Assessment of Physical, Mechanical, Biopharmaceutical Properties of Emulgels and Bigel Containing Ciclopirox Olamine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Production of the Experimental Semi-Solid Formulations
2.2.2. Particle Size and Distribution Measurements
2.2.3. Evaluation of Sol-Gel Transition Temperature
2.2.4. Texture Analysis of Semi-Solid Formulations
2.2.5. pH Measurement
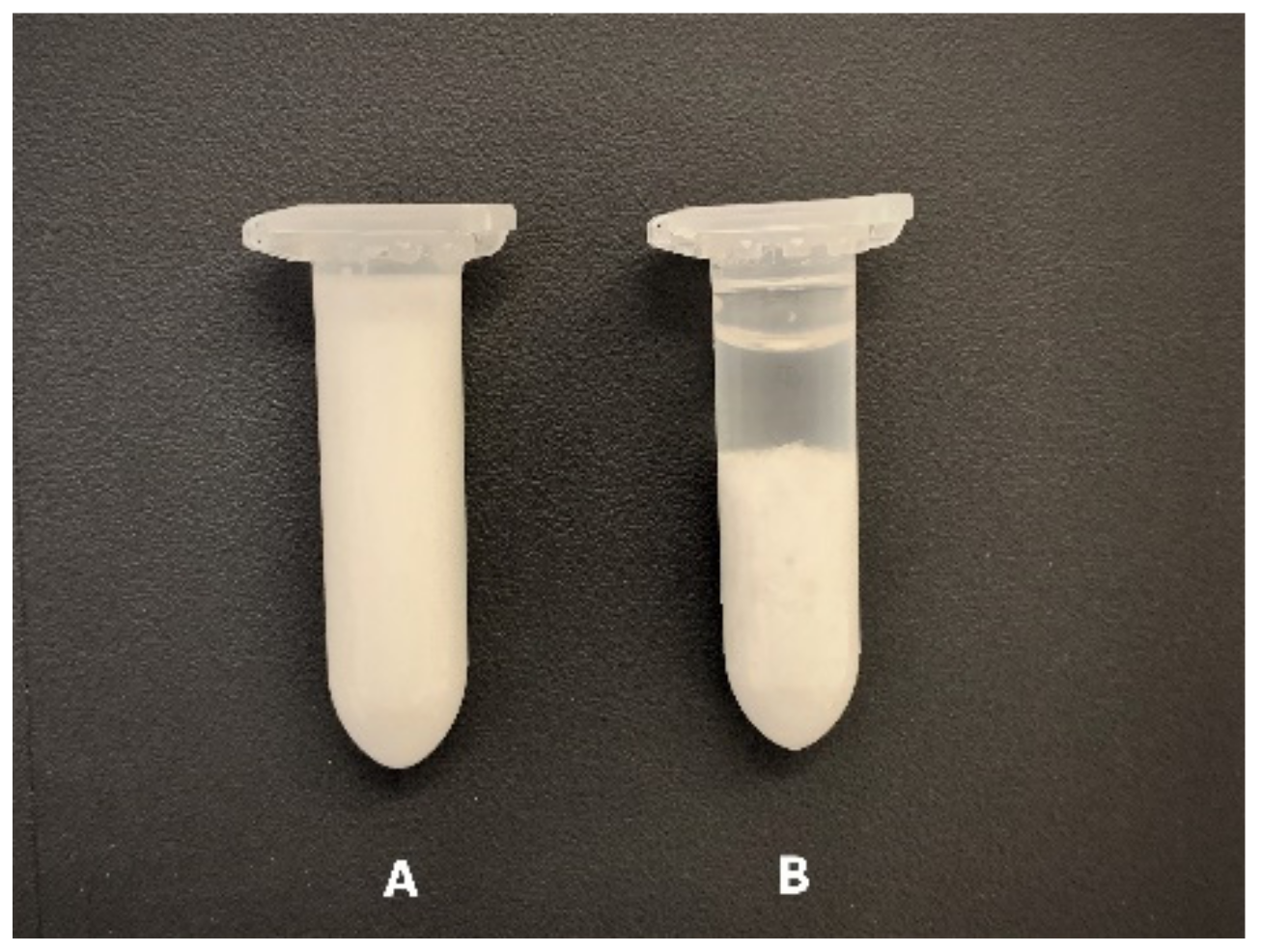
2.2.6. Centrifugation of Semi-Solid Formulations
2.2.7. Stability Test
- The freeze–thaw test consisted of 12 h of freezing (−20 ± 1 °C) followed by 12 h of thawing (20 ± 1 °C). Freeze–thaw cycles were repeated 5 times.
