Physicochemical and Photocatalytic Properties of 3D-Printed TiO2/Chitin/Cellulose Composite with Ordered Porous Structures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of 3D-Printed Photocatalysts
2.2.1. Preparation of TiO2 Nanoparticles
2.2.2. Dissolution of Cellulose in NMMO
2.2.3. 3D Printing of TiO2/Chitin/Cellulose
2.3. Characterization and Instruments
2.4. Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue (MB)
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of 3D-Printed TiO2/Chitin/Cellulose Photocatalysts
3.1.1. Morphological Studies of the Printed TiO2/Chitin/Cellulose Photocatalysts
3.1.2. XRD Analyses
3.1.3. BET Analyses
3.1.4. FT-IR Spectra of 3D-Printed TiO2/Chitin/Cellulose Photocatalysts
3.2. Mechanical Tests
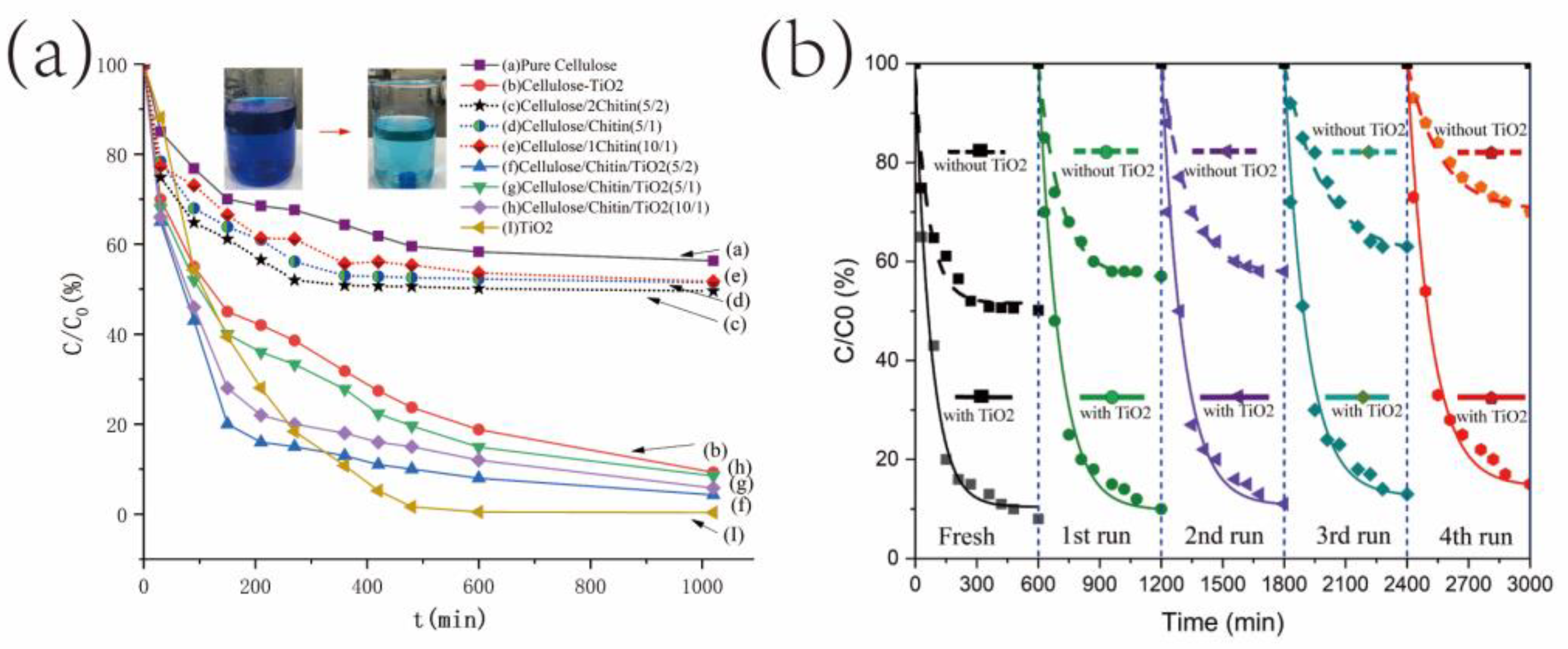
3.3. Photocatalytic Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoffmann, F.; Cornelius, M.; Morell, J.; Froba, M. Silica-based mesoporous organic-inorganic hybrid materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 3216–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Yang, J.; Qi, D.; Sonar, P.; Liu, L.; Lou, Z.; Shen, G.; Wei, Z. Flexible sensors based on organic-inorganic hybrid materials. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2000998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufaud, V.; Davis, M.E. Design of heterogeneous catalysts via multiple active site positioning in organic-inorganic hybrid materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 9403–9413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemm, D.; Kramer, F.; Moritz, S.; Lindstrom, T.; Ankerfors, M.; Gray, D.; Dorris, A. Nanocelluloses: A new family of nature-based materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5438–5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirajudheen, P.; Poovathumkuzhi, N.C.; Vigneshwaran, S.; Chelaveettil, B.M.; Meenakshi, S. Applications of chitin and chitosan based biomaterials for the adsorptive removal of textile dyes from water—A comprehensive review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 273, 118604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, J.; Du, Y. Morphology and Properties of Cellulose/Chitin Blends Membranes from NaOH/Thiourea Aqueous Solution. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 86, 2025–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.N.; Paul, U.; Heredia-Guerrero, J.A.; Liakos, I.; Marras, S.; Scarpellini, A.; Ayadi, F.; Athanassiou, A.; Bayer, I.S. Transparent and flexible amorphous cellulose-acrylic hybrids. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 287, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaraju, B.; Imae, T.; Destaye, A.G. Ag nanoparticle-immobilized cellulose nanofibril films for environmental conservation. Appl. Catal. A–Gen. 2015, 492, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Liu, S.L.; Cai, J.; Zhang, L. TiO2 Immobilized in Cellulose Matrix for Photocatalytic Degradation of Phenol under Weak UV Light Irradition. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 7806–7811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobjork, D.; Osterbacka, R. Paper electronics. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 1935–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Swatloski, R.P.; Maxim, M.L.; Rahman, M.; Harland, A.G.; Haque, A.; Spear, S.K.; Daly, D.T.; Rogers, R.D. Magnetite-embedded cellulose fibers prepared from ionic liquid. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, S.J.; Choi, E.S.; Lee, E.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, S.Y. Eco-friendly cellulose nanofiber paper-derived separator membranes featuring tunable nanoporous network channels for lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 16618–16626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, H.P.; Weigel, P.; Purz, H.J.; Ganster, J. Structure of formation of regenerated cellulose materials from NMMO-solutions. