Barium/Cobalt@Polyethylene Glycol Nanocomposites for Dye Removal from Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis
2.3. Characterization Techniques
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
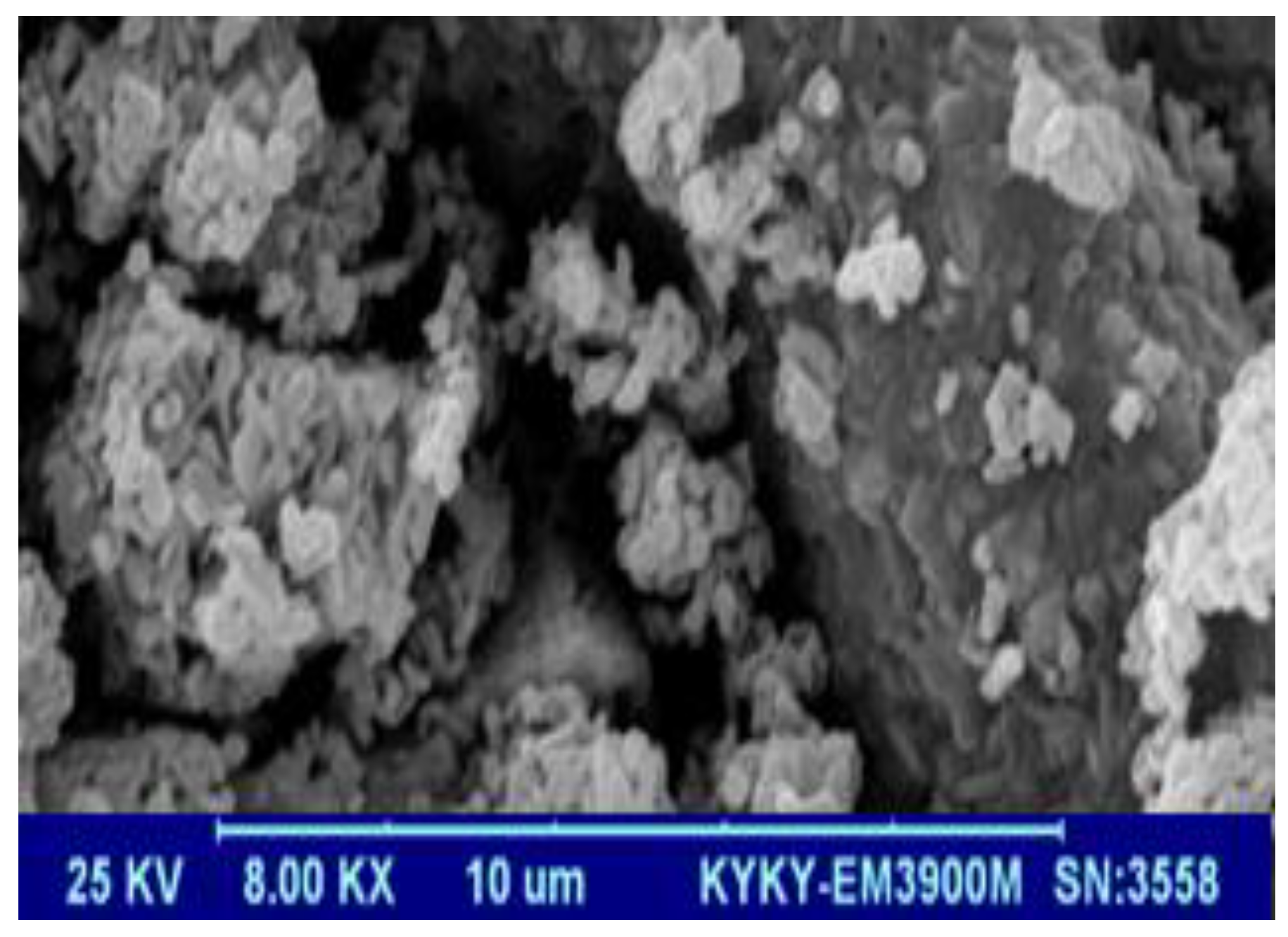
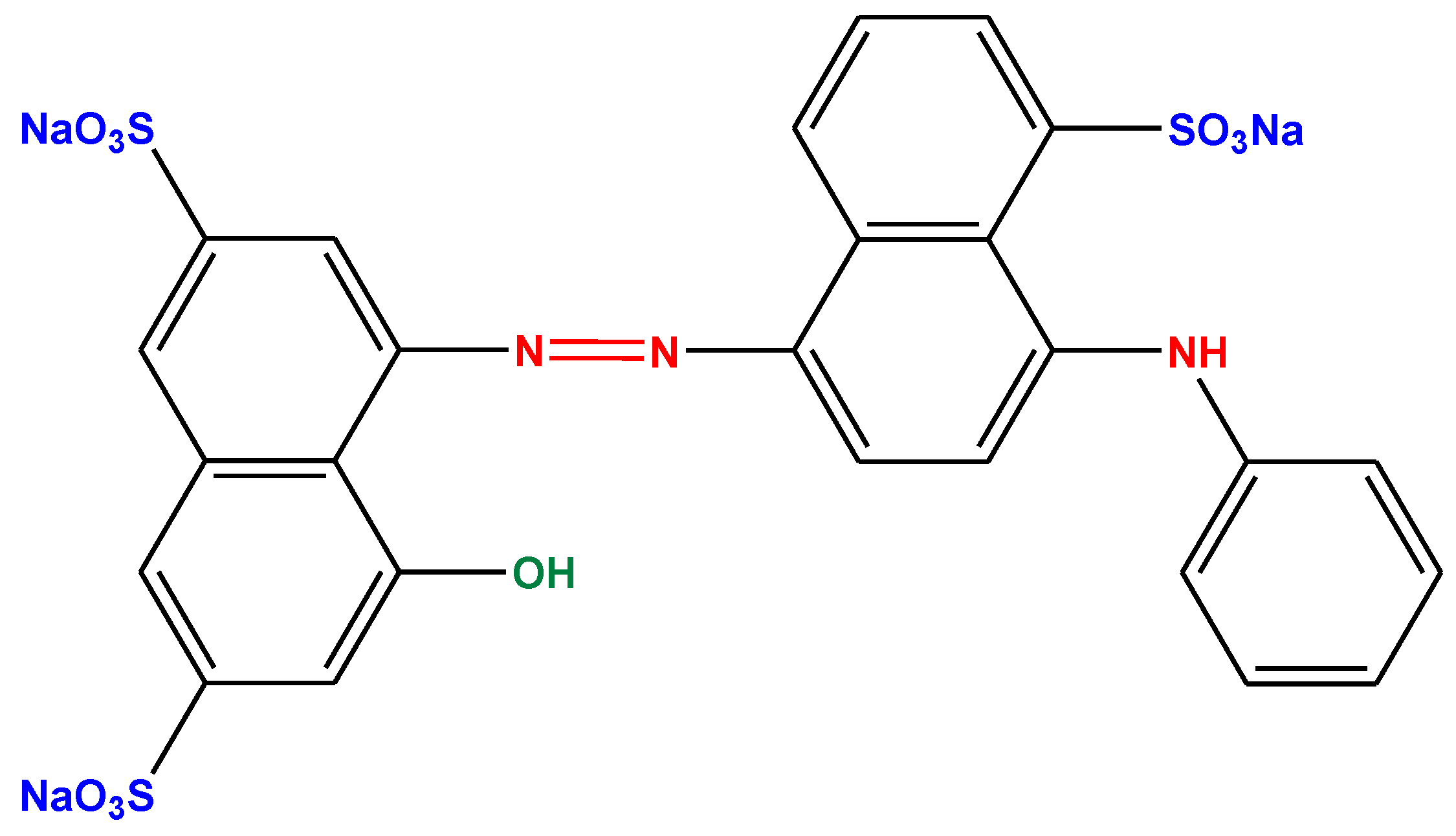
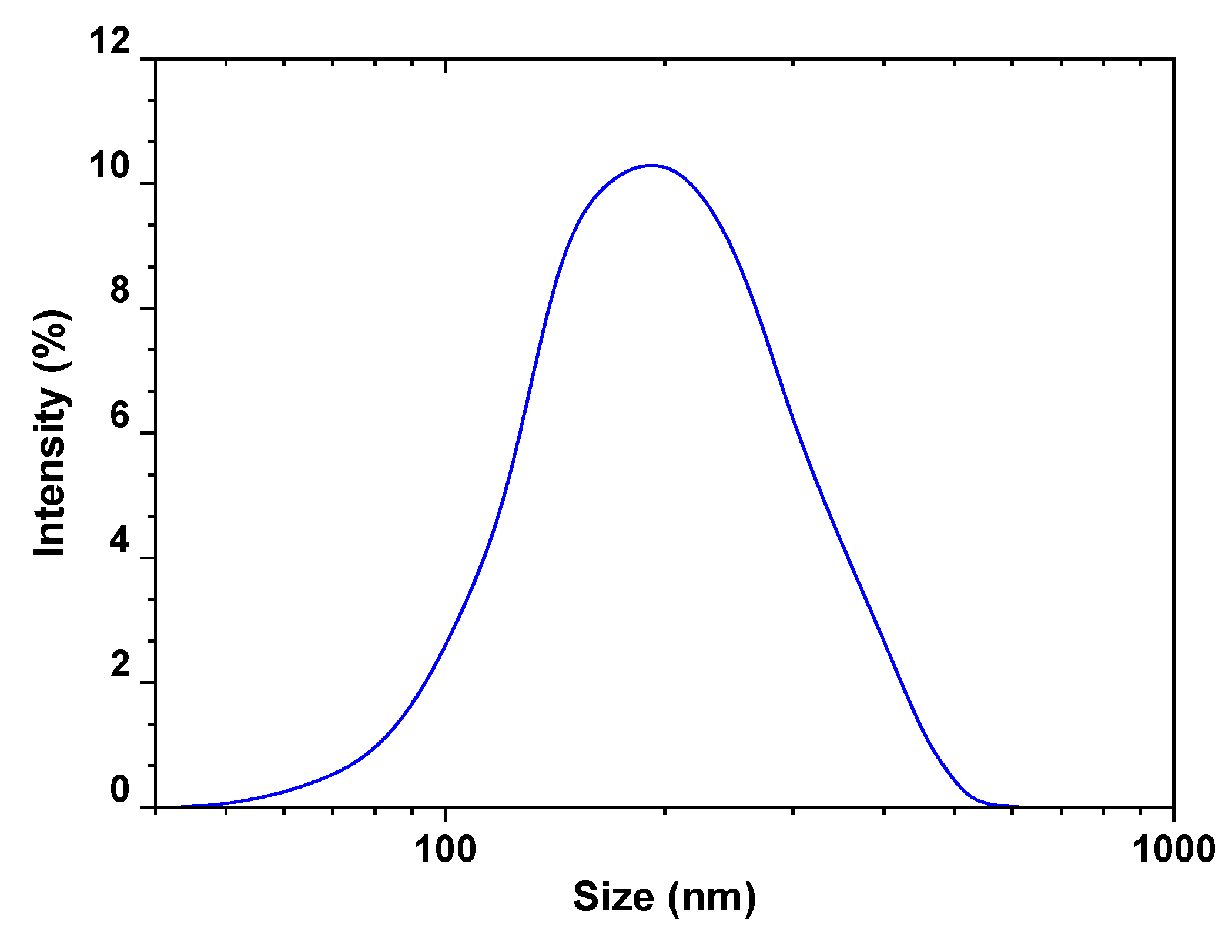
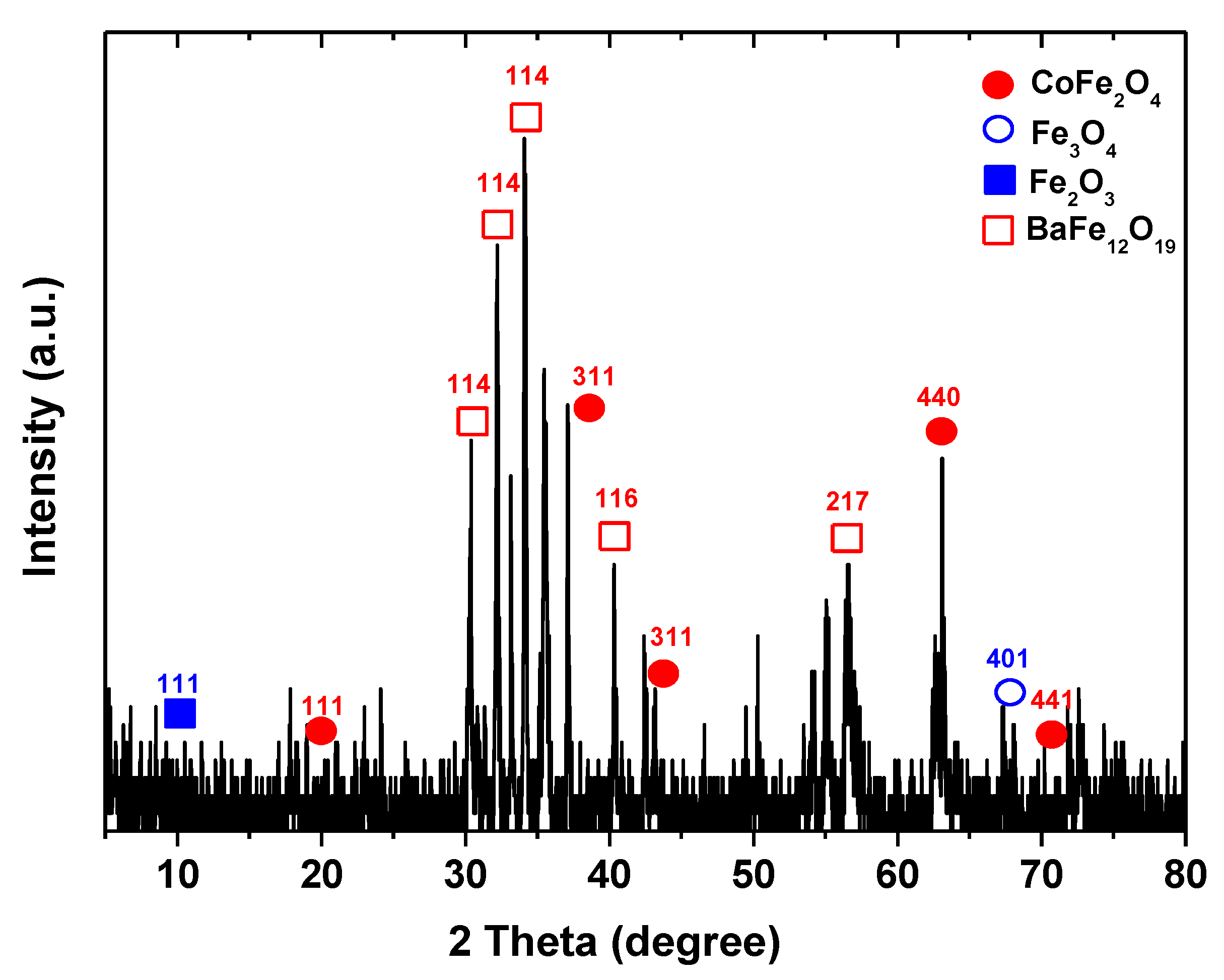
