Effect of Solution Miscibility on the Morphology of Coaxial Electrospun Cellulose Acetate Nanofibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Polymer Solutions
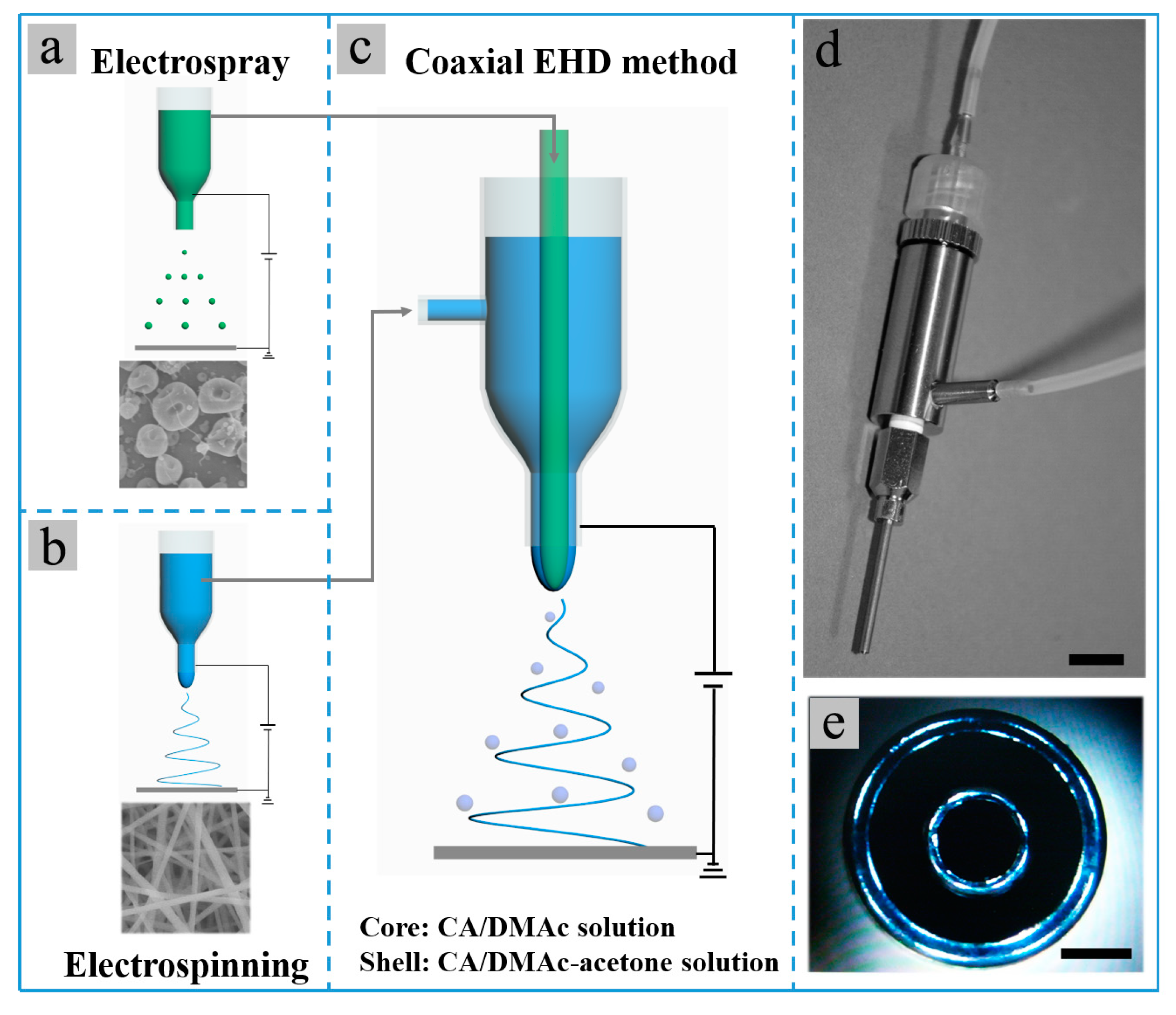
2.3. Single-Nozzle and Coaxial Electrospinning/Electrospray Experiments
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussions
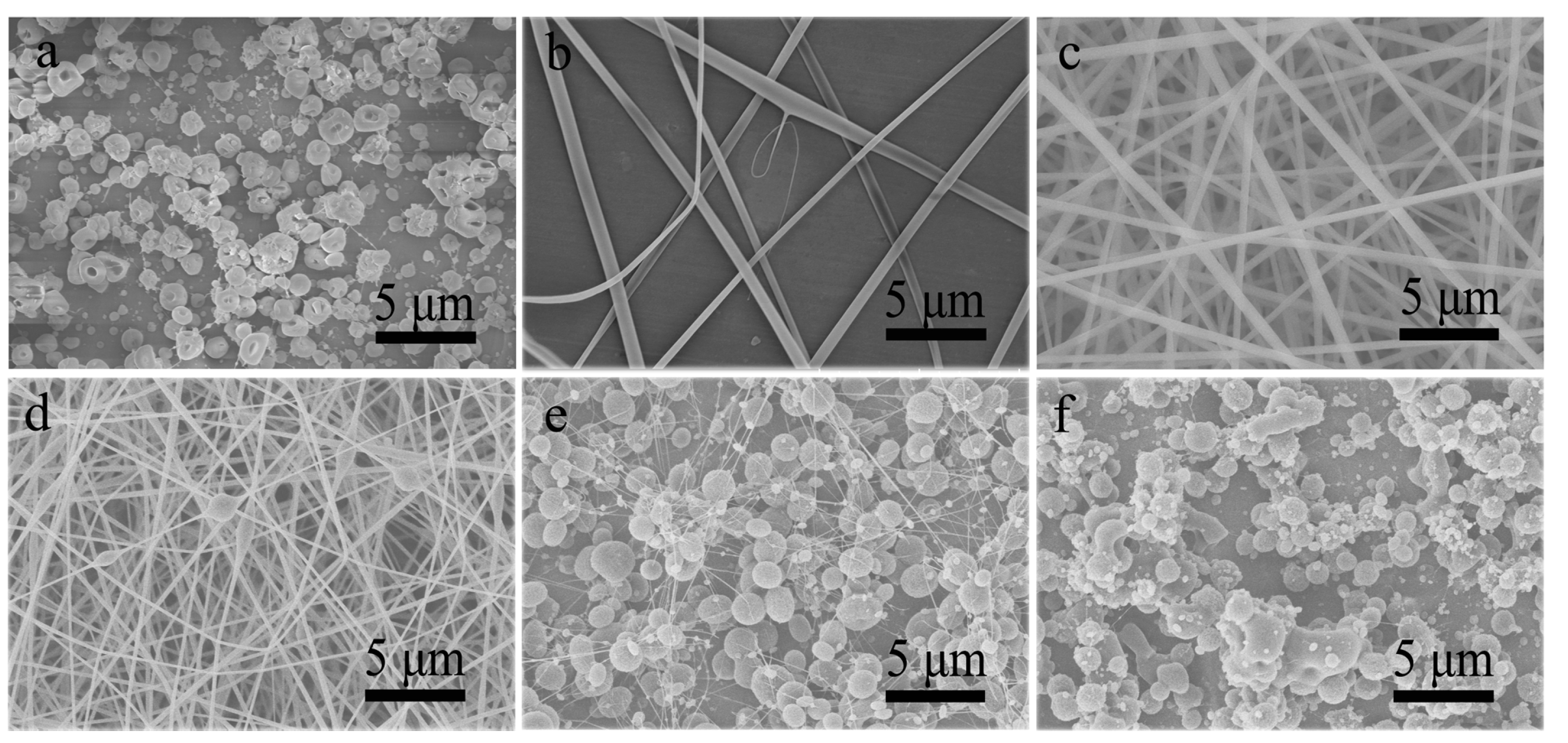
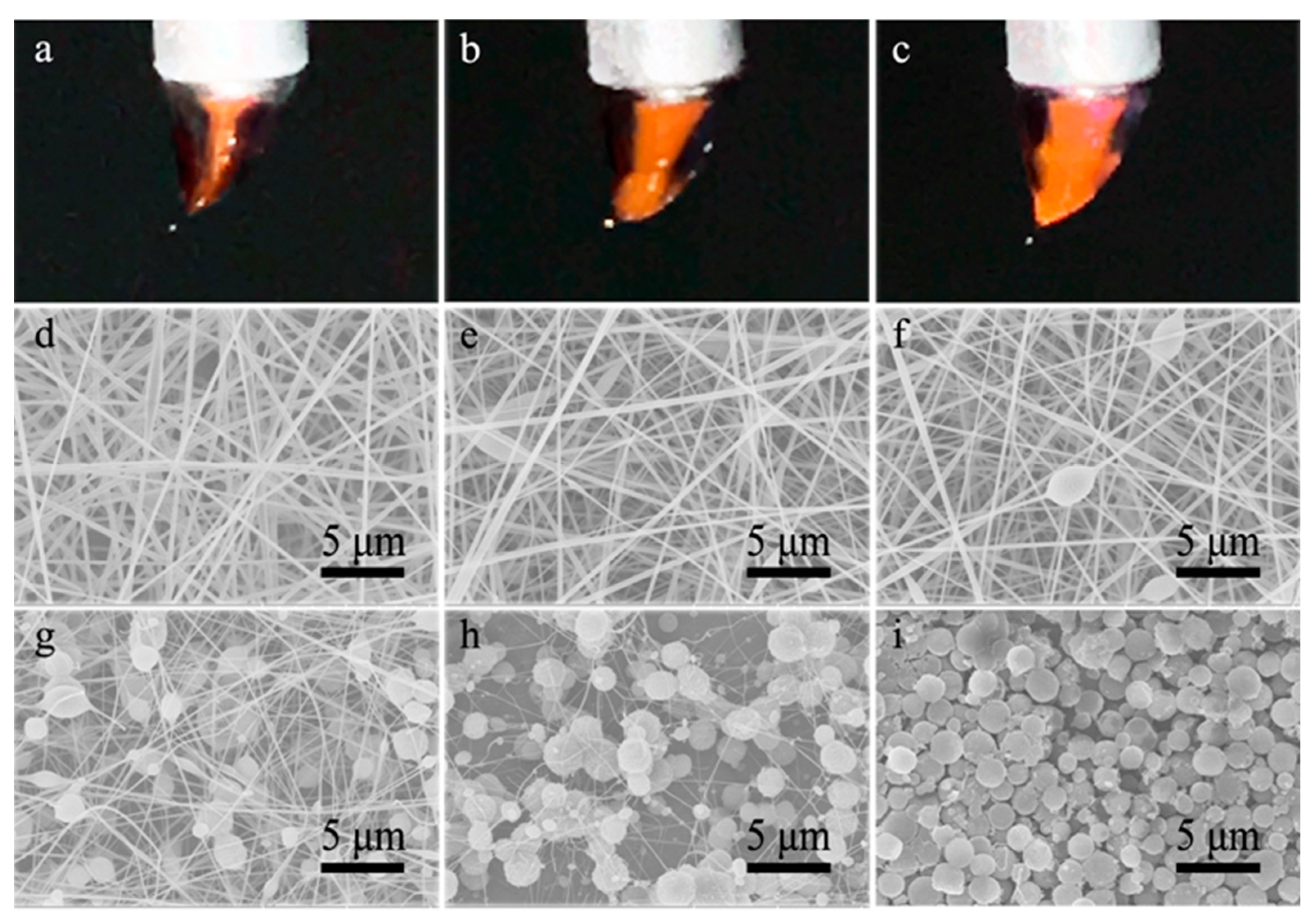
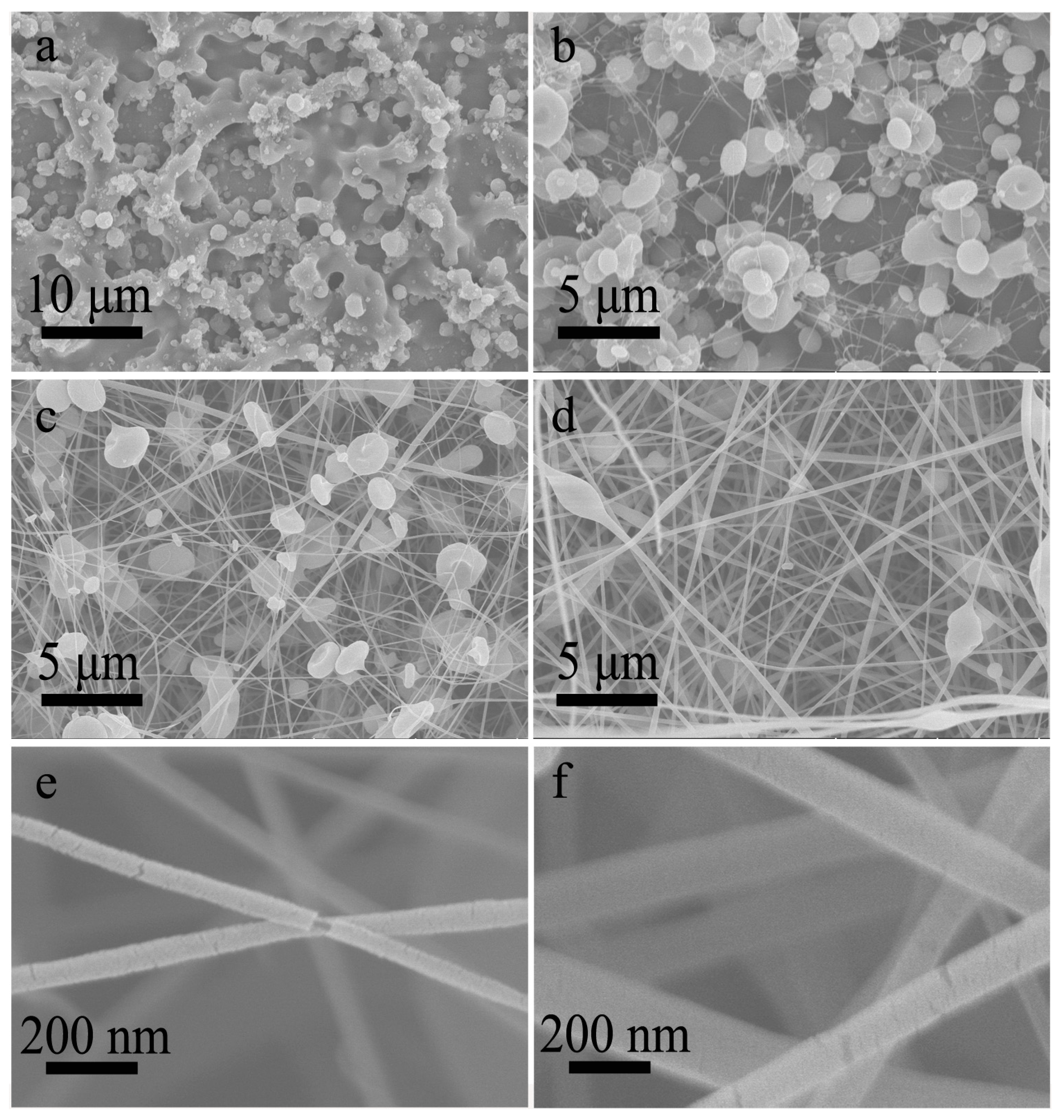
3.1. Single-Nozzle Electrospray/Electrospinning of CA Solutions
3.2. Co-Electrospinning of Core CA-D Solution and Shell CA-AD21 Solution
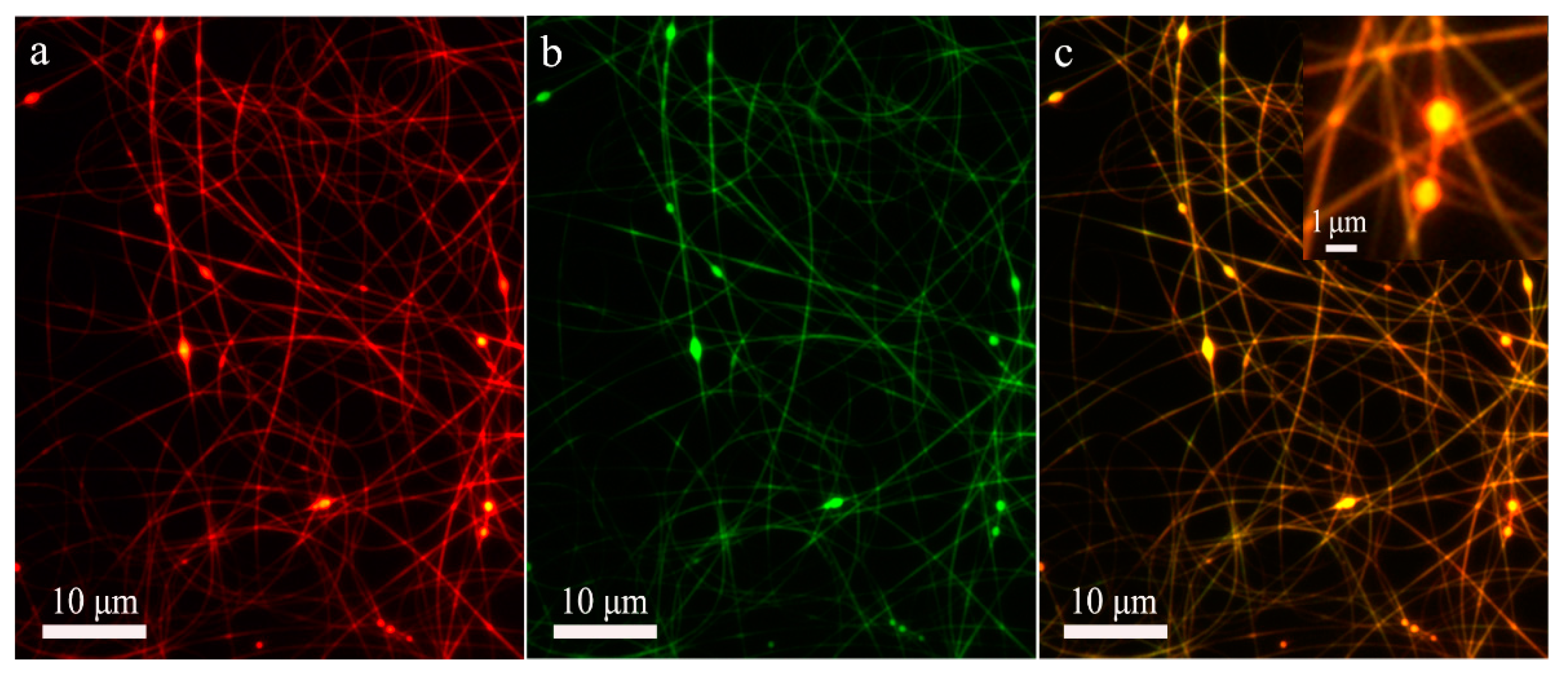
3.2.1. The Structure of Co-Electrospun CA Nanofibers
3.2.2. The Mechanism of Fiber-to-Particle Morphological Transformation
3.3. Co-Electrospinning of Core CA-D Solution and Shell CA-A Solution
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.F.; Xu, H.J.; Huo, Y.P.; Wang, Y.T.; Dong, M.D. Progress of electrospray and electrospinning in energy applications. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 132001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xia, Y.N. Electrospinning of nanofibers: Reinventing the wheel? Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1151–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theerasilp, M.; Crespy, D. Halochromic polymer nanosensors for simple visual detection of local pH in coatings. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 3604–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia, M.F.; Montaser, A.S.; Arifuzzaman, M.; Pitz, M.; Jlassi, K.; Bryant, A.A.; Kelly, S.S.; Alexis, F.; Whitehead, D.C. In situ pho-topolymerization of acrylamide hydrogel to coat cellulose acetate nanofibers for drug delivery system. Polymers 2021, 13, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebrov, I.E.; Lukanina, K.I.; Grigoriev, T.E.; Bakirov, A.V.; Krasheninnikov, S.V.; Dmitryakov, P.V.; Kamyshinsky, R.A.; Antipova, C.G.; Chvalun, S.N.; Khomich, V.Y. Enhanced electrospinning: Multi-level fiber alignment by control of electrohydrodynamic jet motion for tissue engineering. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 418, 126561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busolo, T.; Ura, D.P.; Kim, S.K.; Marzec, M.M.; Bernasik, A.; Stachewicz, U.; Kar-Narayan, S. Surface potential tailoring of PMMA fibers by electrospinning for enhanced triboelectric performance. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.M.; Wang, J.Q.; Fang, L.F.; Lin, H.B.; Liu, F.; Tang, C.Y.Y. Electrosprayed polyamide nanofiltration membrane with in-tercalated structure for controllable structure manipulation and enhanced separation performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 602, 117971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.J.; Edirisinghe, M. Core-liquid-induced transition from coaxial electrospray to electrospinning of low-viscosity poly (lac-tide-co-glycolide) sheath solution. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 7930–7938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.G.; Liu, Q.W.; Yang, Q.B.; Li, Y.C.; Wang, W.; Sun, L.; Zhang, C.Q.; Li, Y.X. Electrospun poly (methyl methacrylate) nanofibers and microparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 1032–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loscertales, I.G.; Barrero, A.; Guerrero, I.; Cortijo, R.; Marquez, M.A.M. Gañán-Calvo; Micro/nano encapsulation via electrified coaxial liquid jets. Science 2002, 295, 1695–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Yang, H.S.; Lee, B.S.; Yu, W.R. Recent progress in coaxial electrospinning: New parameters, various structures, and wide applications. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, P.; Schiffman, J.D. Beyond the single-nozzle: Coaxial electrospinning enables innovative nanofiber chemistries, ge-ometries, and applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2020, 13, 48–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.C.; Zussman, E.; Yarin, A.L.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Compound core–shell polymer nanofibers by co-electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1929–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghdoost, F.; Bahrami, S.H.; Barzin, J.; Ghaee, A. Preparation and characterization of electrospun polyethersul-fone/polyvinylpyrrolidone-zeolite core–shell composite nanofibers for creatinine adsorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 257, 117881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xia, Y.N. Direct fabrication of composite and ceramic hollow nanofibers by electrospinning. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Hwang, J. Fabrication of hollow activated carbon nanofibers (HACNFs) containing manganese oxide catalyst for toluene removal via two-step process of electrospinning and thermal treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Song, Y.L.; Jiang, L. One-step multicomponent encapsulation by compound-fluidic electrospray. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 7800–7801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.S.; Yang, H.S.; Yu, W.R. Fabrication of double-tubular carbon nanofibers using quadruple coaxial electrospinning. Nan-otechnology 2014, 25, 465602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Wang, N.; Di, J.C.; Zhao, Y.; Song, Y.L.; Jiang, L. Nanowire-in-microtube structured core/shell fibers via