Preparation and Characterization of PEDOT:PSS/TiO2 Micro/Nanofiber-Based Gas Sensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Materials
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Preparation of PEDOT/Composite Conductive Woven Fabrics
2.4. Preparation of PEDOT:PSS Micro/Nanofiber Gas Sensors
2.5. Preparation of PEDOT:PSS/TiO2 Micro/Nanofiber Gas Sensors
2.6. Testing and Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
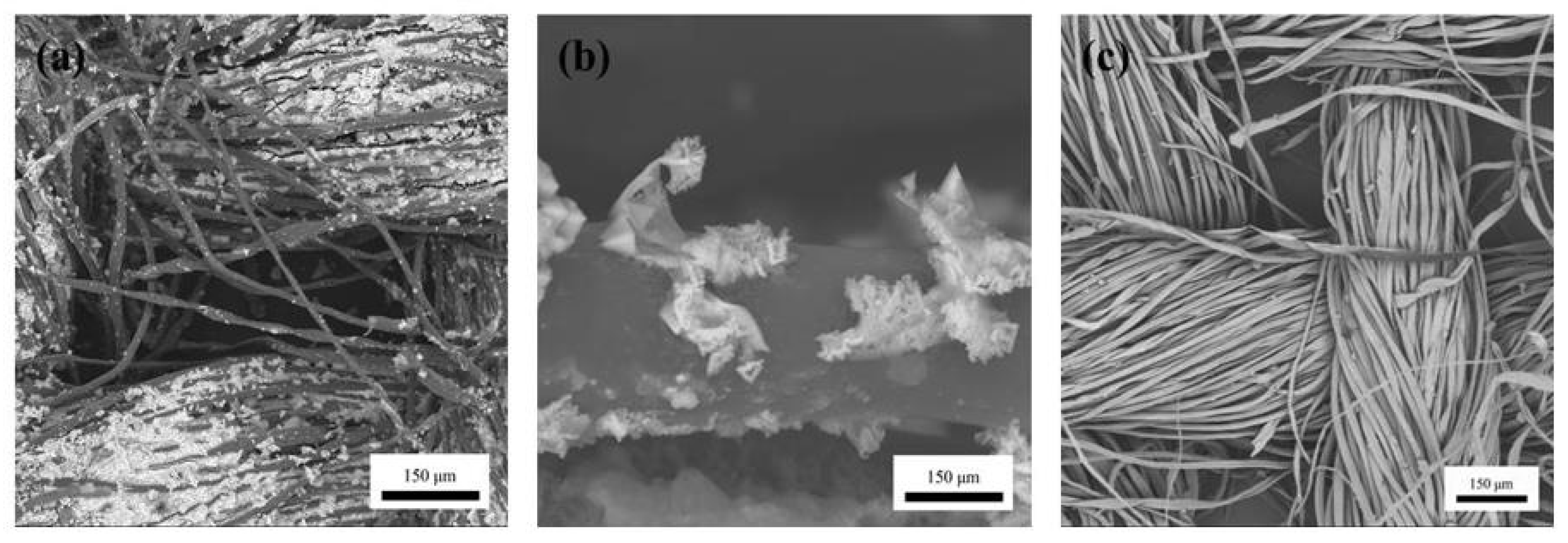
3.1. Surface Morphology of PEDOT/Composite Conductive Woven Fabrics
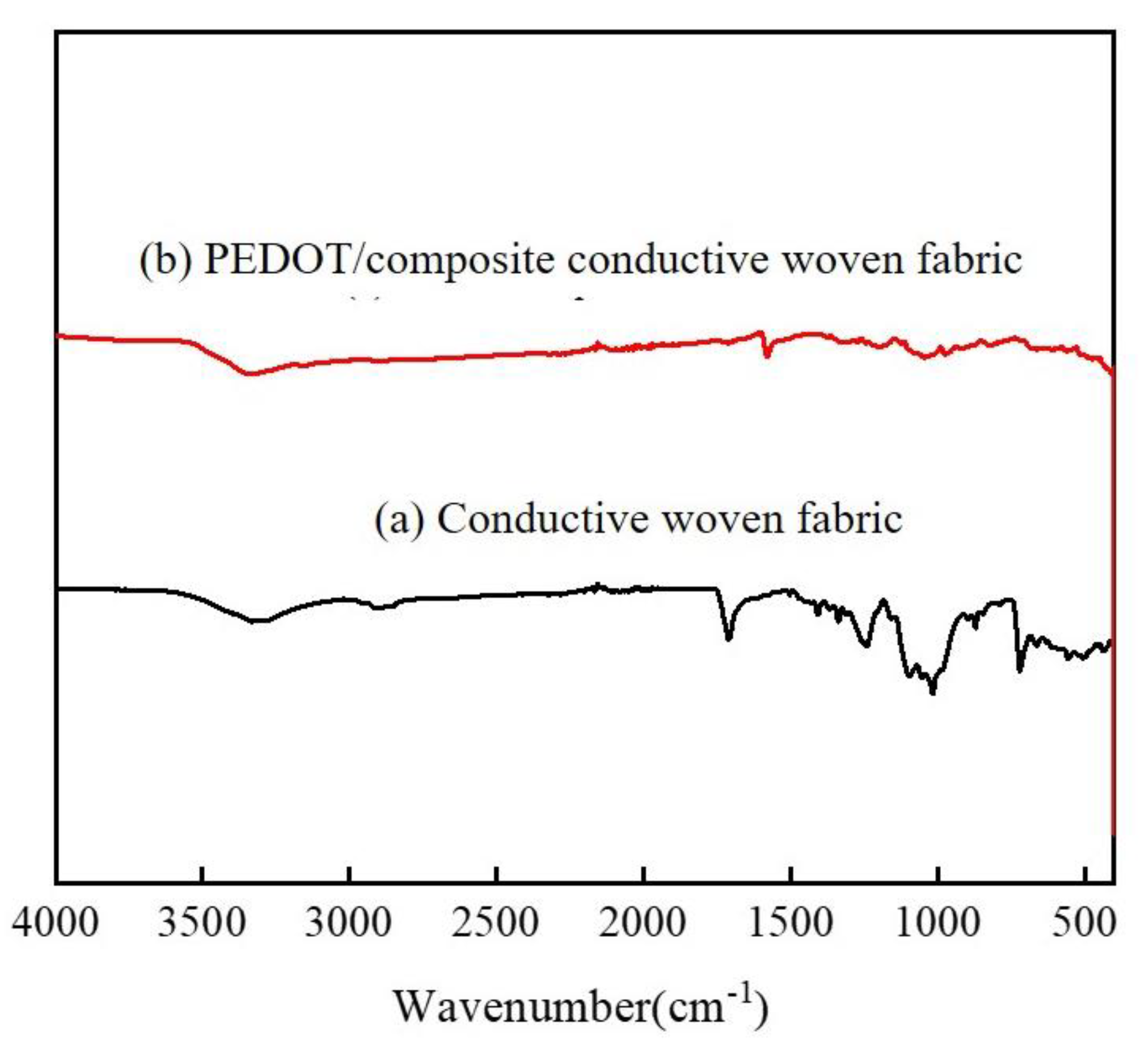
3.2. FT-IR Analysis of PEDOT/Conductive Woven Fabrics
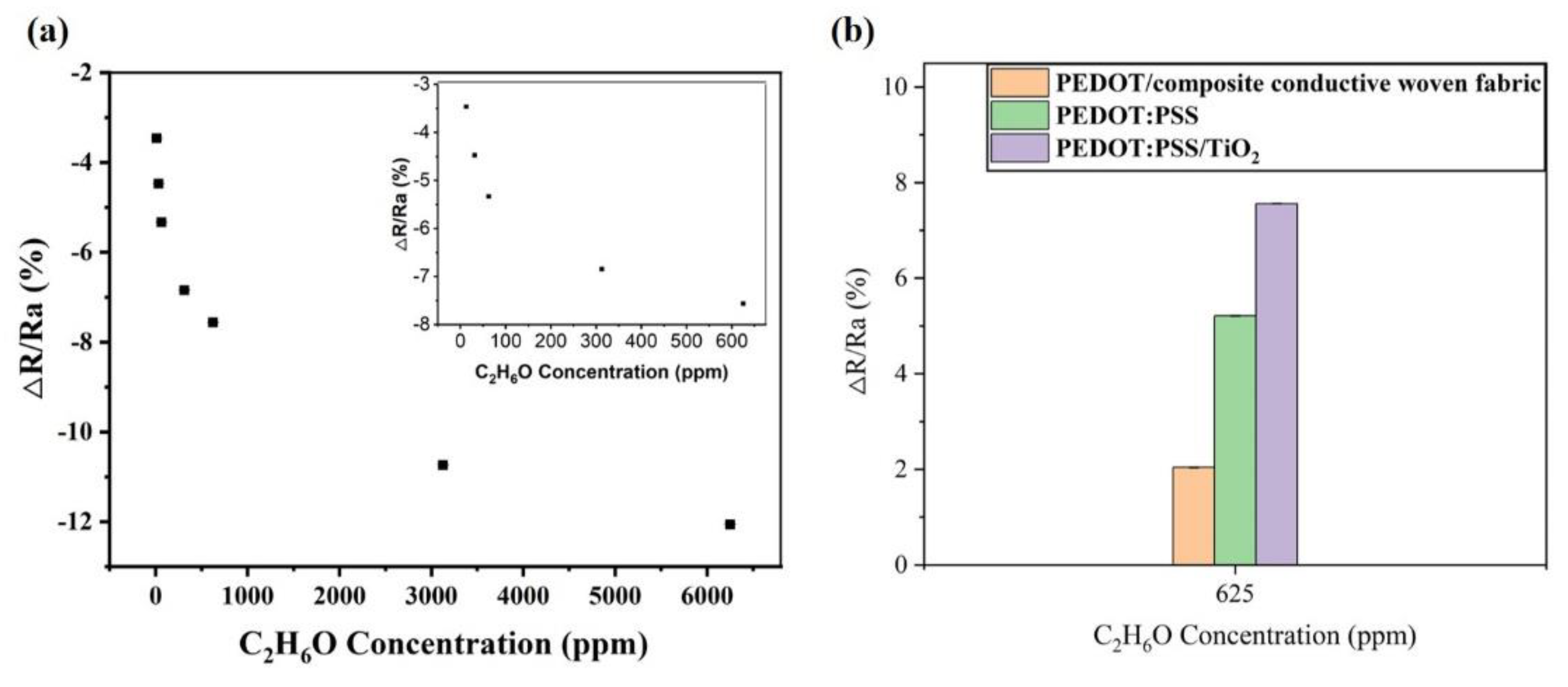
3.3. Gas Sensitivity of PEDOT/Composite Conductive Woven Fabrics
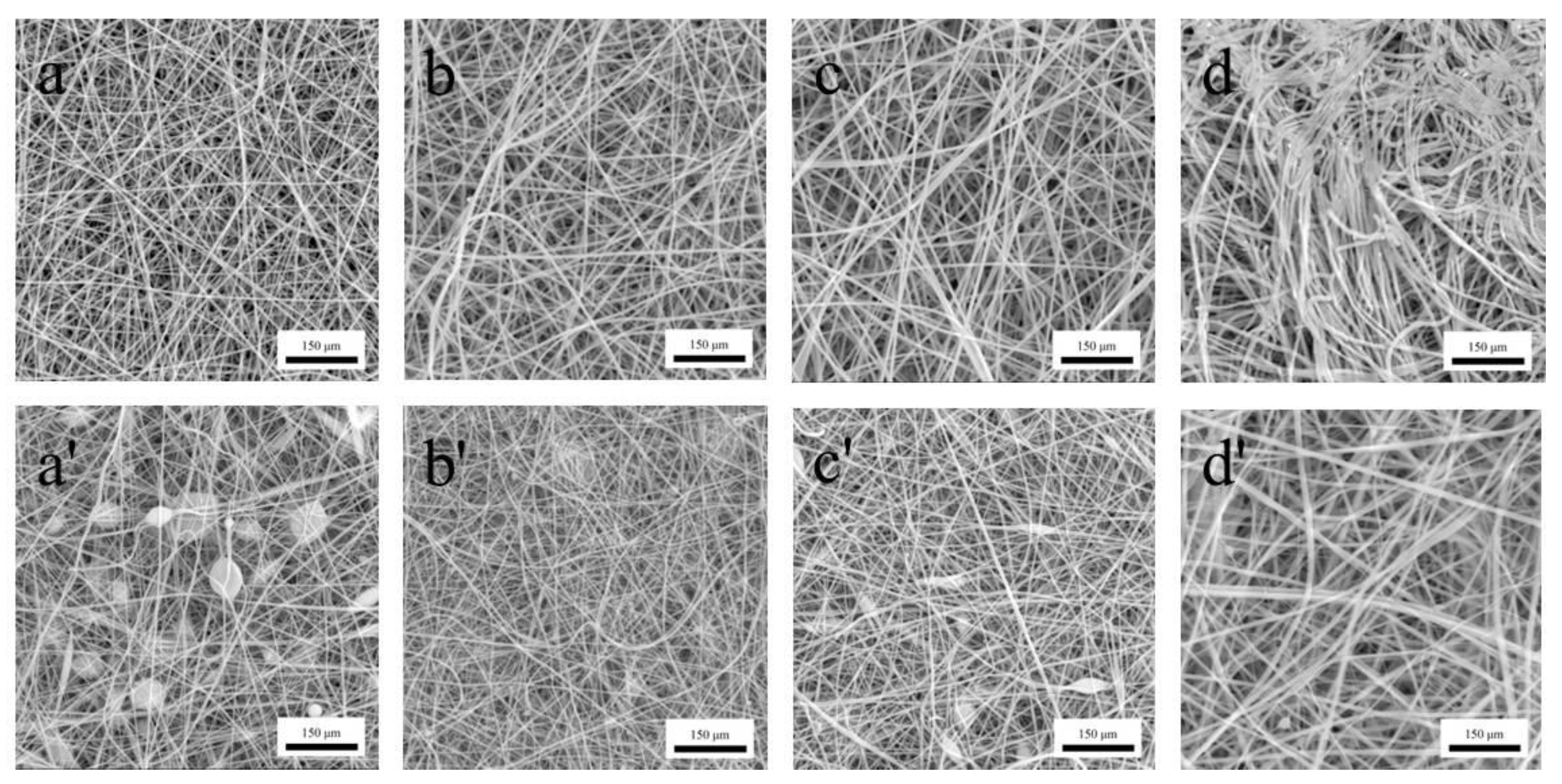
3.4. Morphology Characterization of Gas-Sensing Membranes
3.5. EDS Analysis of Gas-Sensing Membranes
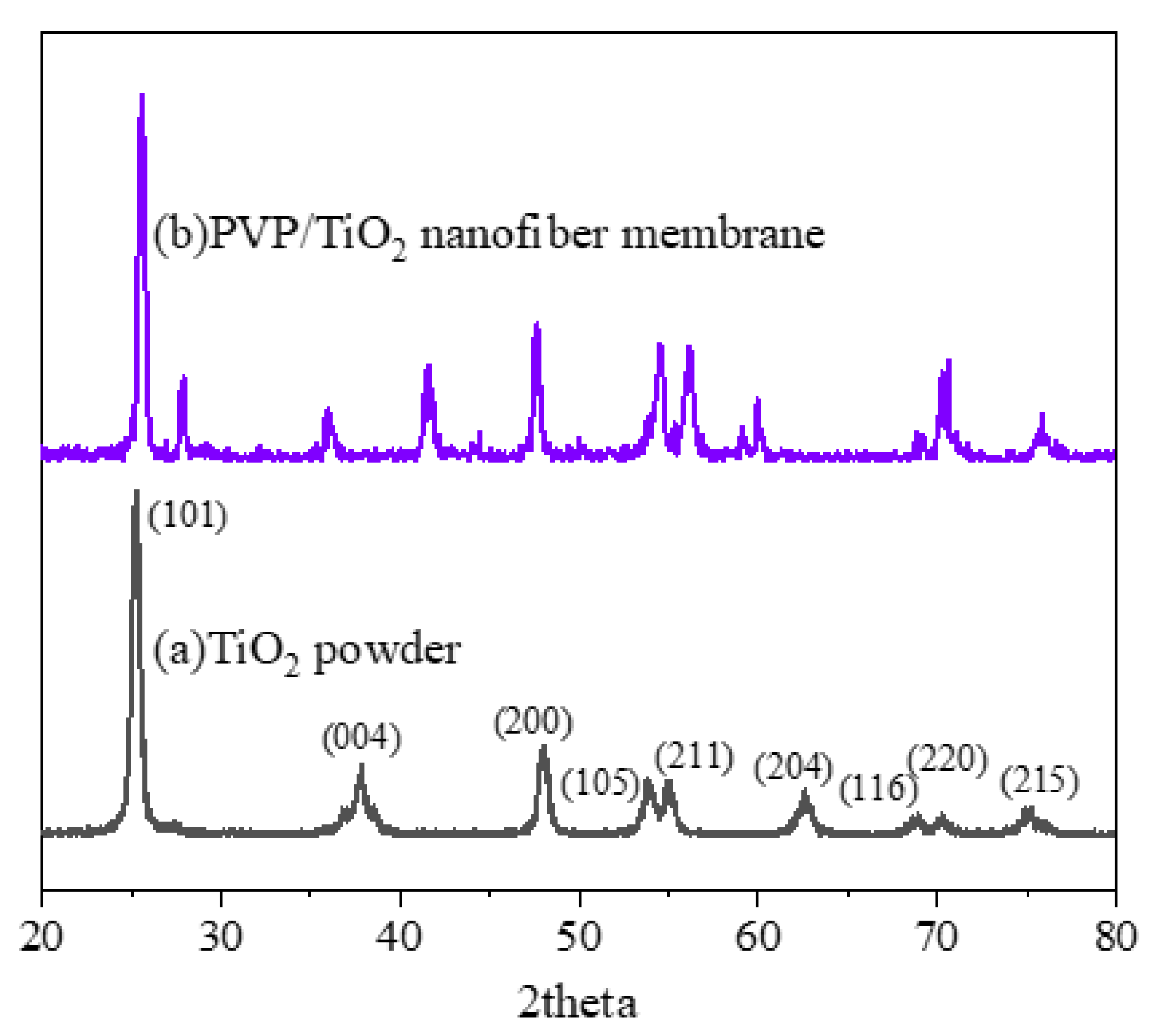
3.6. XRD Analysis of Gas-Sensing Membranes
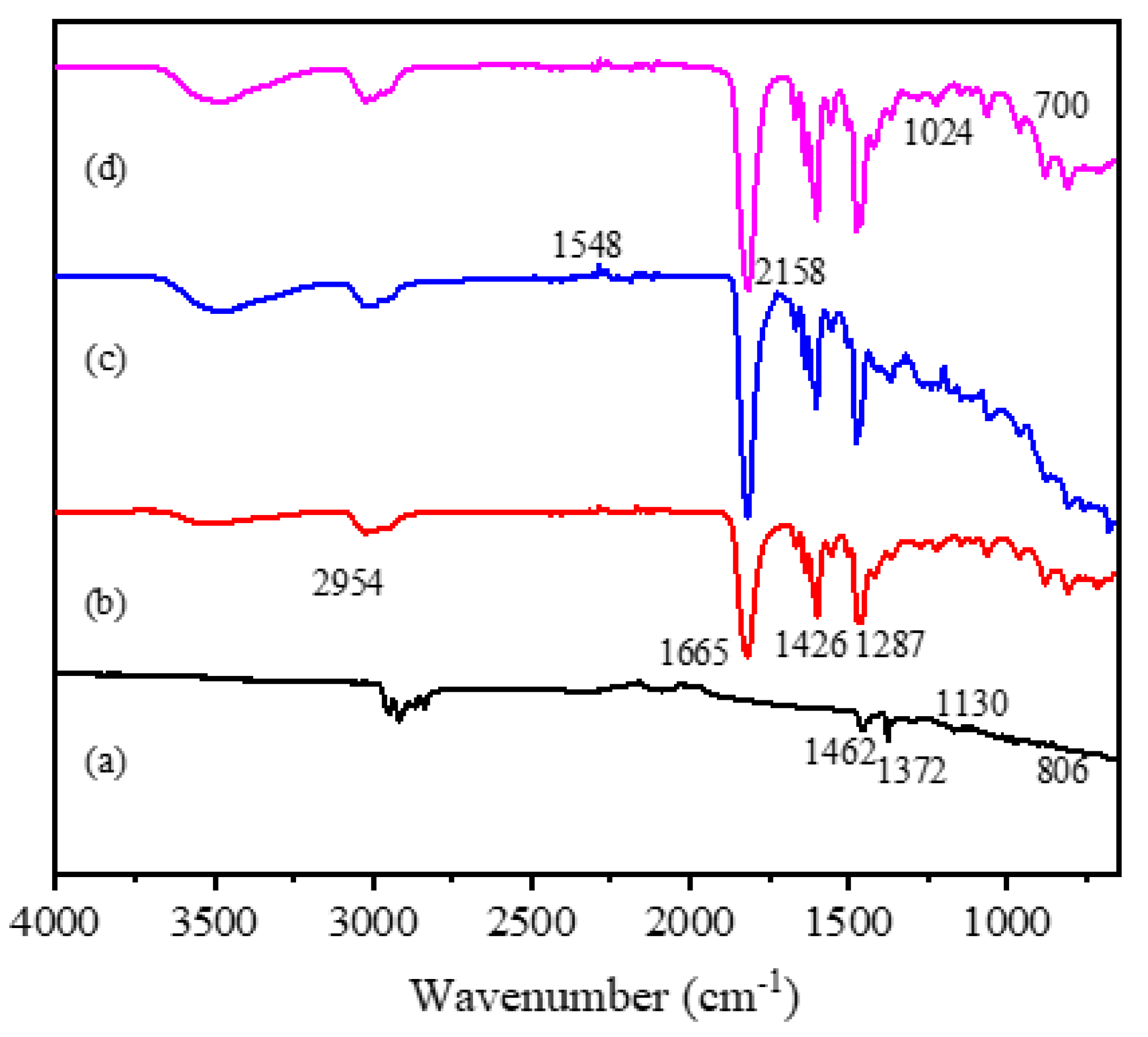
3.7. FT-IR Analysis of Gas-Sensing Membranes
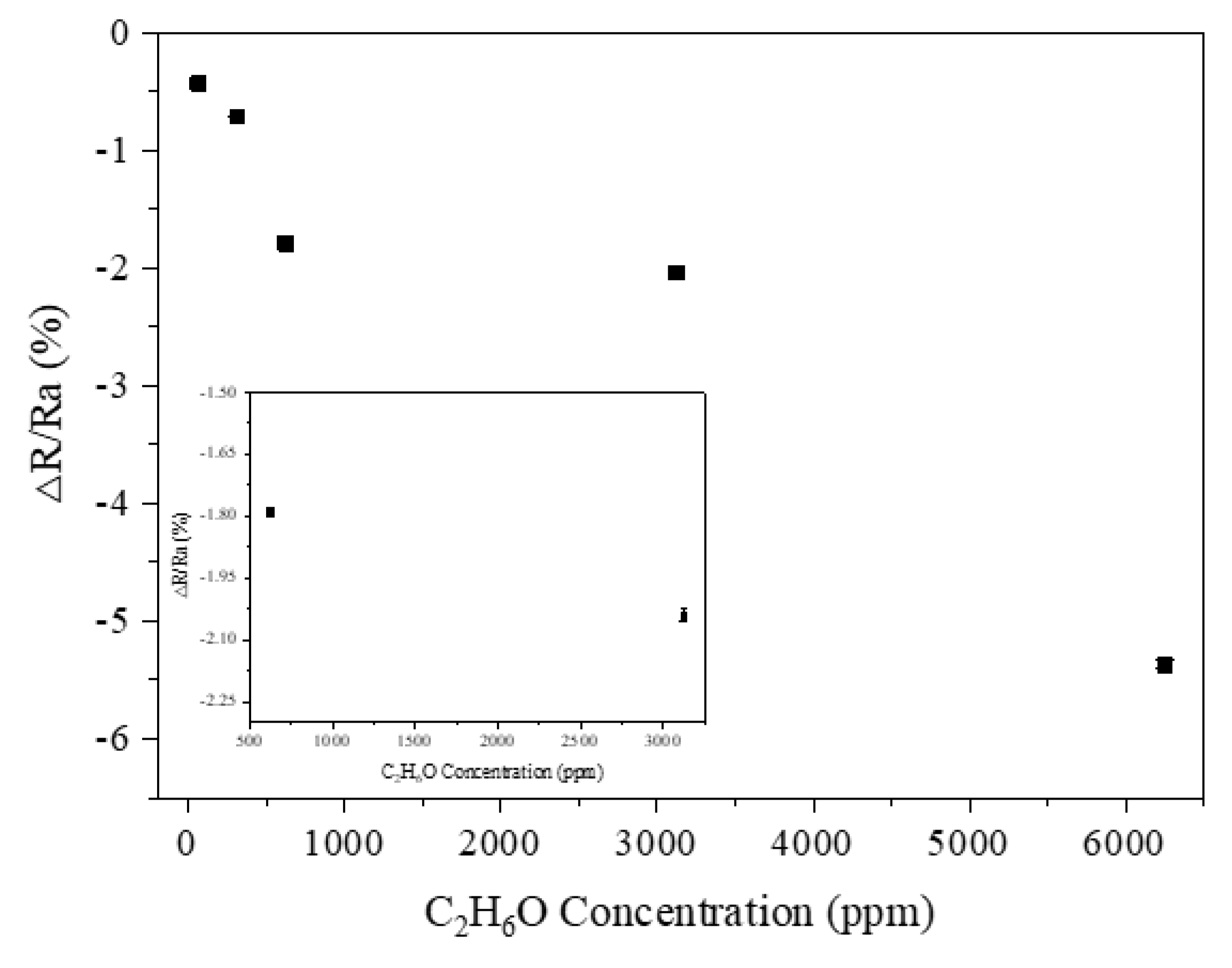
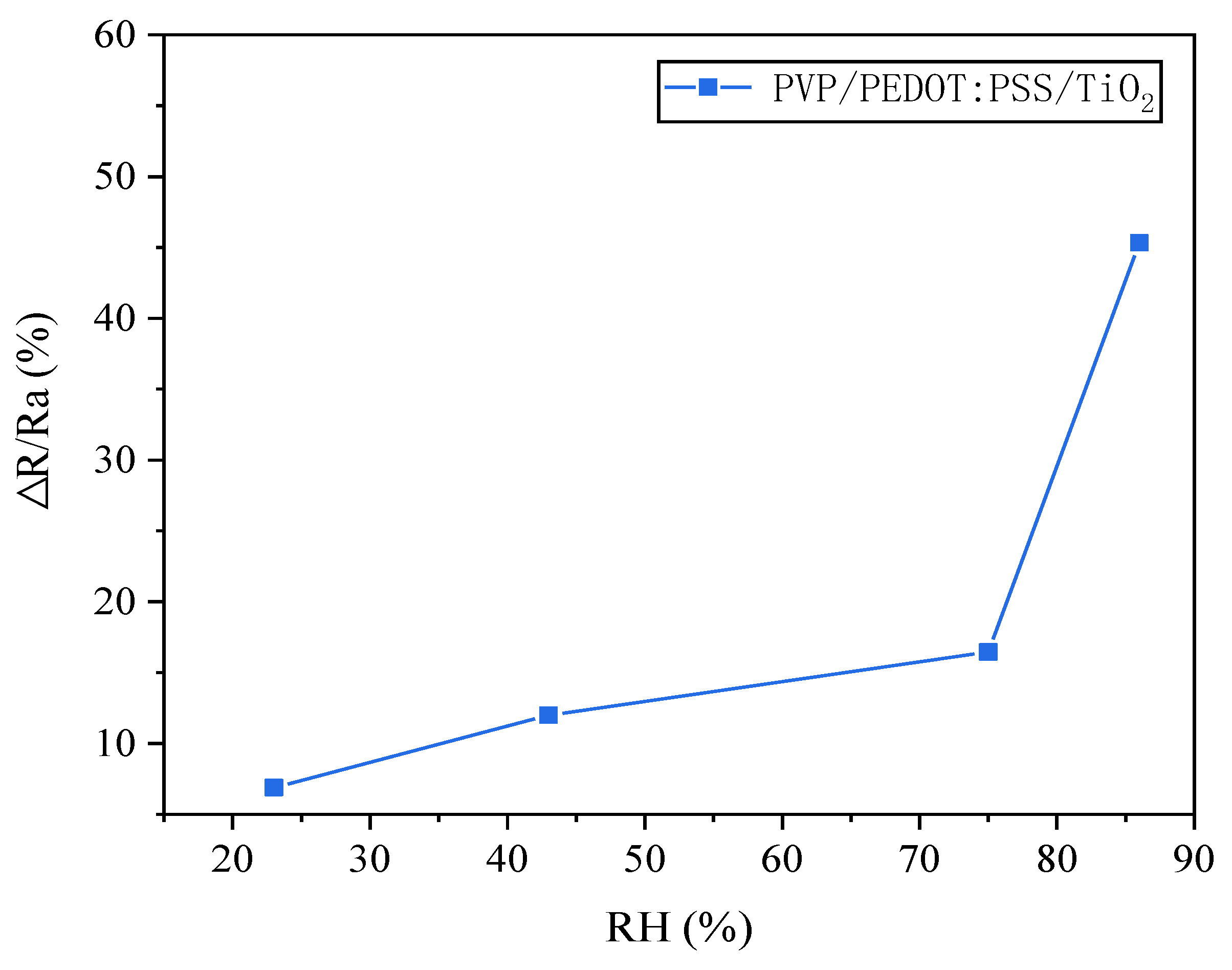
3.8. Gas Sensitivity Response
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heeger, A.J. Semiconducting and metallic polymers: The fourth generation of polymeric materials (Nobel lecture). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 2591–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, I.; Reese, C.; Hormes, J.; Heywang, G.; Jonas, F. The thermal ageing of poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene). An investigation by X-ray absorption and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Chem. Phys. 1995, 194, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenendaal, L.; Jonas, F.; Freitag, D.; Pielartzik, H.; Reynolds, J.R. Poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene) and its derivatives: Past, present, and future. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jia, W.; Strout, T.; Ding, Y.; Lei, Y. Preparation, characterization and sensitive gas sensing of conductive core-sheath TiO2-PEDOT nanocables. Sensors 2009, 9, 6752–6763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidayat, S.N.; Julian, T.; Rianjanu, A.; Kusumaatmadja, A.; Triyana, K. Quartz crystal microbalance coated by PAN nanofibers and PEDOT: PSS for humidity sensor. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Seminar on Sensors, Instrumentation, Measurement and Metrology (ISSIMM), Surabaya, Indonesia, 25–26 August 2017; pp. 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.; Park, D.W.; Shim, S.E. Electrospun PEDOT: PSS/carbon nanotubes/PVP nanofibers as chemiresistors for aromatic volatile organic compounds. Synth. Met. 2012, 162, 1513–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, P.; Xue, F.; Liu, L. A flexible and multifunctional electronic nose using polyaniline/cotton fibrous membrane with a hierarchical structure. Mater. Lett. 2018, 233, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masri, K.; Kalaleh, H.-A.; Alhassan, A. Fabrication of Sensitive and Selective Ammonia Gas Sensors Based on Pyrrole Interfacial Polymerization. J. Electron. Mater. 2019, 48, 5967–5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju Yun, Y.; Hong, W.G.; Choi, N.-J.; Hoon Kim, B.; Jun, Y.; Lee, H.-K. Ultrasensitive and highly selective graphene-based single yarn for use in wearable gas sensor. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Kim, W.-J.; Lee, H.-K.; Lee, D.-S.; Shin, J.-H.; Jun, Y.; Yun, Y.J. Highly flexible, mechanically stable, and sensitive NO2 gas sensors based on reduced graphene oxide nanofibrous mesh fabric for flexible electronics. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 257, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampetti, E.; Macagnano, A.; Pantalei, S.; Bearzotti, A. PEDOT: PSS coated titania nanofibers for NO2 detection: Study of humidity effects. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 179, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Fu, H.; Zhang, L.; An, X.; Xiong, S.; Jiang, X.; Yu, A. Enhanced gas sensing performance based on the fabrication of polycrystalline Ag@ TiO2 core-shell nanowires. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 286, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chen, D.; Miao, J.; Lin, S.; Yu, Z.; Cui, D.; Yang, Z.; Chen, X. Highly sensitive sensor based on ordered porous ZnO nanosheets for ethanol detecting application. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 326, 128952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Fu, J.; Liu, R.; He, H.; Ma, J.; Yu, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Long, Y. Electrospinning of ultrafine conducting polymer composite nanofibers with diameter less than 70 nm as high sensitive gas sensor. Materials 2018, 11, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, P.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qin, X. A fast response ammonia sensor based on coaxial PPy–PAN nanofiber yarn. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pang, Y.; Jian, J.; Tu, T.; Yang, Z.; Ling, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Qiao, Y.; Tian, H.; Yang, Y. Wearable humidity sensor based on porous graphene network for respiration monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 116, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Sun, Z.; Huang, D.; Yang, Z.; Ji, Q.; Hu, N.; Yin, G.; He, D.; Wei, H.; Zhang, Y. Studies on NH3 gas sensing by zinc oxide nanowire-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 252, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.