Effect of Polymer Coatings on the Permeability and Chloride Ion Penetration Resistances of Nano-Particles and Fibers-Modified Cementitious Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Work Method
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mix Proportions
2.3. Treatment of the Polymer Coating on the Specimen Surface
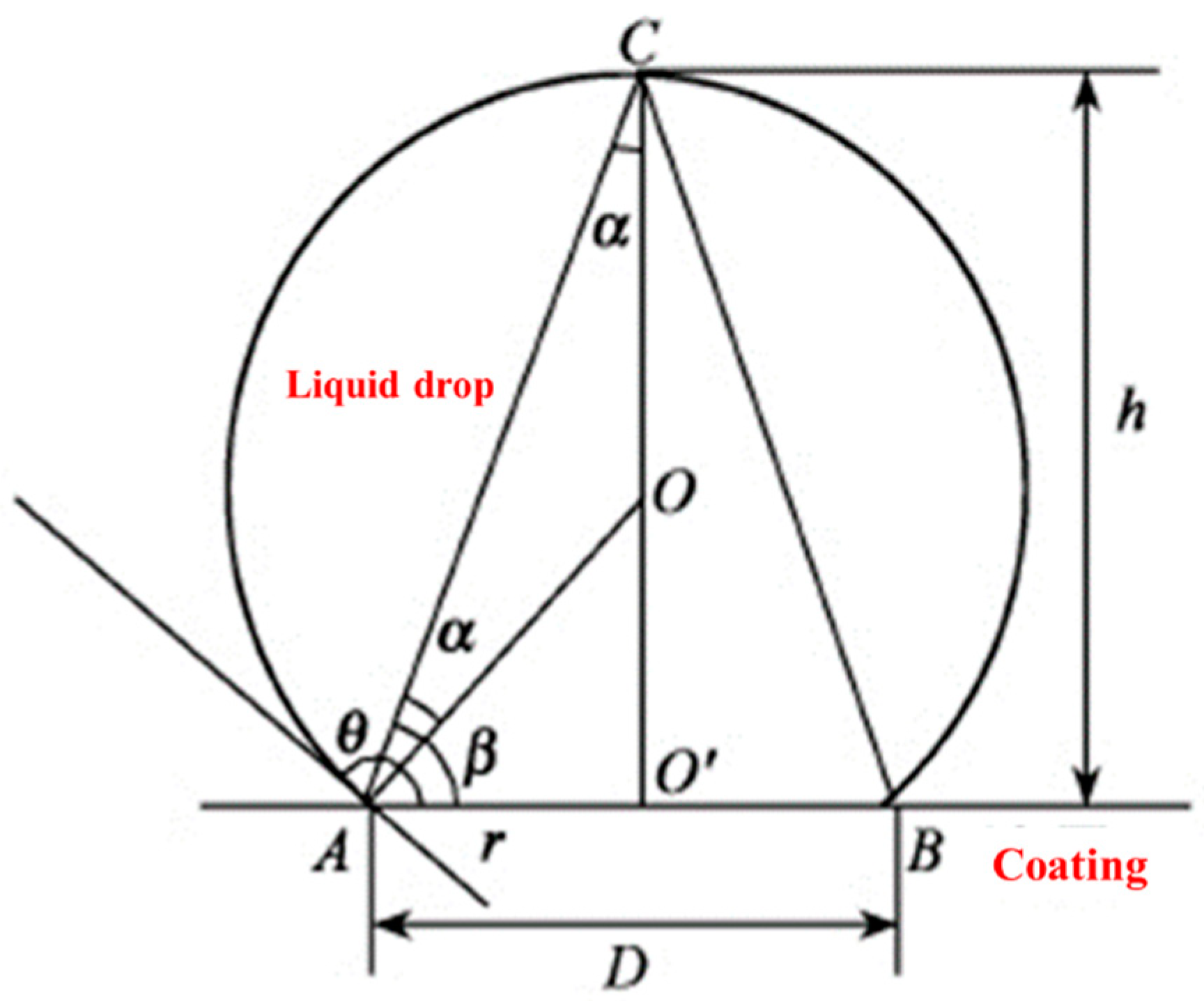
2.4. Water Contact Angle Test
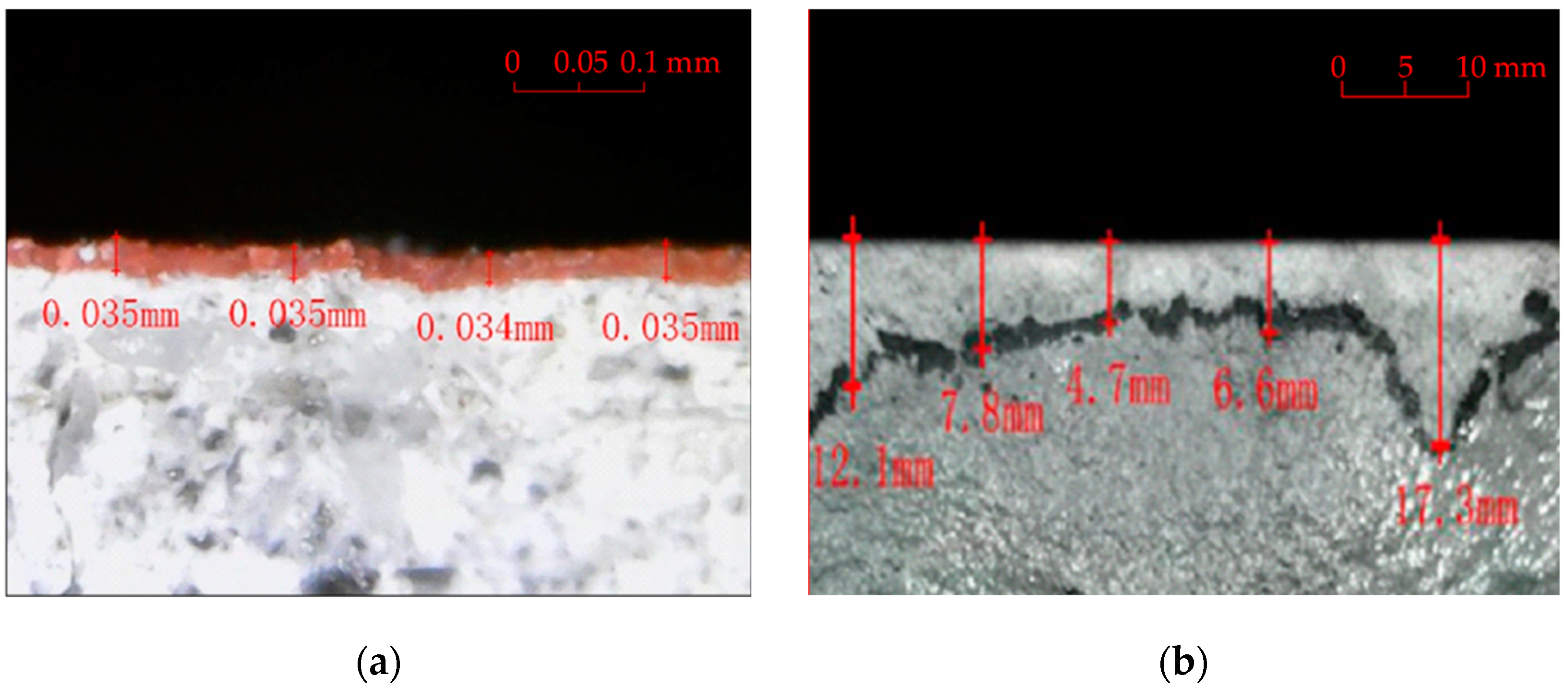
2.5. Permeability Resistance Test
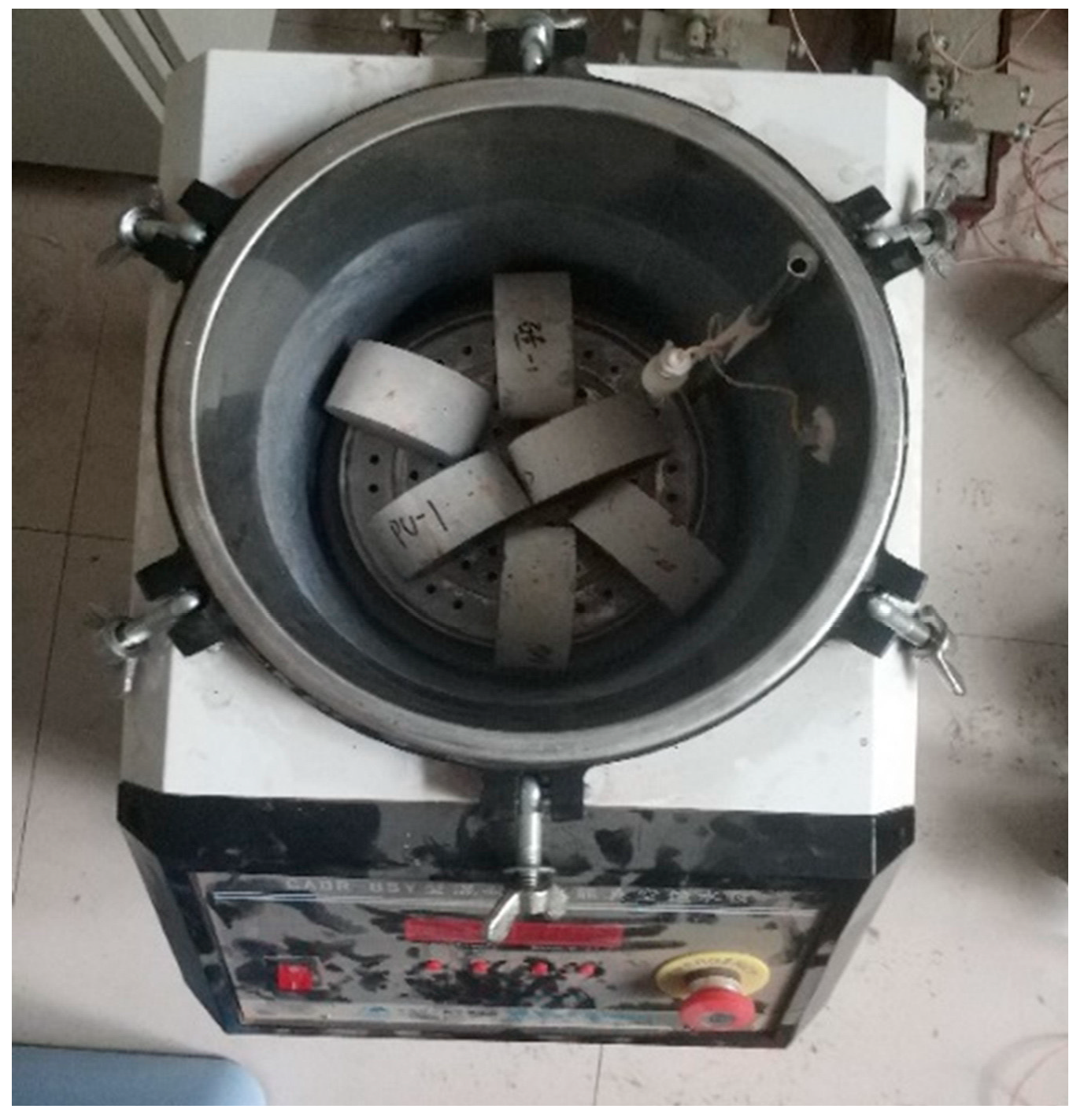
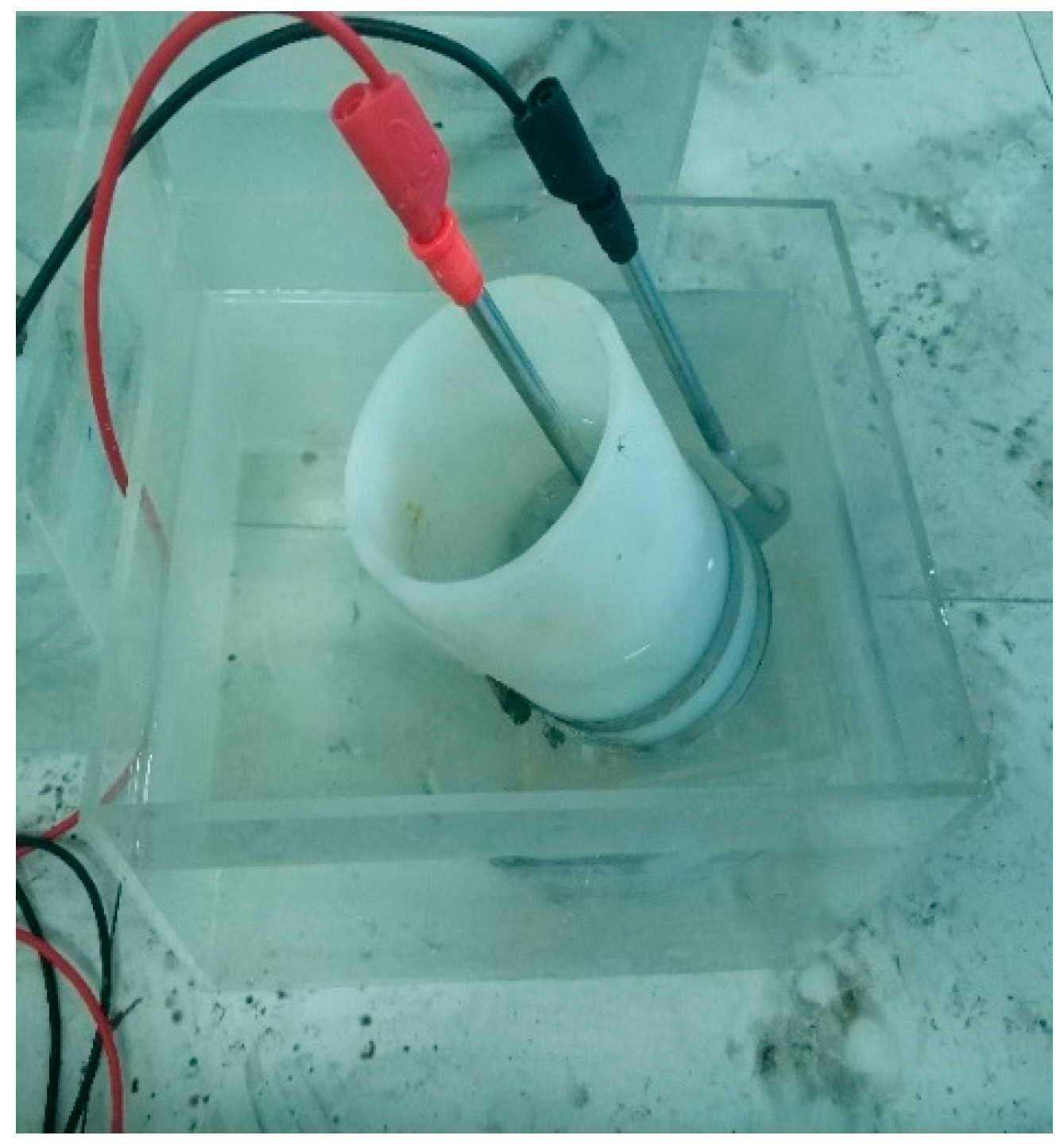
