Effects of Adding Antioxidants on the Lightfastness Improvement of Refined Oriental Lacquer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
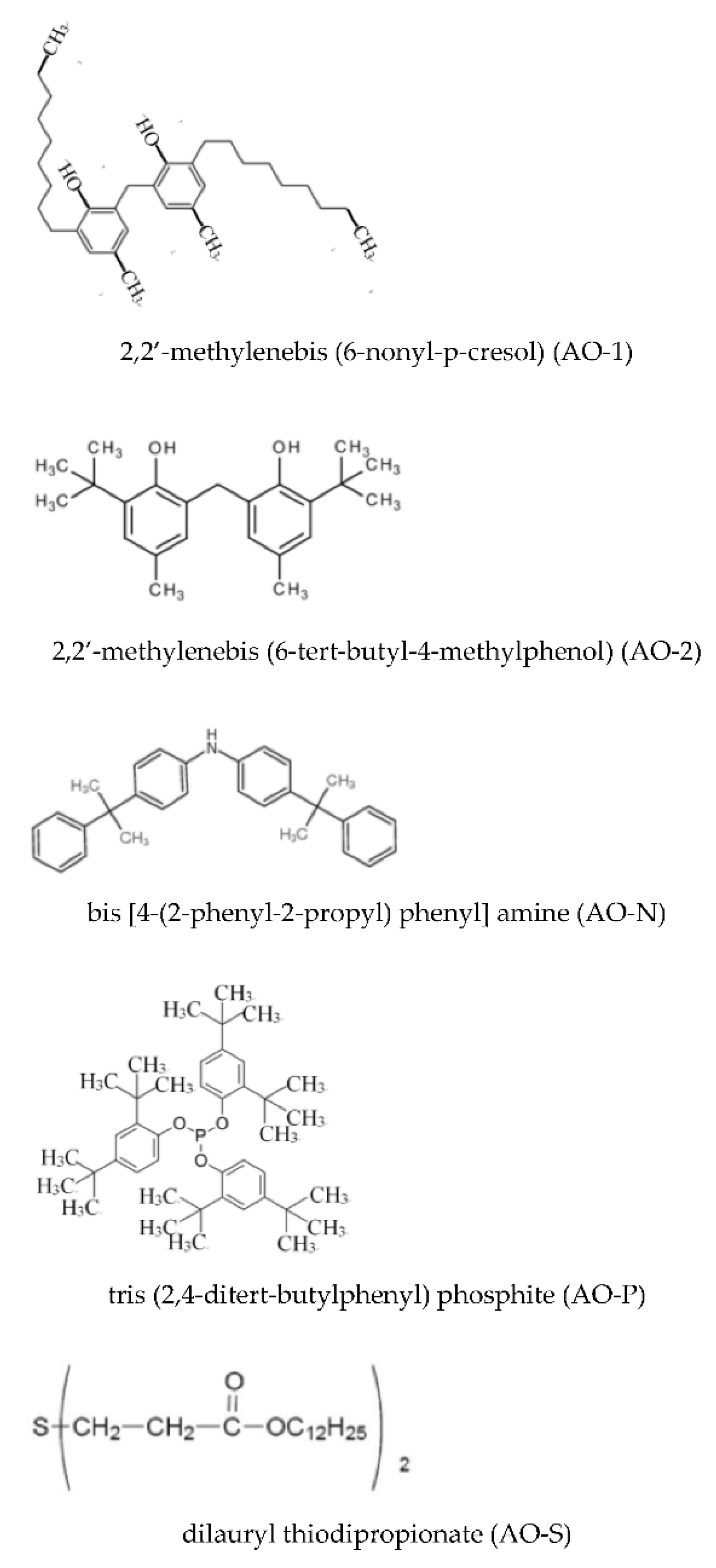
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of ROL
2.3. Preparation of Antioxidant-Containing ROL
2.4. Measurement of Coating Properties
2.5. Preparation and Determination of Film Properties
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Lightfastness of ROL Films with Different Antioxidants
3.2. Coating and Film Properties of ROL with Different Contents of Antioxidant
3.2.1. Coating Properties of ROL
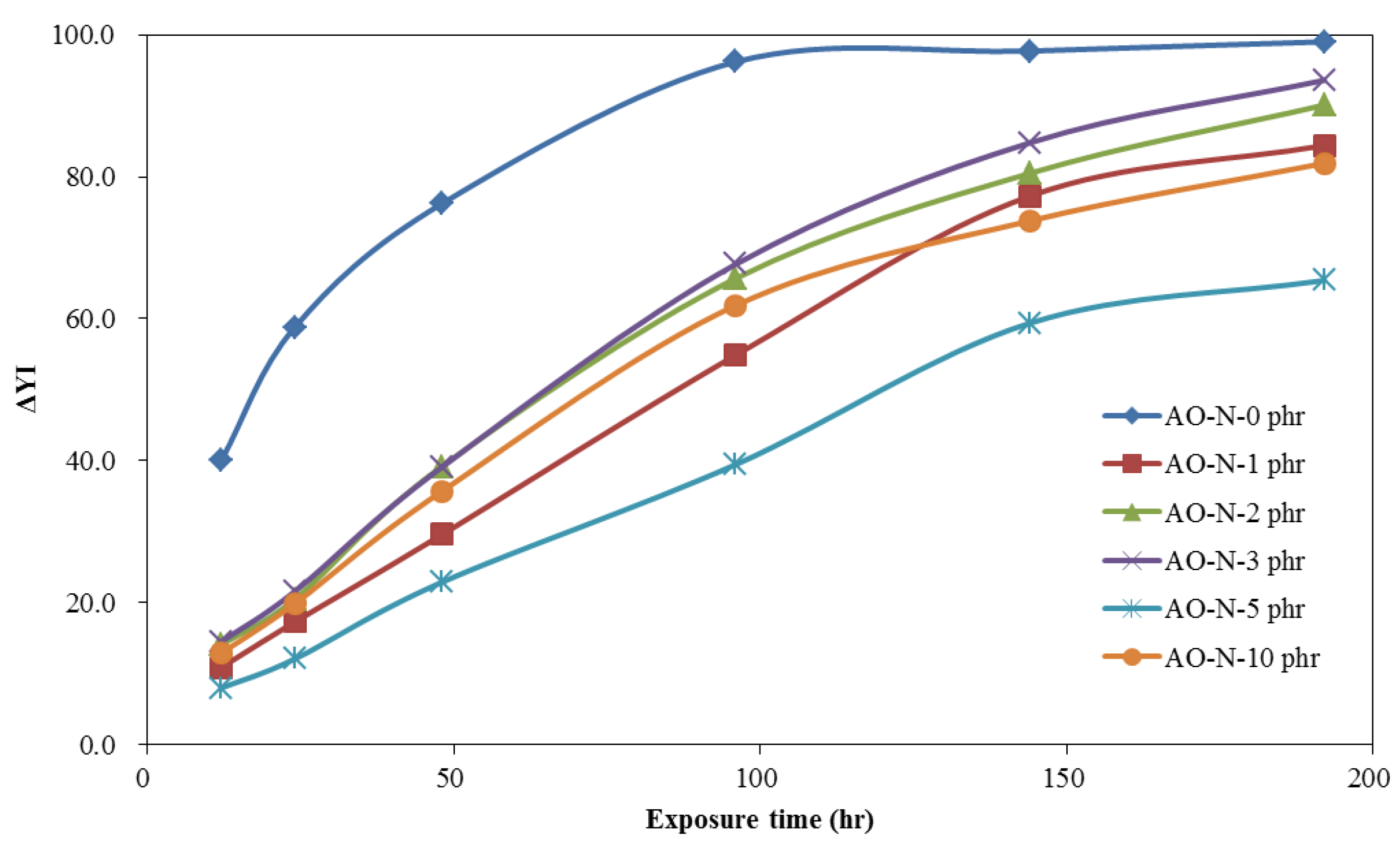
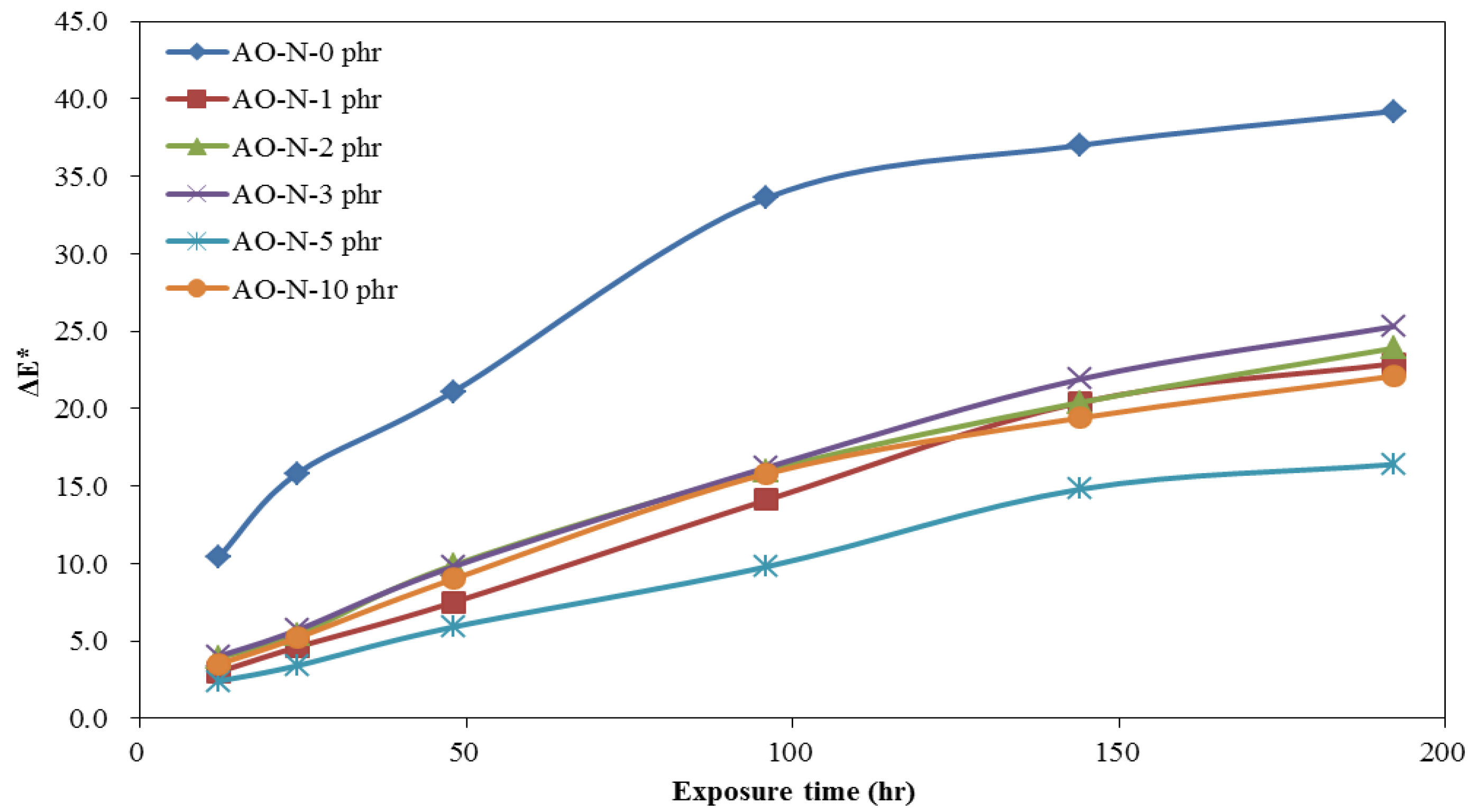
3.2.2. Lightfastness of ROL Films
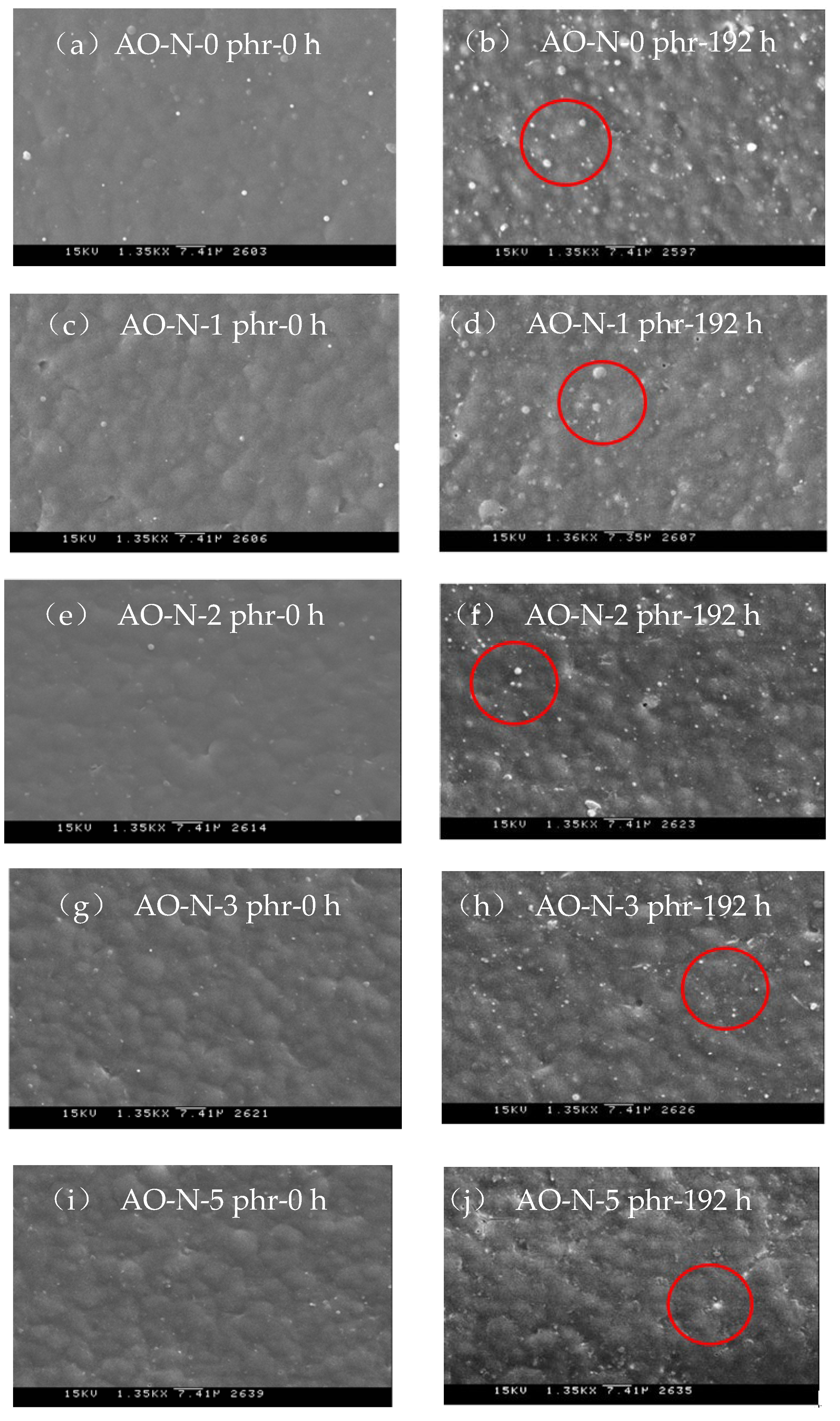
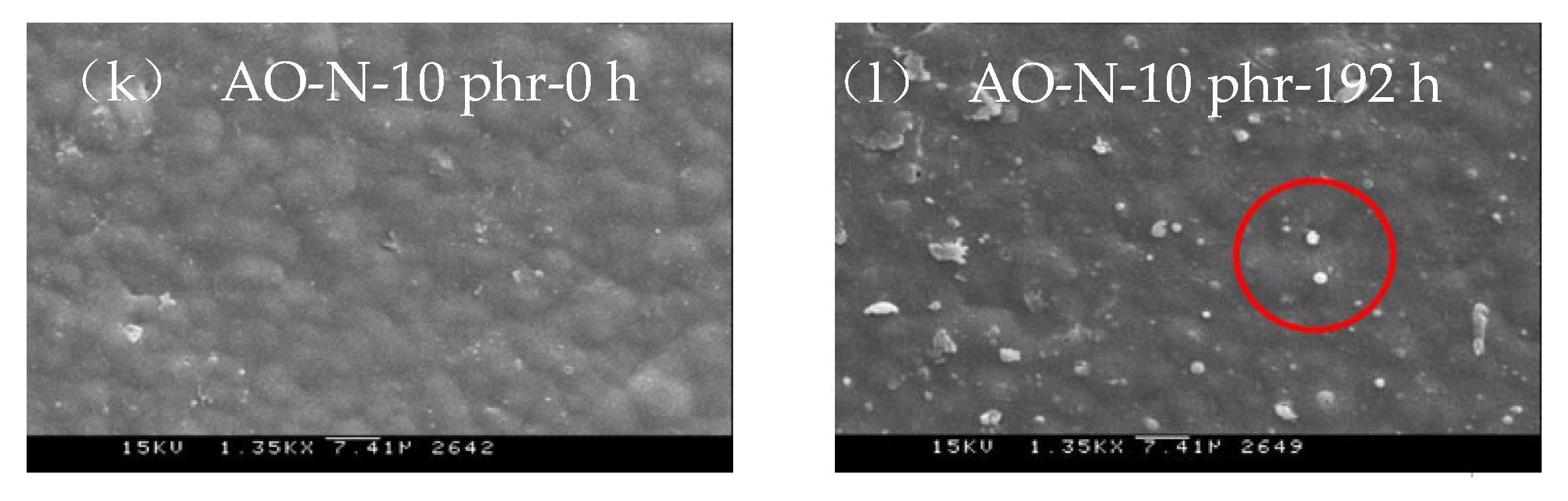
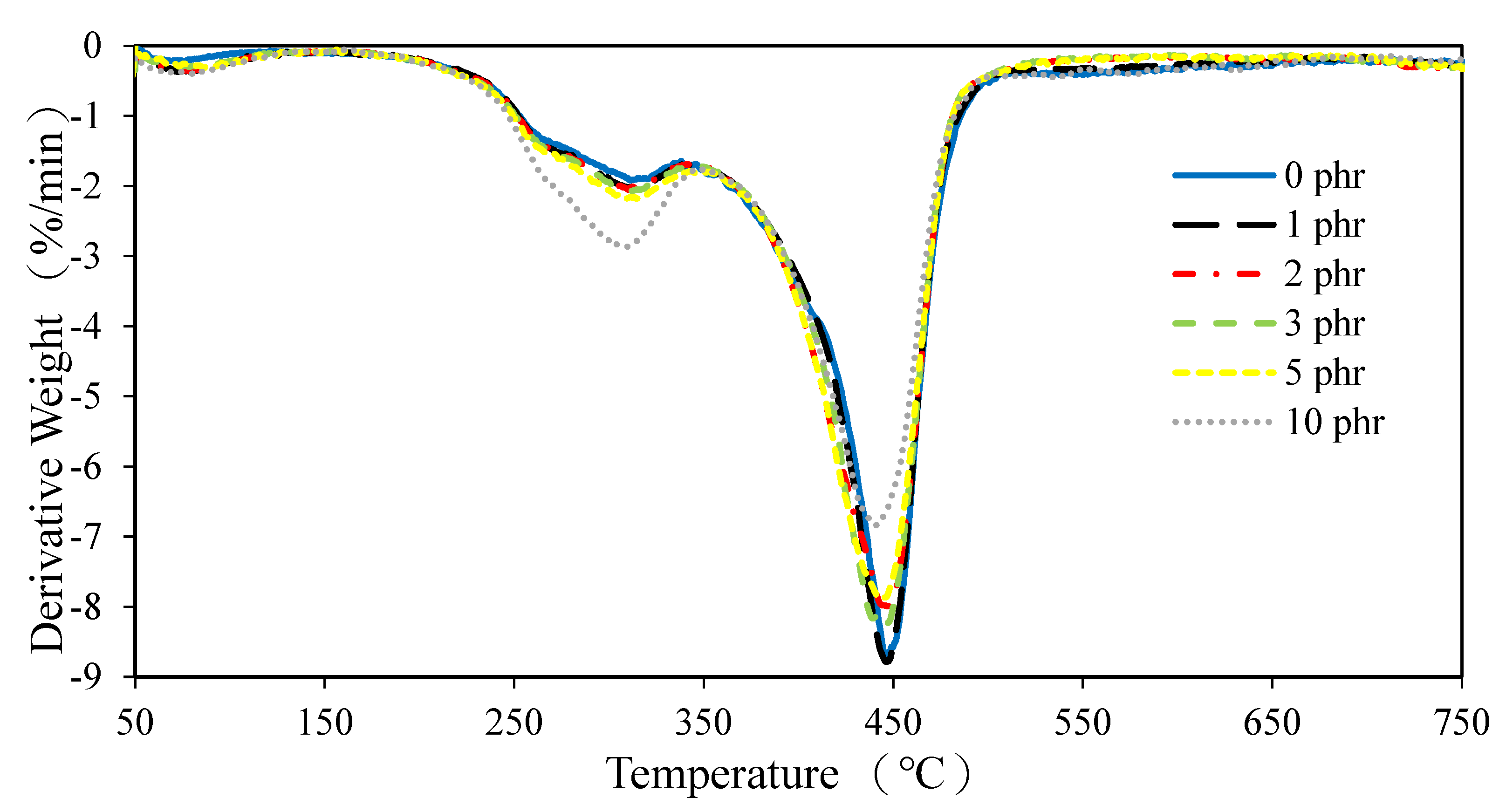
