Light-Activated Elongation/Shortening and Twisting of a Nematic Elastomer Balloon
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Modelling of an Optically-Responsive Nematic Elastomer Balloon
2.1. Governing Equations for the Light-Activated Deformation Behaviors of a Nematic Elastomer Balloon
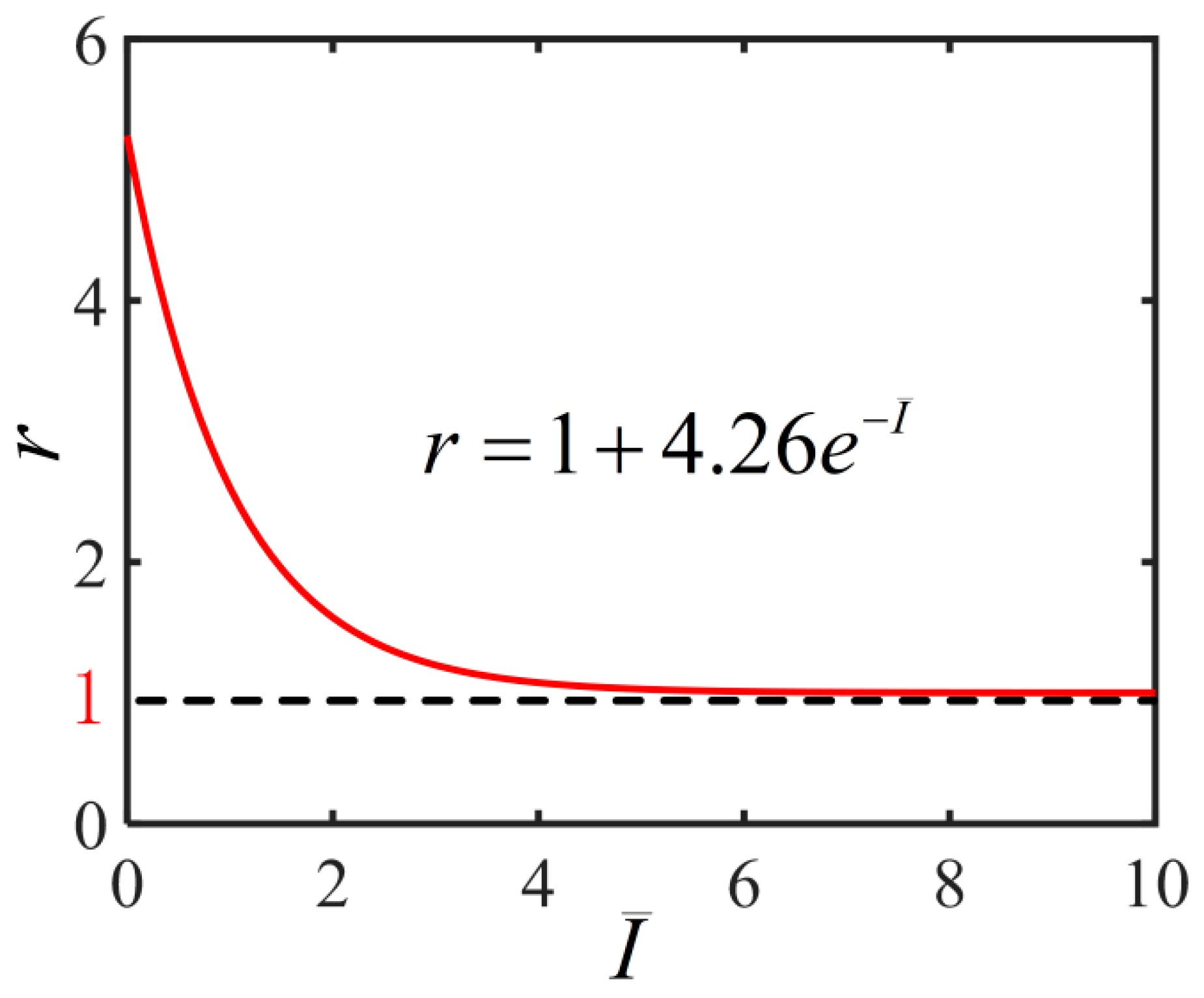
2.2. Light-Dependent Material Parameter r
2.3. Solution Method
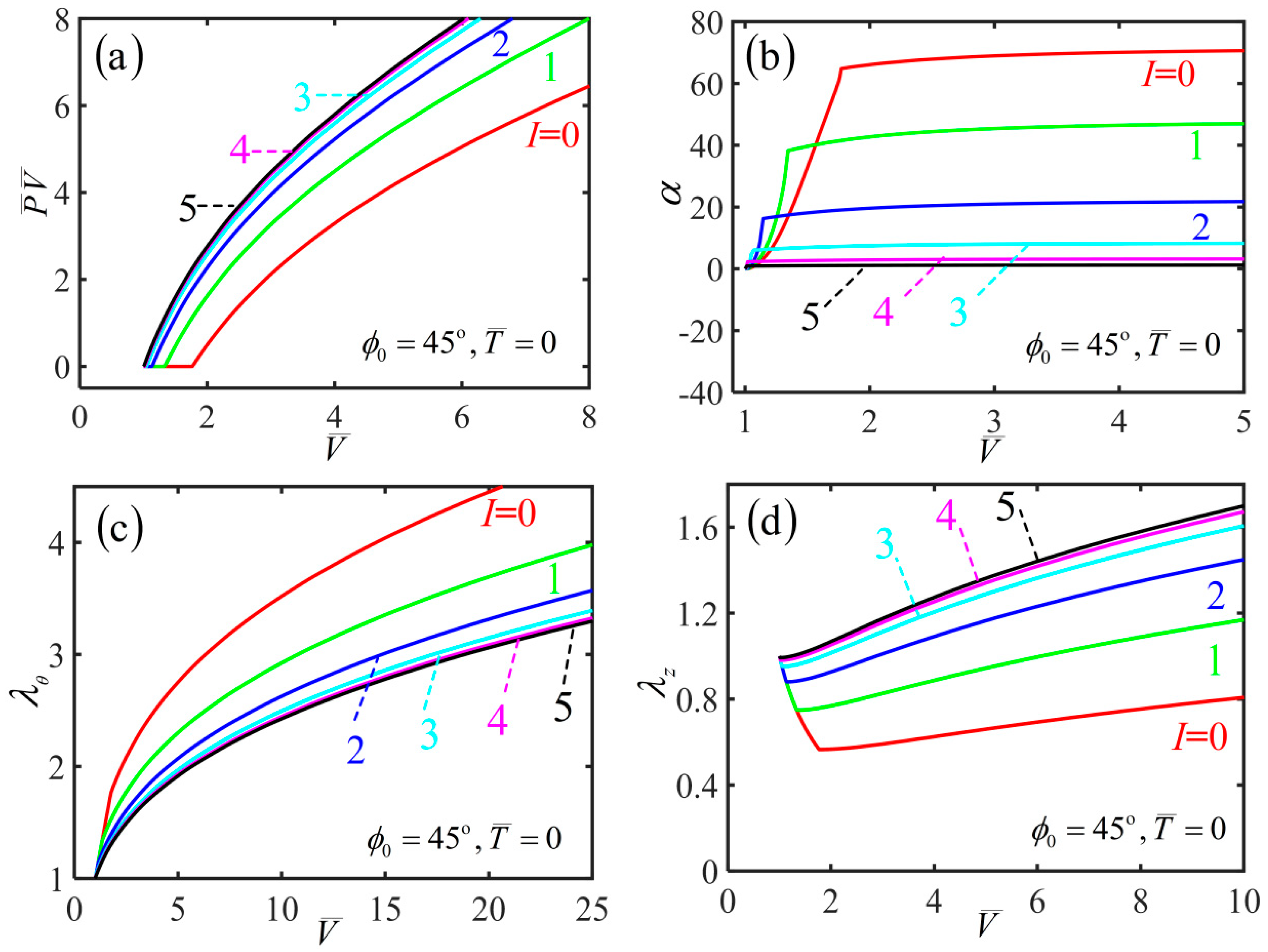
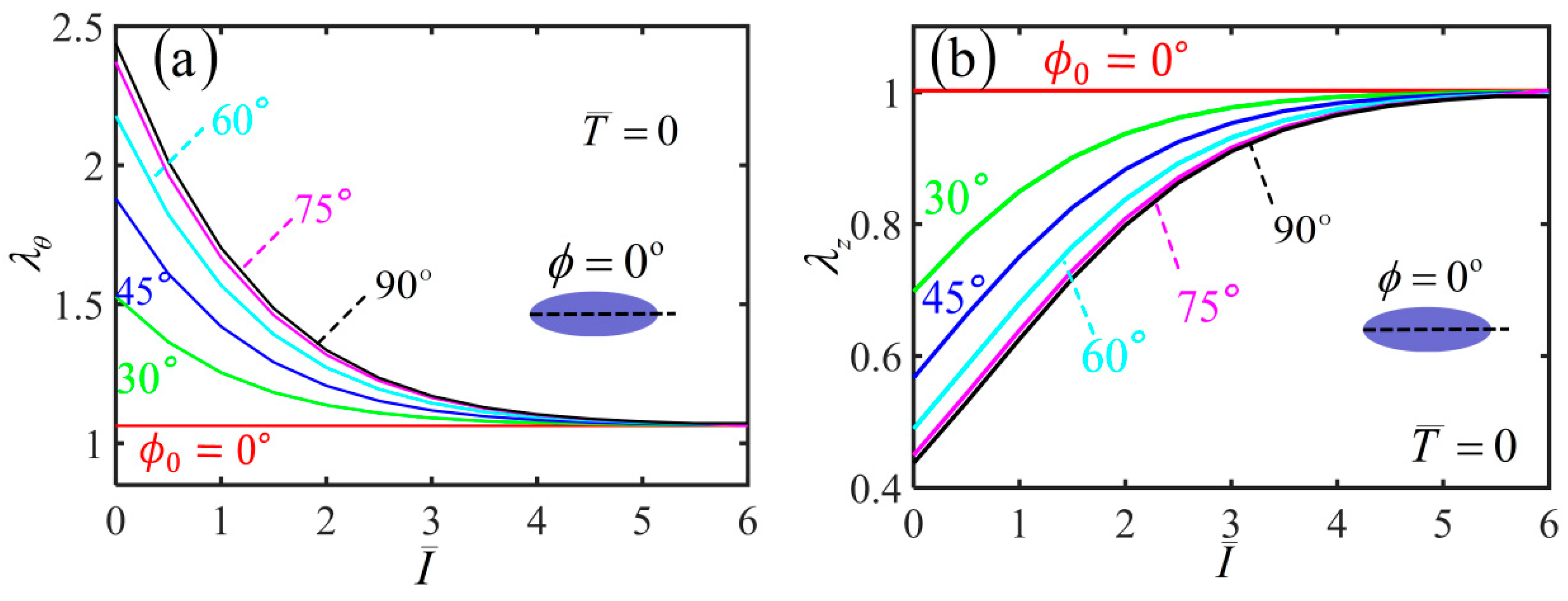
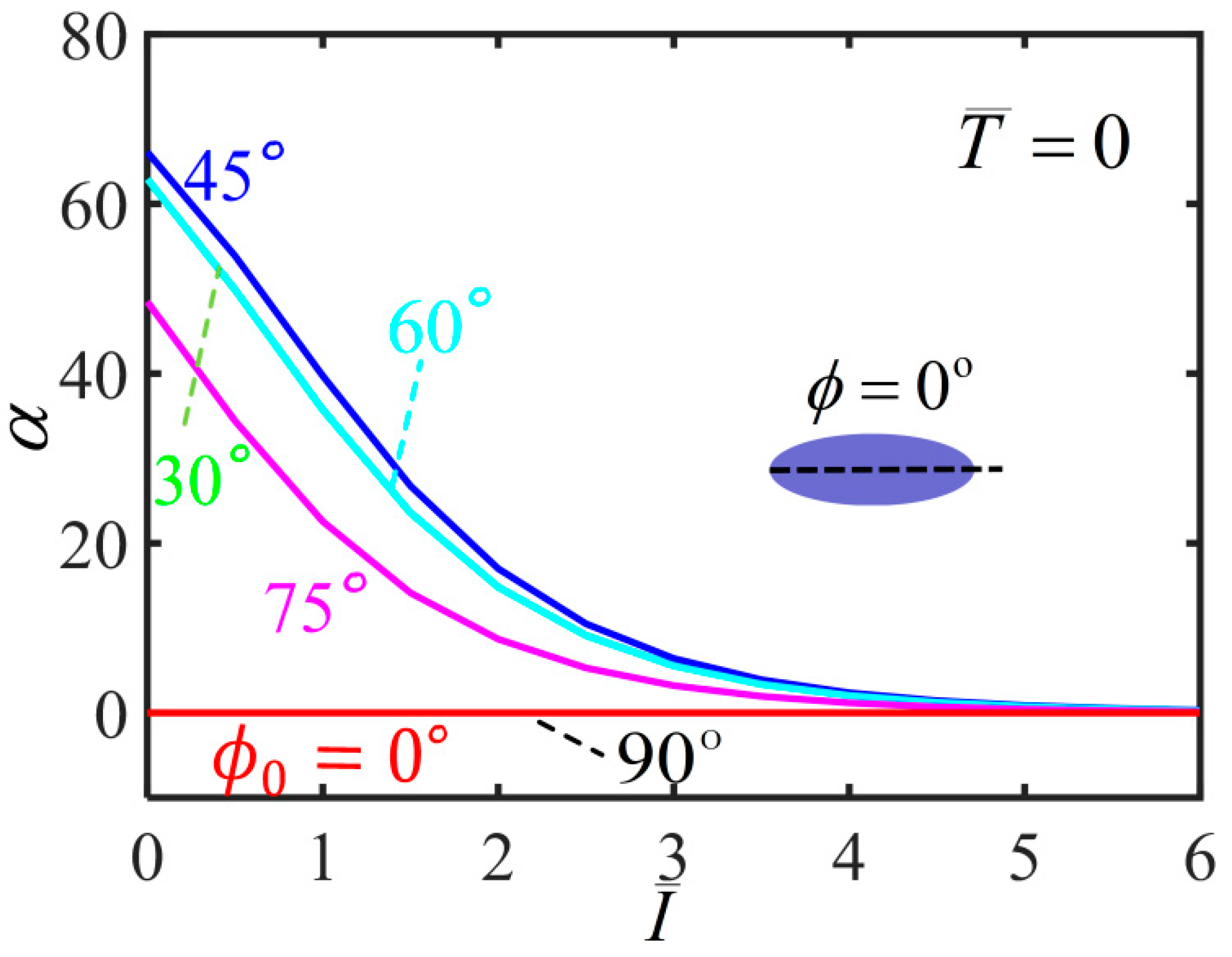
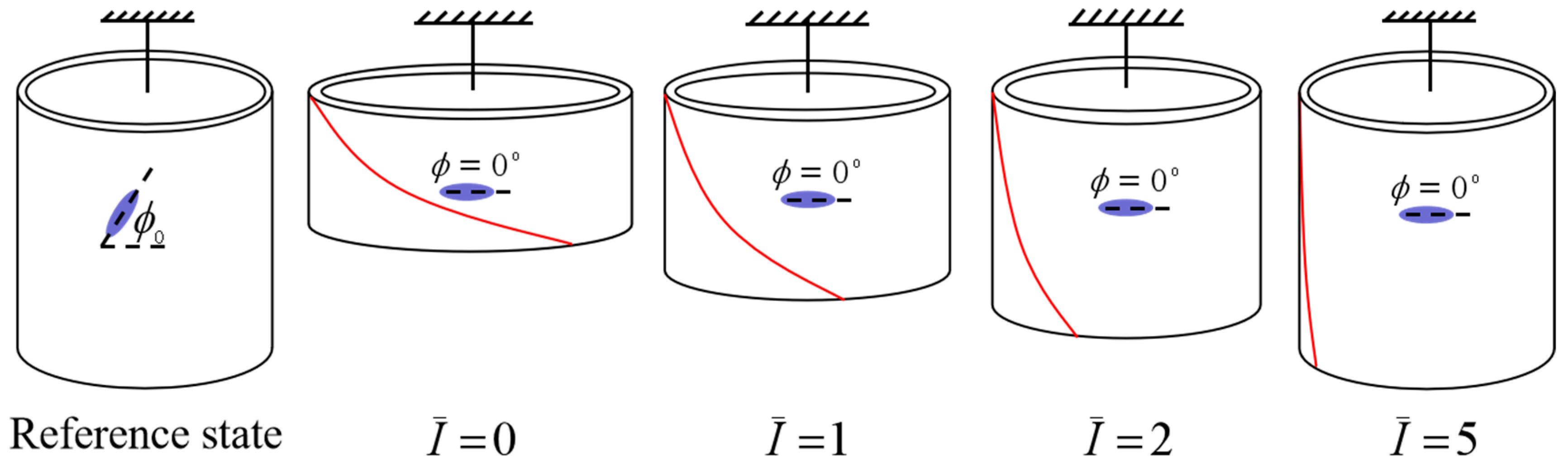
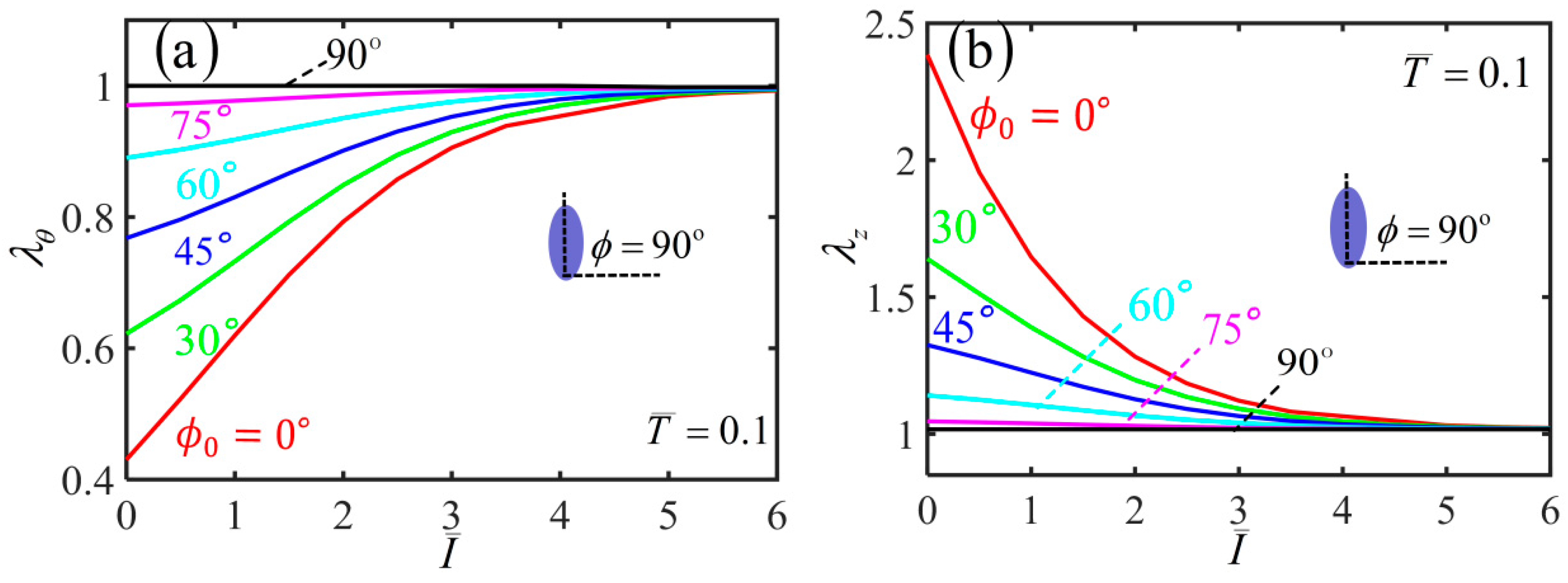
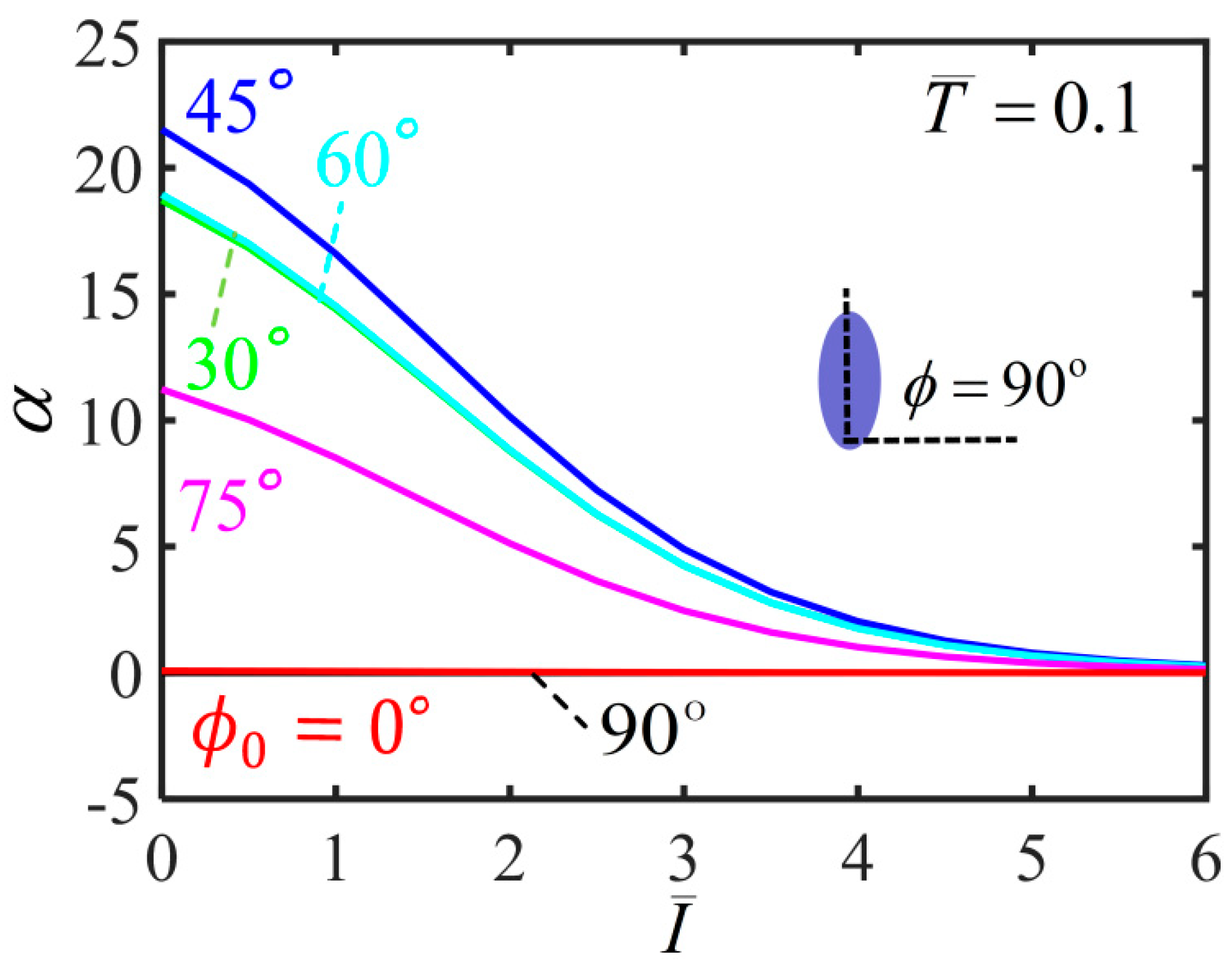
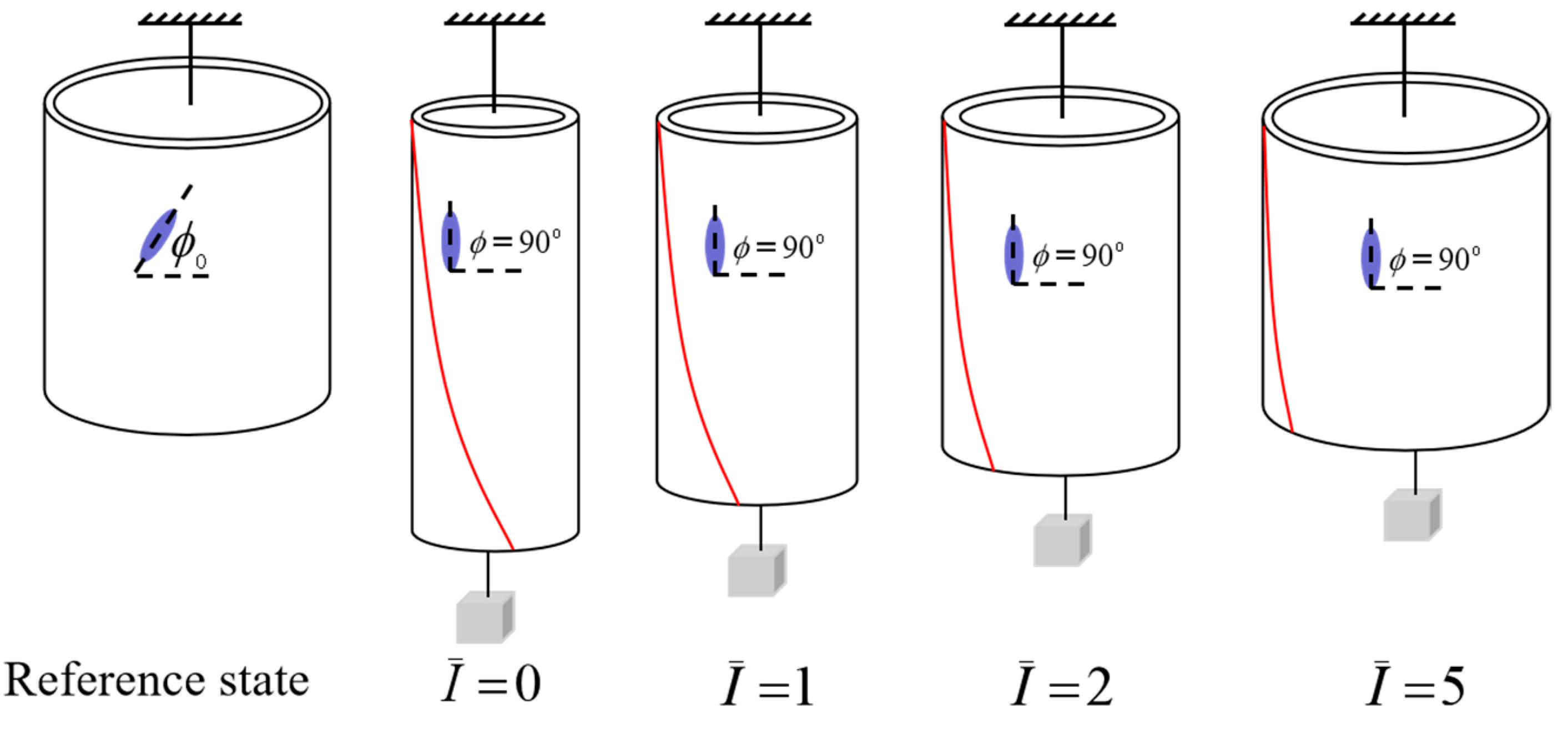
3. Light-Activated Contraction and Twisting of a Free-Standing Nematic Elastomer Balloon
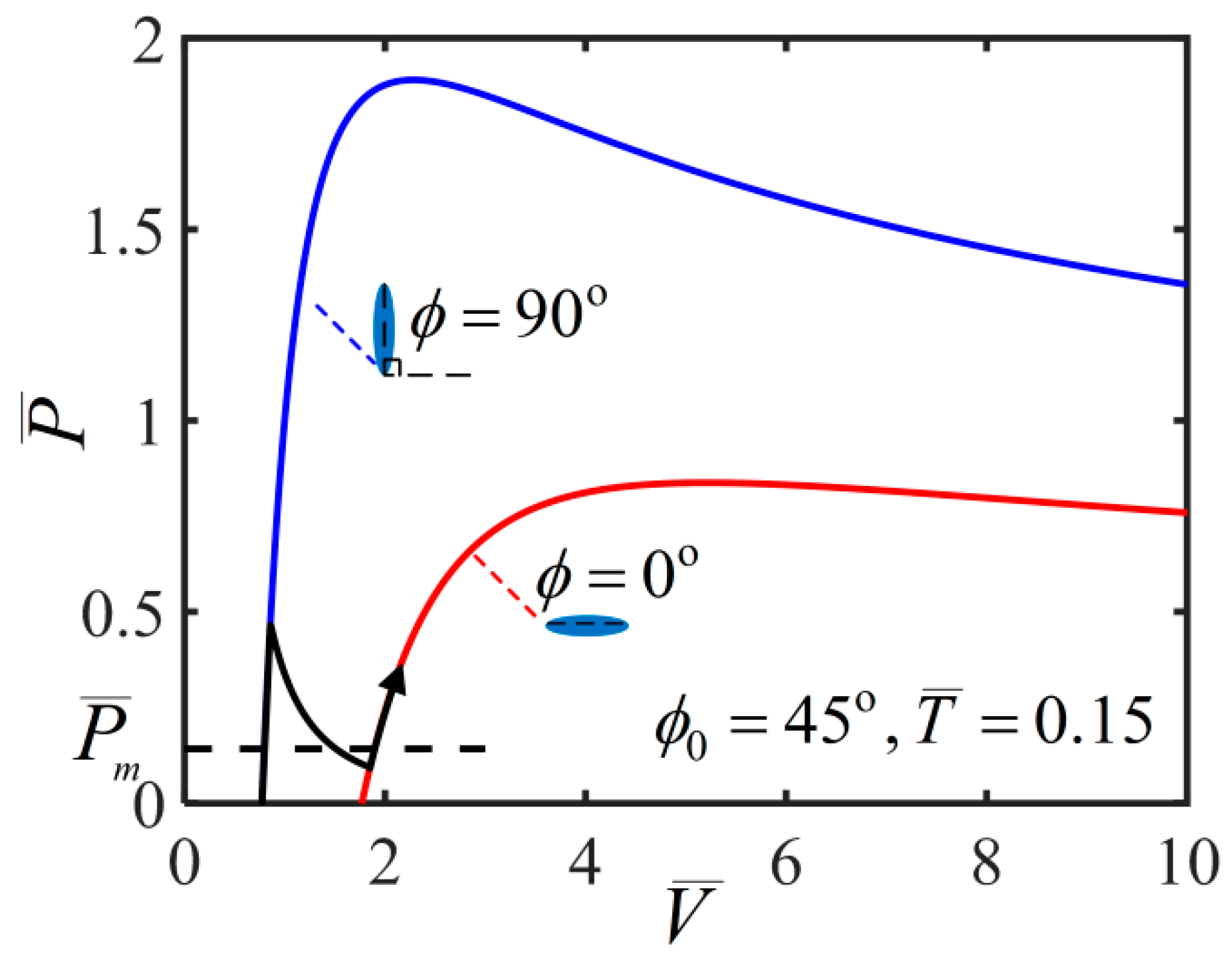
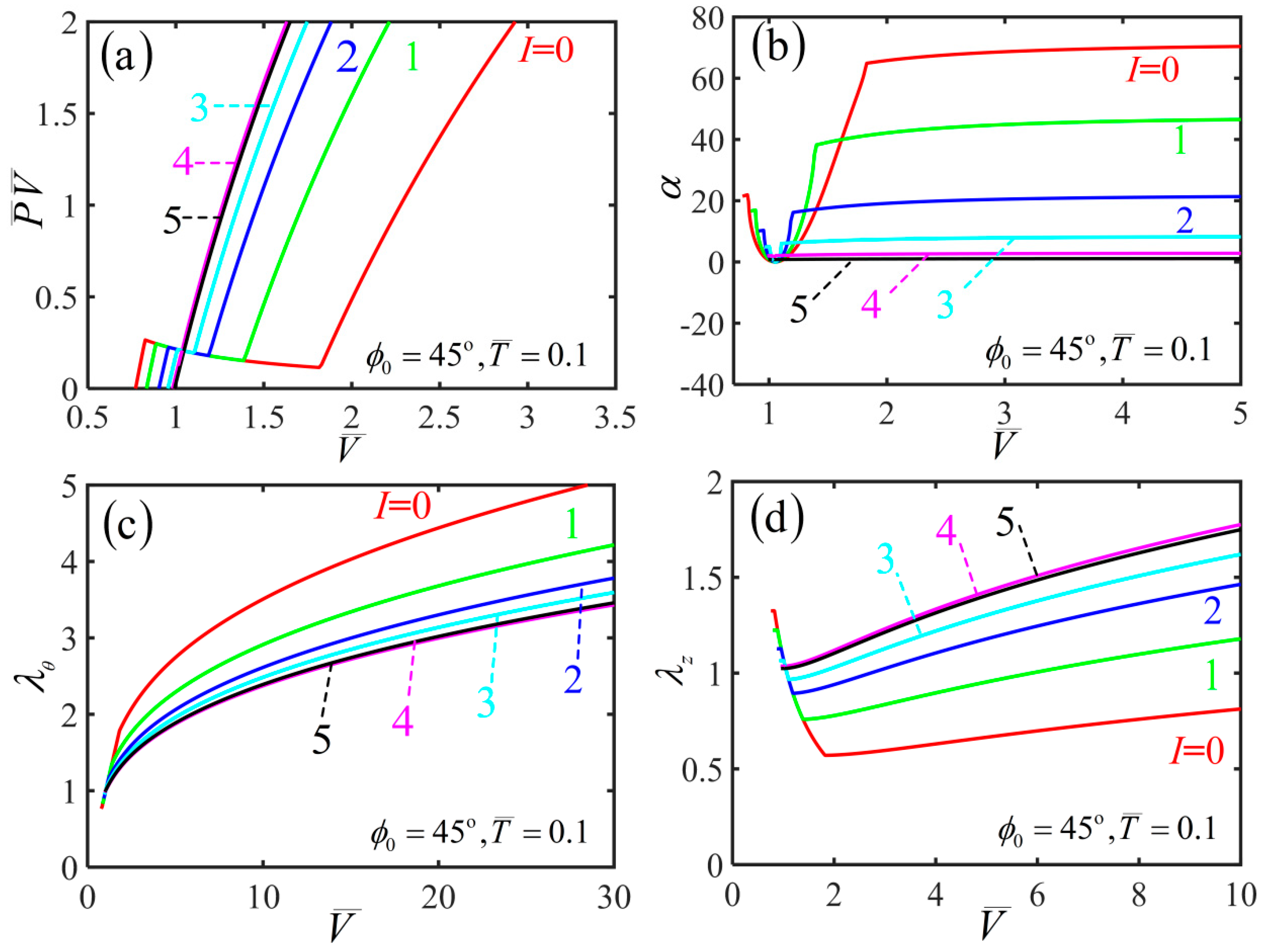
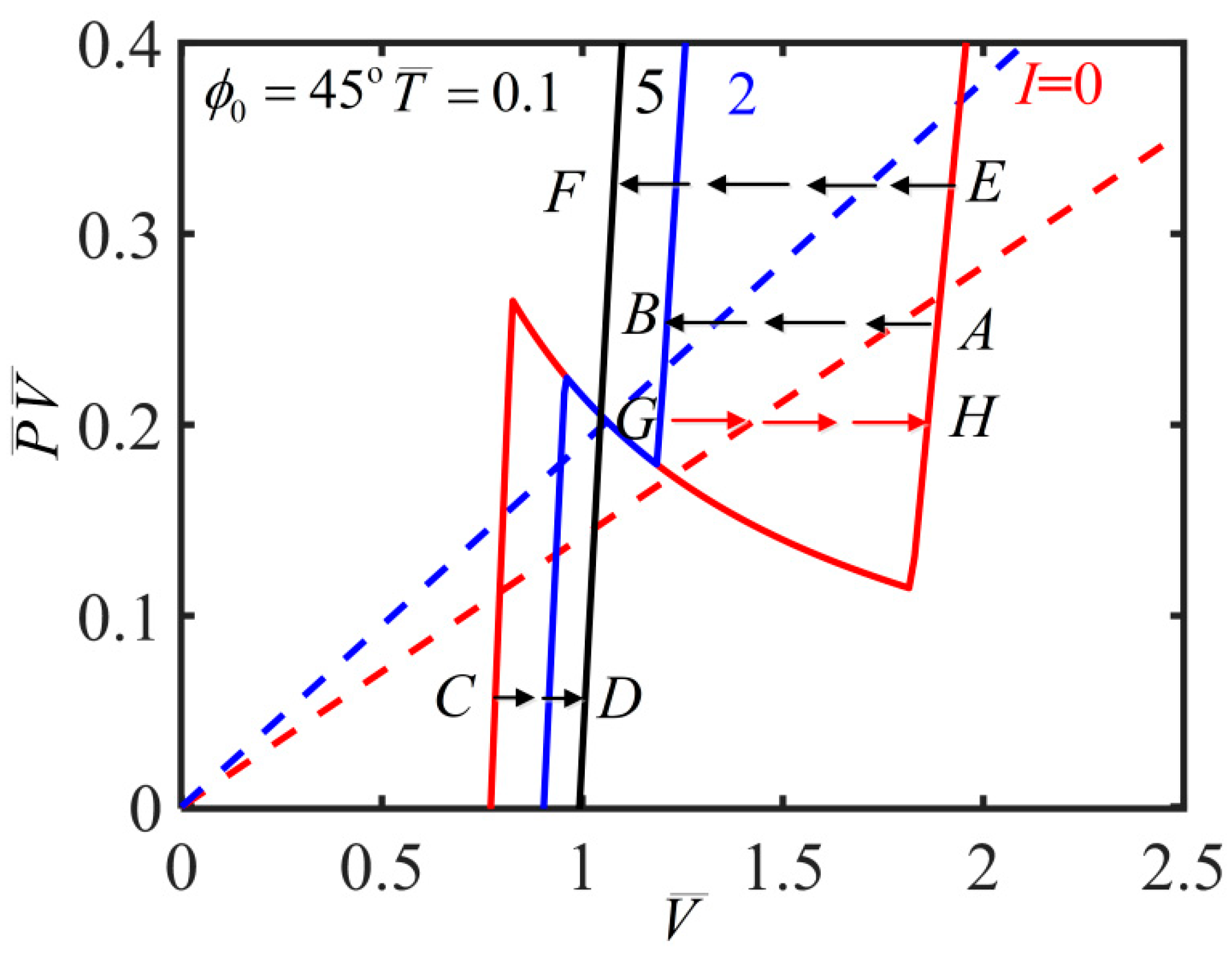
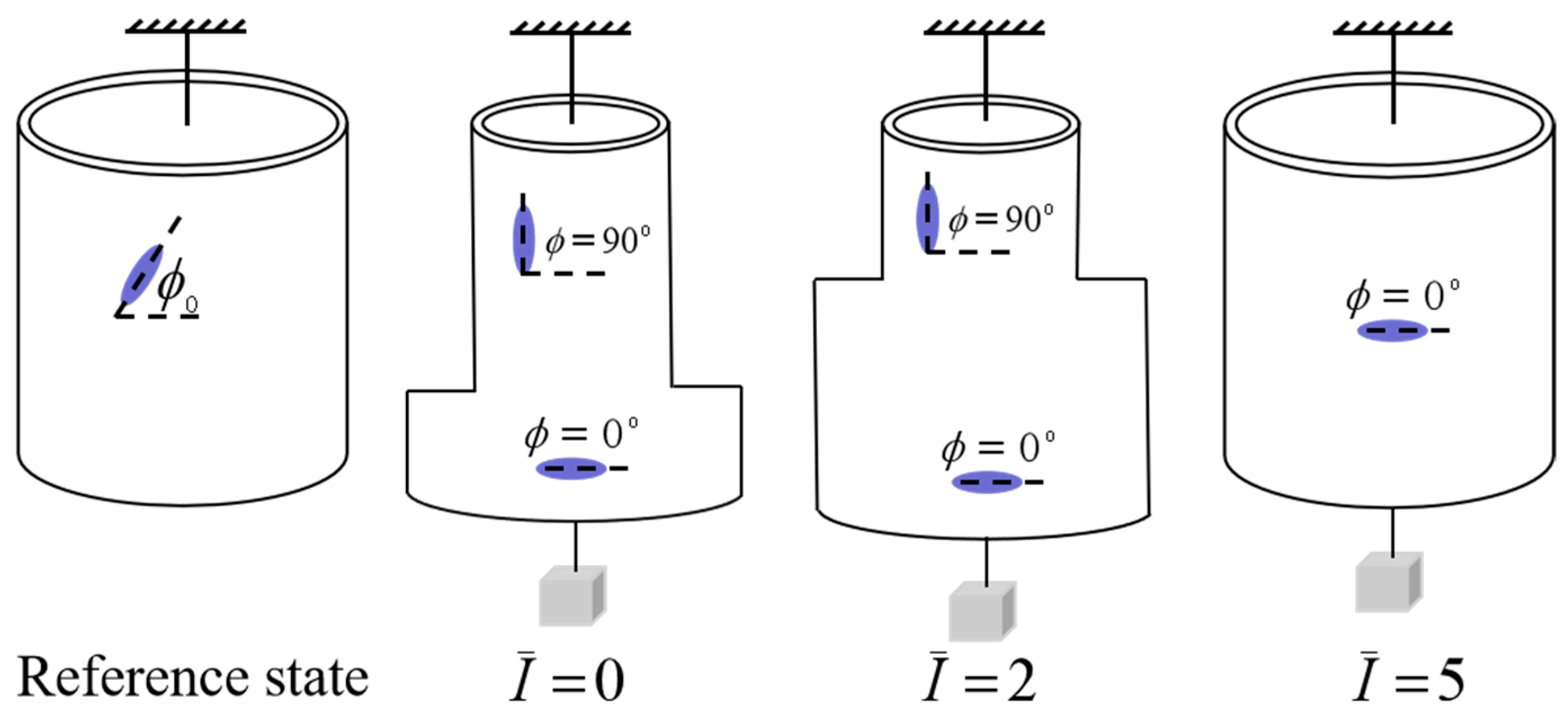
4. Light-Activated Contraction and Twisting of a Nematic Elastomer Balloon Subjected to External Axial Load
- (1)
- The case of small PV
- (2)
- The case of medium PV
- (3)
- The case of large PV
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Finkelmann, H.; Nishikawa, E.; Pereira, G.G.; Warner, M. A New Opto-Mechanical Effect in Solids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 015501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, M.; Terentjev, E.M. Liquid Crystal Elastomers; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Desimone, A. Energetics of fine domain structures. Ferroelectr. Statl. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 1999, 222, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Simone, A.; Dolzmann, G. Material instabilities in nematic elastomers. