Role of Doping Agent Degree of Sulfonation and Casting Solvent on the Electrical Conductivity and Morphology of PEDOT:SPAES Thin Films
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
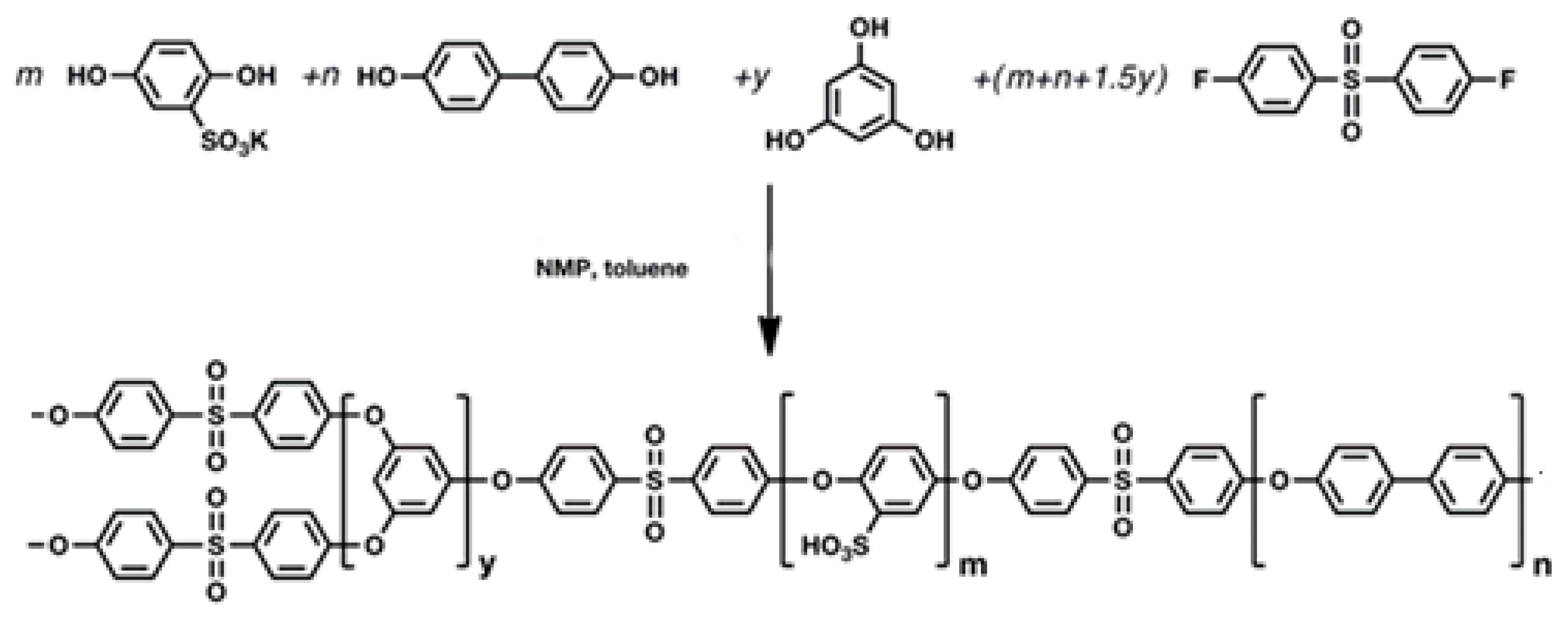
2.2. Synthesis of Sulfonated Polyarylether Sulfone (SPAES)
2.3. Synthesis of PEDOT Doped with SPAES
2.4. Characterization of SPAESs and PEDOT_SPAESs
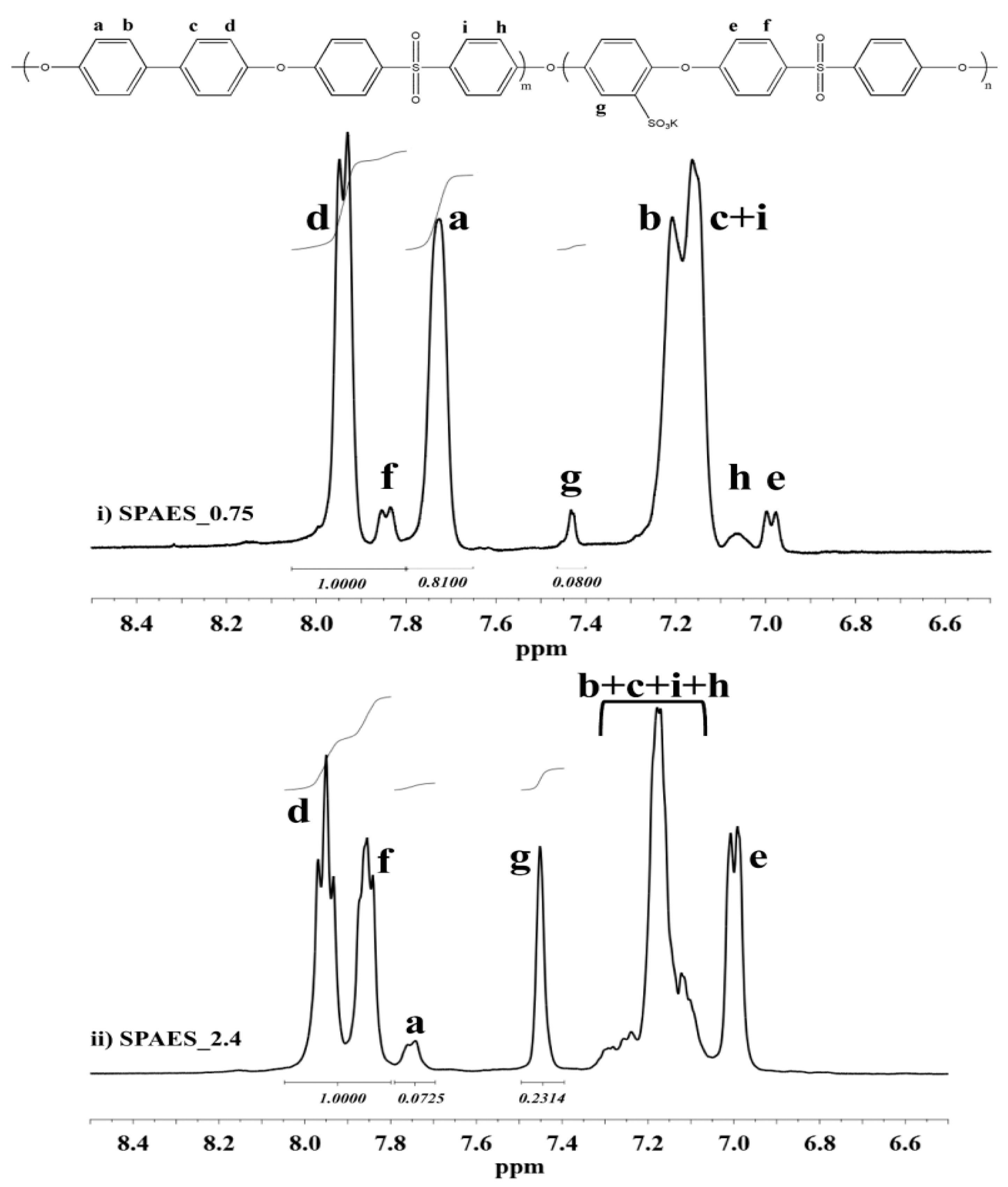
2.4.1. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H-NMR) Spectroscopy
2.4.2. Potentiometric Titration (PT)
2.4.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.4.4. Impedance Spectroscopy
2.4.5. Laser Scanning Microscopy (LSM)
2.4.6. Electrical Conductivity
2.4.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. SPAESs Synthesis and Characterization: 1H-NMR, PT, DSC, and Electrical Conductivity Analyses
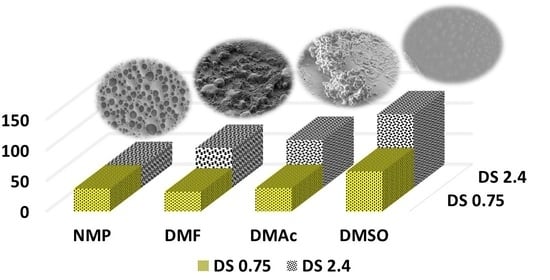
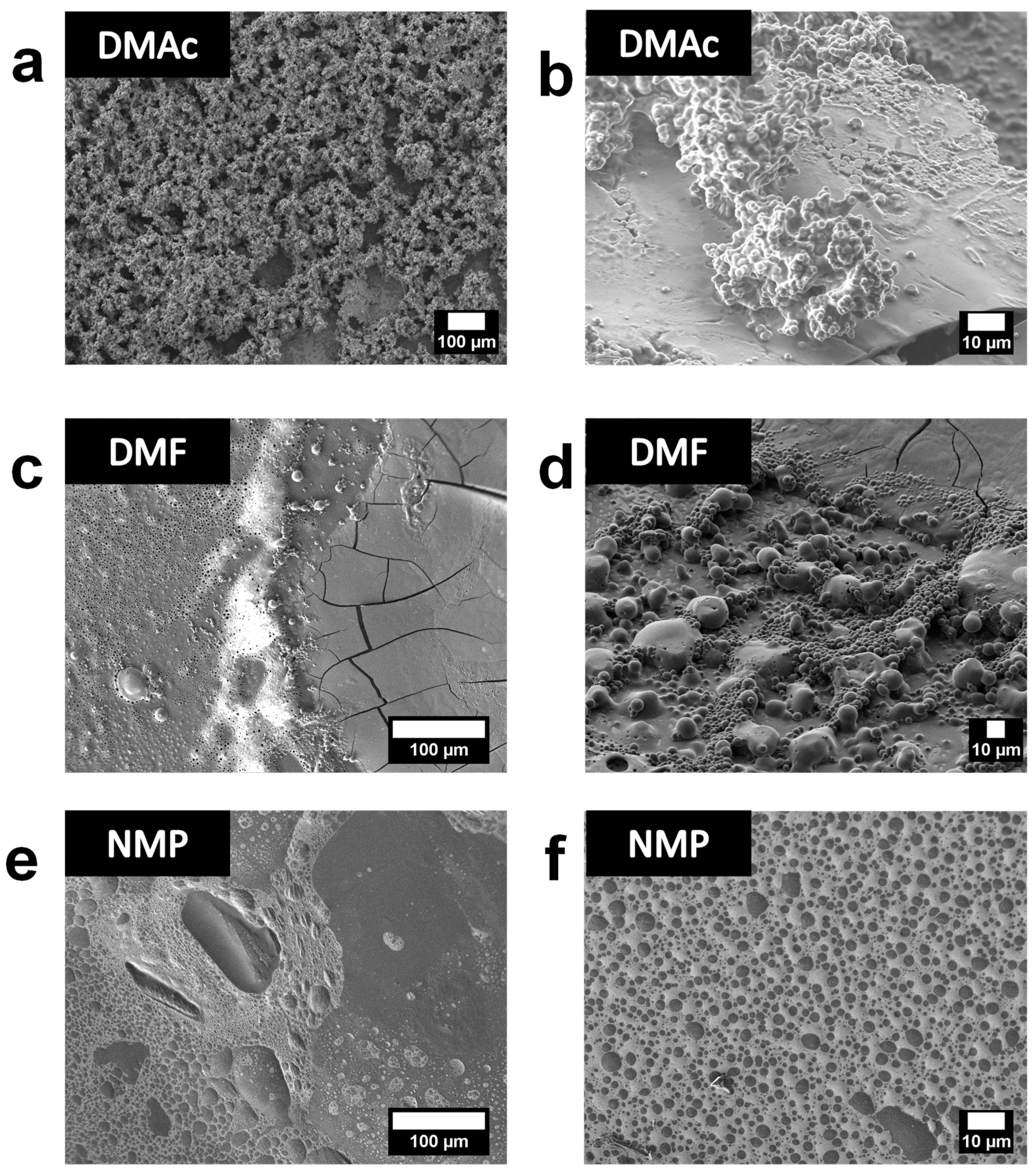
3.2. PEDOT_SPAESs Synthesis and Characterization of: LSM, Electrical Conductivity, and SEM Analyses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roncali, J. Conjugated poly(thiophenes): Synthesis, functionalization, and applications. Chem. Rev. 1992, 92, 711–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubnova, O.; Khan, Z.U.; Wang, H.; Braun, S.; Evans, D.R.; Fabretto, M.; Hojati-Talemi, P.; Dagnelund, D.; Arlin, J.-B.; Geerts, Y.H.; et al. Semi-metallic polymers. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, W.L.; Wang, F.; Mecham, J.B.; Bhanu, V.A.; Hill, M.; Kim, Y.S.; McGrath, J.E. Influence of the bisphenol structure on the direct synthesis of sulfonated poly (arylene ether) copolymers. I. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2003, 41, 2264–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, A.K.; Meek, O.; Eng, A.J.; Yee, S.K. Radial thermoelectric generator fabricated from n- and p-type conducting polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Ouyang, J. Thermoelectric Properties of PEDOT:PSS. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, L.; Ouyang, J.; Zhang, Q. Recent developments in flexible thermoelectrics: From materials to devices. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 137, 110448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Cai, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, G. Improving Resistance-Temperature Characteristic of Polyethylene/Carbon Black Composites by Poly(3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene)-Functionalized Multilayer Graphene. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2020, 221, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowen, L.M.; Atoyo, J.; Carnie, M.J.; Baran, D.; Schroeder, B.C. Review—Organic Materials for Thermoelectric Energy Generation. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2017, 6, N3080–N3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shirakawa, H.; Louis, E.J.; MacDiarmid, A.G.; Chiang, C.K.; Heeger, A.J. Synthesis of electrically conducting organic polymers: Halogen derivatives of polyacetylene, (CH) x. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1977, 16, 578–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.; Park, C.; Kim, B.; Shin, H.; Kim, E. Flexible PEDOT electrodes with large thermoelectric power factors to generate electricity by the touch of fingertips. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crispin, X.; Jakobsson, F.L.E.; Crispin, A.; Grim, P.C.M.; Andersson, P.; Volodin, A.; Van Haesendonck, C.; Van Der Auweraer, M.; Salaneck, W.R.; Berggren, M. The Origin of the High Conductivity of Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)−Poly(styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT−PSS) Plastic Electrodes. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 4354–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etampawala, T.; Tehrani, M.; Nematollahi, A.; He, L.; Dadmun, M. The impact of solvent doping on the morphology and performance of spray-coated PEDOT:dPSS: A USANS and SANS study. Org. Electron. 2017, 51, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabihi, F.; Xie, Y.; Gao, S.; Eslamian, M. Morphology, conductivity, and wetting characteristics of PEDOT:PSS thin films deposited by spin and spray coating. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 338, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timpanaro, S.; Kemerink, M.M.; Touwslager, F.; De Kok, M.; Schrader, S. Morphology and conductivity of PEDOT/PSS films studied by scanning–tunneling microscopy. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 394, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acres, G. Recent advances in fuel cell technology and its applications. J. Power Sources 2001, 100, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, A.J.; Leo, D.J.; Long, T.E. Beyond Nafion: Charged Macromolecules Tailored for Performance as Ionic Polymer Transducers. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 7765–7775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarale, R.; Gohil, G.; Shahi, V.K. Recent developments on ion-exchange membranes and electro-membrane processes. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 119, 97–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, B.C.H.; Heinzel, A. Materials for fuel-cell technologies. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 414, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozière, J.; Jones, D.J. Non-Fluorinated Polymer Materials for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2003, 33, 503–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jutemar, E.P.; Jannasch, P. Locating sulfonic acid groups on various side chains to poly(arylene ether sulfone)s: Effects on the ionic clustering and properties of proton-exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 351, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashihara, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Ueda, M. Sulfonated aromatic hydrocarbon polymers as proton exchange membranes for fuel cells. Polymers 2009, 50, 5341–5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giordano, M.S.; Longhi, L.; Formano, H.; Farina, G.D.S. Electrochemical behaviour of PES ionomer and Pt-free catakyst for PEMFCs. J. Electrochem. Sci. Eng. 2013, 3, 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- Balster, J.; Krupenko, O.; Pünt, I.; Stamatialis, D.; Wessling, M. Preparation and characterisation of monovalent ion selective cation exchange membranes based on sulphonated poly(ether ether ketone). J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 263, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.C.; Choi, J.G.; Tak, T.M. Sulfonated polyethersulfone by heterogeneous method and its membrane performances. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 74, 2046–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohil, G.; Nagarale, R.; Binsu, V.; Shahi, V.K. Preparation and characterization of monovalent cation selective sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) and poly(ether sulfone) composite membranes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 298, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, V.; Checchia, S.; Farina, H.; Ortenzi, M.A. Homogeneous synthesis and characterization of sulfonated polyarylethersulfones having low degree of sulfonation and highly hydrophilic behavior. Macromol. Res. 2016, 24, 800–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrick, J.L.; Mohanty, D.K.; Johnson, B.C.; Viswanathan, R.; Hinkley, J.A.; McGrath, J.E. Radiation resistant amorphous–all aromatic polyarylene ether sulfones: Synthesis, characterization, and mechanical properties. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1986, 24, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliveri, G.; Sabatini, V.; Farina, H.; Ortenzi, M.A.; Meroni, D.; Colombo, A. Double side self-cleaning polymeric materials: The hydrophobic and photoactive approach. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 483, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Omran, A.; Rose, J.B. Synthesis and sulfonation of poly(phenylene ether ether sulfone)s containing methylated hydroquinone residues. Polymers 1996, 37, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checchia, S.; Sabatini, V.; Farina, H.; Ortenzi, M.A. Combining control of branching and sulfonation in one-pot synthesis of random sulfonated polyarylethersulfones: Effects on thermal stability and water retention. Polym. Bull. 2017, 74, 3939–3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falciola, L.; Checchia, S.; Pifferi, V.; Farina, H.; Ortenzi, M.A.; Sabatini, V. Electrodes modified with sulphonated poly(aryl ether sulphone): Effect of casting conditions on their enhanced electroanalytical performance. Electrochimica Acta 2016, 194, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, V.; Farina, H.; Ortenzi, M.A. Conductive inks based on methacrylate end-capped poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) for printed and flexible electronics. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2017, 57, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, H.V.; Farina, M.A.O. Functional End-Capped Conducting Poly (3,4- Ethylenedioxythiophene). Am. Inst. Phys. 2016, 1736, 020082. [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini, V.; Pifferi, V.; Checchia, S.; Rebeccani, S.; Farina, H.; Ortenzi, M.A.; Falciola, L. Electrodes modified with poly(3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene) doped with sulfonated polyarylethersulfones: Towards new conducting polymers. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings, Ischia, Italy, 5–6 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini, V.; Pifferi, V.; Checchia, S.; Rebeccani, S.; Farina, H.; Ortenzi, M.A.; Falciola, L. A Combined XRD, Solvatochromic, and Cyclic Voltammetric Study of Poly (3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene) Doped with Sulfonated Polyarylethersulfones: Towards New Conducting Polymers. Polymers 2018, 10, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaidi, S.M.J.; Mikhailenko, S.D.; Robertson, G.; Guiver, M.; Kaliaguine, S. Proton conducting composite membranes from polyether ether ketone and heteropolyacids for fuel cell applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 173, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Mukaida, M.; Kirihara, K.; Lyu, L.; Wei, Q. Poly(3,4-Ethylene Dioxythiophene)/Poly(Styrene Sulfonate) Electrodes in Electrochemical Cells for Harvesting Waste Heat. Energy Technol. 2020, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmina, W.; El Moudane, M.; Shaim, A.; Zriouil, M.; Taibi, M. Chemical durability, electrical and dielectric properties of the ternary system (50-x)K2O-xMnO-50P2O5 phosphate glasses. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 13, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.Y.; Park, C.M.; Kim, J.E.; Suh, K.S. Electronic, chemical and structural change induced by organic solvents in tosylate-doped poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT-OTs). Synth. Met. 2005, 149, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jung, J.; Lee, D.; Joo, J. Enhancement of electrical conductivity of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/poly(4-styrenesulfonate) by a change of solvents. Synth. Met. 2002, 126, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuş, M.; Okur, S. Electrical characterization of PEDOT:PSS beyond humidity saturation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 143, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, B.; Yuk, H.; Lin, S.; Jian, N.; Qu, K.; Xu, J.; Zhao, X. Pure PEDOT:PSS hydrogels. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Friedel, B.; Keivanidis, P.E.; Brenner, T.J.K.; Abrusci, A.; McNeill, C.R.; Friend, R.H.; Greenham, N.C. Effects of Layer Thickness and Annealing of PEDOT:PSS Layers in Organic Photodetectors. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 6741–6747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, S.; Birgerson, J.; Crispin, X.; Greczynski, G.; Osikowicz, W.; van der Gon, A.D.; Salaneck, W.; Fahlman, M. The effects of solvents on the morphology and sheet resistance in poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)–polystyrenesulfonic acid (PEDOT–PSS) films. Synth. Met. 2003, 139, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Xu, Q.; Chu, C.-W.; Yang, Y.; Li, G.; Shinar, J. On the mechanism of conductivity enhancement in poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrene sulfonate) film through solvent treatment. Polymers 2004, 45, 8443–8450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solvent Physical Properties. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/chemistry/stockroom-reagents/learning-center/technical-library/solvent-properties.html (accessed on 1 December 2020).
- Castagnola, V.; Bayon, C.; Descamps, E.; Bergaud, C. Morphology and conductivity of PEDOT layers produced by different electrochemical routes. Synth. Met. 2014, 189, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E. Preparation and Morphology of Electroconductive PEDOT/PSS/ATO Nanocomposite Microsphere. Polymer Compos. 2015, 36, 1352–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otley, M.T.; Alamer, F.A.; Guo, Y.; Santana, J.; Eren, E.; Li, M.; Lombardi, J.; Sotzing, G.A. Phase segregation of PEDOT:PSS on textile to produce materials of >10A nm-2 current carrying capacity. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2016, 302, 1600348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 ) DS = 0.75, (
) DS = 0.75, (  ) DS = 1.0, (
) DS = 1.0, (  ) DS = 1.3, (
) DS = 1.3, (  ) DS = 1.6, (
) DS = 1.6, (  ) DS = 1.9, (
) DS = 1.9, (  ) DS = 2.1, and (
) DS = 2.1, and (  ) DS = 2.4 (meq R-SO3− g−1 of polymer) measured via impedance spectroscopy. An increasing trend of electrical conductivity with increasing DS can be observed, especially at low frequencies.
) DS = 2.4 (meq R-SO3− g−1 of polymer) measured via impedance spectroscopy. An increasing trend of electrical conductivity with increasing DS can be observed, especially at low frequencies.
 ) DS = 0.75, (
) DS = 0.75, (  ) DS = 1.0, (
) DS = 1.0, (  ) DS = 1.3, (
) DS = 1.3, (  ) DS = 1.6, (
) DS = 1.6, (  ) DS = 1.9, (
) DS = 1.9, (  ) DS = 2.1, and (
) DS = 2.1, and (  ) DS = 2.4 (meq R-SO3− g−1 of polymer) measured via impedance spectroscopy. An increasing trend of electrical conductivity with increasing DS can be observed, especially at low frequencies.
