Malonic Acid Isolated from Pinus densiflora Inhibits UVB-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in HaCaT Keratinocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents
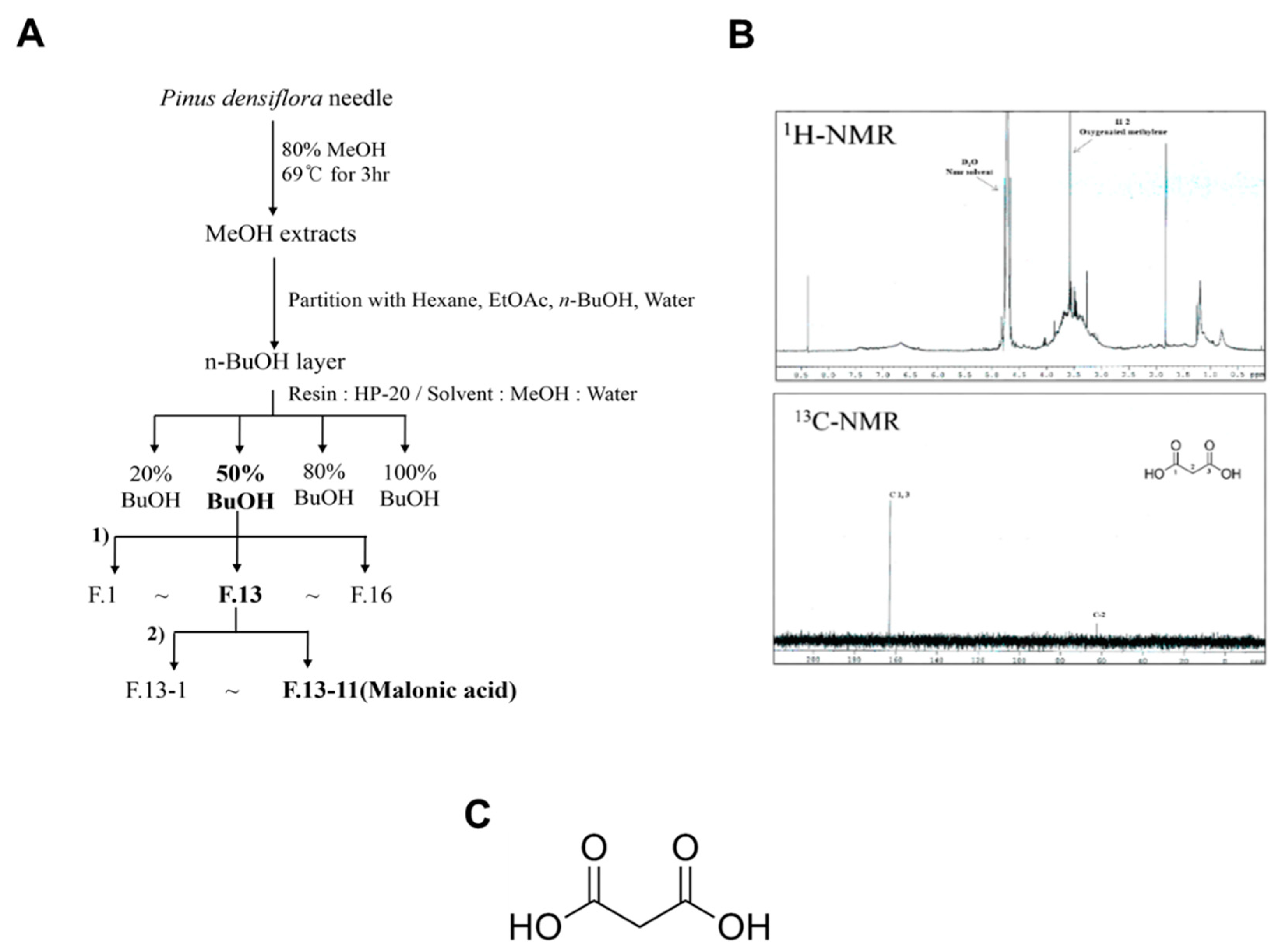
2.2. Plant Materials and Extraction of MA
2.3. Cell Culture and UVB Irradiation
2.4. Cell Viability
2.5. Evaluation of ROS Generation (DCF-DA Assay)
2.6. RNA Isolation, cDNA Synthesis, and Real-time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
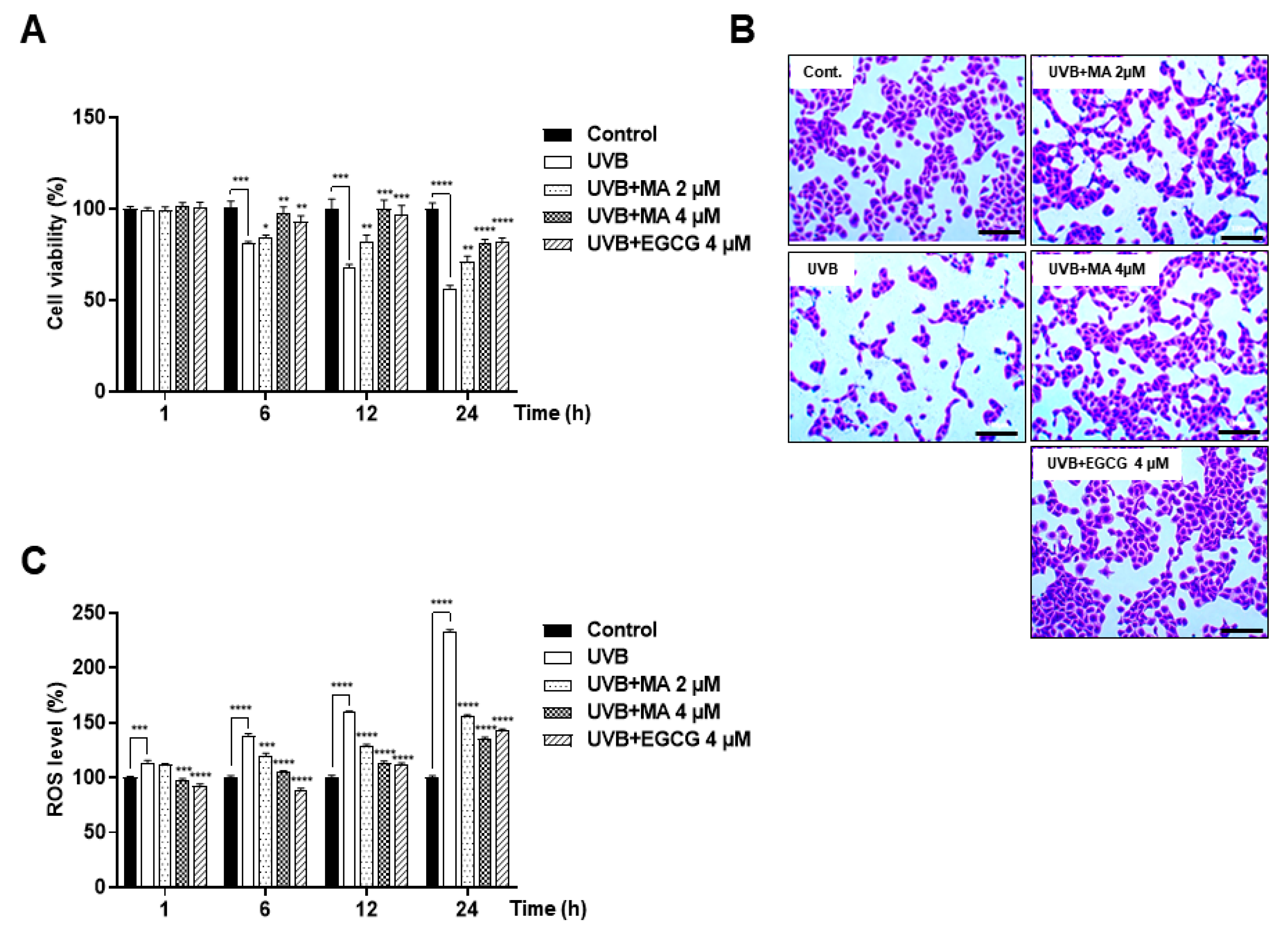
3.1. Effects of MA on Oxidative Stress and Viability in UVB-induced HaCaT Cells
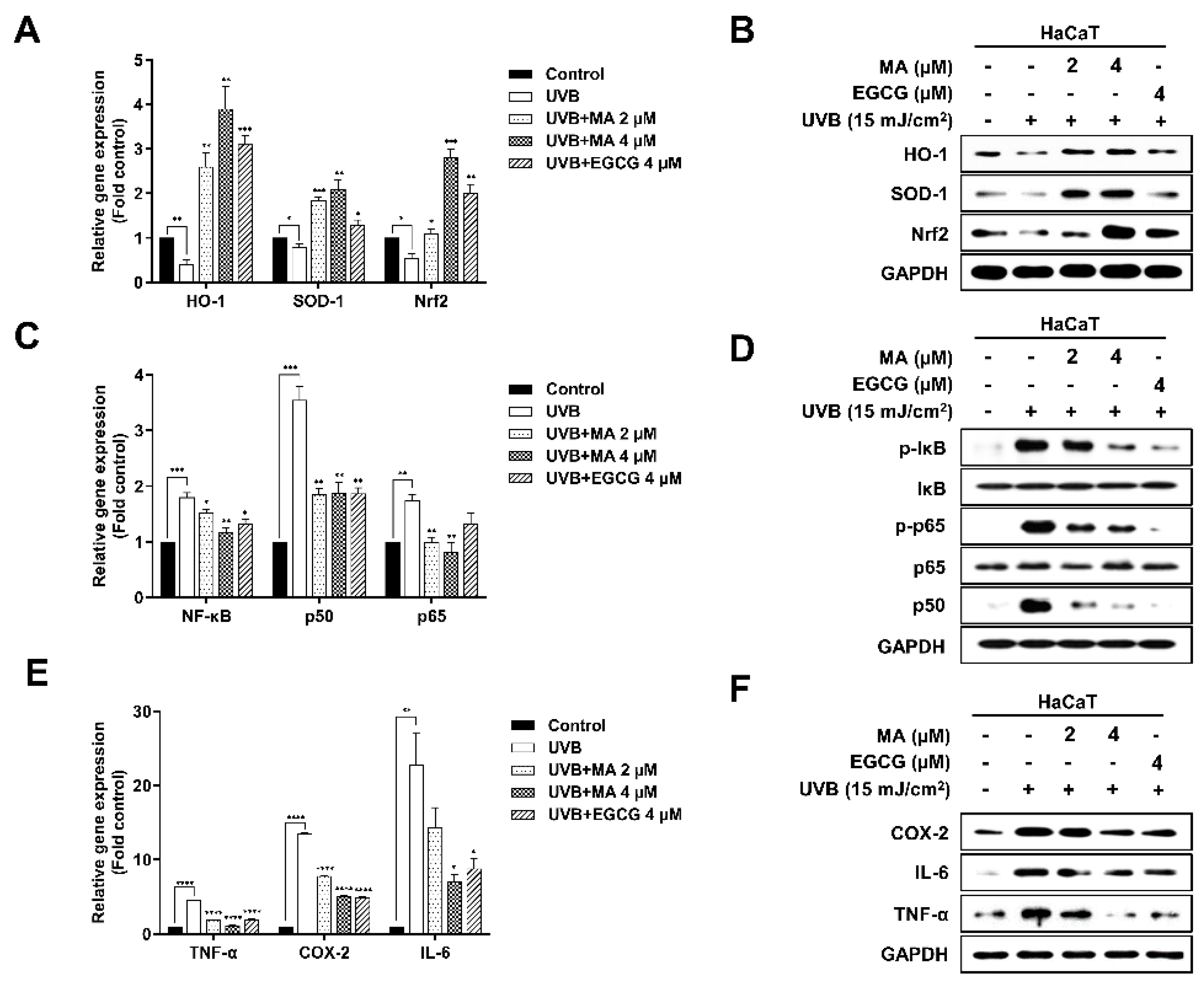
3.2. Effects of MA on UVB-induced Antioxidant Enzyme Expression through Activation of Nrf2 in HaCaT Cells
3.3. Effects of MA on UVB-induced NF-κB Activation and Proinflammatory Factors in HaCaT Cells
3.4. Effects of MA on Phosphorylation during MAPK/AP-1signaling and MMP Expression in UVB-Induced HaCaT Cells
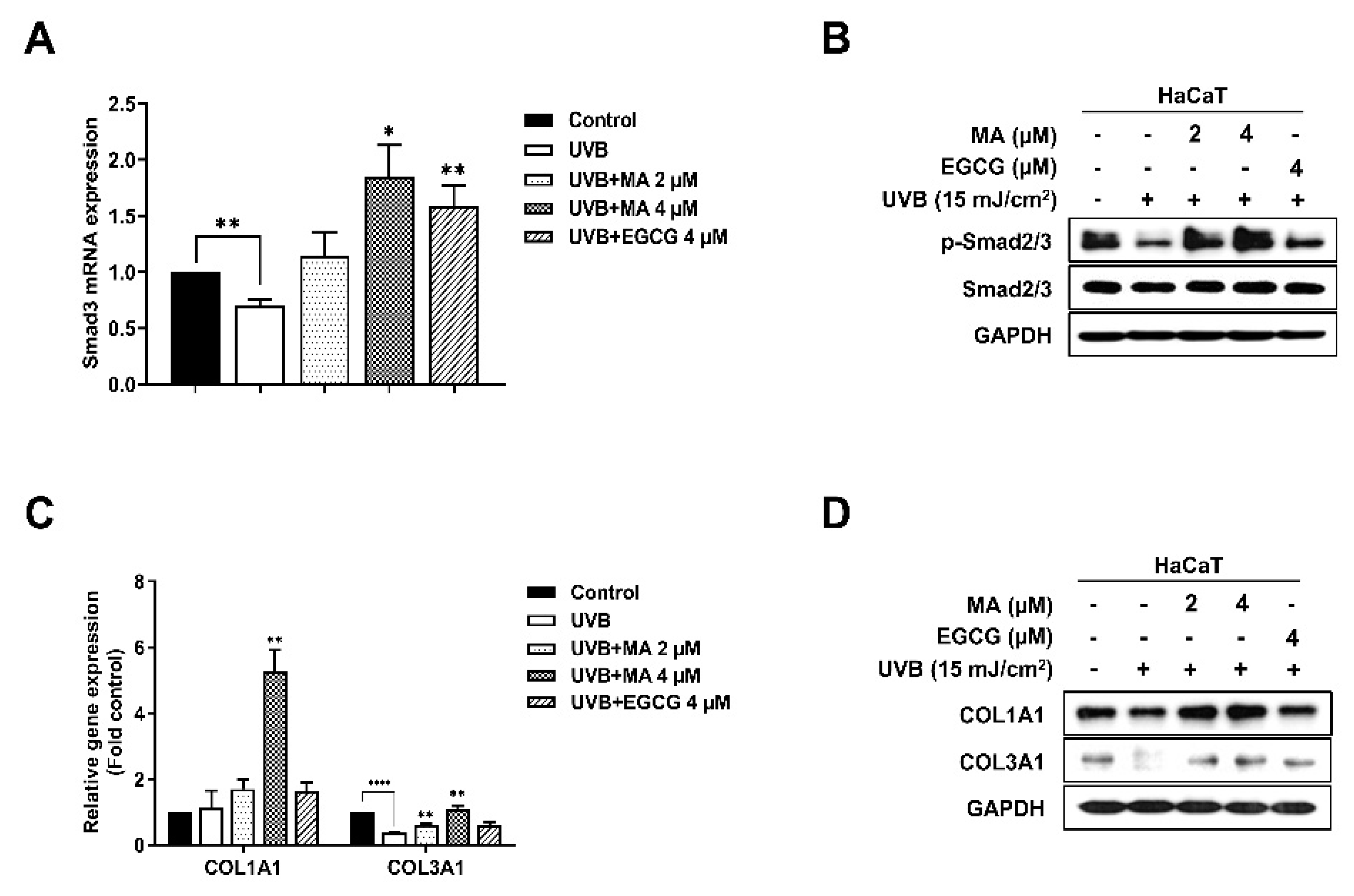
3.5. Effects of MA on the Transforming Growth Factor-β (TGF-β) Signaling Pathway and Collagen Synthesis Factors in UVB-Induced HaCaT Cells
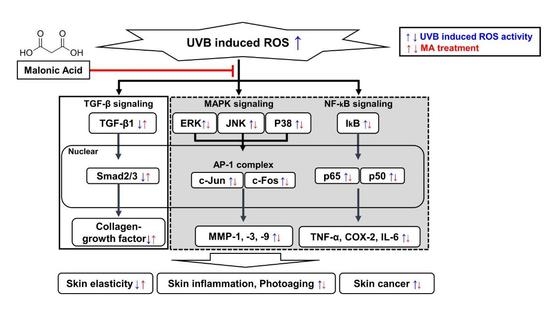
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parrado, C.; Mercado-Saenz, S.; Perez-Davo, A.; Gilaberte, Y.; Gonzalez, S.; Juarranz, A. Environmental stressors on skin aging. Mechanistic insights. Front. Pharm. 2019, 10, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, R.M.; Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Steffen, V.S.; Caviglione, C.V.; Vignoli, J.A.; Barbosa, D.S.; Baracat, M.M.; Georgetti, S.R.; Verri, W.A., Jr.; Casagrande, R. Naringenin inhibits uvb irradiation-induced inflammation and oxidative stress in the skin of hairless mice. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1647–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, R.; Morelli, S.; Tomaino, A.; Pellegrino, M.; Saija, A.; Grumetto, L.; Puglia, C.; Ventura, D.; Bonina, F. Antioxidant and photoprotective activity of a crude extract of culcitium reflexum h.B.K. Leaves and their major flavonoids. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2002, 79, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, K.M.; Clegg, R.M. Observation and quantification of ultraviolet-induced reactive oxygen species in ex vivo human skin. Photochem. Photobiol. 2002, 76, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K. Protective effect of garlic on cellular senescence in uvb-exposed hacat human keratinocytes. Nutrients 2016, 8, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M.; Greten, F.R. Nf-kappab: Linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, S.; Oresajo, C.; Hayward, J. Ultraviolet radiation and skin aging: Roles of reactive oxygen species, inflammation and protease activation, and strategies for prevention of inflammation-induced matrix degradation—A review. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2005, 27, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Park, Y.G.; Lee, H.J.; Lim, S.J.; Nho, C.W. Youngiasides a and c isolated from youngia denticulatum inhibit uvb-induced mmp expression and promote type i procollagen production via repression of mapk/ap-1/nf-kappab and activation of ampk/nrf2 in hacat cells and human dermal fibroblasts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 5428–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Fisher, G.J. Ultraviolet (uv) light irradiation induced signal transduction in skin photoaging. J. Dermatol. Sci. Suppl. 2005, 1, S1–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, T.; Qin, Z.; Xia, W.; Shao, Y.; Voorhees, J.J.; Fisher, G.J. Matrix-degrading metalloproteinases in photoaging. J. Investig. Derm. Symp. Proc. 2009, 14, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, C.W.; Kim, E.K.; Lee, S.J.; Park, N.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, H.K.; Char, K.; Jang, Y.P.; Kim, J.W. Inhibition effect of gynura procumbens extract on uv-b-induced matrix-metalloproteinase expression in human dermal fibroblasts. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittayapruek, P.; Meephansan, J.; Prapapan, O.; Komine, M.; Ohtsuki, M. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in photoaging and photocarcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, T.; Choi, Y.W.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.K. Pinus densiflora needle supercritical fluid extract suppresses the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators inos, il-6 and il-1beta, and activation of inflammatory stat1 and stat3 signaling proteins in bacterial lipopolysaccharide-challenged murine macrophages. Daru 2017, 25, 18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.Y.; Shin, J.C.; Park, S.M.; Kim, N.R.; Kwak, W.; Choi, B.H. Pinus densiflora extract protects human skin fibroblasts against uvb-induced photoaging by inhibiting the expression of mmps and increasing type i procollagen expression. Toxicol. Rep. 2014, 1, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Yang, L.; Yang, P.; Jiang, S.; Liu, X.; Li, Y. Polydopamine free radical scavengers. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 4940–4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Xu, Z.; Liu, G.; Wu, J. Polyphenols as a versatile component in tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2021, 119, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Gu, Z.; Zhu, F.; Li, Y. Structural and functional tailoring of melanin-like polydopamine radical scavengers. CCS Chem. 2020, 2, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Gu, Z.; Li, Y. Ultrasmall nanoparticle ros scavengers based on polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 38, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, K.; Chiba, T.; Takahashi, S.; Ishii, T.; Igarashi, K.; Katoh, Y.; Oyake, T.; Hayashi, N.; Satoh, K.; Hatayama, I.; et al. An nrf2/small maf heterodimer mediates the induction of phase ii detoxifying enzyme genes through antioxidant response elements. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 236, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, A.; Kawachi, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Koga, T.; Hamada, K.; Otsuka, F. Acceleration of uvb-induced photoageing in nrf2 gene-deficient mice. Exp. Derm. 2011, 20, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, P.M.; Piao, M.J.; Kang, K.A.; Ryu, Y.S.; Hewage, S.R.; Chae, S.W.; Hyun, J.W. Rosmarinic acid attenuates cell damage against uvb radiation-induced oxidative stress via enhancing antioxidant effects in human hacat cells. Biomol. Ther. (Seoul) 2016, 24, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, R.; Philips, N.; Suarez-Perez, J.A.; Juarranz, A.; Devmurari, A.; Chalensouk-Khaosaat, J.; Gonzalez, S. Mechanisms of photoaging and cutaneous photocarcinogenesis, and photoprotective strategies with phytochemicals. Antioxidants 2015, 4, 248–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, B.Y.; Wu, Y.M.; Chang, K.J.; Pan, T.M. Dimerumic acid inhibits sw620 cell invasion by attenuating h(2)o(2)-mediated mmp-7 expression via jnk/c-jun and erk/c-fos activation in an ap-1-dependent manner. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.R.; Kim, Y.M.; Lee, M.K.; Kim, I.H.; Choi, Y.H.; Nam, T.J. Pyropia yezoensis peptide promotes collagen synthesis by activating the tgf-beta/smad signaling pathway in the human dermal fibroblast cell line hs27. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, T.; He, T.; Voorhees, J.J.; Fisher, G.J. Ultraviolet irradiation blocks cellular responses to transforming growth factor-beta by down-regulating its type-ii receptor and inducing smad7. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 26349–26356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, T.; He, T.; Kang, S.; Voorhees, J.J.; Fisher, G.J. Solar ultraviolet irradiation reduces collagen in photoaged human skin by blocking transforming growth factor-beta type ii receptor/smad signaling. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 165, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massague, J. How cells read tgf-beta signals. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 1, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macias, M.J.; Martin-Malpartida, P.; Massague, J. Structural determinants of smad function in tgf-beta signaling. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015, 40, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.Y.; Chung, H.J. Flavor compounds of pine sprout tea and pine needle tea. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1269–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.J.; Lee, K.S.; Ahn, Y.J. Growth-inhibiting effects of constituents of pinus densiflora leaves on human intestinal bacteria. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2001, 10, 403–407. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.S.; Jeon, M.H.; Hwang, H.J.; Park, M.R.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, M. Antioxidant activity and analysis of proanthocyanidins from pine (pinus densiflora) needles. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2011, 5, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.L.; Gao, Y. Protective effects of lindera coreana on uvb-induced oxidative stress in human hacat keratinocytes. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 13, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Rigo, L.A.; Da Silva, C.R.; De Oliveira, S.M.; Cabreira, T.N.; De Bona da Silva, C.; Ferreira, J.; Beck, R.C. Nanoencapsulation of rice bran oil increases its protective effects against uvb radiation-induced skin injury in mice. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 93, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikiaris, N.D.; Michailidou, G.; Lazaridou, M.; Christodoulou, E.; Gounari, E.; Ofrydopoulou, A.; Lambropoulou, D.A.; Vergkizi-Nikolakaki, S.; Lykidou, S.; Nikolaidis, N. Innovative skin product emulsions with enhanced antioxidant, antimicrobial and uv protection properties containing nanoparticles of pure and modified chitosan with encapsulated fresh pomegranate juice. Polymers 2020, 12, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimino, F.; Cristani, M.; Saija, A.; Bonina, F.P.; Virgili, F. Protective effects of a red orange extract on uvb-induced damage in human keratinocytes. Biofactors 2007, 30, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, M.; Bhatti, H.; Nerusu, K.C.; Bhagavathula, N.; Kang, S.; Fisher, G.J.; Varani, J.; Voorhees, J.J. Matrix metalloproteinase-1 is the major collagenolytic enzyme responsible for collagen damage in uv-irradiated human skin. Photochem. Photobiol. 2003, 78, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, G.J.; Quan, T.; Purohit, T.; Shao, Y.; Cho, M.K.; He, T.; Varani, J.; Kang, S.; Voorhees, J.J. Collagen fragmentation promotes oxidative stress and elevates matrix metalloproteinase-1 in fibroblasts in aged human skin. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittie, L.; Fisher, G.J. Uv-light-induced signal cascades and skin aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2002, 1, 705–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, M.; Baker, A.H.; Newby, A.C. Nuclear factor kappab activity is essential for matrix metalloproteinase-1 and -3 upregulation in rabbit dermal fibroblasts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 264, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.J.; Cobb, M.H. Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1997, 9, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, S.A.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, E.S.; Eun, S.Y.; Kim, G.H.; Park, M.H.; Woo, I.S.; Kim, H.J.; Chang, K.C.; et al. Ppardelta promotes wound healing by up-regulating tgf-beta1-dependent or -independent expression of extracellular matrix proteins. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 1747–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.J.; Yuan, W.; Mori, Y.; Levenson, A.; Trojanowska, M.; Varga, J. Stimulation of type i collagen transcription in human skin fibroblasts by tgf-beta: Involvement of smad 3. J. Investig. Derm. 1999, 112, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.S.; Yoo, M.S.; Son, D.J.; Jung, H.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Jung, J.K.; Lee, B.C.; Yun, Y.P.; Pyo, H.B.; Hong, J.T. Increase of collagen synthesis by obovatol through stimulation of the tgf-beta signaling and inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase in uvb-irradiated human fibroblast. J. Derm. Sci. 2007, 46, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, C.; Park, J.; Kim, W.-J.; Kim, W.; Cheong, H.; Kim, S.-J. Malonic Acid Isolated from Pinus densiflora Inhibits UVB-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in HaCaT Keratinocytes. Polymers 2021, 13, 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050816
Park C, Park J, Kim W-J, Kim W, Cheong H, Kim S-J. Malonic Acid Isolated from Pinus densiflora Inhibits UVB-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in HaCaT Keratinocytes. Polymers. 2021; 13(5):816. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050816
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Cheolwoo, Jaeyoung Park, Won-Jin Kim, Woong Kim, Hyeonsook Cheong, and Seok-Jun Kim. 2021. "Malonic Acid Isolated from Pinus densiflora Inhibits UVB-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in HaCaT Keratinocytes" Polymers 13, no. 5: 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050816
APA StylePark, C., Park, J., Kim, W.-J., Kim, W., Cheong, H., & Kim, S.-J. (2021). Malonic Acid Isolated from Pinus densiflora Inhibits UVB-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in HaCaT Keratinocytes. Polymers, 13(5), 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050816