Analysis of Functionalized Ferromagnetic Memory Alloys from the Perspective of Developing a Medical Vascular Implant
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Preparation of Ferromagnetic Memory Alloys Based on FePd (30 at% Pd)
2.1.2. Synthesis of Polyglutamic Acid
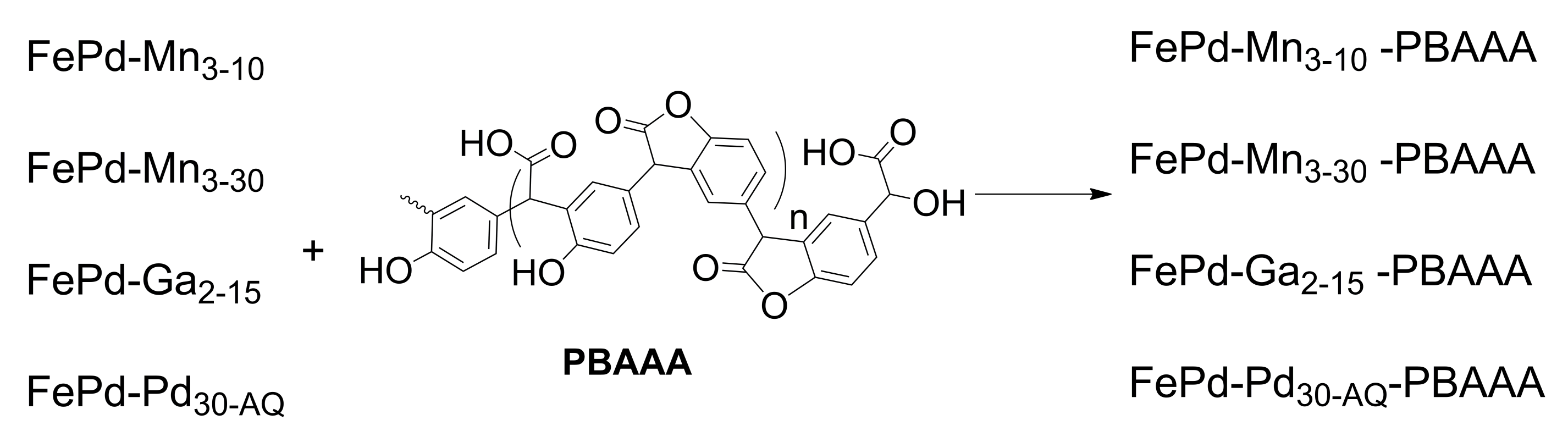
2.1.3. Preparation of Ferromagnetic Memory Alloys, Based on FePd Covered with PBAAA
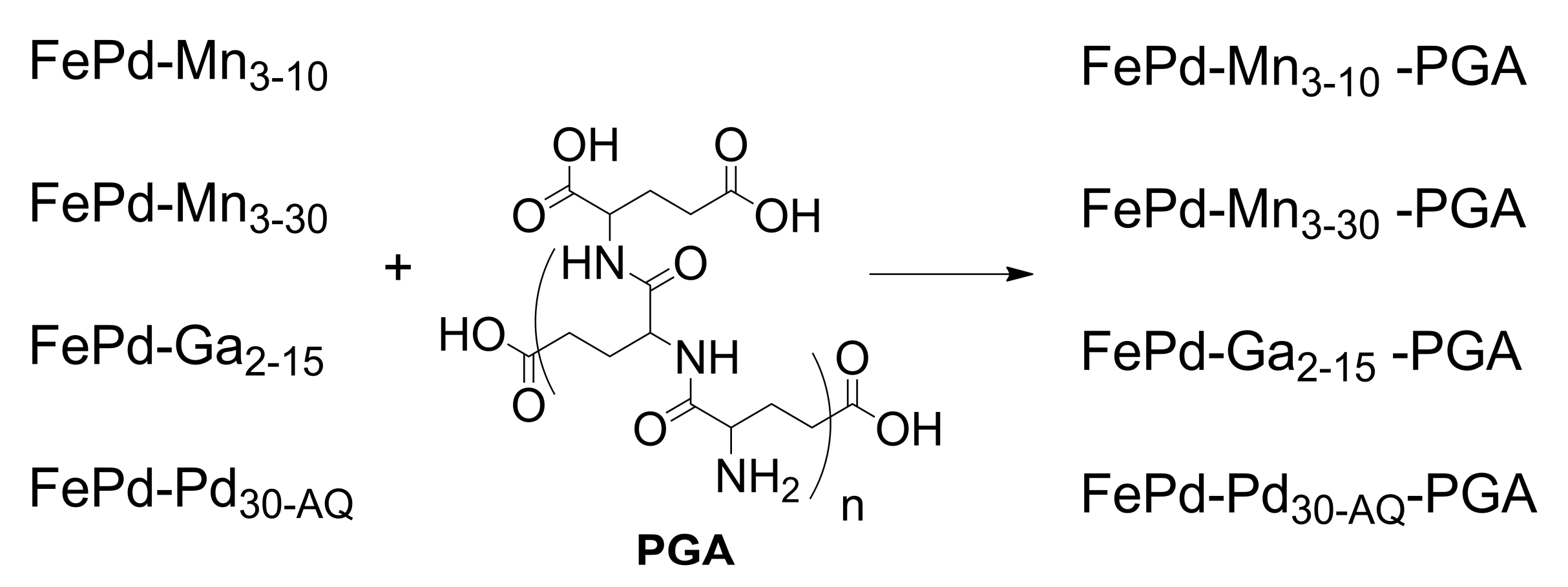
2.1.4. Preparation of Ferromagnetic Memory Alloys, Based on FePd Covered with PGA
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Batch Experiment for Thromboplastin and Prothrombin Times
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Characterisation of Ferromagnetic Memory Alloys, Based on FePd Covered with Polymers
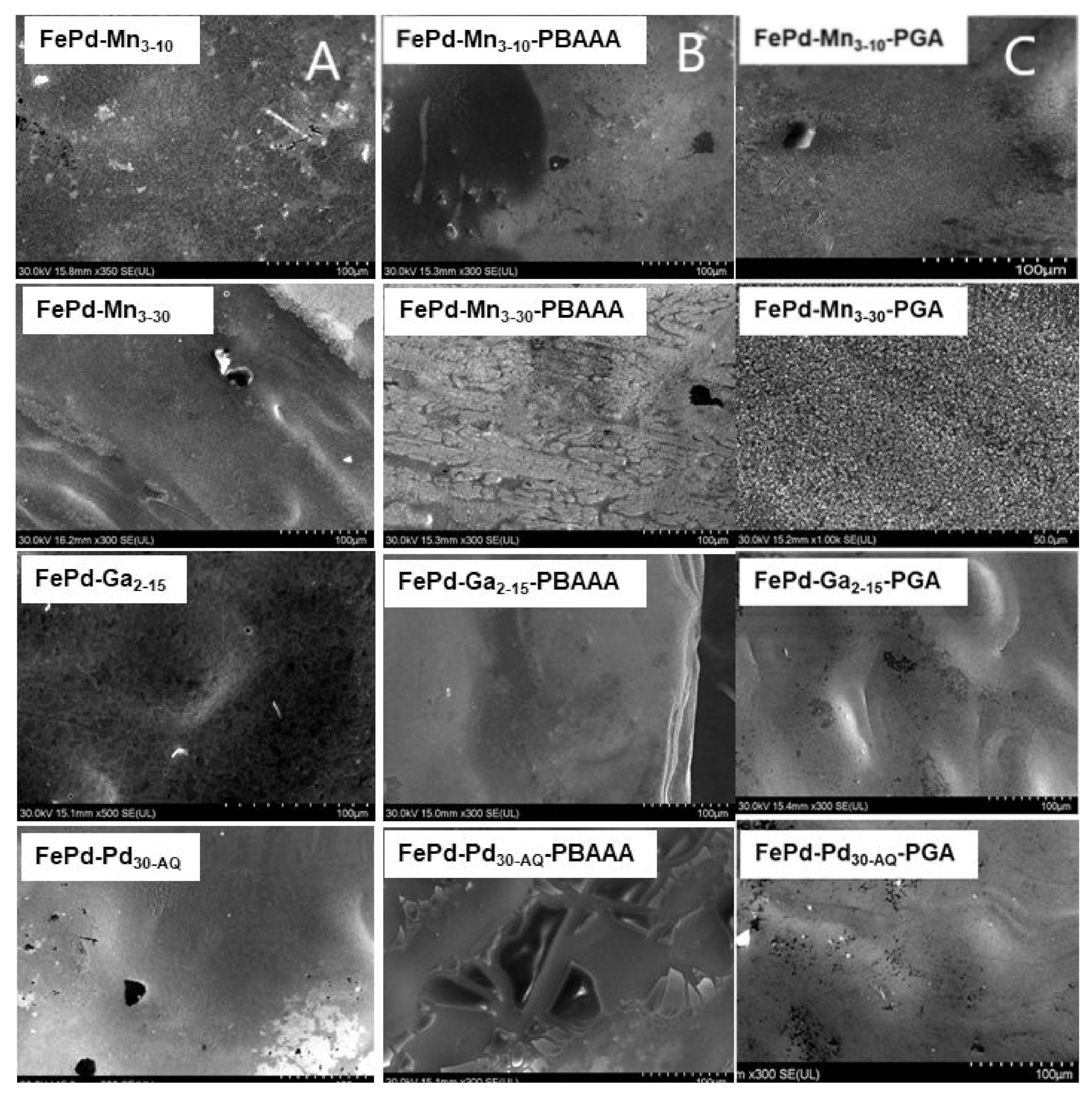
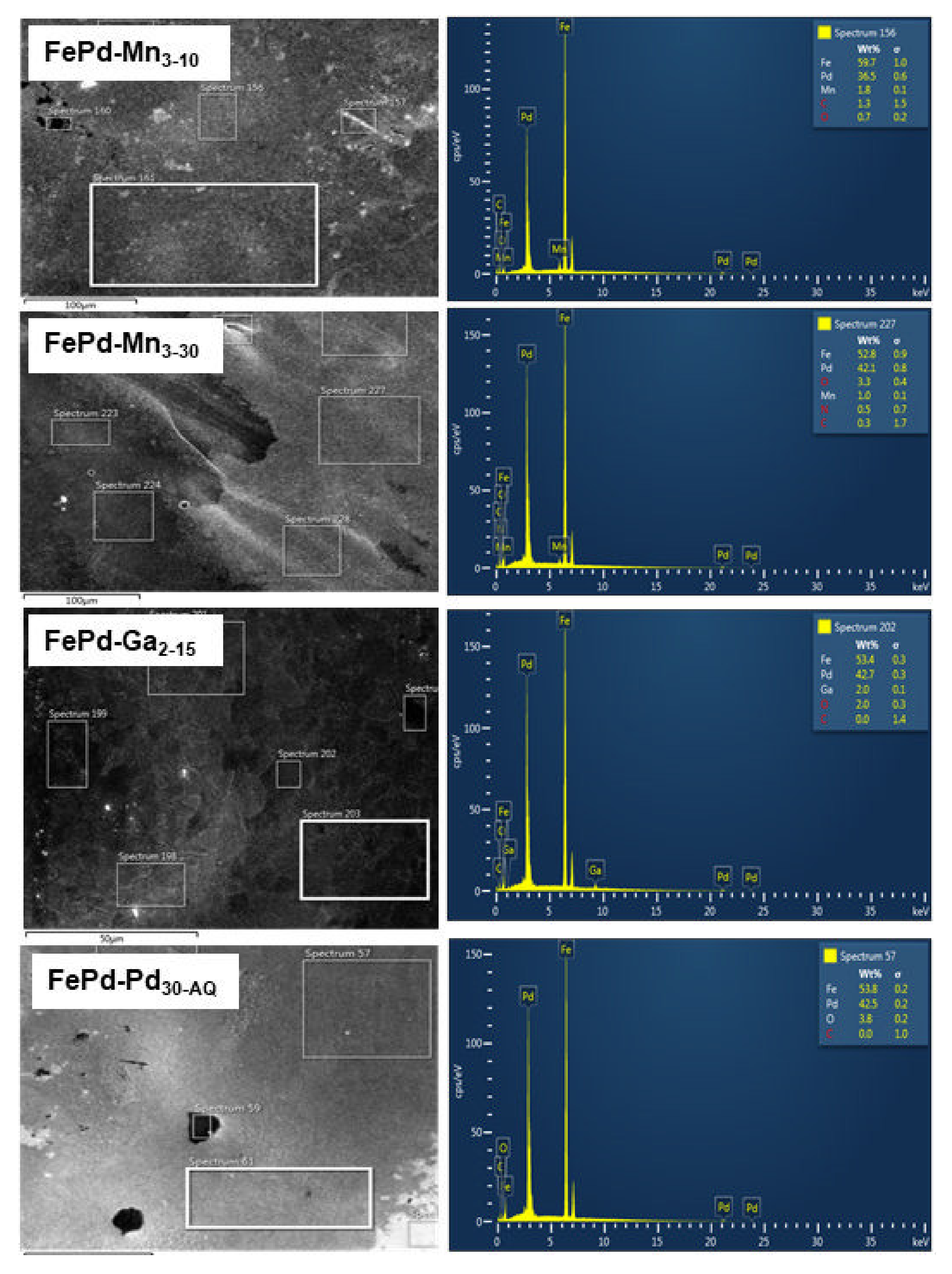
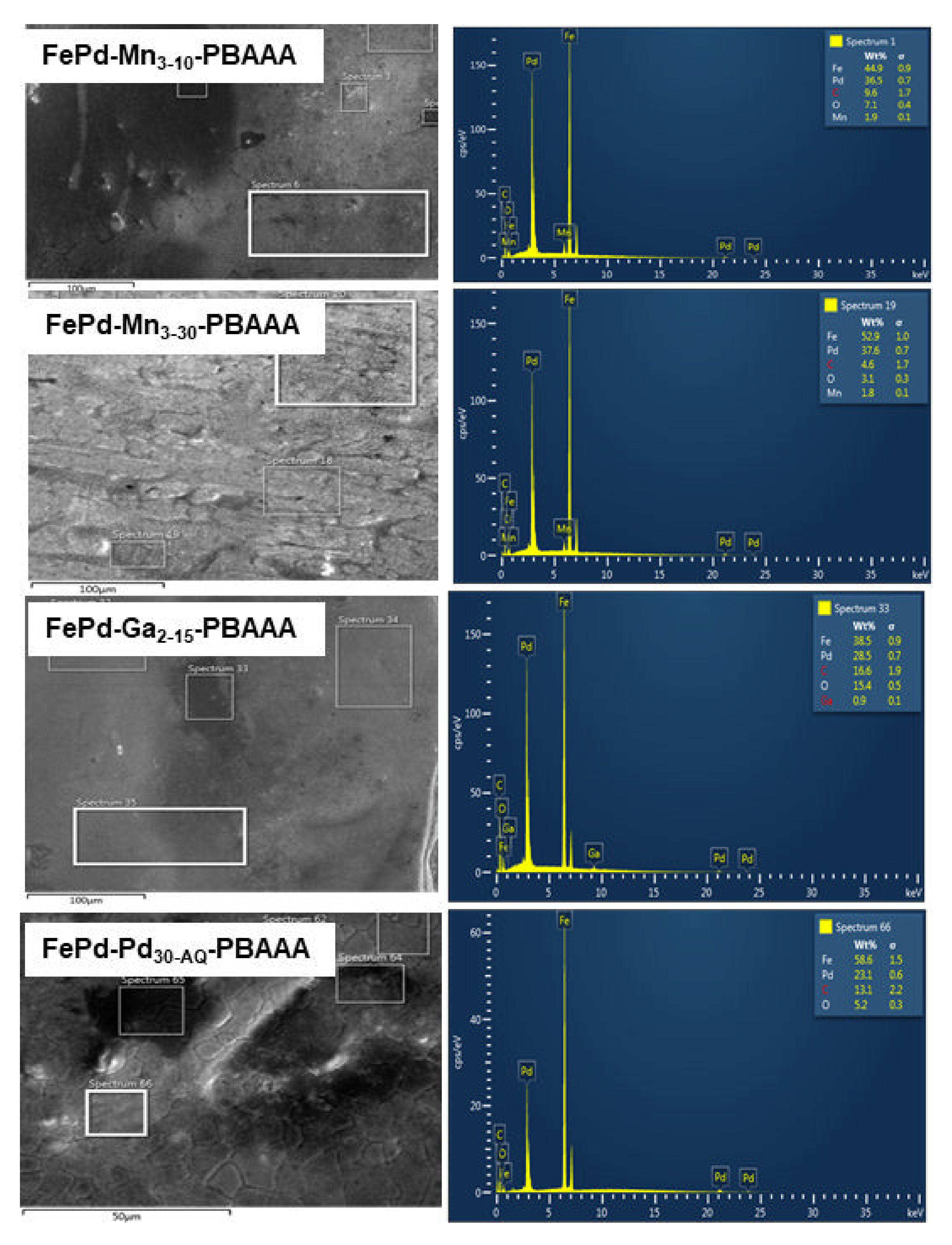
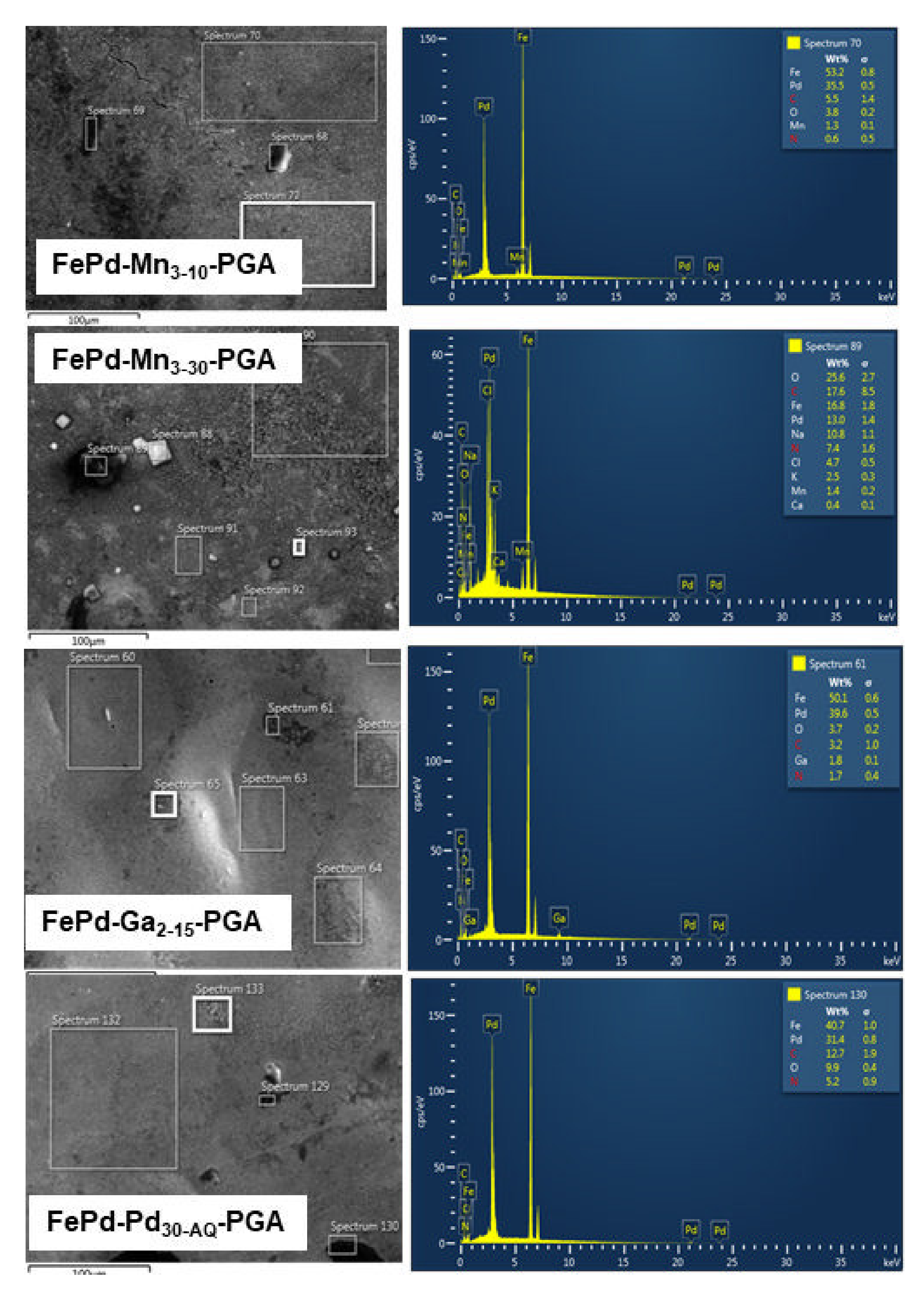
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy and Energy-Dispersive X-ray Analysis
3.2.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.2.2. Energy Dispersive X-ray Analysis
