Flexural Properties of Heat-Polymerized PMMA Denture Base Resins Reinforced with Fibers with Different Characteristics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
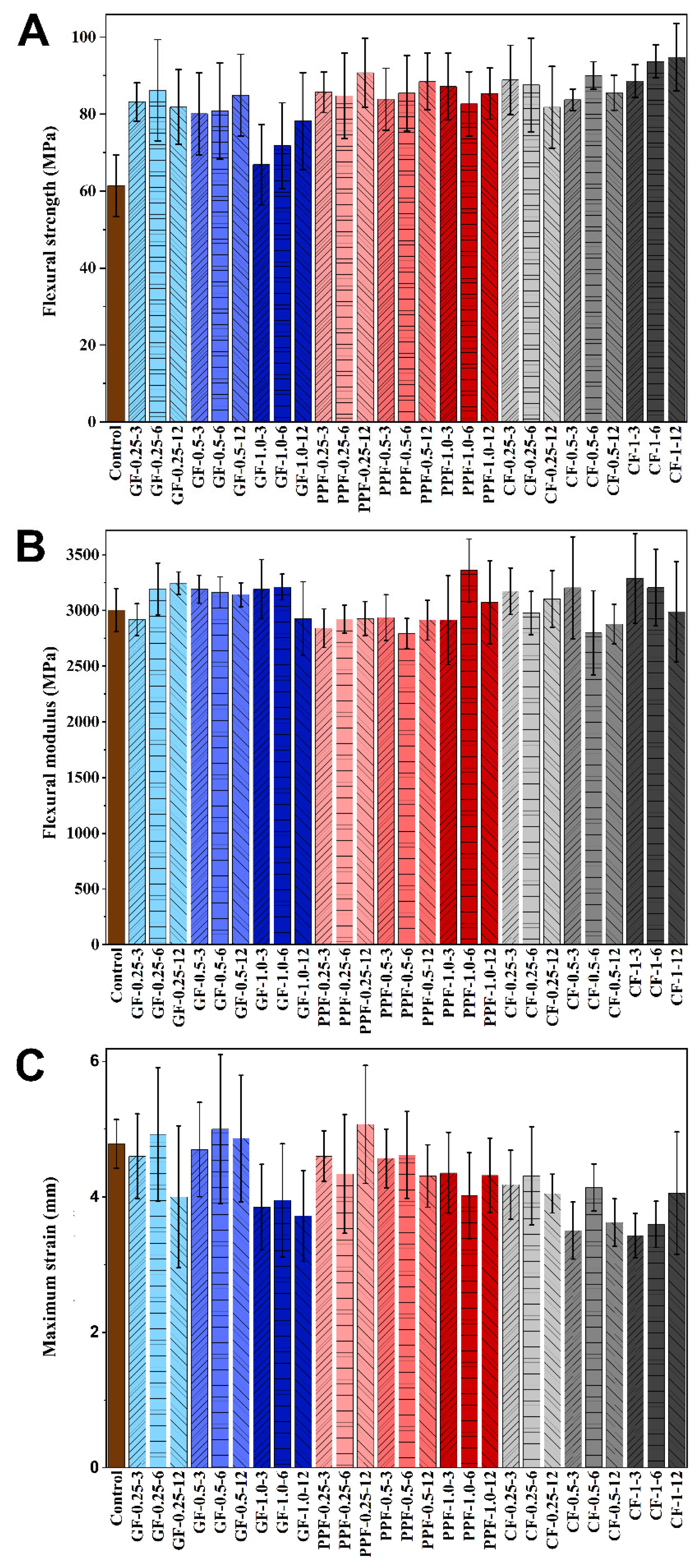
3.1. Three-Point Bending Tests
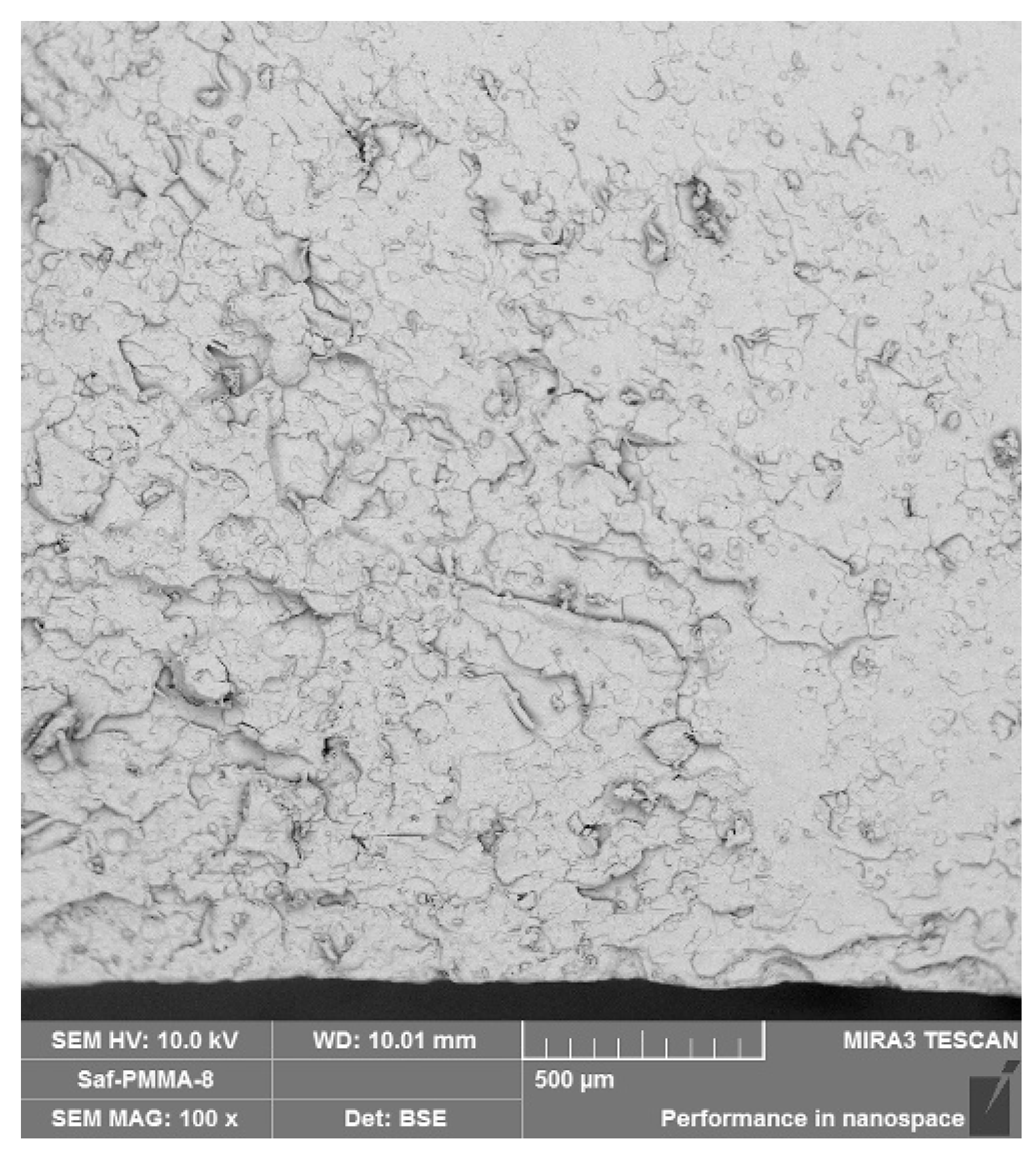
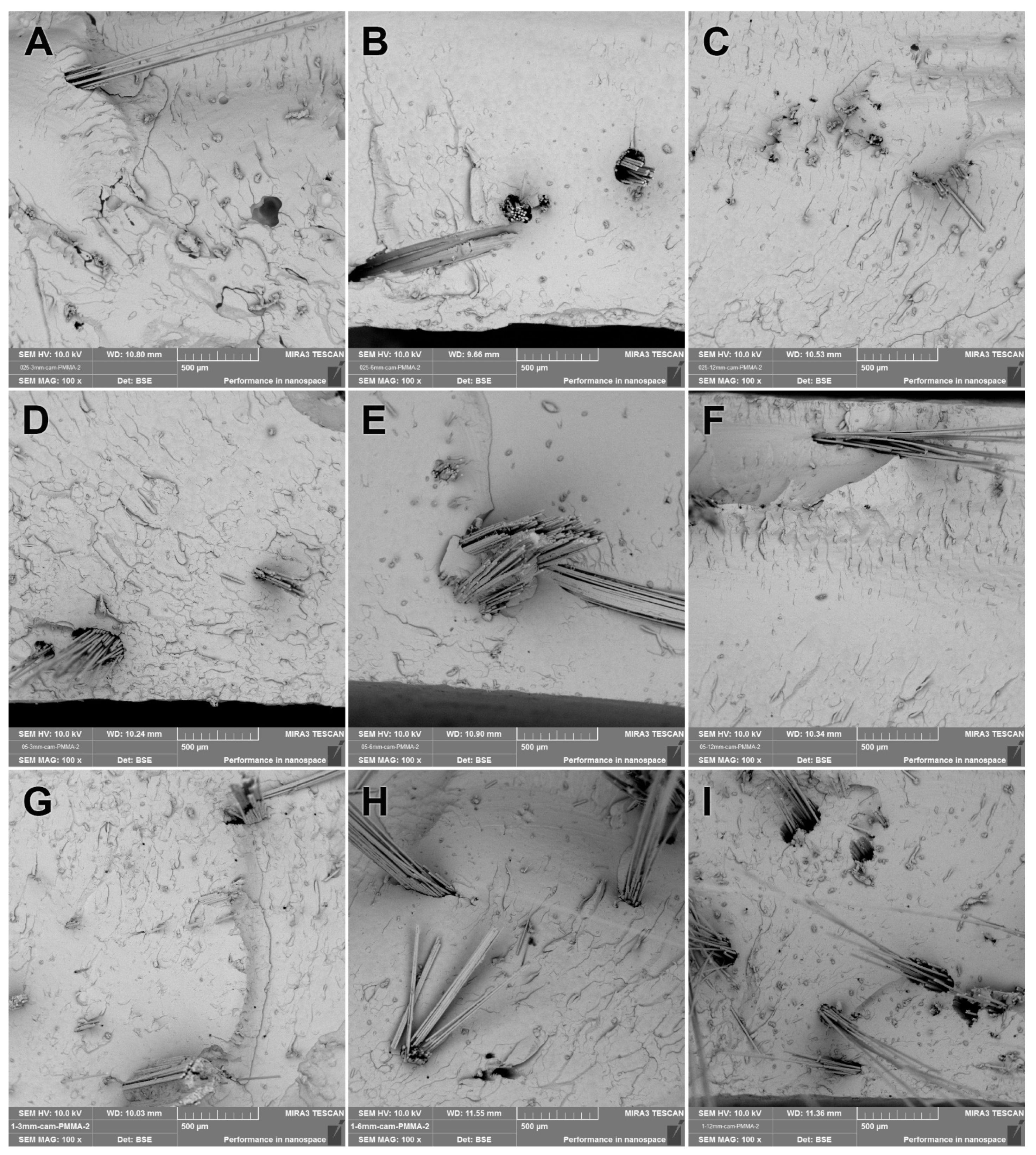
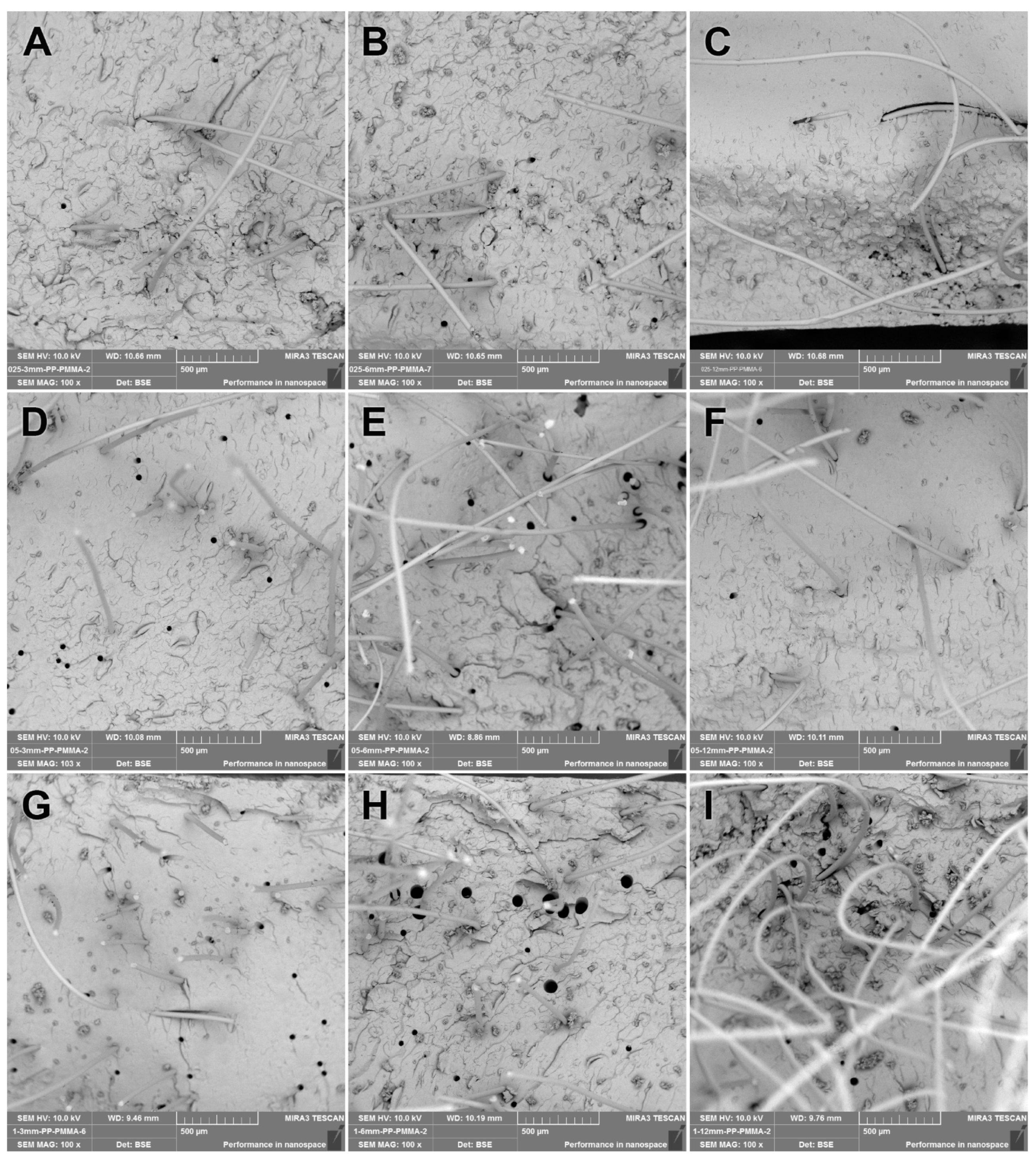
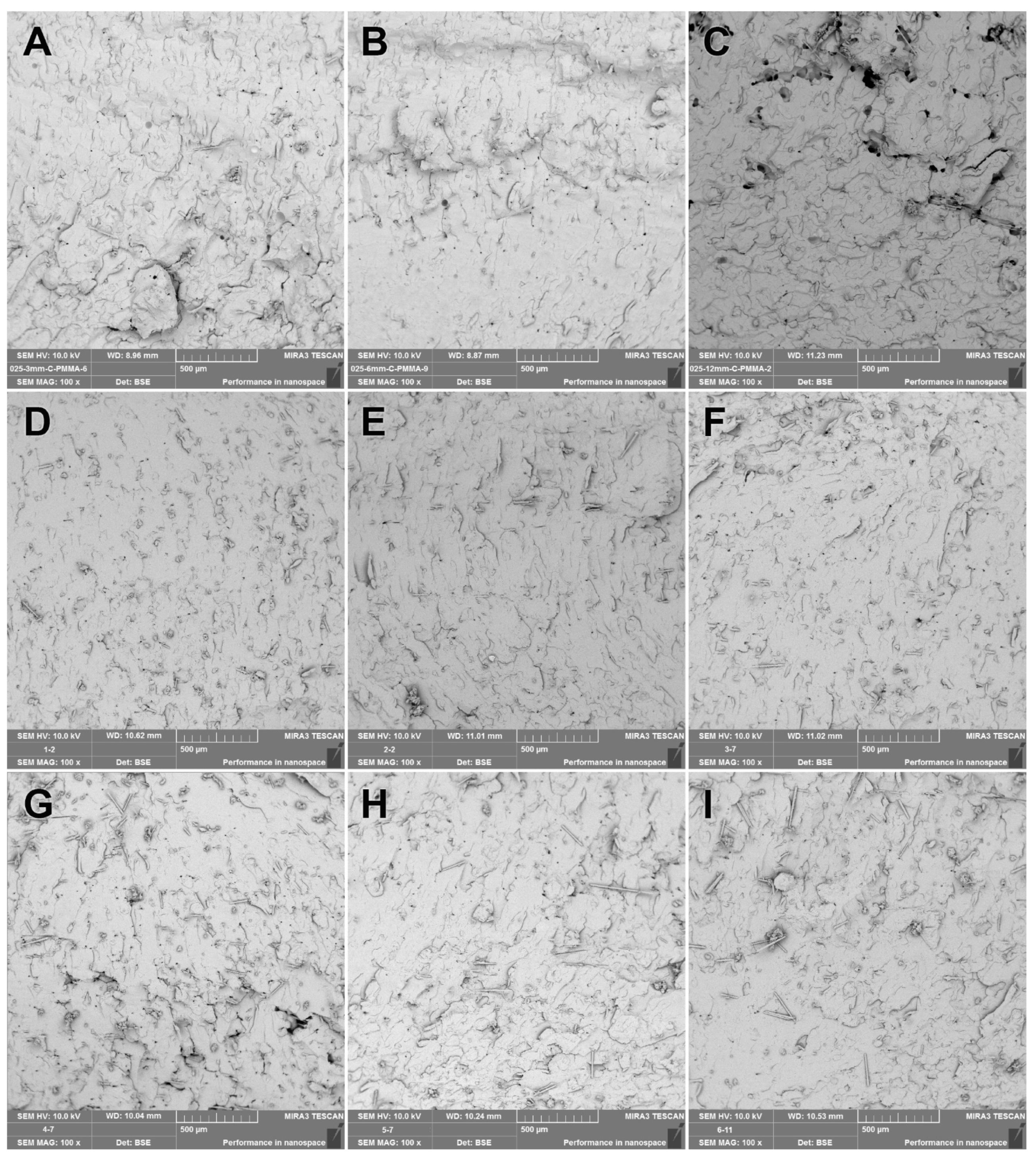
3.2. SEM Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Uzun, G.; Hersek, N.; Tincer, T. Effect of five woven fiber reinforcements on the impact and transverse strength of a denture base resin. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1999, 81, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Dwairi, Z.N.; Tahboub, K.Y.; Baba, N.Z.; Goodacre, C.J.; Özcan, M. A comparison of the surface properties of CAD/CAM and conventional polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA). J. Prosthodont. 2019, 28, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.Y.; Liang, W.M.; Yen, P.S. Reinforcement of acrylic denture base resin by incorporation of various fibers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 58, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gad, M.M.; Abualsaud, R.; Fouda, S.M.; Rahoma, A.; Al-Thobity, A.M.; Khan, S.Q.; Akhtar, S.; Al-Harbi, F.A. Effects of denture cleansers on the flexural strength of PMMA denture base resin modified with ZrO2 nanoparticles. J. Prosthodont. 2021, 30, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, J.; Gangadhar, S.A.; Shah, I. Flexural strength of heat-polymerized polymethyl methacrylate denture resin reinforced with glass, aramid, or nylon fibers. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2001, 86, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spasojevic, P.; Zrilic, M.; Panic, V.; Stamenkovic, D.; Seslija, S.; Velickovic, S. The mechanical properties of a poly (methyl methacrylate) denture base material modified with dimethyl itaconate and di-n-butyl itaconate. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 2015, 561012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zafar, M.S. Prosthodontic Applications of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA): An Update. Polymers 2020, 12, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, M.M.; Al-Thobity, A.M.; Rahoma, A.; Abualsaud, R.; Al-Harbi, F.A.; Akhtar, S. Reinforcement of PMMA denture base material with a mixture of ZrO2 nanoparticles and glass fibers. Int. J. Dent. 2019, 2019, 2489393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Somani, M.V.; Khandelwal, M.; Punia, V.; Sharma, V. The effect of incorporating various reinforcement materials on flexural strength and impact strength of polymethylmethacrylate: A meta-analysis. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2019, 19, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, S.I.; Oleiwi, J.K.; Mohamed, A.S. Investigation of mechanical properties of PMMA composite reinforced with different types of natural powders. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2018, 13, 8889–8900. [Google Scholar]
- Mowade, T.K.; Dange, S.P.; Thakre, M.B.; Kamble, V.D. Effect of fiber reinforcement on impact strength of heat polymerized polymethyl methacrylate denture base resin: In vitro study and SEM analysis. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2012, 4, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Banerjee, S.; Engelmeier, R.L.; O’Keefe, K.L.; Powers, J.M. In vitro tensile bond strength of denture repair acrylic resins to primed base metal alloys using two different processing techniques. J. Prosthodont. 2009, 18, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallittu, P.K.; Lassila, V.P. Effect of metal strengthener’s surface roughness on fracture resistance of acrylic denture base material. J. Oral Rehabil. 1992, 19, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özdemir, A.K.; Özdemir-Doğan, D.; Tuğut, F.; Demir, H.; Akin, H. Effects of boron on the mechanical properties of polymethylmethacrylate denture base material. Eur. Oral Res. 2021, 55, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alla, R.K.; Sajjan, S.; Alluri, V.R.; Ginjupalli, K.; Upadhya, N. Influence of fiber reinforcement on the properties of denture base resins. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2013, 4, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murthy, H.B.M.; Shaik, S.; Sachdeva, H.; Khare, S.; Haralur, S.B.; Roopa, K.T. Effect of reinforcement using stainless steel mesh, glass fibers, and polyethylene on the impact strength of heat cure denture base resin—An in vitro study. J. Int. Oral Health 2015, 7, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Thobity, A.M. The impact of polymerization technique and glass-fiber reinforcement on the flexural properties of denture base resin material. Eur. J. Dent. 2020, 14, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doğan, O.M.; Bolayır, G.; Keskin, S.; Doğan, A.; Bek, B.; Boztuğ, A. The effect of esthetic fibers on impact resistance of a conventional heat-cured denture base resin. Dent. Mater. J. 2007, 26, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanie, T.; Fujii, K.; Arikawa, H.; Inoue, K. Flexural properties and impact strength of denture base polymer reinforced with woven glass fibers. Dent. Mater. 2000, 16, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacir, I.H.; Kama, J.D.; Zortuk, M.; Eskimez, S. Flexural properties of glass fibre reinforced acrylic resin polymers. Aust. Dent. J. 2006, 51, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gad, M.M.; Fouda, S.M.; Al-Harbi, F.A.; Näpänkangas, R.; Raustia, A. PMMA denture base material enhancement: A review of fiber, filler, and nanofiller addition. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 3801–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moreno-Maldonado, V.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Barceló-Santana, F.H.; Vanegas-Lancón, R.D.; Plata-Rodríguez, M.E.; Castano, V.M. Fiber-reinforced nanopigmented poly (methyl methacrylate) as improved denture base. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 126, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostoulas, I.; Kavoura, V.T.; Frangou, M.J.; Polyzois, G.L. Fracture force, deflection, and toughness of acrylic denture repairs involving glass fiber reinforcement. J. Prosthodont. 2008, 17, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, M.; Shenoy, K.; Ravishankar, K.S. Impact strength of poly propylene fiber reinforced PMMA. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2014, 5, 951–955. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, M.; Shenoy, K.; Ravishankar, K.S. Flexural strength of hydrogen plasma-treated polypropylene fiber-reinforced polymethyl methacrylate denture base material. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2018, 18, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, T.A.; Rosenstiel, S.F.; El-Hosary, M.M.; Ibraheem, R.M. Fracture resistance of fiber-reinforced PMMA interim fixed partial dentures. J. Prosthodont. 2006, 15, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerliyurt, K.; Eğri, S. Investigation on the Potential Use of Polypropylene Mesh for the Reinforcement of Heat-Polymerized PMMA Denture Base Resin. Polymers 2022, 14, 3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.O.; Mahfouz, O.A.; Aboushelib, M.N.; Rady, N.A. Evaluation of impact strength of heat cure acrylic resin reinforced with nylon fiber mesh with and without prestressing (in vitro study). Alex. Dent. J. 2021, 46, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, R.B.; Favarão, I.N.; Kasuya, A.V.B.; Abrão, M.; Luz, N.F.M.; Naves, L.Z. Influence of glass fiber wt% and silanization on mechanical flexural strength of reinforced acrylics. J. Mater. Sci. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vallittu, P.K. Flexural properties of acrylic resin polymers reinforced with unidirectional and woven glass fibers. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1999, 81, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanie, T.; Arikawa, H.; Fujii, K.; Ban, S. Deformation and flexural properties of denture base polymer reinforced with glass fiber sheet. Dent. Mater. J. 2005, 24, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, K.; Sharma, S.K.; Negi, P.; Kumar, M.; Rajpurohit, D.; Khobre, P. Comparative evaluation of flexural strength of heat polymerised denture base resins after reinforcement with glass fibres and nylon fibres: An in vitro study. Adv. Hum. Biol. 2016, 6, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calamote, C.; Coelho, I.C.; Silva, A.S.; Esteves, J.L.; Moreira, L.; Pinto, A.C.; Manzanares-Céspedes, M.C.; Escuín, T. Comparison of the masticatory force (with 3D Models) of complete denture base acrylic resins with reline and reinforcing materials. Materials 2021, 14, 3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojvodic, D.; Komar, D.; Schauperl, Z.; Celebic, A.; Mehulic, K.; Zabarovic, D. Influence of different glass fiber reinforcements on denture base polymer strength (Fiber reinforcements of dental polymer). Med. Glas. 2009, 6, 227–234. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Shimizu, H. Effect of location of glass fiber-reinforced composite reinforcement on the flexural properties of a maxillary complete denture in vitro. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2011, 69, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.H.; Lee, Y.; Oh, S.; Cho, H.W.; Oda, Y.; Bae, J.M. Reinforcing effects of different fibers on denture base resin based on the fiber type, concentration, and combination. Dent. Mater. J. 2012, 31, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mathew, M.; Shenoy, K.; Ravishankar, K.S. Flexural strength of polypropylene fiber reinforced PMMA. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Invent. 2017, 6, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Ismaeel, I.J.; Alalwan, H.K.; Mustafa, M.J. The effect of the addition of silanated poly propylene fiber to polymethylmethacrylate denture base material on some of its mechanical properties. J. Baghdad Coll. Dent. 2015, 27, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.C.M.; Chen, C.H. Pultruded fiber reinforced thermoplastic poly (methyl methacrylate) composites. Part II: Mechanical and thermal properties. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1991, 31, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tugut, F.; Coskun, M.E.; Akin, H.; Dogan, D.O. Investigation of impact strength, water sorption and cytotoxicity of denture base resin reinforced with polypropylene fiber: In vitro study. J. Adv. Oral Res. 2020, 11, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Comparison | Flexural Strength (MPa) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | Control | Glass Fiber | PP Fiber | Carbon Fiber | |
| 61.4 ± 8.0 (o) | 79.3 ± 11.9 (n) | 86.0 ± 8.3 (m) | 88.3 ± 8.1 (m) | ||
| Concentration | 0% | 0.25% | 0.50% | 1.0% | |
| 61.4 ± 8.0 (b) | 85.6 ± 9.7 (a) | 84.8 ± 8.5 (a) | 83.2 ± 12.2 (a) | ||
| Length | 0 mm | 3 mm | 6 mm | 12 mm | |
| 61.4 ± 8.0 (y) | 83.1 ± 9.6 (x) | 84.8 ± 11.2 (x) | 85.7 ± 9.9 (x) | ||
| Material × Concentration | Glass Fiber | PP Fiber | Carbon Fiber | ||
| 0.25% | 83.8 ± 9.6 (m,a) | 87.0 ± 8.8 (m,a) | 86.0 ± 10.7 (m,b) | ||
| 0.50% | 81.9 ± 11.0 (m,a) | 85.9 ± 8.3 (m,a) | 86.4 ± 4.5 (m,ab) | ||
