Fabric Insert Injection Molding for the Preparation of Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene/High-Density Polyethylene Two-Component Self-Reinforced Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
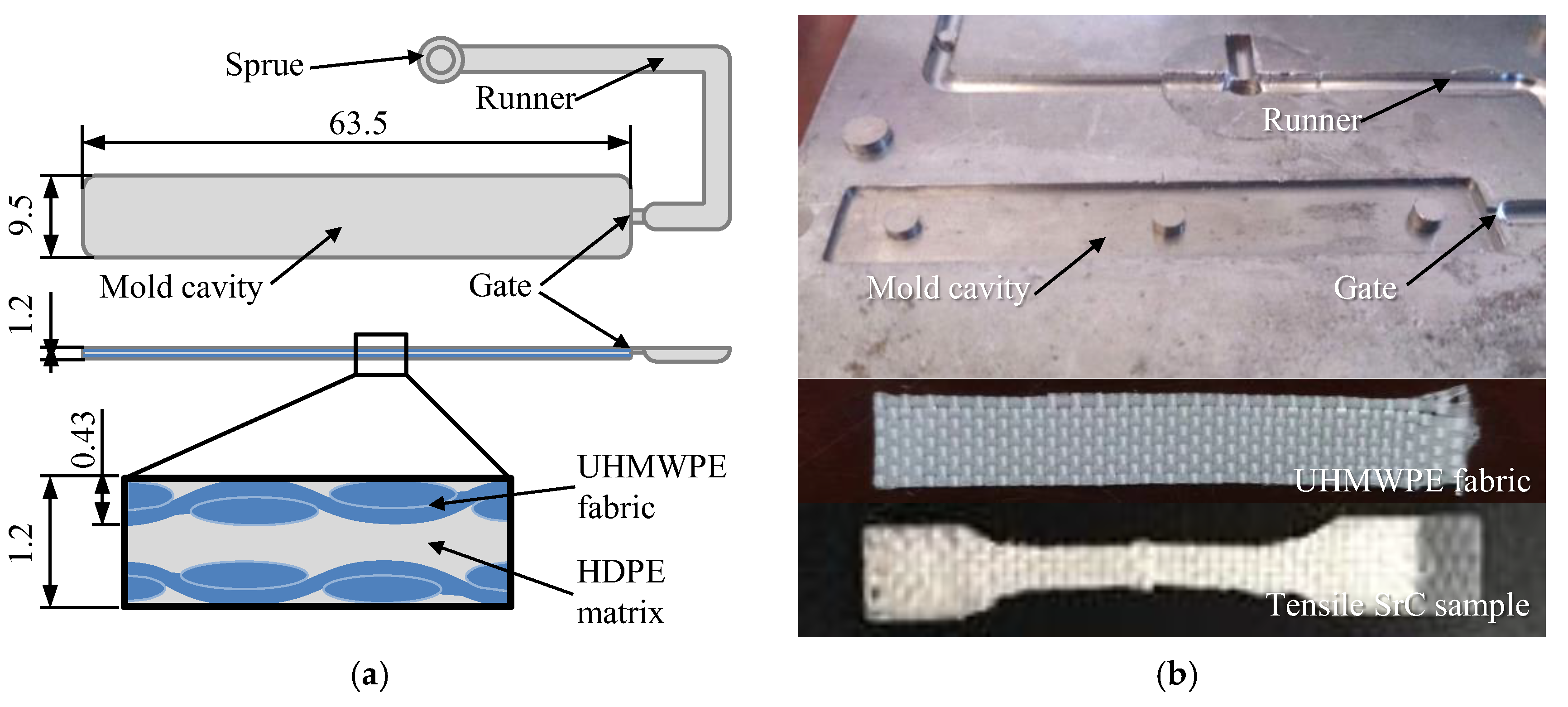
2.2. Preparation Process
2.3. Tensile Tests
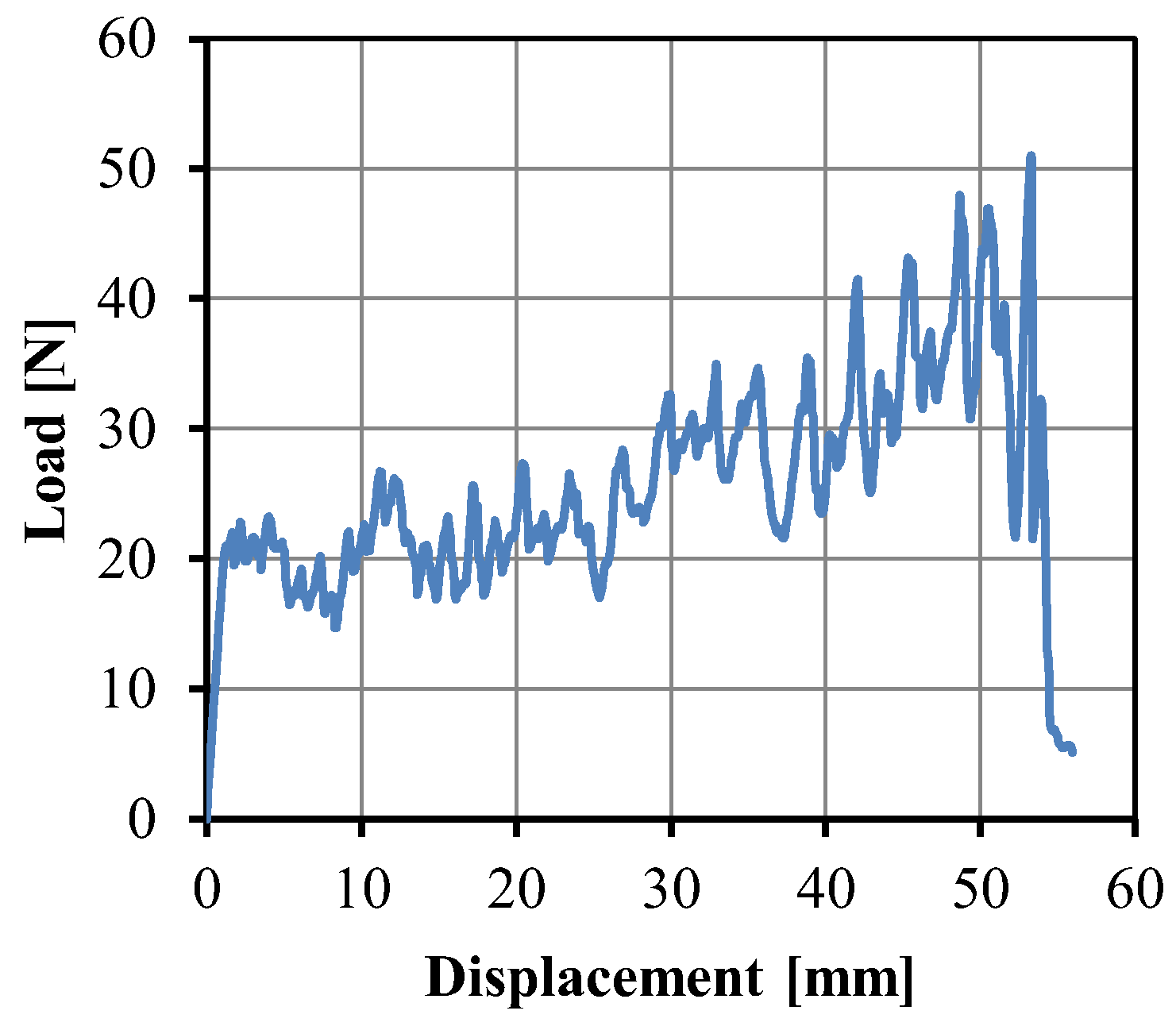
2.4. Peel Test
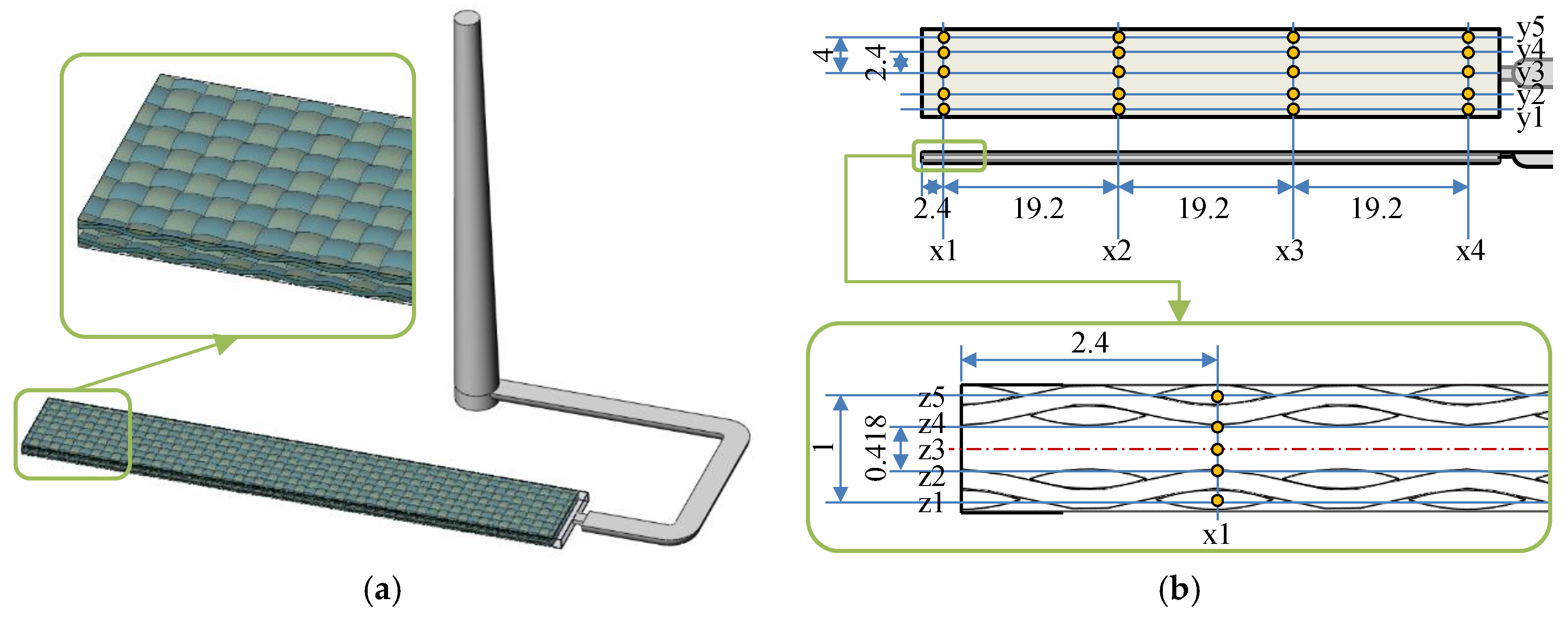
2.5. Numerical Simulation
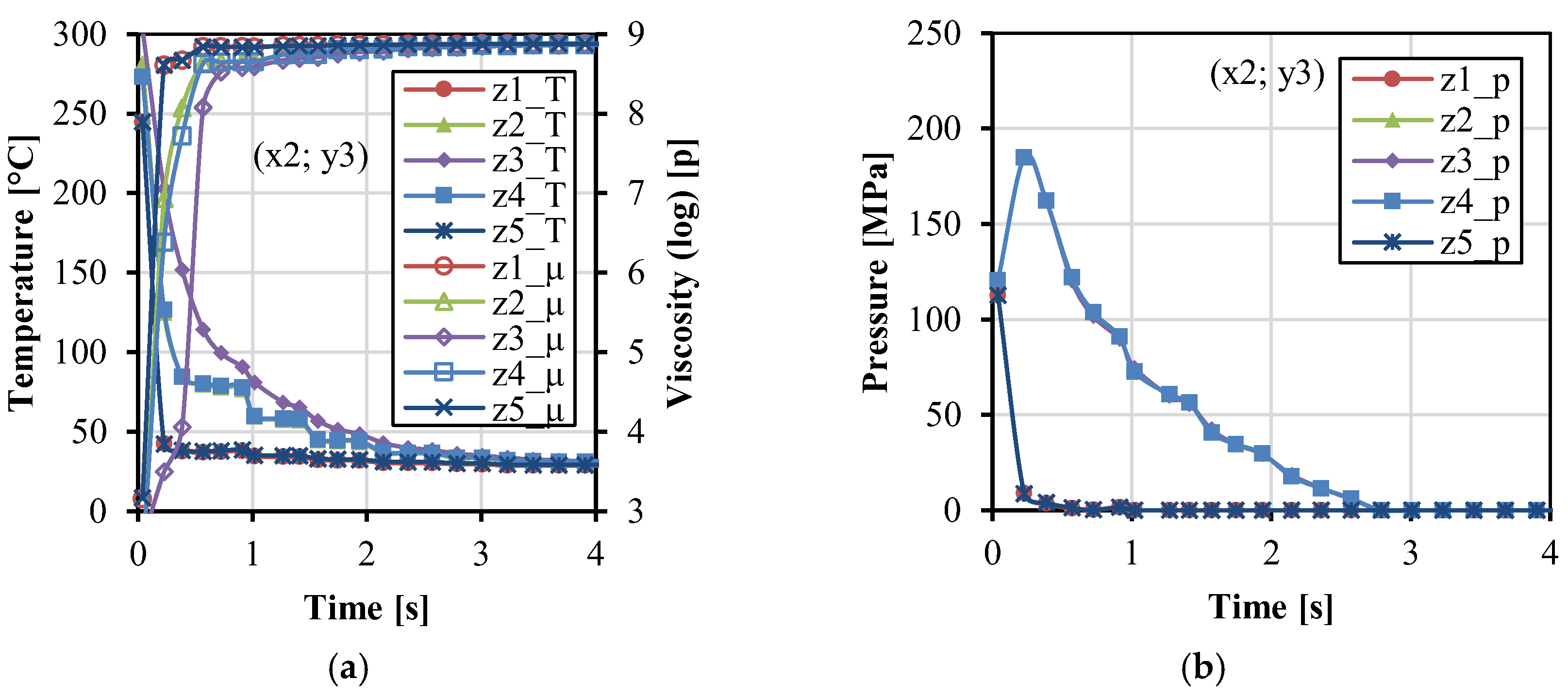
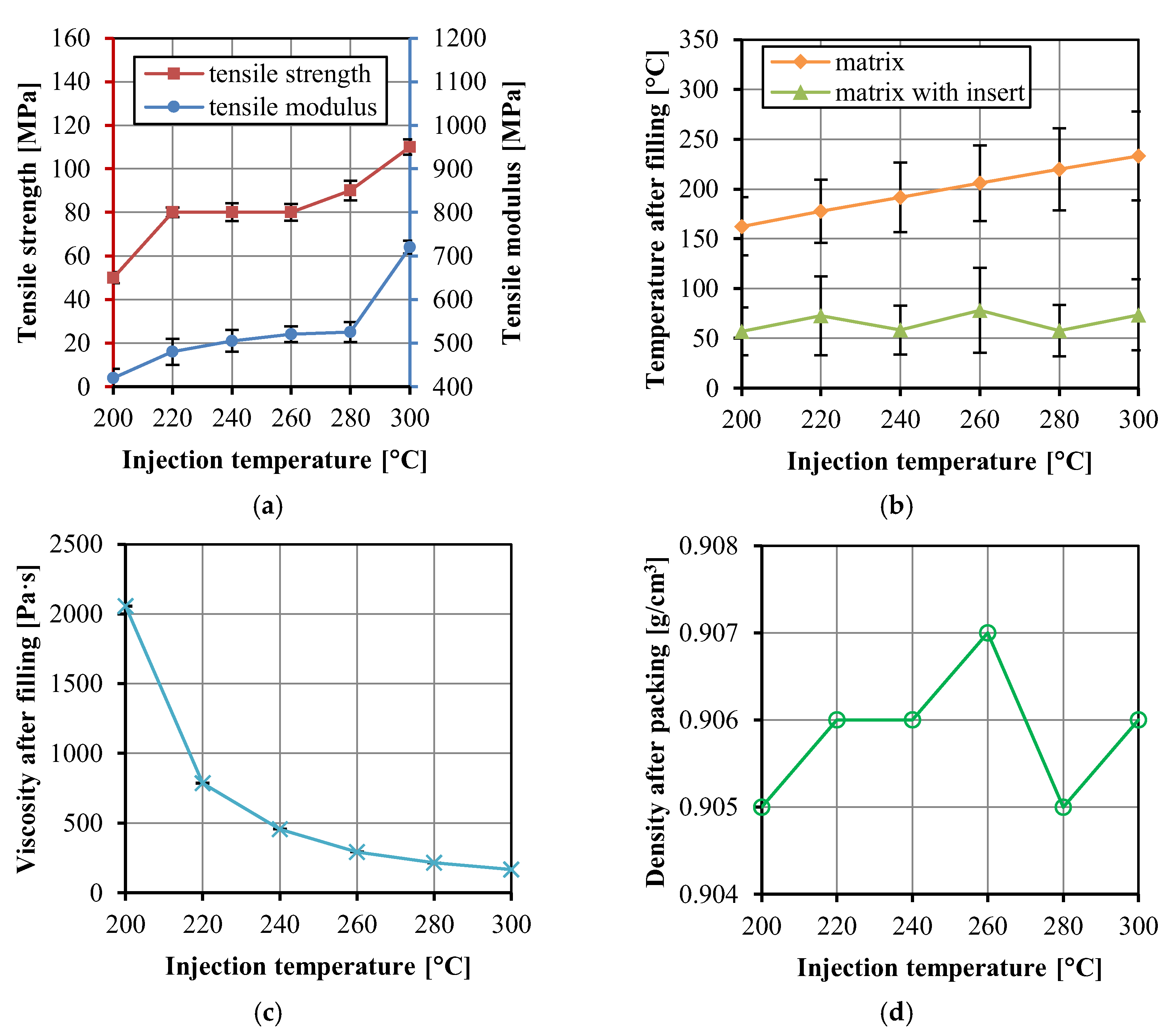
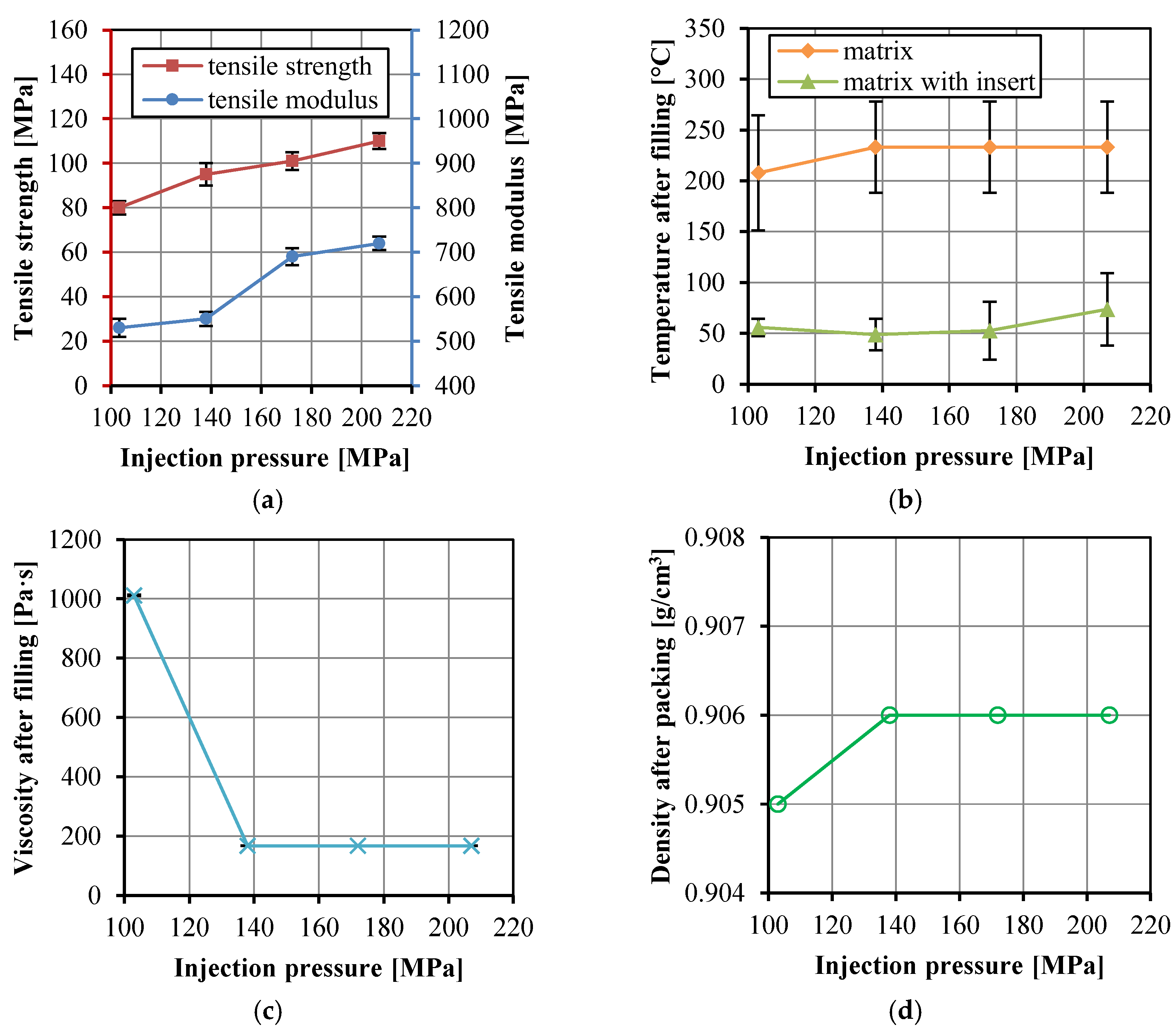
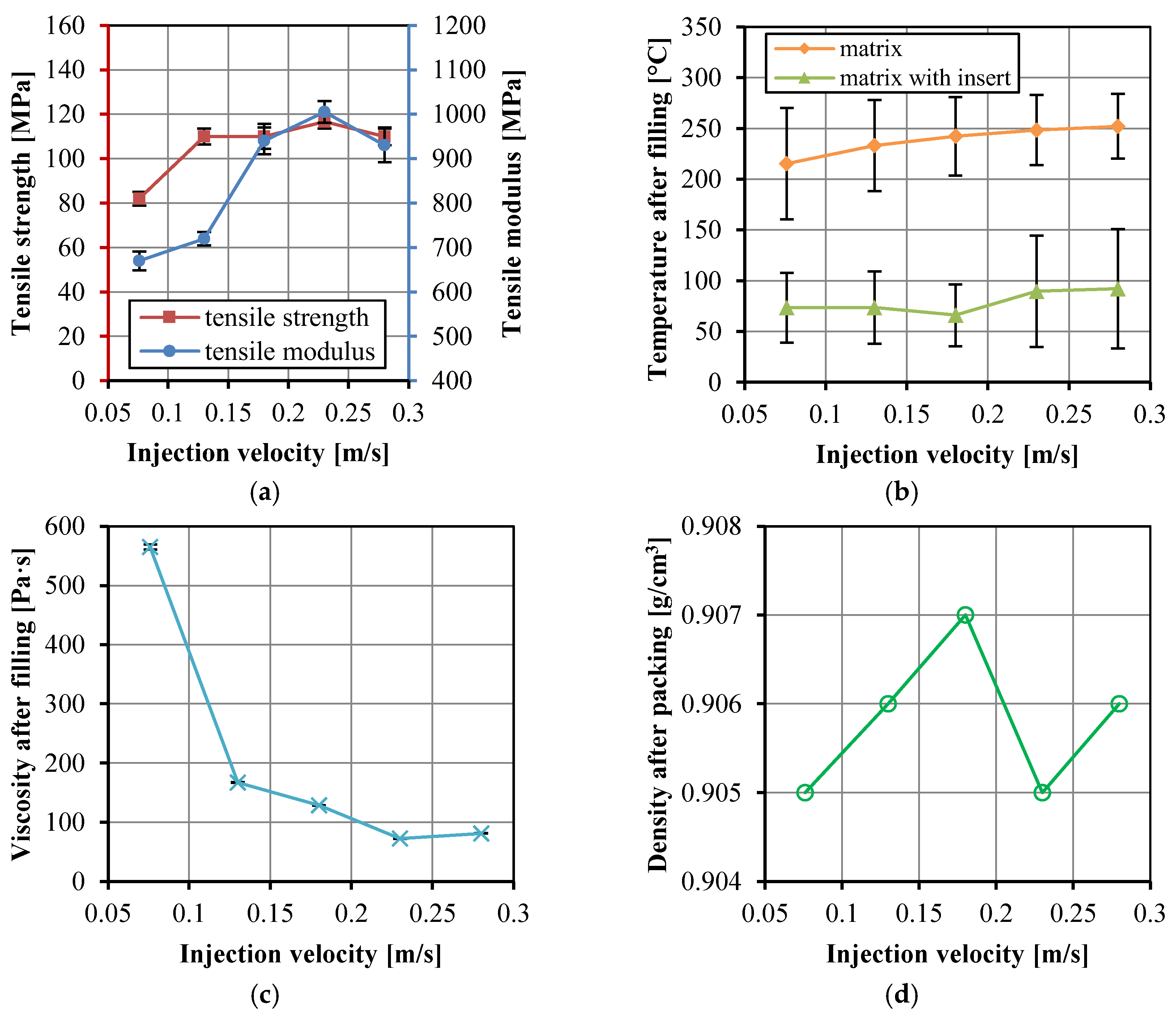
3. Results and Discussion
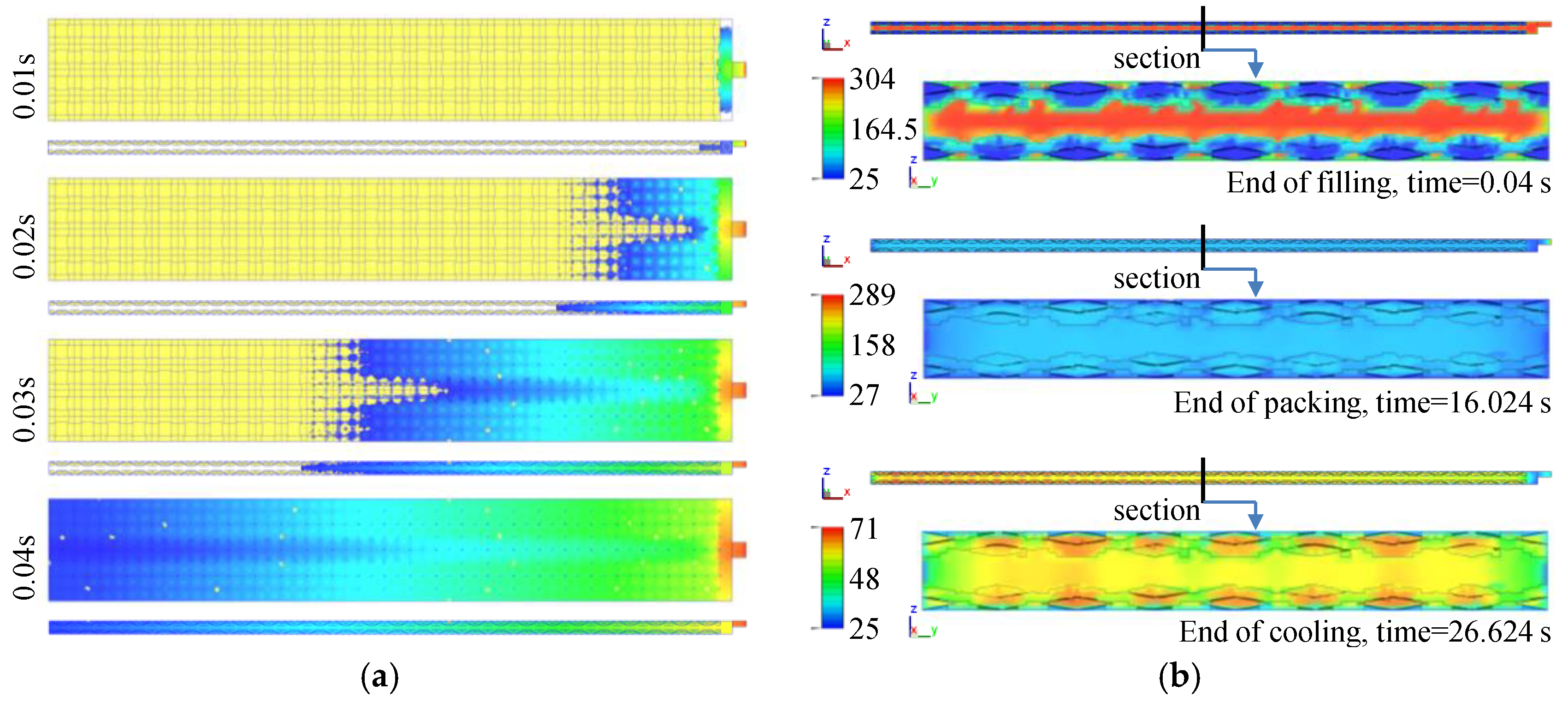
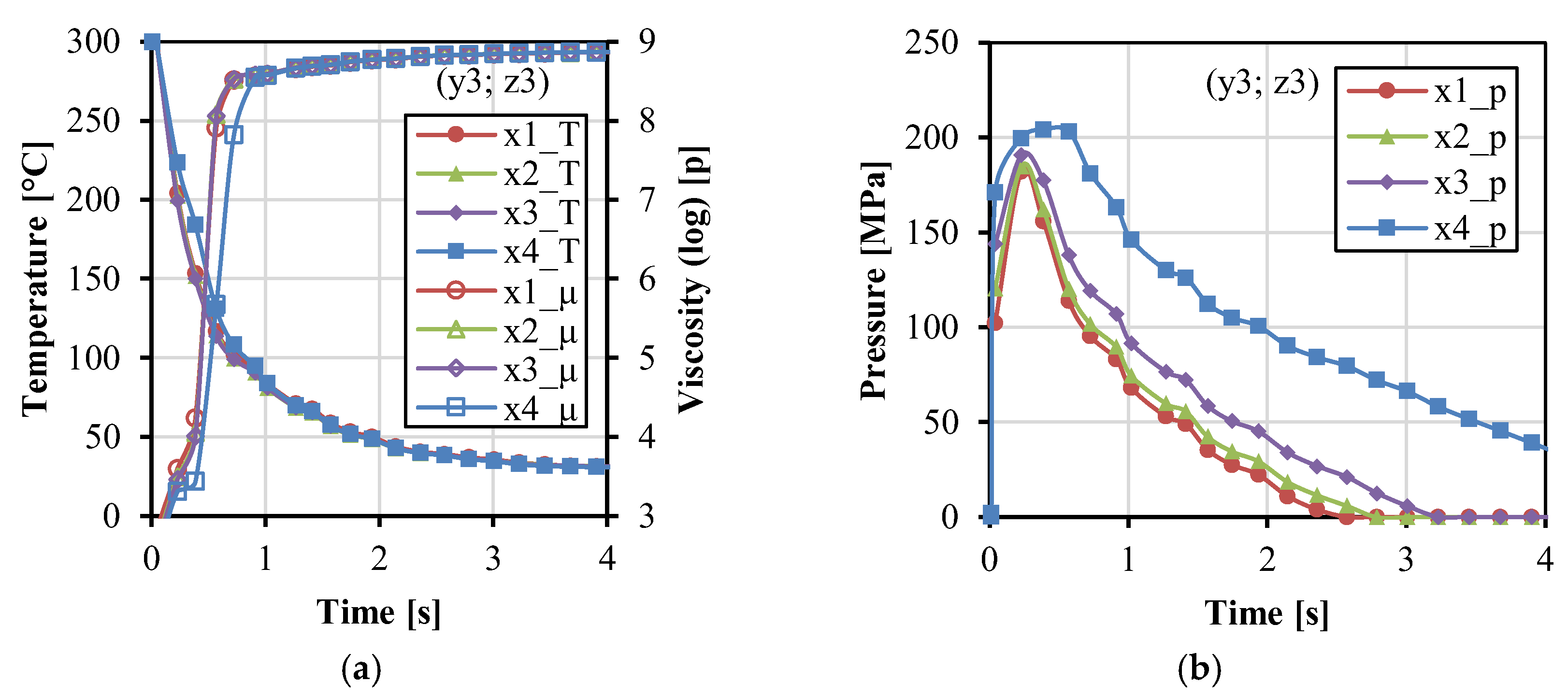
3.1. Fabric Insert Injection Molding Process
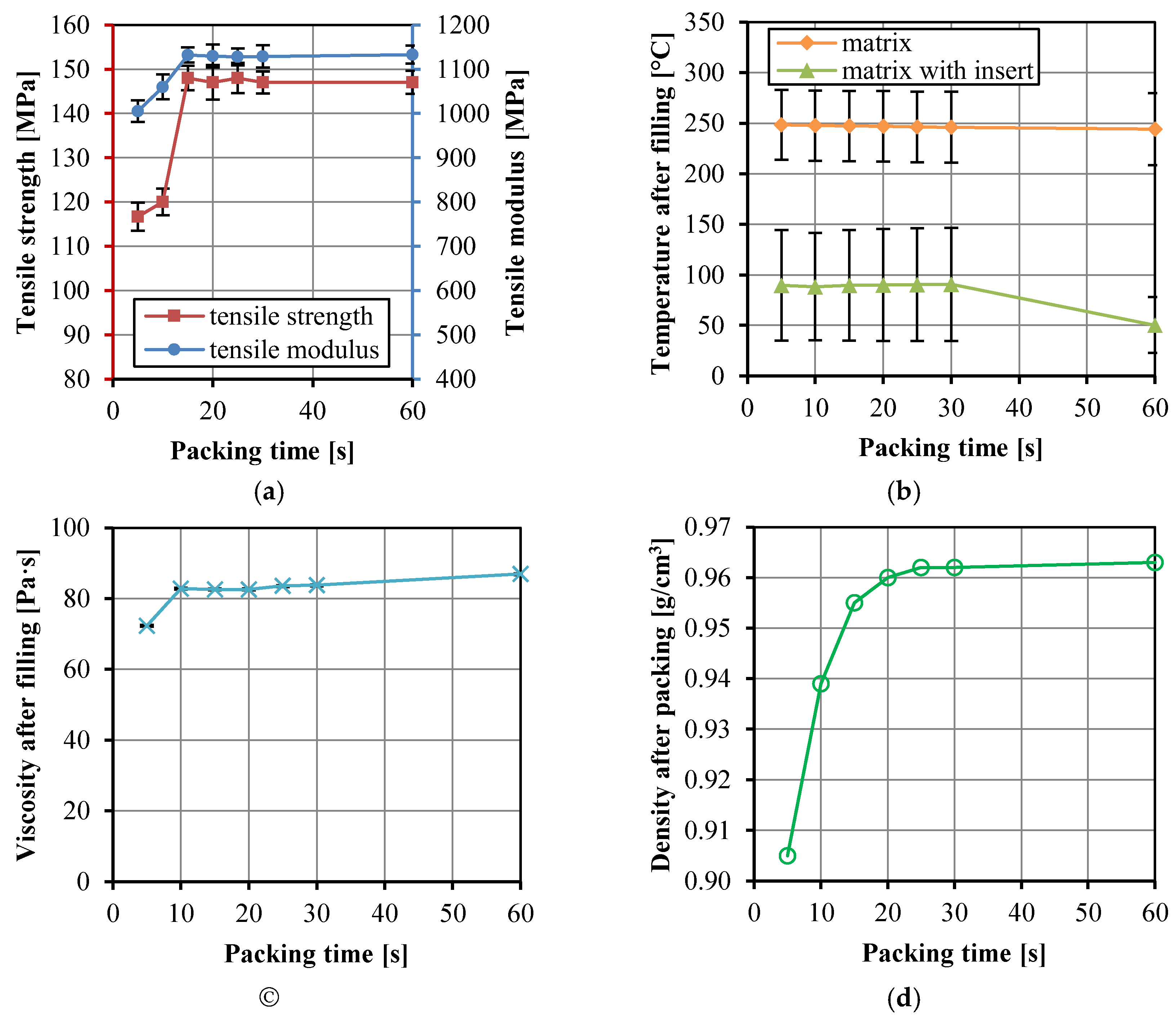
3.2. Effects of Injection Molding Parameters
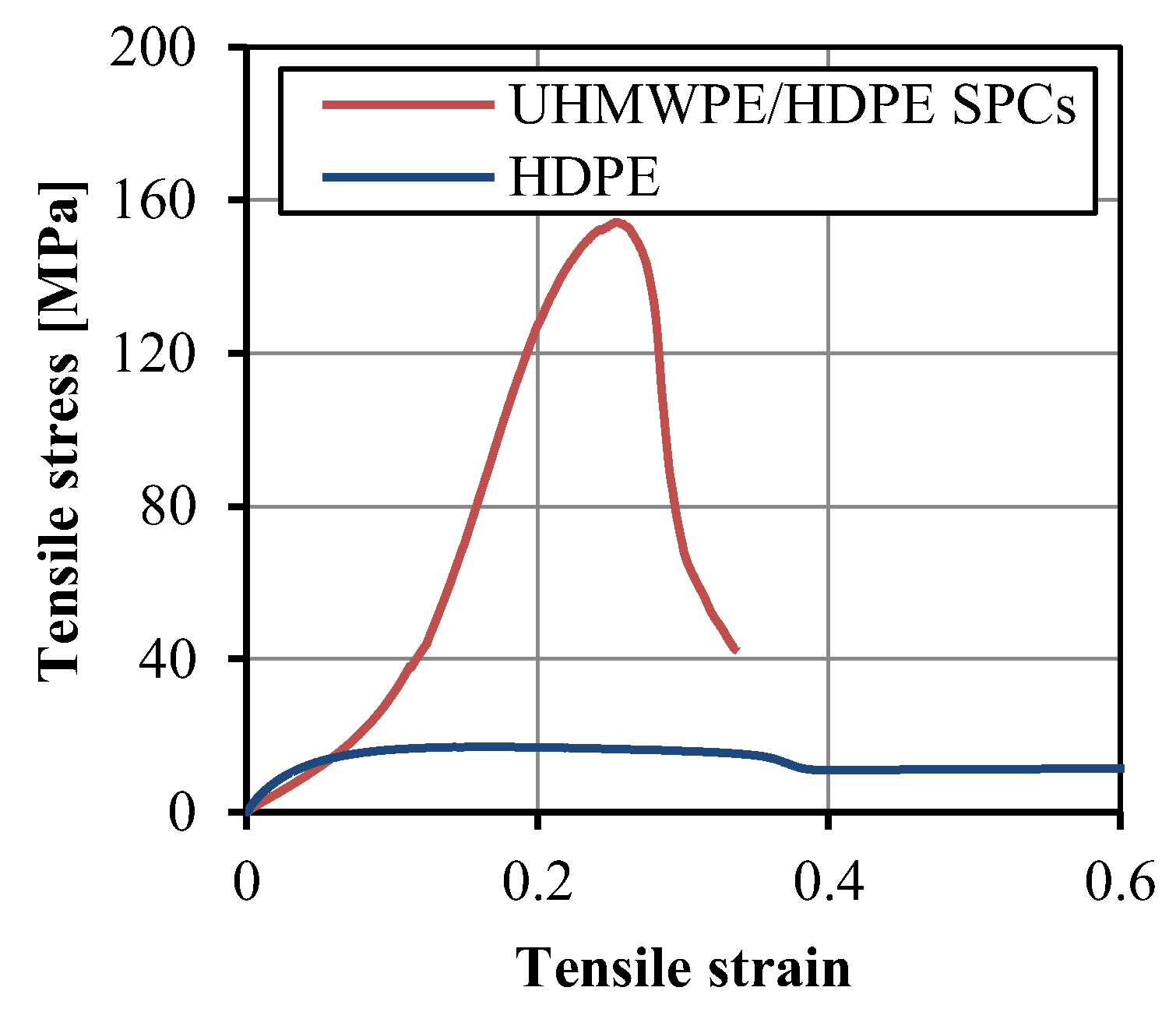
3.3. Optimum Properteis of the UHMWPE/HDPE SrCs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tim, A.O.; Turng, L.-S.; Gramann, P. Injection Molding Handbook; Hanser Publications: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Geminger, T.; Jarka, S. Injection molding of multimaterial systems. In Specialized Injection Molding Techniques; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 165–210. [Google Scholar]
- Drummer, D.; Schmachtenberg, E.; Hülder, G.; Meister, S. MK2—A novel assembly injection molding process for the combination of functional metal surfaces with polymer structures. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2010, 210, 1852–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, H.-P. Specialized Injection Molding Techniques; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mallick, P. Thermoplastics and thermoplastic–matrix composites for lightweight automotive structures. In Materials, Design and Manufacturing for Lightweight Vehicles; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 187–228. [Google Scholar]