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 2000, 136, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finkelmann, H.; Kundler, I.; Terentjev, E.; Warner, M. Critical stripe-domain instability of nematic elas-tomers. Journal de Physique II 1997, 7, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cesana, P.; De Simone, A. Quasiconvex envelopes of energies for nematic elastomers in the small strain regime and applications. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2011, 59, 787–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, S.; De Simone, A.; Dolzmann, G. Semisoft elasticity and director reorientation in stretched sheets of nematic elastomers. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 66, 061710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, P.W.; Liu, C.H. Bio-Inspired Soft Proboscis Actuator Driven by Dielectric Elastomer Fluid Transduc-ers. Polymers 2019, 11, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Connolly, F.; Polygerinos, P.; Walsh, C.J.; Bertoldi, K. Mechanical programming of soft actuators by vary-ing fiber angle. Soft Robot. 2015, 2, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, L.; Xu, K.; Dong, Z.; Ding, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, P. Hydraulically Coupled Dielectric Elastomer Ac-tuators for a Bioinspired Suction Cup. Polymers 2021, 13, 3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, J.-E.; Quan, Y.-J.; Wang, W.; Rodrigue, H.; Song, S.-H.; Ahn, S.-H. A smart soft actuator using a single shape memory alloy for twisting actuation. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 125033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Chen, S.; Chen, F.; Zhu, X. A Unidirectional Soft Dielectric Elastomer Actuator Enabled by Built-In Honeycomb Metastructures. Polymers 2020, 12, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, B.; Zhao, J. A New Spiral-Type Inflatable Pure Torsional Soft Actuator. Soft Robot. 2018, 5, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, K.; Nagai, T.; Shintake, J. Dielectric Elastomer Fiber Actuators with Aqueous Electrode. Polymers 2021, 13, 4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; He, X.; Cai, S. Anomalous inflation of a nematic balloon. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2020, 142, 104013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudici, A.; Biggins, J.S. Giant deformations and soft-inflation in LCE balloons. EPL 2020, 132, 36001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, Y.H.; Choi, D.-S.; Kim, D.E.; Kim, S.-Y. Flexible Vibrotactile Actuator Based on Dielectric Elastomer for Smart Handheld Devices. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 12020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, E.; Sellers, S. Free-energy density functions for nematic elastomers. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2004, 52, 1671–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallock, A., II. Note on the instability of India-rubber tubes and balloons when distended by fluid pressure. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1891, 49, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chater, E.; Hutchinson, J.W. On the propagation of bulges and buckles. J. Appl. Mech. 1984, 51, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakides, S.; Yu-Chung, C. The initiation and propagation of a localized instability in an inflated elastic tube. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1991, 27, 1085–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestringant, C.; Audoly, B. A diffuse interface model for the analysis of propagating bulges in cylindrical balloons. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2018, 474, 20180333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, K.; Wang, Q.; Xu, P. Inflation-induced torsion and bulging of a nematic elastomer balloon. Thin-Walled Struct. 2021, 170, 108621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Guo, Z.; Zhou, L.; Li, L.; Fu, Y. An experimental study of localized bulging in inflated cylindrical tubes guided by newly emerged analytical results. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2019, 124, 536–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.B.; Liu, J.L.; Francisco, G.S. Localized bulging in an inflated cylindrical tube of arbitrary thick-ness-the effect of bending stiffness. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2016, 90, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Althobaiti, A.; Xie, Y.-X. Prevention of localized bulging in an inflated bilayer tube. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2019, 153-154, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Fried, E. Uniaxial nematic elastomers: Constitutive framework and a simple application. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2006, 462, 1295–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, W.; Dai, H.H. Bending-induced director reorientation of a nematic liquid crystal elastomer bonded to a hyperelastic substrate. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 129, 104701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, W.; Dai, H.-H. On a consistent finite-strain plate model of nematic liquid crystal elastomers. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2020, 145, 104169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Zhu, L.; Al-Kaysi, R.O.; Bardeen, C.J. Organic Photomechanical Materials. ChemPhysChem 2014, 15, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cviklinski, J.; Tajbakhsh, A.R.; Terentjev, E.M. UV isomerisation in nematic elastomers as a route to photo-mechanical transducer. Eur. Phys. J. E 2002, 9, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, X.; Tong, F.; Hanson, K.M.; Al-Kaysi, R.O.; Kitagawa, D.; Kobatake, S.; Bardeen, C.J. Hybrid or-ganic–inorganic photon-powered actuators based on aligned diarylethene nanocrystals. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Wasylczyk, P.; Wiersma, D.S.; Priimagi, A. Light robots: Bridging the gap between microrobot-ics and photomechanics in soft materials. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1703554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, M.; Bladon, P.; Terentjev, E.M. “Soft elasticity”-deformation without resistance in liquid crystal elastomers. J. Phys. II 1994, 4, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corbett, D.; Warner, M. Linear and Nonlinear Photoinduced Deformations of Cantilevers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 174302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, M.L. Photomechanics of mono- and polydomain liquid crystal elastomer films. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 102, 013506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Jin, L.; Huo, Y. Quasi-soft opto-mechanical behavior of photochromic liquid crystal elastomer: Linearized stress–strain relations and finite element simulations. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2012, 49, 2668–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kundler, I.; Finkelmann, H. Strain-induced director reorientation in nematic liquid single crystal elasto-mers. Macromol. Rapid Comm. 1995, 16, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fan, W.; He, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liang, X.; Cai, S. A simple and robust way towards reversible mechanochromism: Using liquid crystal elastomer as a mask. Extreme Mech. Lett. 2017, 11, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conti, S.; De Simone, A.; Dolzmann, G. Soft elastic response of stretched sheets of nematic elastomers: A numerical study. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2002, 50, 1431–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modes, C.D.; Bhattacharya, K.; Warner, M. Disclination-mediated thermo-optical response in nematic glass sheets. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 81, 060701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stenull, O.; Lubensky, T.C. Anomalous elasticity of nematic elastomers. Eur. Lett. 2003, 61, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hogan, P.M.; Tajbakhsh, A.R.; Terentjev, E.M. UV manipulation of order and macroscopic shape in ne-matic elastomers. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 65, 041720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Nakano, M.; Ikeda, T. Directed bending of a polymer film by light. Nature 2003, 425, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuenstler, A.S.; Hayward, R.C. Light-induced shape morphing of thin films. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 40, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J. Photomechanical effects in liquid crystalline polymer networks and elastomers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2018, 56, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Yan, Y.; Huo, Y. A gradient model of light-induced bending in photochromic liquid crystal elasto-mer and its nonlinear behaviors. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 2010, 45, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Bhattacharya, K. Photomechanical coupling in photoactive nematic elastomers. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2020, 144, 104115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zheng, Y.; He, Q.; Cai, S. Uniaxial tension of a nematic elastomer with inclined mesogens. Extreme Mech. Lett. 2020, 40, 100936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bladon, P.; Terentjev, E.M.; Warner, M. Transitions and instabilities in liquid crystal elastomers. Phys. Rev. E 1993, 47, R3838–R3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivlin, R.S. Large elastic deformations of isotropic materials VI. Further results in the theory of torsion, shear and flexure. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1949, 242, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericksen, J.L. Deformations possible in every isotropic, incompressible, perfectly elastic body. Zeitschrift für angewandte Mathematik und Physik 1954, 5, 466–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, V.; Bhattacharya, K. Actuation of cylindrical nematic elastomer balloons. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 129, 114701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


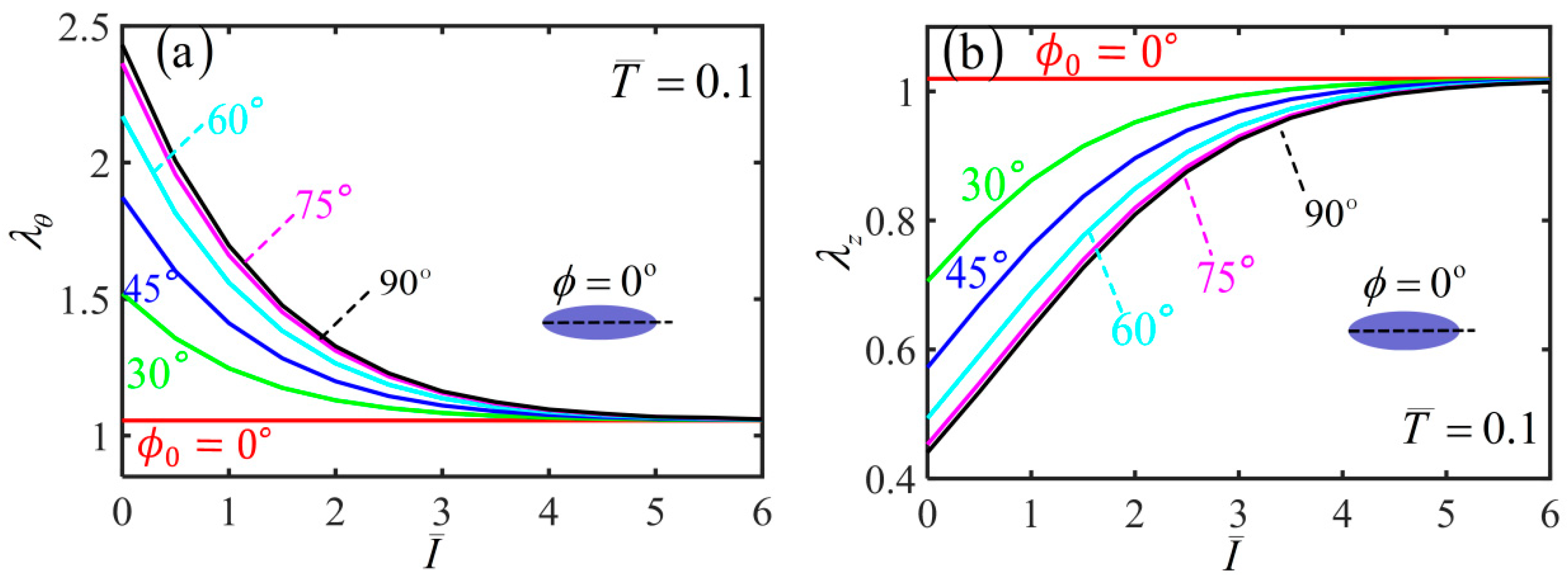
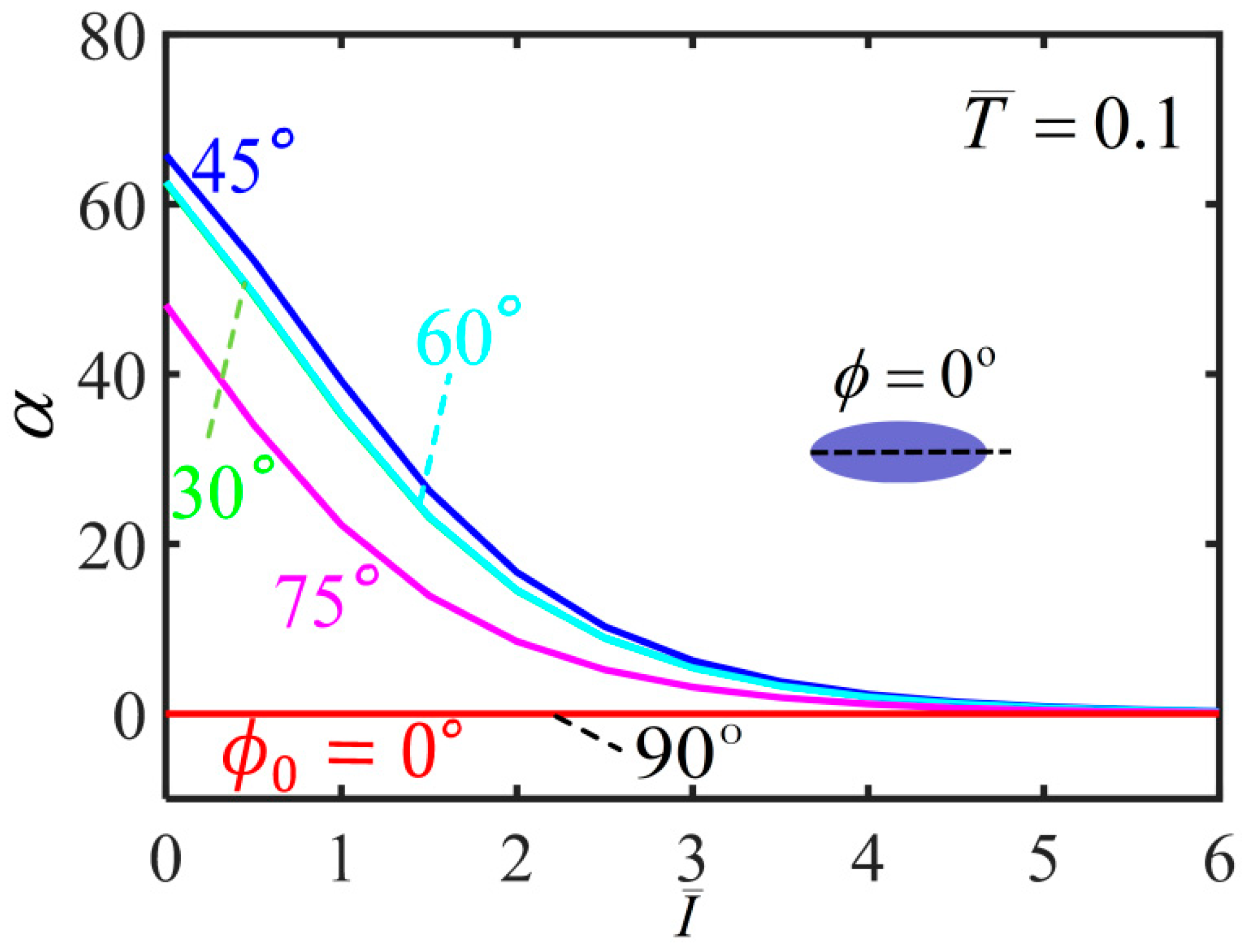
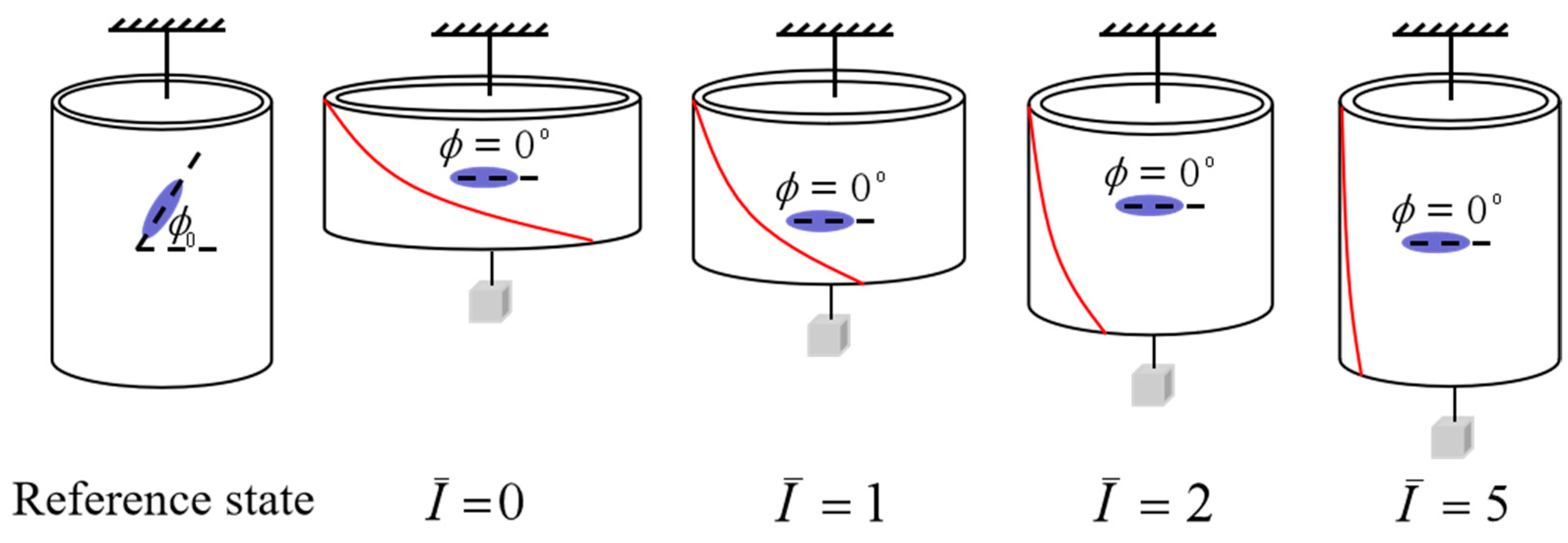
| Parameter | Definition | Value | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| axial load | 0~10 | N | |
| inflating pressure | 0~100 | kPa | |
| the length of the balloon | 100 | mm | |
| the cross-section diameter | 10 | mm | |
| the thickness | 1 | mm | |
| initial mesogen angle | 0~90 | ° | |
| light intensity | 0~10,000 | W/m2 | |
| Light-dependent material parameter | 1~5.26 | - | |
| shear modulus | 0.7 | MPa |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, K. Light-Activated Elongation/Shortening and Twisting of a Nematic Elastomer Balloon. Polymers 2022, 14, 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14061249
Zhou L, Wang Y, Li K. Light-Activated Elongation/Shortening and Twisting of a Nematic Elastomer Balloon. Polymers. 2022; 14(6):1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14061249
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Lin, Yujie Wang, and Kai Li. 2022. "Light-Activated Elongation/Shortening and Twisting of a Nematic Elastomer Balloon" Polymers 14, no. 6: 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14061249
APA StyleZhou, L., Wang, Y., & Li, K. (2022). Light-Activated Elongation/Shortening and Twisting of a Nematic Elastomer Balloon. Polymers, 14(6), 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14061249