) DS = 2.4 (meq R-SO3− g−1 of polymer) measured via impedance spectroscopy. An increasing trend of electrical conductivity with increasing DS can be observed, especially at low frequencies.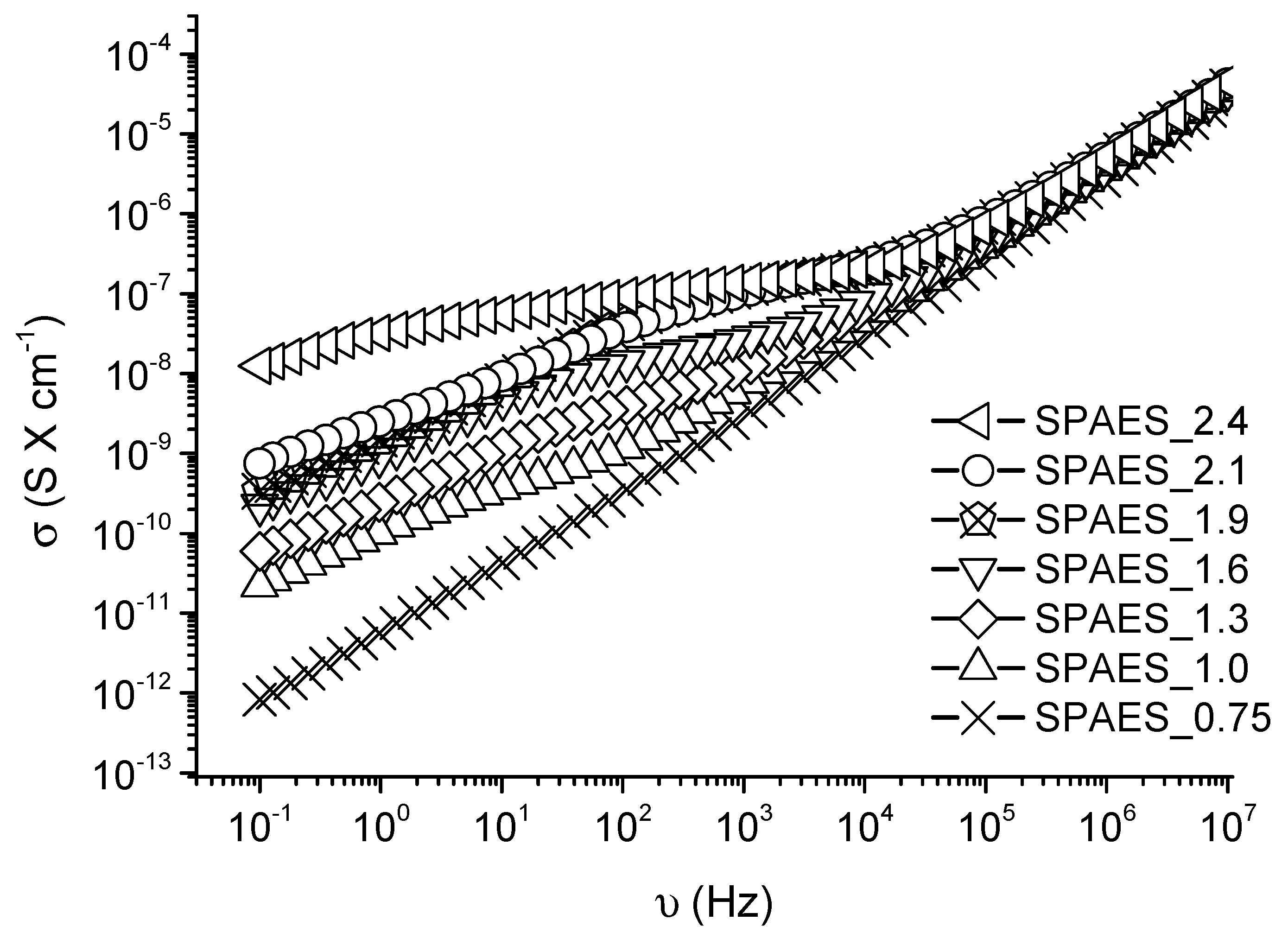
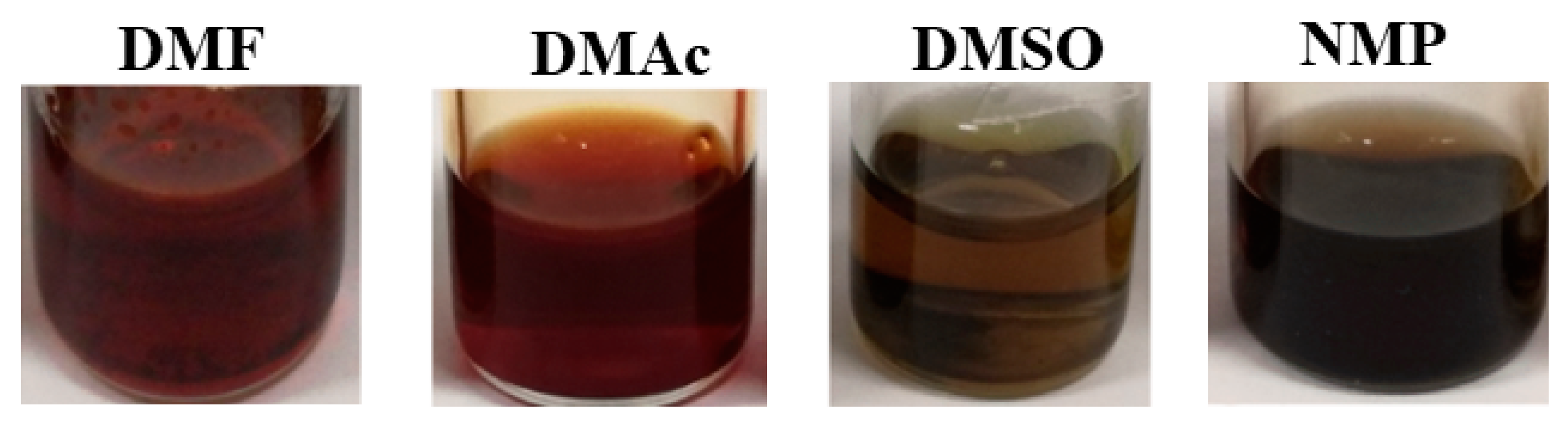
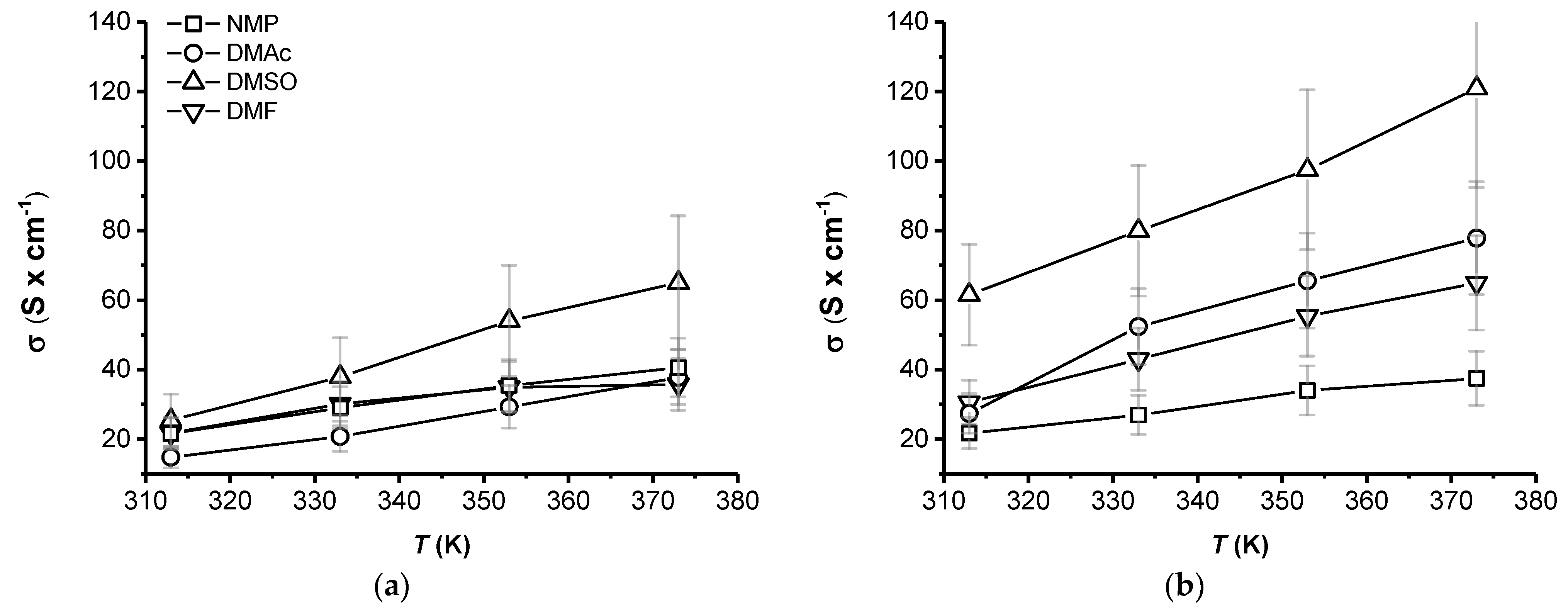
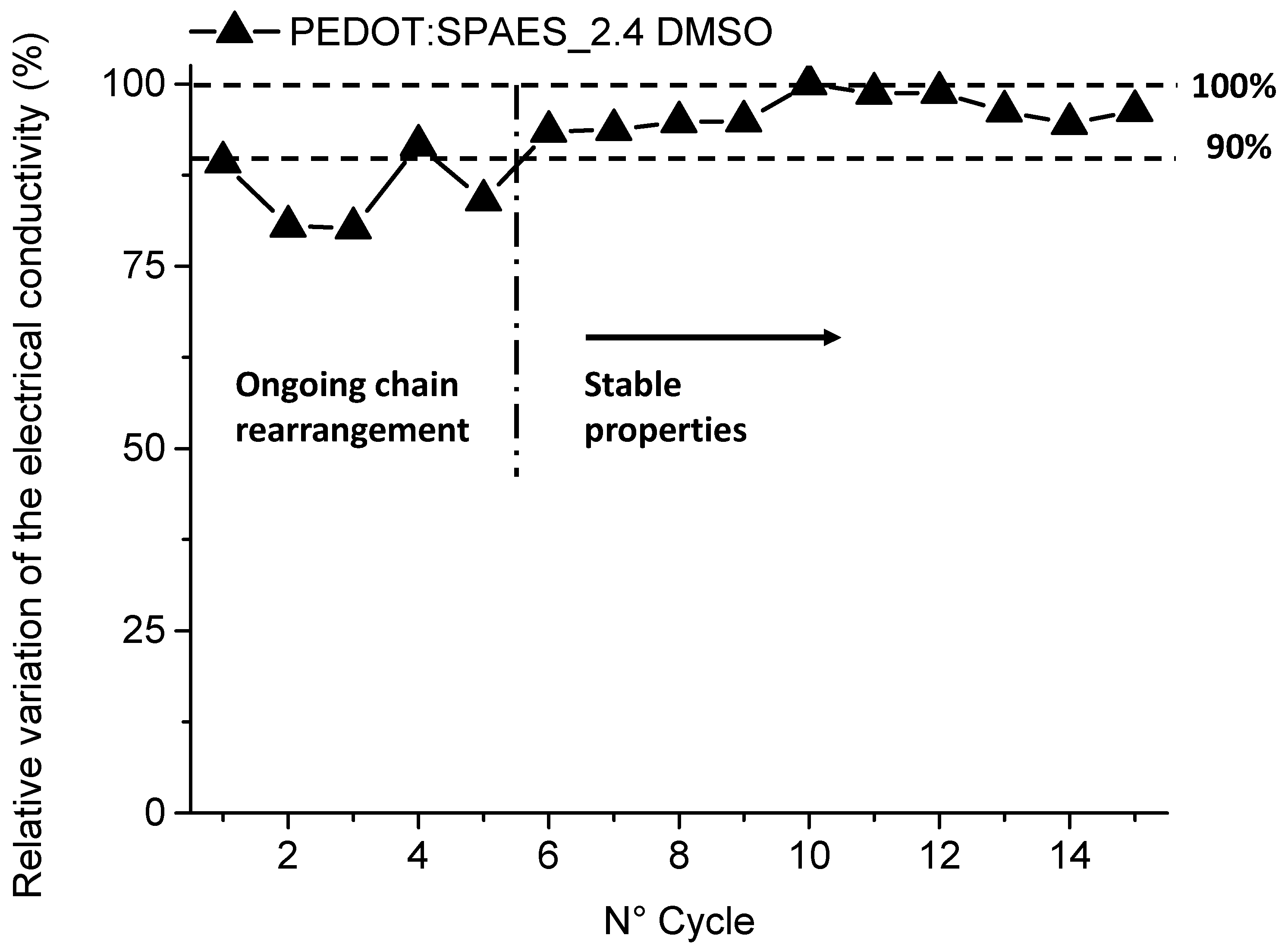


| Sample | Nominal DS (meq R-SO3− × g−1 of Polymer) | BFPS (g) | BHP (g) | SHQ (g) | THB (g) | K2CO3 (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPAES_0.75 | 0.75 | 3.074 | 1.553 | 0.856 | - | 3.677 |
| SPAES_1.0 | 1.0 | 3.041 | 1.296 | 1.141 | - | 3.637 |
| SPAES_1.3 | 1.3 | 3.002 | 0.982 | 1.484 | 0.003 | 3.591 |
| SPAES_1.6 | 1.6 | 2.962 | 0.673 | 1.826 | 0.003 | 3.543 |
| SPAES_1.9 | 1.9 | 2.922 | 0.365 | 2.168 | 0.003 | 3.495 |
| SPAES_2.1 | 2.1 | 2.896 | 0.159 | 2.398 | 0.003 | 3.463 |
| SPAES_2.4 | 2.4 | 2.876 | 0.005 | 2.569 | 0.003 | 3.439 |