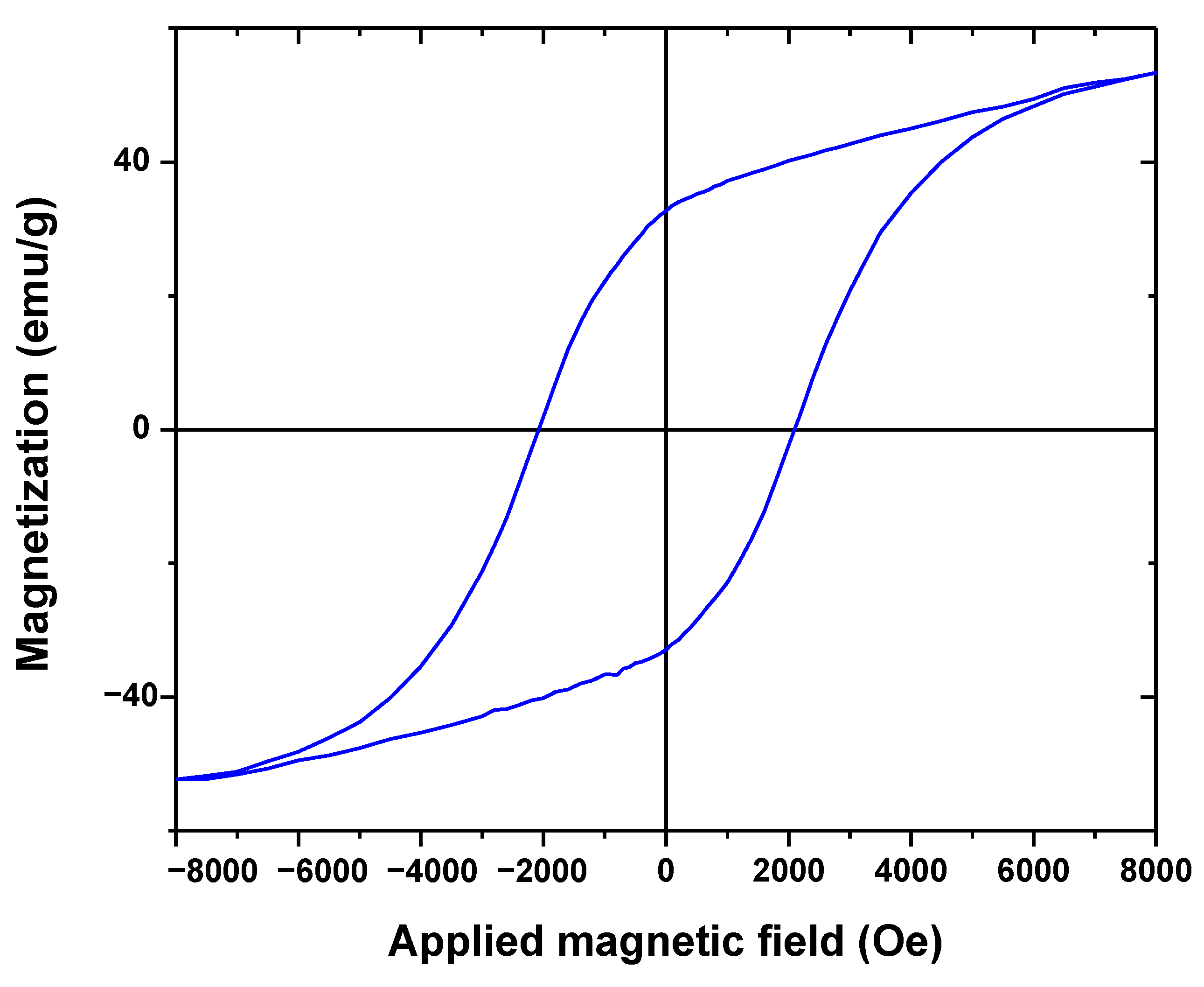
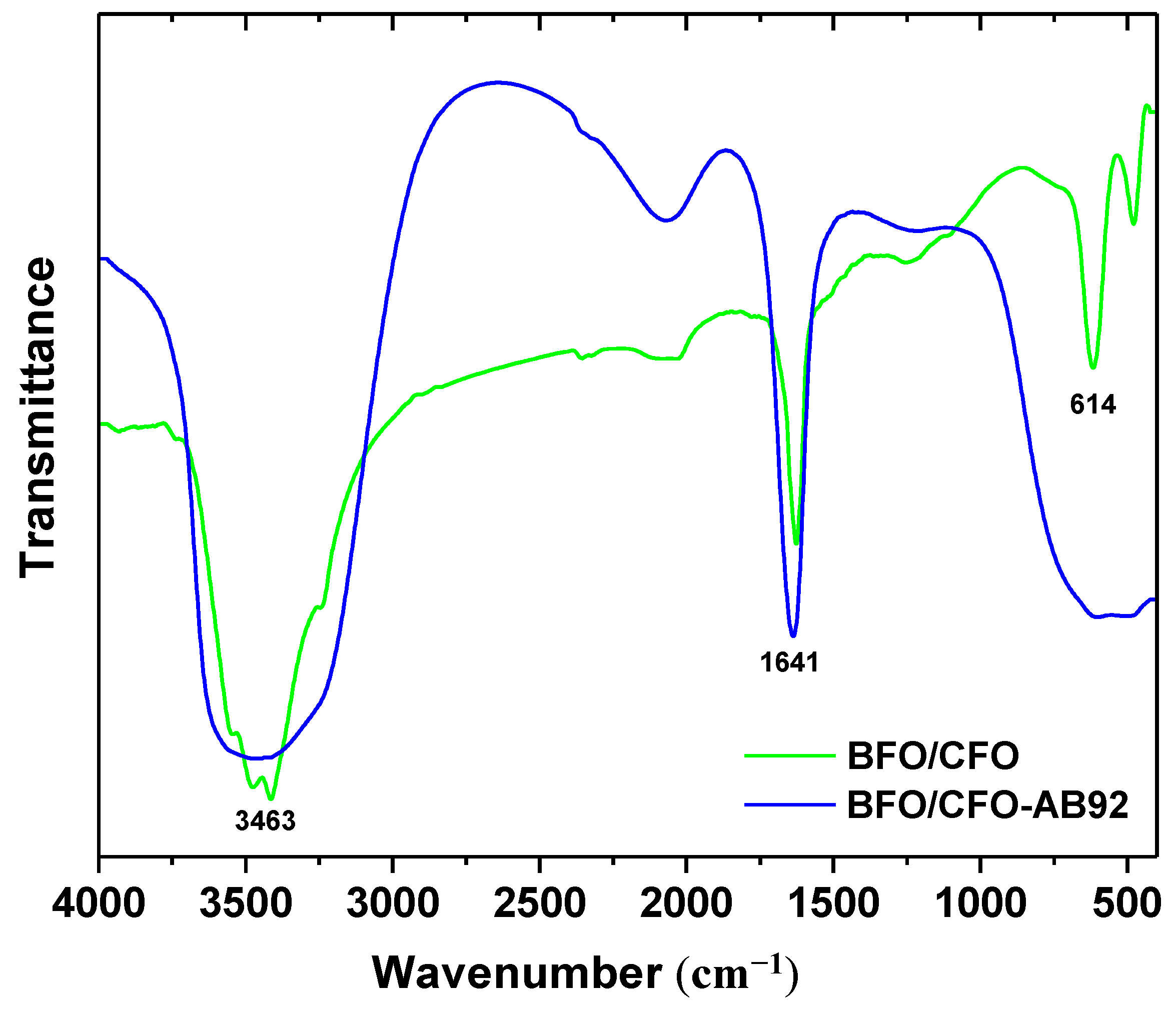
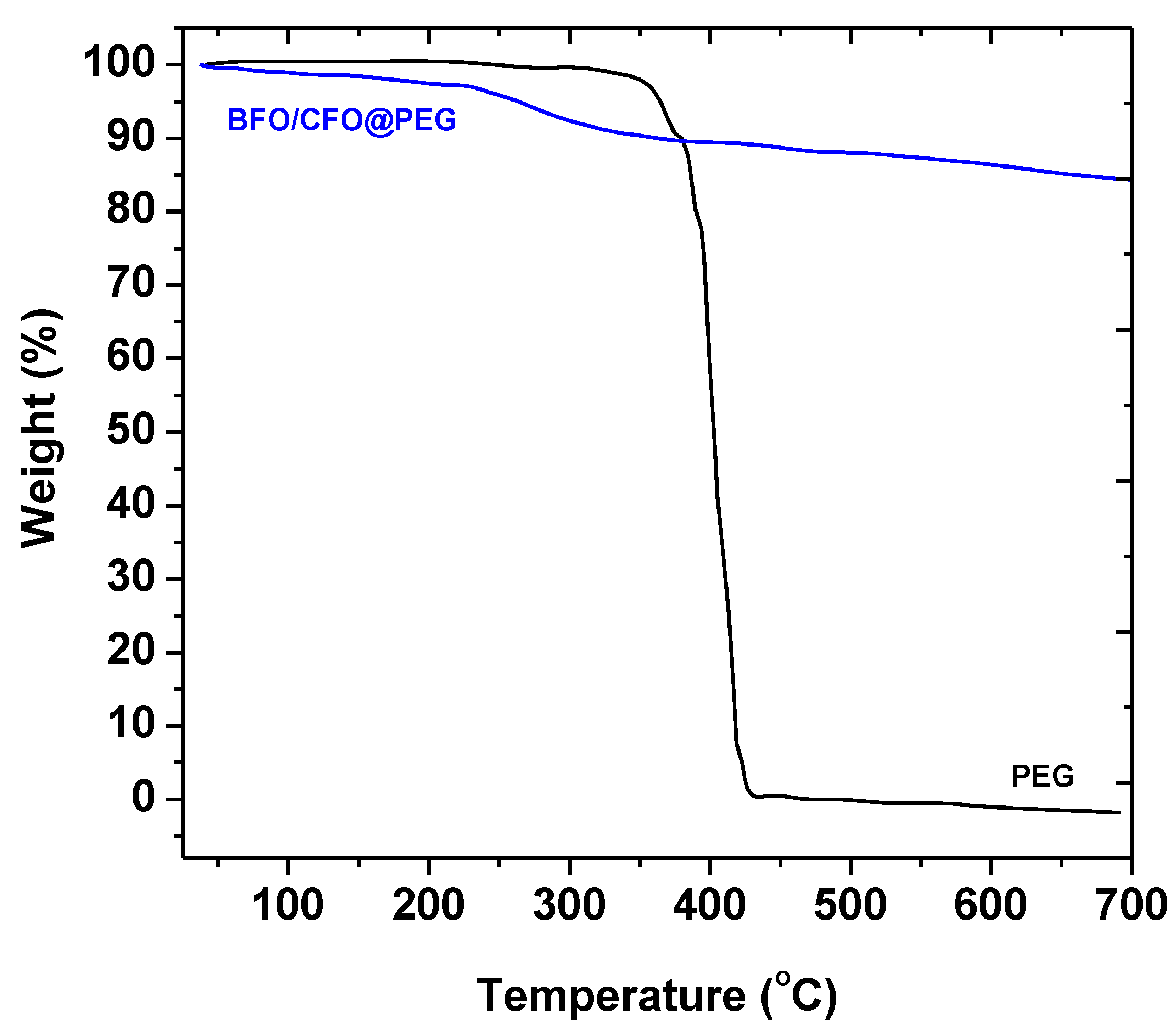
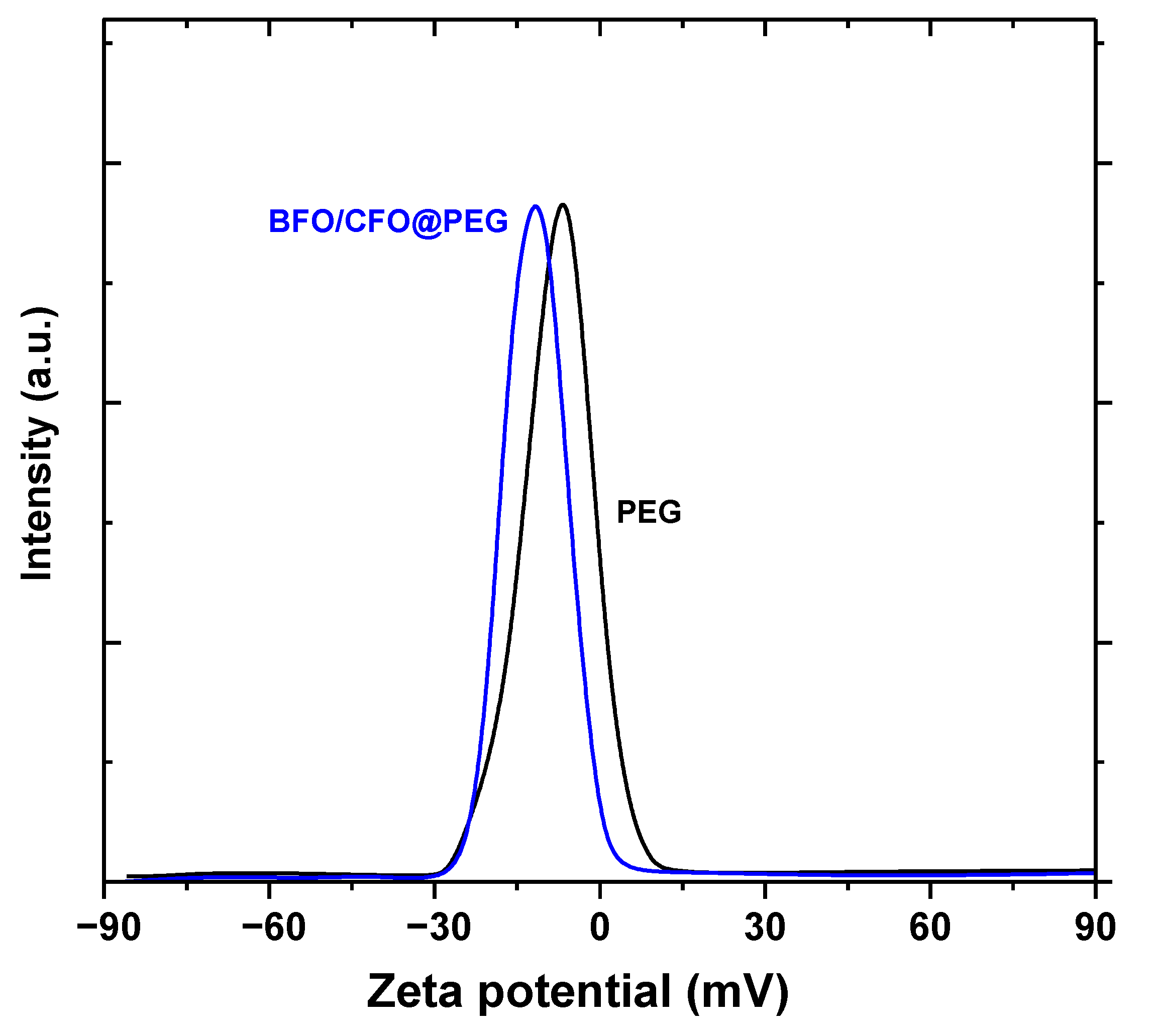
3.1. Characterizations
3.2. Adsorption Evaluation
