Interactions between Sterically Stabilized Nanoparticles: The Effects of Brush Bidispersity and Chain Stiffness
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Microscopic Model
3. Density Functional Theory
4. Results
4.1. Monodisperse Brush: Flexible Chains
4.2. Monodisperse Brush: Semiflexible Chains
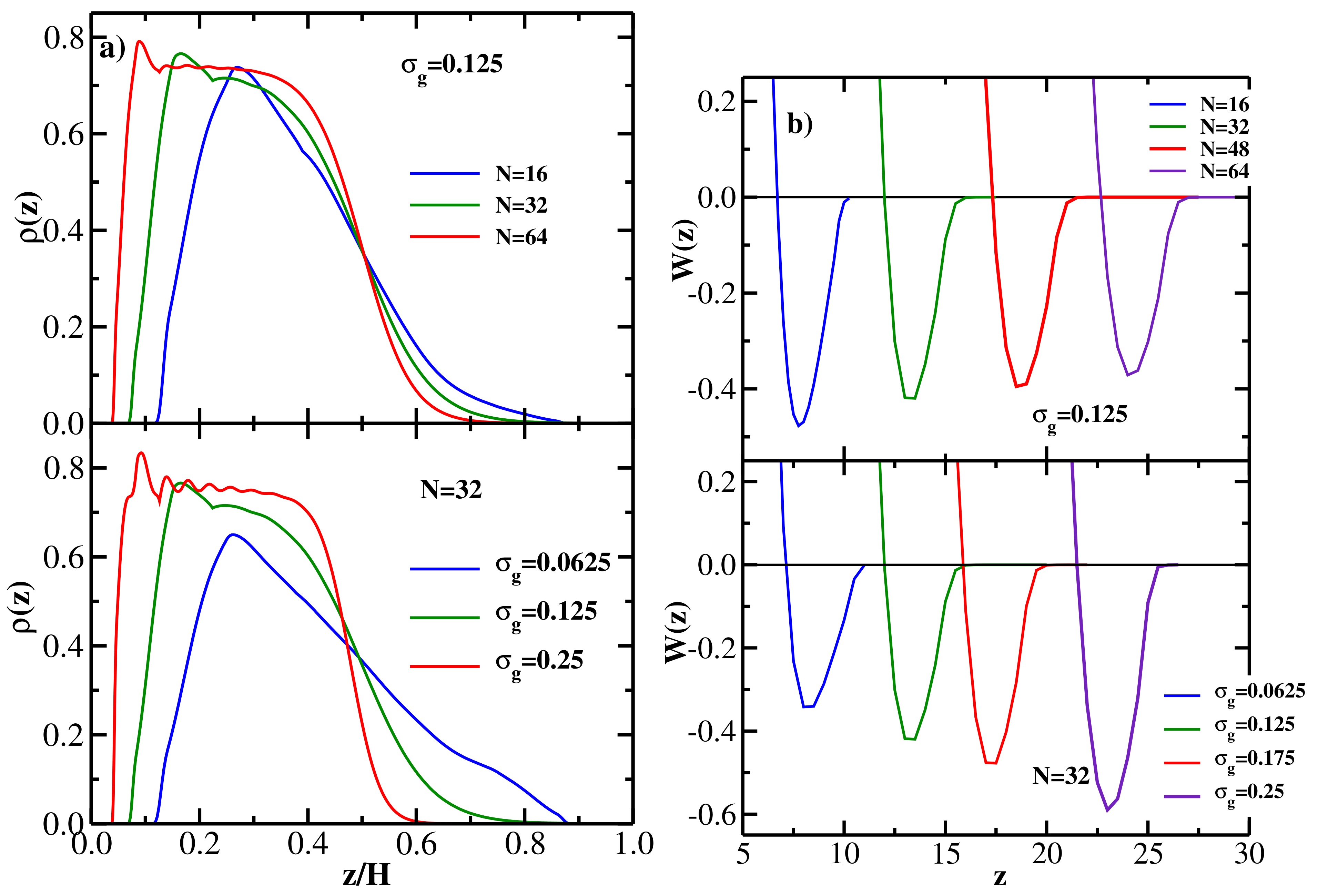
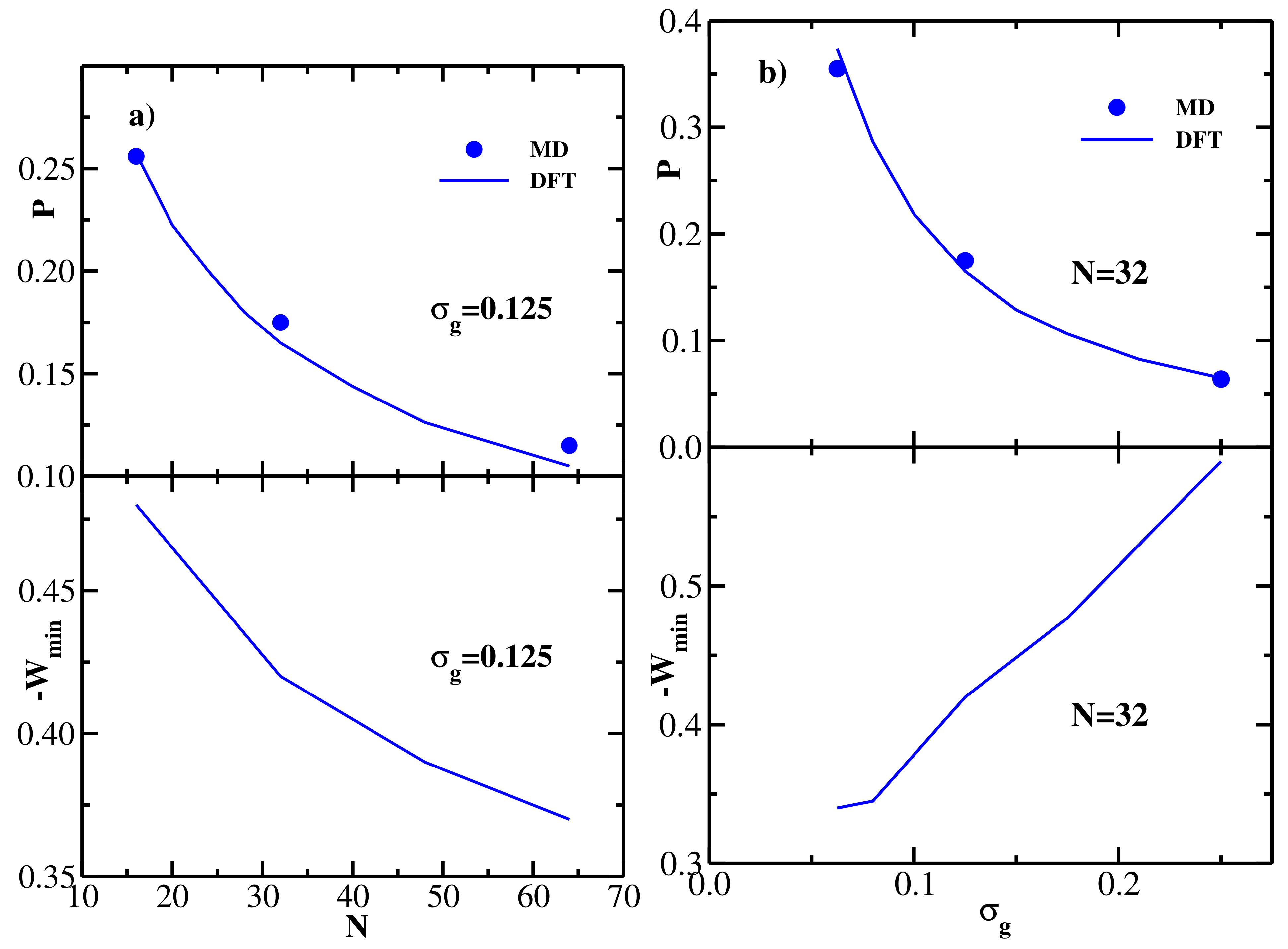
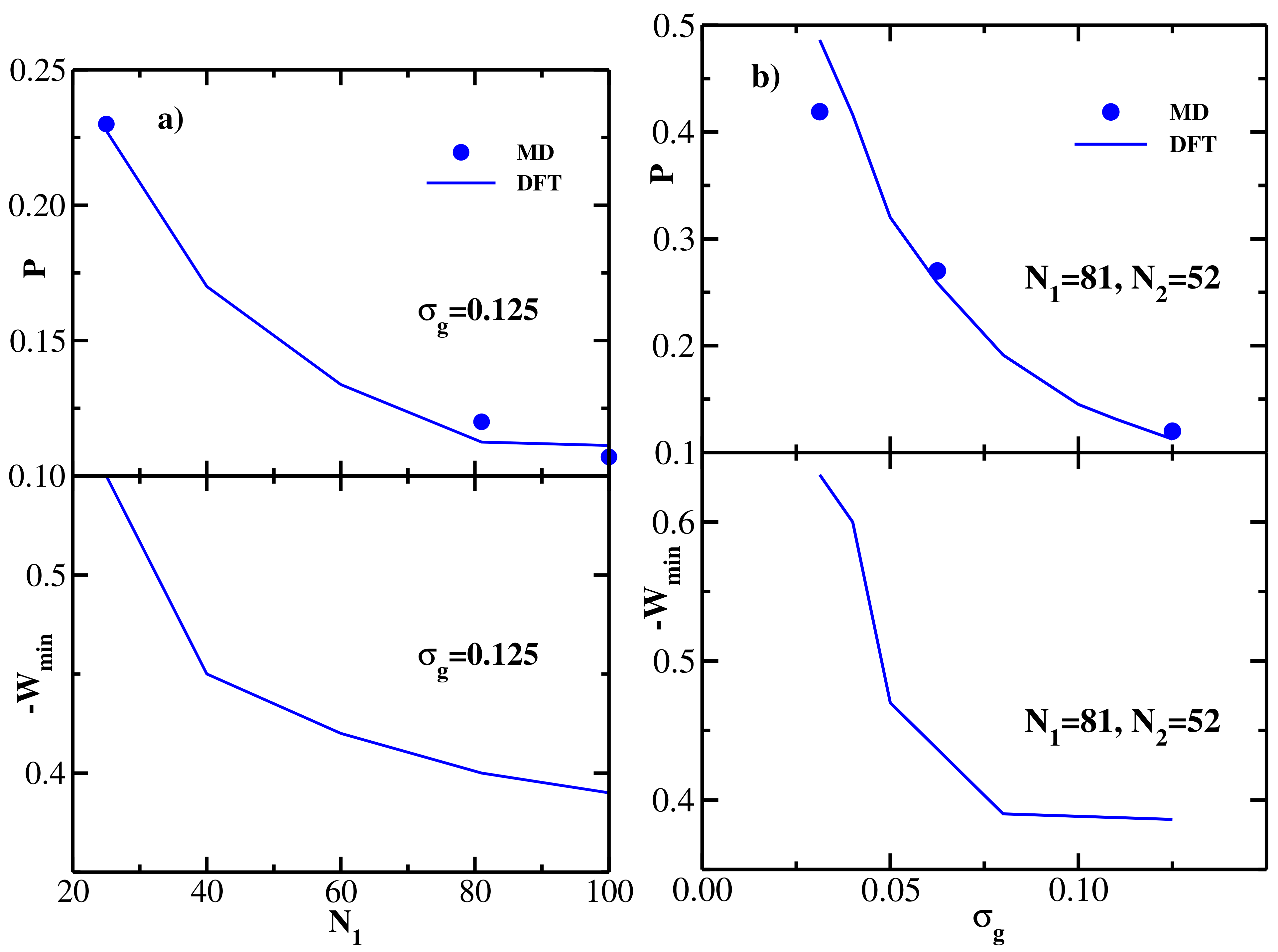
4.3. Bidisperse Brush: Flexible Chains
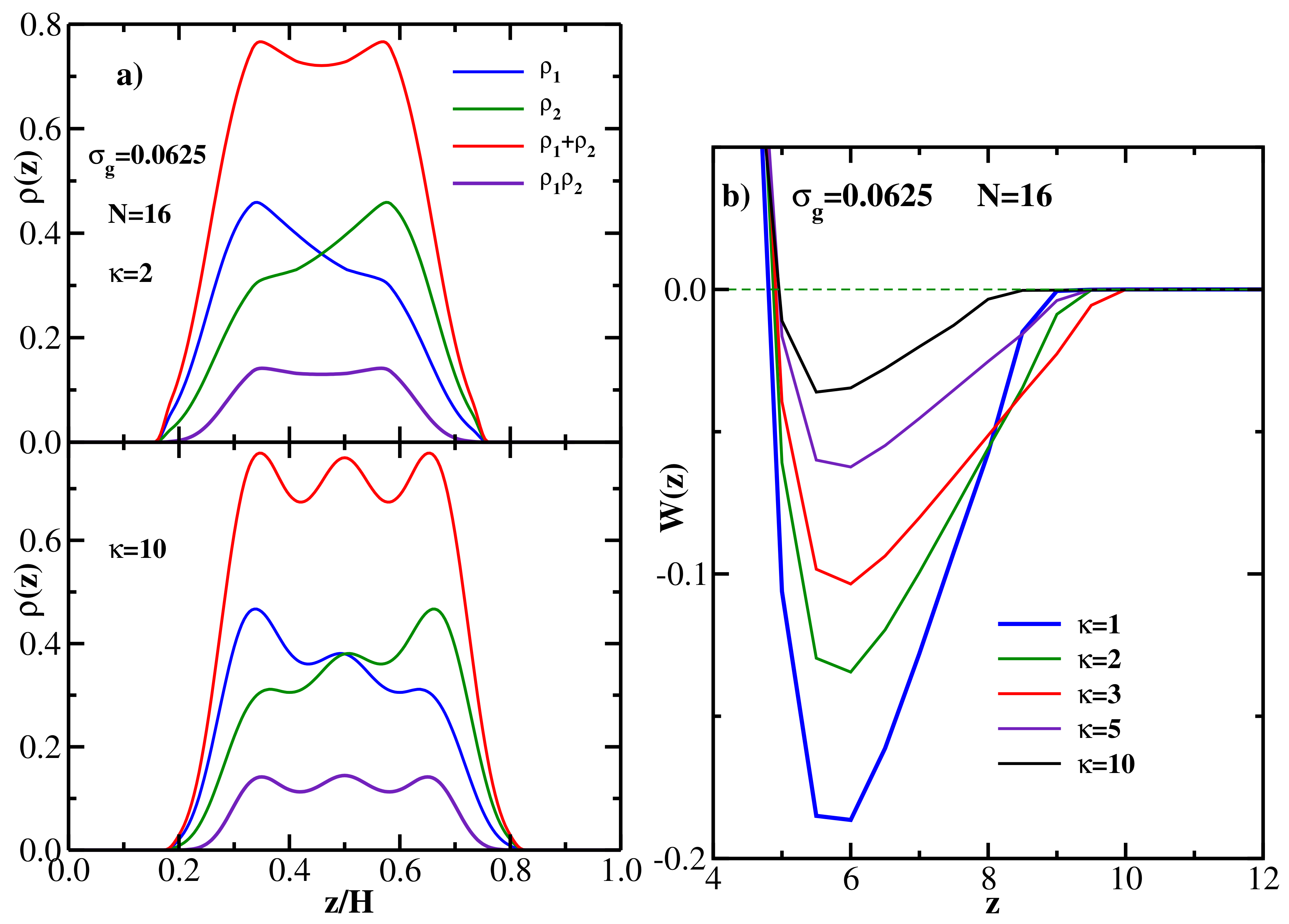
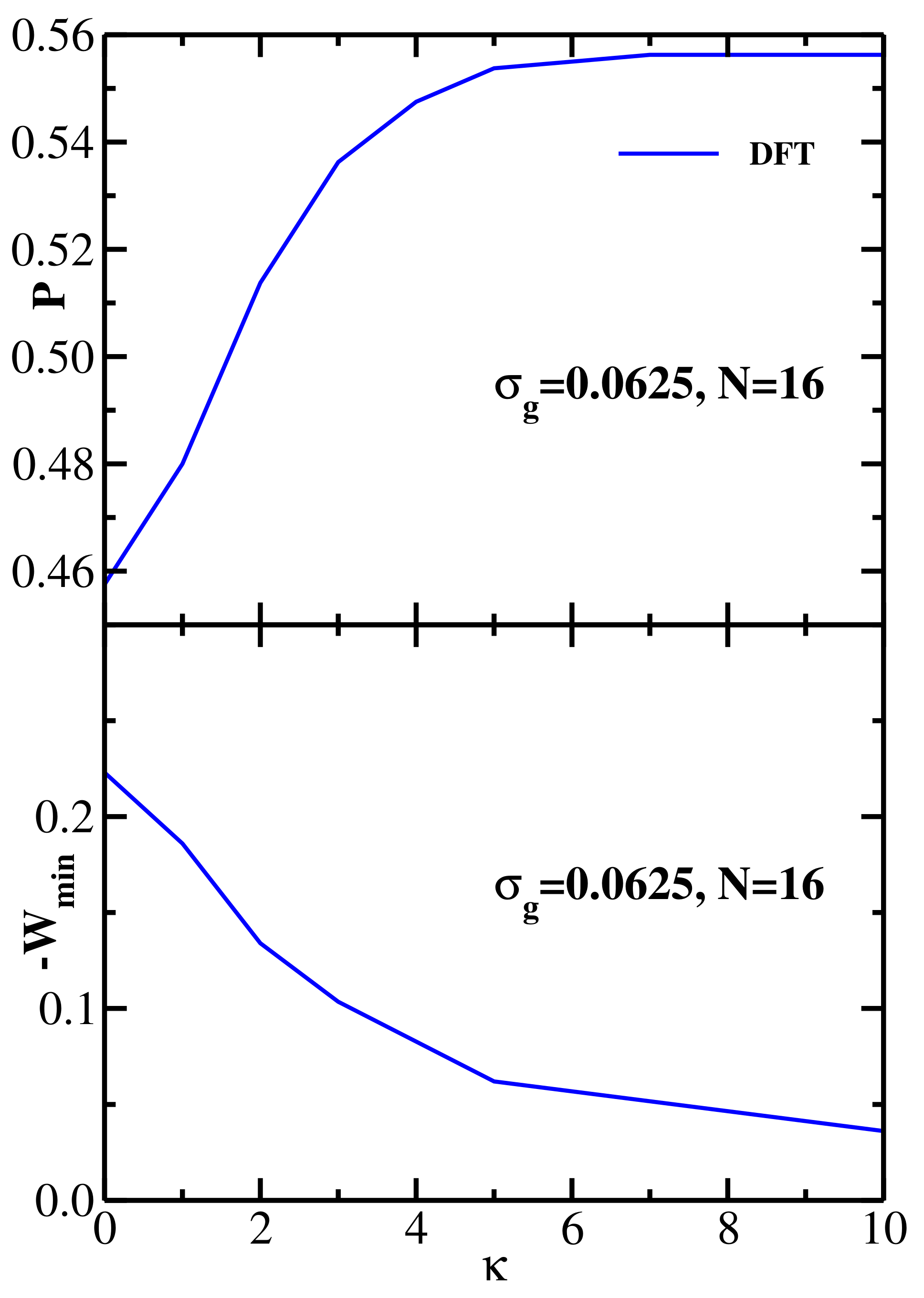
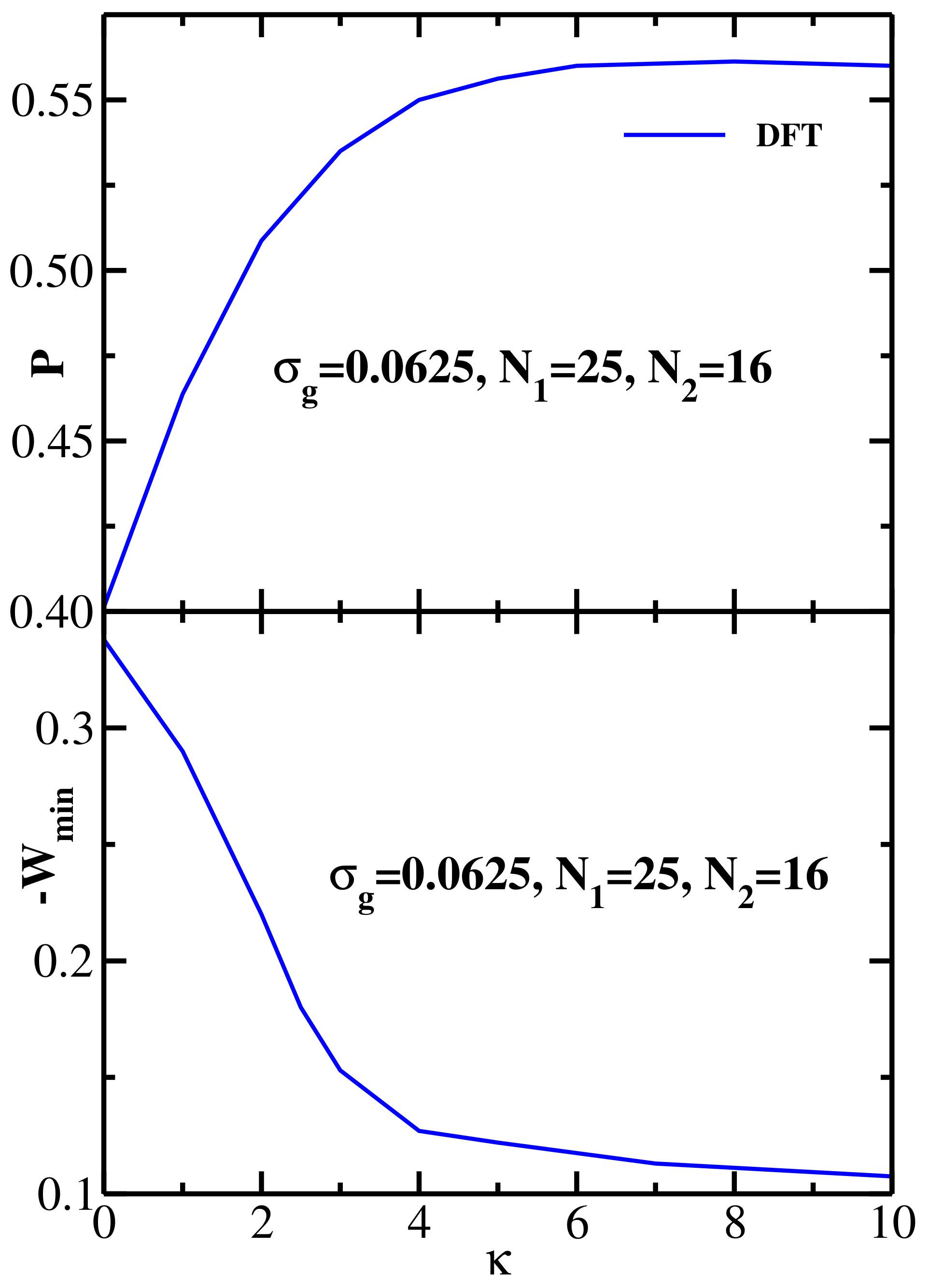
4.4. Bidisperse Brush: Semiflexible Chains
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Napper, D.H. Polymeric Stabilization of Colloid Dispersions; Academic Press: London, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Advincula, R.C.; Brittain, W.J.; Caster, K.C.; Rüehe, J. (Eds.) Polymer Brushes; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Archer, L.A. Nanoscale Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Lubricants. Langmuir 2011, 27, 3083–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleer, G.J.; Stuart, M.A.C.; Scheutjens, J.M.H.M.; Cosgrove, T.; Vincent, B. Polymers at Interfaces; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Akcora, P.; Liu, H.; Kumar, S.K.; Moll, J.; Li, Y.; Benicewicz, B.C.; Schadler, L.S.; Acehan, D.; Panagiotopoulos, A.Z.; Pryamitsyn, V.; et al. Anisotropic self-assembly of spherical polymer-grafted nanoparticles. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEwan, M.E.; Egorov, S.A.; Ilavsky, J.; Green, D.L.; Yang, Y. Mechanical reinforcement of polymer nanocomposites: Theory and ultra-small angle X-ray scattering (USAXS) studies. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 2725–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, V.; Jayaraman, A. Theory and simulation studies of effective interactions, phase behavior and morphology in polymer nanocomposites. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 13–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, D.I.; Milchev, A.; Binder, K. Polymer brushes in solvents of variable quality: Molecular dynamics simulations using explicit solvent. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 127, 084905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Woodward, C.E.; Forsman, J. Theoretical Predictions of Temperature-Induced Gelation in Aqueous Dispersions Containing PEO-Grafted Particles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 3969–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egorov, S.A.; Binder, K. Effect of solvent quality on the dispersibilty of polymer-grafted spherical nanoparticles in polymer solutions. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 137, 094901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorov, S.A. Insertion of nanoparticles into polymer brush under variable solvent conditions. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 137, 134905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LoVerso, F.; Egorov, S.A.; Binder, K. Interactions between brush-coated spherical nanoparticles: Effect of solvent quality. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 8892–8902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.B.; Jayaraman, A. Identifying the Ideal Characteristics of the Grafted Polymer Chain Length Distribution for Maximizing Dispersion of Polymer Grafted Nanoparticles in a Polymer Matrix. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 9144–9150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulshreshtha, A.; Jayaraman, A. Dispersion and Aggregation of Polymer Grafted Particles in Polymer Nanocomposites Driven by the Hardness and Size of the Grafted Layer Tuned by Attractive Graft-Matrix Interactions. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 1302–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.Y.; Koch, D.L. Structure of Solvent-Free Nanoparticle-Organic Hybrid Materials. Langmuir 2010, 26, 16801–16811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.H.; Li, S.; Fang, Y.; Chen, Z.D.; Alyas, M.; Liu, J.; Zeng, X.F.; Zhang, L.Q. Mechanical and Self-Healing Behavior of Matrix-Free Polymer Nanocomposites Constructed via Grafted Graphene Nanosheets. Langmuir 2020, 36, 7427–7438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.L.; Chiou, C.S.; Kumar, S.K.; Lin, J.J.; Sheng, Y.J.; Tsao, H.K. Self-Assembled Superstructures of polymer-grafted nanoparticles: Effects of particle shape and matrix polymer. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Choudhury, S.; Archer, L.A. A highly conductive, non-flammable polymer-nanoparticle hybrid electrolyte. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 20800–20809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.P.; Yang, T.H.; Wang, K.; Fan, H.W.; Houm, C.Y.; Zhang, Q.H.; Li, Y.G.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.Z. Mechanical design of brush coating technology for the alignment of one-dimension nanomaterials. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 2021, 583, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, P.; Kim, S.A.; Archer, L.A. Crowded, Confined, and Frustrated: Dynamics of Molecules Tethered to Nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 