| Sample | Real DS (meq R-SO3 × g−1 of Polymer) via 1H NMR spectroscopy | IEC (meq R-SO3 * g−1 of polymer) via PT Analyses | Tg (°C) | Electrical Conductivity (S × cm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPAES_0.75 | 0.70 | 0.74 | 290.9 | 8.26 × 10−13 |
| SPAES_1.0 | 0.94 | 0.90 | 295.3 | 2.19 × 10−11 |
| SPAE_1.3 | 1.33 | 1.30 | 245.3 | 5.95 × 10−11 |
| SPAES_1.6 | 1.52 | 1.55 | 243.5 | 2.23 × 10−10 |
| SPAES_1.9 | 1.83 | 1.87 | ~241.3 | 3.38 × 10−10 |
| SPAES_2.1 | 2.00 | 2.05 | ~230.4 | 7.49 × 10−10 |
| SPAES_2.4 | 2.20 | 2.25 | 197.2 | 1.25 × 10−8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomasino, D.V.; Wolf, M.; Farina, H.; Chiarello, G.; Feldhoff, A.; Ortenzi, M.A.; Sabatini, V. Role of Doping Agent Degree of Sulfonation and Casting Solvent on the Electrical Conductivity and Morphology of PEDOT:SPAES Thin Films. Polymers 2021, 13, 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040658
Tomasino DV, Wolf M, Farina H, Chiarello G, Feldhoff A, Ortenzi MA, Sabatini V. Role of Doping Agent Degree of Sulfonation and Casting Solvent on the Electrical Conductivity and Morphology of PEDOT:SPAES Thin Films. Polymers. 2021; 13(4):658. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040658
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomasino, Daniela Valeria, Mario Wolf, Hermes Farina, Gianluca Chiarello, Armin Feldhoff, Marco Aldo Ortenzi, and Valentina Sabatini. 2021. "Role of Doping Agent Degree of Sulfonation and Casting Solvent on the Electrical Conductivity and Morphology of PEDOT:SPAES Thin Films" Polymers 13, no. 4: 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040658
APA StyleTomasino, D. V., Wolf, M., Farina, H., Chiarello, G., Feldhoff, A., Ortenzi, M. A., & Sabatini, V. (2021). Role of Doping Agent Degree of Sulfonation and Casting Solvent on the Electrical Conductivity and Morphology of PEDOT:SPAES Thin Films. Polymers, 13(4), 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040658