- The cooling–heating test consisted of 12 h of cooling (5 ± 1 °C) followed by 12 h of heating (40 ± 1 °C). Cooling–heating cycles were repeated 5 times.
2.2.8. In Vitro Release Test
2.2.9. Antifungal Activity Study
2.2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
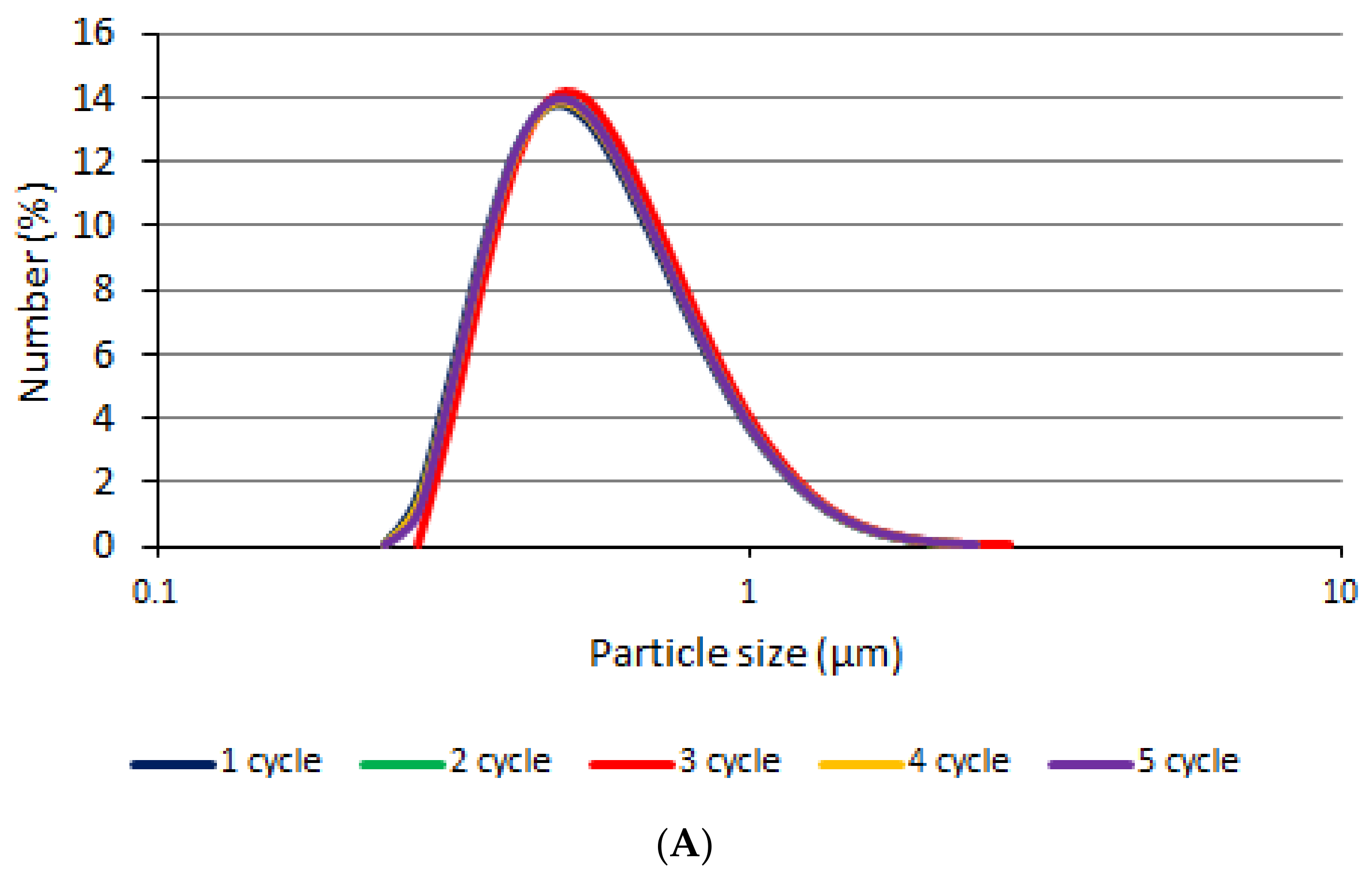
3.1. Particle Size and Distribution Measurements
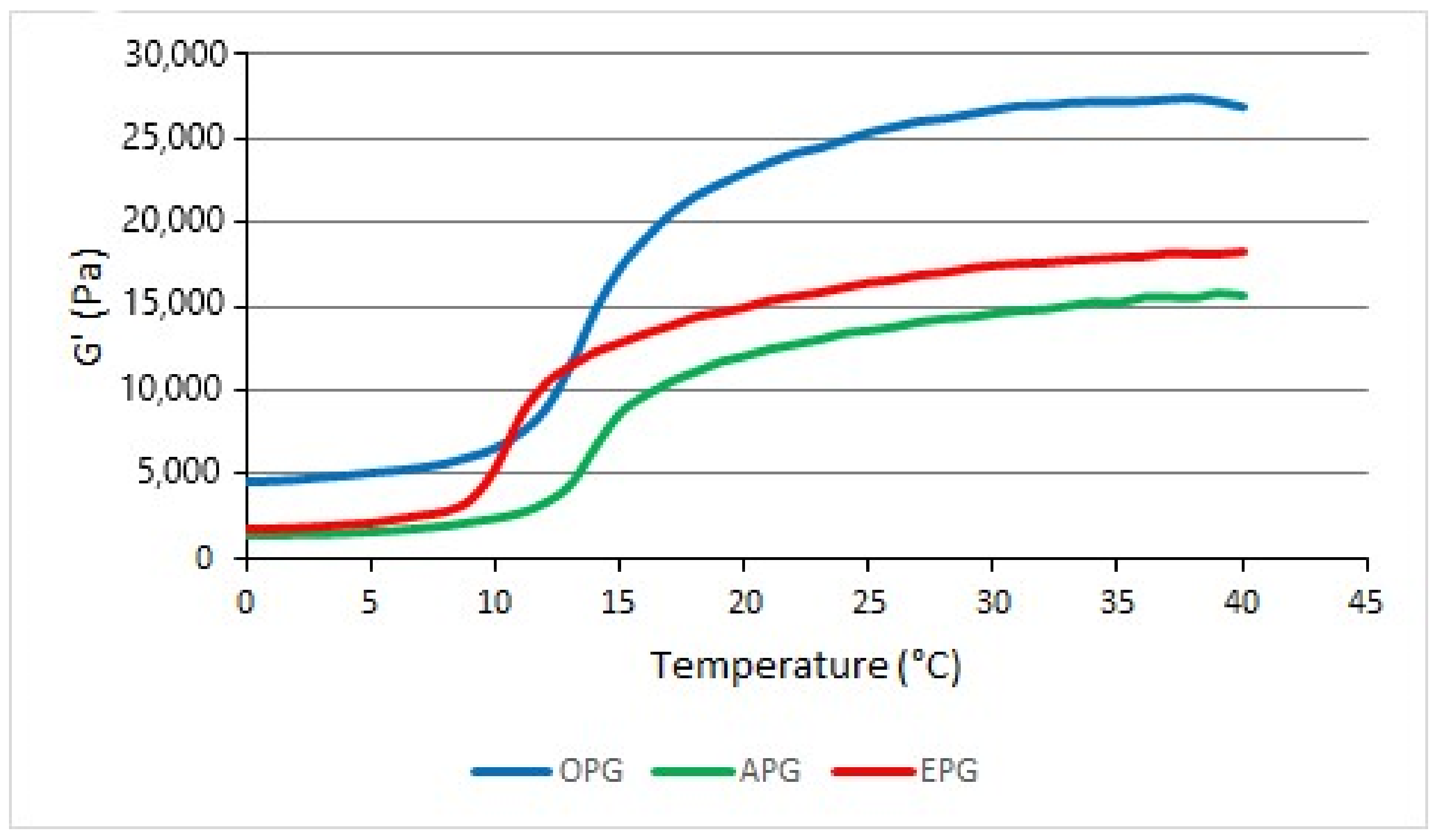
3.2. Evaluation of Sol-Gel Transition Temperature
3.3. Texture Analysis of Semi-Solid Formulations
3.4. pH Measurement
3.5. Centrifugation of Semi-Solid Formulations
3.6. Stability Test
3.7. In Vitro Release Test
3.8. Antifungal Activity Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costa, C.; Rosa, P.; Filipe, A.; Medronho, B.; Romano, A.; Liberman, L.; Talmon, Y.; Norgren, M. Cellulose-Stabilized Oil-in-Water Emulsions: Structural Features, Microrheology, and Stability. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 252, 117092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Tao, D. An Experimental Study of Stability of Oil-Water Emulsion. Fuel Process. Technol. 2005, 86, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kori, A.H.; Mahesar, S.A.; Sherazi, S.T.H.; Khatri, U.A.; Laghari, Z.H.; Panhwar, T. Effect of Process Parameters on Emulsion Stability and Droplet Size of Pomegranate Oil-in-Water. Grasas Aceites 2021, 72, e410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wu, J.; Yang, X.; Tu, Z.; Wang, Y. Investigation of Oil-in-Water Emulsion Stability with Relevant Interfacial Characteristics Simulated by Dissipative Particle Dynamics. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 2018, 546, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Tang, J.; Xu, M.; Lyu, F.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, J.; Ding, Y. Whey Protein and Maltodextrin-Stabilized Oil-in-Water Emulsions: Effects of Dextrose Equivalent. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 128094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traynor, M.P.; Burke, R.; Frías, J.M.; Gaston, E.; Barry-Ryan, C. Formation and Stability of an Oil in Water Emulsion Containing Lecithin, Xanthan Gum and Sunflower Oil. Int. Food Res. J. 2013, 20, 2173–2181. [Google Scholar]
- Charyulu, N.R.; Joshi, P.; Dubey, A.; Shetty, A. Emulgel: A Boon for Enhanced Topical Drug Delivery. J. Young Pharm. 2021, 13, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheetlani, J.; Singh Thakur, B. Preparation and Enlargement of Topical Flurbiprofen Emulgel by with Xanthan Gum. Int. J. Sci. Res. Eng. Technol. 2020, 29, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Mao, L.; Hou, Z.; Miao, S.; Gao, Y. Development of Emulsion Gels for the Delivery of Functional Food Ingredients: From Structure to Functionality. Food Eng. Rev. 2019, 11, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satapathy, S.; Singh, V.K.; Sagiri, S.S.; Agarwal, T.; Banerjee, I.; Bhattacharya, M.K.; Kumar, N.; Pal, K. Development and Characterization of Gelatin-Based Hydrogels, Emulsion Hydrogels, and Bigels: A Comparative Study. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasneem, R.; Khan, H.M.S.; Zaka, H.S.; Khan, P. Development and Cosmeceutical Evaluation of Topical Emulgel Containing Albizia Lebbeck Bark Extract. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 21, 1588–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, A.; Farooq, U.; Iqbal, T.; Yasin, S.; Lupi, F.R.; Gabriele, D. Key Characteristics and Modelling of Bigels Systems: A Review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 97, 932–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, A.; Lupi, F.R.; Gabriele, D.; Baldino, N.; de Cindio, B. Bigels: A Unique Class of Materials for Drug Delivery Applications. Soft Mater. 2018, 16, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, R.M.; Magalhães, W.V.; Sufi, B.d.S.; Padovani, G.; Nazato, L.I.S.; Velasco, M.V.R.; Lannes, S.C.d.S.; Baby, A.R. Vitamin E-Loaded Bigels and Emulsions: Physicochemical Characterization and Potential Biological Application. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 201, 111651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Illana, A.; Notatio-Perez, F.; Cazorla-Luna, R.; Ruiz-Caro, R.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Tamayo, A.; Veiga, M.D. Bigels as Drug Delivery Systems: From Their Components to Their Applications. Drug Discov. Today 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueiras-Nieto, L.; Sobarzo-Sánchez, E.; Gómez-Amoza, J.L.; Otero-Espinar, F.J. Competitive displacement of drugs from cyclodextrin inclusion complex by polypseudorotaxane formation with poloxamer: Implications in drug solubilization and delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 80, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćirin, D.; Krstonošić, V.; Poša, M. Properties of poloxamer 407 and polysorbate mixed micelles: Influence of polysorbate hydrophobic chain. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 25, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mfoafo, K.; Kwon, Y.; Omidi, Y.; Omidian, H. Contemporary applications of thermogelling PEO-PPO-PEO triblock copolymers. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 70, 103182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talasaz, A.H.H.; Ghahremankhani, A.A.; Moghadam, S.H.; Malekshahi, M.R.; Atyabi, F.; Dinarvand, R. In Situ Gel Forming Systems of Poloxamer 407 and Hydroxypropyl Cellulose or Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose Mixtures for Controlled Delivery of Vancomycin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 109, 