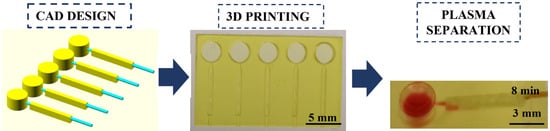
High-Resolution 3D Printing Fabrication of a Microfluidic Platform for Blood Plasma Separation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
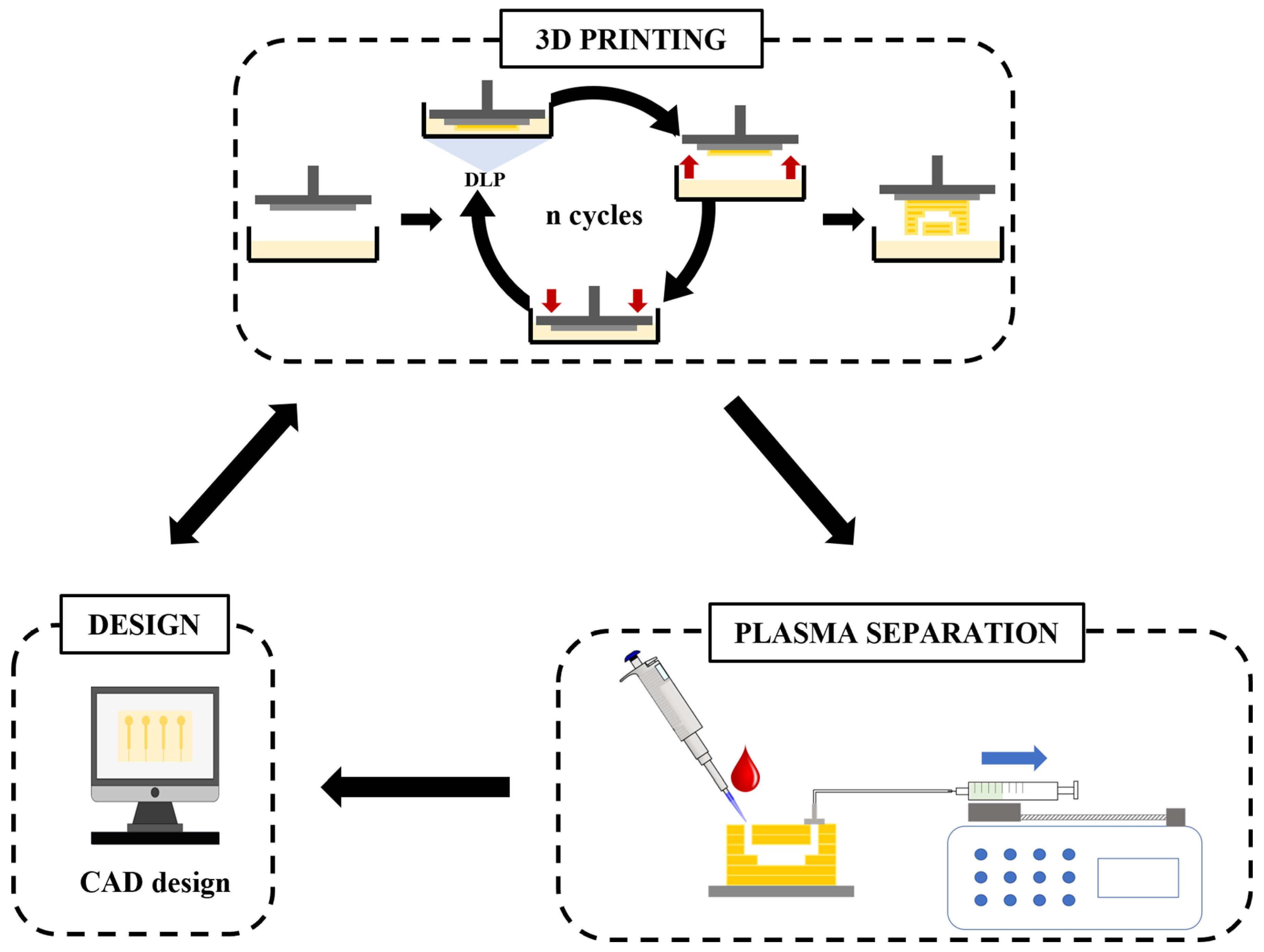
2.1. Microfabrication by High-Resolution Additive Manufacturing Technology
2.2. Whole Human Blood
2.3. Plasma Separation by Sedimentation
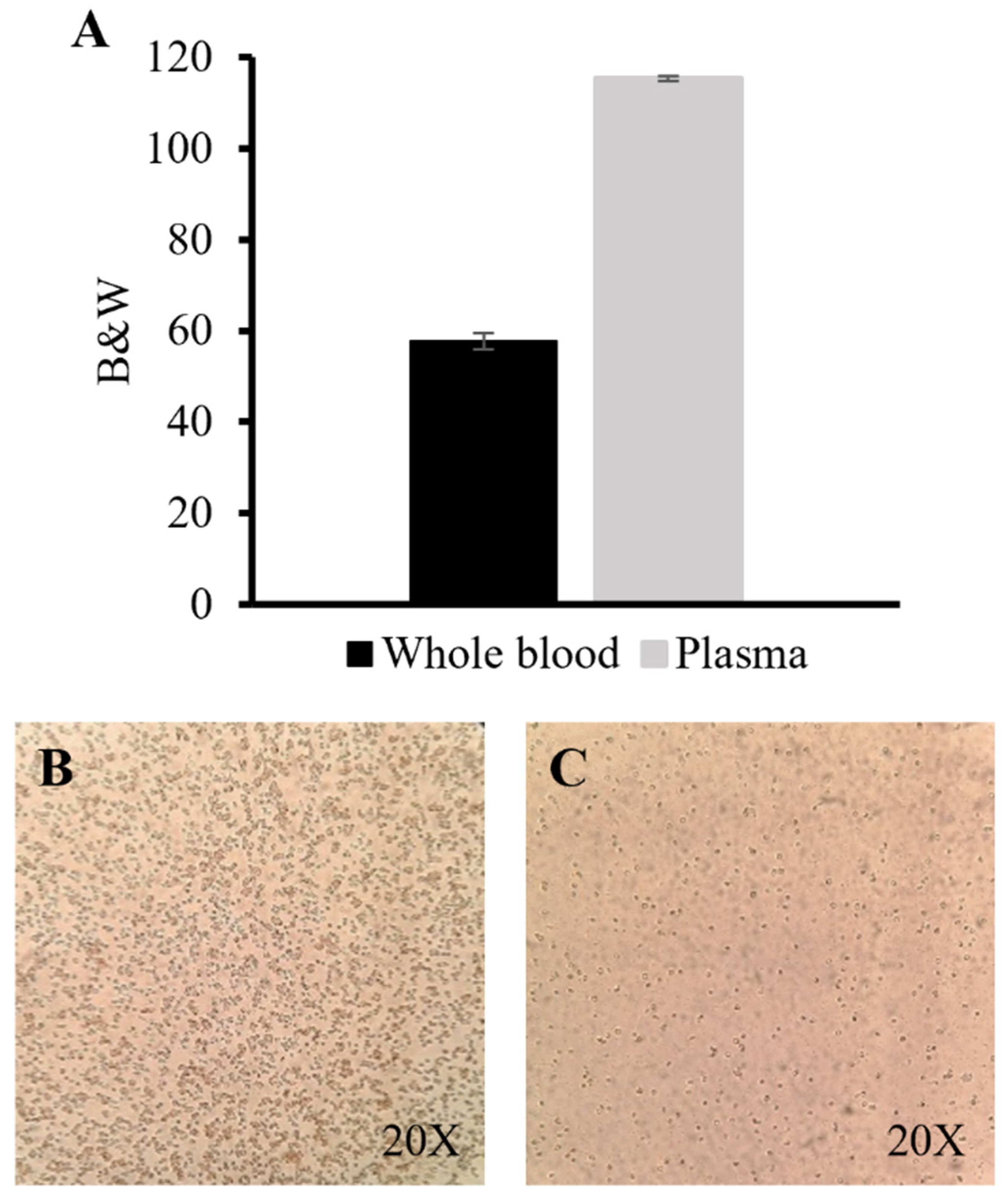
2.4. Image Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
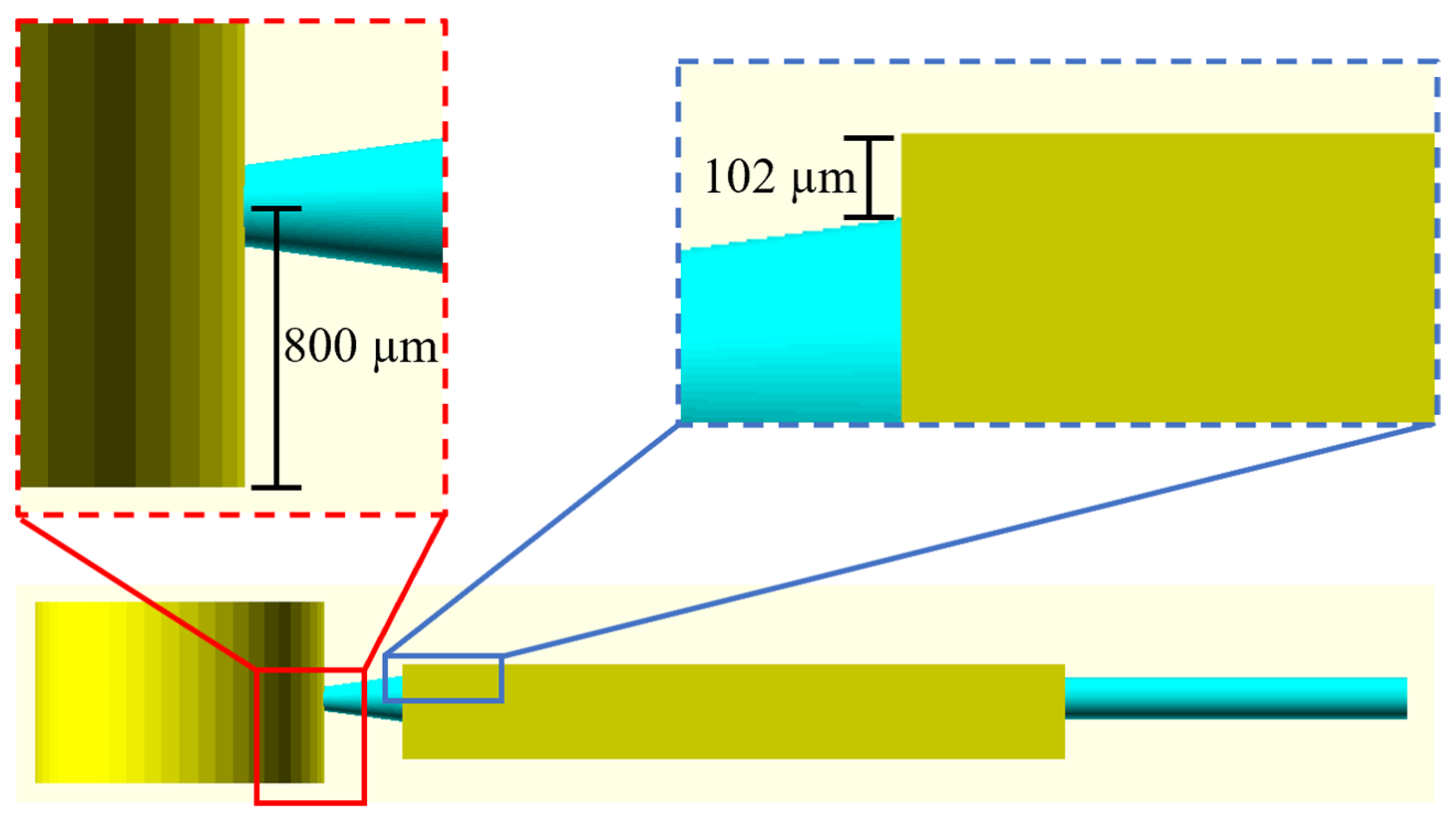
3.1. Iterative 3D Printing Fabrication Process
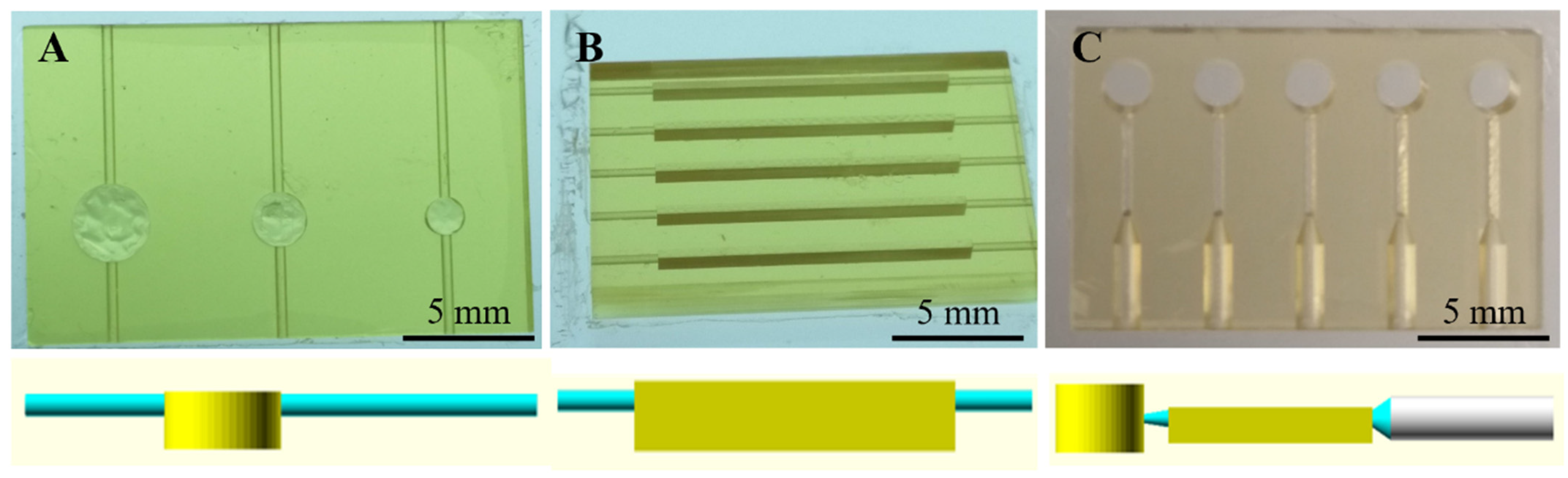
3.2. Round-Like Sedimentation Trench (Devices 1–3)
3.3. Rectangle-Like Sedimentation Trench (Devices 4–9)
3.4. Towards the Final Prototype (Devices 10–14)
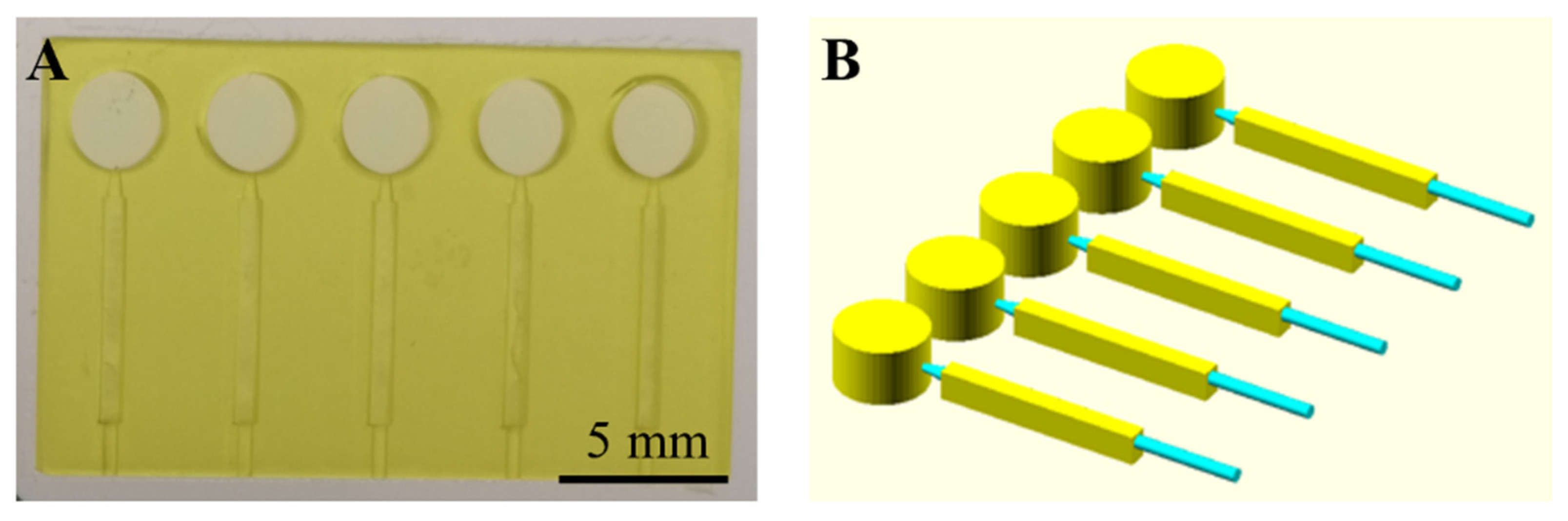
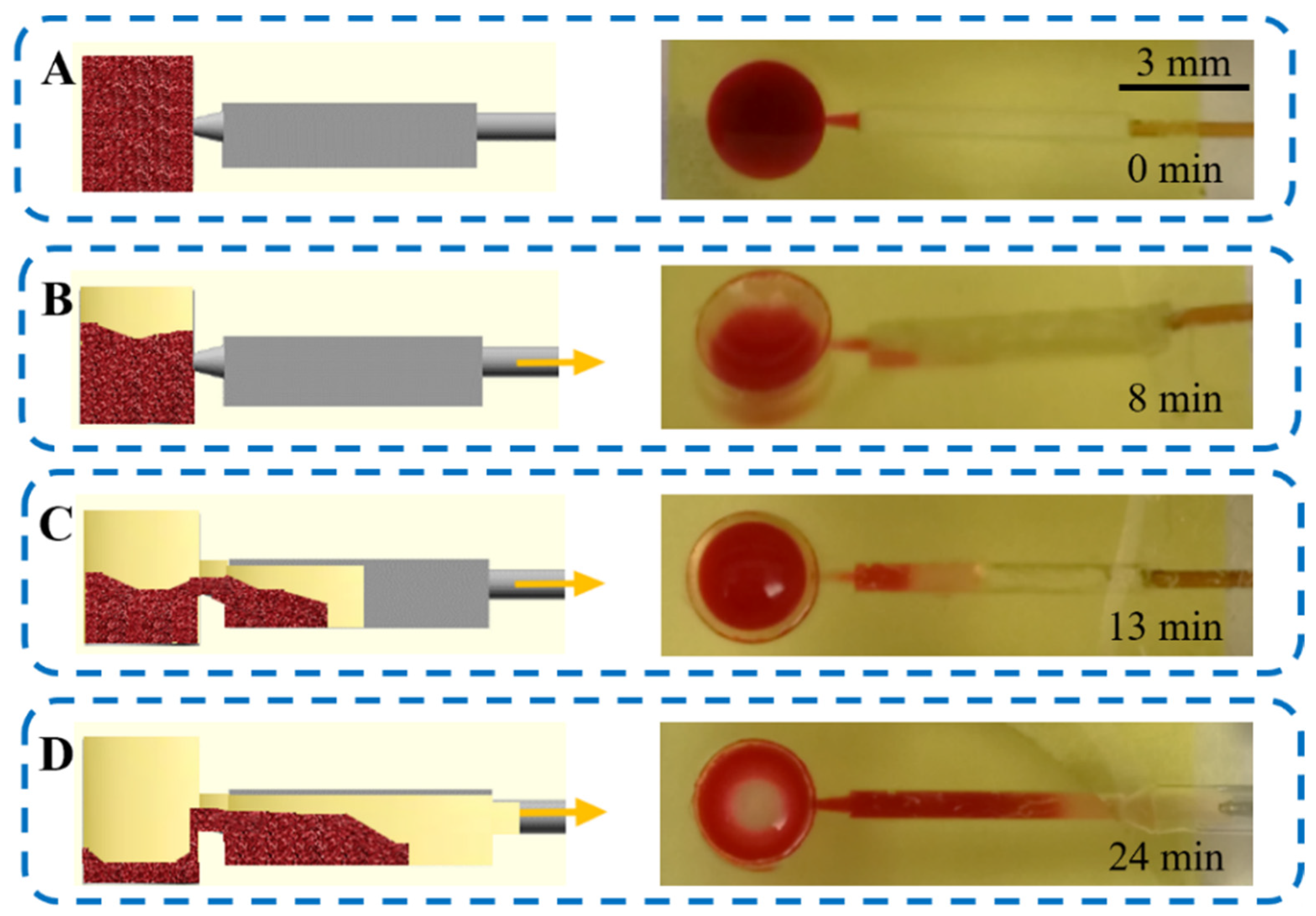
3.5. Optimized Microfluidic Device for Plasma Separation (Device 15)
3.6. Plasma Separation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Waheed, S.; Cabot, J.M.; Macdonald, N.P.; Lewis, T.; Guijt, R.M.; Paull, B.; Breadmore, M.C. 3D printed microfluidic devices: Enablers and barriers. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 1993–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Au, A.K.; Huynh, W.; Horowitz, L.F.; Folch, A. 3D-Printed Microfluidics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 55, 3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.; Woolley, A.T.; Nordin, G.P. High density 3D printed microfluidic valves, pumps, and multiplexers. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 2450–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.; Woolley, A.T.; Nordin, G.P. 3D printed selectable dilution mixer pumps. Biomicrofluidics 2019, 13, 14106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiaux, A.D.; Selemani, M.A.; Ward, M.A.; Martin, R.S. Fully 3D printed fluidic devices with integrated valves and pumps for flow injection analysis. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 5017–5024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimi, O.A.; Meijboom, R. Current and future trends of additive manufacturing for chemistry applications: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 16824–16850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Mehl, B.T.; Munshi, A.S.; Townsend, A.D.; Spence, D.M.; Martin, R.S. 3D-printed Microfluidic Devices: Fabrication, Advantages and Limitations-a Mini Review. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 6005–6012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, A.V.; Beauchamp, M.J.; Nordin, G.P.; Woolley, A.T. 3D Printed Microfluidics. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 13, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagac, M.; Hajnys, J.; Ma, Q.P.; Jancar, L.; Jansa, J.; Stefek, P.; Mesicek, J. A Review of Vat Photopolymerization Technology: Materials, Applications, Challenges, and Future Trends of 3D Printing. Polymers 2021, 13, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.K.; Vaze, A.; Rusling, J.F. Automated 3D-printed unibody immunoarray for chemiluminescence detection of cancer biomarker proteins. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafeldin, M.; Kadimisetty, K.; Bhalerao, K.R.; Bist, I.; Jones, A.; Chen, T.; Lee, N.H.; Rusling, J.F. Accessible Telemedicine Diagnostics with ELISA in a 3D Printed Pipette Tip. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 7394–7402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinke, C.; Neumsteir, N.V.; Roberto de Oliveira, P.; Janegitz, B.C.; Bonacin, J.A. Sensing of L-methionine in biological samples through fully 3D-printed electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1142, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesaei, S.; Song, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ruan, X.; Du, D.; Gozen, A.; Lin, Y. Micro additive manufacturing of glucose biosensors: A feasibility study. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1043, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielczarek, W.S.; Obaje, E.A.; Bachmann, T.T.; Kersaudy-Kerhoas, M. Microfluidic blood plasma separation for medical diagnostics: Is it worth it? Lab Chip 2016, 16, 