3.3. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy
3.4. Batch Experiments for Thromboplastin and Prothrombin Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Braune, S.; Latour, R.A.; Reinthaler, M.; Landmesser, U.; Lendlein, A.; Jung, F. In Vitro Thrombogenicity Testing of Biomaterials. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, e1900527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Desai, N.P.; Hubbell, J.A. Surface modifications of polymeric biomaterials for reduced thrombogenicity. In Proceedings of the ACS Division of Polymeric Materials: Science and Engineering, Boston, MA, USA, 1 April 1990; pp. 731–735. [Google Scholar]
- Sofronie, M.; Tolea, F.; Kuncser, V.; Valeanu, M.; Filoti, G. Magneto-Structural Properties and Magnetic Behaviour of FePd Ribbons. IEEE Trans. Mag. 2015, 51, 2500404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofronie, M.; Tolea, F.; Tolea, M.; Popescu, B.; Valeanu, M. Magnetic and magnetostrictive properties of the ternary Fe67.5Pd30.5Ga2 ferromagnetic shape memory ribbons. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2020, 142, 109446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofronie, M.; Enculescu, M.; Crisan, A.D.; Tolea, F. Effect of Mn substitution on the structural, magnetic and magnetostrictive properties of FePd ferromagnetic shape memory ribbons. Rom. Rep. Phys. 2020, 72, 502. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Yuan, L.; Li, D.; Tang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G.; Chen, H.; Brash, J.L. Blood compatible materials: State of the art. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 5718–5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewster, L.P.; Bufallino, D.; Ucuzian, A.; Greisler, H.P. Growing a living blood vessel: Insights for the second hundred years. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 5028–5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joner, M.; Finn, A.V.; Farb, A.; Mont, E.K.; Kolodgie, F.D.; Ladich, E.; Kutys, R.; Skorija, K.; Gold, H.K.; Virmani, R. Pathology of Drug-Eluting Stents in Humans: Delayed Healing and Late Thrombotic Risk. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 48, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reinthaler, M.; Jung, F.; Landmesser, U.; Lendlein, A. Trend to move from