2369–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grela, K.P.; Marciniak, D.M.; Karolewicz, B. Poloxamer 407-Based Thermosensitive Emulgel as a Novel Formulation Providing a Controlled Release of Oil-Soluble Pharmaceuticals—Ibuprofen Case Study. Materials 2021, 14, 7266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza Ferreira, S.B.; Bruschi, M.L. Investigation of the Physicochemical Stability of Emulgels Composed of Poloxamer 407 and Different Oil Phases Using the Quality by Design Approach. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 332, 115856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kracht, T.; Müller-Goymann, C.C. Antifungal Efficacy of Liquid Poloxamer 407-Based Emulsions Loaded with Sertaconazole Nitrate. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 585, 119400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćirin, D.; Krstonošić, V. Influence of Poloxamer 407 on Surface Properties of Aqueous Solutions of Polysorbate Surfactants. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2020, 23, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, M. Dispersion stability and rheological properties of silica suspensions in aqueous solutions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 284, 102248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertini, B.; Passerini, N.; González-Rodríguez, M.L.; Perissutti, B.; Rodriguez, L. Effect of Aerosil® on the properties of lipid controlled release microparticles. J. Control. Release 2004, 100, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutrín-Gómez, E.; Conde-Penedo, A.; Anguiano-Igea, S.; Gómez-Amoza, J.L.; Otero-Espinar, F.J. Optimization of Drug Permeation from 8% Ciclopirox Cyclodextrin/Poloxamer-soluble Polypseudorotaxane-based Nail Lacquers. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaikh, K.S.; Chellampillai, B.; Pawar, A.P. Studies on Nonionic Surfactant Bilayer Vesicles of Ciclopirox Olamine. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2010, 36, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanholi, K.d.S.S.; da Silva, J.B.; Batistela, V.R.; Gonçalves, R.S.; Said dos Santos, R.; Balbinot, R.B.; Lazarin-Bidóia, D.; Bruschi, M.L.; Nakamura, T.U.; Nakamura, C.V.; et al. Design and Optimization of Stimuli-Responsive Emulsion-Filled Gel for Topical Delivery of Copaiba Oil-Resin. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 111, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayunin, Q.; Miatmoko, A.; Soeratri, W.; Erawati, T.; Susanto, J.; Legowo, D. Improving the Anti-Ageing Activity of Coenzyme Q10 through Protransfersome-Loaded Emulgel. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Täuber, A.; Müller-Goymann, C.C. In Vitro Permeation and Penetration of Ciclopirox Olamine from Poloxamer 407-Based Formulations—Comparison of Isolated Human Stratum Corneum, Bovine Hoof Plates and Keratin Films. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 489, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasaruddin, F.; Chin, N.L.; Yusof, Y.A. Effect of Processing on Instrumental Textural Properties of Traditional Dodol Using Back Extrusion. Int. J. Food Prop. 2012, 15, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, N.; Alonso-Miravalles, L.; O’Mahony, J.A. Composition, Physicochemical and Sensorial Properties of Commercial Plant-Based Yogurts. Foods 2020, 9, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Najgebauer-Lejko, D.; Witek, M.; Zmudzinski, D.; Ptaszek, A. Changes in the viscosity, textural properties, and water status in yogurt gel upon supplementation with green and Pu-erh teas. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 11039–11049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, A.J.; Silva, P.; Maciel, F.; Pastrana, L.M.; Cunha, R.L.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Vicente, A.A. Hybrid Gels: Influence of Oleogel/Hydrogel Ratio on Rheological and Textural Properties. Food Res. Int. 2019, 116, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gajdošová, M.; Vetchý, D.; Muselík, J.; Gajdziok, J.; Juřica, J.; Vetchá, M.; Hauptman, K.; Jekl, V. Bilayer Mucoadhesive Buccal Films with Prolonged Release of Ciclopirox Olamine for the Treatment of Oral Candidiasis: In Vitro Development, Ex Vivo Permeation Testing, Pharmacokinetic and Efficacy Study in Rabbits. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 592, 120086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurkevičiūtė, A.; Ramanauskienė, K.; Ivaškienė, M.; Grigonis, A.; Briedis, V. Modelling and Biopharmaceutical Evaluation of Ciclopirox Olamine Gels. Acta Poloniae Pharm. 2017, 74, 543–549. [Google Scholar]
- Iorizzo, M.; Hartmane, I.; Derveniece, A.; Mikazans, I. Ciclopirox 8% HPCH Nail Lacquer in the Treatment of Mild-to-Moderate Onychomycosis: A Randomized, Double-Blind Amorolfine Controlled Study Using a Blinded Evaluator. Skin Appendage Disord. 2015, 1, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Täuber, A.; Müller-Goymann, C.C. In Vitro Evaluation of the Antifungal Efficacy of Poloxamer 407-Based Formulations in an Infected Nail Plate Model. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 505, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Components | APG (%) | EPG (%) | OPG (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purified water | 36.5 | 36.5 | 36.5 |
| Poloxamer 407 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 12.5 |
| Mineral oil (light) | 50.0 | 47.5 | 47.5 |
| Silicon dioxide | – | – | 2.5 |
| Polysorbate 80 | – | 2.5 | – |