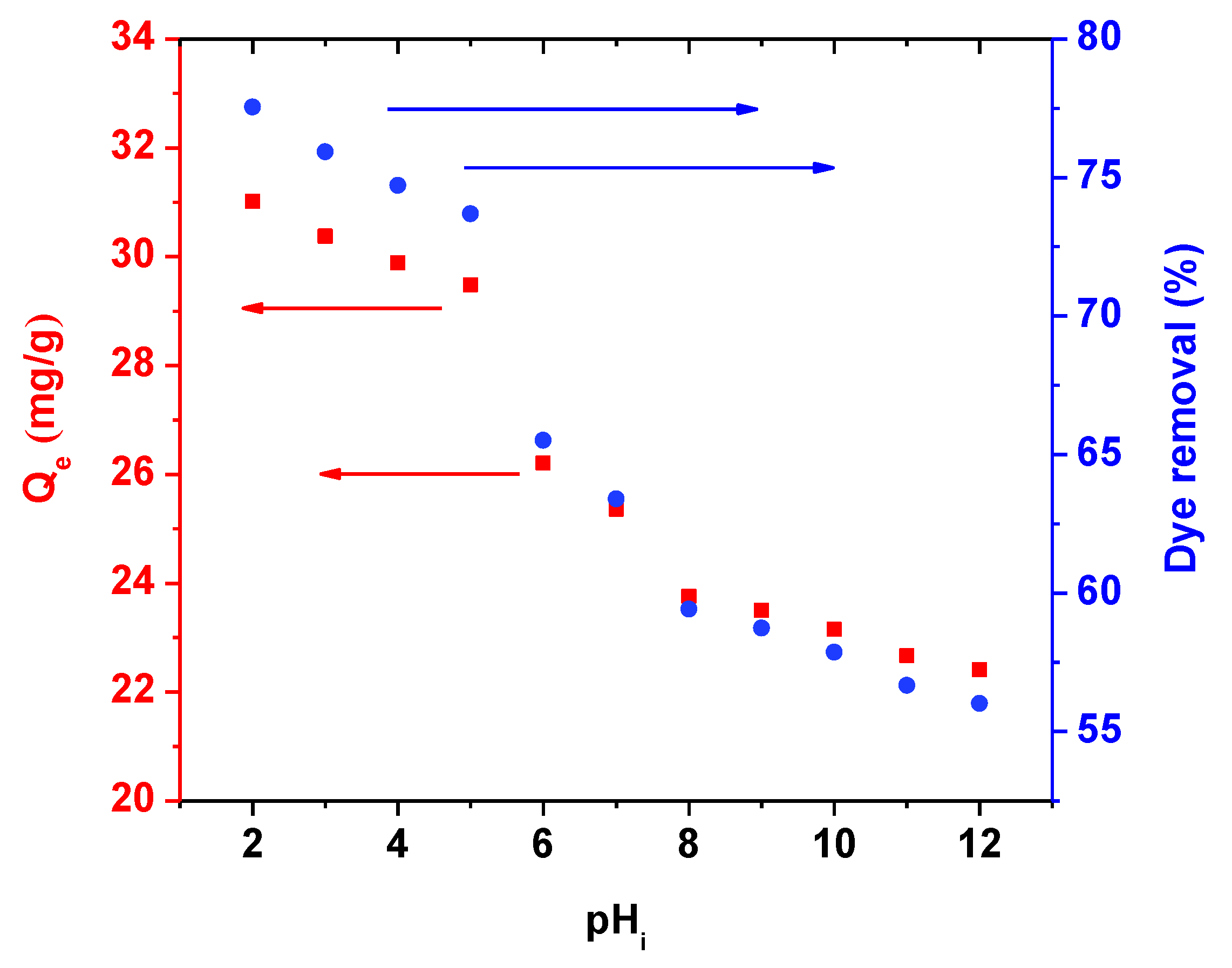
3.2.1. pH Effect
3.2.2. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage
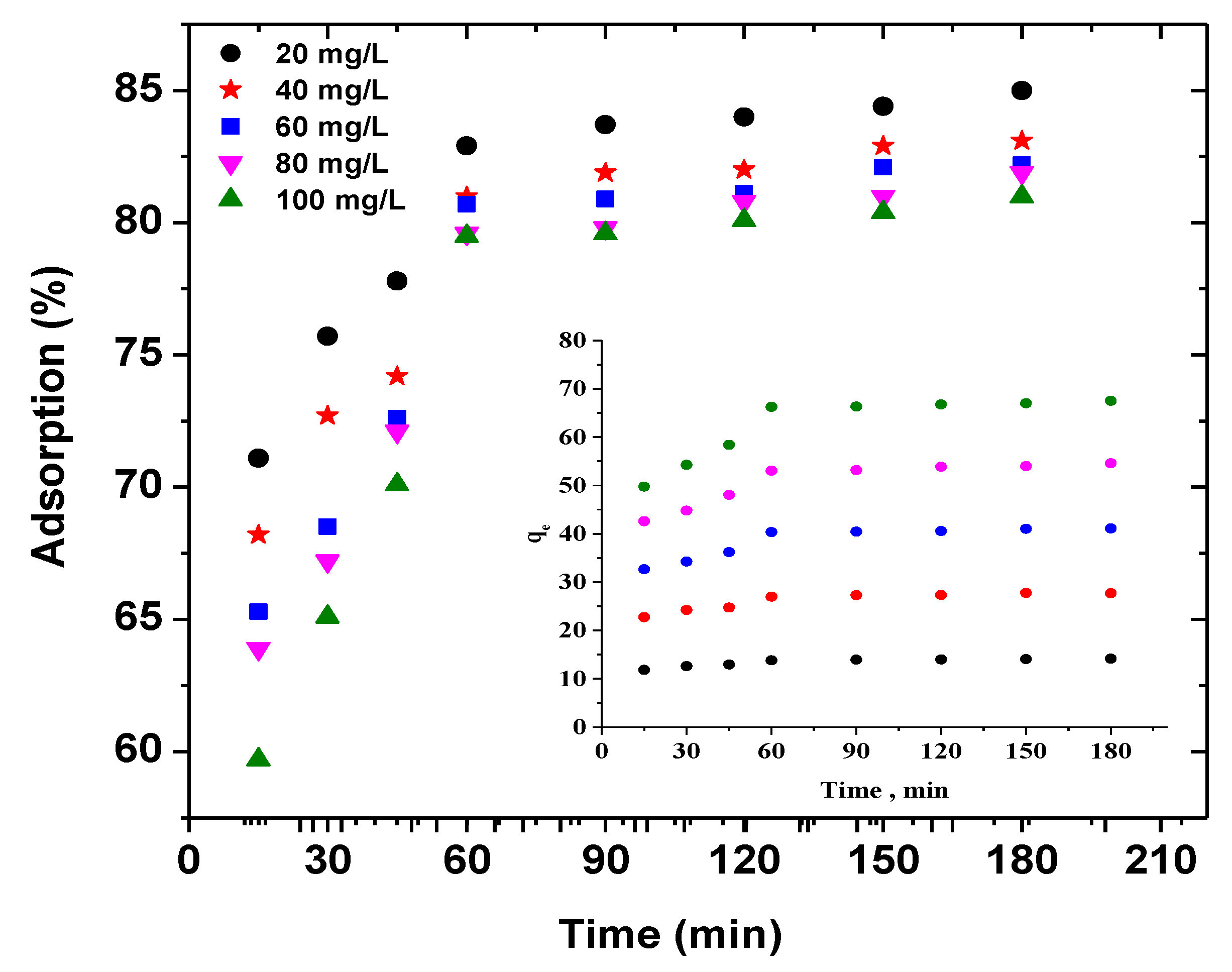
3.2.3. Isotherms and Kinetics