permanent metals to degradable, multifunctional polymer or metallic implants in the example of coronary stents. Expert Rev. Med Devices 2016, 13, 1001–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wenaweser, P.; Rey, C.; Eberli, F.R.; Togni, M.; Tuller, D.; Locher, S.; Remondino, A.; Seiler, C.; Hess, O.M.; Meier, B.; et al. Stent thrombosis following bare-metal stent implantation: Success of emergency percutaneous coronary intervention and predictors of adverse outcome. Eur. Heart J. 2005, 26, 1180–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Windecker, S.; Meier, B. Late Coronary Stent Thrombosis. Circulation 2007, 116, 1952–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strohbach, A.; Busch, R. Polymers for Cardiovascular Stent Coatings. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 2015, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allenstein, U.; Ma, Y.; Arabi-Hashemi, A.; Zink, M.; Mayr, S. Fe–Pd based ferromagnetic shape memory actuators for medical applications: Biocompatibility, effect of surface roughness and protein coatings. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 5845–5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maitz, M. Applications of synthetic polymers in clinical medicine. Biosurf. Biotribol. 2015, 1, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nappi, F.; Nenna, A.; Larobina, D.; Martuscelli, G.; Singh, S.S.A.; Chello, M.; Ambrosio, L. The Use of Bioactive Polymers for Intervention and Tissue Engineering: The New Frontier for Cardiovascular Therapy. Polymers 2021, 13, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rykowska, I.; Nowak, I.; Nowak, R. Drug-Eluting Stents and Balloons—Materials, Structure Designs, and Coating Techniques: A Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Peng, F.; Zhang, T.; Chi, B.; Xu, H.; Mao, C.; Feng, S. Poly(γ-glutamic acid), coagulation? Anticoagulation? J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2016, 27, 1599–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, A.; Bunge, A.; Cîrcu, M.; Petran, A.; Hădade, N.D.; Filip, X. Poly(benzofuran-co-arylacetic acid)—A new type of highly functionalized polymers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 3504–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čapek, J.; Šárka, M.; Jablonská, E.; Lipovc, J.; Vojtěch, D. A