| Ciclopirox olamine | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| OPG (µm) | APG (µm) | EPG (µm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 week | 0.337 (0.051) | 0.327 (0.027) | 0.286 (0.008) |
| 1 week | 0.285 (0.025) | 0.330 (0.014) | 0.275 (0.016) |
| 2 weeks | 0.284 (0.028) | 0.337 (0.020) | 0.287 (0.009) |
| 3 weeks | 0.284 (0.026) | 0.338 (0.028) | 0.290 (0.010) |
| 4 weeks | 0.283 (0.023) | 0.371 (0.009) | 0.297 (0.021) |
| OPG (µm) | APG (µm) | EPG (µm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 week | 0.420 (0.046) | 0.484 (0.055) | 0.470 (0.085) |
| 1 week | 0.421 (0.034) | 0.495 (0.029) | 0.404 (0.036) |
| 2 weeks | 0.422 (0.039) | 0.508 (0.039) | 0.427 (0.012) |
| 3 weeks | 0.422 (0.036) | 0.510 (0.048) | 0.433 (0.014) |
| 4 weeks | 0.422 (0.033) | 0.567 (0.015) | 0.442 (0.030) |
| OPG (µm) | APG (µm) | EPG (µm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 week | 0.700 (0.077) | 0.865 (0.102) | 0.716 (0.021) |
| 1 week | 0.705 (0.058) | 0.869 (0.080) | 0.681 (0.064) |
| 2 weeks | 0.705 (0.064) | 0.893 (0.094) | 0.725 (0.02) |
| 3 weeks | 0.707 (0.058) | 0.890 (0.101) | 0.732 (0.019) |
| 4 weeks | 0.708 (0.055) | 0.992 (0.026) | 0.744 (0.037) |
| OPG | APG | EPG | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Firmness (g) | 2213.31 (46.16) | 1562.08 (91.21) | 1763.37 (134.02) |
| Consistency (g·s) | 8257.48 (492.92) | 6024.86 (348.29) | 6653.80 (741.92) |
| Cohesiveness (g) | −1983.57 (60.44) | −1414.63 (76.24) | −1623.47 (142.97) |
| Index of viscosity (g·s) | −6793.20 (868.51) | −5255.84 (237.74) | −5526.72 (257.89) |
| OPG (mm) | APG (mm) | EPG (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibition zone diameter | 49.8 (0.84) | 49.8 (1.48) | 47.2 (1.48) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mazurkevičiūtė, A.; Matulytė, I.; Ivaškienė, M.; Žilius, M. Assessment of Physical, Mechanical, Biopharmaceutical Properties of Emulgels and Bigel Containing Ciclopirox Olamine. Polymers 2022, 14, 2783. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142783
Mazurkevičiūtė A, Matulytė I, Ivaškienė M, Žilius M. Assessment of Physical, Mechanical, Biopharmaceutical Properties of Emulgels and Bigel Containing Ciclopirox Olamine. Polymers. 2022; 14(14):2783. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142783
Chicago/Turabian StyleMazurkevičiūtė, Agnė, Inga Matulytė, Marija Ivaškienė, and Modestas Žilius. 2022. "Assessment of Physical, Mechanical, Biopharmaceutical Properties of Emulgels and Bigel Containing Ciclopirox Olamine" Polymers 14, no. 14: 2783. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142783
APA StyleMazurkevičiūtė, A., Matulytė, I., Ivaškienė, M., & Žilius, M. (2022). Assessment of Physical, Mechanical, Biopharmaceutical Properties of Emulgels and Bigel Containing Ciclopirox Olamine. Polymers, 14(14), 2783. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142783