3.2.4. Isotherm Models
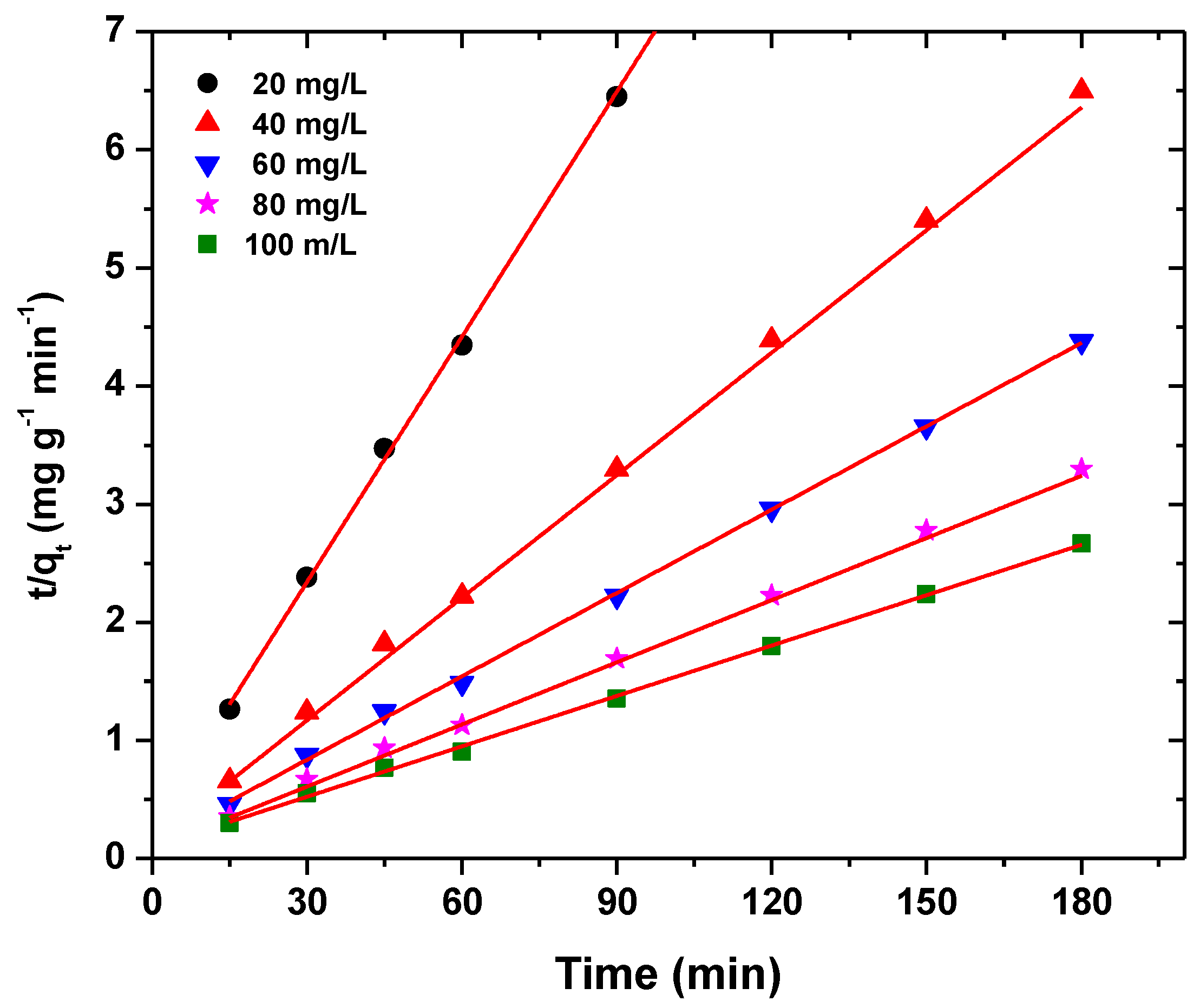
3.2.5. Kinetic Models
3.3. Comparisons
3.4. Perspectives/Limitations
- High ability to remove various organic and inorganic pollutants.