3.2.3. SEM Inspection of ROL Films
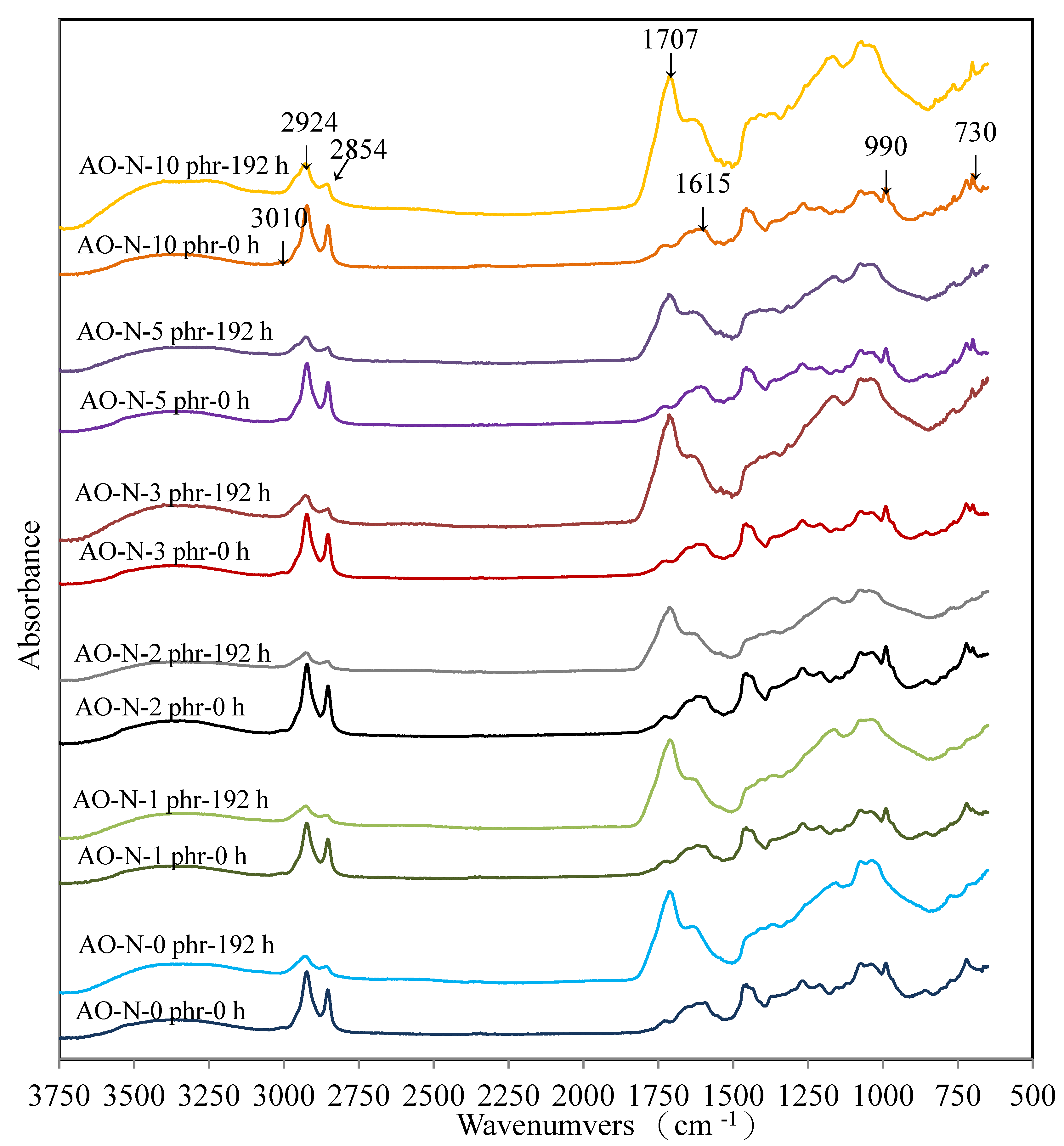
3.2.4. FTIR Analysis of ROL Films
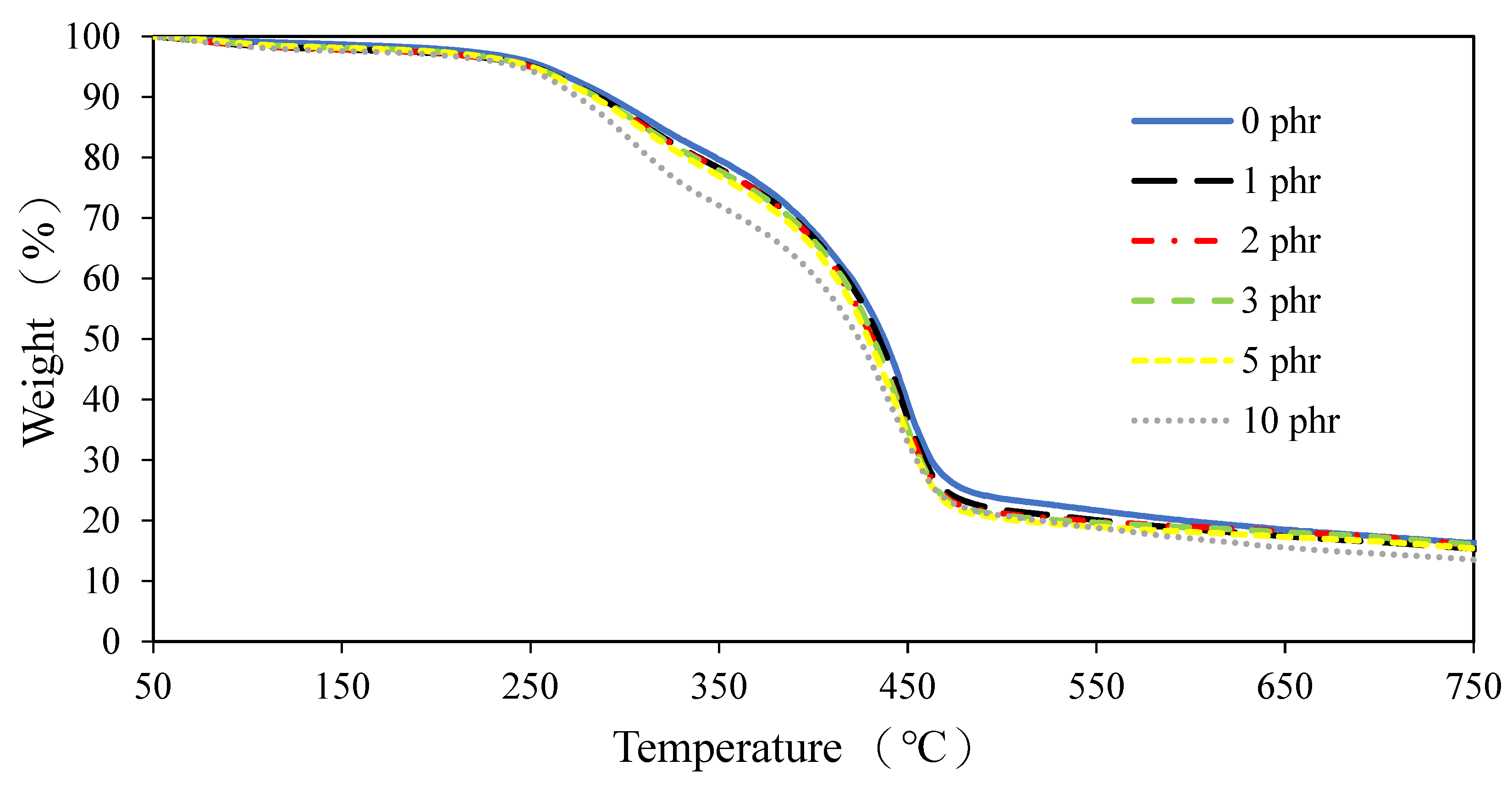
3.2.5. Film Properties of ROL
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Niimura, N.; Miyakoshi, T.; Onodera, J.; Higuchi, T. Characterization of Rhus vernicifera and Rhus succedanea Lacquer Films and Their Pyrolysis Mechanisms Studied Using Two-stage Pyrolysis-gas Chromatography/mass Spectrometry. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 1996, 37, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, T.; Lu, R.; Sakai, R.; Ishimura, T.; Miyakoshi, T. Characterization and Comparison of Asian Lacquer Saps. Prog. Org. Coat. 2008, 61, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumanotani, J. Urushi (Oriental Lacquer)—A Natural Aesthetic Durable and Future-Promising