multifluidic coaxial electrospinning. Langmuir 2010, 26, 11291–11296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.S.; Jeon, S.Y.; Park, H.; Lee, G.; Yang, H.S.; Yu, W.R. New electrospinning nozzle to reduce jet instability and its application to manufacture of multi-layered nanofibers. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghe, A.K.; Gupta, B.S. Coaxial electrospinning for nanofiber structures: Preparation and applications. Polym. Rev. 2008, 48, 353–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.Y.; Huang, Z.M. Numerical study on two-phase flow patterns in coaxial electrospinning. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 084307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakravan, M.; Heuzey, M.C.; Ajji, A. Core–shell structured PEO-chitosan nanofibers by coaxial electrospinning. Biomacromol-Ecules 2012, 13, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.W.; Steckl, A.J. Superhydrophobic and oleophobic fibers by coaxial electrospinning. Langmuir 2009, 25, 9454–9462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.C.; Davoodi, P.; Tong, Y.W.; Wang, C.H. Computational study of core-shell droplet formation in coaxial electrohydro-dynamic atomization process. AIChE J. 2016, 62, 4259–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.H.; Fridrikh, S.V.; Rutledge, G.C. Production of submicrometer diameter fibers by two-fluid electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1562–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriel, H.; Sanderson, R.D.; Smit, E. Coaxial electrospinning of miscible PLLA-core and PDLLA-shell solutions and indirect vis-ualisation of the core-shell fibres obtained. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2012, 20, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- McCann, J.T.; Li, D.