Water Jet Erosion Performance of Carbon Fiber and Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methodology
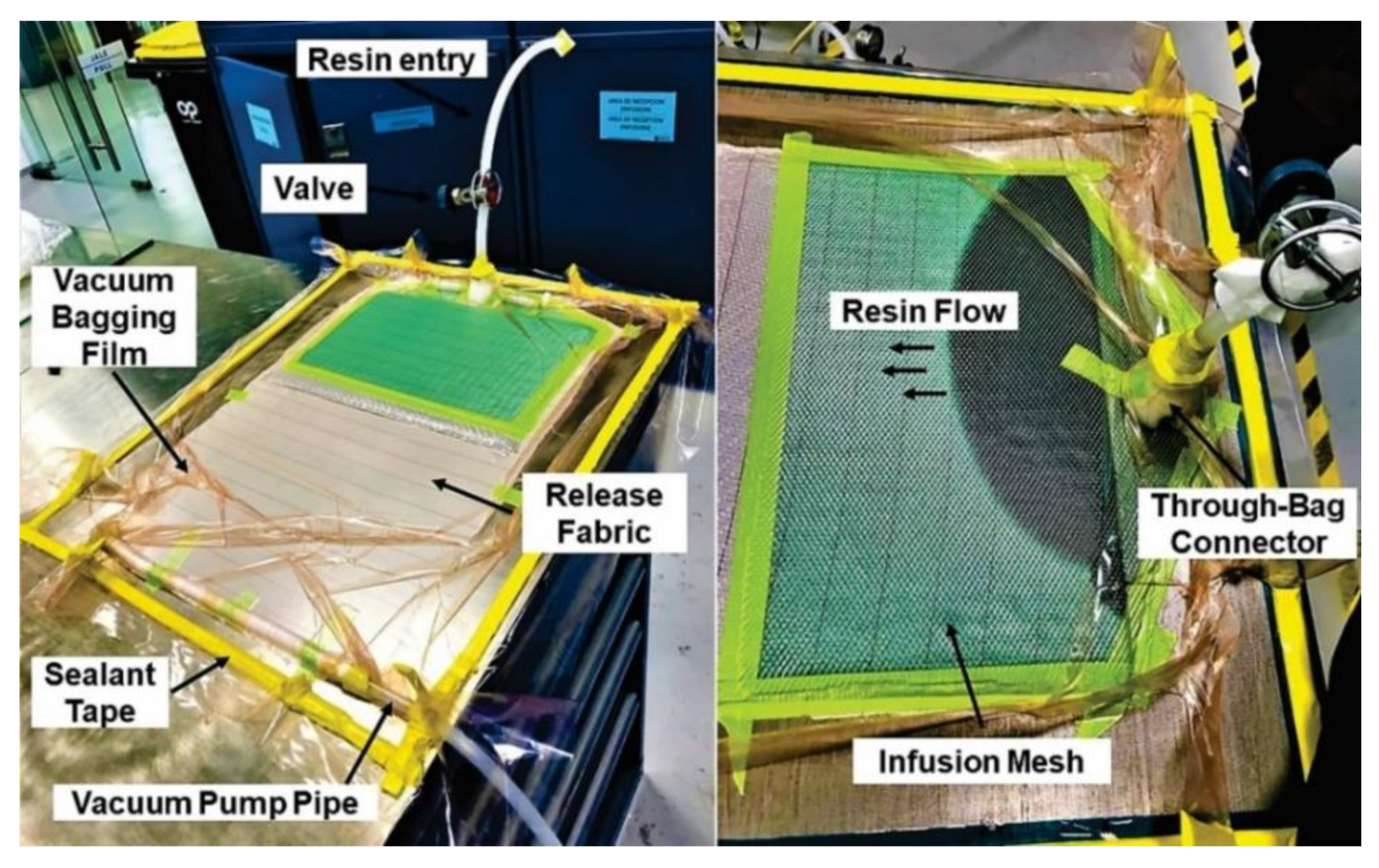