- Akkerman, R.; Bouwman, M.; Wijskamp, S. Analysis of the thermoplastic composite overmolding process: Interface strength. Front. Mater. 2020, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.-J.; Yu, M.-H.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, J.-W.; Kim, H.-S. Design and manufacture of automotive composite front bumper assemble component considering interfacial bond characteristics between over-molded chopped glass fiber polypropylene and continuous glass fiber polypropylene composite. Compos. Struct. 2020, 236, 111849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.; Kim, Y.; Hong, S.; Yoon, K.; Lee, S. Innovative Injection Molding Process for the Fabrication of Woven Fabric Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites. Polymers 2022, 14, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, T.; Huang, Z.; Peng, X.; Chen, C.; Lu, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, H. Injection over-molding warpage prediction of continuous fiber-reinforced thermoplastic composites considering yarn reorientation. Thin Wall. Struct. 2022, 180, 109804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.; Tielas, A.; Prado, T.; Fenollera, M.; Pérez, J.A. Processing and testing of reinforced PA66 based composites. Materials 2021, 14, 7299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramasivam, A.; Timmaraju, M.V.; Velmurugan, R. Influence of preheating on the fracture behavior of over-molded short/continuous fiber reinforced polypropylene composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2021, 55, 4387–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capiati, N.J.; Porter, R.S. The