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153256
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Fan, Ming Gao, Hui-Xiong Wang, Xue-Lian Wu, Hong Liu, Chao Ma, Quan-Tong Yao, and Hui-Yan Zhao. 2023. "Effect of Discharge Voltage on the Microstructure of Graphene/PEKK Composite Samples by Electromagnetic Powder Molding" Polymers 15, no. 15: 3256. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153256
APA StyleXu, F., Gao, M., Wang, H.-X., Wu, X.-L., Liu, H., Ma, C., Yao, Q.-T., & Zhao, H.-Y. (2023). Effect of Discharge Voltage on the Microstructure of Graphene/PEKK Composite Samples by Electromagnetic Powder Molding. Polymers, 15(15), 3256. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153256