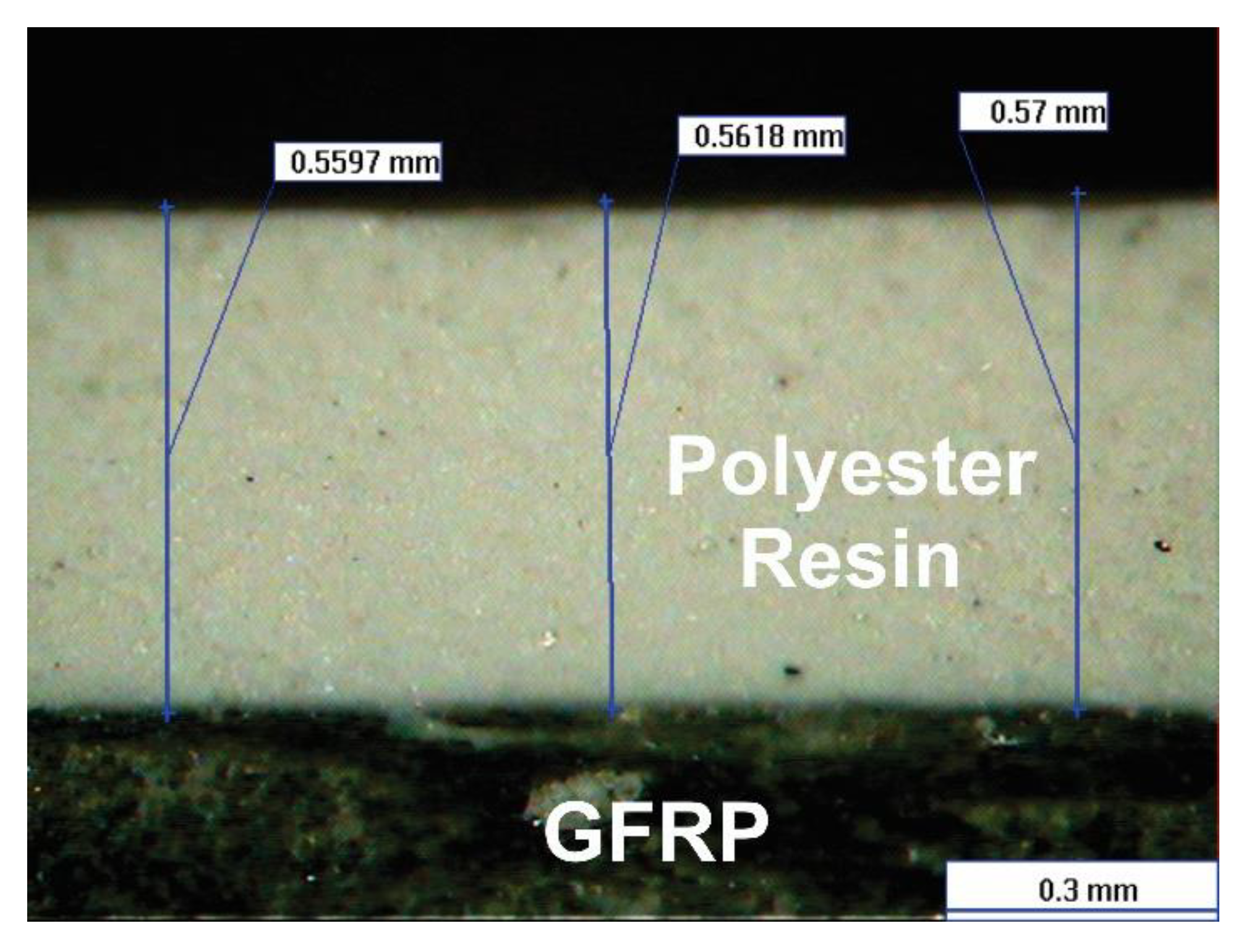
2.1. Specimens
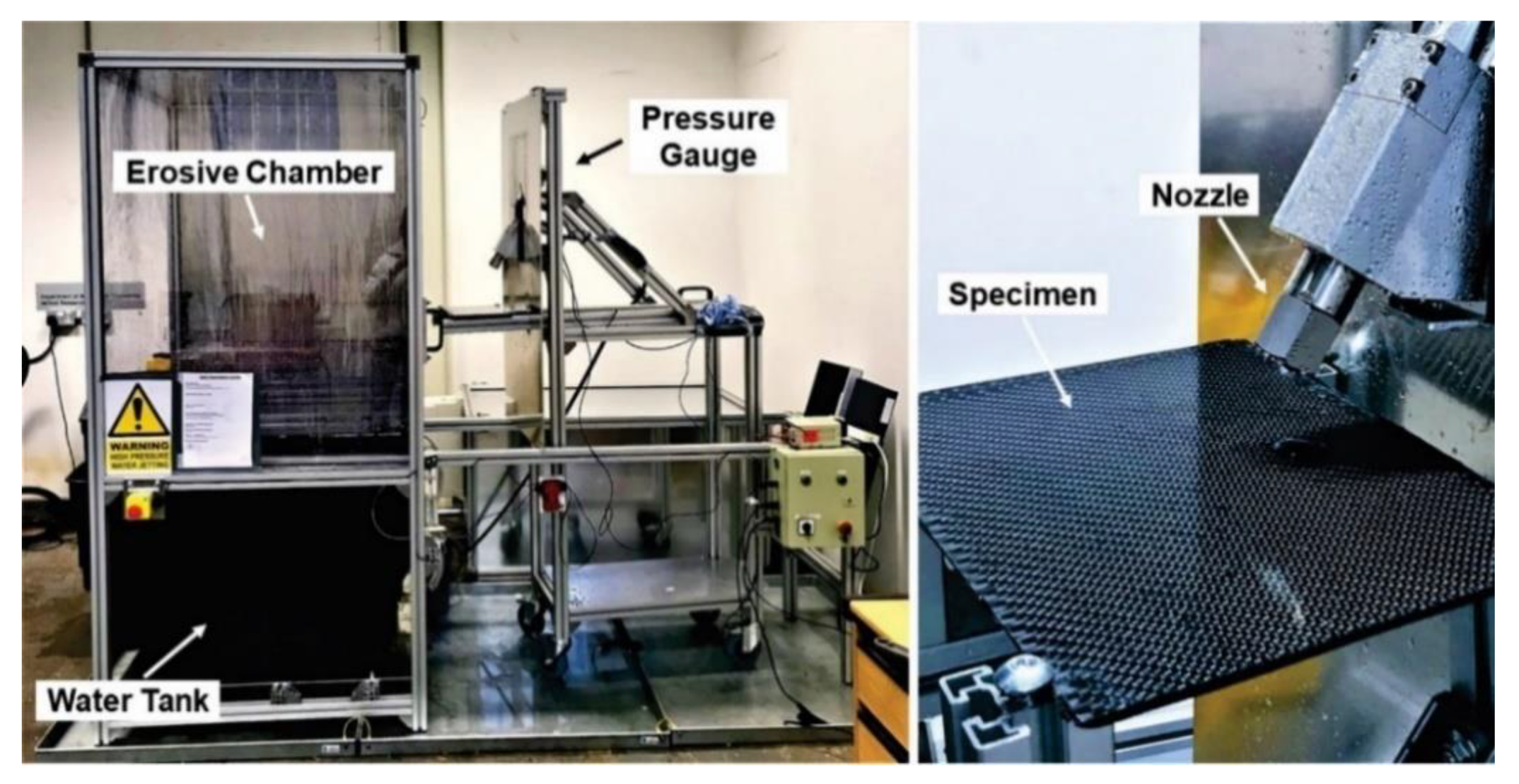
2.2. Test Conditions
3. Results and Discussion