-G.; Peng, Y.-T. Fabrication of a room-temperature H2S gas sensor based on PPy/WO3 nanocomposite films by in-situ photopolymerization. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Yin, C.; Luo, Y.; Duan, G. Facile synthesis of the composites of polyaniline and TiO2 nanoparticles using self-assembly method and their application in gas sensing. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sonker, R.K.; Yadav, B.; Gupta, V.; Tomar, M. Fabrication and characterization of ZnO-TiO2-PANI (ZTP) micro/nanoballs for the detection of flammable and toxic gases. J. Mater. 2019, 370, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-D.; Yan, X.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Yu, G.-F.; Han, W.-P.; Zhang, J.-C.; Long, Y.-Z. Electrospun PEDOT: PSS/PVP nanofibers for CO gas sensing with quartz crystal microbalance technique. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2016, 2016, 3021353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Lee, J.; Choi, J.; Jung, D.; Shim, S.E. Electrospun PEDOT: PSS/PVP nanofibers as the chemiresistor in chemical vapour sensing. Synth. Met. 2010, 160, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; He, J.; Qiang, R.; Nan, N.; You, X.; Zhou, Y.; Shao, W.; Liu, F.; Liu, R. Electrospun conductive nanofiber yarn for a wearable yarn supercapacitor with high volumetric energy density. Materials 2019, 12, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, W.; Zeng, W.; Li, Y. A nest-like TiO2 nanostructures for excellent performance ethanol sensor. Mater. Lett. 2019, 248, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Tang, N.; Zhou, C.; Han, Z.; Qu, H.; Duan, X. A chemiresistive sensor array from conductive polymer nanowires fabricated by nanoscale soft lithography. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 20578–20586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, C.; Huang, K.; Li, J.; Wang, P.; Duan, X.; Chen, K.; Liu, K.; Liu, Z. Massive growth of graphene quartz fiber as a multifunctional electrode. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5938–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Lee, J.; Hyeon, T.; Lee, M.; Kim, D.H. Fabric-based integrated energy devices for wearable activity monitors. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6329–6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büscher, G.H.; Kõiva, R.; Schürmann, C.; Haschke, R.; Ritter, H.J. Flexible and stretchable fabric-based tactile sensor. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2015, 63, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeo, J.C.; Lim, C.T. Emerging flexible and wearable physical sensing platforms for healthcare and biomedical applications. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2016, 2, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Indarit, N.; Kim, Y.-H.; Petchsang, N.; Jaisutti, R. Highly sensitive polyaniline-coated fiber gas sensors for real-time monitoring of ammonia gas. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 26773–26779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, K.H.; Oh, K.W.; Kang, T.J. Polyaniline–nylon 6 composite fabric for ammonia gas sensor. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qin, X. Flexible and conductive nanofiber-structured single yarn sensor for smart wearable devices. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 252, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.J.; Hong, W.G.; Kim, H.J.; Jun, Y.; Lee, H.-K. E-textile gas sensors composed of molybdenum disulfide and reduced graphene oxide for high response and reliability. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 248, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Jung, H.G.; Kim, I.; Lee, D.; Kim, W.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, J.-H.; Park, J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, G. Highly Conductive and Flexible Dopamine–Graphene Hybrid Electronic Textile Yarn for Sensitive and Selective NO2 Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 46629–46638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; Wei, Y. Preparation and characterization of polypyrrole/TiO2 coaxial nanocables. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2006, 27, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xia, Y. Fabrication of titania nanofibers by electrospinning. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Ye, J.; Song, W.; Shen, Q. Synthesis of polyaniline nanotubes with controlled rectangular or square pore shape. Mater. Lett. 2014, 121, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasha, A.; Khasim, S.; Khan, F.A.; Dhananjaya, N. Fabrication of gas sensor device using poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly (styrenesulfonate)-doped reduced graphene oxide organic thin films for detection of ammonia gas at room temperature. Iran. Polym. J. 2019, 28, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasim, S.; Pasha, A.; Badi, N.; Lakshmi, M.; Al-Ghamdi, S.; AL-Aoh, H.A. PVA Treated PEDOT-PSS: TiO2 Nanocomposite Based High-Performance Sensors Towards Detection of Relative Humidity and Soil Moisture Content for Agricultural Applications. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, D. Function and Applications of Gas Sensors; Institute of Physics Publishing: Giessen, Germany, 2001; pp. R125–R149. [Google Scholar]
