Comparative Study of Durability Behaviors of Thermoplastic Polypropylene and Thermosetting Epoxy Exposed to Elevated Temperature, Water Immersion and Sustained Bending Loading
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials and Sample Preparation
2.2. Immersion Conditions
2.3. Water Uptake Test
2.4. Tensile Test
2.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis Test (TGA)
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3. Results and Discussion
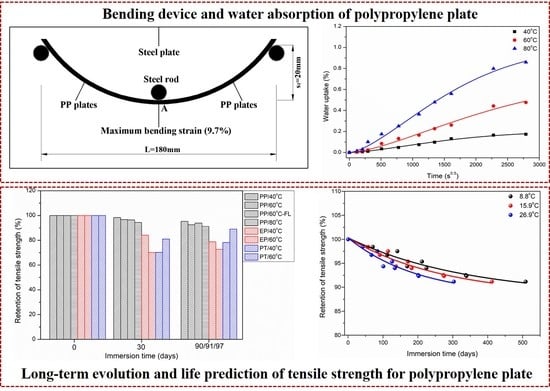
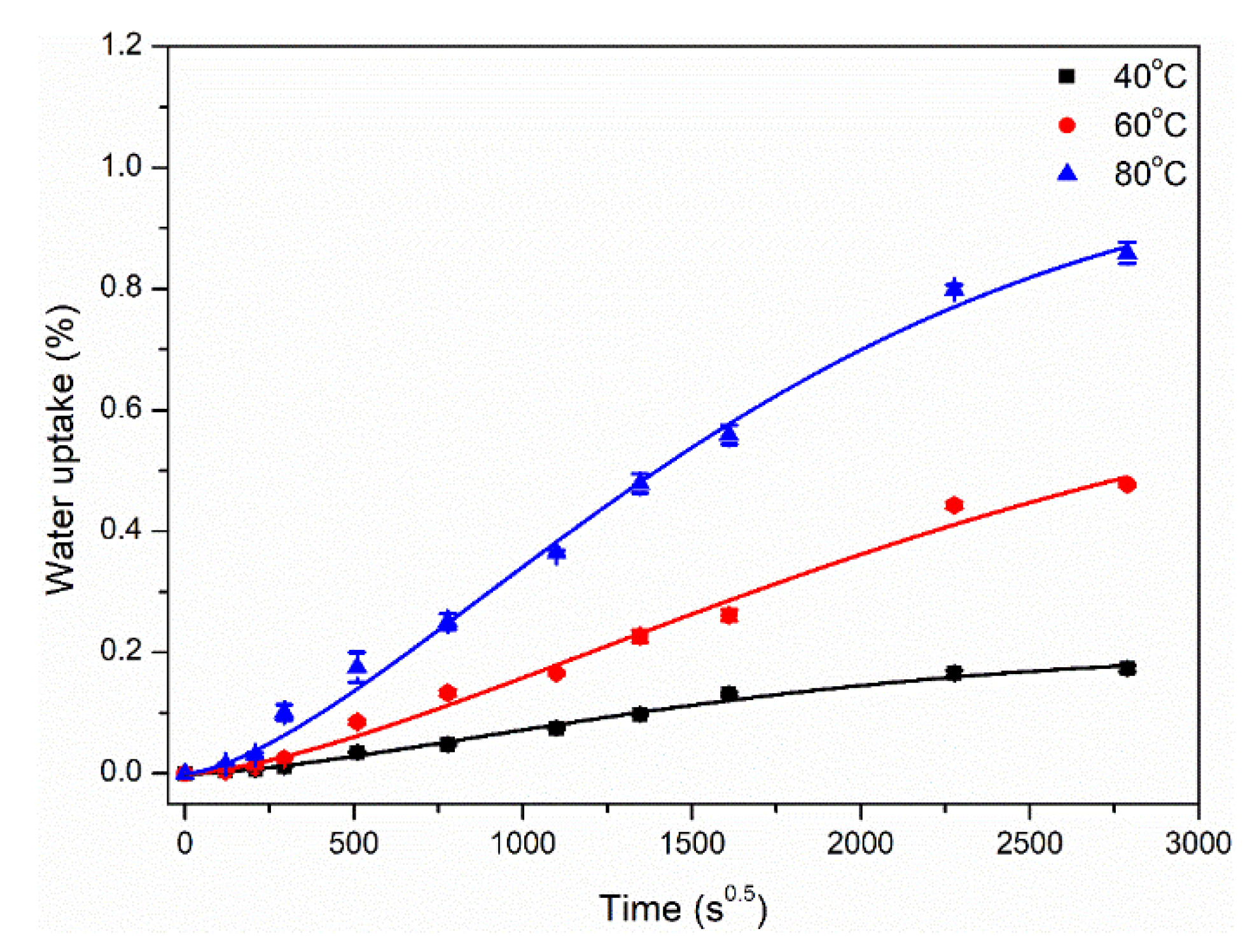