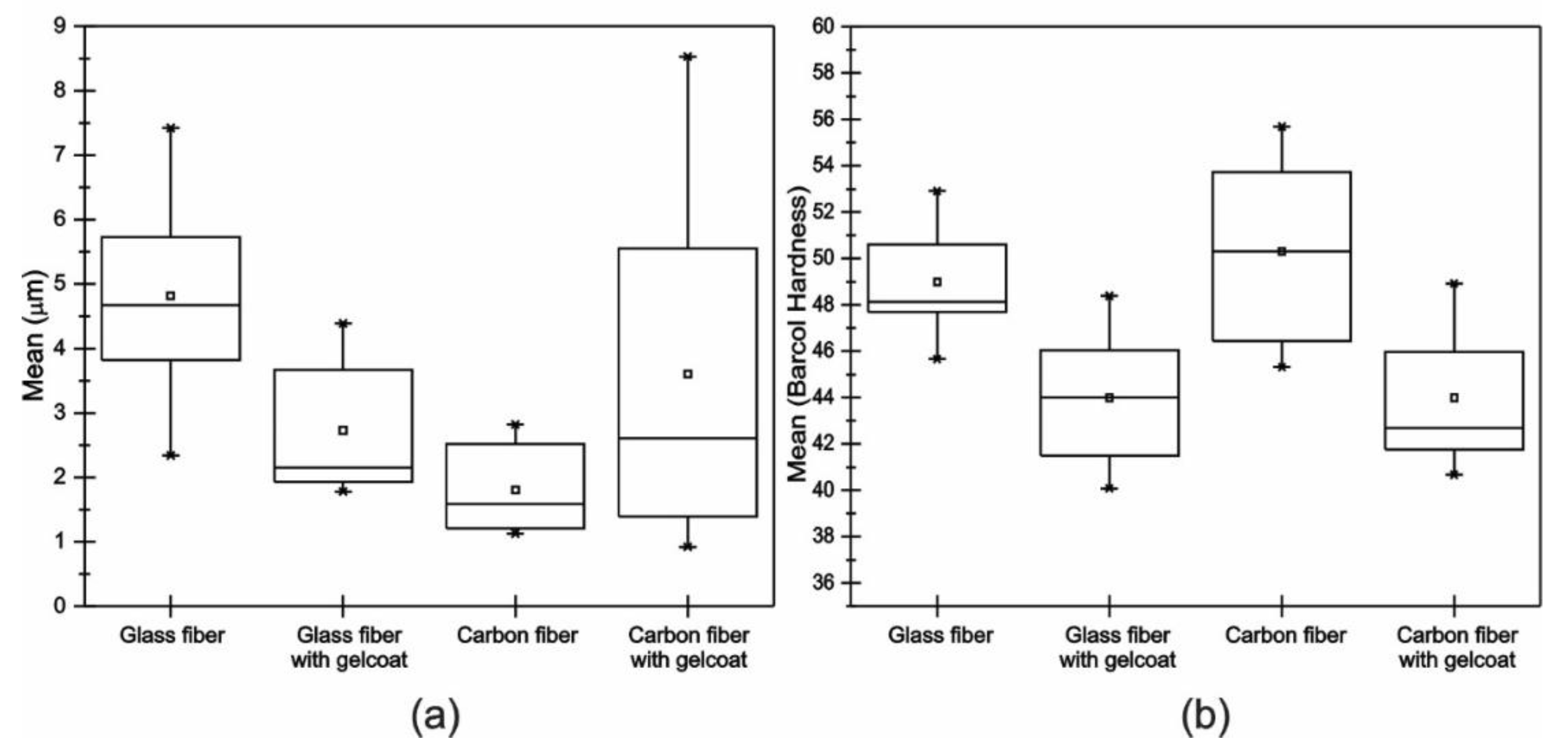
3.1. Roughness and Hardness
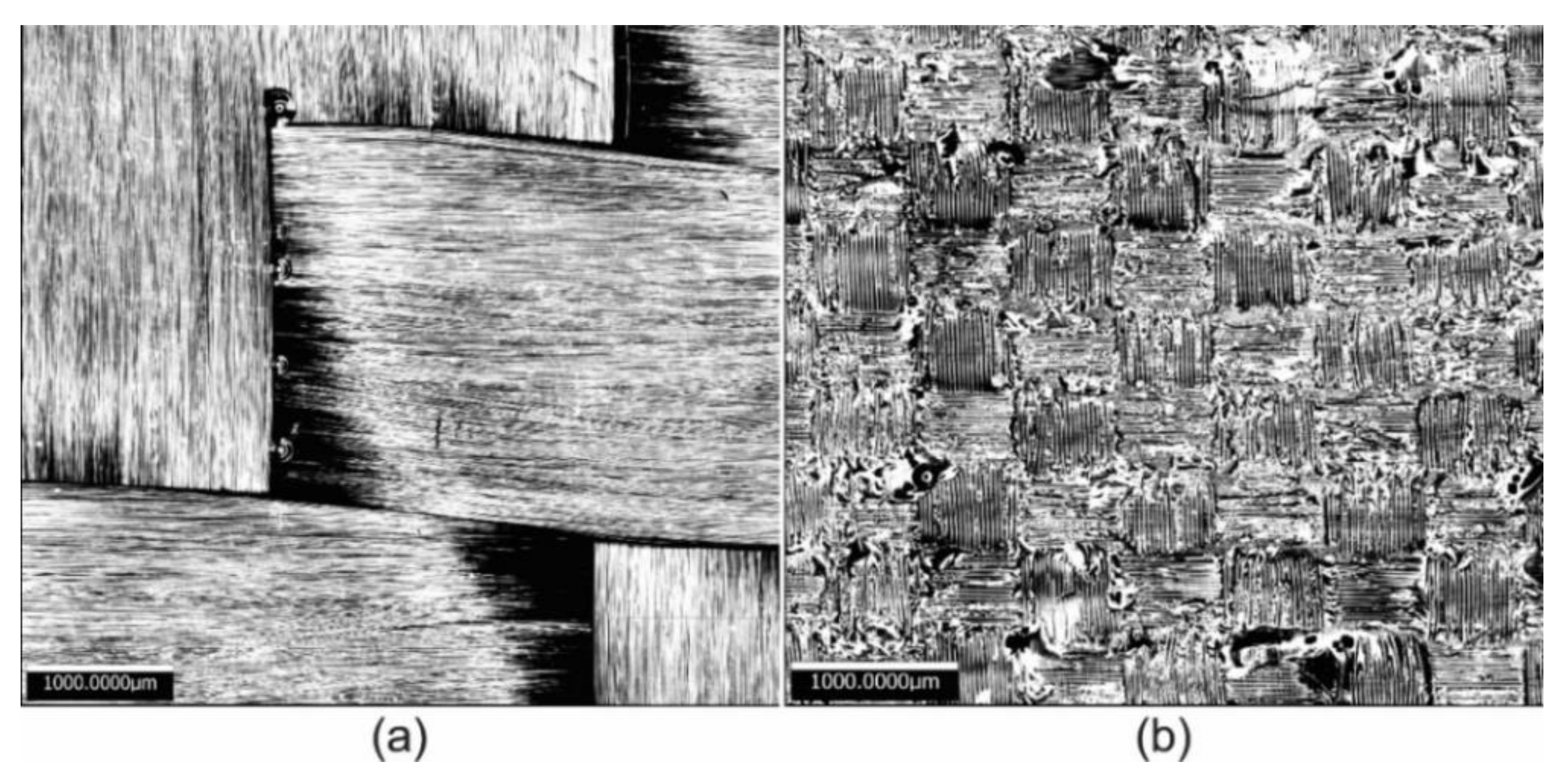
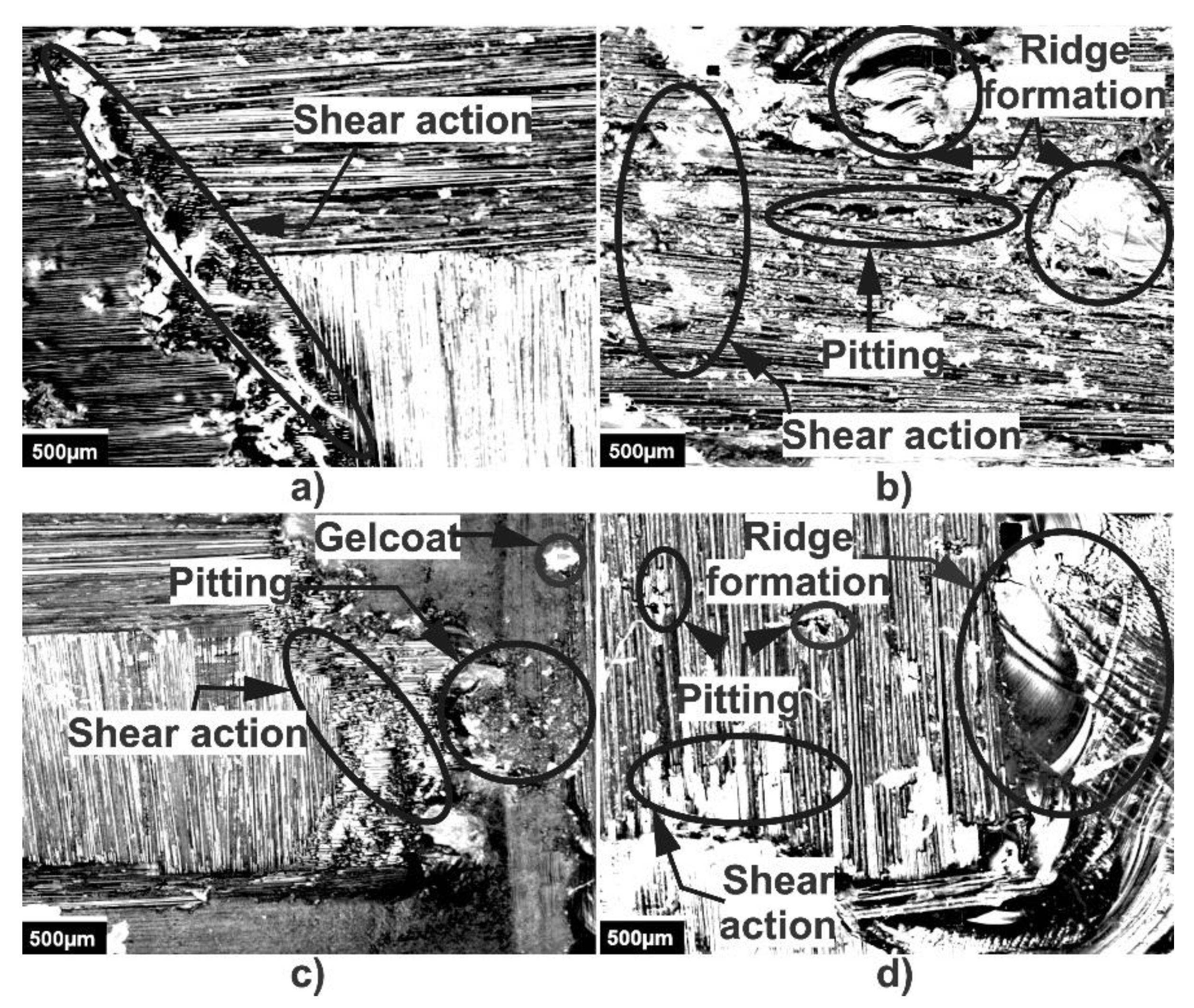