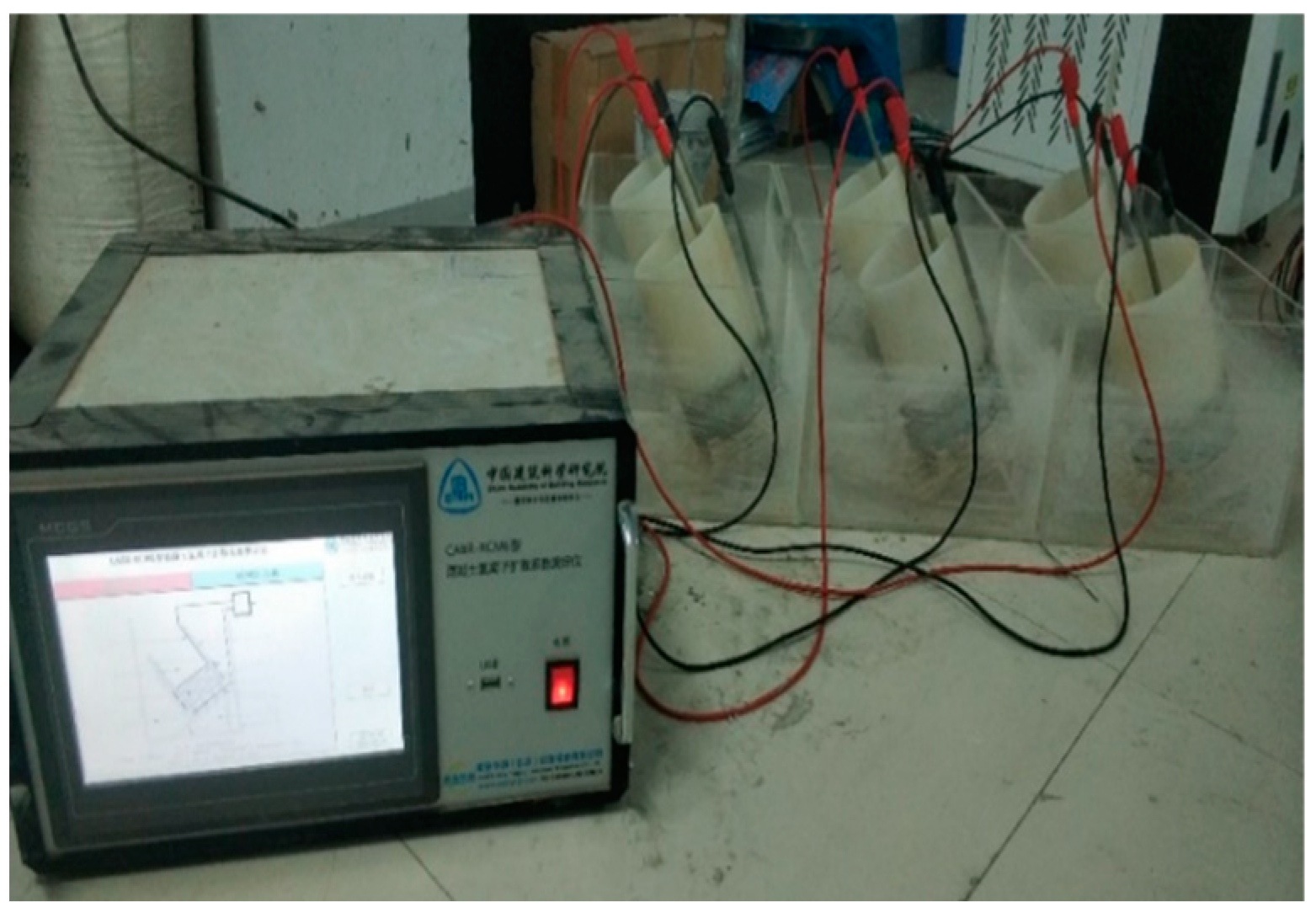
2.6. Chloride Ion Penetration Resistance Test
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Water Contact Angle
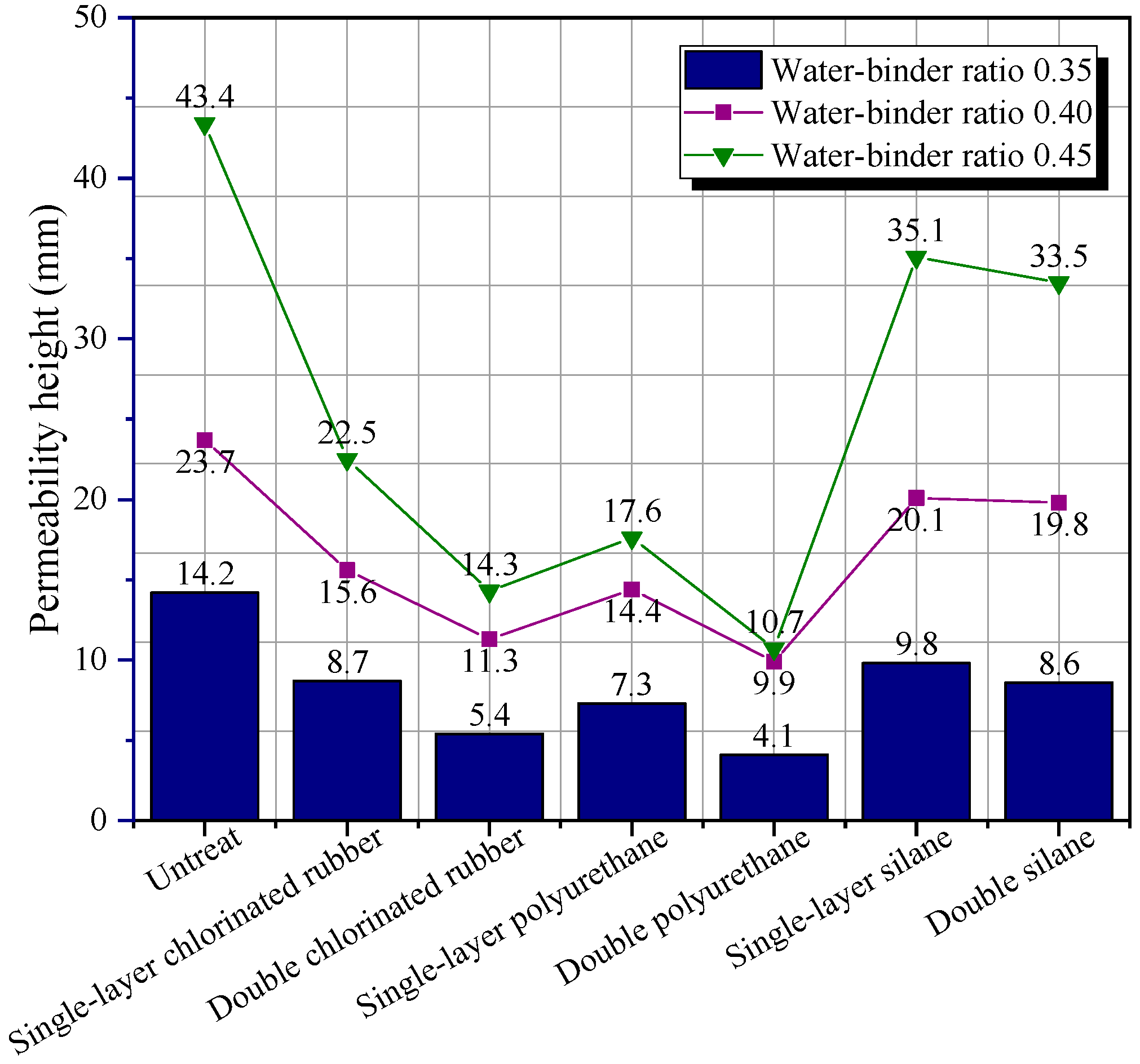
3.2. Permeability Resistance
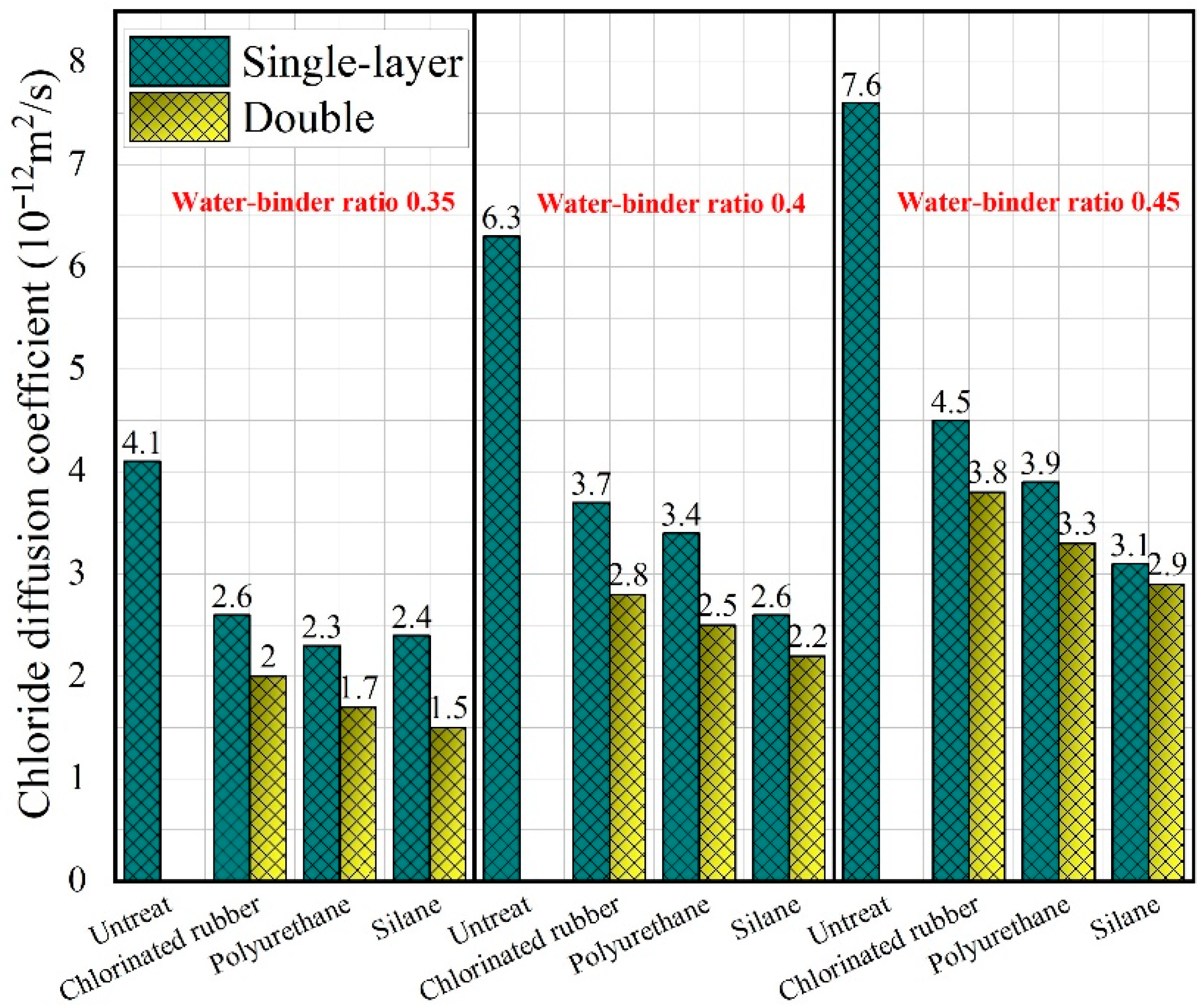
3.3. Chloride Ion Penetration Resistance
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Chlorinated rubber coating, polyurethane coating, and silane coating can turn the surface of the cementitious composite into a hydrophobic surface. The surface water contact angle of the single-layer silane-coated material was 221.2% higher than that of the specimen without protective treatment. Increasing the number of coating layers and the water–binder ratio of the material had no significant effect on the water contact angle of the material surface.