3441–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tripathi, S.; Kumar, Y.V.B.; Agrawal, A.; Prabhakar, A.; Joshi, S.S. Microdevice for plasma separation from whole human blood using bio-physical and geometrical effects. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuan, D.H.; Wu, C.C.; Su, W.Y.; Huang, N.T. A Microfluidic Device for Simultaneous Extraction of Plasma, Red Blood Cells, and On-Chip White Blood Cell Trapping. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimov, I.K.; Basabe-Desmonts, L.; Garcia-Cordero, J.L.; Ross, B.M.; Ricco, A.J.; Lee, L.P. Stand-alone self-powered integrated microfluidic blood analysis system (SIMBAS). Lab Chip 2011, 11, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liao, S.C.; Song, J.; Mauk, M.G.; Li, X.; Wu, G.; Ge, D.; Greenberg, R.M.; Yang, S.; Bau, H.H. A high-efficiency superhydrophobic plasma separator. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, X.; Chen, H.; Jia, S.; Wang, W. A 3D printed three-dimensional centrifugal fluidic system for blood separation. Microsyst. Technol. 2021, 27, 2639–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, M.J.; Gong, H.; Woolley, A.T.; Nordin, G.P. 3D Printed Microfluidic Features Using Dose Control in X, Y, and Z Dimensions. Micromachines 2018, 9, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, H.; Bickham, B.P.; Woolley, A.T.; Nordin, G.P. Custom 3D printer and resin for 18 μm × 20 μm microfluidic flow channels. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 2899–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauchamp, M.J.; Nielsen, A.V.; Gong, H.; Nordin, G.P.; Woolley, A.T. 3D Printed Microfluidic Devices for Microchip Electrophoresis of Preterm Birth Biomarkers. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 7418–7425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bickham, A.V.; Pang, C.; George, B.Q.; Topham, D.J.; Nielsen, J.B.; Nordin, G.P.; Woolley, A.T. 3D Printed Microfluidic Devices for Solid-Phase Extraction and On-Chip Fluorescent Labeling of Preterm Birth Risk Biomarkers. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 12322–12329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warr, C.; Valdoz, J.C.; Bickham, B.P.; Knight, C.J.; Franks, N.A.; Chartrand, N.; Van Ry, P.M.; Christensen, K.A.; Nordin, G.P.; Cook, A.D. Biocompatible PEGDA Resin for 3D Printing. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 2239–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, H.; Sakthivel, K.; Mohamed, M.G.A.; Boras, E.; Shin, S.R.; Kim, K. Designing Gelatin Methacryloyl (GelMA)-Based Bioinks for Visible Light Stereolithographic 3D Biofabrication. Macromol. Biosci. 2021, 21, 2000317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almughamsi, H.M.; Howell, M.K.; Parry, S.R.; Esene, J.E.; Nielsen, J.B.; Nordin, G.P.; Woolley, A.T. Immunoaffinity monoliths for multiplexed extraction of preterm birth biomarkers from human blood serum in 3D printed microfluidic devices. Analyst 2022, 147, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxebarria-Elezgarai, J.; Alvarez-Braña, Y.; Garoz-Sanchez, R.; Benito-Lopez, F.; Basabe-Desmonts, L. Large-Volume Self-Powered Disposable Microfluidics by the Integration of Modular Polymer Micropumps with Plastic Microfluidic Cartridges. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 22485–22491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zastrow, M. 3D printing gets bigger, faster and stronger. Nature 2020, 578, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez Noriega, J.L.; Chartrand, N.A.; Valdoz, J.C.; Cribbs, C.G.; Jacobs, D.A.; Poulson, D.; Viglione, M.S.; Woolley, A.T.; Van Ry, P.M.; Christensen, K.A.; et al. Spatially and optically tailored 3D printing for highly miniaturized and integrated microfluidics. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darkes-Burkey, C.; Shepherd, R.F. High-resolution 3D printing in seconds. Nature 2020, 588, 594–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Design | Working Pressure | Resin Composition | Resin Character | Trench Shape | Plasma Separation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Positive | PEGDA, NPS, Irg | Hydrophilic | Circular | N/A |