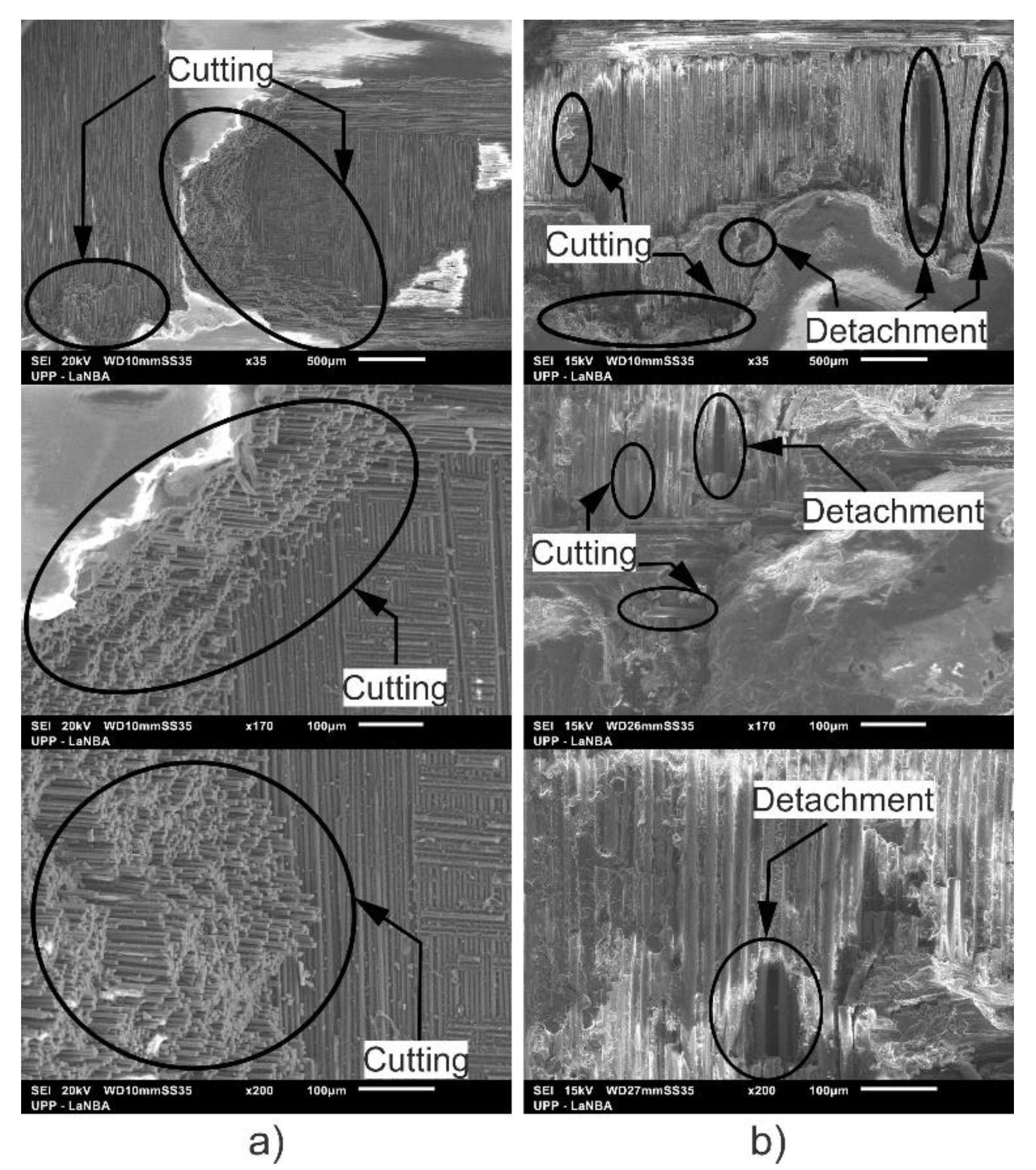
3.2. 3D Optical Microscopy and SEM
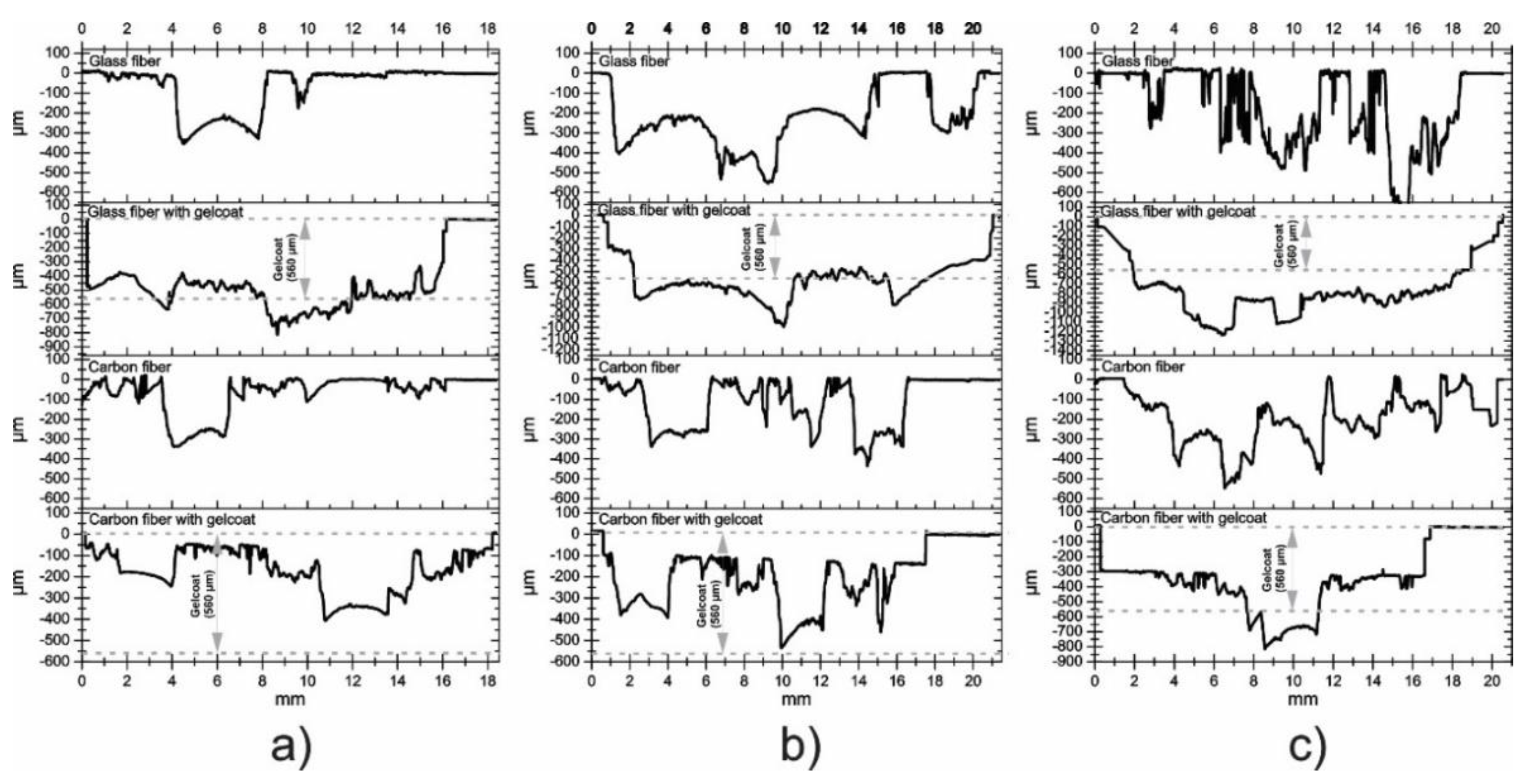
3.3. Volume Loss and Profilometry
4. Conclusions