concept of one polymer composites modelled with high density polyethylene. J. Mater. Sci. 1975, 10, 1671–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matabola, K.; De Vries, A.; Moolman, F.; Luyt, A. Single polymer composites: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 6213–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Polypropylene Single-Polymer Composites. Polypropylene-Based Biocomposites and Bionanocomposites; Visakh, P.M., Poletto, M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 177–246. [Google Scholar]
- Karger-Kocsis, J.; Bárány, T. Single-polymer composites (SPCs): Status and future trends. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 92, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karger-Kocsis, J.; Siengchin, S. Single-polymer composites: Concepts, realization and outlook. KMUTNB Int. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2014, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ward, I.; Hine, P. The science and technology of hot compaction. Polymer 2004, 45, 1413–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hine, P.; Unwin, A.; Ward, I. The use of an interleaved film for optimising the properties of hot compacted polyethylene single polymer composites. Polymer 2011, 52, 2891–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chang, C.; Wang, C.; Lin, C. Optimum consolidation of all-polyester woven fabric-reinforced composite laminates by film stacking. Polym. Compos. 2012, 33, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrzejewski, J.; Szostak, M.; Barczewski, M.; Krasucki, J.; Sterzynski, T. Fabrication of the self-reinforced composites using co-extrusion technique. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 41180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcock, B.; Peijs, T. Technology and development of self-reinforced polymer composites. In Polymer Composites–Polyolefin Fractionation–Polymeric Peptidomimetics–Collagens; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–76. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Song, F.; Yu, M. Unidirectional continuous fiber-reinforced polypropylene single-polymer composites prepared by extrusion–calendering process. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2022, 35, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Du, Z.; Lian, T. Extrusion–calendering process of single-polymer composites based on polyethylene. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2018, 58, 2156–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Jung, Y.C.; Kim, S.Y.; Song, J.M.; Kim, M.; Kim, J. Development of a continuous manufacturing process for self-reinforced composites using multi-step highly drawn polypropylene tapes. Polymer 2020, 191, 122267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakirov, S. Nano-and microfibrillar single-polymer composites: A review. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 298, 9–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Mao, Q.; Chen, J. Preparation of polypropylene single-polymer composites by injection molding. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 2176–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrzejewski, J.; Przyszczypkowski, P.; Szostak, M. Development and characterization of poly (ethylene terephthalate) based injection molded self-reinforced composites. Direct reinforcement by overmolding the composite inserts. Mater. Des. 2018, 153, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Mao, Q.; Jiang, N.; Chen, J. Effects of injection molding parameters on properties of insert-injection molded polypropylene single-polymer composites. Polymers 2021, 14, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, E.