| 1.0% | 72.3 ± 11.9 (o,b) | 85.0 ± 7.8 (n,a) | 92.3 ± 6.5 (m,a) | ||
| Material × Length | Glass Fiber | PP Fiber | Carbon Fiber | ||
| 3 mm | 76.7 ± 11.3 (n,x) | 85,6 ± 7,3 (m,x) | 87,0 ± 6,2 (m,x) | ||
| 6 mm | 79,6 ± 13,2 (n,x) | 84,3 ± 9,5 (mn,x) | 90,4 ± 7,9 (m,x) | ||
| 12 mm | 81,6 ± 10,9 (n,x) | 88,2 ± 7,7 (m,x) | 87,4 ± 9,8 (mn,x) | ||
| Concentration × Length | 3 mm | 6 mm | 12 mm | ||
| 0.25% | 85.9 ± 6.8 (a,x) | 86.2 ± 11.7 (a,x) | 84.8 ± 10.3 (a,x) | ||
| 0.50% | 82.6 ± 7.7 (a,x) | 85.4 ± 9.8 (a,x) | 86.3 ± 7.7 (a,x) | ||
| 1.0% | 80.9 ± 12.8 (a,x) | 82.7 ± 12.2 (a,x) | 86.1 ± 11.5 (a,x) | ||
| Material × Concentration × Length | Glass Fiber | PP Fiber | Carbon Fiber | ||
| 3 mm | 0.25% | 83.1 ± 5.0 (m,a,x) | 85.7 ± 5.3 (m,a,x) | 88.9 ± 9.0 (m,a,x) | |
| 0.50% | 80.1 ± 10.7 (m,a,x) | 83.9 ± 8.0 (m,a,x) | 83.7 ± 2.8 (m,a,x) | ||
| 1.0% | 66.9 ± 10.4 (n,b,y) | 87.1 ± 8.7 (m,a,x) | 88.6 ± 4.3 (m,a,x) | ||
| 6 mm | 0.25% | 86.2 ± 13.2 (m,a,x) | 84.8 ± 11.2 (m,a,x) | 87.6 ± 12.2 (m,a,x) | |
| 0.50% | 80.8 ± 12.5 (m,ab,x) | 85.4 ± 9.8 (m,a,x) | 90.0 ± 3.6 (m,a,x) | ||
| 1.0% | 71.8 ± 11.2 (n,b,xy) | 82.6 ± 8.3 (n,a,x) | 93.7 ± 4.3 (m,a,x) | ||
| 0.25% | 81.8 ± 9.7 (m,a,x) | 90.7 ± 9.0 (m,a,x) | 81.8 ± 10.6 (m,b,x) | ||
| 12 mm | 0.50% | 84.9 ± 10.7 (m,a,x) | 88.5 ± 7.4 (m,a,x) | 85.6 ± 4.6 (m,ab,x) | |
| 1.0% | 78.2 ± 12.6 (n,a,x) | 85.3 ± 6.7 (mn,a,x) | 94.8 ± 8.8 (m,a,x) | ||
| Comparison | Flexural Modulus (MPa) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | Control | Glass Fiber | PP Fiber | Carbon Fiber | |
| 1924.1 ± 199.7 (o) | 2738.9 ± 243.9 (n) | 2829.1 ± 179.0 (n) | 3004.3 ± 365.2 (m) | ||
| Concentration | 0% | 0.25% | 0.50% | 1.0% | |
| 1924.1 ± 199.7 (b) | 2829.6 ± 206.6 (a) | 2864.8 ± 276.4 (a) | 2877.8 ± 376.1 (a) | ||
| Length | 0 mm | 3 mm | 6 mm | 12 mm | |
| 1924.1 ± 199.7 (y) | 2869.8 ± 354.3 (x) | 2826.4 ± 271.3 (x) | 2876.0 ± 247.4 (x) | ||
| Material × Concentration | Glass Fiber | PP Fiber | Carbon Fiber | ||
| 0.25% | 2743.6 ± 183.9 (m,a) | 2852.5 ± 164.4 (m,a) | 2892.7 ± 241.9 (m,b) | ||
| 0.50% | 2784.7 ± 204.1 (m,a) | 2850.1 ± 169.5 (m,a) | 2959.6 ± 386.2 (m,b) | ||
| 1.0% | 2688.2 ± 321.2 (n,a) | 2784.7 ± 200.1 (n,a) | 3160.6 ± 404.2 (m,a) | ||
| Material × Length | Glass Fiber | PP Fiber | Carbon Fiber | ||