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2001, 26, 1473–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swatloski, R.P.; Spear, S.K.; Holbrey, J.D.; Rogers, R.D. Dissolution of Cellulose with Ionic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 4974–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Zhang, L. Rapid Dissolution of Cellulose in LiOH/Urea and NaOH/Urea Aqueous Solutions. Macromol. Biosci. 2005, 5, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.L.; Lin, D.Q.; Yao, S.J.; Zhu, Z.Q. Preparation of an anion exchanger based on TiO2-densified cellulose beads forexpanded bed adsorption. React. Funct. Polym. 2005, 62, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.M.K.; Ganesan, K.; Milow, B.; Ratke, L. The effect of zinc oxide (ZnO) addition on the physical and morphological properties of cellulose aerogel beads. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 90193–90201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Wan, C.; Li, J. Room-temperature embedment of anatase titania nanoparticles into porous cellulose aerogels. Appl. Catal. A–Gen. 2015, 120, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, R.T.; Samir, M.A.S.A.; Salzar-Alvarez, G.; Belova, L.; Strom, V.; Berglumd, L.A.; Ikkala, O.; Nogues, J.; Gedde, U.W. Making flexible magnetic aerogels and stiff magnetic nanopaper using cellulose nanofibrils as templates. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.W.; Feng, J.C.; Wu, P.Y. Graphene-Oxide-Sheet-Induced Gelation of Cellulose and Promoted Mechanical Properties of Composite Aerogels. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 8063–8068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Jiao, Y.; Sun, Q.F.; Li, J. Preparation, Characterization, and antibacterial properties of silver nanoparticles embedded into cellulose aerogels. Polym. Compos. 2016, 37, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asahi, R.; Morikawa, T.; Ohwaki, T.; Aoki, K.; Taga, Y. Visible-Light Photocatalysis in Nitrogen-Doped Titanium Oxides. Science 2001, 293, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, M.E.; Sierra, M.; Mendez-Ramos, J.; Acosta-Mora, P.; Ruiz-Morales, J.C.; Esparza, P. Solar degradation of contaminants in water: TiO2 solar photocatalysis assisted by up-conversion luminescent materials. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2016, 155, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, T.E.; Regmi, C.; Schafer, A.I.; Richards, B.S. Photocatalytic degradation of organic dye via atomic layer deposited TiO2 on ceramic membranes in single-pass flow-through operation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 604, 118015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, W.S.; Daoud, W.A. Self-cleaning fibers via nanotechnology: A virtual reality. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 7858–7869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, K.; Xin, J.H.; Dauud, W.A. Functionalizing polyester fiber with a self-cleaning property using anatase TiO2 and low-temperature plasma treatment. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2007, 4, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, K.; Daoud, W.A.; Xin, J.H.; Mark, C.L.; Tang, W.Z.; Cheug, W.P. Self-cleaning cotton. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 4567–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushnie, T.P.T.; Robertson, P.K.J.; Officer, S.; Pollar, P.M.; Prabhu, R.; McCullagh, C.; Robertson, J.M.C. Photobactericidal effects of TiO2 thin films at low temperatures—A preliminary study. J. Photochem. Photbiol. A Chem. 2010, 216, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, H.; Zhao, Y.; Tan, T. Antimicrobial activities of hydrophilic polyurethane/titanium dioxide complex film under visible light irradiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2008, 199, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, Q.; Shu, S.; Xie, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, B.; Dong, W. Preparation and Characterization of regenerated cellulose/TiO2/ZnO nanocomposites and its photocatalytic activity. Mater. Lett. 2014, 117, 234–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortelli, S.; Blosi, M.; Albonetti, S.; Vaccari, A.; Dondi, M.; Costa, A.L. TiO2 based nano-photocatalysis immobilized on cellulose substrates. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2014, 276, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Ul-Islam, M.; Khattak, W.A.; Ullah, M.W.; Park, J.K. Bacterial cellulose-titanium dioxide nanocomposites: Nanostructural characteristics, antibacterial mechanism, and biocompatibility. Cellulose 2015, 22, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.J.; Cesano, F.; Bonino, F.; Bordiga, S.; Spoto, G.; Scarano, D.; Zecchina, A. Photoactive TiO2 films on cellulose fibres: Synthesis and characterization. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2007, 189, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaoka, S.; Hamasaki, Y.; Ishihara, S.; Nagata, M.; Iio, K.; Nagasawa, C.; Ihara, H. Preparation of carbon/TiO2 microsphere composites from cellulose/TiO2 microsphere composites and their evaluation. J. Mol. Catal. A–Chem. 2002, 177, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Bai, H.; Zhao, Y.; Kang, S.; Yi, H.; Zhang, T.; Song, S. Synthesis of chitosan cross-linked 3D network-structured hydrogel for methylene blue removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 141, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Koura, Z.; Cazzanelli, M.; Bazzanella, N.; Patel, N.; Fernandes, R.; Arnaoutakis, G.E.; Gakamsky, A.; Dick, A.; Quaranta, A.; Miotello, A. Synthesis and characterization of Cu and N codoped RF-Sputtered TiO2 films: Photoluminescence Dynamics of Charge Carriers Relevant for Water Splitting. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 12042–12050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arularasu, M.V.; Harb, M.; Sundaram, R. Synthesis and characterization of cellulose/TiO2 nanocomposite: Evaluation of in vitro antibacterial and in silico molecular docking studies. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 249, 116868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.X.