Coating. Prog. Org. Coat. 1995, 26, 163–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.W.; Lee, H.L.; Lu, K.T. Manufacture and Characteristics of Oil-Modified Refined Lacquer for Wood Coatings. Coatings 2019, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Harigaya, S.; Ishimura, T.; Nagase, K.; Miyakoshi, T. Development of A Fast-Drying Lacquer Based on Raw Lacquer Sap. Prog. Org. Coat. 2004, 51, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niimura, N.; Miyakoshi, T. Structural Study of Oriental Lacquer Films During the Hardening Process. Talanta 2006, 70, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niimura, N.; Miyakoshi, T. Characterization of Synthesized Lacquer Analogue Films Using X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. Surf. Interface Anal. 2000, 29, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okahisa, Y.; Narita, C.; Yoshimura, T. Resistance of Wood Coated with Oriental Lacquer (Urushi) Against Damage Caused by Subterranean Termite. Wood Sci. 2019, 65, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiles, D.M.; Carlsson, D.J. Stop photodegradation. Chemtech 1981, 11, 158–161. [Google Scholar]
- Rabek, J.F. Polymer Photodegradation-Mechanisms and Experimental Methods; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1995; pp. 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J.W.; Park, M.Y.; Kim, H.K.; Choi, J.O. UV-degradation Chemistry of Oriental Lacquer Coating Containing Hinder Amine Light Stabilizer. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2000, 21, 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.W.; Lee, J.J.; Lu, K.T. The Effects of Adding Different HALS on the Curing