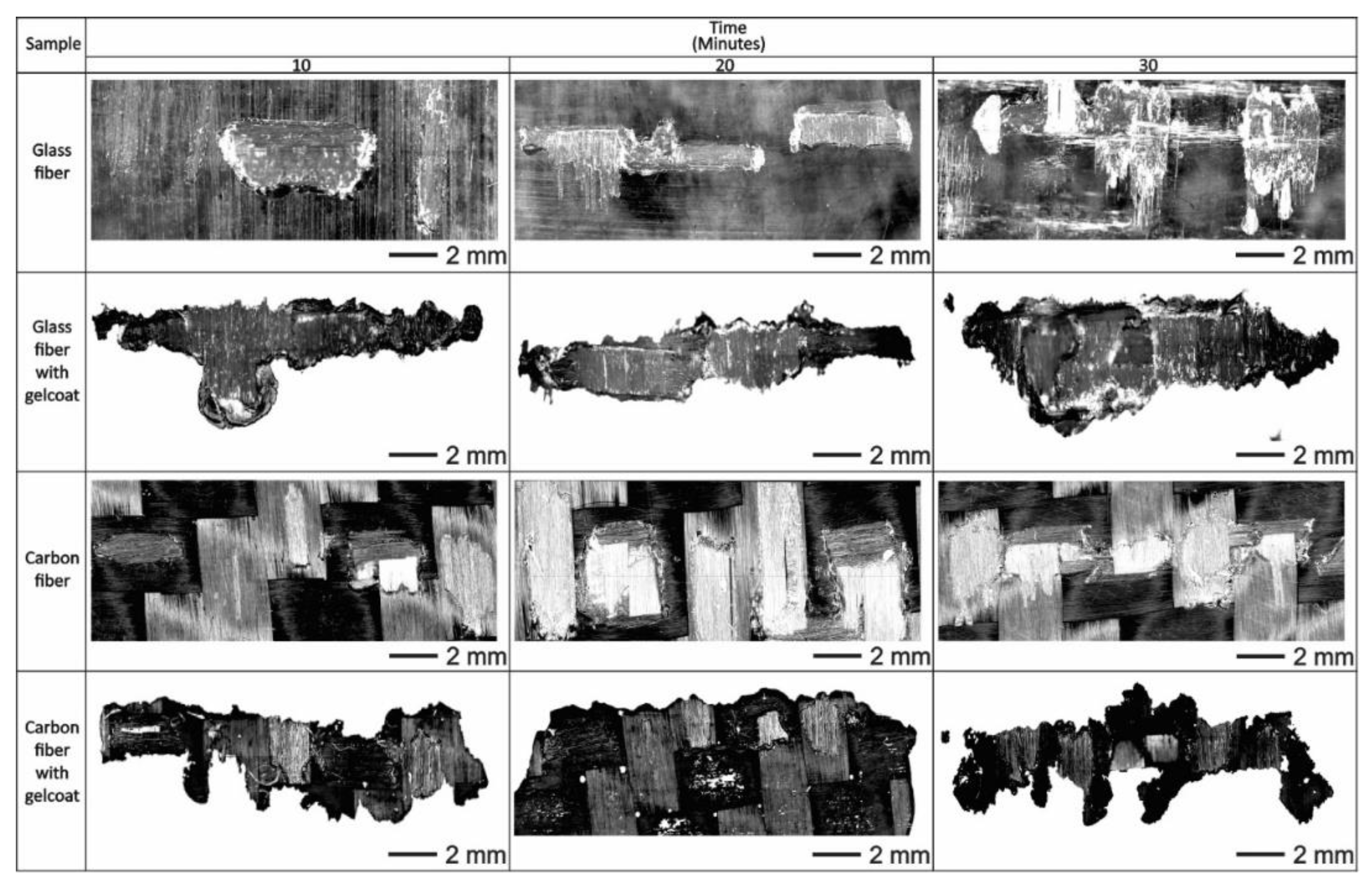
- According to the SEM micrographs, on the eroded zones, it was possible to confirm the presence of cutting action on the fibers, a detachment of the coating and the formation of ridges in the direction of impact, which caused an increase in the surface roughness.