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Z.; Han, W.; Qiu, W.; Zhao, T. Bacterial cellulose derived monolithic titania aerogel consisting of 3D reticulate titania nanofibers. Cellulose 2018, 25, 7189–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saheed, I.O.; Oh, W.D.; Suah, F.B.M. Chitosan modifications for adsorption of pollutants—A review. J. Hazard Mater. 2021, 408, 124889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Ma, B.; Sun, J. The preparation and properties of cellulose/chitin blend filaments. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 2777–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rais, M.H.; Li, Y.; Ahmed, I. Dynamic-thermal and localized filament-kinetic attacks on fused filament fabrication based 3D printing process. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 46, 102200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubio, C.R.; Guitian, F.; Gil, A. Fabrication of ZnO periodic structures by 3D printing. J. Eur Ceram. Soc. 2016, 36, 3409–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, D.S.P.; Piccin, J.S.; Lima, E.C.; Dotto, G.L. Interpretations about methylene blue adsorption by surface modified chitin using the statical physics treatment. Adsorption 2015, 21, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Ihara, K.; Aita, Y.; Komatsu, M.; Sato, T. Visible-light induce photocatalytic activity of TiO2-xAy (A = N, S) prepared by precipitation route. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2006, 179, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurkan, M.V.; Voronkina, A.; Khrunyk, Y.; Wysokowski, M.; Petrenko, I.; Ehrlich, H. Progress in chitin analytics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 252, 117204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, H.P.; Hofmann, D.; Philipp, B. Some aspects of lateral chain order in cellulosics from X-ray scattering. Cellulose 1995, 2, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Kim, J.H.; Li, Y.; Kim, J. Alignment of cellulose chains of regenerated cellulose by corona poling and its piezoelectricity. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 083301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rongpipi, S.; Ye, D.; Gomez, E.D.; Gomez, E.W. Progress and opportunities in the characterization of cellulose—An important regulator of cell wall growth and mechanics. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, L.; Creely, J.; Martin, A.; Conrad, C. An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of Native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Text. Res. J. 1959, 29, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Chang, C.; Zhang, L. Efficient adsorption of Hg2+ iions on chitin/cellulose composite membranes prepared via environmentally friendly pathway. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 173, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavillon, R.; Budtova, T. Aerocellulose: New highly porous prepared from cellulose-NaOH aqueous solutions. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebner, F.; Potthast, A.; Rosenau, T.; Haimer, E.; Wendland, M. Cellulose aerogels: Highly porous, ultra-lightweight materials. Holzforschung 2008, 62, 129–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebner, F.; Haimer, E.; Potthast, A.; Loidl, D.; Tschegg, S.; Neouze, M.A.; Wendland, M.; Rosenau, T. Cellulosic aerogels as ultra-lightweight materials. Part 2: Synthesis and properties. Holzforschung 2009, 63, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neil, A.R.G.; Goodday, G.W.; Russell, J.D.; Wilson, M.J. Infrared and X-ray diffraction data on chitins of variable structure. Carbohydr. Res. 1987, 165, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X. Hydrophilic modification of cellulose nanocrystals improves the physicochemical properties of cassava starch-based nanocomposite films. LWT 2017 86, 318–326. [CrossRef]
- Biswal, D.R.; Singh, R.P. Characterisation of carboxymethyl cellulose and polyacrylamide graft copolymer. Carboghydr. Polym. 