Structure–Property Relationship in Melt-Spun Poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hexanoate) Monofilaments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Melt-Spinning of PHBH Monofilaments
2.3. Analysis of Thermal Properties
2.4. Analysis of Rheological Properties
2.5. Analysis of Morphological Properties
2.6. Analysis of Fiber Diameters
2.7. Analysis of Mechanical Properties
2.8. Analysis of Structural Properties
3. Results and Discussion
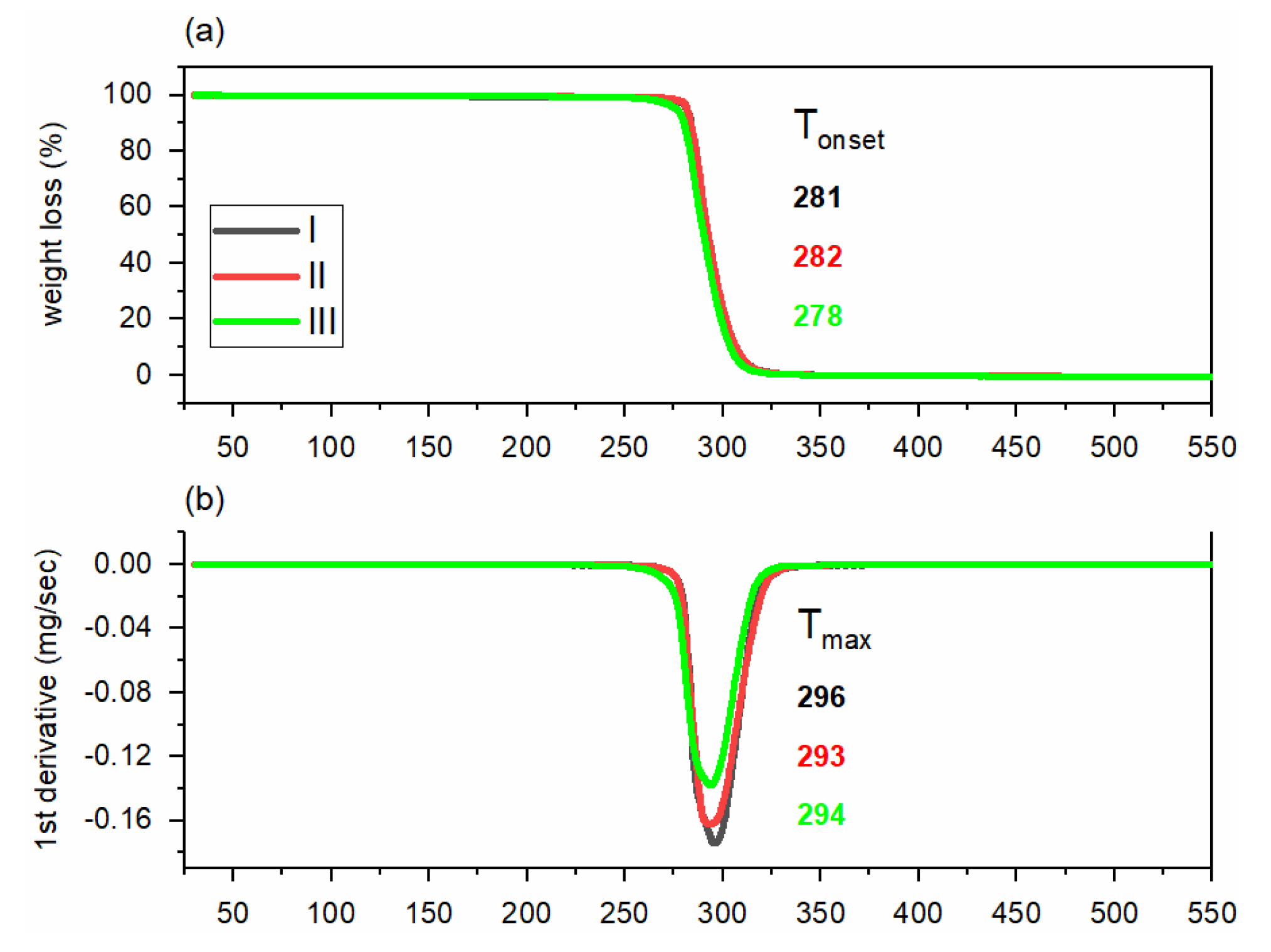
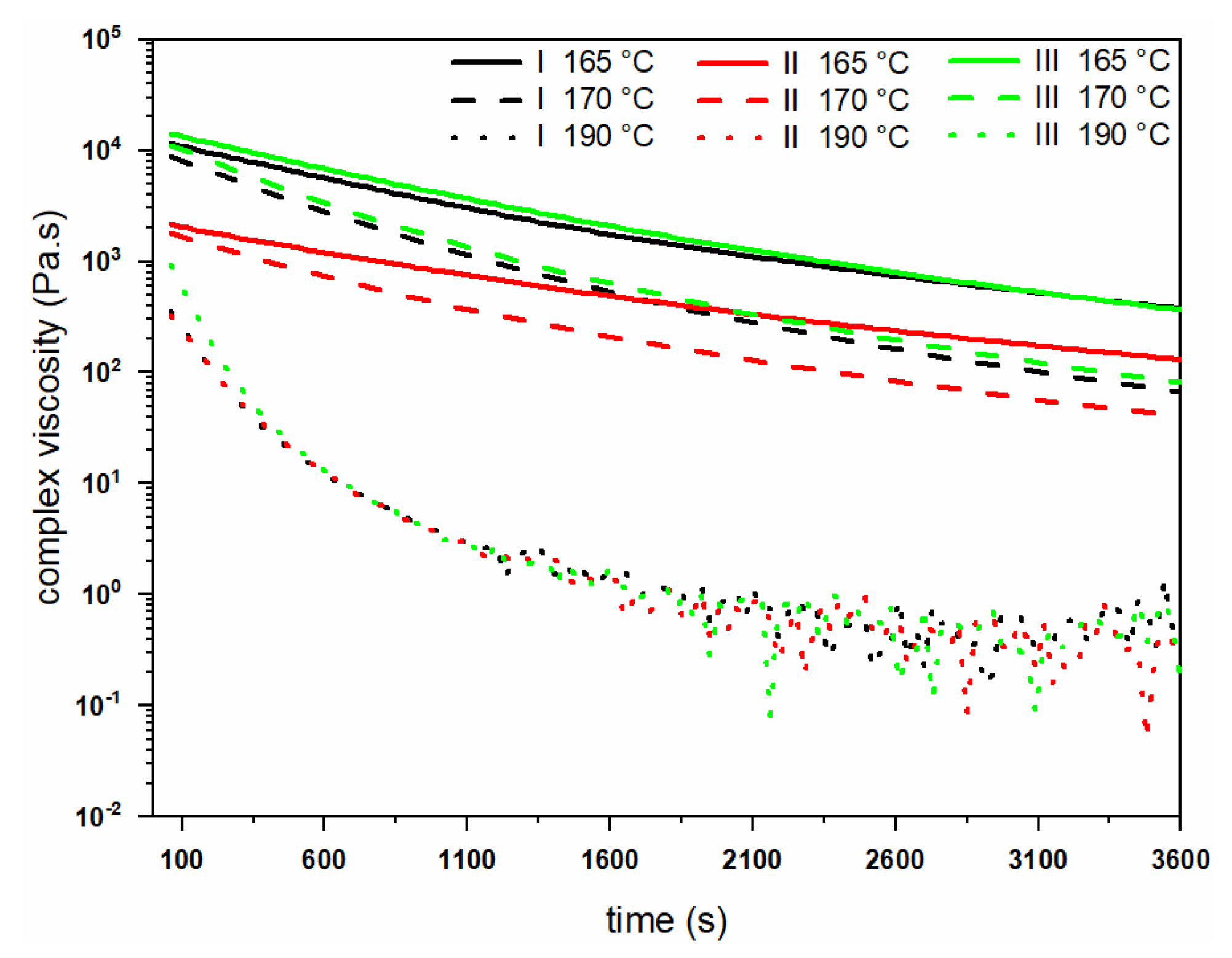
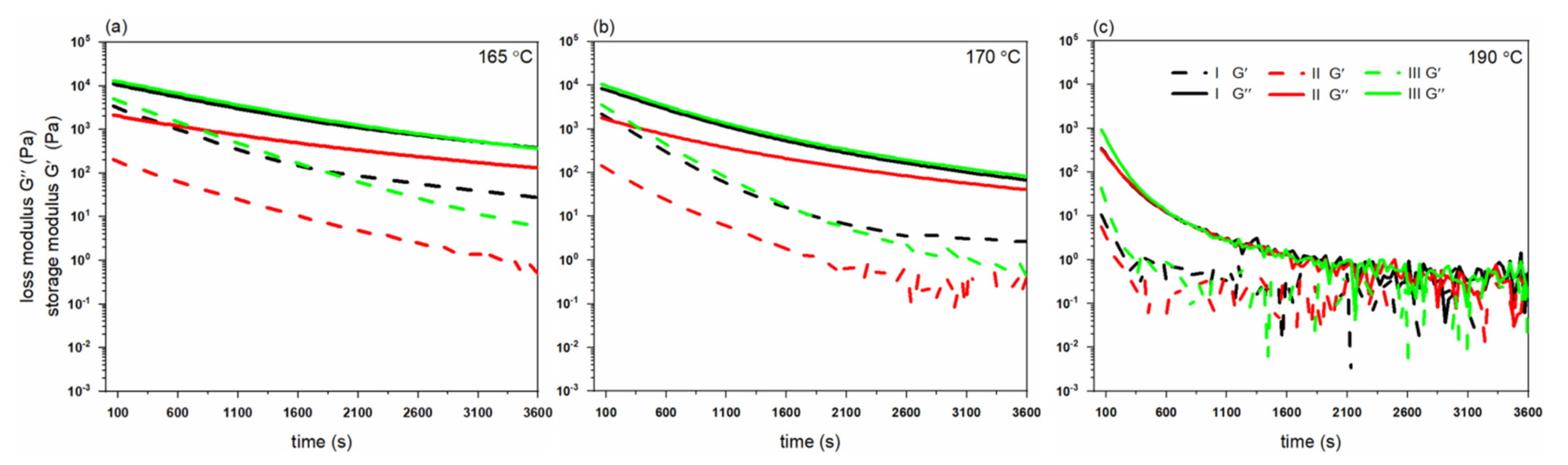
3.1. Thermal and Rheological Properties of PHBH Polymer Grades
3.2. Morphological Properties and Fineness of PHBH Monofilaments
3.3. Thermal Properties of PHBH Monofilaments
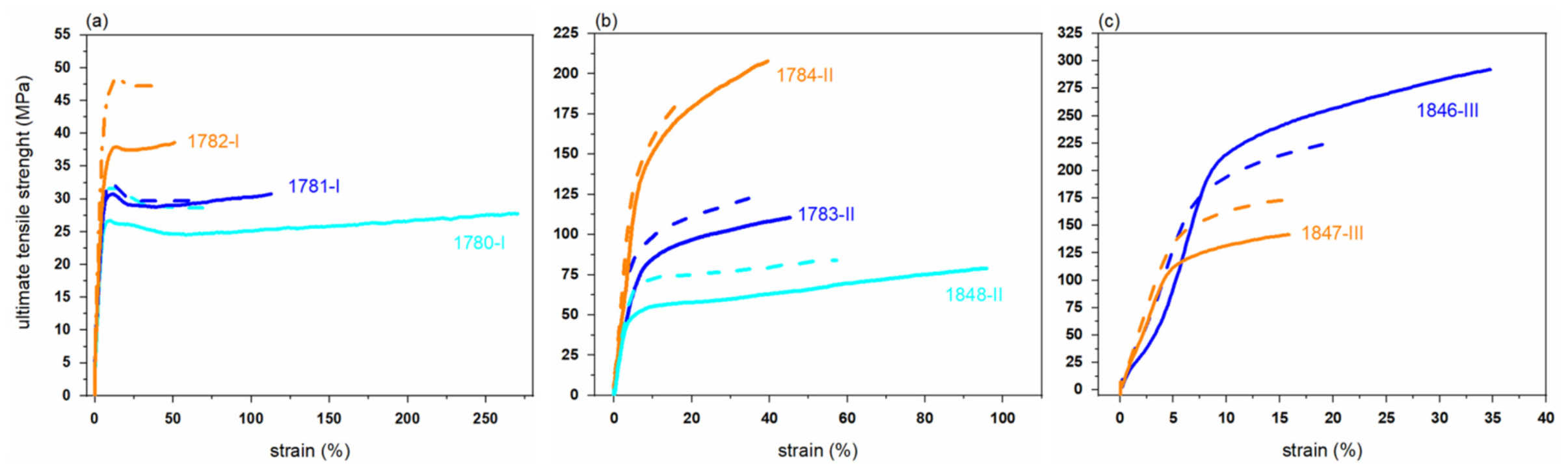
3.4. Mechanical Properties of PHBH Monofilaments
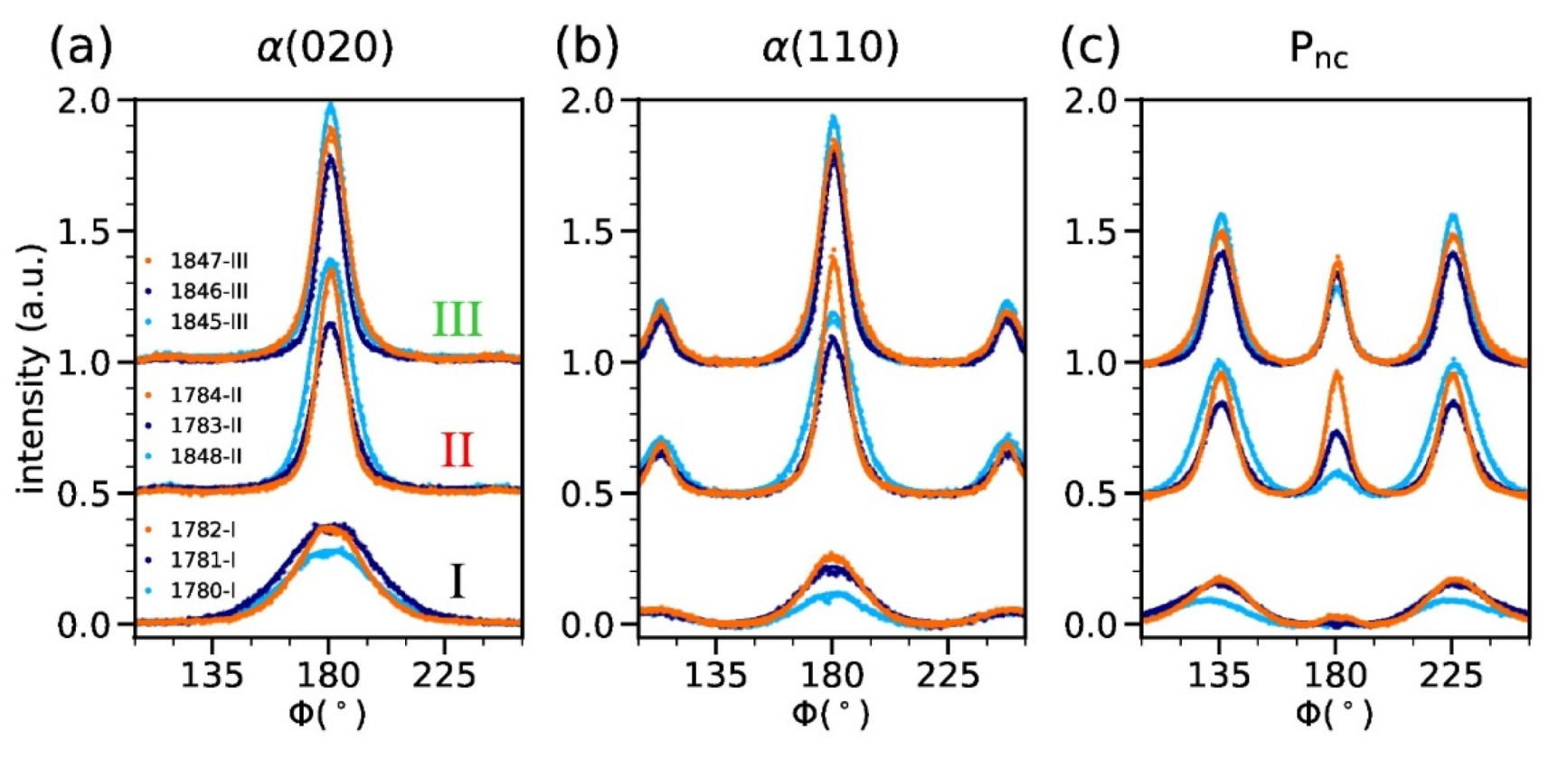
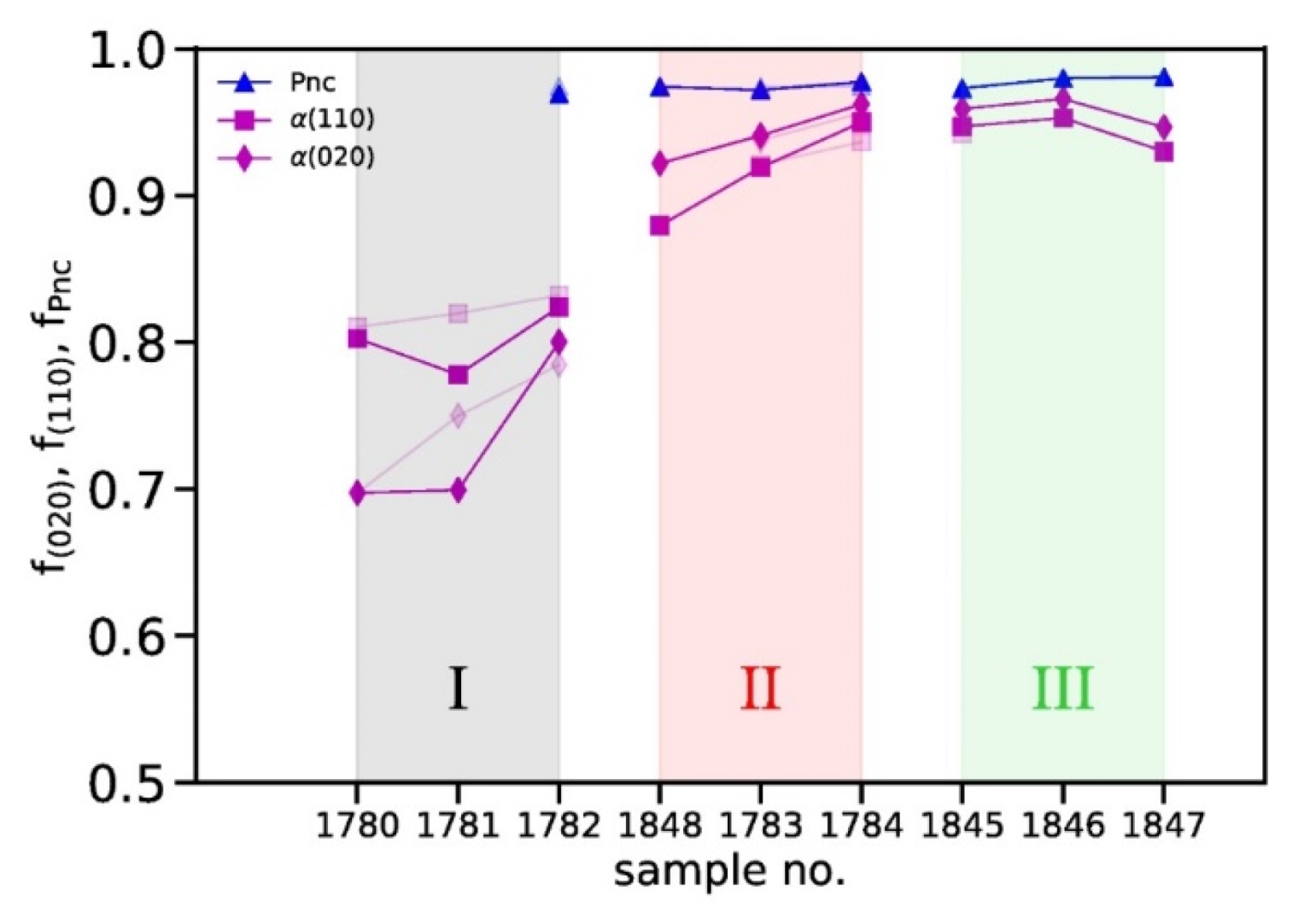
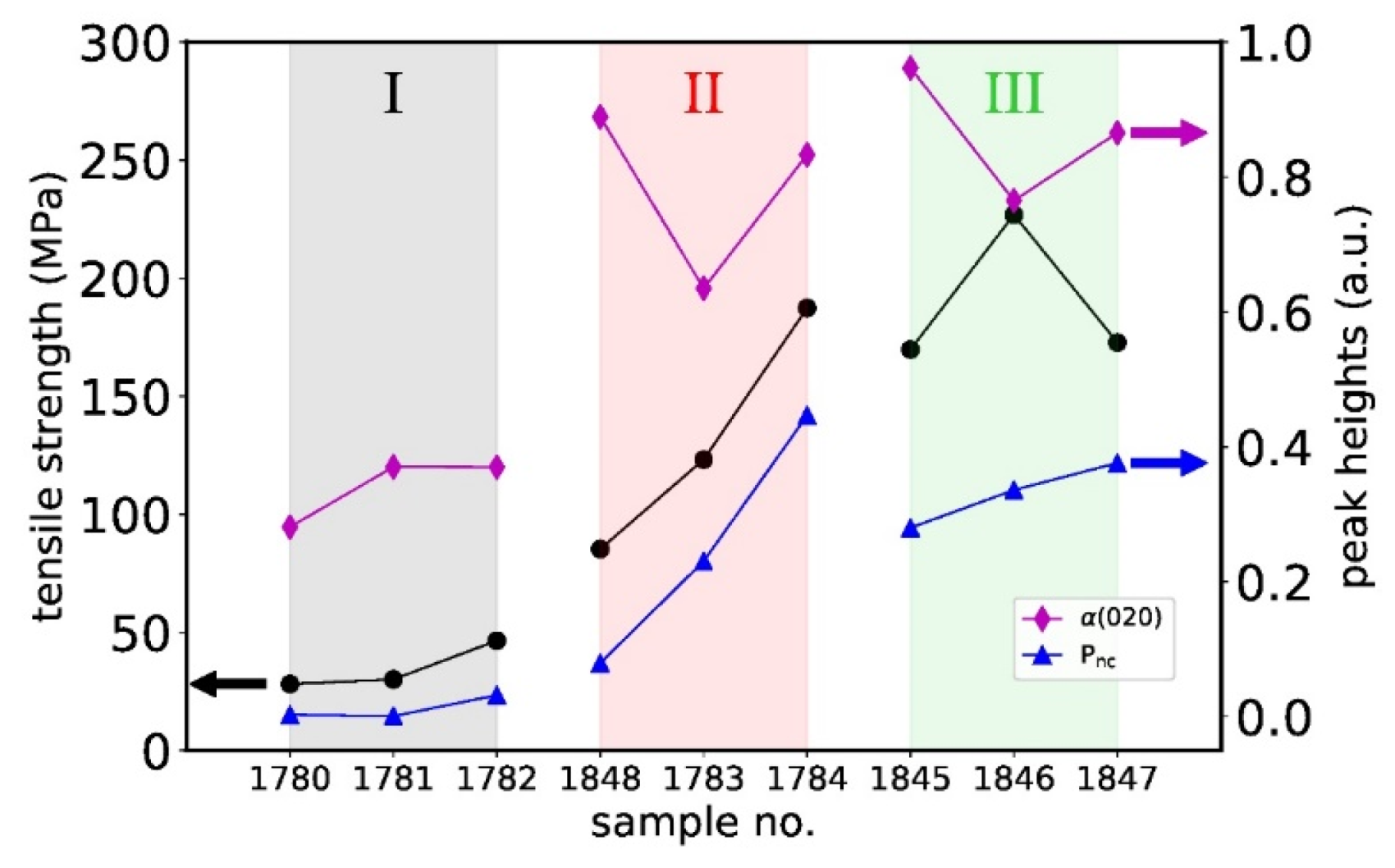
3.5. Structural Properties of PHBH Monofilaments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, G.-Q. A microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) based bio- and materials industry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2434–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, M. Advances in Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Production, Volume 2. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneka Corporation. Biodegradable Polymer PHBH; Kaneka Corporation: Minato City, Tokyo, 2017; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Meereboer, K.W.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Review of recent advances in the biodegradability of polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) bioplastics and their composites. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 5519–5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinmulewo, A.B.; Nwinyi, O.C. Polyhydroxyalkanoate: A biodegradable polymer (a mini review). J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1378, 042007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, S.; Keshavarz, T.; Roy, I. Polyhydroxyalkanoates: Biodegradable polymers with a range of applications. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2007, 82, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Cao, Y.; Lv, P.; Ma, P.; Dong, W.; Bai, H.; Wang, W.; Du, M.; Chen, M. Enhanced crystallization kinetics of bacterially synthesized poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanate) with structural optimization of oxalamide compounds as nucleators. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 154, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Watanabe, T.; Wang, Y.; Kichise, T.; Fukuchi, T.; Chen, G.-Q.; Doi, Y.; Inoue, Y. Studies on Comonomer Compositional Distribution of Bacterial Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate)s and Thermal Characteristics of Their Factions. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; He, Y.; Fukuchi, T.; Inoue, Y. Comonomer Compositional Distribution and Thermal Characteristics of Bacterially Synthesized Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate)s. Macromol. Biosci. 2001, 1, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alata, H.; Aoyama, T.; Inoue, Y. Effect of Aging on the Mechanical Properties of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate). Macromolecules 2007, 40, 4546–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivorra-Martinez, J.; Verdu, I.; Fenollar, O.; Sanchez-Nacher, L.; Balart, R.; Quiles-Carrillo, L. Manufacturing and Properties of Binary Blend from Bacterial Polyester Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) and Poly(caprolactone) with Improved Toughness. Polymers 2020, 12, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyama, T.; Sato, H.; Ozaki, Y. Crystallization of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) during melt extrusion promoted by residual crystals. Polym. Cryst. 2019, 2, e10076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, K.; Dong, T.; Hirose, K.; Aoyama, T.; Inoue, Y. Inducing Rapid Crystallization of Slowly-crystallizable Copolyester by in situ Generation of Crystalline Nuclei in Melt of Copolyester. Polym. J. 2008, 40, 300–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.; Yu, J. Crystallization Kinetics of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) Granules in Different Environmental Conditions. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 2, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asrar, J.; Valentin, H.E.; Berger, P.A.; Tran, M.; Padgette, S.R.; Garbow, J.R. Biosynthesis and Properties of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-3-hydroxyhexanoate) Polymers. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zini, E.; Focarete, M.L.; Noda, I.; Scandola, M. Bio-composite of bacterial poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) reinforced with vegetable fibers. