Interactive Effects of Copper-Doped Urological Implants with Tissue in the Urinary Tract for the Inhibition of Cell Adhesion and Encrustation in the Animal Model Rat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Implant Preparation
2.1.1. Implants with Copper Coating Beads
- Group 1 (glass)
- Group 2 (Cu)
- Group 3 (Cu+)
2.1.2. Impants with a-C:H/Cu-Mulitilayer Coating
- Group A: Elastollan®, provided with the X-ray contrast agent barium sulphate, Institute for Polymer Technologies e.V., Wismar, Germany 2.
- Group B: Elastollan®, provided with the X-ray contrast agent barium sulphatesulphate and a-C:H/Cu-multilayer coating in combination with copper doping, Materion GmbH, Wismar, Germany.
2.2. In Vitro Studies
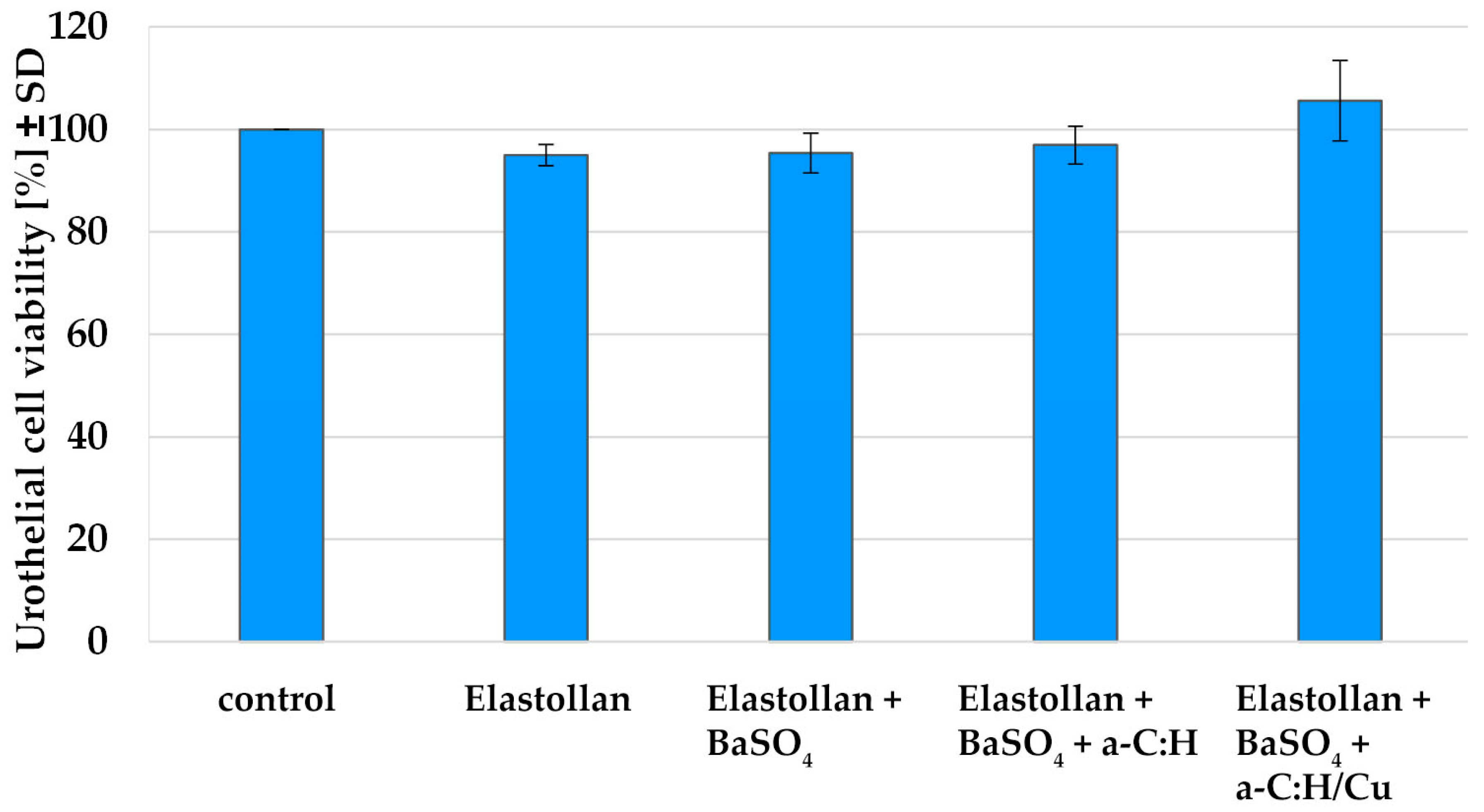
2.2.1. Biocompatibility of the Materials
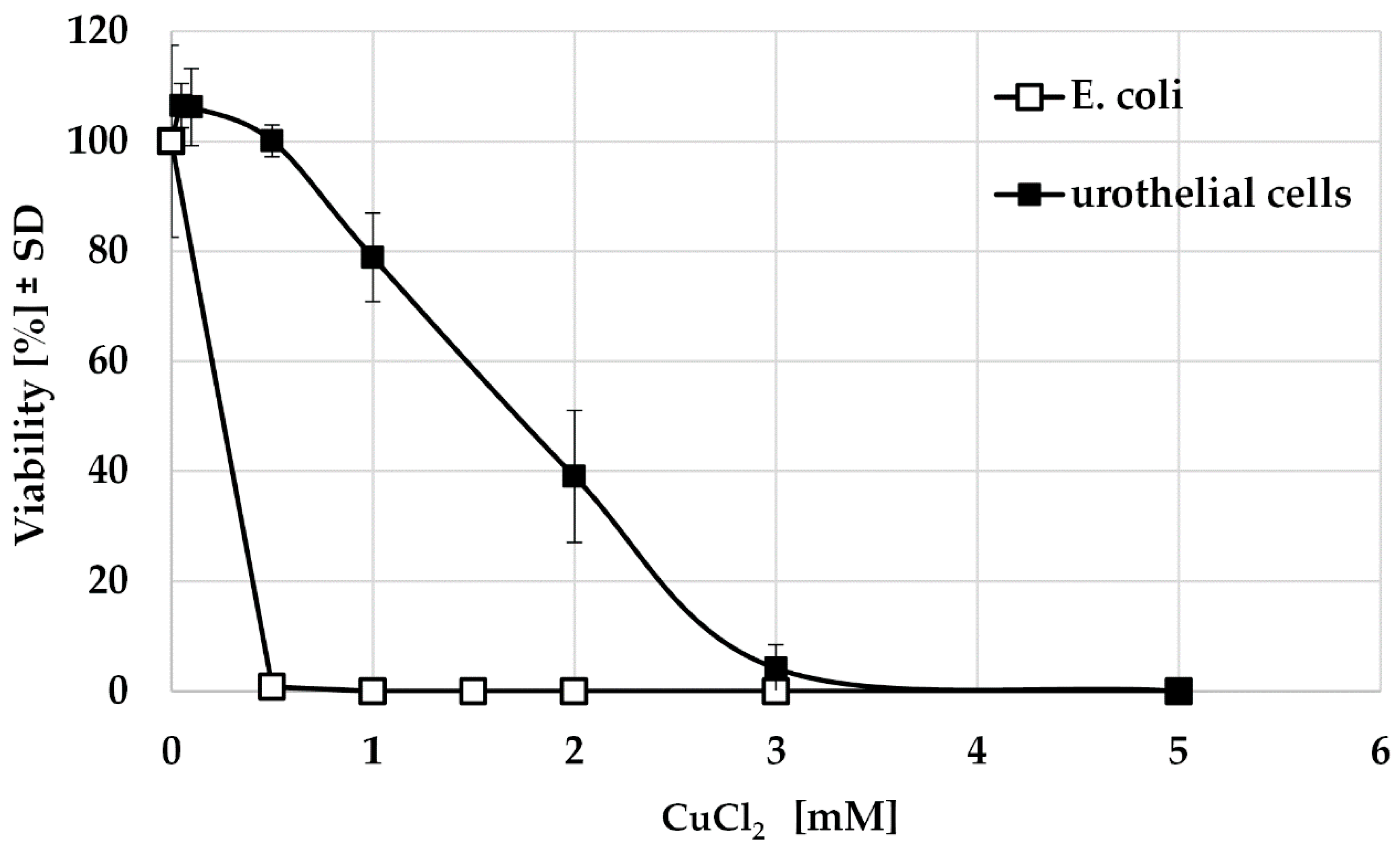
2.2.2. Anti-Bacterial Effect of Copper
2.3. Animals and Housing Conditions
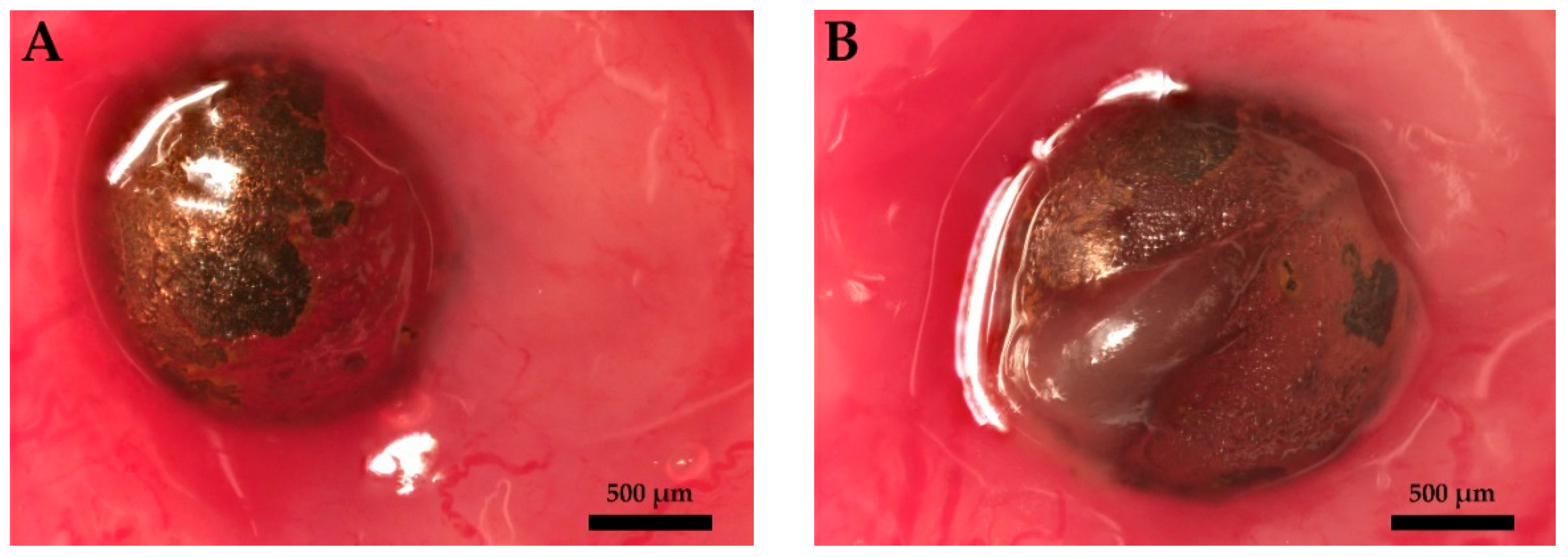
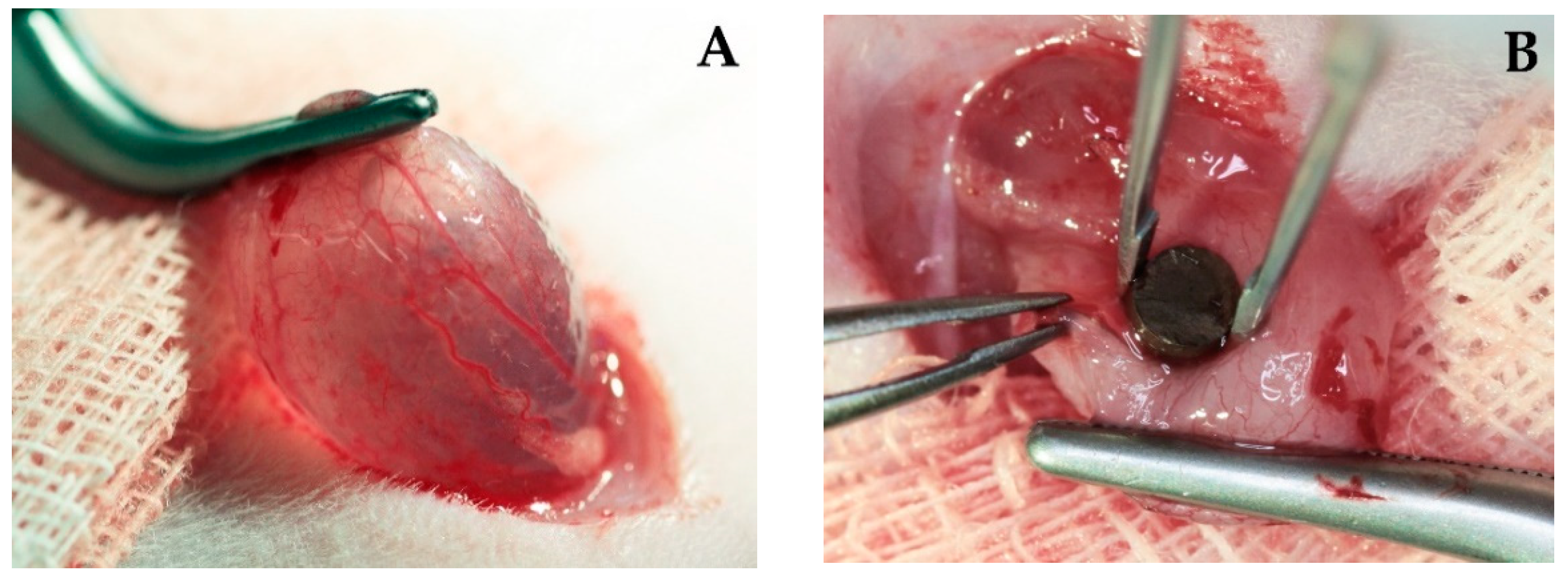
2.3.1. Interaction of Copper-Doped Implants with the Tissues of the Urinary Tract
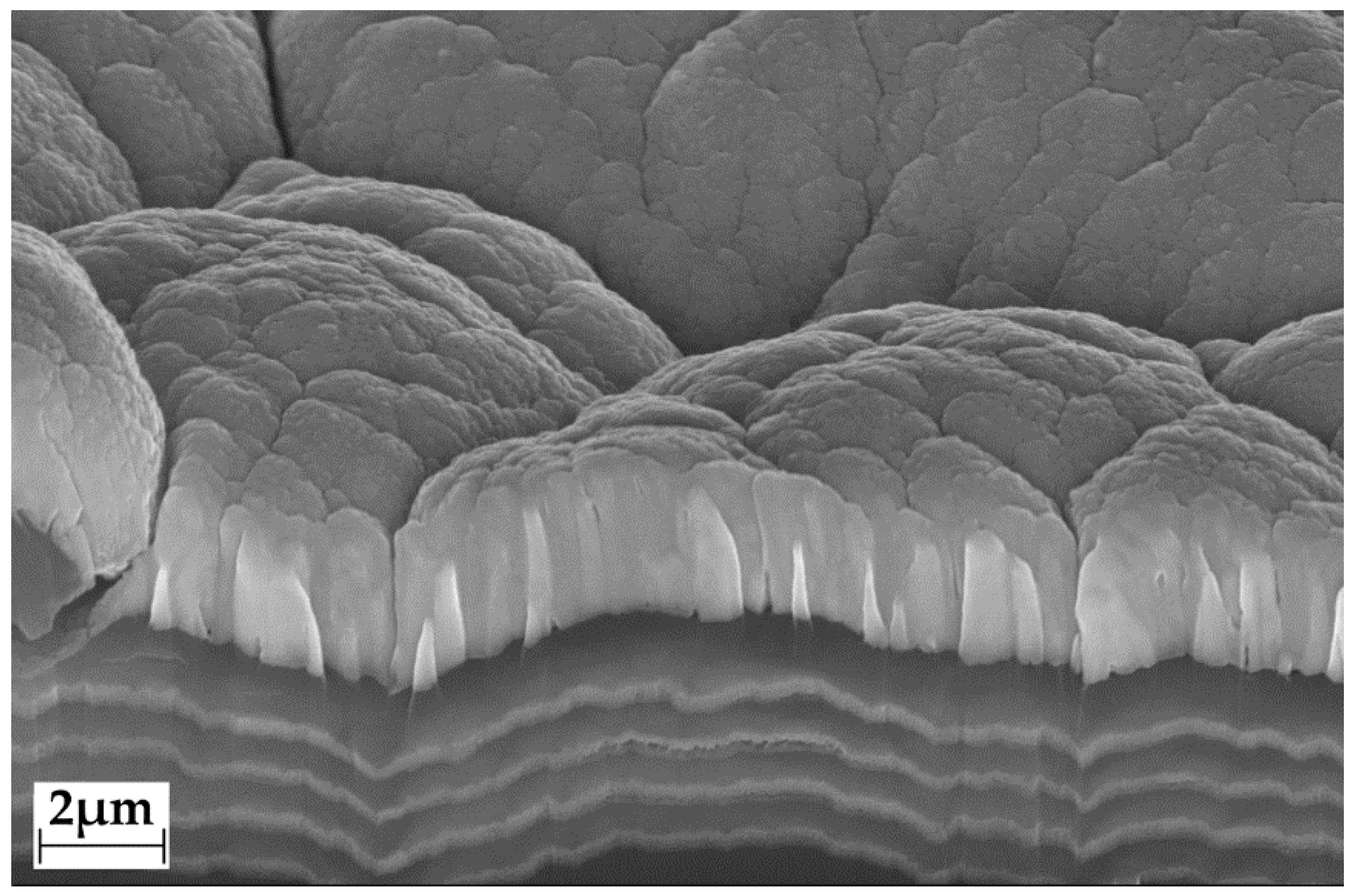
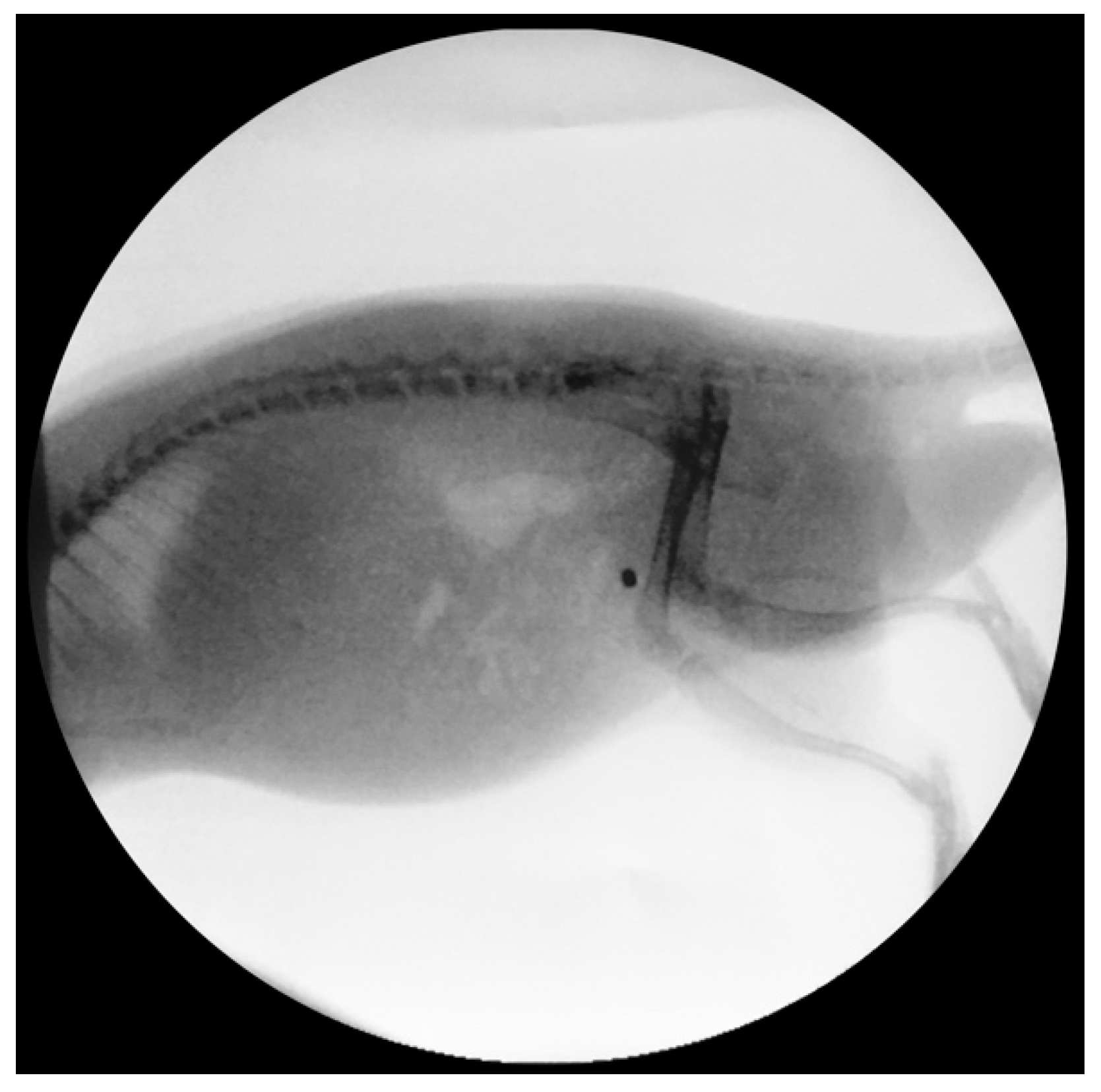
2.3.2. Encrustation of Elastollan® with a-C:H/Cu-Mulitilayer Coating
2.4. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. In Vitro Studies
3.1.1. Biocompatibility of the Materials
3.1.2. Anti-Bacterial Effect of Copper
3.2. Animal Studies
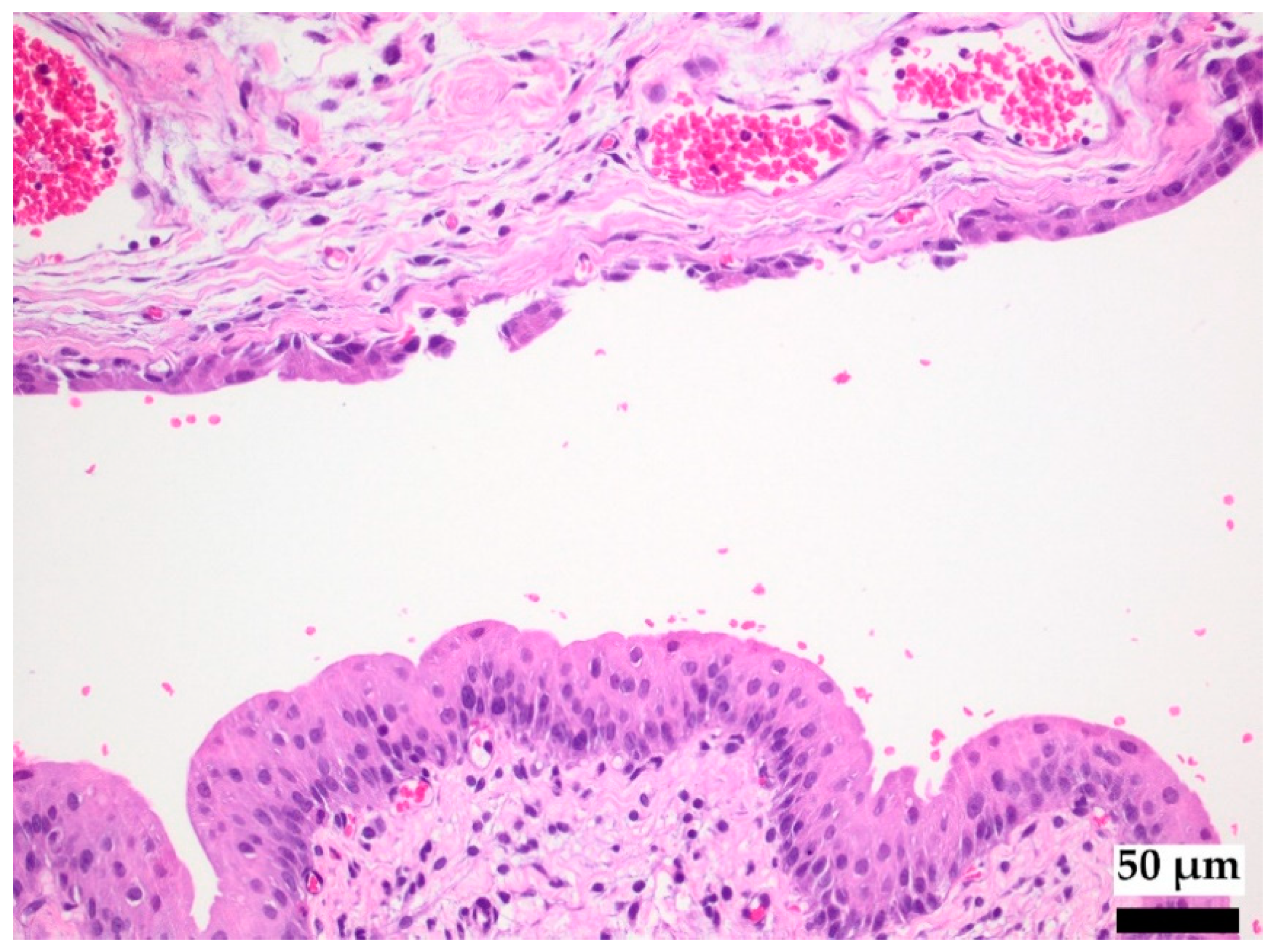
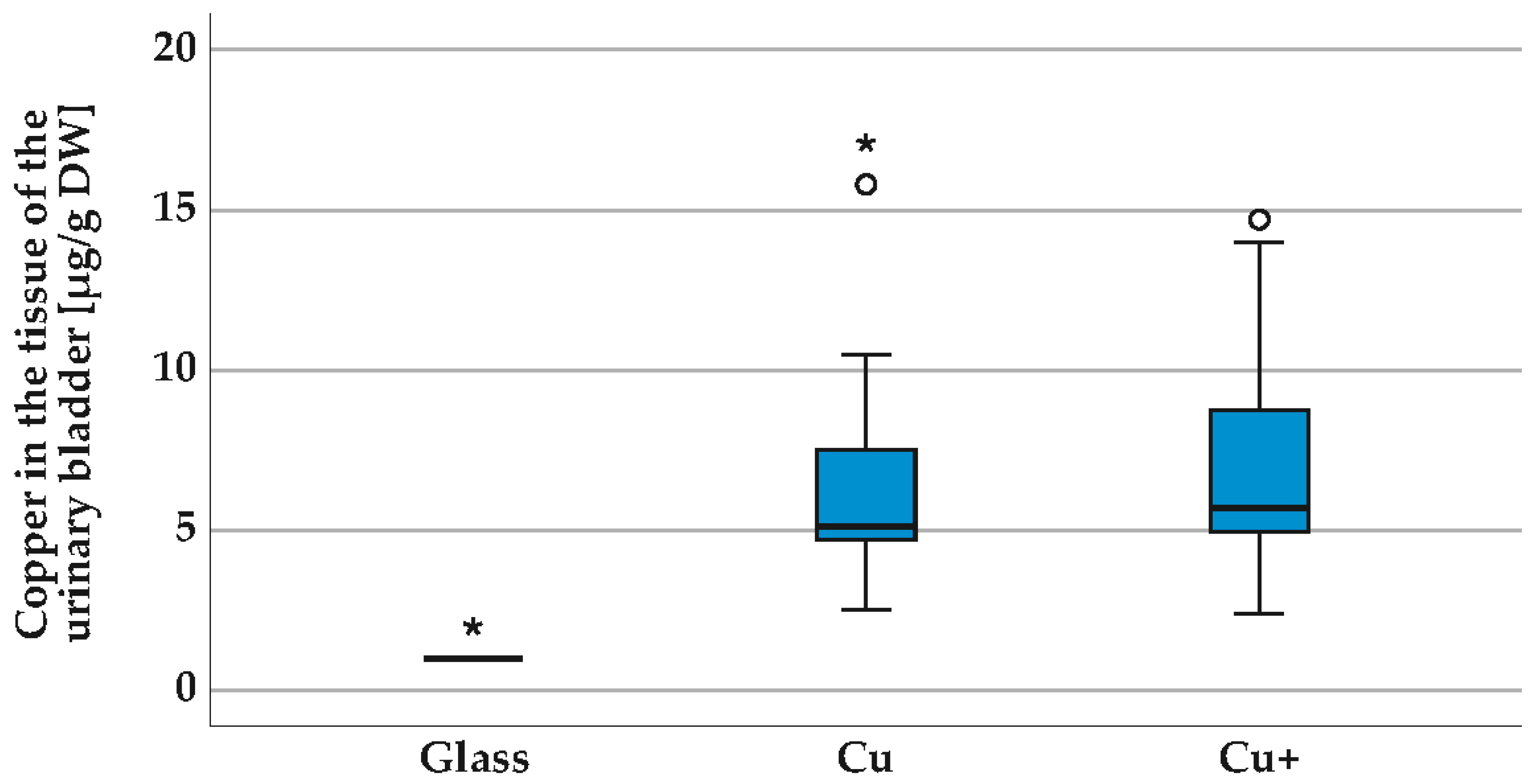
3.2.1. Interaction of Copper-Doped Implants with the Tissue of the Urinary Tract
3.2.2. Encrustation of Elastollan with a-C:H/Cu-Mulitilayer Coating
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scotland, K.B.; Kung, S.H.; Chew, B.H.; Lange, D. Uropathogens Preferrentially Interact with Conditioning Film Components on the Surface of Indwelling Ureteral Stents Rather than Stent Material. Pathogens 2020, 9, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grases, F.; Sohnel, O.; Costa-Bauza, A.; Ramis, M.; Wang, Z. Study on concretions developed around urinary catheters and mechanisms of renal calculi development. Nephron 2001, 88, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumeran, C.; Mottet-Auselo, B.; Forestier, C.; Nana, P.A.; Hennequin, C.; Robin, F.; Souweine, B.; Traore, O.; Lautrette, A. A prospective study on the pathogenesis of catheter-associated bacteriuria in critically ill patients. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenke, P.; Kovacs, B.; Jackel, M.; Nagy, E. The role of biofilm infection in urology. World J. Urol. 2006, 24, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Gupta, Y.; Agrawal, R.; Khare, P.; Jain, S.K. Biofilms—A microbial life perspective: A critical review. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2007, 24, 393–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choong, S.; Whitfield, H. Biofilms and their role in infections in urology. BJU Int. 2000, 86, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, C.; Scotland, K.B.; Lange, D.; Chew, B.H. Innovations in Ureteral Stent Technology. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 46, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebl, H.; Renner, J.; Kram, W.; Springer, A.; Fritsch, N.; Hansmann, H.; Hakenberg, O.W.; Nebe, J.B. Prevention of Encrustation on Ureteral Stents: Which Surface Parameters Provide Guidance for the Development of Novel Stent Materials? Polymers 2020, 12, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, N.S.; Stickler, D.J. The effect of urease inhibitors on the encrustation of urethral catheters. Urol. Res. 1998, 26, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari Zare, H.; Juhart, V.; Vass, A.; Franz, G.; Jocham, D. Efficacy of silver/hydrophilic poly(p-xylylene) on preventing bacterial growth and biofilm formation in urinary catheters. Biointerphases 2017, 12, 011001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Yuan, X. Antimicrobial strategies for urinary catheters. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2019, 107, 445–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jastrzebski, K.; Bialecki, J.; Jastrzebska, A.; Kaczmarek, A.; Para, M.; Niedzielski, P.; Bociaga, D. Induced Biological Response in Contact with Ag-and Cu-Doped Carbon Coatings for Potential Orthopedic Applications. Materials 2021, 14, 1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, E.; Zhao, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, R.; Fu, S.; Qin, G. Antibacterial metals and alloys for potential biomedical implants. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 2569–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.-c.; Witte, F.; Li, J.; Guan, S. The increased ratio of Mg2+/Ca2+ from degrading magnesium alloys directs macrophage fate for functionalized growth of endothelial cells. Smart Mater. Med. 2022, 3, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidenau, F.; Mittelmeier, W.; Detsch, R.; Haenle, M.; Stenzel, F.; Ziegler, G.; Gollwitzer, H. A novel antibacterial titania coating: Metal ion toxicity and in vitro surface colonization. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2005, 16, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostek, A.; Breisch, M.; Pappert, K.; Loza, K.; Heggen, M.; Koller, M.; Sengstock, C.; Epple, M. Comparative biological effects of spherical noble metal nanoparticles (Rh, Pd, Ag, Pt, Au) with 4–8 nm diameter. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2763–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.W.; Kuo, T.H.; Chang, J.H.; Yeh, J.M.; Chan, W.H. Induction of cytotoxicity and apoptosis in mouse blastocysts by silver nanoparticles. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 197, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, D.P.; Musher, D.M.; Itin, C. Urease. The primary cause of infection-induced urinary stones. Investig. Urol. 1976, 13, 346–350. [Google Scholar]