2004, 57, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ruan, D.; Zhou, J. Structure and Properties of Regenerated Cellulose Films Prepared from Cotton Linters in NaOH/Urea Aqueous Solution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 5923–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, Y. 3D bioprinting of cellulose with controlled porous structures from NMMO. Mater. Lett. 2018, 210, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suligoj, A. Synergism in TiO2 photocatalytic ozonation for the removal of dichloroacetic acid and thiacloprid. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 110982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
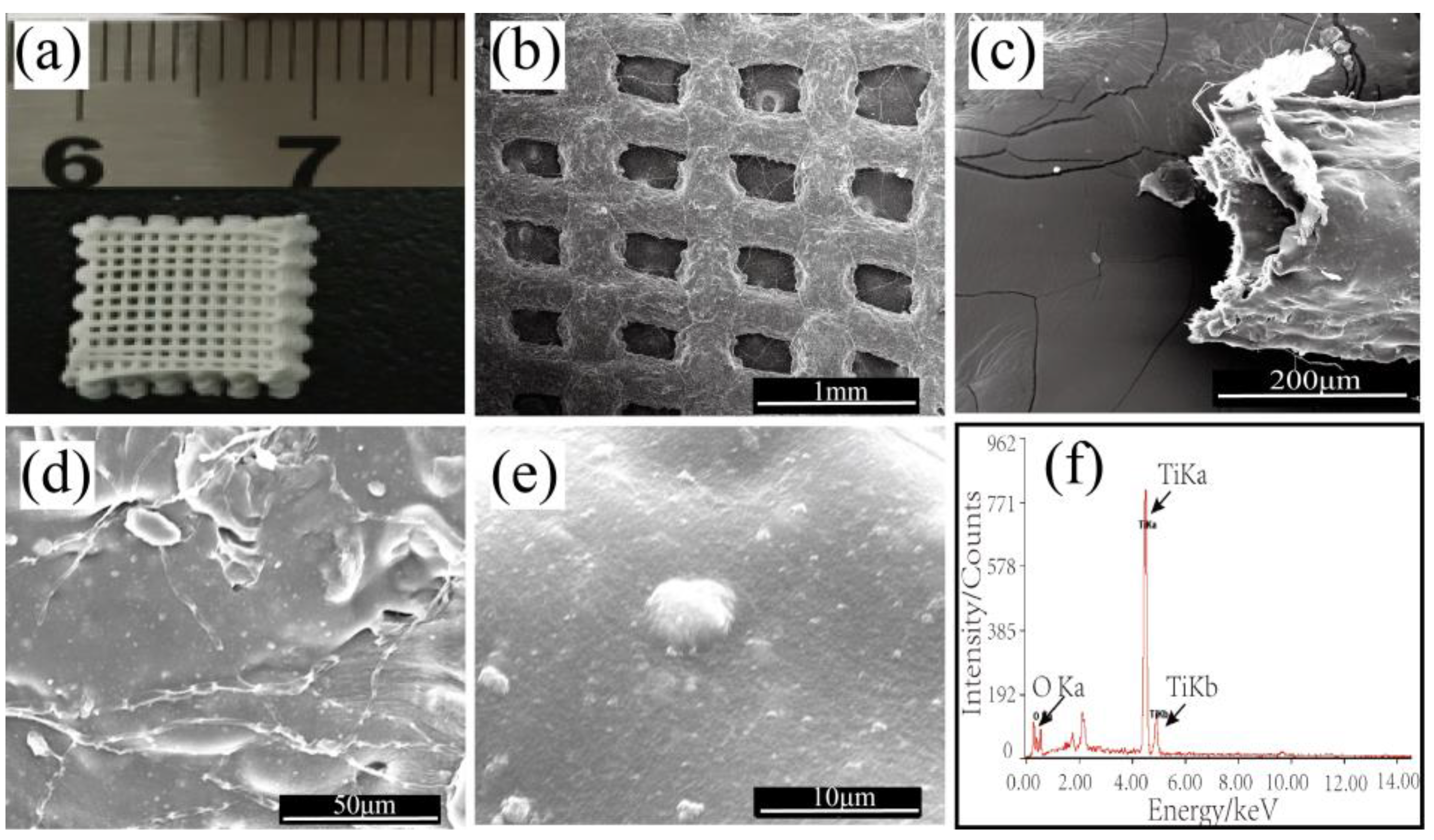
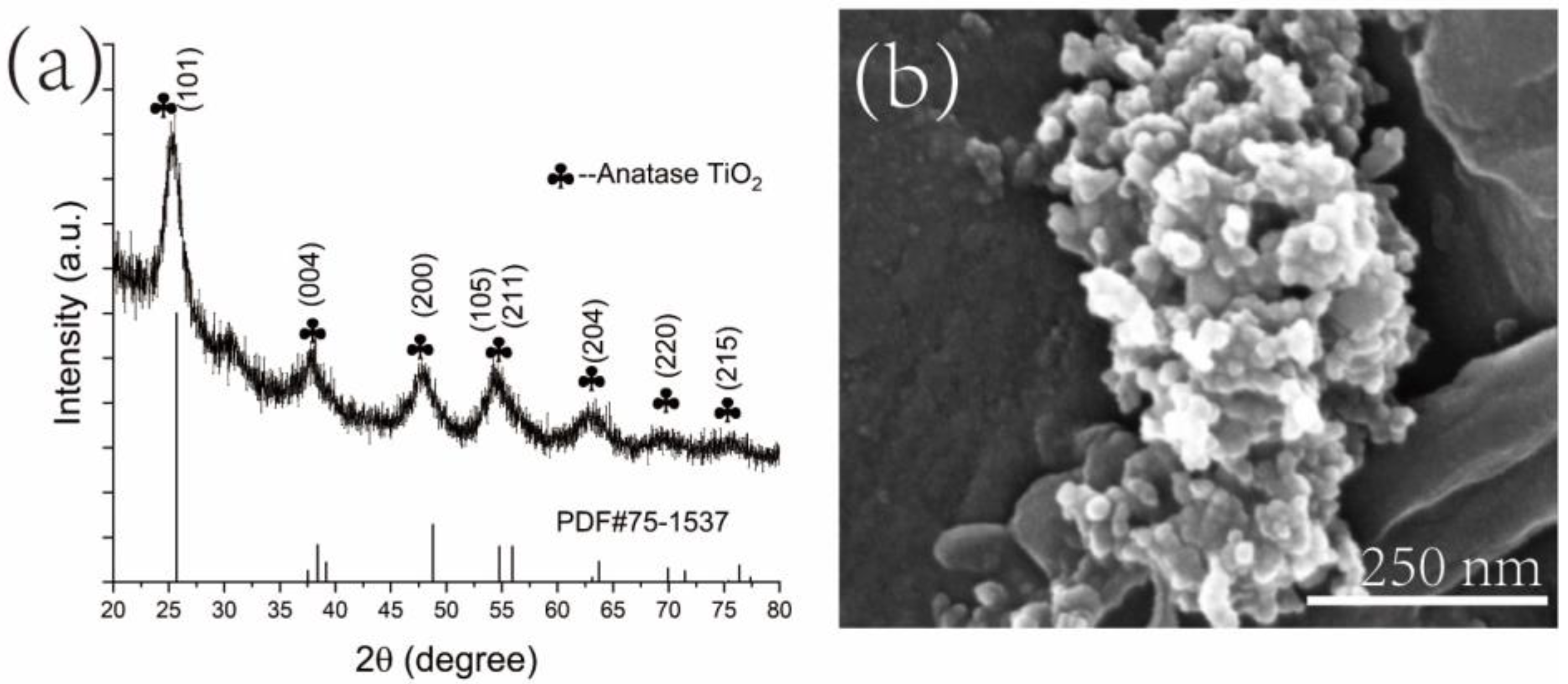
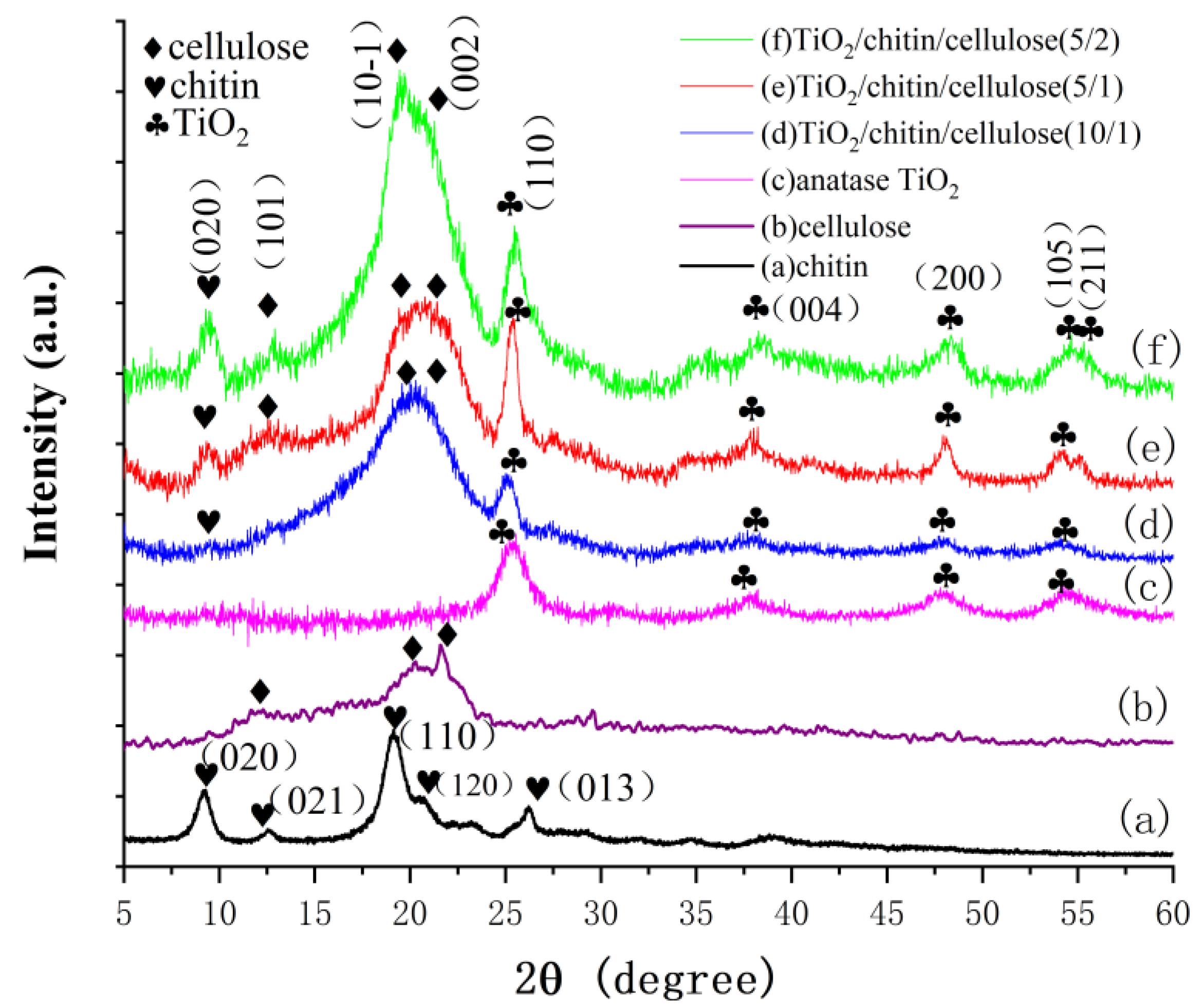


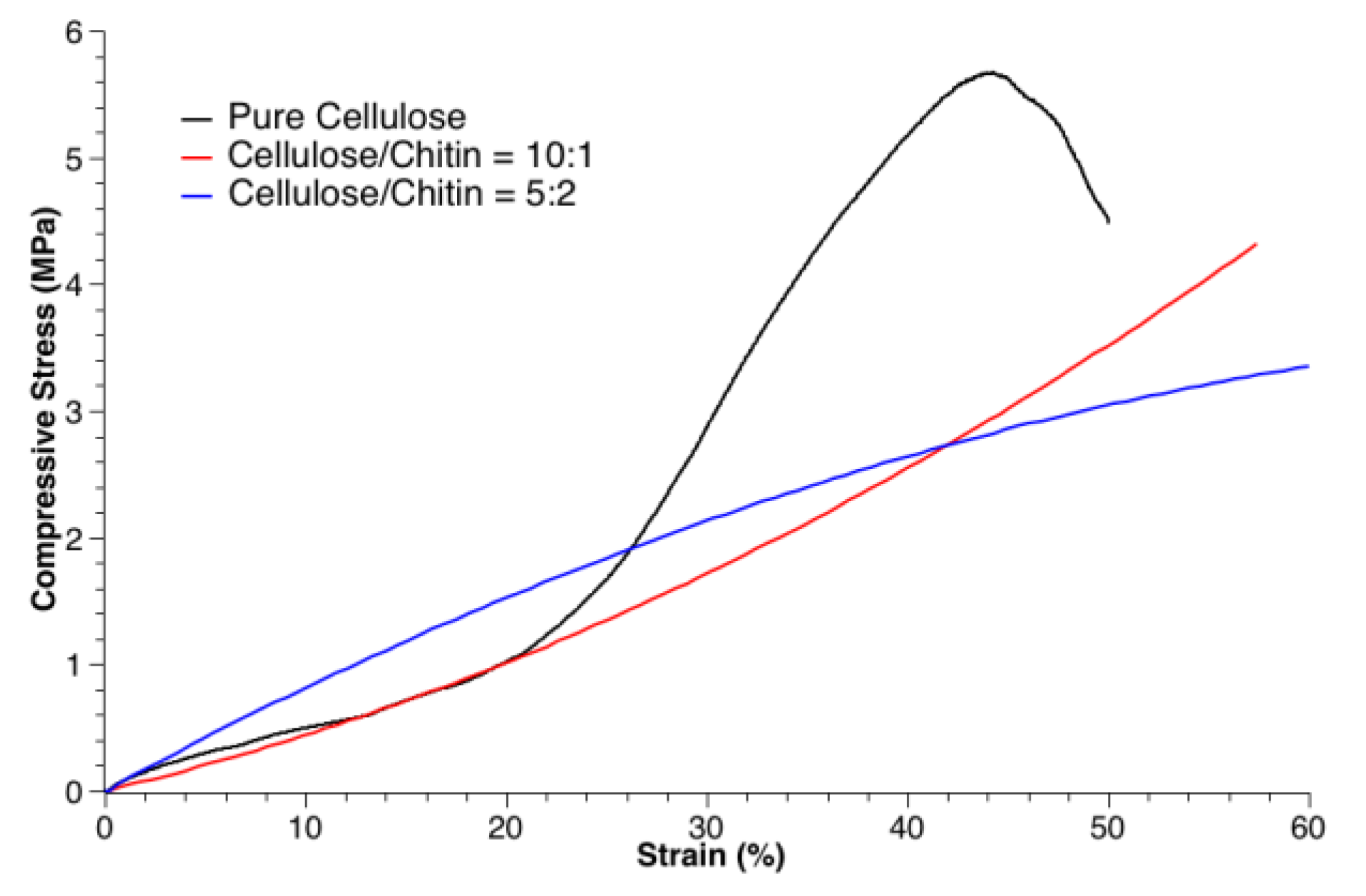
| Sample | SBET (m2/g) | Peaks of Pore Size (nm) | VBJH (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2 | 50 | 2.4 | 0.163 |
| Cellulose | 15 | 3.4 | 0.064 |
| TiO2/Cellulose | 1 | 2.3/3.4 | 0.004 |
| TiO2/Chitin/Cellulose | 3 | 7.7/30.8 | 0.018 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Li, J.; Luo, H.; Li, S.; Yang, J. Physicochemical and Photocatalytic Properties of 3D-Printed TiO2/Chitin/Cellulose Composite with Ordered Porous Structures. Polymers 2022, 14, 5435. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14245435
Li L, Li J, Luo H, Li S, Yang J. Physicochemical and Photocatalytic Properties of 3D-Printed TiO2/Chitin/Cellulose Composite with Ordered Porous Structures. Polymers. 2022; 14(24):5435. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14245435
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Lei, Jingdan Li, Hao Luo, Shengjuan Li, and Junhe Yang. 2022. "Physicochemical and Photocatalytic Properties of 3D-Printed TiO2/Chitin/Cellulose Composite with Ordered Porous Structures" Polymers 14, no. 24: 5435. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14245435
APA StyleLi, L., Li, J., Luo, H., Li, S., & Yang, J. (2022). Physicochemical and Photocatalytic Properties of 3D-Printed TiO2/Chitin/Cellulose Composite with Ordered Porous Structures. Polymers, 14(24), 5435. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14245435








