Removal, Adsorption, and Cleaning of Pharmaceutical on Polyamide RO and NF Membranes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Membranes and Chemicals
2.2. Infrared Spectrometer with Fourier Transformation and Goniometer
2.3. Analytical Methods
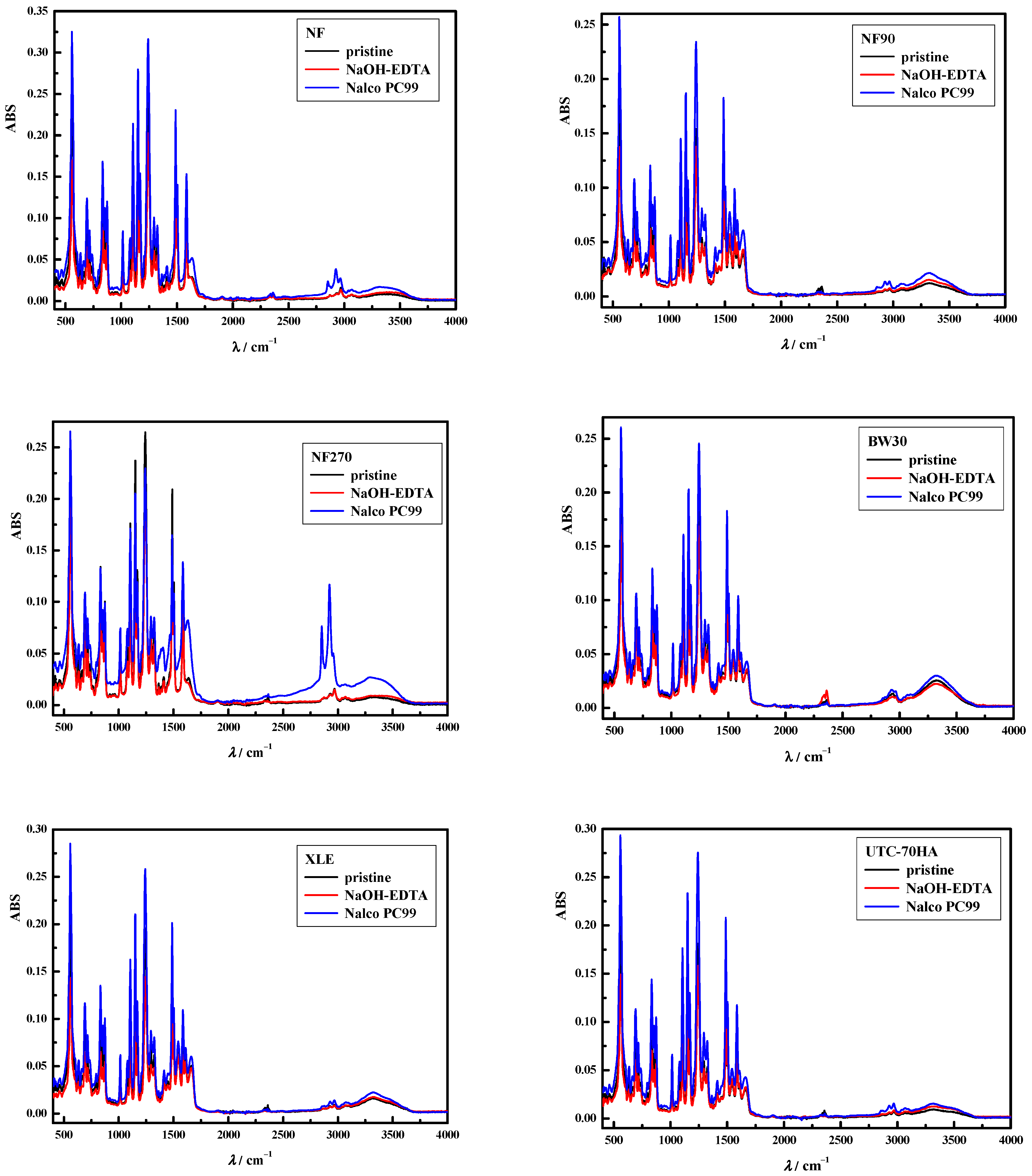
2.4. Membrane Cleaning Reagents
2.5. RO/NF Laboratory System
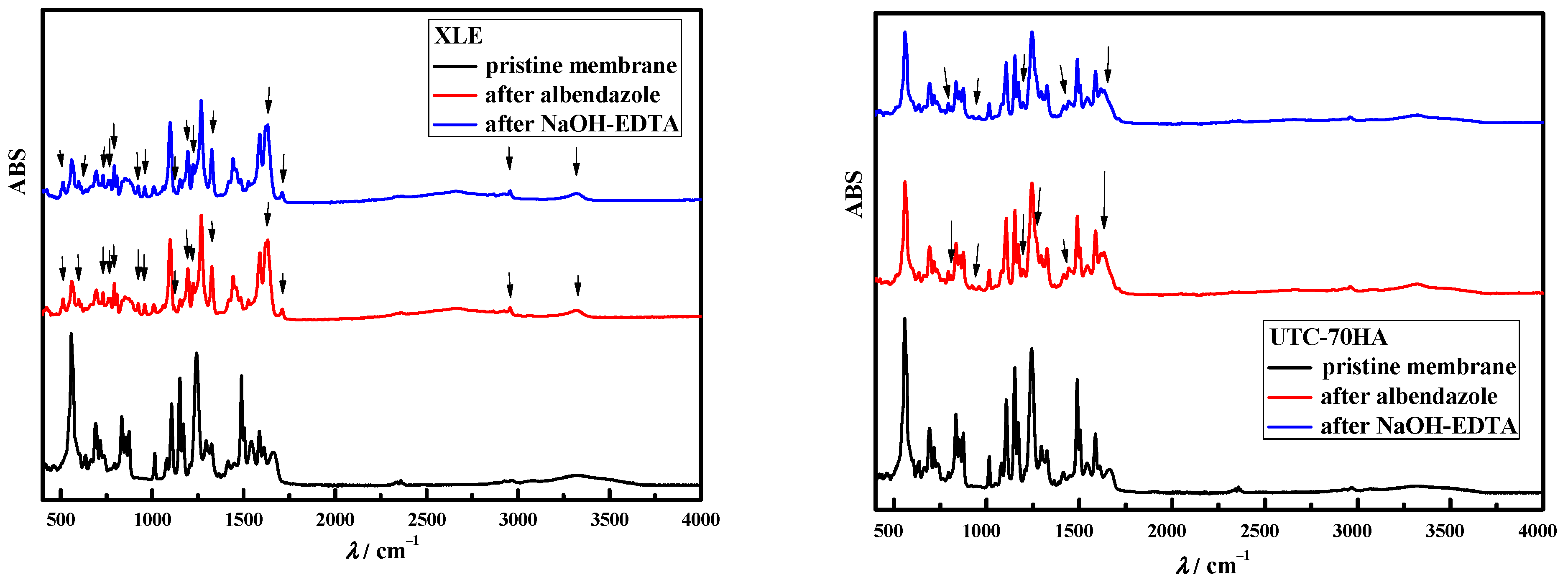
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rejection Factor and Removal Mechanism of Albendazole on Used Membranes
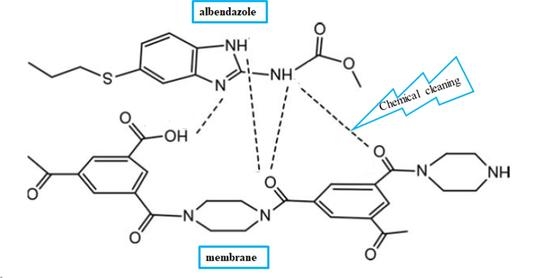
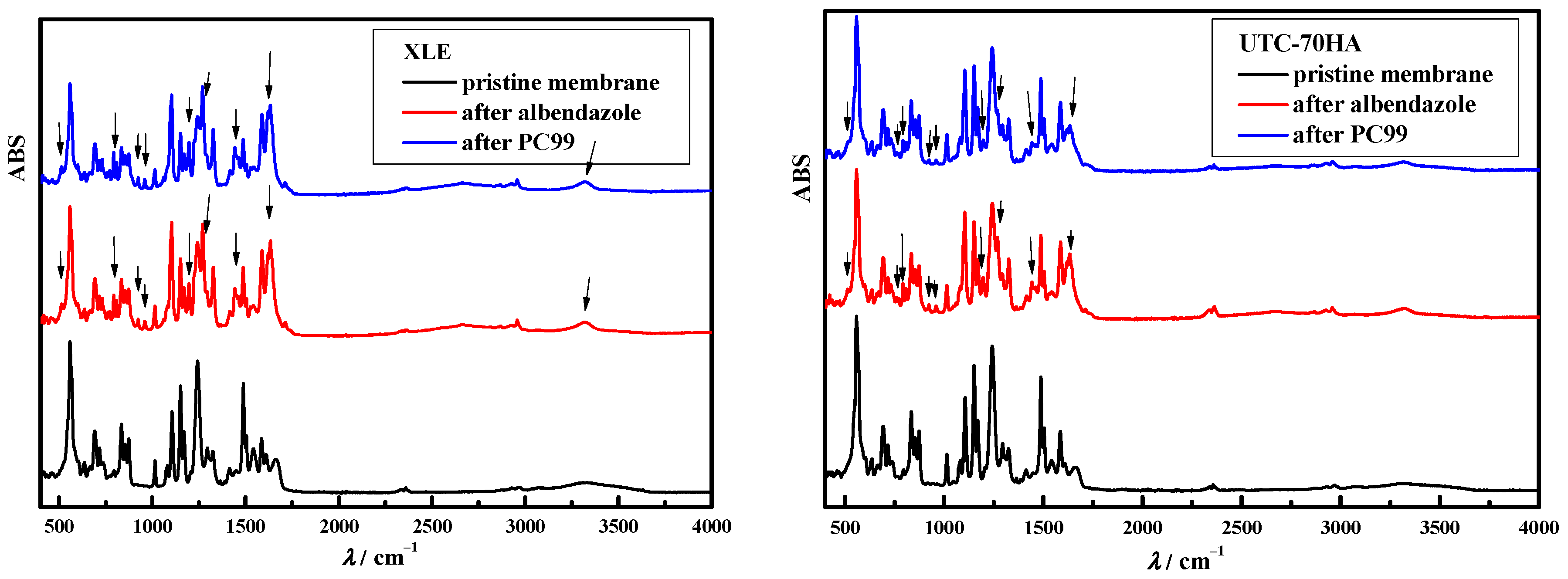
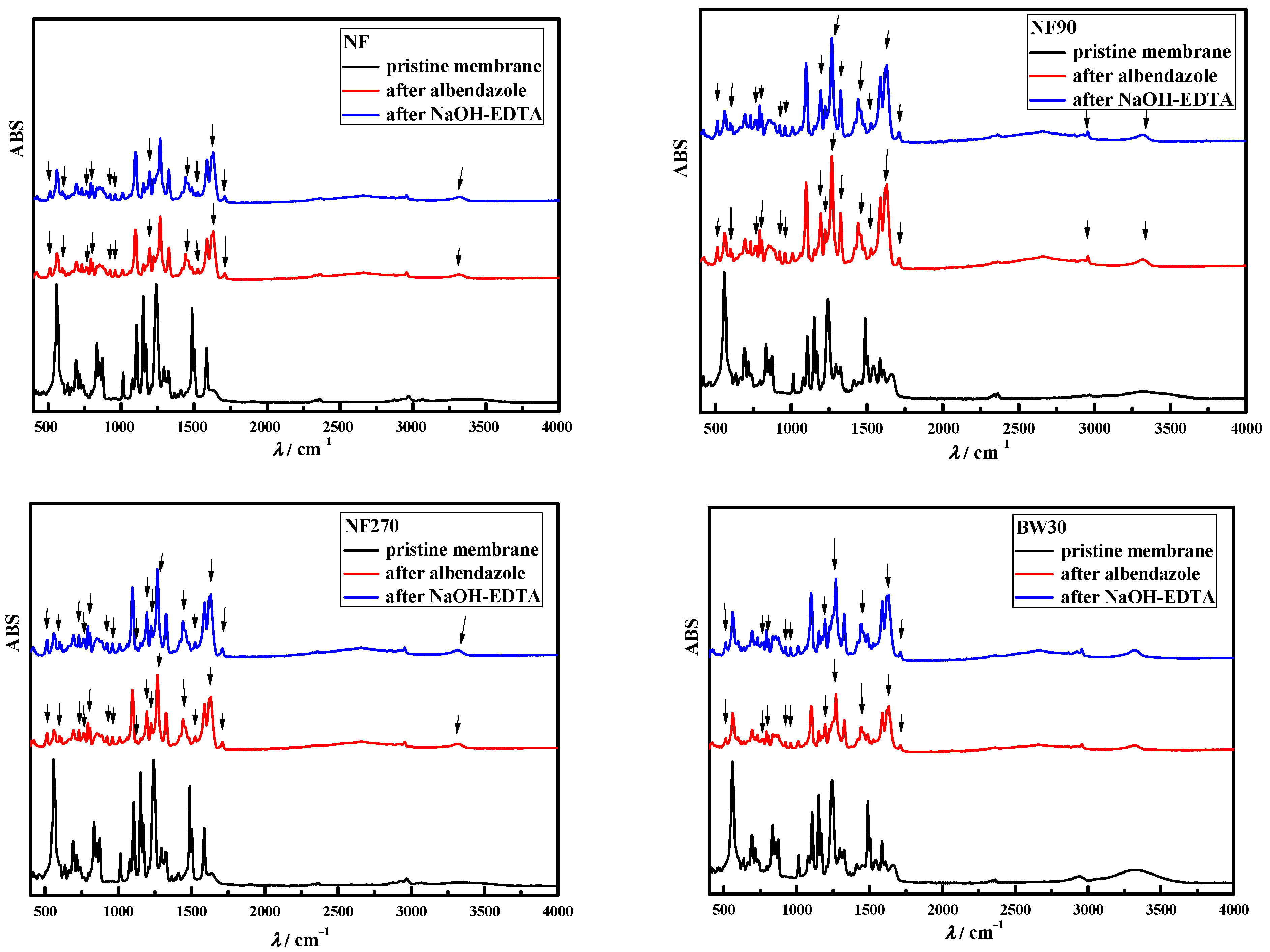
3.2. Chemical Cleaning of Adsorbed Albendazole on RO/NF Membranes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Chu, L.; Wojnárovits, L.; Takács, E. Occurrence and fate of antibiotics, antibiotic resistant genes (ARGs) and antibiotic resistant bacteria (ARB) in municipal wastewater treatment plant: An overview. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.; Silva, L.; Laranjeiro, C.; Pena, A. Assessment of Human Pharmaceuticals in Drinking Water Catchments, Tap and Drinking Fountain Waters. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Jiang, L.; Li, G. Occurrence and distribution of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCPs) in wastewater related riverbank groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 153372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, C.F.; Lange, L.C.; Amaral, M.C.S. Occurrence, fate and removal of pharmaceutically active compounds (PhACs) in water and wastewater treatment plants—A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 32, 100927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.K.; Kalaria, R.K.; Jokhakar, P.H.; Patel, C.R.; Patel, B.Y. Chapter 17—Removal of emerging contaminants in water treatment by an application of nanofiltration and reverse osmosis. In Development in Wastewater Treatment Research and Processes; Shah, M., Rodriguez-Couto, S., Biswas, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, B.; Shrivastav, A. Chapter 26—Removal of emerging contaminants in water treatment by nanofiltration and reverse osmosis. In Development in Wastewater Treatment