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning of nanofibers with core-sheath, hollow, or porous structures. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurban, Z.; Lovell, A.; Bennington, S.M.; Jenkins, D.W.K.; Ryan, K.R.; Jones, M.O.; Skipper, N.T.; David, W.I.F. A solution selection model for coaxial electrospinning and its application to nanostructured hydrogen storage materials. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 21201–21213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.G.; Branford-White, C.; Bligh, S.W.A.; White, K.; Chatterton, N.P.; Zhu, L.M. Improving polymer nanofiber quality using a modified co-axial electrospinning process. Macromol. Rapid Comm. 2011, 32, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.G.; Yu, J.H.; Chen, L.; Williams, G.R.; Wang, X. Modified coaxial electrospinning for the preparation of high-quality keto-profen-loaded cellulose acetate nanofibers. Carbohyd. Polym. 2012, 90, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, G.; Spretz, R.; Velarde-Ortiz, R. Use of coaxial gas jackets to stabilize Taylor cones of volatile solutions and to induce particle-to-fiber transitions. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wsoo, M.A.; Shahir, S.; Bohari, S.P.M.; Nayan, N.H.M.; Razak, S.L.A. A review on the properties of electrospun cellulose acetate and its application in drug delivery systems: A new perspective. Carbohyd. Res. 2020, 491, 107978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makadia, H.K.; Siegel, S.J. Poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) as biodegradable controlled drug delivery carrier. Polymers 2011, 3, 1377–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Hsieh, Y.L. Ultrafine fibrous cellulose membranes from electrospinning of cellulose