-C.; Yoon, K.-H.; Lee, S.-H. A study on the improvement of impregnation on the surface of injection-molded thermoplastic woven carbon fabric composite. J. Korea Soc. Die Mold Eng. 2021, 15, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Jerpdal, L.; Schuette, P.; Ståhlberg, D.; Åkermo, M. Influence of temperature during overmolding on the tensile modulus of self-reinforced poly (ethylene terephthalate) insert. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, D.; Wang, S.; Du, Z.; Jiang, N.; Peng, J. Insert injection molding of low-density polyethylene single-polymer composites reinforced with ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene fabric. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2018, 31, 1013–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roiron, C.; Lainé, E.; Grandidier, J.-C.; Garois, N.; Voillequin, B.; Vix-Guterl, C. Positioning of a self-reinforced polyethylene in the industrial composites market. Matériaux Tech. 2022, 110, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-F.; Xu, J.-Z.; Li, J.-S.; He, B.-X.; Xu, L.; Li, Z.-M. Mechanical properties and biocompatibility of melt processed, self-reinforced ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 6687–6697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Shalaby, S.W. Properties of self-reinforced ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene composites. Biomaterials 1997, 18, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukov, D.; Kharitonov, A.; Tcherdyntsev, V.; Zherebtsov, D.; Maksimkin, A. Structure and mechanical properties of self-reinforced ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene. J. Compos. Mater. 