Process, Film Properties and Lightfastness of Refined Oriental Lacquer. Polymers 2020, 12, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.J.; Chang, C.W.; Lu, K.T. Effect of Adding Amounts of HALS on the Lightfastness Improvement of Refined Oriental Lacquer. For. Prod. Ind. 2018, 37, 193–203. [Google Scholar]
- Linsebigler, A.L.; Lu, G.; Yates, J.T. Photocatalysis on TiO2 Surfaces: Principles, Mechanisms, and Selected Results. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 735–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valet, A. Light Stabilization of Radiation Cured Coating. Eur. Polym. Paint Colour J. 1992, 182, 406–411. [Google Scholar]
- Rabek, J.F. Photostabilization of Polymers: Principles and Applications; Elsevier Applied Science: East Lansing, MI, USA, 1990; pp. 357–368. [Google Scholar]
- René, D.L. Polymer Stabilizers. A Survey with Reference to Possible Applications in The Conservation Field. Stud. Conserv. 1988, 33, 9–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.J.; Lu, K.T. Effects of Adding Amounts of TiO2 on the Lightfastness Improvement and Film Properties of Refined Oriental Lacquer. Q. J. Chin. For. 2019, 52, 17–34. [Google Scholar]
- Breese, K.D.; LameÁthe, J.F.; DeArmitt, C. Improving Synthetic Hindered Phenol Antioxidants: Learning from Vitamin E. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2000, 70, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrogi, V.; Carfagna, C.; Cerruti, P.; Marturano, V. Additives in Polymers. Modification of Polymer Properties; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 87–108. [Google Scholar]
- CNS 2810 Method of Test for Chinese Lacquer; CNS: Taipei, Taiwan, 1986.