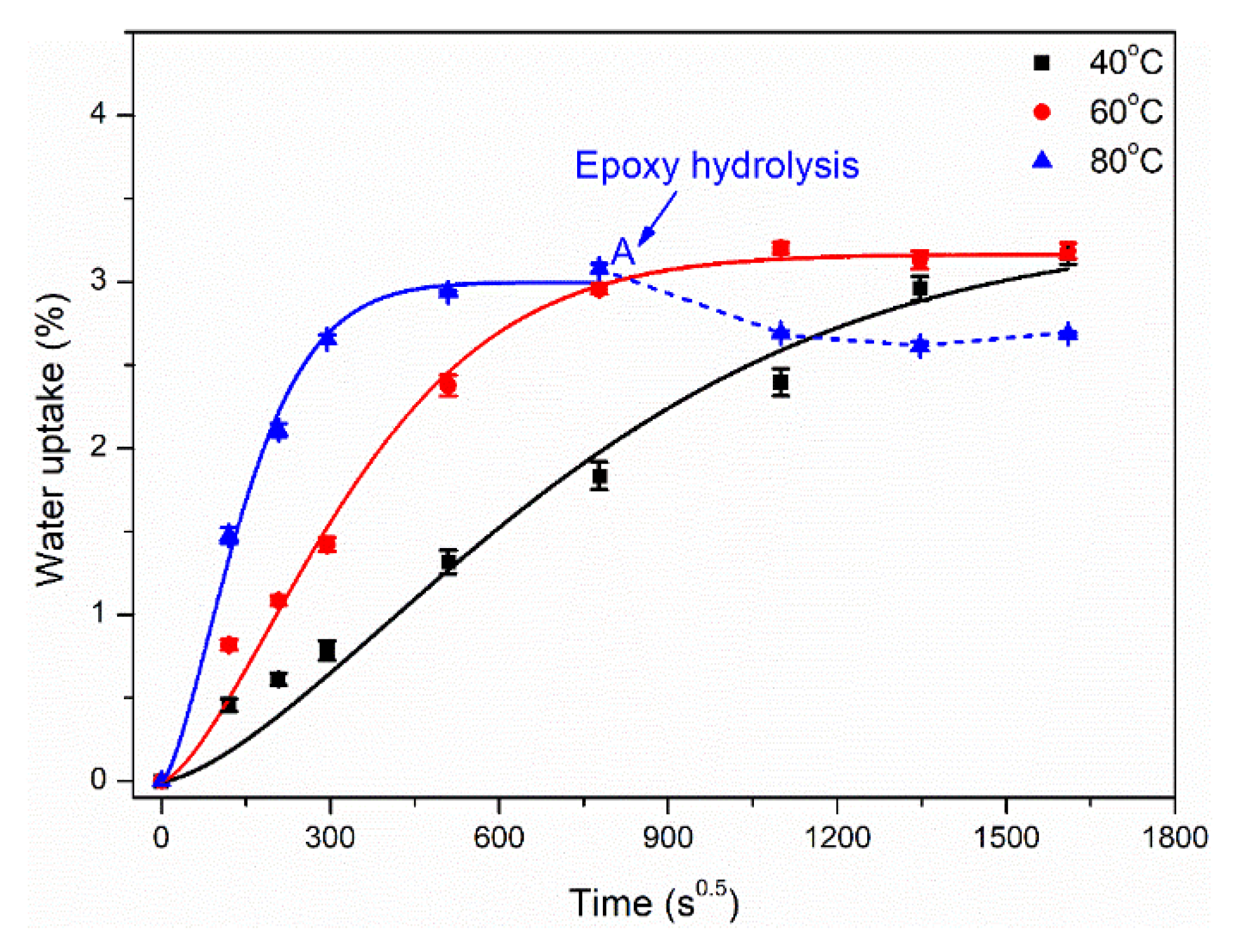
3.1. Water Absorption and Diffusion Behavior
3.2. Effect of Immersion on Mechanical Properties
3.2.1. Tensile Properties
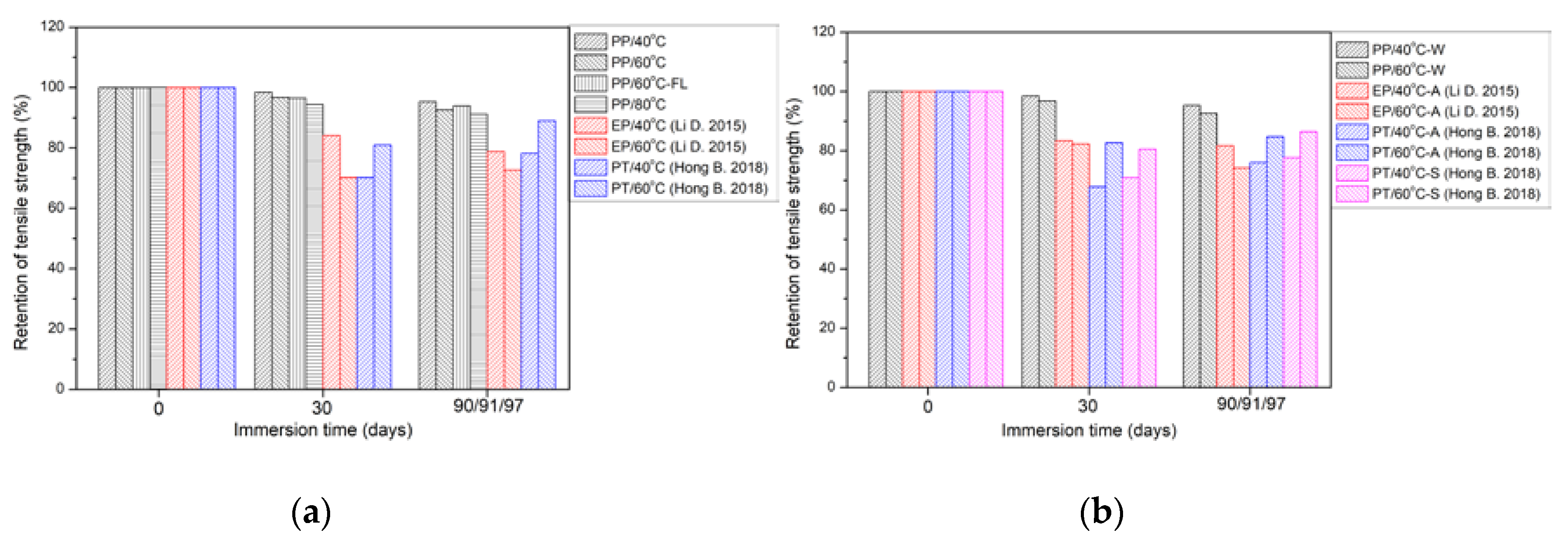
3.2.2. Comparison of Tensile Strength with the Epoxy and Polyurethane
3.3. Effect of Immersion on Thermal Properties
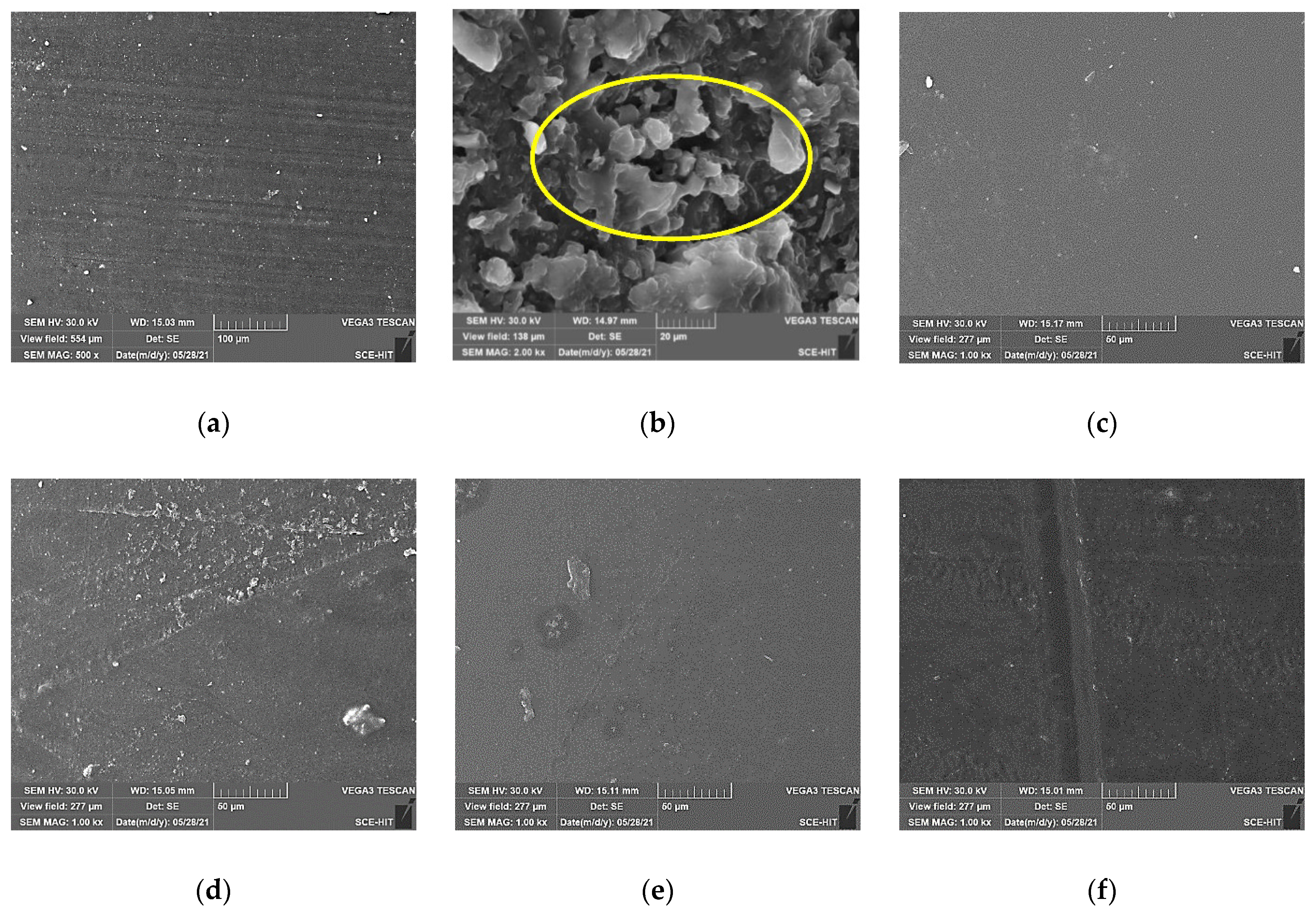
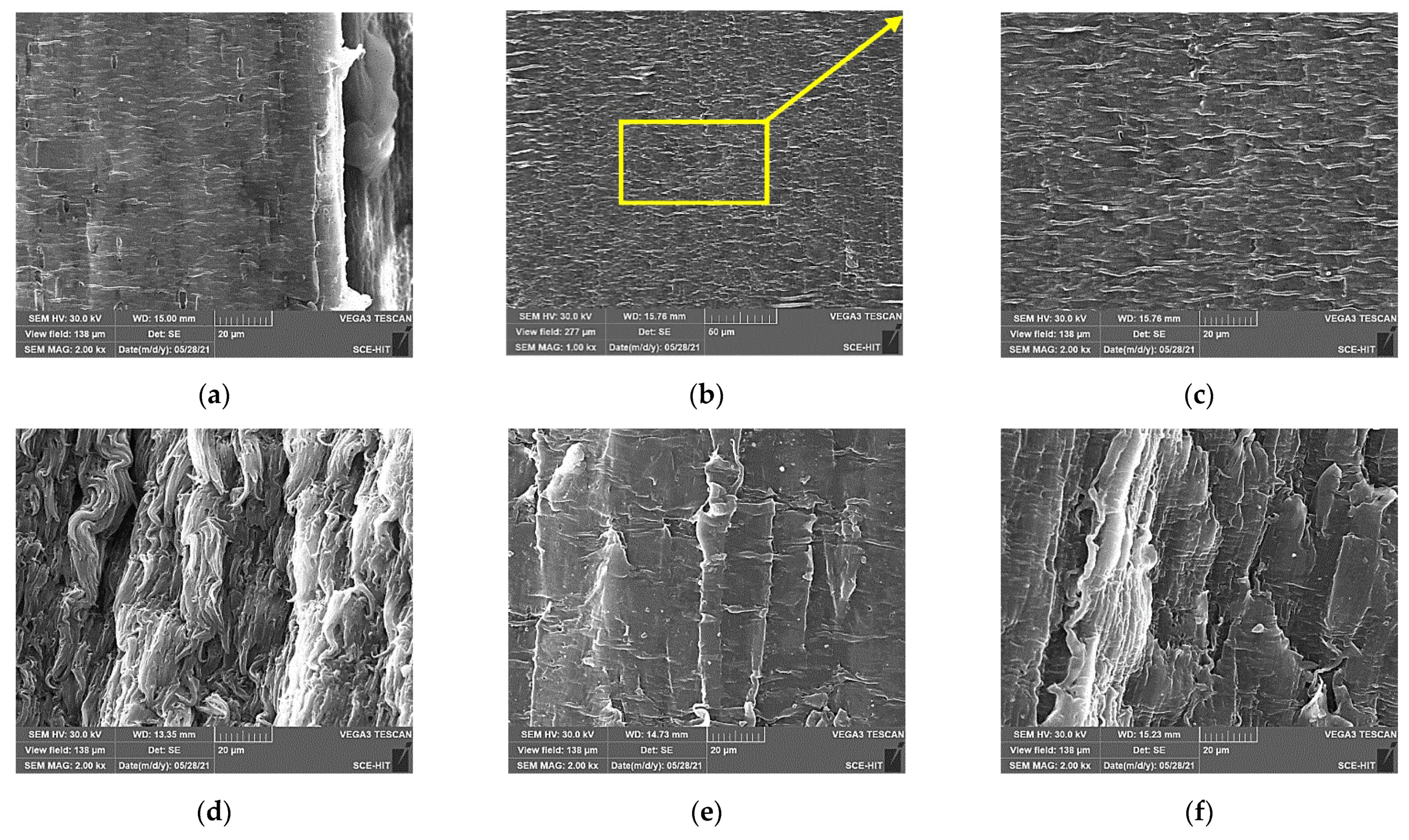
3.4. Surface Morphology Analysis
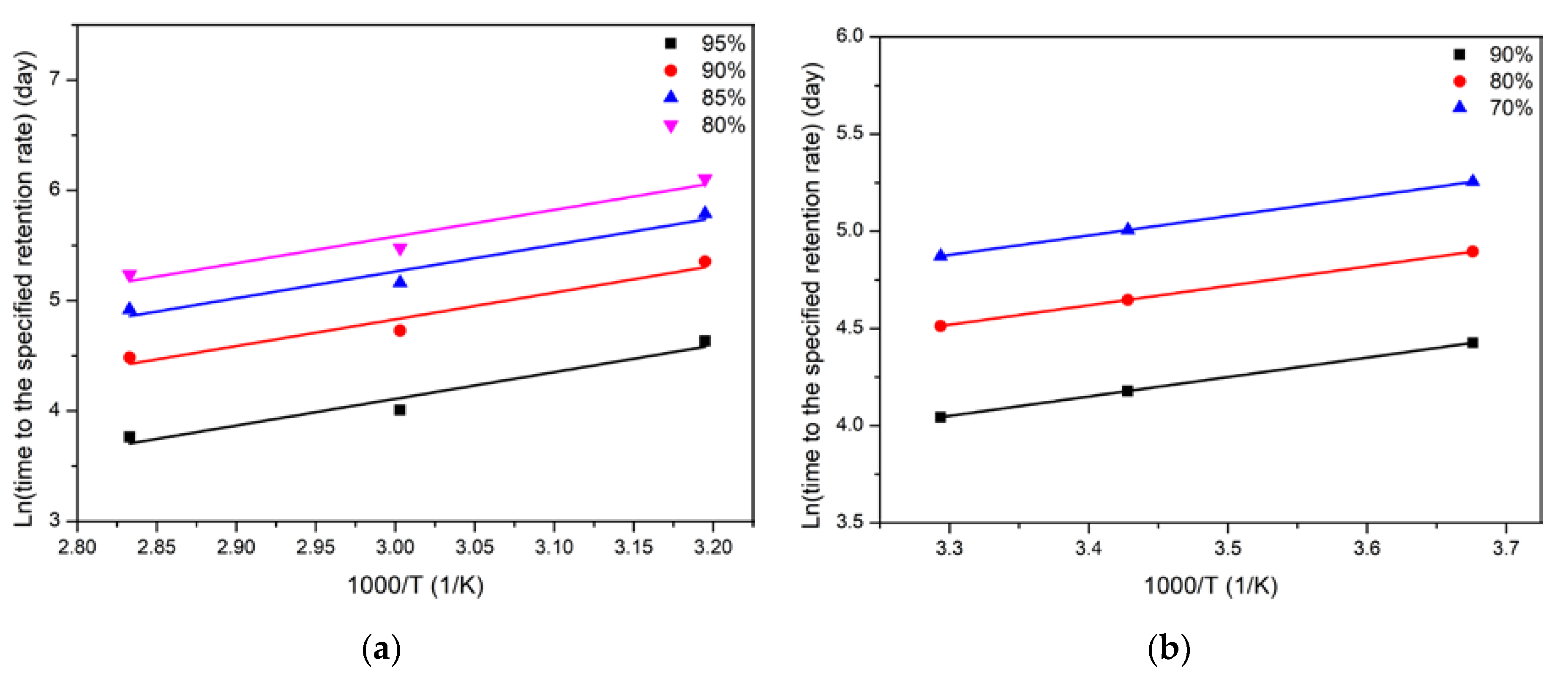
3.5. Long-Term Life Prediction of Tensile Strength