2018, 52, 1689–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukov, D.I.; Zherebtsov, D.D.; Olifirov, L.K.; Torokhov, V.G.; Maksimkin, A.V. Comparison between self-reinforced composites based on ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fibers and isotropic UHMWPE. Mendeleev Commun. 2020, 30, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mészáros, L.; Tatár, B.; Toth, K.; Földes, A.; Nagy, K.S.; Jedlovszky-Hajdu, A.; Tóth, T.; Molnár, K. Novel, injection molded all-polyethylene composites for potential biomedical implant applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 17, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, D.; Kurek, A.; Thomann, R.; Schwabe, J.; Mark, S.; Enders, M.; Hees, T.; Mülhaupt, R. Tailored nanostructured HDPE wax/UHMWPE reactor blends as additives for melt-processable all-polyethylene composites and in situ UHMWPE fiber reinforcement. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 8129–8139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, F.; Schwabe, J.; Hofmann, D.; Meier, J.; Thomann, R.; Enders, M.; Mülhaupt, R. All-polyethylene composites reinforced via extended-chain UHMWPE nanostructure formation during melt processing. Polymer 2018, 140, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stürzel, M.; Kurek, A.G.; Hees, T.; Thomann, Y.; Blattmann, H.; Mülhaupt, R. Multisite catalyst mediated polymer nanostructure formation and self-reinforced polyethylene reactor blends with improved toughness/stiffness balance. Polymer 2016, 102, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Component | Material | Brand | Melting Point (°C) | Density (g/cm3) | Tensile Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matrix | HDPE | Marlex 9035 | 126 | 0.952 | 24 |