- Existence of a wide range of new adsorbent with high adsorption capacity.
- Use of cheap absorbents.
- Fast and simple procedure of removing pollutants.
- The ability to reuse some used adsorbent.
- The cost of the initial investment is cheap.
- Dependence of performance on the type of used adsorbent.
- Low capacity of some adsorbent to remove various pollutants.
- Rapid saturation of some adsorbents and reduction of their adsorption capacity.
- Non-selective pollutant for removing in a binary solution.
- Problems related to desorption of the used adsorbent after the adsorption process.
- Dependence of the adsorption process to various parameters such as temperature, time, and pH.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gonawala, K.; Mehta, M.J. Removal of Color from Different Dye Wastewater by Using Ferric Oxide as an Adsorbent. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2014, 5, 102–109. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Gong, W.; Luo, J.; Zou, C.; Yang, Y.; Yang, S. Selective adsorption of cationic dyes from aqueous solution by polyoxometalate-based metal–organic framework composite. Appl. Surface Sci. 2016, 362, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagub, M.T.; Sen, T.K.; Afroze, S.; Ang, H.M. Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkaim, A.F.; Sadik, Z.; Mahdi, D.K.; Alshrefi, S.M.; Al-Sammarraie, A.M.; Alamgir, F.M.; Singh, P.M.; Aljeboree, A.M. Preparation, structure and adsorption properties of synthesized multiwall carbon nanotubes for highly effective removal of maxilon blue dye. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 32, 2456–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydartaemeh, M.R.; Aslani, S.; Ardejani, F. Loess Soil Nanoparticles as A Novel Adsorbent for Adsorption of Green Malachite Dye. J. Chromatogr. Sep. Tech. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; He, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Lu, C. In situ synthesis of MnO2 coated cellulose nanofibers hybrid for effective removal of methylene blue. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 110, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akar, S.T.; Özcan, A.S.; Akar, T.; Özcan, A.; Kaynak, Z. Biosorption of a reactive textile dye from aqueous solutions utilizing an agro-waste. Desalination 2009, 249, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhoum, N.; Monser, L.; Bellakhal, N.; Belgaied, J.-E. Treatment of electroplating wastewater containing Cu2+, Zn2+ and Cr(VI) by electrocoagulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 112, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, M.R.G.; Goulart, M.O.F.; Tonholo, J.; Zanta, C.L.P.S. The application of electrochemical technology to the remediation of oily wastewater. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, N.; Drogui, P.; Montané, C.; Hausler, R.; Mercier, G.; Blais, J.-F. Comparison between electrocoagulation and chemical precipitation for metals removal from acidic soil leachate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Siafaka, P.I.; Pavlidou, E.G.; Chrissafis, K.J.; Bikiaris, D.N. Synthesis and adsorption application of succinyl-grafted chitosan for the simultaneous removal of zinc and cationic dye from binary hazardous mixtures. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakolian, M.; Wiebe, H.; Sadeghi, M.A.; van de Ven, T.G.M. Dye Removal Using Hairy Nanocellulose: Experimental and Theoretical Investigations. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 5040–5049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.R.; Sharma, S.K.; Lindström, T.; Hsiao, B.S. Nanocellulose-Enabled Membranes for Water Purification: Perspectives. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2020, 4, 1900114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhan, C.; Wu, J.; Cui, Z.; Si, J.; Wang, Q.; Peng, X.; Turng, L.-S. Highly Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from an Aqueous Solution Using Cellulose Acetate Nanofibrous Membranes Modified by Polydopamine. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 5389–5400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Cao, X.; Zhang, C.; Yu, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Niu, X.; Sun, X.; Liu, Y.; Ma, L.; Li, Z. Enhanced adsorptive removal of anionic and cationic dyes from single or mixed dye solutions using MOF PCN-222. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 16273–16281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.Q.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Ardiyanta, D.; Shimoyama, Y. CO2-Activated Adsorption: A New Approach to Dye Removal by Chitosan Hydrogel. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 14103–14110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Ing, A.W.C.; Abdullah, W.R.W.; Hamzah, S.; Azaman, F. Preparation of high-performance adsorbent from low-cost agricultural waste (Peanut husk) using full factorial design: Application to dye removal. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2020, 10, 6619–6628. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.F.A.; Gad, E.S. Investigation of an adsorbent based on novel starch/chitosan nanocomposite in extraction of indigo carmine dye from aqueous solutions. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2020, 10, 5556–5563. [Google Scholar]
- Anuar, F.I.; Hadibarata, T.; Syafrudin, M.; Fona, Z. Removal of procion red MX-5B from aqueous solution by adsorption on parkia speciosa (Stink bean) peel powder. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2020, 10, 4774–4779. [Google Scholar]
- Cotrim, A.C.M.; França, E.L.; França, A.C.H.; Martins, J.S.; Silva, K.P.G.; Ghalfi, Y.C.; Machado, I.T.; Tozetti, I.A. Effect of polyethylene glycol microspheres adsorbed with melatonin on oxidative stress and viscosity of cervical mucus samples infected with human papillomavirus. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2020, 10, 6757–6772. [Google Scholar]
- El-Desouky, M.G.; Hassan, N.; Shahat, A.; El-Didamony, A.; El-Bindary, A.A. Synthesis and characterization of porous magnetite nanosphere iron oxide as a novel adsorbent of anionic dyes removal from aqueous solution. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 11, 13377–13401. [Google Scholar]
- Iroha, N.B.; Maduelosi, N.J. Corrosion inhibitive action and adsorption behaviour of justicia secunda leaves extract as an eco-friendly inhibitor for aluminium in acidic media. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 11, 13019–13030. [Google Scholar]
- Kassimi, A.E.; Achour, Y.; Himri, M.E.; Laamari, M.R.; Haddad, M.E. High efficiency of natural Safiot Clay to remove industrial dyes from aqueous media: Kinetic, isotherm adsorption and thermodynamic studies. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 11, 12717–12731. [Google Scholar]
- Kit, N.H.; Hadibarata, T.; Yuniarto, A.; Sari, A.A. Removal of triphenylmethane dye from aqueous solutions through an adsorption process over waste materials. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2020, 10, 5772–5779. [Google Scholar]
- Salim, N.A.A.; Fulazzaky, M.A.; Puteh, M.H.; Khamidun, M.H.; Yusoff, A.R.M.; Abdullah, N.H.; Ahmad, N.; Lazim, Z.M.; Nuid, M. Adsorption of phosphate from aqueous solution onto iron-coated waste mussel shell: Physicochemical characteristics, kinetic, and isotherm studies. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 11, 12831–12842. [Google Scholar]
- Shaikh, T.M.A. Adsorption of pb(II) from wastewater by natural and synthetic adsorbents. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2020, 10, 6522–6539. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, P.K.; Malviya, R. Role of different parameters and mathematical models for metal ions adsorption from industrial waste water. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2020, 10, 5516–5523. [Google Scholar]