3.6. Application Prospect Analysis of Polypropylene
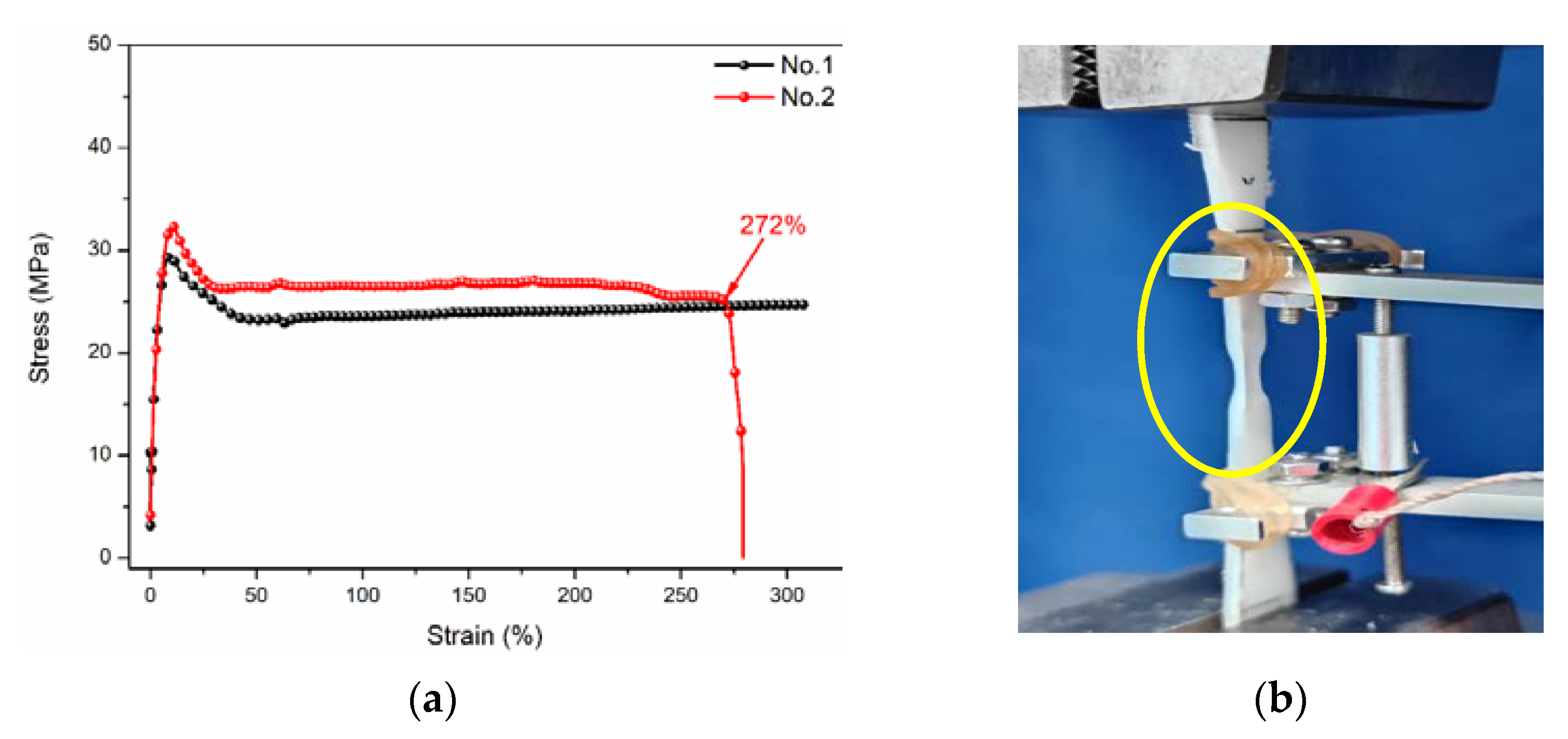
3.6.1. Failure Strain Analysis
3.6.2. Long Term Performance Analysis
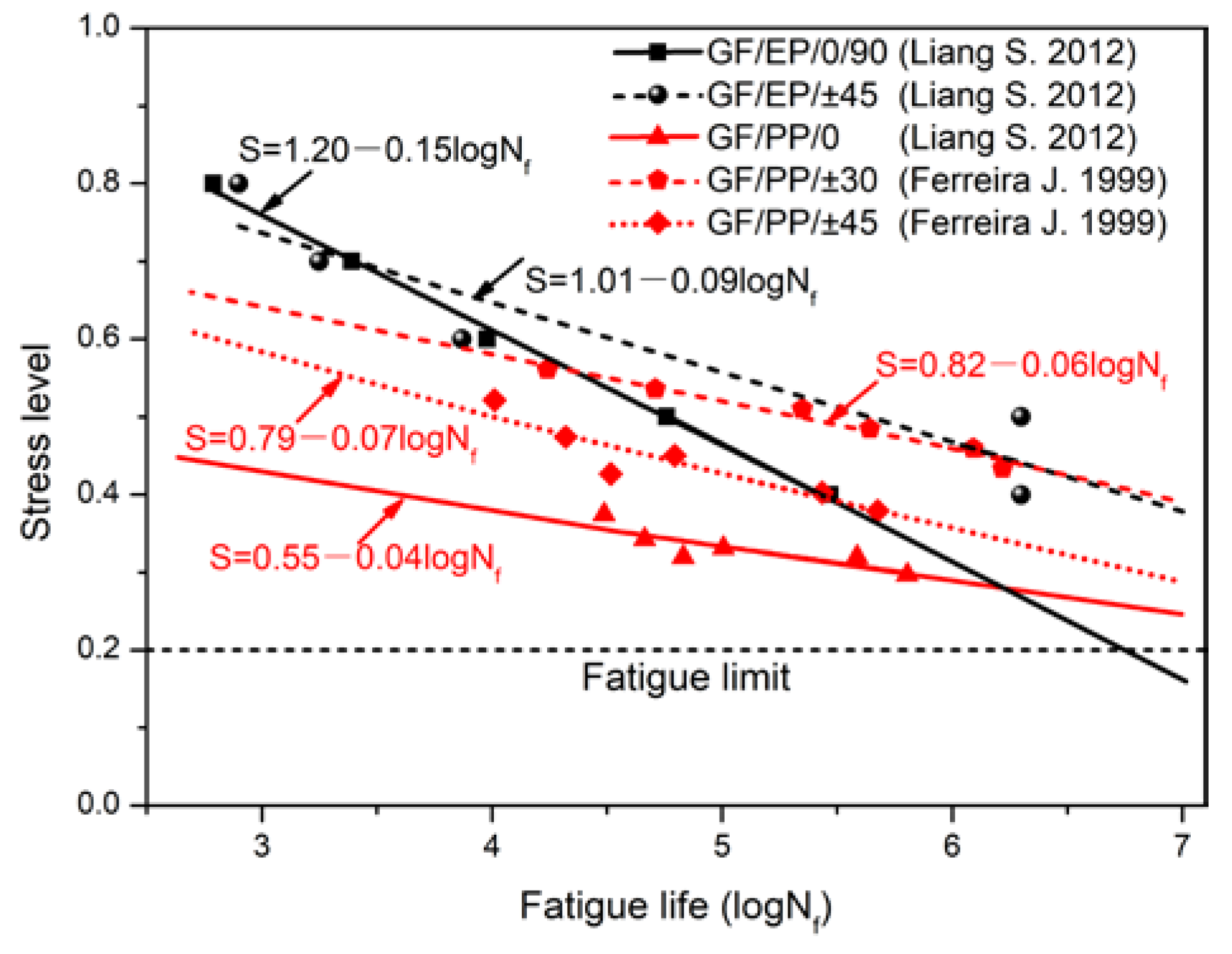
3.6.3. Fatigue Performance Analysis
4. Conclusions
- (1)
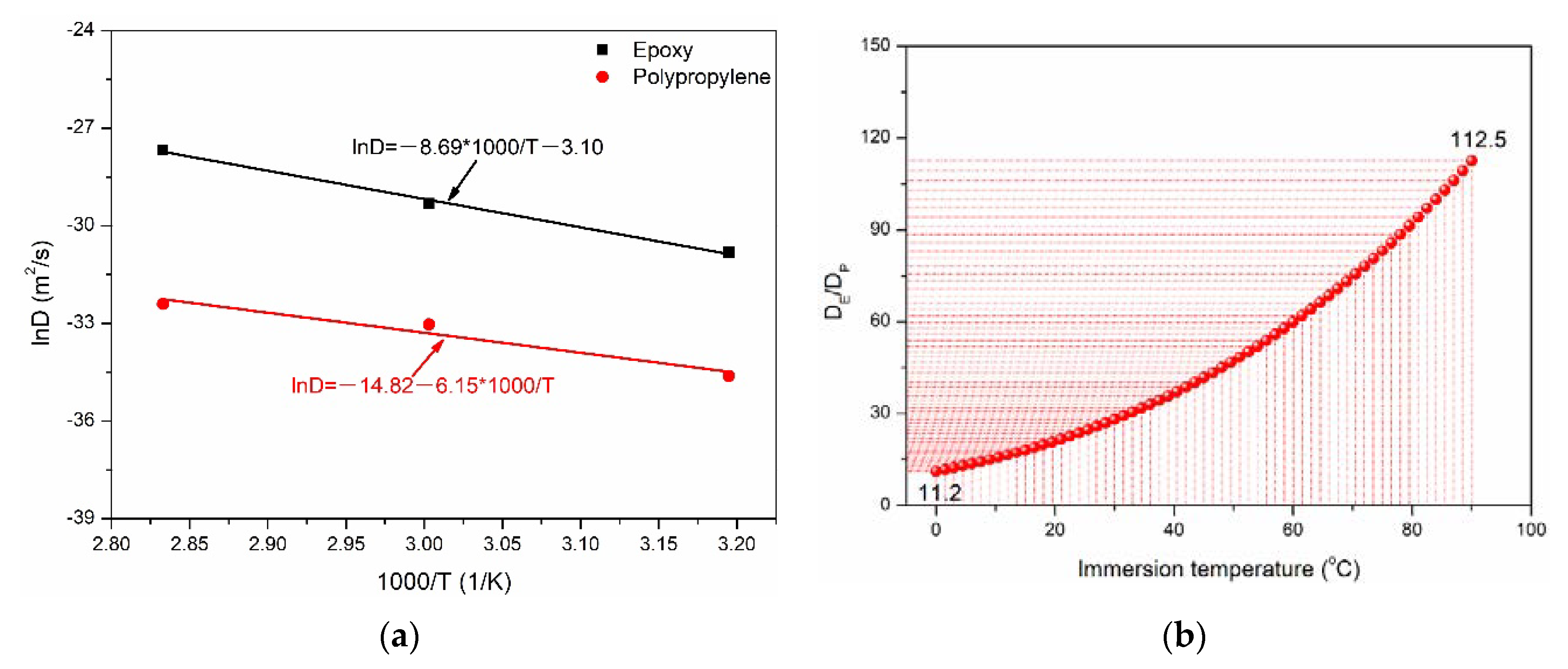
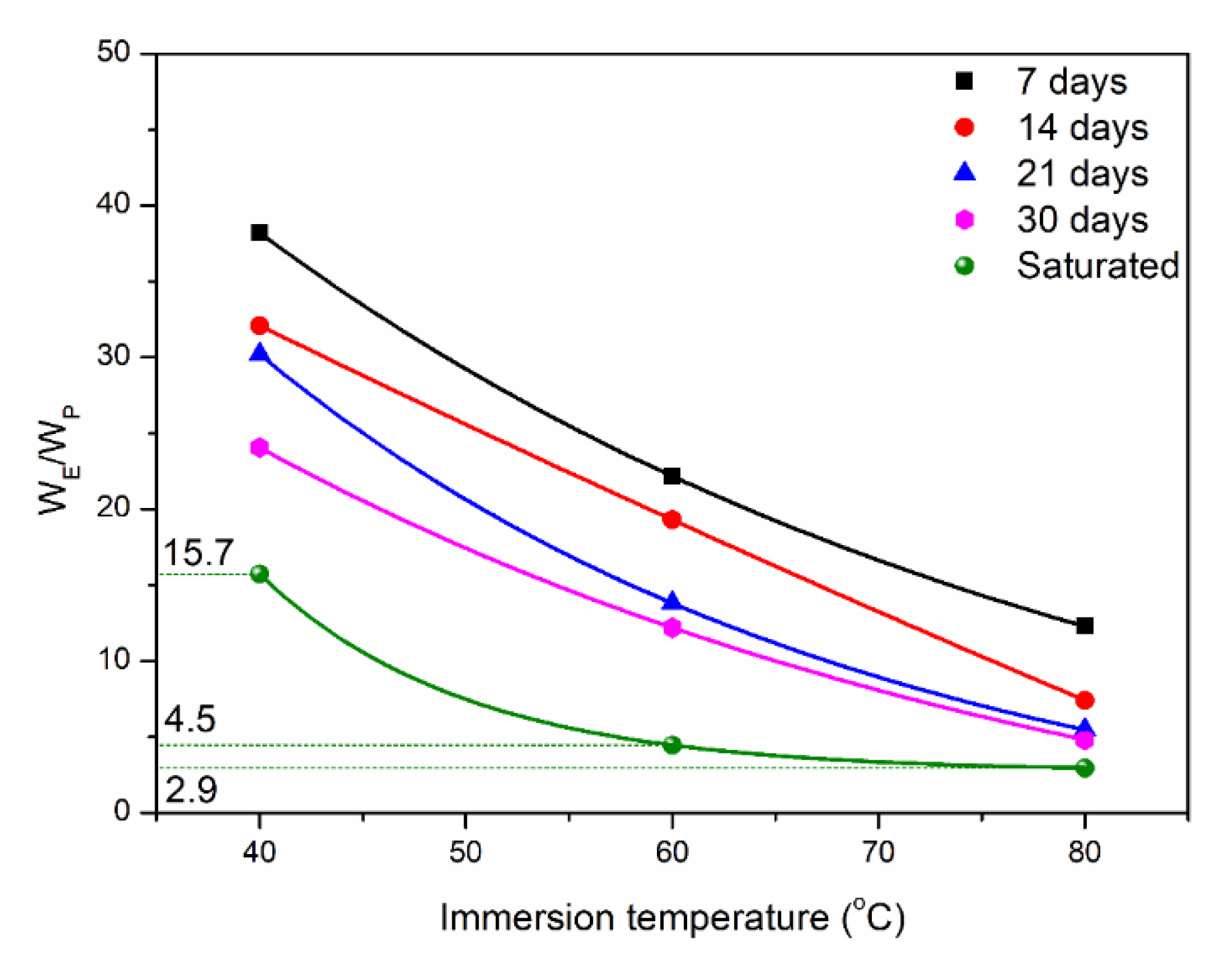
- Simplified Fick’s diffusion model can well describe the water absorption and diffusion behavior of two matrices. Water molecules were easier to diffuse in epoxy than polypropylene at the same immersion