| Reinforcement | UHMWPE fiber | Spectra 900 | 147 | 0.97 | 2610, single fiber 300, fabric |
| Experimental No. | Injection Temperature (°C) | Injection Pressure (kpsi) | Injection Velocity (in/s) | Packing Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 200 | 30 | 5 | 5 |
| 2 | 220 | 30 | 5 | 5 |
| 3 | 240 | 30 | 5 | 5 |
| 4 | 260 | 30 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 280 | 30 | 5 | 5 |
| 6 | 300 | 30 | 5 | 5 |
| 7 | 300 | 15 | 5 | 5 |
| 8 | 300 | 20 | 5 | 5 |
| 9 | 300 | 25 | 5 | 5 |
| 10 | 300 | 30 | 3 | 5 |
| 11 | 300 | 30 | 7 | 5 |
| 12 | 300 | 30 | 9 | 5 |
| 13 | 300 | 30 | 11 | 5 |
| 14 | 300 | 30 | 9 | 10 |
| 15 | 300 | 30 | 9 | 15 |
| 16 | 300 | 30 | 9 | 20 |
| 17 | 300 | 30 | 9 | 25 |
| 18 | 300 | 30 | 9 | 30 |
| 19 | 300 | 30 | 9 | 60 |
| Reference | Materials | Methods | Type of Reinforcement | Fiber Fraction | Tensile Strength [MPa] | Tensile Modulus [MPa] | Break Strain [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This work | UHMWPE/HDPE | Insert injection molding | Plain fabric | 20 wt% | 148 | 1132 | 33 |
| [31] | UHMWPE/LDPE | Insert injection molding | Plain fabric | 5 wt% | 23.8 | - | 60 |
| [32] | UHMWPE/LDPE | Compression molding (Film stacking) | Plain fabric | 14 vol% | 70.1 | 2354 | <5 |
| [23] | UHMWPE/LDPE | Extrusion-calendering | Plain fabric | 11 vol% | 78.8 | 676.6 | - |
| [33] | UHMWPE/ULMWPE | Compounding and injection molding | Tailored blend | 90.2 wt% | 65.5 | 1248.7 | 83.9 |
| [34] | UHMWPE | Compression molding (Powder impregnation) | Cross-ply laminates | 5 wt% | 56 | 1400 | - |
| [35] | UHMWPE | Compression molding (Powder impregnation) | Short fiber | 30 wt% | 65.2 | 2260 | 16 |
| [36] | UHMWPE | Compression molding (Hot compaction) | Unidirectional fibers | ~100% | 460 ± 12 | 21.1 ± 0.8 | <5 |