- Vasylyeva, H.; Mironyuk, I.; Strilchuk, M.; Tryshyn, V.; Gaidar, O.; Vasyliev, O. Adsorption of zirconium ions by X-type zeolite. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 11, 13421–13431. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.A.; Momina; Siddiqui, M.R.; Otero, M.; Alshareef, S.A.; Rafatullah, M. Removal of rhodamine b from water using a solvent impregnated polymeric dowex 5wx8 resin: Statistical optimization and batch adsorption studies. Polymers 2020, 12, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liakos, E.V.; Mone, M.; Lambropoulou, D.A.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Kyzas, G.Z. Adsorption evaluation for the removal of nickel, mercury, and barium ions from single-component and mixtures of aqueous solutions by using an optimized biobased chitosan derivative. Polymers 2021, 13, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, L.; Rahdar, A.; Khaksefidi, R.; Ghamkhari, A.; Fytianos, G.; Kyzas, G.Z. Polystyrene magnetic nanocomposites as antibiotic adsorbents. Polymers 2020, 12, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mone, M.; Lambropoulou, D.A.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Kyzas, G. Chitosan grafted with biobased 5-hydroxymethyl-furfural as adsorbent for copper and cadmium ions removal. Polymers 2020, 12, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, T.D.; Vu, T.N.; Nguyen, H.L.; Le, P.H.P.; Hoang, T.S. Adsorptive removal of antibiotic ciprofloxacin from aqueous solution using protein-modified nanosilica. Polymers 2020, 12, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaipulizan, N.S.; Jamil, S.N.A.M.; Kamaruzaman, S.; Subri, N.N.S.; Adeyi, A.A.; Abdullah, A.H.; Abdullah, L.C. Preparation of ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA)-based terpolymer as potential sorbents for pharmaceuticals adsorption. Polymers 2020, 12, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ofomaja, A.E. Sorption dynamics and isotherm studies of methylene blue uptake on to palm kernel fibre. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 126, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohmood, I.; Lopes, C.B.; Lopes, I.; Ahmad, I.; Duarte, A.C.; Pereira, E. Nanoscale materials and their use in water contaminants removal—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 1239–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Dubey, S.; Gautam, R.K.; Chattopadhyaya, M.C.; Sharma, Y.C. Adsorption characteristics of alumina nanoparticles for the removal of hazardous dye, Orange G from aqueous solutions. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 5339–5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkhaya, S.; M’Rabet, S.; El Harfi, A. Classifications, properties, recent synthesis and applications of azo dyes. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Mohammadi, L.; Rahdar, A.; Rahdar, S.; Dehghani, R.; Adaobi Igwegbe, C.; Kyzas, G.Z. Acid Dye Removal from Aqueous Solution by Using Neodymium(III) Oxide Nanoadsorbents. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Mohammadi, L.; Igwegbe, C.A.; Rahdar, S.; Banach, A.M. Application of response surface methodology in the degradation of Reactive Blue 19 using H2O2/MgO nanoparticles advanced oxidation process. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 2018, 9, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, S.; Pan, G.T.; Chong, S.; Yang, T.C.K. Ultrasonically induced sulfur-doped carbon nitride/cobalt ferrite nanocomposite for efficient sonocatalytic removal of organic dyes. Processes 2020, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.T.; Nguyen, H.T.T.; Nguyen, D.T.C.; Le, H.T.N.; Nguyen, T.T.; Le, N.T.H.; Lim, K.T.; Nguyen, T.D.; Van Tran, T.; Bach, L.G. Process optimization by a response surface methodology for adsorption of Congo red dye onto exfoliated graphite-decorated MnFe2O4 nanocomposite: The pivotal role of surface chemistry. Processes 2019, 7, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.Z.M.; Ibrahim, I.H.M.; Ali, H.M.; Helmy, H.M. Assessment of the use of natural extracted dyes and pancreatin enzyme for dyeing of four natural textiles: HPLC analysis of phytochemicals. Processes 2020, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saroyan, H.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Deliyanni, E.A. Effective dye degradation by graphene oxide supported manganese oxide. Processes 2019, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, B.S.; Le, P.T.; Werner, D.; Phuong, N.H.; Luu, T.L. Rice husk biochars modified with magnetized iron oxides and nano zero valent iron for decolorization of dyeing wastewater. Processes 2019, 7, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, M.; Lin, Y.; Yang, Y. Simultaneous enhancements of remanence and (BH)max in BaFe12O19/CoFe2O4 nanocomposite powders. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 631, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radmanesh, M.A.; Seyyed Ebrahimi, S.A. Synthesis and magnetic properties of hard/soft SrFe 12O 19/Ni 0.7Zn 0.3Fe 2O 4 nanocomposite magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 3094–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Q. Preparation and magnetic properties of BaFe12O19/Ni0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4 nanocomposite ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 3024–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivashankar, R.; Sathya, A.B.; Vasantharaj, K.; Sivasubramanian, V. Magnetic composite an environmental super adsorbent for dye sequestration—A review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2014, 1, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Araque, J.S.; Guimaraes, R.R.; Toma, H.E. Chemistry of ternary monocarboxyterpyridine-bipyridine-trimercaptotriazine ruthenium complexes and application in dye sensitized solar cells. Polyhedron 2020, 182, 114513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiswarya, K.M.; Raguram, T.; Rajni, K.S. Synthesis and characterisation of nickel cobalt sulfide nanoparticles by the solvothermal method for dye-sensitized solar cell applications. Polyhedron 2020, 176, 114267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, M.A.; Ye, J.; Wang, G.; Shi, L.; Liu, Z.; Lu, H.; Zhang, S.; Ning, G. Bifunctional chemosensor based on a dye-encapsulated metal-organic framework for highly selective and sensitive detection of Cr2O72− and Fe3+ ions. Polyhedron 2020, 185, 114604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimard, P. Fabrication and kinetic study of Nd-Ce doped Fe3O4-chitosan nanocomposite as catalyst in Fenton dye degradation. Polyhedron 2019, 171, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; He, H.; Du, L.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Guo, S. Porous Pr(III)-based organic framework for dye-adsorption and photo degradation with (4,5)-c net. Polyhedron 2019, 171, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Zong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Su, B.; Zhu, Z.; Bi, C.; Fan, Y. Syntheses, structural diversity and photo-degradation and dye adsorption properties of novel Ni(II)/Co(II) coordination polymers modulated by 4-(4-carboxylphenylmethylthio)benzoic acid ligand. Polyhedron 2019, 170, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghomshehzadeh, S.G.; Nobakht, V.; Pourreza, N.; Mercandelli, P.; Carlucci, L. A new pillared Cd-organic framework as adsorbent of organic dyes and as precursor of CdO nanoparticles. Polyhedron 2020, 176, 114265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Zheng, Q.M.; Ma, X.R.; Lai, Z.Z.; Ye, T.Q.; Qin, L. One luminescence probe and the impact of dye-adsorption on the luminescent property. Polyhedron 2020, 177, 114323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hao, C.; Cui, L.; Wang, Y. An anionic cadmium-organic framework with an uncommon 3,3,4,8-c network for efficient organic dye separation. Polyhedron 2020, 188, 114685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, B.; Roy, A.S.; Kapri, S.; Bhattacharyya, S. Efficient Dye Degradation Catalyzed by Manganese Oxide Nanoparticles and the Role of Cation Valence. Chem. Select 2016, 1, 4265–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biglari, H. Evaluation of Phenol Removal from Aqueous Solution by Banana Leaf Ash. J. Glob. Pharma Technol. 2017, 9, 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- Bazrafshan, E.; Kord Mostafapour, F.; Faridi, H.; Farzadkia, M.; Sargazi, S.; Sohrabi, A.L.I. Removal of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2, 4-d) from aqueous environments using single-walled carbon nanotubes. Health Scope 2013, 2, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshani, E.; Naghizadeh, A.; Khodadadi, M. Application of Different Isotherm Models for Humic Acid Adsorption on to Bentonite and Montmorillonite Nanoparticles. Health Scope 2017, 6, e40416. [Google Scholar]