- CNS 9007 Method of Test for Paints-Sampling and General Condition; CNS: Taipei, Taiwan, 1995.
- Lu, R.; Honda, T.; Ishimura, T.; Miyakoshi, T. Study of a Naturally Drying Lacquer Hybridized with Organic Silane. Polym. J. 2005, 37, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CNS 10756 K6800 Method of Test for Paints (Film Formability of Paints); CNS: Taipei, Taiwan, 1994.
- JIS K 5400 Testing Methods for Paints; Japanese Standards Association: Tokyo, Japan, 1990.
- ASTM D638 Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- Zweifel, H. Stabilization of Polymeric Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya, Y.; Lu, R.; Kumamoto, T.; Honda, T.; Miyakoshi, T. Deterioration of Surface Structure of Lacquer Films due to Ultraviolet Irradiation. Surf. Interface Anal. 2006, 38, 1311–1315. [Google Scholar]
- Kumanotani, J. Enzyme Catalyzed Durable and Authentic Oriental Lacquer: A Natural Microgelprintable Coating by Polysaccharide-Glycoprotein-Phenolic Lipid Complexes. Prog. Org. Coat. 1998, 34, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niimura, N.; Iijima, Y.; Miyakoshi, T. Hardening Process and Surface Structure of Lacquer Films Studied by X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. Surf. Interface Anal. 1996, 24, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
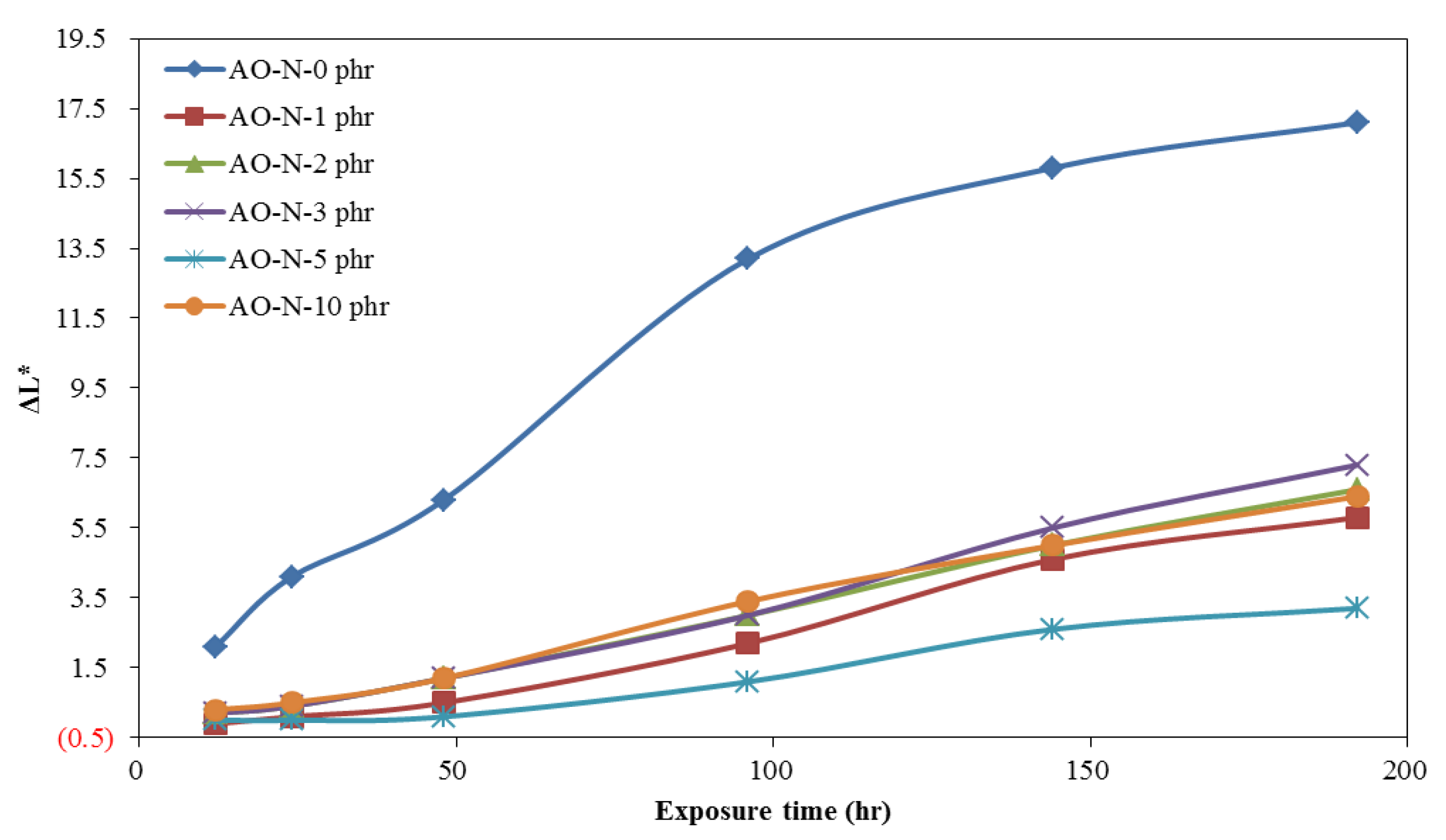
| Antioxidants (2 phr) | ΔL* after UV Exposure (h) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 24 | 48 | 96 | 144 | 192 | |
| Blank a | 1.5 | 2.7 | 5.2 | 9.5 | 11.1 | 12.3 |
| AO-1 b | 1.6 | 2.6 | 5.1 | 9.1 | 11.6 | 11.9 |
| AO-2 c | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 1.8 | 2.0 | 2.7 |
| AO-N d | −0.2 | −0.4 | −0.2 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| AO-P e | 2.2 | 4.4 | 7.7 | 12.7 | 15.1 | 16.6 |
| AO-S f | 0.9 | 1.9 | 4.6 | 8.7 | 9.4 | 12.5 |
| Antioxidants (2 phr) | ΔYI after UV Exposure (h) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 24 | 48 | 96 | 144 | 192 | |
| Blank a | 32.4 | 49.2 | 72.4 | 91.3 | 98.2 | 99.9 |
| AO-1 b | 34.3 | 49.8 | 69.7 | 92.3 | 98.3 | 101.4 |
| AO-2 c | 8.3 | 11.5 | 19.8 | 31.9 | 38.7 | 45.7 |
| AO-N d | 1.5 | 2.9 | 5.9 | 11.7 | 16.5 | 22.3 |
| AO-P e | 39.6 | 63.2 | 82.4 | 97.9 | 102.0 | 102.8 |
| AO-S f | 20.4 | 39.7 | 65.8 | 91.4 | 94.8 | 102.1 |
| Antioxidants (2 phr) | ΔE* after UV Exposure (h) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 24 | 48 | 96 | 144 | 192 | |