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 2085–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-C.; Kato, N.; Sakurai, S.; Yamane, H. Mechanical properties and higher-order structures of biaxially drawn bacterial poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-(R)-3-hydroxyhexanote] films. Macromol. Res. 2011, 20, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ma, X.; Li, J.; Zhu, L. Preparation and characterization of a bionanocomposite from poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) and cellulose nanocrystals. Cellulose 2019, 26, 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.K.; Cheng, B.W.; Wu, Q. Mechanical Properties and Ordered Structure of Bacterial Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) Fibers Stretched after Isothermal Crystallization near Tg. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 284–286, 1774–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hufenus, R.; Yan, Y.; Dauner, M.; Kikutani, T. Melt-Spun Fibers for Textile Applications. Materials 2020, 13, 4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Q.; Takarada, W.; Kikutani, T. Fiber Structure Development of PHBH through Stress-Induced Crystallization in High-Speed Melt Spinning Process. J. Fiber Sci. Technol. 2017, 73, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kabe, T.; Hongo, C.; Tanaka, T.; Hikima, T.; Takata, M.; Iwata, T. High Tensile Strength Fiber of Poly (R)-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-(R)-3-hydroxyhexanoate Processed by Two-Step Drawing with Intermediate Annealing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyao, Y.; Takarada, W.; Kikutani, T. Improvement of mechanical properties of biodegradable PHBH fibers through high-speed melt spinning process equipped with a liquid isothermal bath. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2289, 020038. [Google Scholar]
- Rebia, R.A.; Shizukuishi, K.; Tanaka, T. Characteristic changes in PHBH isothermal crystallization monofilaments by the effect of heat treatment and dip-coating in various solvents. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 134, 109808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Nakamura, M.; Padermshoke, A.; Yamaguchi, H.; Terauchi, H.; Ekgasit, S.; Noda, I.; Ozaki, Y. Thermal Behavior and Molecular Interaction of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) Studied by Wide-Angle X-ray Diffraction. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 3763–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perret, E.; Hufenus, R. Insights into strain-induced solid mesophases in melt-spun polymer fibers. Polymer 2021, 229, 124010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perret, E.; Reifler, F.A.; Gooneie, A.; Chen, K.; Selli, F.; Hufenus, R. Structural response of melt-spun poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) fibers to stress and temperature. Polymer 2020, 197, 122503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perret, E.; Reifler, F.A.; Gooneie, A.; Hufenus, R. Tensile study of melt-spun poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) P3HB fibers: Reversible transformation of a highly oriented phase. Polymer 2019, 180, 121668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perret, E.; Sharma, K.; Tritsch, S.; Hufenus, R. Reversible mesophase in stress-annealed poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) fibers: A synchrotron x-ray and polarized ATR-FTIR study. Polymer 2021, 231, 124141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepto, R.F.T. Dispersity in polymer science (IUPAC Recommendations 2009). Pure Appl. Chem. 2009, 81, 351–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hufenus, R.; Reifler, F.A.; Maniura-Weber, K.; Spierings, A.; Zinn, M. Biodegradable Bicomponent Fibers from Renewable Sources: Melt-Spinning of Poly(lactic acid) and Poly[(3-hydroxybutyrate)-co-(3-hydroxyvalerate)]. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2012, 297, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifin, W.; Kuboki, T. Effects of thermoplastic elastomers on mechanical and thermal properties of glass fiber reinforced poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) composites. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, E1331–E1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunsell, A.R.; Joannes, S.; Marcellan, A. Testing and characterization of fibers. In Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres, 2nd ed.; Bunsell, A.R., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 21–55. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, H.-M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.-H.; Chen, G.-Q.; Xu, J. Different thermal behaviors of microbial polyesters poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate). Polymer 2010, 51, 6037–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakov, A.A.; Mordvintsev, D.A.; Schick, C. Melting and reorganization of poly(ethylene terephthalate) on fast heating (1000 K/s). Polymer 2004, 45, 3755–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuniwa, M.; Satou, T. Multiple melting behavior of poly(butylene succinate). I. Thermal analysis of melt-crystallized samples. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2002, 40, 2411–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srimoaon, P.; Dangseeyun, N.; Supaphol, P. Multiple melting behavior in isothermally crystallized poly(trimethylene terephthalate). Eur. Polym. J. 2004, 40, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Cheung, M.K.; Yu, P.H.F. Crystallization kinetics and melting behaviour of microbial poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate). Polym. Int. 2005, 54, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sato, H.; Noda, I.; Ozaki, Y. Multiple melting behavior of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) investigated by differential scanning calorimetry and infrared spectroscopy. Polymer 2007, 48, 4777–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourne, F. Synthetic Fibers Machines and Equipment, Manufacture, Properties—Handbook for Plant Engineering, Machine Design, and Operation; Hanser Publications: Munich, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- The Society of Fiber Science and Technology Concepts. High Performance and Specialty Fibers; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2016; pp. 49–66. [Google Scholar]
- Kabe, T.; Sugiura, T.; Hikima, T.; Takata, M.; Iwata, T. Effect of Molecular Weight on Physical and Crystallization Properties of UHMW-poly [(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-(R)-3-hydroxyhexanoate]. J. Fiber Sci. Technol. 2018, 74, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hufenus, R.; Reifler, F.A.; Fernández-Ronco, M.P.; Heuberger, M. Molecular orientation in melt-spun poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) fibers: Effect of additives, drawing and stress-annealing. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 71, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.B.; Kothari, V.K. (Eds.) Manufactured Fibre Technology; Springer: New Delhi, India, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, R.; Voigt, D.; Tändler, B.; Gohs, U.; Häussler, L.; Brünig, H. Melt spinning of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) for tissue engineering using electron-beam-irradiated poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) as nucleation agent. Macromol. Biosci. 2008, 8, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Tashiro, K. Reinvestigation of Crystal Structure and Intermolecular Interactions of Biodegradable Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) α-Form and the Prediction of Its Mechanical Property. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobntbekt, J.; Mabchessault, R.H. Physical properties of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate: IV. Conformational analysis and crystalline structure. J. Mol. Biol. 1972, 71, 735–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokouchi, M.; Chatani, Y.; Tadokoro, H.; Teranishi, K.; Tani, H. Structural studies of polyesters: 5. Molecular and crystal structures of optically active and racemic poly (β-hydroxybutyrate). Polymer 1973, 14, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perret, E.; Braun, O.; Sharma, K.; Tritsch, S.; Muff, R.; Hufenus, R. High-resolution 2D Raman mapping of mono- and bicomponent filament cross-sections. Polymer 2021, 229, 124011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selli, F.; Erdoğan, U.H.; Hufenus, R.; Perret, E. Mesophase in melt-spun poly(ε-caprolactone) filaments: Structure–mechanical property relationship. Polymer 2020, 206, 122870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selli, F.; Erdoğan, U.H.; Hufenus, R.; Perret, E. Properties, X-ray data and 2D WAXD fitting procedures of melt-spun poly(ε-caprolactone). Data in Brief 2020, 32, 106223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, J.J.; Hermans, P.H.; Vermaas, D.; Weidinger, A. Quantitative Evaluation of Orientation in Cellulose Fibres from the X-Ray Fibre Diagram. Recl. Trav. Chim. Pays-Bas J. R. Neth. Chem. Soc. 1946, 65, 427–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perret, E.; Reifler, F.A.; Gooneie, A.; Hufenus, R. X-ray data from a cyclic tensile study of melt-spun poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) P3HB fibers: A reversible mesophase. Data in Brief 2019, 25, 104376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

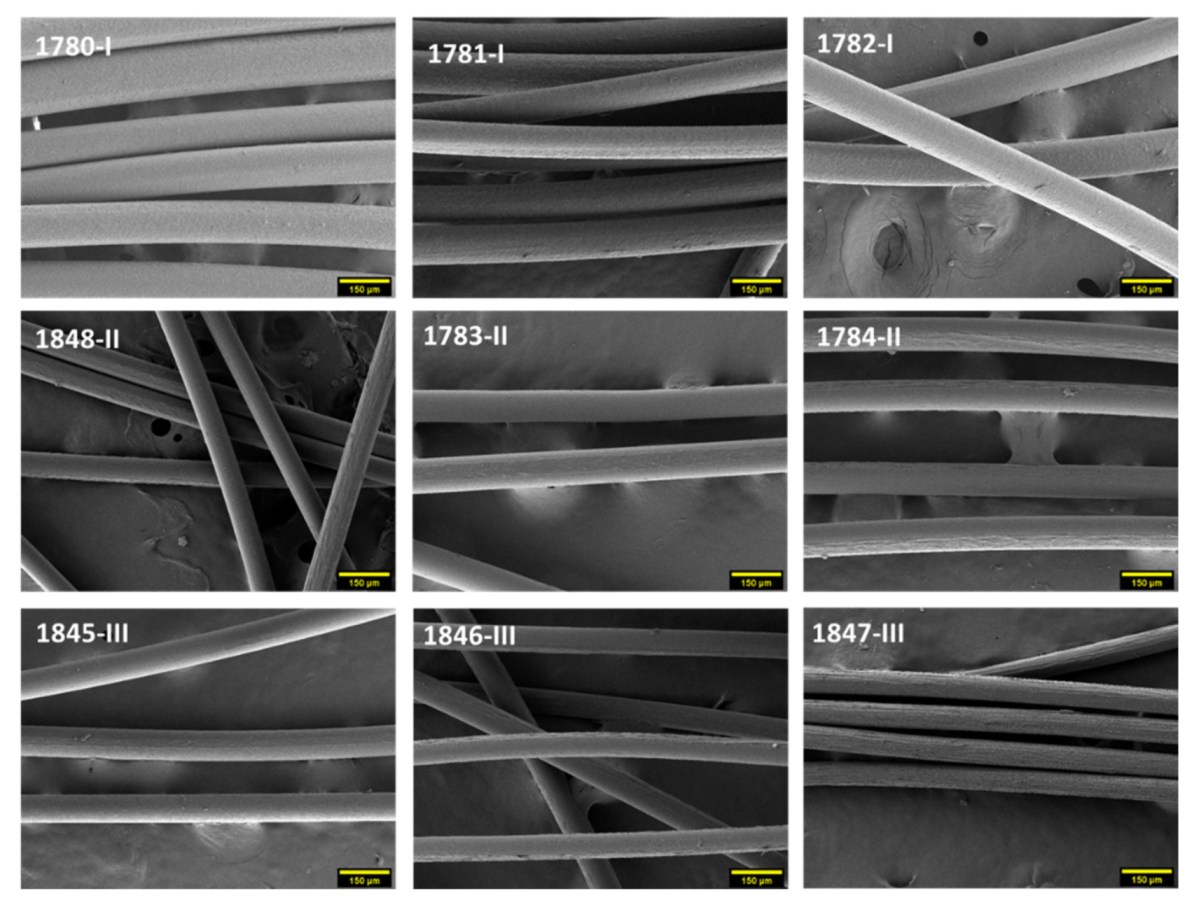


| Grade | I | II | III |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3-hydroxy hexanoate (mol%) | 11 | 6 | 6 |
| melting point (°C) | 126 | 145 | 145 |
| glass transition temperature (°C) | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| crystallization temperature (°C) | 50–60 | >70–80 | 70–80 |
| melt flow index (g/10 min) * | 3 | 12 | 3 |
| molecular weight (kDa) | 500 | 300 | 500 |
| dispersity [30] | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| density (g/cm3) | 1.19 | 1.20 | 1.20 |