| 3 mm | 2676.5 ± 259.8 (n,x) | 2810.2 ± 202.7 (n,x) | 3122.8 ± 411.7 (m,x) | ||
| 6 mm | 2715.9 ± 212.0 (n,x) | 2805.5 ± 180.2 (mn,x) | 2957.8 ± 344.4 (m,xy) | ||
| 12 mm | 2824.1 ± 242.8 (m,x) | 2871.6 ± 150.2 (m,x) | 2932.3 ± 318.3 (m,y) | ||
| Concentration × Length | 3 mm | 6 mm | 12 mm | ||
| 0.25% | 2823.4 ± 220.7 (a,x) | 2783.0 ± 133.8 (a,x) | 2882.3 ± 245.0 (a,x) | ||
| 0.50% | 2932.7 ± 338.4 (a,x) | 2778.8 ± 272.5 (a,x) | 2882.9 ± 185.0 (a,x) | ||
| 1.0% | 2853.3 ± 466.5 (a,x) | 2917.4 ± 349.4 (a,x) | 2862.8 ± 307.2 (a,x) | ||
| Material × Concentration × Length | Glass Fiber | PP Fiber | Carbon Fiber | ||
| 3 mm | 0.25% | 2732.6 ± 220.0 (m,a,x) | 2860.9 ± 141.6 (m,a,x) | 2876.8 ± 277.9 (m,b,x) | |
| 0.50% | 2801.5 ± 96.8 (n,a,x) | 2793.4 ± 177.1 (n,a,x) | 3203.3 ± 458.3 (m,a,x) | ||
| 1.0% | 2495.4 ± 324.1 (n,a,y) | 2776.3 ± 281.1 (n,a,x) | 3288.3 ± 402.1 (m,a,x) | ||
| 6 mm | 0.25% | 2739.2 ± 103.4 (m,a,x) | 2740.3 ± 121.1 (m,a,x) | 2869.6 ± 143.5 (m,b,x) | |
| 0.50% | 2679.3 ± 171.7 (m,a,x) | 2858.5 ± 229.3 (m,a,x) | 2798.6 ± 378.1 (m,b,y) | ||
| 1.0% | 2729.1 ± 324.4 (n,a,xy) | 2817.8 ± 176.6 (n,a,x) | 3205.3 ± 343.8 (m,a,x) | ||
| 0.25% | 2758.9 ± 227.2 (m,a,x) | 2956.4 ± 165.3 (m,a,x) | 2931.7 ± 303.1 (m,a,x) | ||
| 12 mm | 0.50% | 2873.4 ± 275.8 (m,a,x) | 2898.4 ± 64.0 (m,a,x) | 2876.9 ± 178.5 (m,a,y) | |
| 1.0% | 2840.2 ± 241.0 (m,a,x) | 2760.0 ± 139.2 (m,a,x) | 2988.2 ± 449.5 (m,a,x) | ||
| Comparison | Maximum Deformation (mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | Control | Glass Fiber | PP Fiber | Carbon Fiber | |
| 4.8 ± 0.4 (m) | 4.4 ± 1.0 (m) | 4.5 ± 0.7 (m) | 3.9 ± 0.6 (n) | ||
| Concentration | 0% | 0.25% | 0.50% | 1.0% | |
| 4.8 ± 0.4 (a) | 4.5 ± 0.8 (a) | 4.4 ± 0.8 (a) | 3.9 ± 0.7 (b) | ||
| Length | 0 mm | 3 mm | 6 mm | 12 mm | |
| 4.8 ± 0.4 (x) | 4.2 ± 0.7 (x) | 4.3 ± 0.9 (x) | 4.2 ± 0.9 (x) | ||
| Material × Concentration | Glass Fiber | PP Fiber | Carbon Fiber | ||
| 0.25% | 4.5 ± 1.0 (m,a) | 4.7 ± 0.8 (m,a) | 4.2 ± 0.6 (m,a) | ||
| 0.50% | 4.9 ± 1.0 (m,a) | 4.5 ± 0.6 (m,a) | 3.8 ± 0.5 (n,a) | ||
| 1.0% | 3.8 ± 0.7 (mn,b) | 4.2 ± 0.6 (m,a) | 3.7 ± 0.6 (n,a) | ||
| Material × Length | Glass Fiber | PP Fiber | Carbon Fiber | ||
| 3 mm | 4.4 ± 0.8 (m,x) | 4.5 ± 0.5 (m,x) | 3.7 ± 0.5 (n,x) | ||