| 2 | Positive | PEGDA, NPS, Irg | Hydrophilic | Circular | N/A |
| 3 | Positive | PEGDA, NPS, Irg | Hydrophilic | Circular | N/A |
| 4 | Positive | PEGDA, NPS, Irg | Hydrophilic | Rectangle | Bad |
| 5 | Positive | PEGDA, NPS, Irg | Hydrophilic | Rectangle | Bad |
| 6 | Positive | PEGDA, NPS, Irg | Hydrophilic | Rectangle | N/A |
| 7 | Positive | PEGDA, NPS, Irg | Hydrophilic | Rectangle | N/A |
| 8 | Positive | PEGDA, NPS, Irg | Hydrophilic | Rectangle | N/A |
| 9 | Positive | PEGDA, NPS, Irg | Hydrophilic | Rectangle | N/A |
| 10 | Negative | PEGDA, NPS, Irg | Hydrophilic | Rectangle | N/A |
| 11 | Negative | PEGDA, NPS, Irg | Hydrophilic | Rectangle | N/A |
| 12 | Negative | PEGDA, NPS, Irg | Hydrophilic | Rectangle | N/A |
| 13 | Negative | PEGDA, NPS, Irg | Hydrophilic | Rectangle | N/A |
| 14 | Negative | PEGDA, NPS, Irg | Hydrophilic | Rectangle | N/A |
| 15 | Negative | PEGDA, NPS, Irg | Hydrophilic | Rectangle | Good |
| 16 | Negative | PEGDA, Avo, Irg | Hydrophilic | Rectangle | N/A |
| 17 | Negative | HDDA, Avo, Irg | Hydrophobic | Rectangle | N/A |
| Device 3 | Device 4 | Device 14 | Device 15 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inlet reservoir volume | N/A | N/A | 12 µL | 12 µL |
| Sedimentation trench volume/µL | 1.72–6.79 | 7.66 | 3.34 | 5.20 |
| Sample | Distilled water | Diluted human blood | Whole human blood | Whole human blood |