- (2)
- All three types of polymer coatings can reduce the permeability height of the composite. The polyurethane coating had the most obvious improvement in the permeability resistance of specimens. Compared with the control group, the permeability height of the specimens with a water–binder ratio of 35 wt.% coated with single-layer and double polyurethane coating decreased by 48.6% and 71.1%, respectively. There was a negative correlation between the permeability resistance and the water–binder ratios of the NFCC.
- (3)
- The unsteady chloride ion diffusion coefficient of the NFCC decreased to a certain extent after the composites were treated with different types and numbers of layers of polymer coatings. This enhancement efficiency was more obvious for silane coating. When the number of layers of polymer coating was increased to two, the chloride ion penetration resistance of the NFCC was increased by another 10–15%.
- (4)
- With the increase in global carbon dioxide concentration and the frequent occurrence of severe weather, carbonation failure and freeze–thaw cycle failure have become common problems threatening the durability of cementitious composites. In this paper, only the influence of polymer coating on the water contact angle, permeability resistance, and chloride ion permeability resistance of cementitious composites was studied, and the carbonation resistance and freeze–thaw cycle resistance of materials were lacking. Future research should supplement the research content on the effect of polymer coatings on carbonation resistance and freeze–thaw cycle resistance of cementitious composites.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.; Luo, R.Y.; Zhang, W.; Jin, M.M.; Tang, S.W. Effects of fineness and content of phosphorus slag on cement hydration, permeability, pore structure and fractal dimension of concrete. Fractals 2021, 29, 2140004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Johannesson, B.; Geiker, M. A review: Self-healing in cementitious materials and engineered cementitious composite as a self-healing material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 28, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Kang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, B. Influence of SiO2 /Na2O molar ratio on mechanical properties and durability of metakaolin-fly ash blend alkali-activated sustainable mortar incorporating manufactured sand. J. Mater. Res. Technol. JMRT 2022, 18, 3553–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, Q.-F.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y.; Ling, Y. Effect of PVA fiber on durability of cementitious composite containing nano-SiO2. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2019, 8, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golewski, G.L.; Szostak, B. Strengthening the very early-age structure of cementitious composites with coal fly ash via incorporating a novel nanoadmixture based on C-S-H phase activators. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 312, 125426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, A.R.; Ganesh, P. Effect of steel fibres and nano silica on fracture properties of medium strength concrete. Adv. Concr. Constr. 2019, 7, 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, Y.M.; Khan, M.I. Fiber-matrix interactions in fiber-reinforced concrete: A review. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2016, 41, 1183–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Hu, S. Influence of fibers on the mechanical properties and durability of ultra-high-performance concrete: A review. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 52, 104370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Gao, Z.; Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Wang, T. Influencing factors analysis and optimized prediction model for rheology and flowability of nano-SiO2 and PVA fiber reinforced alkali-activated composites. J. Clean Prod. 2022, 366, 132988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Guo, F.X.; Yang, H.M.; Wang, Y.; Tang, S.W. Comparison of fly ash, PVA fiber, MgO and shrinkage-reducing admixture on the frost resistance of face slab concrete via pore structural and fractal analysis. Fractals 2021, 29, 2140002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakravan, H.R.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. Synthetic fibers for cementitious composites: A critical and in-depth review of recent advances. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 207, 491–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Wang, K.X.; Zhang, T.H. Interfacial properties of geopolymer mortar and concrete substrate: Effect of polyvinyl alcohol fiber and nano-SiO2 contents. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 315, 125735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Xu, Z.L.; Liu, Z.L.; Jiang, J.H. Effect of silica fume and polyvinyl alcohol fiber on mechanical properties and frost resistance of concrete. Buildings 2022, 12, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Majidi, M.H.; Lampropoulos, A.P.; Cundy, A.B.; Tsioulou, O.T.; Al-Rekabi, S. A novel corrosion resistant repair technique for existing reinforced concrete (RC) elements using polyvinyl alcohol fibre reinforced geopolymer concrete (PVAFRGC). Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 164, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Z.; Zhang, P.; Guo, J.J.; Wang, K.X. Bonding behavior of concrete matrix and alkali-activated mortar incorporating nano-SiO2 and polyvinyl alcohol fiber: Theoretical analysis and prediction model. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 31638–31649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Chang, H.L.; Liu, X.; Ye, S.X.; Shu, X.; Ran, Q.P. The significance of dispersion of nano-SiO2 on early age hydration of cement pastes. Mater. Des. 2020, 186, 108320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Huang, C.X.; Chen, Y. Experimental study on photocatalytic degradation efficiency of mixed crystal nano-TiO2 concrete. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2020, 9, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nazari, A.; Riahi, S. The effects of curing medium on the flexural strength and water permeability of cementitious composites containing Fe2O3 nanofillers. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2011, 102, 1312–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Shen, S.H.; Pang, Y.Y.; Gao, D.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Sheikh, M.N. Mechanical properties of fiber and nano-Al2O3 reinforced magnesium phosphate cement composite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 270, 121861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, M.R.; Bassuoni, M.T. Effect of nano-based coatings on concrete under aggravated exposures. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2020, 32, 04020284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, A.R.; Ganesh, P.; Kumar, S.S.; Iyer, N.R. Fracture energy and tension softening relation for nano-modified concrete. Struct. Eng. Mech. 2015, 54, 1201–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.Y.; Zhang, P.; Wu, J.J.; Jing, Y.T.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, T.H. Comprehensive review of the properties of fly ash-based geopolymer with additive of nano-SiO2. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2022, 11, 1478–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.P.; Karade, S.R.; Bhattacharyya, S.K.; Yousuf, M.M.; Ahalawat, S. Beneficial role of nanosilica in cement based materials—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szostak, B.; Golewski, G.L. Rheology of cement pastes with siliceous fly ash and the CSH nano-admixture. Materials 2021, 14, 3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.M.; Zhang, P.; Wang, T.Y.; Zheng, Y.; Qiu, L.H.; Sun, S.W. Compressive strength and anti-chloride ion penetration assessment of geopolymer mortar merging PVA fiber and nano-SiO2 using RBF-BP composite neural network. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2022, 11, 1181–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almusallam, A.A.; Khan, F.M.; Dulaijan, S.U.; Al-Amoudi, O.S.B. Effectiveness of surface coatings in improving concrete durability. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2003, 25, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzenski, S.; Flores-Vivian, I.; Sobolev, K. Durability of superhydrophobic engineered cementitious composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 81, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, T.; Poultney, S. Waterborne silicone-organic hybrid coatings for exterior applications. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2007, 4, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.F.; Xiong, J.P.; Tang, Y.M.; Zuo, Y. EIS study on failure process of two polyurethane composite coatings. Prog. Organ. Coat. 2010, 69, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocijan, A.; Conradi, M.; Hocevar, M. The influence of surface wettability and topography on the bioactivity of TiO2/epoxy coatings on AISI 316L stainless steel. Materials 2019, 12, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ji, W.G.; Hu, J.M.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J.Q.; Cao, C.N. Water uptake of epoxy coatings modified with gamma-APS silane monomer. Prog. Organ. Coat. 2006, 57, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbucci, A.; Delucchi, M.; Cerisola, G. Organic coatings for concrete protection: Liquid water and water vapour permeabilities. Prog. Organ. Coat. 1997, 30, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamanti, M.V.; Brenna, A.; Bolzoni, F.; Berra, M.; Pastore, T.; Ormellese, M. Effect of polymer modified cementitious coatings on water and chloride permeability in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 720–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadati, S.; Arezoumandi, M.; Shekarchi, M. Long-term performance of concrete surface coatings in soil exposure of marine environments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 94, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB175-2007; Common Portland Cement. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2007.
- GB/T 50146-2014; Technical Code for Application of Fly Ash Concrete. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- United Nation Quality Detection. Chemical Compositions of Fly Ash; Datang Luoyang Thermoelectric Co., Ltd.: Henan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- United Nation Quality Detection. Physical Parameters of SiO2; Japan Cola Li Co., Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- United Nation Quality Detection. Physical Parameters of PVA Fiber; Hangzhou Wanjing New Material Co., Ltd.: Zhejiang, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- United Nation Quality Detection. Particle Size of Silica Sand; Yuan Heng Water Purification Material Factory: Gongyi, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Beijing Yingjun Testing Technology Service Co., Ltd. Technical Parameters of Chlorinated Rubber Coating and Polyurethane Coating; Nanjing Lishui Tianlong Chemical Co., Ltd.: Nanjing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Beijing Yingjun Testing Technology Service, Co., Ltd. Technical Parameters of Silane Coating; Beijing Montai Weiye Building Materials Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wenqin, D.; Yingzhu, W. Comparison of hypsometry and goniometry in contact angle measurement. J. Text. Res. 2007, 28, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 50082-2009; Standard for Test Methods of Long-Term Performance and Durability of Ordinary Concrete. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Hao, L.; Wang, H.; Chen, R. Organic–inorganic hybrid hydrophobic Mg(OH)2−xFx–MTES coating with ultraviolet durability and high visible transmittance. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 13569–13578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Bian, L.; Liu, Y.; Guan, Z. Superhydrophobic coating based on organic/inorganic double component adhesive and functionalized nanoparticles with good durability and anti-corrosion for protection of galvanized steel. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 640, 128360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, J.; Huang, J.; Tu, W.; Yang, Z. Preparation and properties of permeable organosiloxane protective paste used for concrete protection. J. Build. Mater. 2016, 19, 496–502. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito Corcione, C.; De Simone, N.; Santarelli, M.L.; Frigione, M. Protective properties and durability characteristics of experimental and commercial organic coatings for the preservation of porous stone. Prog. Organ. Coat. 2017, 103, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Huang, G.; Li, J.; Niu, Z.; Gao, B. A review on durability of basalt fiber reinforced concrete. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 225, 109519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lu, X.; Liu, L.S.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, G.; Guo, F.X.; Li, L. Influence of MgO on the hydration and shrinkage behavior of low heat Portland cement-based materials via pore structural and fractal analysis. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogas, J.A.; Real, S. A review on the carbonation and chloride penetration resistance of structural lightweight aggregate concrete. Materials 2019, 12, 3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, C.; Kang, L.; Zhao, X.; Li, W. Permeability resistance of concrete coatings. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 35, 1378–1384. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.L.; Liu, P.; Ma, L.N.; Yang, Z.J.; Chen, H.S.; Zhu, H.X.; Xiao, H.G.; Li, J. Research on the corrosion/permeability/frost resistance of concrete by experimental and microscopic mechanisms under different water-binder ratios. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2020, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Cheng, X.Q.; Li, X.G.; Jin, Z.; Liu, H.X. Corrosion behavior of Cr modified HRB400 steel rebar in simulated concrete pore solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 93, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.N.; Wang, H.G.; Liu, Z.Y. Evaluation on mechanical properties of high-performance biocomposite bridge deck structure: A review. Polym. Compos. 2021, 42, 6265–6297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reale, T.; O’Connor, A. A review and comparative analysis of corrosion-induced time to first crack models. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 36, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.A. Application of epoxy resins in building materials: Progress and prospects. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 1949–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; Luo, H.; Fan, W.; Shi, N.; Wang, H. Research progress of new carbon nanomaterials used in organic anticorrosive coatings. Surf. Technol. 2021, 50, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, H.Y.; Shin, D.G.; Choi, D.S. Evaluation of the durability of mortar and concrete applied with inorganic coating material and surface treatment system. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. Influencing factors of chloride ion permeability resistance of concrete in cold and arid regions of northwest China. J. High. Trans. Res. Dev. 2020, 37, 8. [Google Scholar]








| Chemical Compositions (wt.%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | Na2O | K2O | SO3 | |
| Fly ash | 9.12 | 52.12 | 17.86 | 6.57 | 3.26 | 2.38 | 2.05 | 0.23 |
| Cement | 63.14 | 21.05 | 5.28 | 2.57 | 3.58 | 0.17 | 0.58 | 2.39 |
| Fiber Length (mm) | Fiber Diameter (μm) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Dry Fracture Elongation (%) | Water Absorption (%) | Alkali Resistance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 40 | 1400 | 17 | <1 | 98 |
| Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | SiO2 Content (%) | Average Particle Size (nm) | pH Value | Bulk Density (g/cm3) | Heating Loss (%) | Ignition Loss (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 99.5 | 30 | 6 | 0.055 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Group | Water–Binder Ratio (wt.%) | Cement (kg/m3) | Fly Ash (kg/m3) | Nano-SiO2 (kg/m3) | PVA Fiber (kg/m3) | Silica Sand (kg/m3) | Water-Reducingagent (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 35 | 637 | 350 | 13 | 8.19 | 500 | 3 |
| B | 40 | 637 | 350 | 13 | 8.19 | 500 | 1.3 |
| C | 45 | 637 | 350 | 13 | 8.19 | 500 | — |
| Group | Type of Coating | Number of Layers |
|---|---|---|
| A | Chlorinated rubber coating | One Two |
| Polyurethane coating | ||
| Silane coating | ||
| B | Chlorinated rubber coating | One Two |
| Polyurethane coating | ||
| Silane coating | ||
| C | Chlorinated rubber coating | One Two |
| Polyurethane coating | ||
| Silane coating |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, P.; Wang, W.; Lv, Y.; Gao, Z.; Dai, S. Effect of Polymer Coatings on the Permeability and Chloride Ion Penetration Resistances of Nano-Particles and Fibers-Modified Cementitious Composites. Polymers 2022, 14, 3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14163258
Zhang P, Wang W, Lv Y, Gao Z, Dai S. Effect of Polymer Coatings on the Permeability and Chloride Ion Penetration Resistances of Nano-Particles and Fibers-Modified Cementitious Composites. Polymers. 2022; 14(16):3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14163258
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Peng, Wenshuai Wang, Yajun Lv, Zhen Gao, and Siyuan Dai. 2022. "Effect of Polymer Coatings on the Permeability and Chloride Ion Penetration Resistances of Nano-Particles and Fibers-Modified Cementitious Composites" Polymers 14, no. 16: 3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14163258
APA StyleZhang, P., Wang, W., Lv, Y., Gao, Z., & Dai, S. (2022). Effect of Polymer Coatings on the Permeability and Chloride Ion Penetration Resistances of Nano-Particles and Fibers-Modified Cementitious Composites. Polymers, 14(16), 3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14163258