temperature, which indicated that polypropylene has better hydrophobic behavior compared to epoxy. For example, the ratios of the diffusion coefficient and saturated water uptake between the two matrices were 114.4 and 2.94 at 80 °C.
- (2)
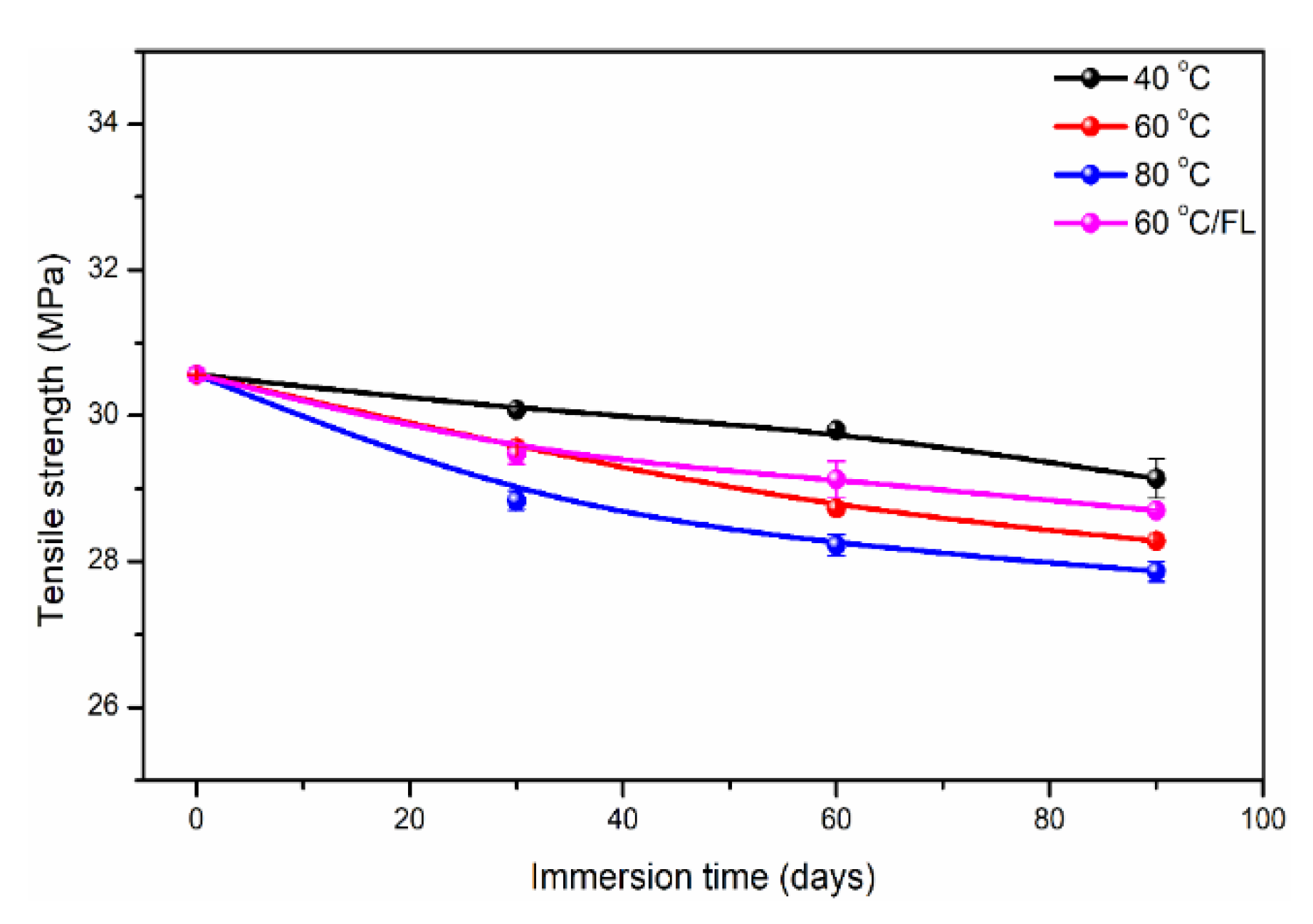
- At the longest immersion time of 90 days, the degradation percentages of tensile strength were 4.7% (40 °C), 7.5% (60 °C) and 8.8% (80 °C), respectively, which had the higher strength retention (>90%). The maximum strength increase multiples of polypropylene/epoxy and polypropylene/polyurethane were 1.95 and 1.75, respectively. The bending loading led to a maximum increase in tensile strength (~1.47%) owing to the oxygen isolation effect.
- (3)
- Tensile strength degradation for polypropylene was the active functional groups reacted with oxygen, resulting in local chain segment fracture. For epoxy and polypropylene, water molecules reacted with the hydroxyl groups or interrupted the intermolecular Van der Waals force/hydrogen bond, resulting in irreversible hydrolysis and property degradation.