- Demers, G.; Griffin, G.; De Vroey, G.; Haywood, J.R.; Zurlo, J.; Bedard, M. Animal research. Harmonization of animal care and use guidance. Science 2006, 312, 700–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, I.G.; Baylan, B.; Gok, A.; Sagnak, A.L.; Karakoyunlu, N.; Cakici, M.C.; Kaymak, S.; Karabacak, O.R.; Topaloglu, H.; Ersoy, H. The Association of Encrustation and Ureteral Stent Indwelling Time in Urolithiasis and KUB Grading System. Urol. J. 2018, 15, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, T.; Ito, H.; Terao, H.; Yoshida, M.; Matsuzaki, J. Ureteral stent encrustation, incrustation, and coloring: Morbidity related to indwelling times. J. Endourol. 2012, 26, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elwood, C.N.; Lo, J.; Chou, E.; Crowe, A.; Arsovska, O.; Adomat, H.; Miyaoka, R.; Tomlinson-Guns, E.; Monga, M.; Chew, B.H.; et al. Understanding urinary conditioning film components on ureteral stents: Profiling protein components and evaluating their role in bacterial colonization. Biofouling 2013, 29, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, C.Y.; Poindexter, J.R.; Adams-Huet, B.; Pearle, M.S. Predictive value of kidney stone composition in the detection of metabolic abnormalities. Am. J. Med. 2003, 115, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roupret, M.; Daudon, M.; Hupertan, V.; Gattegno, B.; Thibault, P.; Traxer, O. Can ureteral stent encrustation analysis predict urinary stone composition? Urology 2005, 66, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sighinolfi, M.C.; Sighinolfi, G.P.; Galli, E.; Micali, S.; Ferrari, N.; Mofferdin, A.; Bianchi, G. Chemical and Mineralogical Analysis of Ureteral Stent Encrustation and Associated Risk Factors. Urology 2015, 86, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betschart, P.; Zumstein, V.; Buhmann, M.T.; Albrich, W.C.; Nolte, O.; Gusewell, S.; Schmid, H.P.; Ren, Q.; Abt, D. Influence of biofilms on morbidity associated with short-term indwelling ureteral stents: A prospective observational study. World J. Urol. 2019, 37, 1703–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betschart, P.; Zumstein, V.; Buhmann, M.T.; Altenried, S.; Babst, C.; Mullhaupt, G.; Gusewell, S.; Schmid, H.P.; Ren, Q.; Abt, D. Symptoms Associated with Long-term Double-J Ureteral Stenting and Influence of Biofilms. Urology 2019, 134, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrecilla, C.; Fernandez-Concha, J.; Cansino, J.R.; Mainez, J.A.; Amon, J.H.; Costas, S.; Angerri, O.; Emiliani, E.; Arrabal Martin, M.A.; Arrabal Polo, M.A.; et al. Reduction of ureteral stent encrustation by modulating the urine pH and inhibiting the crystal film with a new oral composition: A multicenter, placebo controlled, double blind, randomized clinical trial. BMC Urol. 2020, 20, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.M.; Shenkin, A.; Amrein, K.; Augsburger, M.; Biesalski, H.K.; Bischoff, S.C.; Casaer, M.P.; Gundogan, K.; Lepp, H.L.; de Man, A.M.E.; et al. ESPEN micronutrient guideline. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 1357–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daymond, R.; Curtis, S.L.; Mishra, V.; Roberts, N.B. Assay in serum of exchangeable copper and total copper using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS): Development, optimisation and evaluation of a routine procedure. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2020, 80, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldhaber, S.B. Trace element risk assessment: Essentiality vs. toxicity. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. RTP 2003, 38, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moini, M.; To, U.; Schilsky, M.L. Recent advances in Wilson disease. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobesky, R.; Guillaud, O.; Bouzbib, C.; Sogni, P.; Poujois, A.; Woimant, F.; Duclos-Vallee, J.C.; Bourliere, M.; de Ledinghen, V.; Ganne-Carrie, N.; et al. Non-invasive diagnosis and follow-up of rare genetic liver diseases. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2022, 46, 101768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for Study of Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Wilson’s disease. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streng, T.; Hedlund, P.; Talo, A.; Andersson, K.E.; Gillespie, J.I. Phasic non-micturition contractions in the bladder of the anaesthetized and awake rat. Bju. Int. 2006, 97, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Materion GmbH. Temporäre Implantate Und Instrumente Aus Kunststoffen Für Die Anwendung in Der Urologie Mit Angepasster Antibakterieller Und Inkrustrations-Hemmender Oberfläche, uro-antibak-teilvorhaben: Entwicklung Einer Biokompatiblen Beschichtung Mit Zeitlich Definiertem Release Antibakterieller Species: Schlussbericht: Laufzeit Des Vorhabens: 01.08.16-31.07.19; Materion GmbH: Wismar, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wataha, J.C.; Nelson, S.K.; Lockwood, P.E. Elemental release from dental casting alloys into biological media with and without protein. Dent. Mater. Off. Publ. Acad. Dent. Mater. 2001, 17, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.S., Jr.; Humphrey, P.A.; Rayala, H.J.; Gardner, S.M.; Mackey, R.B.; Clayman, R.V. Comparative ureteral microanatomy. J. Endourol. 1996, 10, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzieżyc, K.; Litwin, T.; Członkowska, A. Other organ involvement and clinical aspects of Wilson disease. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Członkowska, A., Schilsky, M.L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 142, pp. 157–169. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, S.M.; Ohnishi, T.; Clark, N.M.; He, J.; Arnold, L.L. Investigations of rodent urinary bladder carcinogens: Collection, processing, and evaluation of urine and bladders. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevock, P.N.; Khan, S.R.; Hackett, R.L. Urinary chemistry of the normal Sprague-Dawley rat. Urol. Res. 1993, 21, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition, and Allergies (NDA). Allergies. Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for water. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyre, A.; Casanova-Hampton, K.; Subashchandrabose, S. Copper Homeostatic Mechanisms and Their Role in the Virulence of Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica. EcoSal Plus 2021, 9, eESP00142020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyre, A.N.; Kavanagh, K.; Kock, N.D.; Donati, G.L.; Subashchandrabose, S. Copper Is a Host Effector Mobilized to Urine during Urinary Tract Infection To Impair Bacterial Colonization. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, e01041-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowdy, R.P. Copper metabolism. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1969, 22, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, E.; Lutsenko, S.; Bandmann, O. Animal models of Wilson disease. J. Neurochem. 2018, 146, 356–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazato, K.; Nakajima, K.; Nakano, T.; Kodaira, T.; Nakayama, K.; Satoh, M.; Nagamine, T. Metallothionein (MT) 1/2 expression in MT 1/2 and MT 3 knock-out mice and Long-Evans Cinnamon (LEC) rats. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 37, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Owen, C.A., Jr.; Hazelrig, J.B. Copper deficiency and copper toxicity in the rat. Am. J. Physiol. 1968, 215, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grass, G.; Rensing, C.; Solioz, M. Metallic copper as an antimicrobial surface. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreini, C.; Banci, L.; Bertini, I.; Rosato, A. Occurrence of copper proteins through the three domains of life: A bioinformatic approach. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, J.H.; Quintana, J.; Ramirez, D.; Laubenbacher, R.; Arguello, J.M.; Mendes, P. An important role for periplasmic storage in Pseudomonas aeruginosa copper homeostasis revealed by a combined experimental and computational modeling study. Mol. Microbiol. 2018, 110, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volentini, S.I.; Farias, R.N.; Rodriguez-Montelongo, L.; Rapisarda, V.A. Cu(II)-reduction by Escherichia coli cells is dependent on respiratory chain components. Biomet. Int. J. Role Met. Ions Biol. Biochem. Med. 2011, 24, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rensing, C.; Grass, G. Escherichia coli mechanisms of copper homeostasis in a changing environment. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 27, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaweeteerawat, C.; Chang, C.H.; Roy, K.R.; Liu, R.; Li, R.; Toso, D.; Fischer, H.; Ivask, A.; Ji, Z.; Zink, J.I.; et al. Cu Nanoparticles Have Different Impacts in Escherichia coli and Lactobacillus brevis than Their Microsized and Ionic Analogues. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7215–7225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalecki, A.G.; Crawford, C.L.; Wolschendorf, F. Copper and Antibiotics: Discovery, Modes of Action, and Opportunities for Medicinal Applications. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2017, 70, 193–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, D.K.; Lau, W.Y.; Chan, W.T.; Yan, A. Copper efflux is induced during anaerobic amino acid limitation in Escherichia coli to protect iron-sulfur cluster enzymes and biogenesis. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 4556–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Nishioka, H. Intracellular generation of superoxide by copper sulphate in Escherichia coli. Mutat. Res. 1997, 389, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Nguyen, T.T.; Yoon, J.; Lee, C. Role of reactive oxygen species in Escherichia coli inactivation by cupric ion. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11299–11304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, E.I.; Robinson, A.E.; Bandara, N.; Rogers, B.E.; Henderson, J.P. Copper import in Escherichia coli by the yersiniabactin metallophore system. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 1016–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova-Hampton, K.; Carey, A.; Kassam, S.; Garner, A.; Donati, G.L.; Thangamani, S.; Subashchandrabose, S. A genome-wide screen reveals the involvement of enterobactin-mediated iron acquisition in Escherichia coli survival during copper stress. Met. Integr. Biomet. Sci. 2021, 13, mfab052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Yu, Z.H.; Au-Yeung, H.Y.; Hirayama, T.; Sun, H.; Yan, A. Zinc excess increases cellular demand for iron and decreases tolerance to copper in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 16978–16991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, J.L.; Shen, J.K.; Keheila, M.; Abourbih, S.R.; Lee, A.; Stokes, P.K.; Li, R.; Alsyouf, M.; Lightfoot, M.A.; Baldwin, D.D. Kidney, Ureter, and Bladder (KUB): A Novel Grading System for Encrusted Ureteral Stents. Urology 2016, 97, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhmann, M.T.; Abt, D.; Nolte, O.; Neu, T.R.; Strempel, S.; Albrich, W.C.; Betschart, P.; Zumstein, V.; Neels, A.; Maniura-Weber, K.; et al. Encrustations on ureteral stents from patients without urinary tract infection reveal distinct urotypes and a low bacterial load. Microbiome 2019, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.L.; Guo, P.; Li, X.W.; Wang, A.Y. Comparative study on structure and wetting properties of diamond-like carbon films by W and Cu doping. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2017, 73, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nißen, S.; Heeg, J.; Wienecke, M.; Behrend, D.; Warkentin, M.; Rokosz, K.; Gaiaschi, S.; Chapon, P. Surface Characterization and Copper Release of a-C:H:Cu Coatings for Medical Applications. Coatings 2019, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Handschuh-Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, Y. Robust Biomimetic Hierarchical Diamond Architecture with a Self-Cleaning, Antibacterial, and Antibiofouling Surface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 24432–24441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, M.; Tobe, S.; Takeuchi, L. Effects of diamond-like carbon thin film and wrinkle microstructure on cell proliferation. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2018, 90, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Q.; Li, L.J.; Wei, B.; Wen, F.; Cao, H.T.; Pei, Y.T. Effect of sputtering pressure on the surface topography, structure, wettability and tribological performance of DLC films coated on rubber by magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 365, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzocchi, T.; Lucarini, G.; Roehrer, I.; Menciassi, A.; Ricotti, L. PDMS and DLC-coated unidirectional valves for artificial urinary sphincters: Opening performance after 126 days of immersion in urine. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2022, 110, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.H.; Huang, C.F.; Ou, K.L.; Peng, P.W. Mechanical properties and antibacterial activity of copper doped diamond-like carbon films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 206, 1037–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchholz, N.; Budia, A.; Cruz, J.; Kram, W.; Humphreys, O.; Reches, M.; Valero Boix, R.; Soria, F. Urinary Stent Development and Evaluation Models: In Vitro, Ex Vivo and In Vivo-A European Network of Multidisciplinary Research to Improve Urinary Stents (ENIUS) Initiative. Polymers 2022, 14, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.; Mi, G.; Wang, M.; Webster, T.J. In vitro and ex vivo systems at the forefront of infection modeling and drug discovery. Biomaterials 2019, 198, 228–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.C., Jr.; Gambaro, G.; Rodgers, A.; Asplin, J.; Bonny, O.; Costa-Bauza, A.; Ferraro, P.M.; Fogazzi, G.; Fuster, D.G.; Goldfarb, D.S.; et al. Urine and stone analysis for the investigation of the renal stone former: A consensus conference. Urolithiasis 2021, 49, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.R.; Kok, D.J. Modulators of urinary stone formation. Front. Biosci. A J. Virtual Libr. 2004, 9, 1450–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kram, W.; Buchholz, N.; Hakenberg, O.W. Ureteral stent encrustation. Pathophysiology. Arch. Esp. De Urol. 2016, 69, 485–493. [Google Scholar]
- Broomfield, R.J.; Morgan, S.D.; Khan, A.; Stickler, D.J. Crystalline bacterial biofilm formation on urinary catheters by urease-producing urinary tract pathogens: A simple method of control. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 1367–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stickler, D.J. Clinical complications of urinary catheters caused by crystalline biofilms: Something needs to be done. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 276, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloutier, J.; Villa, L.; Traxer, O.; Daudon, M. Kidney stone analysis: “Give me your stone, I will tell you who you are!”. World J. Urol. 2015, 33, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, G. Stone analysis. Urol. Res. 2006, 34, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Xie, L.; Arada, R.; Patel, R.M.; Landman, J.; Clayman, R.V. Qualitative Review of Clinical Guidelines for Medical and Surgical Management of Urolithiasis: Consensus and Controversy 2020. J. Urol. 2021, 205, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Ortiz, E.J.; Eisner, B.H.; Lange, D.; Gerlach, R. Current insights into the mechanisms and management of infection stones. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2019, 16, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, C.; Petrik, A.; Sarica, K.; Seitz, C.; Skolarikos, A.; Straub, M.; Knoll, T. EAU Guidelines on Diagnosis and Conservative Management of Urolithiasis. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klis, R.; Szymkowiak, S.; Madej, A.; Blewniewski, M.; Krzeslak, A.; Forma, E.; Brys, M.; Lipinski, M.; Rozanski, W. Rate of positive urine culture and double-J catheters colonization on the basis of microorganism DNA analysis. Cent. Eur. J. Urol. 2014, 67, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lifshitz, D.A.; Winkler, H.Z.; Gross, M.; Sulkes, J.; Baniel, J.; Livne, P.M. Predictive value of urinary cultures in assessment of microbial colonization of ureteral stents. J. Endourol. 1999, 13, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



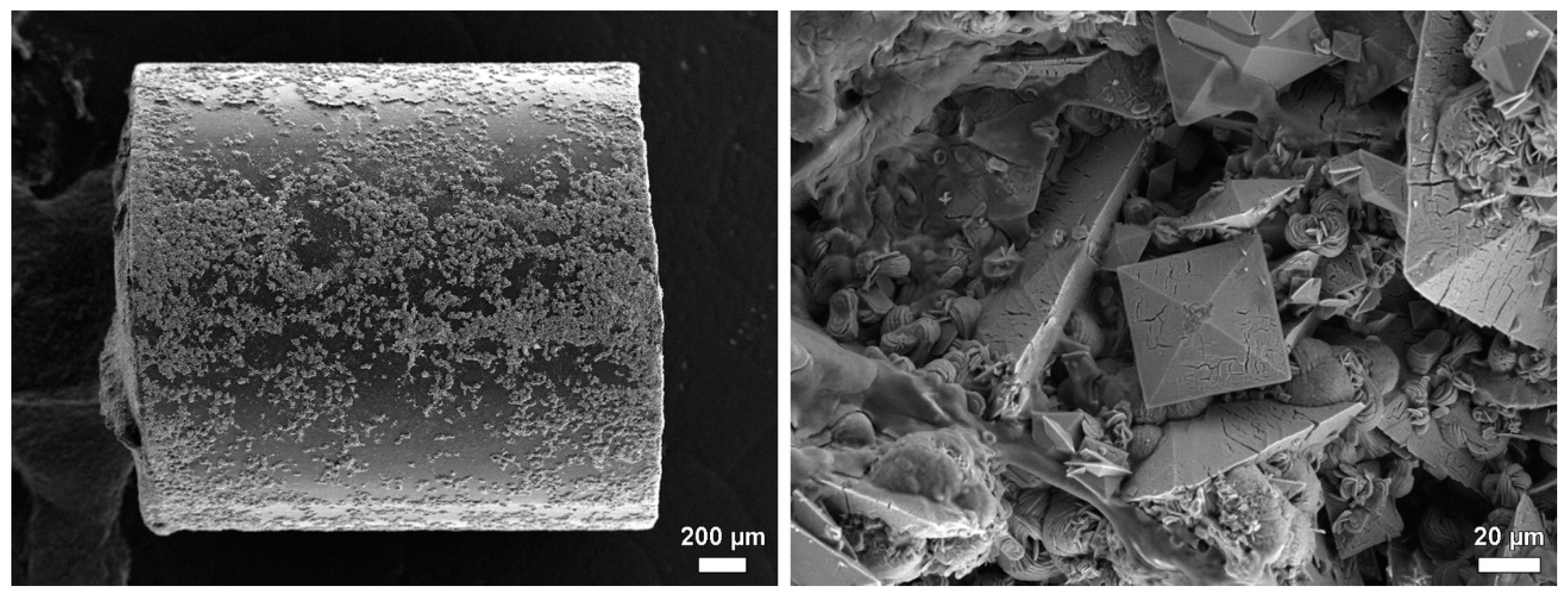
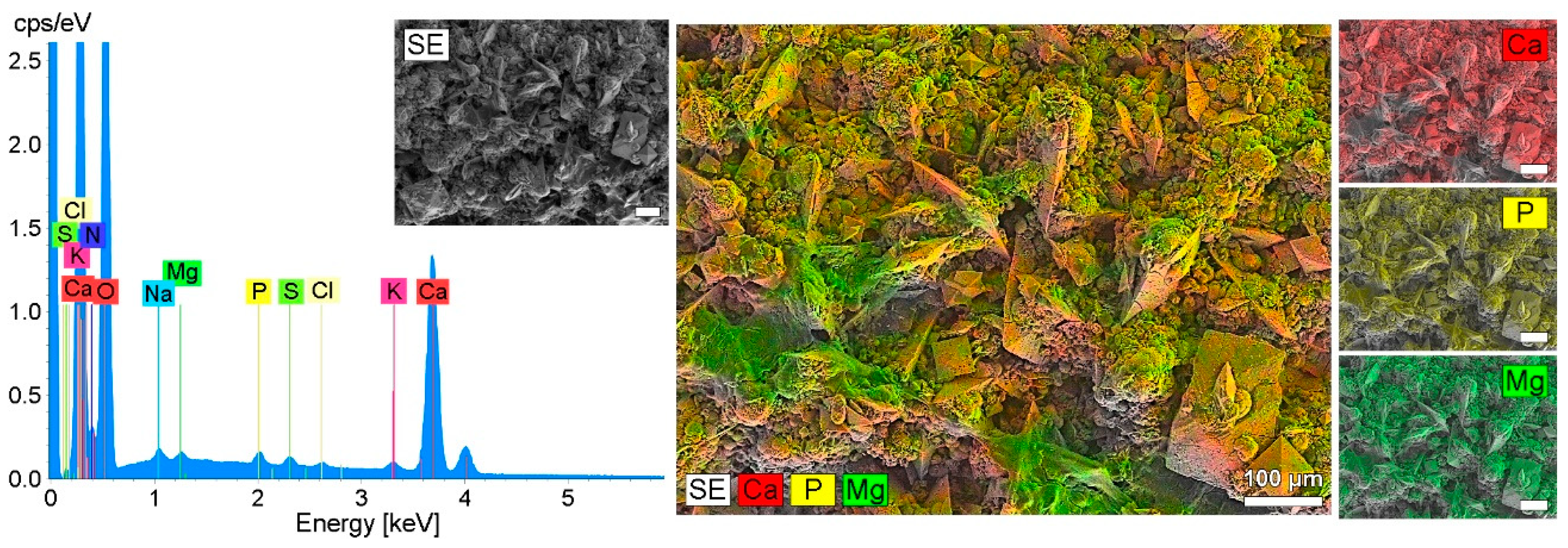


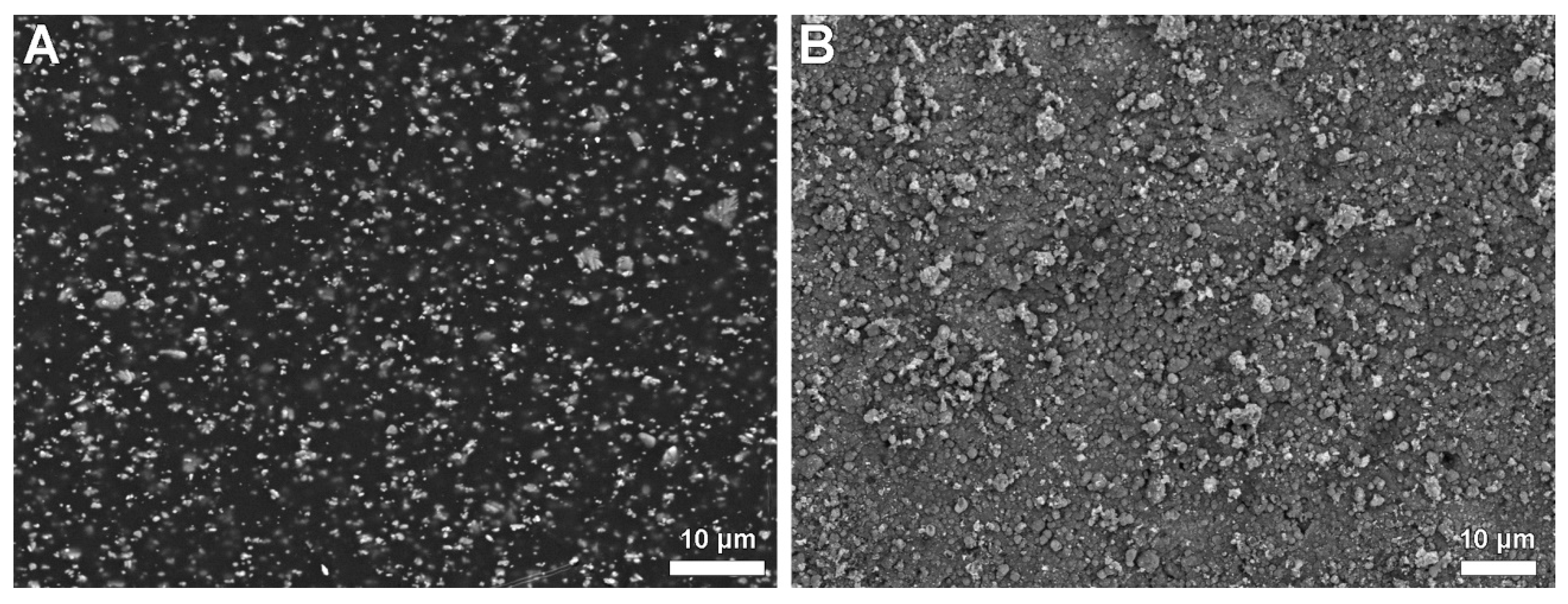
| No. | Process | Gasflow | Pressure Mbar | RF Excitation Power/W | Bias Voltage/V | Time/min | Thickness/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PECVD a-C:H | 7 sccm Ar + 50 sccm C2H2 | 2.3 × 10−2 | 250 | 230 | 10 | 200 |
| 2 | PVD magnetron sputtering Cu | 50 sccm Ar | 3.8 × 10−2 | 150 | 130 | 10 | 200 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kram, W.; Rebl, H.; de la Cruz, J.E.; Haag, A.; Renner, J.; Epting, T.; Springer, A.; Soria, F.; Wienecke, M.; Hakenberg, O.W. Interactive Effects of Copper-Doped Urological Implants with Tissue in the Urinary Tract for the Inhibition of Cell Adhesion and Encrustation in the Animal Model Rat. Polymers 2022, 14, 3324. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14163324
Kram W, Rebl H, de la Cruz JE, Haag A, Renner J, Epting T, Springer A, Soria F, Wienecke M, Hakenberg OW. Interactive Effects of Copper-Doped Urological Implants with Tissue in the Urinary Tract for the Inhibition of Cell Adhesion and Encrustation in the Animal Model Rat. Polymers. 2022; 14(16):3324. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14163324
Chicago/Turabian StyleKram, Wolfgang, Henrike Rebl, Julia E. de la Cruz, Antonia Haag, Jürgen Renner, Thomas Epting, Armin Springer, Federico Soria, Marion Wienecke, and Oliver W. Hakenberg. 2022. "Interactive Effects of Copper-Doped Urological Implants with Tissue in the Urinary Tract for the Inhibition of Cell Adhesion and Encrustation in the Animal Model Rat" Polymers 14, no. 16: 3324. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14163324
APA StyleKram, W., Rebl, H., de la Cruz, J. E., Haag, A., Renner, J., Epting, T., Springer, A., Soria, F., Wienecke, M., & Hakenberg, O. W. (2022). Interactive Effects of Copper-Doped Urological Implants with Tissue in the Urinary Tract for the Inhibition of Cell Adhesion and Encrustation in the Animal Model Rat. Polymers, 14(16), 3324. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14163324