- Dan, Y.; Cao, Y.; Mallouk, T.E.; Evoy, S.; Johnson, A.C. Gas sensing properties of single conducting polymer nanowires and the effect of temperature. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 434014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ram, M.K.; Yavuz, O.; Aldissi, M. NO2 gas sensing based on ordered ultrathin films of conducting polymer and its nanocomposite. Synth. Met. 2005, 151, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huyen, D.N.; Tung, N.T.; Thien, N.D.; Thanh, L.H. Effect of TiO2 on the gas sensing features of TiO2/PANi nanocomposites. Sensors 2011, 11, 1924–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdelrahman, M.S.; Khattab, T.A.; Aldalbahi, A.; Hatshan, M.R.; El-Naggar, M.E. Facile development of microporous cellulose acetate xerogel immobilized with hydrazone probe for real time vapochromic detection of toxic ammonia. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muckley, E.S.; Jacobs, C.B.; Vidal, K.; Mahalik, J.P.; Kumar, R.; Sumpter, B.G.; Ivanov, I.N. New insights on electro-optical response of poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene): Poly (styrenesulfonate) film to humidity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 15880–15886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Chen, S.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Q.; Lv, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, X. Achieving humidity-insensitive ammonia sensor based on Poly (3, 4-ethylene dioxythiophene): Poly (styrenesulfonate). Org. Electron. 