- (4)
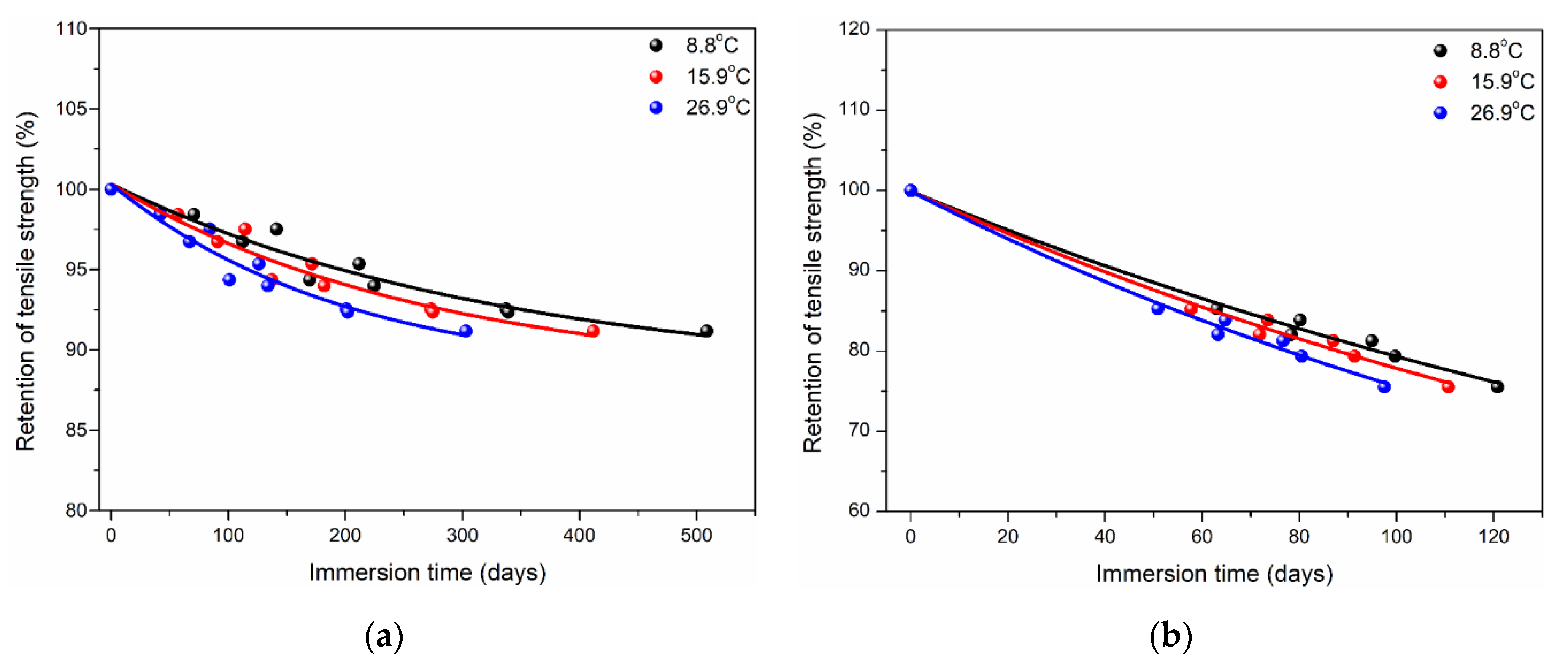
- Long-term life prediction of tensile strength showed when the service time was 500 days, the retention of tensile strength for polypropylene was close to 90% at 8.8 °C. In contrast, the retention of tensile strength of epoxy was only ~75% for the service time of 120 days. In terms of failure strain, long-term and fatigue performances, polypropylene and its composites have outstanding advantages compared to epoxy and polypropylene, which can achieve great application prospects in engineering applications when considering the complex service environment.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, J.W.; Li, C.G.; Xian, G.J. Reciprocating friction and wear performances of nanometer sized-TiO2 filled epoxy composites. Polym. Compos. 2021, 42, 2061–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, M.; Yao, K.; Zhu, X.; Fang, D. Fire protection design for composite lattice sandwich structure. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2017, 24, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, S.; Singh, R.; Kumar, A. Silica and Silane based polymer composite coating on glass slide by dip-Coating Method. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 19, 100472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guo, R.; Xian, G.; Li, H. Innovative compound-type anchorage system for a large-diameter pultruded carbon/glass hybrid rod for bridge cable. Mater. Struct. 2020, 53, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bifulco, A.; Parida, D.; Salmeia, K.A.; Nazir, R.; Lehner, S.; Stämpfli, R.; Markus, H.; Malucelli, G.; Branda, F.; Gaan, S. Fire and mechanical properties of DGEBA-based epoxy resin cured with a cycloaliphatic hardener: Combined action of silica, melamine and DOPO-derivative. Mater. Des. 2020, 193, 108862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthaman, A.; Lal, H.; Li, C.; Xian, G.; Thomas, S. Mechanical and Water Uptake Properties of Epoxy Nanocomposites with Surfactant-Modified Functionalized Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.K. Study of the Durability Performances of Fiber Reinforced Polymer (FRP) Bars Exposed to Simulated Seawater and Sea Sand Concrete Pore Solution. Ph.D. Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Xian, G.; Li, H. Effect of postcuring immersed in water under hydraulic pressure on fatigue performance of large-diameter pultruded carbon/glass hybrid rod. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2019, 42, 1148–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Xian, G.; Zhang, Y. Numerical modelling of bond behaviour between steel and CFRP laminates with a ductile adhesive. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2021, 104, 102753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-T.; Liu, S.-S.; Liu, Q.-L.; Pang, Y.-Y.; Shi, J.-W. Influences of the joint and epoxy adhesive type on the CFRP-steel interfacial behavior. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 43, 103167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Hu, R.; Bai, S.; Dong, W.; Zhao, Z.; Song, L. Mechanical performance of concrete strengthened by modified epoxy resin bonded CFRP. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2021, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Sui, L.; Xian, G. Effects of adhesive property and thickness on the bond performance between carbon fiber reinforced polymer laminate and steel. Thin-Walled Struct. 2021, 158, 107176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, A.; Kausar, A.; Siddiq, M. Role of polymeric composite in civil engineering applications: A review. Polym. Technol. Mater. 2020, 59, 1023–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Xian, G.; Li, C.; Huang, X.; Xin, M. Effect of fiber hybridization types on the mechanical properties of carbon/glass fiber reinforced polymer composite rod. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xie, J.; Liu, F.; Lu, Z. A critical review and assessment for FRP-concrete bond systems with epoxy resin exposed to chloride environments. Compos. Struct. 2019, 229, 111372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-B.; Ikeda, T.; Miyazaki, N.; Choi, N.-S. Damage zone around crack tip and fracture toughness of rubber-modified epoxy resin under mixed-mode conditions. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2002, 69, 1363–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morano, C.; Tao, R.; Alfano, M.; Lubineau, G. Effect of Mechanical Pretreatments on Damage Mechanisms and Fracture Toughness in CFRP/Epoxy Joints. Materials 2021, 14, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yin, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xian, G. Mechanical property evolution and service life prediction of pultruded carbon/glass hybrid rod exposed in harsh oil-well condition. Compos. Struct. 2020, 246, 112418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, G.; Guo, R.; Li, C.; Hong, B. Effects of rod size and fiber hybrid mode on the interface shear strength of carbon/glass fiber composite rods exposed to freezing-thawing and outdoor environments. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 2812–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yin, X.; Liu, Y.; Guo, R.; Xian, G. Long-term service evaluation of a pultruded carbon/glass hybrid rod exposed to elevated temperature, hydraulic pressure and fatigue load coupling. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 134, 105480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, S.A.; Mahini, S.S.; Tucker, S.J.; Fellows, C.M. Evaluation of the performance of microcrystalline cellulose in retarding degradation of two epoxy resin systems. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2019, 24, 150–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, S.A.; Mahini, S.S.; Fellows, C.M. Modification of the resistance of two epoxy resins to accelerated weathering using calcium sulfate as a photostabilizer. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2019, 56, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, G.J.; Guo, R.; Li, C. Combined effects of sustained bending loading, water immersion and fiber hybrid mode on the mechanical properties of carbon/glass fiber reinforced polymer composite. Compos. Struct. 2021, 281, 115060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Xian, G.; Li, C.; Hong, B.; Huang, X.; Xin, M.; Huang, S. Water uptake and interfacial shear strength of carbon/glass fiber hybrid composite rods under hygrothermal environments: Effects of hybrid modes. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2021, 193, 109723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Xian, G.; Li, F.; Li, C.; Hong, B. Hydrothermal resistance of pultruded carbon, glass and carbon/glass hybrid fiber reinforced epoxy plate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 315, 125710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marouani, S.; Curtil, L.; Hamelin, P. Ageing of carbon/epoxy and carbon/vinylester composites used in the reinforcement and/or the repair of civil engineering structures. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 2020–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khotbehsara, M.M.; Manalo, A.; Aravinthan, T.; Ferdous, W.; Nguyen, K.T.; Hota, G. Ageing of particulate-filled epoxy resin under hygrothermal conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 249, 118846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Pacheco, E.; Cauich-Cupul, J.I.; Valadez-González, A.; Herrera-Franco, P.J. Effect of moisture absorption on the mechanical behavior of carbon fiber/epoxy matrix composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 48, 1873–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, D.W.; Ku, M.K.; Nam, J.D.; Kim, B.S.; Yoon, S.C. Equilibrium water uptake of epoxy/carbon fiber composites in hygrothermal environmental conditions. J. Compos. Mater. 