| Fiber No.-Grade | Melt Temp.(°C) | Spin Press. (bar) | Mass Throughput (g/min) | Air Cool. Temp. (°C) | Godet 1 Speed/ Temp. (m/min, °C) | Godet 2 Speed/ Temp. (m/min, °C) | Godet 3 Speed/ Temp. (m/min, °C) | Godet 4 Speed/ Temp. (m/min, °C) | Godet 5 Speed/ Temp. (m/min, °C) | Godet 6 Speed/ Temp. (m/min, °C) | Godet 7 Speed/ Temp. (m/min, °C) | Winder Speed (m/min) | Draw Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1780-I | 150 | 143 | 5.85 | 26 | 60/70 | 270/50 | 360/40 | - | 360/60 | 375/40 | 390/30 | 390 | 6.5 |
| 1781-I | 150 | 150 | 6.00 | 20 | 60/63 | 300/70 | 420/60 | 550/50 | 550/60 | 575/50 | 600/30 | 600 | 10.0 |
| 1782-I | 154 | 150 | 7.20 | 20 | 60/63 | 300/65 | 420/55 | 550/45 | 550/60 | 575/50 | 600/35 | 600 | 10.0 |
| 1848-II | 153 | 72 | 4.00 | 12.5 | 100/10 | 700/60 | 800/60 | 800/50 | 800/40 | 800/35 | 800/35 | 800 | 8.0 |
| 1783-II | 153 | 65 | 7.68 | 19 | 120/50 | 900/50 | 950/50 | 950/40 | 950/50 | 955/40 | 960/30 | 960 | 8.0 |
| 1784-II | 154 | 68 | 6.48 | 19 | 100/50 | - | 780/40 | 805/40 | 805/40 | 810/40 | 810/30 | 810 | 8.1 |
| 1845-III | 157 | 112 | 5.95 | 19 | 100/30 | 550/30 | 600/30 | 600/40 | 600/50 | 600/40 | 600/30 | 595 | 6.0 |
| 1846-III | 166 | 90 | 4.80 | 16 | 100/65 | 700/60 | 800/60 | 800/50 | 800/50 | 800/40 | 800/30 | 800 | 8.0 |
| 1847-III | 166 | 90 | 4.32 | 16 | 100/50 | 700/60 | 800/60 | 800/50 | 800/50 | 800/40 | 800/30 | 800 | 8.0 |
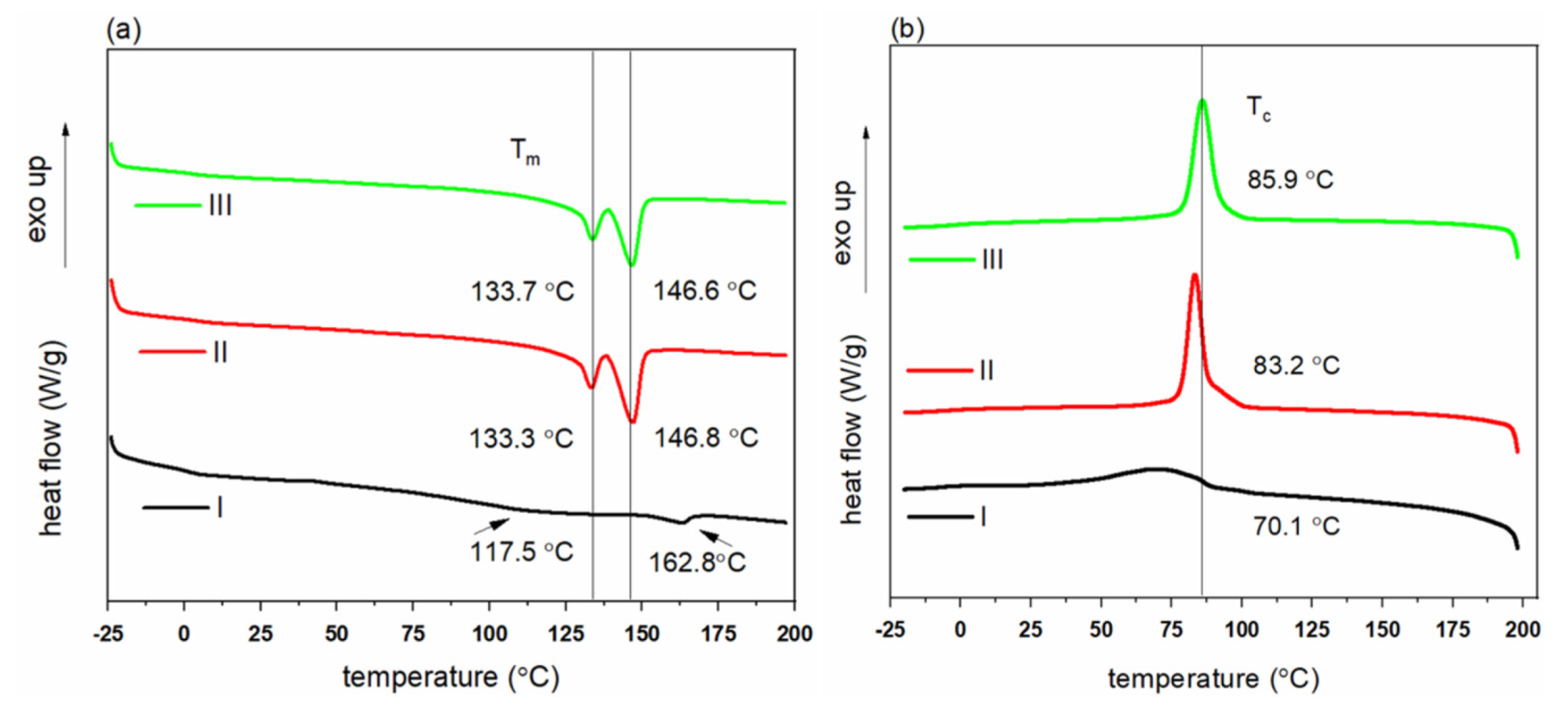
| Grade | Tm (°C) | ∆Hm (J/g) | Xc (%) | Tc (°C) | ∆Hc (J/g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 117.5 | 162.8 | 15.94 | 10.92 | 70.1 | 27.08 |
| II | 133.3 | 146.8 | 46.07 | 31.55 | 83.2 | 50.63 |
| III | 133.7 | 146.6 | 47.38 | 32.45 | 85.9 | 50.42 |
| Fiber No.-Grade | Draw Ratio (DR) | Fineness (Tex = mg/m) | Diameter (µm) Calculated | Diameter (µm) Observed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1780-I | 6.5 | 15 | 126.7 | 119.9 ± 3.9 |
| 1781-I | 10.0 | 10 | 103.5 | 96.4 ± 4.5 |
| 1782-I | 10.0 | 12 | 113.3 | 101.1 ± 6.8 |
| 1848-II | 8.0 | 5 | 72.9 | 74.4 ± 2.1 |
| 1783-II | 8.0 | 8 | 92.2 | 86.1 ± 1.7 |
| 1784-II | 8.1 | 8 | 92.2 | 93.9 ± 1.6 |
| 1845-III | 5.95 | 10 | 103.0 | 96.0 ± 1.4 |
| 1846-III | 8.0 | 6 | 79.8 | 83.9 ± 3.3 |
| 1847-III | 8.0 | 5.4 | 75.7 | 78.9 ± 1.3 |
| Fiber No.-Grade | Tm (°C) | ∆Hm (J/g) | Xc (%) | Tc (°C) | ∆Hc (J/g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1780-I | 123.9 | 163.7 | 16.33 | 11.18 | - | - |
| 1781-I | 110.7 | 163.2 | 17.43 | 11.94 | 72.5 | 29.49 |
| 1782-I | 122.6 | 162.5 | 39.01 | 26.72 | 65.5 | 54.68 |
| 1848-II | 138.5 | 146.2 | 48.24 | 33.04 | 80.7 | 52.30 |
| 1783-II | 137.8 | 145.4 | 48.47 | 33.20 | 81.5 | 43.69 |