novel high-strength and highly corrosive biodegradable FePd alloy: Structural, mechanical and in vitro corrosion and cytotoxicity study. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 79, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sample | Atomic Concentrations (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | Pd | C | O | N | |
| FePd-Pd30-AQ-PGA | 1.008 | 0.275 | 70.439 | 26.959 | 1.319 |
| Sample | PT/INR (s) | APTT (s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Static | Dynamic | Static | Dynamic | |
| Normal | 10.7/0.9 | 10.5/0.9 | 30.0 | 31.5 |
| Positive Control | 11/0.9 | 11.5/0.9 | 32.0 | 32.2 |
| FePd-Mn3-10-PBAAA | 13.2/1.0 | 12.7/1.0 | 25.4 | 25.2 |
| FePd-Mn3-30-PBAAA | 12.6/1.0 | 12.2/0.9 | 24.3 | 26.5 |
| FePd-Ga2-15-PBAAA | 14.4/0.9 | 13.7/0.9 | 30.5 | 33.7 |
| FePd-Pd30-AQ-PBAAA | 12.2/0.9 | 12.5/1.0 | 23.2 | 25.5 |
| FePd-Mn3-10-PGA | 11.2/0.9 | 10.8/0.9 | 36.5 | 43.2 |
| FePd-Mn3-30-PGA | 11.7/1.0 | 11.2/0.9 | 33.2 | 40.5 |
| FePd-Ga2-15-PGA | 13.4/1.0 | 13.3/1.1 | 35.6 | 42.3 |
| FePd-Pd30-AQ-PGA | 12.8/0.9 | 10.5/0.9 | 30.5 | 39.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nan, A.; Turcu, R.; Tudoran, C.; Sofronie, M.; Chiriac, A. Analysis of Functionalized Ferromagnetic Memory Alloys from the Perspective of Developing a Medical Vascular Implant. Polymers 2022, 14, 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14071397
Nan A, Turcu R, Tudoran C, Sofronie M, Chiriac A. Analysis of Functionalized Ferromagnetic Memory Alloys from the Perspective of Developing a Medical Vascular Implant. Polymers. 2022; 14(7):1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14071397
Chicago/Turabian StyleNan, Alexandrina, Rodica Turcu, Cristian Tudoran, Mihaela Sofronie, and Alexandru Chiriac. 2022. "Analysis of Functionalized Ferromagnetic Memory Alloys from the Perspective of Developing a Medical Vascular Implant" Polymers 14, no. 7: 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14071397
APA StyleNan, A., Turcu, R., Tudoran, C., Sofronie, M., & Chiriac, A. (2022). Analysis of Functionalized Ferromagnetic Memory Alloys from the Perspective of Developing a Medical Vascular Implant. Polymers, 14(7), 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14071397