2001, 35, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, D.; Xian, G.; Li, C. Effect of Immersion in Water or Alkali Solution on the Structures and Properties of Epoxy Resin. Polymers 2021, 13, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.; Xian, G. Ageing of a thermosetting polyurethane and its pultruded carbon fiber plates subjected to seawater immersion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 165, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.; Xian, G.; Li, H. Effects of water or alkali solution immersion on the water uptake and physicomechanical properties of polyurethane. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2018, 58, 2276–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, G.; Guo, R.; Li, C.; Wang, Y. Mechanical performance evolution and life prediction of prestressed CFRP plate exposed to hygrothermal and freeze-thaw environments. Compos. Struct. 2022, 293, 115719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomies, F.; Carlsson, L.A. Analysis of Modulus and Strength of Dry and Wet Thermoset and Thermoplastic Composites Loaded in Transverse Tension. J. Compos. Mater. 1994, 28, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, W.L.; Grant, T.S. The effect of the moisture absorption on the interfacial strength of polymeric matrix composites. J. Mater. Sci. 1995, 30, 5537–5542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sideridis, E.P.; Bikakis, G.S. BGSSpaldrocpgecsbsttpbt, and the effect of moisture absorption. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 2244–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, H.M.; Uthaman, A.; Li, C.; Xian, G.; Thomas, S. Combined effects of cyclic/sustained bending loading and water immersion on the interface shear strength of carbon/glass fiber reinforced polymer hybrid rods for bridge cable. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 314, 125587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, G.; Guo, R.; Li, C.; Hong, B. Mechanical properties of carbon/glass fiber reinforced polymer plates with sandwich structure exposed to freezing-thawing environment: Effects of water immersion, bending loading and fiber hybrid mode. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2022, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guo, R.; Xian, G.; Li, H. Effects of elevated temperature, hydraulic pressure and fatigue loading on the property evolution of a carbon/glass fiber hybrid rod. Polym. Test. 2020, 90, 106761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xian, G.; Li, H. Influence of immersion in water under hydraulic pressure on the interfacial shear strength of a unidirectional carbon/glass hybrid rod. Polym. Test. 2018, 72, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xian, G.; Li, H. Combined effects of temperature, hydraulic pressure and salty concentration on the water uptake and mechanical properties of a carbon/glass fibers hybrid rod in salty solutions. Polym. Test. 2019, 76, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xian, G.; Li, H. Water Absorption and Distribution in a Pultruded Unidirectional Carbon/Glass Hybrid Rod under Hydraulic Pressure and Elevated Temperatures. Polymers 2018, 10, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ageyeva, T.; Sibikin, I.; Kovács, J.G. A Review of Thermoplastic Resin Transfer Molding: Process Modeling and Simulation. Polymers 2019, 11, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Obande, W.; Brádaigh, C.M.; Ray, D. Continuous fibre-reinforced thermoplastic acrylic-matrix composites prepared by liquid resin infusion—A review. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 215, 108771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, C.; Hailatihan, B.; Mi, L.; Baheti, Y.; Yan, Y. Effect of the Addition of Thermoplastic Resin and Composite on Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Epoxy Resin. Polymers 2022, 14, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.L. A Study in the Mechanically Fastened Joint of Glass Fiber Reinforced Thermoplastic Composite. Master’s Thesis, Donghua University, Shanghai, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrmann, G.; Steiner, M.; Freitag-Wolf, S.; Kern, M. Resin bonding to three types of polyaryletherketones (PAEKs)—Durability and influence of surface conditioning. Dent. Mater. 2014, 30, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbelaiz, A.; Fernández, B.; Ramos, J.; Retegi, A.; Llano-Ponte, R.; Mondragon, I. Mechanical properties of short flax fibre bundle/polypropylene composites: Influence of matrix/fibre modification, fibre content, water uptake and recycling. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 1582–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panthapulakkal, S.; Sain, M. Injection-molded short hemp fiber/glass fiber-reinforced polypropylene hybrid composites—Mechanical, water absorption and thermal properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 103, 2432–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Reynolds, C.; Cabrera, N.; Barkoula, N.-M.; Alcock, B.; Peijs, T. The water absorption behaviour of all-polypropylene composites and its effect on mechanical properties. Compos. Part B Eng. 2010, 41, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveci, S.; Oner, M. Effects of thermo-fatigue loading, hydrostatic pressure, and heat aging on the free-volume and crystalline structure of polypropylene-co-ethylene random copolymer pipes. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2015, 55, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Gong, X.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Y. A Study about water/alkali treatments of hemp fiber on ultraviolet ageing of the reinforced polypropylene composites. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 2572–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, H.Y.; Li, Y.F.; Zhao, J.H.; Yang, R. Infectious Effect of organic small molecules on photo-oxidative aging of polypropylene. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. Chin. 2020, 41, 2838–2844. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, N.Z.M.; Othman, N.; Ahmad, Z.; Ismail, H. Effect of pro-degradant additive on photo-oxidative aging of polypropylene film. Sains Malays. 2011, 40, 803–808. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, J.K.; Reddy, K.R.; Kumar, A.P.; Singh, R.P. An overview on the degradability of polymer nanocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2005, 88, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiebig, J.; Gahleitner, M.; Paulik, C.; Wolfschwenger, J. Ageing of polypropylene: Processes and consequences. Polym. Test. 1999, 18, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.H. Evolution of the Properties of an Epoxy Resin Submitted to Water and Alkaline Immersion and the Molecular Dynamic Simulation. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kafodya, I.; Xian, G.; Li, H. Durability study of pultruded CFRP plates immersed in water and seawater under sustained bending: Water uptake and effects on the mechanical properties. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 70, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.