| 6 mm | 4.6 ± 1.1 (m,x) | 4.3 ± 0.8 (mn,x) | 4.0 ± 0.6 (n,x) | ||
| 12 mm | 4.2 ± 1.0 (mn,x) | 4.6 ± 0.8 (m,x) | 3.9 ± 0.6 (n,x) | ||
| Concentration × Length | 3 mm | 6 mm | 12 mm | ||
| 0.25% | 4.5 ± 0.6 (a,x) | 4.5 ± 0.9 (a,x) | 4.4 ± 1.0 (a,x) | ||
| 0.50% | 4.3 ± 0.8 (ab,x) | 4.6 ± 0.9 (a,x) | 4.3 ± 0.8 (a,x) | ||
| 1.0% | 3.9 ± 0.7 (b,x) | 3.9 ± 0.7 (b,x) | 4.0 ± 0.8 (a,x) | ||
| Material × Concentration × Length | Glass Fiber | PP Fiber | Carbon Fiber | ||
| 3 mm | 0.25% | 4.6 ± 0.7 (m,a,xy) | 4.6 ± 0.4 (m,a,x) | 4.2 ± 0.6 (m,a,x) | |
| 0.50% | 4.7 ± 0.7 (m,a,x) | 4.6 ± 0.5 (m,a,x) | 3.5 ± 0.4 (n,a,x) | ||
| 1.0% | 3.9 ± 0.7 (mn,a,x) | 4.4 ± 0.6 (m,a,x) | 3.4 ± 0.3 (n,a,x) | ||
| 6 mm | 0.25% | 4.9 ± 1.1 (m,a,x) | 4.3 ± 0.9 (m,a,x) | 4.3 ± 0.8 (m,a,x) | |
| 0.50% | 5.0 ± 1.2 (m,a,x) | 4.6 ± 0.7 (mn,a,x) | 4.1 ± 0.4 (n,a,x) | ||
| 1.0% | 4.0 ± 0.9 (m,b,x) | 4.0 ± 0.7 (m,a,x) | 3.6 ± 0.3 (m,a,x) | ||
| 0.25% | 4.0 ± 1.1 (n,b,y) | 5.1 ± 0.9 (m,a,x) | 4.1 ± 0.3 (n,a,x) | ||
| 12 mm | 0.50% | 4.9 ± 1.0 (m,a,x) | 4.3 ± 0.5 (mn,a,x) | 3.6 ± 0.4 (n,a,x) | |
| 1.0% | 3.7 ± 0.7 (m,b,x) | 4.3 ± 0.6 (m,a,x) | 4.1 ± 0.9 (m,a,x) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yerliyurt, K.; Taşdelen, T.B.; Eğri, Ö.; Eğri, S. Flexural Properties of Heat-Polymerized PMMA Denture Base Resins Reinforced with Fibers with Different Characteristics. Polymers 2023, 15, 3211. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153211
Yerliyurt K, Taşdelen TB, Eğri Ö, Eğri S. Flexural Properties of Heat-Polymerized PMMA Denture Base Resins Reinforced with Fibers with Different Characteristics. Polymers. 2023; 15(15):3211. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153211
Chicago/Turabian StyleYerliyurt, Kaan, Taha Buğra Taşdelen, Özlem Eğri, and Sinan Eğri. 2023. "Flexural Properties of Heat-Polymerized PMMA Denture Base Resins Reinforced with Fibers with Different Characteristics" Polymers 15, no. 15: 3211. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153211
APA StyleYerliyurt, K., Taşdelen, T. B., Eğri, Ö., & Eğri, S. (2023). Flexural Properties of Heat-Polymerized PMMA Denture Base Resins Reinforced with Fibers with Different Characteristics. Polymers, 15(15), 3211. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153211