| 1784-II | 138.2 | 144.2 | 47.39 | 32.46 | 80.1 | 42.37 |
| 1845-III | 136.3 | 145.8 | 51.78 | 35.47 | 83.3 | 45.05 |
| 1846-III | 134.1 | 144.5 | 52.06 | 35.66 | 84.3 | 47.98 |
| 1847-III | 136.2 | 144.8 | 52.08 | 35.67 | 93.6 | 47.18 |
| Fiber No.-Grade | Draw Ratio | Fineness (tex = mg/m) | Specific Tensile Stress (cN/tex) | Ultimate Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st day | 33th month | 1st day | 33th month | 1st day | 33th month | |||
| 1780-I | 6.5 | 15 | 2.4 ± 0.2 | 2.4 ± 0.3 | 28.6 ± 3.1 | 28.1 ± 3.3 | 263.1 ± 70.7 | 78.2 ± 32.0 |
| 1781-I | 10.0 | 10 | 2.6 ± 0.3 | 2.5 ± 0.2 | 30.6 ± 3.2 | 30.1 ± 2.7 | 112.4 ± 28.4 | 62.8 ± 15.8 |
| 1782-I | 10.0 | 12 | 3.2 ± 0.2 | 3.9 ± 0.3 | 37.9 ± 2.6 | 46.5 ± 3.2 | 50.8 ± 8.2 | 35.9 ± 11.1 |
| 1848-II | 8.0 | 5 | 6.6 ± 1.0 | 7.1 ± 0.8 | 79.3 ± 12.0 | 85.3 ± 9.8 | 93.7 ± 11.4 | 57.7 ± 24.8 |
| 1783-II | 8.0 | 8 | 9.3 ± 1.2 | 10.3 ± 1.5 | 111.7 ± 14.3 | 123.2 ± 17.8 | 46.3 ± 4.5 | 32.5 ± 10.9 |
| 1784-II | 8.1 | 8 | 17.2 ± 1.5 | 15.6 ± 1.9 | 205.9 ± 18.2 | 187.4 ± 23.1 | 41.8 ± 5.6 | 22.1 ± 5.4 |
| 1845-III | 6.0 | 10 | * | 14.2 ± 1.2 | * | 169.8 ± 14.4 | * | 34.8 ± 6.0 |
| 1846-III | 8.0 | 6 | 24.2 ± 1.9 | 18.9 ± 1.2 | 290.9 ± 22.9 | 226.9 ± 13.9 | 37.3 ± 7.9 | 19.5 ± 3.6 |
| 1847-III | 8.0 | 5.4 | 11.6 ± 1.9 | 14.4 ± 1.0 | 139.1 ± 23.5 | 172.8 ± 12.3 | 15.9 ± 4.3 | 15.8 ± 4.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Selli, F.; Hufenus, R.; Gooneie, A.; Erdoğan, U.H.; Perret, E. Structure–Property Relationship in Melt-Spun Poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hexanoate) Monofilaments. Polymers 2022, 14, 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14010200
Selli F, Hufenus R, Gooneie A, Erdoğan UH, Perret E. Structure–Property Relationship in Melt-Spun Poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hexanoate) Monofilaments. Polymers. 2022; 14(1):200. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14010200
Chicago/Turabian StyleSelli, Figen, Rudolf Hufenus, Ali Gooneie, Umit Halis Erdoğan, and Edith Perret. 2022. "Structure–Property Relationship in Melt-Spun Poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hexanoate) Monofilaments" Polymers 14, no. 1: 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14010200
APA StyleSelli, F., Hufenus, R., Gooneie, A., Erdoğan, U. H., & Perret, E. (2022). Structure–Property Relationship in Melt-Spun Poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hexanoate) Monofilaments. Polymers, 14(1), 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14010200