Research and Processes; Shah, M., Rodriguez-Couto, S., Biswas, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 605–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheran, M.; Brar, S.K.; Verma, M.; Surampalli, R.Y.; Zhang, T.C.; Valero, J.R. Membrane processes for removal of pharmaceutically active compounds (PhACs) from water and wastewaters. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 547, 60–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca Couto, C.; Lange, L.C.; Santos Amaral, M.C. A critical review on membrane separation processes applied to remove pharmaceutically active compounds from water and wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 26, 156–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevallos-Mendoza, J.; Amorim, C.G.; Rodríguez-Díaz, J.M.; Montenegro, M.D.C.B.S.M. Removal of Contaminants from Water by Membrane Filtration: A Review. Membranes 2022, 12, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellona, C.; Drewes, J.E.; Xu, P.; Amy, G. Factors affecting the rejection of organic solutes during NF/RO treatment—A literature review. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2795–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Toshima, S.; Amy, G.; Watanabe, Y. Rejection of neutral endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs) and pharmaceutical active compounds (PhACs) by RO membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 245, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; He, Q.; Luo, J.; Wan, Y.; Darling, S.B. Sharpening Nanofiltration: Strategies for Enhanced Membrane Selectivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 39948–39966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, A.; Jillani, S.M.S.; Baig, U.; Ihsanullah, I.; Alhooshani, K. Removal of pharmaceutically active compounds from water sources using nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes: Comparison of removal efficiencies and in-depth analysis of rejection mechanisms. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 338, 117682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Cheng, X.Q.; Liu, Y.; Quan, S.; Ma, J.; Zhao, S.Z.; Wang, K.Y. Newly developed nanofiltration (NF) composite membranes by interfacial polymerization for Safranin O and Aniline blue removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 430, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alturki, A.A.; Tadkaew, N.; McDonald, J.A.; Khan, S.J.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Combining MBR and NF/RO membrane filtration for the removal of trace organics in indirect potable water reuse applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 365, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, S.; Peto, R.; Read, S.; Richards, S.M.; Pande, V.; Bundy, D.; DEVTA (Deworming and Enhanced Vitamin A) Team. Population deworming every 6 months with albendazole in 1 million pre-school children in North India: DEVTA, a cluster-randomised trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 1478–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, J. Human gastrointestinal helminth infections: Are they now neglected diseases? Trends Parasitol. 2003, 19, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardila, J.A.; de Alvarenga Junior, B.R.; Durango, L.C.; Soares, F.L.F.; Perlatti, B.; de Oliveira Cardoso, J.; Oliveira, R.V.; Forim, M.R.; Carneiro, R.L. Design of experiments applied to stress testing of pharmaceutical products: A case study of Albendazole. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 165, 105939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belew, S.; Suleman, S.; Wynendaele, E.; Duchateau, L.; De Spiegeleer, B. Environmental risk assessment of the anthelmintic albendazole in Eastern Africa, based on a systematic review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolar, D.; Pelko, S.; Košutić, K.; Horvat, A.J.M. Removal of anthelmintic drugs and their photodegradation products from water with RO/NF membranes. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2012, 90, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comerton, A.M.; Andrews, R.C.; Bagley, D.M.; Yang, P. Membrane adsorption of endocrine disrupting compounds and pharmaceutically active compounds. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 303, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, A.I.; Akanyeti, I.; Semião, A.J.C. Micropollutant sorption to membrane polymers: A review of mechanisms for estrogens. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 164, 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licona, K.P.M.; Geaquinto, L.R.D.O.; Nicolini, J.V.; Figueiredo, N.G.; Chiapetta, S.C.; Habert, A.C.; Yokoyama, L. Assessing potential of nanofiltration and reverse osmosis for removal of toxic pharmaceuticals from water. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 25, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-L.; Lee, C.-H. Elucidating the Rejection Mechanisms of PPCPs by Nanofiltration and Reverse Osmosis Membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 6798–6806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, C.F.; Santos, A.V.; Amaral, M.C.S.; Lange, L.C.; de Andrade, L.H.; Foureaux, A.F.S.; Fernandes, B.S. Assessing potential of nanofiltration, reverse osmosis and membrane distillation drinking water treatment for pharmaceutically active compounds (PhACs) removal. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 33, 101029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nghiem, L.D.; Schäfer, A.I.; Elimelech, M. Removal of Natural Hormones by Nanofiltration Membranes: Measurement, Modeling and Mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1888–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braeken, L.; Ramaekers, R.; Zhang, Y.; Maes, G.; Bruggen, B.V.D.; Vandecasteele, C. Influence of hydrophobicity on retention in nanofiltration of aqueous solutions containing organic compounds. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 252, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiso, Y.; Sugiura, Y.; Kitao, T.; Nishimura, K. Effects of hydrophobicity and molecular size on rejection of aromatic pesticides with nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 192, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braeken, L.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Vandecasteele, C. Flux Decline in Nanofiltration Due to Adsorption of Dissolved Organic Compounds: Model Prediction of Time Dependency. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 2957–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Bruggen, B.; Braeken, L.; Vandecasteele, C. Flux decline in nanofiltration due to adsorption of organic compounds. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2002, 29, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Amy, G.; Drewes, J.; Watanabe, Y. Adsorption of hydrophobic compounds onto NF/RO membranes: An artifact leading to overestimation of rejection. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 221, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amoudi, A. Effect of chemical cleaning agents on virgin nanofiltration membrane as characterized by positron annihilation spectroscopy. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 110, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Kappelhof, J.W.N.M.; Heijrnan, S.G.J.; Schippers, J.C.; van der Kooija, D. Tools for fouling diagnosis of NF and RO membranes and assessment of the fouling potential of feed water. Desalination 2003, 157, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amoudi, A.; Lovitt, R.W. Fouling strategies and the cleaning system of NF membranes and factors affecting cleaning efficiency. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 303, 4–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujioka, T.; Khan, S.J.; McDonald, J.A.; Roux, A.; Poussade, Y.; Drewes, J.E.; Nghiem, L.D. N-nitrosamine rejection by reverse osmosis: Effects of membrane exposure to chemical cleaning reagents. Desalination 2014, 343, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.-J.; Kiso, Y.; Yamada, T.; Shibata, T.; Lee, T.-G. Chemical cleaning of reverse osmosis membranes used for treating wastewater from a rolling mill process. Desalination 2006, 190, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.; McDonald, J.A.; Khan, S.J.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Effects of caustic cleaning on pore size of nanofiltration membranes and their rejection of trace organic chemicals. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 447, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Effects of chemical cleaning on the nanofiltration of pharmaceutically active compounds (PhACs). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 88, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Influence of formulated chemical cleaning reagents on the surface properties and separation efficiency of nanofiltrationmembranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 432, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Changes in surface properties and separation efficiency of a nanofiltration membrane after repeated fouling and chemical cleaning cycles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 113, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Impact of chemical cleaning on the nanofiltration of pharmaceutically active compounds (PhACs): The role of cleaning temperature. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2013, 44, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolar, D.; Drašinac, N.; Košutić, K.; Škorić, I.; Ašperger, D. Adsorption of hydrophilic and hydrophobic pharmaceuticals on RO/NF membranes: Identification of interactions using FTIR. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B. Gaussian 09, Revision A.02; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dolar, D.; Vuković, A.; Ašperger, D.; Košutić, K. Effect of water matrices on removal of veterinary pharmaceuticals by nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaño Osorio, S.; Biesheuvel, P.M.; Spruijt, E.; Dykstra, J.E.; van der Wal, A. Modeling micropollutant removal by nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes: Considerations and challenges. Water Res. 2022, 225, 119130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-L.; Wang, X.-M.; Yang, H.-W.; Xie, Y.F. Adsorption of pharmaceuticals onto isolated polyamide active layer of NF/RO membranes. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-L.; Wang, X.-M.; Yang, H.-W.; Xie, Y.F. Quantifying the influence of solute-membrane interactions on adsorption and rejection of pharmaceuticals by NF/RO membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 551, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolar, D.; Košutić, K.; Ašperger, D. Influence of adsorption of pharmaceuticals onto RO/NF membranes on their removal from water. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, O.; Temelli, F. Probing the hydrophobicity of commercial reverse osmosis membranes produced by interfacial polymerization using contact angle, XPS, FTIR, FE-SEM and AFM. Desalination 2011, 278, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrado, S.; Torrado, S.; Cadorniga, R.; Torrado, J.J. Formulation parameters of albendazole solution. Int. J. Pharm. 1996, 140, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Molecular Structure | Direction of Dipole Moment | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CAS number | 54965-21-8 | 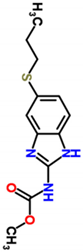 |  |
| Molecular weight, Mw (g/mol) | 265.33 | ||
| Water solubility (mg/L) 1 | 46.39 | ||
| width (nm) 2 | 0.482 | ||
| height (nm) 2 | 0.279 | ||
| length (nm) 2 | 1.632 | ||
| log KO/W | 3.07 | ||
| log D (pH = 7.4) 3 | 3.06 | ||
| pKa 4 | 6.90 | ||
| Dipole moment, μ (D) 5 | 4.33 | ||
| Charge at pH 7 | negative |
| MWCO t/h | UTC-70HA 100 | XLE 100 | BW30 100 | NF90 100 | NF 150–300 | NF270 150–300 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R/% | ||||||
| 0 | 78.1 | 78.6 | 78.5 | 79.1 | 73.8 | 65.4 |
| 4 | 61.2 | 63.7 | 62.8 | 62.4 | 44.8 | 43.8 |
| γp/mg/L | ||||||
| 0 | 3.39 | 3.32 | 3.33 | 3.24 | 4.06 | 3.24 |
| 4 | 3.91 | 3.66 | 3.75 | 3.79 | 5.56 | 3.79 |
| t/h | γF/mg/L |
|---|---|
| 0 | 15.50 |
| 1 | 12.76 |
| 2 | 12.41 |
| 3 | 11.96 |
| 4 | 10.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dolar, D.; Ćurić, I.; Ašperger, D. Removal, Adsorption, and Cleaning of Pharmaceutical on Polyamide RO and NF Membranes. Polymers 2023, 15, 2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15122745
Dolar D, Ćurić I, Ašperger D. Removal, Adsorption, and Cleaning of Pharmaceutical on Polyamide RO and NF Membranes. Polymers. 2023; 15(12):2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15122745
Chicago/Turabian StyleDolar, Davor, Iva Ćurić, and Danijela Ašperger. 2023. "Removal, Adsorption, and Cleaning of Pharmaceutical on Polyamide RO and NF Membranes" Polymers 15, no. 12: 2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15122745
APA StyleDolar, D., Ćurić, I., & Ašperger, D. (2023). Removal, Adsorption, and Cleaning of Pharmaceutical on Polyamide RO and NF Membranes. Polymers, 15(12), 2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15122745