acetate. J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Phys. 2002, 40, 2119–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tungprapa, S.; Puangparn, T.; Weerasombut, M.; Jangchud, I.; Fakum, P.; Semongkhol, S.; Meechaisue, C.; Supaphol, P. Electrospun cellulose acetate fibers: Effect of solvent system on morphology and fiber diameter. Cellulose 2007, 14, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Meng, G.W.; Huang, Z.L.; Zhou, N.N. Electrosprayed large-area membranes of Ag-nanocubes embedded in cellulose acetate microspheres as homogeneous SERS substrates. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.L.; Meng, G.W.; Huang, Q.; Chen, B.; Zhou, F.; Hu, X.Y.; Qian, Y.W.; Tang, H.B.; Han, F.M.; Chu, Z.Q. Polyacrylic acid sodium salt film entrapped Ag-nanocubes as molecule traps for SERS detection. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, D.; Heinrich, S.; Greil, P. Solvent control of cellulose acetate nanofibre felt structure produced by electrospinning. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koski, A.; Yim, K.; Shivkumar, S. Effect of molecular weight on fibrous PVA produced by electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2004, 58, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokanović, V.; Čolović, B.; Marković, D.; Petrović, M.; Jokanović, M.; Milosavljević, P.; Sopta, J. In Vivo investigation of ALBO-OS scaffold based on hydroxyapatite and PLGA. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 3948768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganji, F.; Abdekhodaie, M.J. Chitosan–g-PLGA copolymer as a thermosensitive membrane. Carbohyd. Polym. 2010, 80, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, P.; Liao, L.; Cheng, B.; Song, J. Quantitative analysis of cellulose acetate with a high degree of substitution by FTIR and its application. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 6194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Solution | Polymer | Solvent | Acetone-to-DMAc Ratio (v/v) | Viscosity (mPa·s) | Surface Tension (mN/m) | Product Morphology | Average Fiber Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA-D | CA | DMAc | / | 1246 | 33.33 | Particles | / |
| CA-A | acetone | / | 370 | 23.62 | Few fibers | 574 | |
| CA-AD21 | Acetone/ DMAc | 2:1 | 544 | 25.52 | Fibers | 405 | |
| CA-AD12 | 1:2 | / | / | Beaded fibers | 218 | ||
| CA-AD14 | 1:4 | / | / | Particles and few fibers | / | ||
| CA-AD18 | 1:8 | / | / | Particles | / | ||
| PLGA-D | PLGA | DMAc | / | 825 | 32.82 | Particles | / |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, K.; Le, Y.; Mengen, H.; Zhongbo, L.; Zhulin, H. Effect of Solution Miscibility on the Morphology of Coaxial Electrospun Cellulose Acetate Nanofibers. Polymers 2021, 13, 4419. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13244419
Yan K, Le Y, Mengen H, Zhongbo L, Zhulin H. Effect of Solution Miscibility on the Morphology of Coaxial Electrospun Cellulose Acetate Nanofibers. Polymers. 2021; 13(24):4419. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13244419
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Ke, Yao Le, Hu Mengen, Li Zhongbo, and Huang Zhulin. 2021. "Effect of Solution Miscibility on the Morphology of Coaxial Electrospun Cellulose Acetate Nanofibers" Polymers 13, no. 24: 4419. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13244419
APA StyleYan, K., Le, Y., Mengen, H., Zhongbo, L., & Zhulin, H. (2021). Effect of Solution Miscibility on the Morphology of Coaxial Electrospun Cellulose Acetate Nanofibers. Polymers, 13(24), 4419. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13244419