| Working pressure | Positive | Positive | Negative | Negative |
| Flow rate/µL min−1 | 15 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Plasma separation | No | Yes | No | Yes |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garcia-Rey, S.; Nielsen, J.B.; Nordin, G.P.; Woolley, A.T.; Basabe-Desmonts, L.; Benito-Lopez, F. High-Resolution 3D Printing Fabrication of a Microfluidic Platform for Blood Plasma Separation. Polymers 2022, 14, 2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132537
Garcia-Rey S, Nielsen JB, Nordin GP, Woolley AT, Basabe-Desmonts L, Benito-Lopez F. High-Resolution 3D Printing Fabrication of a Microfluidic Platform for Blood Plasma Separation. Polymers. 2022; 14(13):2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132537
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcia-Rey, Sandra, Jacob B. Nielsen, Gregory P. Nordin, Adam T. Woolley, Lourdes Basabe-Desmonts, and Fernando Benito-Lopez. 2022. "High-Resolution 3D Printing Fabrication of a Microfluidic Platform for Blood Plasma Separation" Polymers 14, no. 13: 2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132537
APA StyleGarcia-Rey, S., Nielsen, J. B., Nordin, G. P., Woolley, A. T., Basabe-Desmonts, L., & Benito-Lopez, F. (2022). High-Resolution 3D Printing Fabrication of a Microfluidic Platform for Blood Plasma Separation. Polymers, 14(13), 2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132537