2018, 62, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuş, M.; Okur, S. Electrical characterization of PEDOT: PSS beyond humidity saturation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 143, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Yin, L.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, D.; Gao, R. Metal oxide gas sensors: Sensitivity and influencing factors. Sensors 2010, 10, 2088–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Qahtani, S.D.; Habeebullah, T.M.; Alsoliemy, A.; Alzahrani, H.K.; Alfi, R.A.A.; El-Metwaly, N.M. Preparation of polyvinyl alcohol reinforced with microcrystalline cellulose to function as test strips immobilized with a hydrazone chromophore for colorimetric identification of toxic ammonia. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 275, 125218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shiu, B.-C.; Liu, Y.-L.; Yuan, Q.-Y.; Lou, C.-W.; Lin, J.-H. Preparation and Characterization of PEDOT:PSS/TiO2 Micro/Nanofiber-Based Gas Sensors. Polymers 2022, 14, 1780. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091780
Shiu B-C, Liu Y-L, Yuan Q-Y, Lou C-W, Lin J-H. Preparation and Characterization of PEDOT:PSS/TiO2 Micro/Nanofiber-Based Gas Sensors. Polymers. 2022; 14(9):1780. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091780
Chicago/Turabian StyleShiu, Bing-Chiuan, Yan-Ling Liu, Qian-Yu Yuan, Ching-Wen Lou, and Jia-Horng Lin. 2022. "Preparation and Characterization of PEDOT:PSS/TiO2 Micro/Nanofiber-Based Gas Sensors" Polymers 14, no. 9: 1780. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091780
APA StyleShiu, B.-C., Liu, Y.-L., Yuan, Q.-Y., Lou, C.-W., & Lin, J.-H. (2022). Preparation and Characterization of PEDOT:PSS/TiO2 Micro/Nanofiber-Based Gas Sensors. Polymers, 14(9), 1780. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091780