| Blanka | 8.3 | 12.5 | 19.4 | 27.4 | 30.8 | 32.4 |
| AO-1 b | 8.7 | 12.5 | 18.4 | 26.7 | 30.7 | 31.8 |
| AO-2 c | 2.3 | 2.9 | 5.0 | 7.9 | 9.4 | 11.1 |
| AO-N d | 0.6 | 0.9 | 1.5 | 2.8 | 3.9 | 5.3 |
| AO-P e | 10.2 | 16.7 | 23.7 | 32.6 | 36.8 | 39.0 |
| AO-S f | 5.3 | 10.1 | 17.4 | 26.6 | 28.0 | 33.0 |
| Contents of AO-N (phr) | pH | Viscosity (cps, 25 °C) | Drying Time (h (25 °C, 80% RH) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TF a | HD b | |||
| 0 | 3.5 | 113 | 5.0 | 11.0 |
| 1 | 3.5 | 116 | 5.0 | 12.5 |
| 2 | 3.5 | 129 | 5.5 | 13.5 |
| 3 | 3.4 | 131 | 5.5 | 13.5 |
| 5 | 3.4 | 136 | 6.0 | 15.0 |
| 10 | 3.5 | 148 | 6.0 | 20.0 |
| Contents of AO-N (phr) | Hardness (König, s) | Mass Retention (wt. %) | Tg (°C) | Impact Resistance (300 g, cm) | Adhesion (Grade) | Bending Resistance (mm) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 78 ± 2 | 93.7 ± 0.8 | 103 | 10 | 10 | 6 | 16.5 ± 0.9 | 10.8 ± 1.0 |
| 1 | 72 ± 4 | 92.7 ± 1.4 | 98 | 5 | 10 | 6 | 15.4 ± 0.2 | 11.6 ± 1.3 |
| 2 | 74 ± 1 | 93.0 ± 1.4 | 97 | 5 | 8 | 6 | 15.3 ± 0.1 | 11.8 ± 0.9 |
| 3 | 74 ± 1 | 91.8 ± 0.3 | 95 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 13.9 ± 0.9 | 13.2 ± 0.0 |
| 5 | 75 ± 1 | 90.3 ± 0.6 | 88 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 12.3 ± 0.5 | 10.9 ± 0.7 |
| 10 | 67 ± 3 | 86.7 ± 0.8 | 86 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 4.9 ± 0.2 | 3.3 ± 0.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, K.-T.; Lee, J.-J. Effects of Adding Antioxidants on the Lightfastness Improvement of Refined Oriental Lacquer. Polymers 2021, 13, 1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071110
Lu K-T, Lee J-J. Effects of Adding Antioxidants on the Lightfastness Improvement of Refined Oriental Lacquer. Polymers. 2021; 13(7):1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071110
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Kun-Tsung, and Jia-Jhen Lee. 2021. "Effects of Adding Antioxidants on the Lightfastness Improvement of Refined Oriental Lacquer" Polymers 13, no. 7: 1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071110
APA StyleLu, K.-T., & Lee, J.-J. (2021). Effects of Adding Antioxidants on the Lightfastness Improvement of Refined Oriental Lacquer. Polymers, 13(7), 1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071110