- From optical microscopy, it was observed that the fiberglass presented a deeper wear scar compared to the carbon fiber where less damage was observed, which corresponds to the detachment of the polymer matrix, leaving the fibers exposed. After 30 min of testing, the repeated impacts of the liquid particles caused the presence of cuts in the upper carbon fibers and the accumulation of removed material around the wear trace.
- Under the conditions tested in this research work, the resistance to water jet erosion in glass fiber was lower than in carbon fiber. This is due to the good properties of CFRP such as high stiffness, high tensile strength and high modulus, as well as the excellent interaction between the epoxy matrix and fibers.
- Based on the data obtained, in most of the tests carried out, a linear behavior was observed between the lost volume and the test time, confirming the existence of progressive damage on the surface and concluding that the increase in roughness is proportional to the increase in erosion wear.
- The water jet erosion platform developed for this research work showed a very acceptable performance, applying a constant pressure throughout the tests and generating a uniform wear on the surface of the tested composite materials.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kirols, H.S.; Mahdipoor, M.S.; Kevorkov, D.; Uihlein, A.; Medraj, M. Energy based approach for understanding water droplet erosion. Mater. Des. 2016, 104, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrate, S. Soft impacts on aerospace structures. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2016, 81, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartolome, L.; Julie, T. Prospective challenges in the experimentation of the rain erosion on the leading edge of wind turbine blades. Wind Energy 2019, 22, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendoza, J.M.; Cardenas, E.V.; Perez, A.M.; Ledesma, S.L.; Torres, M.V. Experimental study of temperature erosion tests on bidirectional coated and uncoated composites materials. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.I.; Mamoun, M. Water Droplet Erosion of Wind Turbine Blades: Mechanics, Testing, Modeling and Future Perspectives. Materials 2020, 13, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grundwürmer, M.; Nuyken, O.; Meyer, M.; Wehr, J.; Schupp, N. Sol–gel derived erosion protection coatings against damage caused by liquid impact. Wear 2007, 263, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagol, E.; Reggio, M.; Ilinca, A. Issues concerning roughness on wind turbine blades. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 23, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KWood, R.; Lu, P. Leading edge topography of blades—A critical review. Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop. 2021, 9, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Burson-Thomas, C.B.; Wellman, R.; Harvey, T.J.; Wood, R.J. Water droplet erosion of aeroengine fan blades: The importance of form. Wear 2019, 426, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, D.; Harvey, T.J.; Wellman, R.G.; Wood, R.J. Characterization of rain erosion at ex-service turbofan blade leading edges. Wear 2019, 426, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Carroll, A.; Hardiman, M.; Tobin, E.F.; Young, T.M. Correlation of the rain erosion performance of polymers to mechanical and surface properties measured using nanoindentation. Wear 2018, 412, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slot, H.M.; IJzerman, R.M.; Le Feber, M.; Nord-Varhaug, K.; van der Heide, E. Rain erosion resistance of injection moulded and compression moulded polybutylene terephthalate PBT. Wear 2018, 414, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groucott, S.; Pugh, K.; Zekos, I.; M Stack, M. A Study of Raindrop Impacts on a Wind Turbine Material: Velocity and Impact Angle Effects on Erosion MAPS at Various Exposure Times. Lubricants 2021, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, R.; Dyer, K.; Martin, F.; Ward, C. The increasing importance of leading edge erosion and a review of existing protection solutions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 115, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momber, A.W. Effects of erodent flow energy and local exposure time on the erosion of cement-based composites at high-speed hydro-abrasive flow. Wear 2017, 378, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Dam-Johansen, K.; Nørkjær, S.; Bernad Jr, P.L.; Kiil, S. Erosion of wind turbine blade coatings—Design and analysis objet-based laboratory equipment for performance evaluation. Prog. Org. Coat. 2015, 78, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Dam-Johansen, K.; Bernad Jr, P.L.; Kiil, S. Rain erosion of wind turbine blade coatings using discrete water jets: Effects of water cushioning, substrate geometry, impact distance, and coating properties. Wear 2015, 328–329, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Trevarthen, J.A.; Deng, T.; Bradley, M.S.; Rahatekar, S.S.; Koziol, K.K. Aligned carbon nanotube reinforced high performance polymer composites with low erosive wear. Compos. Part. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2014, 67, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, N.; Natarajan, S.; Kumaresh Babu, S.P.; Siddaramaiah, S.; Lee, J.H. Studies on erosive wear behavior of UHMWPE-filled aramid-epoxy hybrid composites. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2012, 27, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D2583-95. Indentation Hardness of Rigid Plastics by Means of Barcol Impressor; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM G73-10. Standard Test Method for Liquid Impingement Erosion Using Rotating Apparatus; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa, K.; Yamagata, T.; Fujisawa, N. Liquid droplet impingement erosion on groove roughness. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2018, 330, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargmann, H.W. The mechanics of erosion by liquid and solid impact. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1992, 29, 1685–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, N.; Takano, S.; Fujisawa, K.; Yamagata, T. Experiments on liquid droplet impingement erosion on a rough surface. Wear 2018, 398–399, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosato, D.V. Fabricating processes. Reinf. Plast. Handb. Elsevier Sci. 2005, 254–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL-Wazery, M.S.; EL-Elamy, M.I.; Zoalfakar, S.H. Mechanical Properties of Glass Fiber Reinforced Polyester Composites. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Technol. 2017, 14, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakin, R. Relationship between Barcol hardness and flexural modulus degradation of composite sheets subjected to flexural fatigue. Steel Compos. Struct. 2015, 19, 1531–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihtili, H. An experimental investigation of wear of glass fibre-epoxy resin and glass fibre-polyester resin composite materials. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.Q.; Wang, X.T.; Zhu, J.; Qiu, D.H.; Cheng, X.W.; Guan, Q.F. Friction and wear behavior of carbon fiber reinforced brake materials. Front. Mater. Sci. China 2009, 3, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cai, C.L. Friction and Wear Properties of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene Composites. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 284–286, 2380–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, J. ELSI conference: Invited lecture. Wear 1999, 233–235, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.M.; Zheng, S.R.; Zheng, Y.P. Polymer Matrix Composites and Technology, 1st ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sari, N.; Sinmazçelik, T. Erosive wear behaviour of carbon fibre/polyetherimide composites under low particle speed. Mater. Des. 2007, 28, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, U.S.; Harsha, A.P.; Häger, A.M.; Friedrich, K. Solid particle erosion of carbon fibre and glass fibre epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmet, B. Influence of fiber orientation on solid particle erosion of uni/multidirectional carbon fiber/glass fiber reinforced epoxy composites. J. Eng. Tribol. 2016, 231, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Vigneshwaran, S.; Uthayakumar, M.; Arumugaprabu, V. A review on erosion studies of fiber-reinforced polymer composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2017, 36, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahiaoui, M.; Chabert, F.; Paris, J.Y.; Nassiet, V.; Denape, J. Friction, acoustic emission, and wear mechanisms of a PEKK polymer. Tribol. Int. 2019, 132, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fouad, Y.; El-Meniawi, M.; Afifi, A. Erosion behaviour of epoxy based unidirectionl (GFRP) composite materials. Alex. Eng. J. 2011, 50, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patnaik, A.; Satapathy, A.; Mahapatra, S.S. A modeling approach for prediction of erosion behavior of glass fiber-polyester composites. J. Polym. Res. 2008, 15, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, A.; Satapathy, A.; Mahapatra, S.S.; Dash, R.R. A Taguchi approach for investigation of erosion of glass fiber—Polyester composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2008, 27, 871–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, A.; Satapathy, A.; Mantry, S.; Sahoo, A.; Mohanty, T. Erosion wear performance analysis of polyester-GF-granite hybrid composites using the Taguchi method. Procedia Eng. 2012, 38, 1863–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patnaik, A.; Satapathy, A.; Mahapatra, S.S.; Dash, R.R. Parametric optimization erosion wear of polyester-GF-alumina hybrid composites using the Taguchi method. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2008, 27, 1039–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesser, M.B.; Field, J.E. The Impact of Compressible Liquids. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2003, 15, 97–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohardani, O.; Williamson, D.M.; Hammond, D.W. Multiple liquid impacts on polymeric matrix composites reinforced with carbon nanotubes. Wear 2012, 294–295, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, H.; Najafi, S.H.M.; Ashori, A. Mechanical performance of epoxy/carbon fiber laminated composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2014, 33, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurrekoetxea, J.; Agirregomezkorta, A.; Aretxaga, G.; Sarrionandia, M. Impact behavior of carbon fiber/epoxy composite manufactured by vacuum-assisted compression resin transfer molding. J. Compos. Mater. 2012, 46, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcikowski, M.; Królikowski, W. Effect of resin modification on the impact strength of glass-polyester composites. Polimery 2013, 58, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valaker, E.A.; Armada, S.; Wilson, S. Droplet erosion protection coatings for offshore wind turbine blades. Energy Procedia 2015, 80, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Material | Roughness Ra, μm | Hardness Barcol |
|---|---|---|
| Glass fiber | 4.484 | 49 |
| Glass fiber with Gelcoat | 2.731 | 44 |
| Carbon fiber | 2.074 | 50 |
| Carbon fiber with Gelcoat | 3.610 | 44 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mendoza Mendoza, J.C.; Vera Cardenas, E.E.; Lewis, R.; Mai, W.; Avila Davila, E.O.; Martínez Pérez, A.I.; Ledesma Ledesma, S.; Moreno Rios, M. Water Jet Erosion Performance of Carbon Fiber and Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymers. Polymers 2021, 13, 2933. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13172933
Mendoza Mendoza JC, Vera Cardenas EE, Lewis R, Mai W, Avila Davila EO, Martínez Pérez AI, Ledesma Ledesma S, Moreno Rios M. Water Jet Erosion Performance of Carbon Fiber and Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymers. Polymers. 2021; 13(17):2933. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13172933
Chicago/Turabian StyleMendoza Mendoza, Jesus Cornelio, Edgar Ernesto Vera Cardenas, Roger Lewis, William Mai, Erika Osiris Avila Davila, Armando Irvin Martínez Pérez, Saul Ledesma Ledesma, and Marisa Moreno Rios. 2021. "Water Jet Erosion Performance of Carbon Fiber and Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymers" Polymers 13, no. 17: 2933. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13172933
APA StyleMendoza Mendoza, J. C., Vera Cardenas, E. E., Lewis, R., Mai, W., Avila Davila, E. O., Martínez Pérez, A. I., Ledesma Ledesma, S., & Moreno Rios, M. (2021). Water Jet Erosion Performance of Carbon Fiber and Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymers. Polymers, 13(17), 2933. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13172933