-L.; Xian, G.; Wu, G.; Raman, R.S.; Al-Saadi, S. Effect of sustained load and seawater and sea sand concrete environment on durability of basalt- and glass-fibre reinforced polymer (B/GFRP) bars. Corros. Sci. 2018, 138, 200–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.; Xian, G.; Li, H. Effects of water or alkali solution immersion on the water uptake and physicochemical properties of a pultruded carbon fiber reinforced polyurethane plate. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Lucas, J.P. Hygrothermal effects of epoxy resin. Part II: Variations of glass transition temperature. Polymer 1999, 40, 5513–5522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; He, W.D.; Wu, Y.F.; Wang, N.; Chen, X.L.; Guo, J.B. The evolution of morphology, crystallization and static and dynamic mechanical properties of long glass-fibre-reinforced polypropylene composites under thermo-oxidative ageing. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2019, 32, 544–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; He, W.; Wang, N.; Chen, X.; Guo, J.; Ci, S. Effect of thermo-oxidative aging on the mechanical and flame retardant properties of long glass fiber-reinforced polypropylene composites filled with red phosphorus. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, 2634–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; He, W.D.; Wu, Y.F.; Xu, D.H.; Chen, X.L.; He, M.; Guo, G. Influence of thermo-oxidative aging on flame retardancy, thermal stability, and mechanical properties of long glass fiber-reinforced polypropylene composites filled with organic montmorillonite and intumescent flame retardant. J. Fire Sci. 2019, 37, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B. Study of the Resistance to Water, Alkali and Salt Solutions of Pultruded Polyurethane-Based CFRP Plates. Doctoral Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.-L.; Xian, G.; Wu, G.; Raman, R.S.; Al-Saadi, S.; Haque, A. Long-term durability of basalt- and glass-fibre reinforced polymer (BFRP/GFRP) bars in seawater and sea sand concrete environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 139, 467–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S. Effect of Sample Size on the Long-Term Properties of Epoxy Resins Immersed Water and Alkaline Solution. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Dong, Z.-Q.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, Z.-S. Prediction of Long-Term Performance and Durability of BFRP Bars under the Combined Effect of Sustained Load and Corrosive Solutions. J. Compos. Constr. 2015, 19, 04014058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Gning, P.B.; Guillaumat, L. A comparative study of fatigue behaviour of flax/epoxy and glass/epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2012, 72, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, J.; Costa, J.; Reis, P.; Richardson, M. Analysis of fatigue and damage in glass-fibre-reinforced polypropylene composite materials. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1999, 59, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
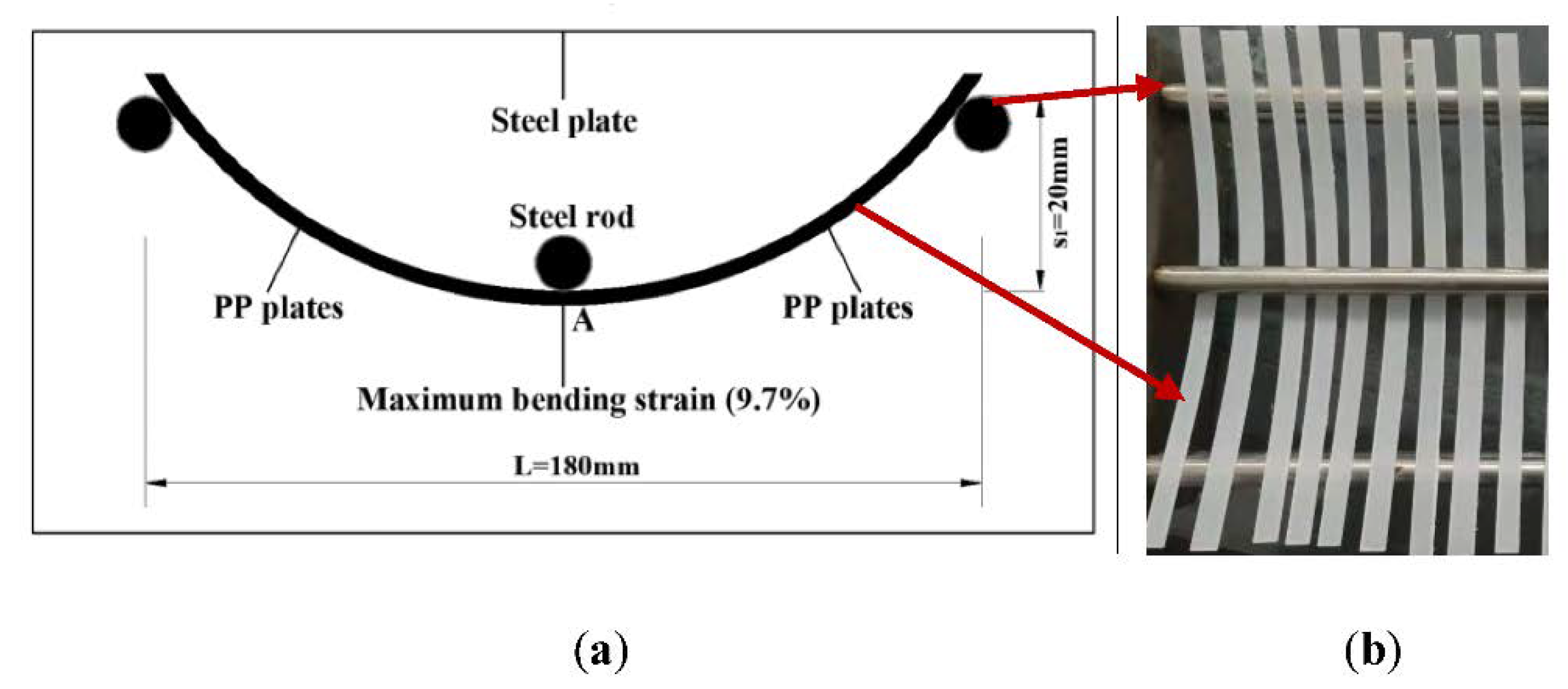


| Matrix Type | Exposure Time (Days) | Bending Deflection (mm)/Strain (%) | Exposure Temperature (°C) | Exposure Medium |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene (PP) | 0 | 20/0.54 (60 °C) | 40/60/80 | Distilled water |
| 30 | ||||
| 60 | ||||
| 90 | ||||
| Epoxy (EP) | 0 | / | 40/60/80 | Distilled water |
| 30 | ||||
| 60 | ||||
| 90 |
| Matrix Type | Immersion Temperature (°C) | Saturated Water Uptake | Diffusion Coefficient D (mm2/s, ×10−8) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene | 40 | 0.21 | 0.93 |
| 60 | 0.71 | 4.55 | |
| 80 | 1.02 | 8.49 | |
| Epoxy | 40 | 3.30 | 41.49 |
| 60 | 3.16 | 186.5 | |
| 80 | 3.00 | 971.0 |
| Immersion Time (days) | 40 °C | 60 °C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP/EP | PP/PT | PP/EP | PP/PT | |
| 30 | 1.88 | 1.75 | 1.38 | 1.19 |
| 90 | 1.95 | 1.52 | 1.27 | 1.04 |
| Matrix Type | Control | 60 °C-30 | 40 °C-90 | 60 °C-90 | 60 °C-90-FL | 80 °C-90 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDT-PP | 443.34 | 444.10 | 444.52 | 443.04 | 452.05 | 447.30 |
| UDT-PP | 455.88 | 456.10 | 455.61 | 454.20 | 465.99 | 458.93 |
| MDT-EP | 389.76 | / | / | 391.18 | / | / |
| UDT-EP | 410.26 | / | / | 407.22 | / | / |
| Matrix Type | Immersion Temperature/°C | τ | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PP | 40 | 310.2 | 0.98 |
| 60 | 224.7 | 0.97 | |
| 80 | 178.6 | 0.85 | |
| EP [61] | 20 | 374.8 | 0.99 |
| 40 | 292.5 | 0.99 | |
| 60 | 255.7 | 0.99 |
| Matrix Type | Strength Retention/% | Ea/R | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PP | 95 | 2420 | 0.91 |
| 90 | 2420 | 0.91 | |
| 85 | 2420 | 0.91 | |
| 80 | 2420 | 0.91 | |
| EP [61] | 95 | 1000 | 0.99 |
| 85 | 1000 | 0.99 | |
| 75 | 1000 | 0.99 | |
| 65 | 1000 | 0.99 |
| Matrix Type | Immersion Temperature (°C) | Time-Shift Factor (TSF) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shenyang Youth Bridge (T = 8.8 °C) | Jiangsu Yangtze River Bridge (T = 15.9 °C) | Hainan Century Bridge (T = 26.9 °C) | ||
| PP | 40 | 2.35 | 1.91 | 1.40 |
| 60 | 3.74 | 3.03 | 2.23 | |
| 80 | 5.65 | 4.58 | 3.37 | |
| EP [61] | 20 | 1.15 | 1.05 | 0.92 |
| 40 | 1.42 | 1.31 | 1.15 | |
| 60 | 1.73 | 1.58 | 1.39 | |
| Service Time (Years) | PP | EP [67] | PT [65] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.8 °C | 15.9 °C | 26.9 °C | 8.8 °C | 15.9 °C | 26.9 °C | 20 °C-W | 20 °C-A | 20 °C-S | |
| 0.5 | 95.3 | 94.5 | 93.2 | 68.1 | 66.2 | 63.5 | 57.94 a | 57.74 a | 57.58 b |
| 1 | 92.3 | 91.4 | 90.2 | 52.9 | 51.2 | 49.0 | 69.61 c | 69.65 c | 68.89 c |
| 2 | 89.6 | 89.0 | 88.5 | 42.8 | 42.1 | 41.4 | / | / | / |
| 3 | 88.6 | 88.4 | 88.2 | 40.6 | 40.4 | 40.2 | / | / | / |
| Stress Level (%) | GF/EP/0/90 [69] | GF/EP/±45 [69] | GF/PP/0 [70] | GF/PP/±30 [70] | GF/PP/±45 [70] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 46,416 | 464,158 | 18 | 215,443 | 13,895 |
| 40 | 215,443 | >2,000,000 | 5623 | >2,000,000 | 372,759 |
| 35 | 464,159 | >2,000,000 | 100,000 | >2,000,000 | >2,000,000 |
| 30 | 1,000,000 | >2,000,000 | 1,778,279 | >2,000,000 | >2,000,000 |
| Slope (S-N) | −0.15 | −0.09 | −0.04 | −0.06 | −0.07 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, P.; Tian, J.; Li, C.; Tang, Z. Comparative Study of Durability Behaviors of Thermoplastic Polypropylene and Thermosetting Epoxy Exposed to Elevated Temperature, Water Immersion and Sustained Bending Loading. Polymers 2022, 14, 2953. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142953
Zhou P, Tian J, Li C, Tang Z. Comparative Study of Durability Behaviors of Thermoplastic Polypropylene and Thermosetting Epoxy Exposed to Elevated Temperature, Water Immersion and Sustained Bending Loading. Polymers. 2022; 14(14):2953. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142953
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Ping, Jingwei Tian, Chenggao Li, and Zhecheng Tang. 2022. "Comparative Study of Durability Behaviors of Thermoplastic Polypropylene and Thermosetting Epoxy Exposed to Elevated Temperature, Water Immersion and Sustained Bending Loading" Polymers 14, no. 14: 2953. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142953
APA StyleZhou, P., Tian, J., Li, C., & Tang, Z. (2022). Comparative Study of Durability Behaviors of Thermoplastic Polypropylene and Thermosetting Epoxy Exposed to Elevated Temperature, Water Immersion and Sustained Bending Loading. Polymers, 14(14), 2953. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142953