| [37] | UHMWPE/HDPE | Compounding and injection molding | Chopped and irradiated fibers | 20 wt% | 41.1 | 1620 | 17.1 |
| [38] | UHMWPE/HDPE wax/PE reactor blend | Compounding and injection molding | Tailored blend | 12 wt% | 134.2 | 3770 | 12 |
| [39] | UHMWPE/HDPE/PE reactor blend | Compounding and injection molding | Tailored blend | 24 wt% | 160 | 4200 | <5 |
| [40] | UHMWPE/HDPE reactor blends prepared with CrQCp and nBuZr | Compounding and injection molding | Tailored blend | 18.6 wt% | 171 | 2345 | 13.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Mao, Q.; Chen, J. Fabric Insert Injection Molding for the Preparation of Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene/High-Density Polyethylene Two-Component Self-Reinforced Composites. Polymers 2022, 14, 4384. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204384
Wang J, Wang D, Mao Q, Chen J. Fabric Insert Injection Molding for the Preparation of Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene/High-Density Polyethylene Two-Component Self-Reinforced Composites. Polymers. 2022; 14(20):4384. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204384
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jian, Da Wang, Qianchao Mao, and Jinnan Chen. 2022. "Fabric Insert Injection Molding for the Preparation of Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene/High-Density Polyethylene Two-Component Self-Reinforced Composites" Polymers 14, no. 20: 4384. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204384
APA StyleWang, J., Wang, D., Mao, Q., & Chen, J. (2022). Fabric Insert Injection Molding for the Preparation of Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene/High-Density Polyethylene Two-Component Self-Reinforced Composites. Polymers, 14(20), 4384. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204384