- Salas, G.; Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S.; Morales, M.d.P. Relationship between physico-chemical properties of magnetic fluids and their heating capacity. Int. J. Hyperth. 2013, 29, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G. Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: A review. Bioresour.Technol. 2006, 97, 1061–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahmoradi, B.; Maleki, A.; Byrappa, K. Removal of Disperse Orange 25 using in situ surface-modified iron-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 53, 3615–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, A.; Norozi, R.; Samadi, M.T.; Afkhami, A. Hexavalent Chromium Removal from Rqueous Solution by Produced Iron Nanoparticles. Iran. J. Health Environ. 2009, 1, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Bazrafshan, E.; Kord Mostafapour, F.; Rahdar, S.; Mahvi, A.H. Equilibrium and thermodynamics studies for decolorization of Reactive Black 5 (RB5) by adsorption onto MWCNTs. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 54, 2241–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazlzadeh, M.; Rahmani, K.; Zarei, A.; Abdoallahzadeh, H.; Nasiri, F.; Khosravi, R. A novel green synthesis of zero valent iron nanoparticles (NZVI) using three plant extracts and their efficient application for removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, P.; Kamaraj, R.; Vasudevan, S. Application of isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic models for the adsorption of nitrate ions on graphene from aqueous solution. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2013, 44, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahdar, A.; Ahmadi, S.; Fu, J.; Rahdar, S. Iron oxide nanoparticle preparation and its use for the removal of fluoride from aqueous solution: Application of isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamics. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 137, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The Adsorption of Gases on Plane Surfaces of Glass, Mica and Platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Over the adsorption in solution. Z. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar]
- Temkin, M.; Pyzhev, V. Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promoted iron catalysts. Acta Physicochim. URSS 1940, 12, 327–356. [Google Scholar]
- Dubinin, M.M. The Potential Theory of Adsorption of Gases and Vapors for Adsorbents with Energetically Nonuniform Surfaces. Chem. Rev. 1960, 60, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahdar, S.; Rahdar, A.; Igwegbe, C.; Moghadam, F.; Ahmadi, S. Synthesis and physical Characterization of Nickel oxide nanoparticle and its application study in the Removal of ciprofloxacin from contaminated water by adsorption: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 141, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Jin, J.; Liu, Z.; Liang, X.; Shang, C. Adsorption of acid dyes from aqueous solutions by the ethylenediamine-modified magnetic chitosan nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Kong, J. Novel magnetic Fe3O4C nanoparticles as adsorbents for removal of organic dyes from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 193, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Qian, D.; Wu, D.; Ma, X. Magnetic halloysite nanotubes/iron oxide composites for the adsorption of dyes. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 959–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inbaraj, B.S.; Chen, B.H. Bioresour. Technol. J. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 8868. [Google Scholar]
- Debrassi, A.; Baccarin, T.; Demarchi, C.A.; Nedelko, N.; Ślawska-Waniewska, A.; Dłużewski, P.; Bilska, M.; Rodrigues, C.A. Adsorption of Remazol Red 198 onto magnetic N-lauryl chitosan particles: Equilibrium, kinetics, reuse and factorial design. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 1594–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debrassi, A.; Corrêa, A.F.; Baccarin, T.; Nedelko, N.; Ślawska-Waniewska, A.; Sobczak, K.; Dłuzewski, P.; Greneche, J.M.; Rodrigues, C.A. Removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solutions using N-benzyl-O-carboxymethylchitosan magnetic nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 183, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Gupta, S.; Singh, A.K.; Sinha, S. Optimizing adsorption of crystal violet dye from water by magnetic nanocomposite using response surface modeling approach. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1462–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Miao, S.; Liu, S.; Ma, L.P.; Sun, H.; Wang, S. Synthesis, characterization, and adsorption properties of magnetic Fe 3O 4@graphene nanocomposite. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 184, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M. Magnetic ferrite nanoparticle-alginate composite: Synthesis, characterization and binary system dye removal. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2013, 44, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Luo, C.; Sun, M.; Li, X.; Lu, F.; Qiu, H. Preparation of novel magnetic chitosan/graphene oxide composite as effective adsorbents toward methylene blue. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 114, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E. Advantages and disadvantages of techniques used for wastewater treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- .Reddy, D.H.K.; Lee, S.-M. Application of magnetic chitosan composites for the removal of toxic metal and dyes from aqueous solutions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 201, 68–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donia, A.M.; Atia, A.A.; Elwakeel, K.Z. Selective separation of mercury(II) using magnetic chitosan resin modified with Schiff’s base derived from thiourea and glutaraldehyde. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 151, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Experiment | pHi | T (°C) | C0 (mg/L) | N (rpm) | t (min) | m/V (g/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect of pH | 2–12 | 25 | 80 | 150 | 40 | 0.1 |
| Effect of dosage | 2 | 25 | 80 | 150 | 40 | 0.02–0.10 |
| Effect of contact time | 2 | 52 | 80 | 150 | 0–180 | 0.06 |
| Effect of initial dye concentration | 2 | 25 | 20–100 | 150 | 180 | 0.1 |
| Isotherm Model | Parameters | |
|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | KL (L/ mg) | 0.02 |
| qm (mg/g) | 215.08 | |
| R2 | 0.998 | |
| Freundlich | KF(mg/g) | 4.64 |
| n | 0.14 | |
| R2 | 0.999 | |
| Temkin | KT | 5.046 |
| B | 0.032 | |
| R2 | 0.994 | |
| Dubinin–Radushkevich | β | 0.0142 |
| qm (mg/g) | 3.142 | |
| R2 | 0.959 | |
| Kinetic Model | Parameters | |
|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order | k1 (1/min) | 1.001 |
| qe (mg/g) | 1.024 | |
| R2 | 0.921 | |
| Pseudo-second-order | K2 (g/mg.min) | 0.0177 |
| qe (mg/g) | 14.471 | |
| R2 | 0.9998 | |
| Intra-particle-diffusion | K (mg/g.min) | 0.23 |
| C (mg/g) | 11.409 | |
| R2 | 0.83 | |
| Ritchie | kr | 0.296 |
| qe (mg/g) | 14.347 | |
| R2 | 0.936 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahdar, S.; Rahdar, A.; Sattari, M.; Hafshejani, L.D.; Tolkou, A.K.; Kyzas, G.Z. Barium/Cobalt@Polyethylene Glycol Nanocomposites for Dye Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Polymers 2021, 13, 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071161
Rahdar S, Rahdar A, Sattari M, Hafshejani LD, Tolkou AK, Kyzas GZ. Barium/Cobalt@Polyethylene Glycol Nanocomposites for Dye Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Polymers. 2021; 13(7):1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071161
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahdar, Somayeh, Abbas Rahdar, Mostafa Sattari, Laleh Divband Hafshejani, Athanasia K. Tolkou, and George Z. Kyzas. 2021. "Barium/Cobalt@Polyethylene Glycol Nanocomposites for Dye Removal from Aqueous Solutions" Polymers 13, no. 7: 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071161
APA StyleRahdar, S., Rahdar, A., Sattari, M., Hafshejani, L. D., Tolkou, A. K., & Kyzas, G. Z. (2021). Barium/Cobalt@Polyethylene Glycol Nanocomposites for Dye Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Polymers, 13(7), 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071161