258301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.Y.; Srivastava, S.; Archer, L.A.; Koch, D.L. Structure factor of blends of solvent-free nanoparticle-organic hybrid materials: Density-functional theory and small angle X-ray scattering. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 9120–9135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Wenning, B.M.; Choudhury, S.; Archer, L.A. Interactions, Structure, and Dynamics of Polymer-Tethered Nanoparticle Blends. Langmuir 2016, 32, 8698–8708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.Y.; Koch, D.L. Self-diffusion and linear viscoelasticity of solvent-free nanoparticle-organic hybrid materials. J. Rheol. 2014, 58, 369–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riest, J.; Athanasopoulou, L.; Egorov, S.A.; Likos, C.N.; Ziherl, P. Elasticity of polymeric nanocolloidal particles. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Midya, J.; Rubinstein, M.; Kumar, S.K.; Nikoubashman, A. Structure of Polymer-Grafted Nnaoparticle Melts. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 15505–15516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.Y.; Yu, H.Y. Structural and Dynamical Coupling in Solvent-Free Polymer Brushes Elucidated by Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Langmuir 2021, 37, 3331–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tao, P.; Viswanath, A.; Benicewicz, B.C.; Schadler, L.S. Bimodal Surface Ligand Engineering: The Key to Tunable Nanocomposites. Langmuir 2013, 29, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, N.; Wentzel, N.; Jayaraman, A. Effect of bidispersity in grafted chain length on grafted chain conformations and potential of mean force between polymer grafted nanoparticles in a homopolymer matrix. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 198, 194906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, E.K.; Gast, A.P. Self-consistent field calculations of interactions between chains tethered to spherical interfaces. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgouros, A.P.; Revelas, C.J.; Lakkas, A.T.; Theodorou, D.N. Potential of Mean Force between Bare or Grafted Silica/Polystyrene Surfaces from Self-Consistent Field Theory. Polymers 2021, 13, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaraman, A.; Schweizer, K.S. Effective Interactions, Structure, and Phase Behavior of Lightly Tethered Nanoparticles in Polymer Melts. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 9430–9438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, A.; Schweizer, K.S. Effective interactions and self-assembly of hybrid polymer-grafted nanoparticles in a homopolymer matrix. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 8423–8434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabani, E.; Egorov, S.A. Solvophobic and solvophilic effects on the potential of mean force between two nanoparticles in binary mixtures. Nanoletters 2002, 2, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabani, E.; Egorov, S.A. Integral equation theory for the interactions between passivated nanocrystals in supercritical fluids: Solvophobic and solvophilic cases. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 6771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Egorov, S.A. Dispersing nanotubes with surfactants: A microscopic statistical mechanical analysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 14124–14125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, C.H.; Pan, G.T.; Yu, H.Y. Entropic Effects in Solvent-Free Bidisperse Polymer Brushes Investigated Using Density Functional Theories. Langmuir 2019, 35, 16835–16849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palli, B.; Padmanabhan, V. Chain flexibility for tuning effective interactions in blends of polymers and polymer-grafted nanoparticles. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 6777–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.X.; Zheng, Z.J.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.P.; Zhang, L.Q. Tuning the Mechanical Properties of Polymer Nanocomposites Filled with Grafted Nanoparticles by Varying the Grafted Chain Length and Flexibility. Polymers 2016, 8, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Egorov, S.A.; Hsu, H.P.; Milchev, A.; Binder, K. Semiflexible Polymer Brushes and Brush-Mushroom Crossover. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 2604–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egorov, S.A.; Milchev, A.; Binder, K. Anomalous fluctuations of nematic order in solutions of semiflexible polymers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 187801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egorov, S.A.; Milchev, A.; Virnau, P.; Binder, K. A New Insight into the Isotropic—Nematic phase transition in lyotropic solutions of semiflexible polymers: Density-Functional Theory tested by Molecular Dynamics. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 4944–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.P.; Paul, W.; Binder, K. Standard Definitions of Persistence Length Do Not Describe the Local “Intrinsic” Stiffness of Real Polymer Chains. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 3094–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R. Nature of the liquid-vapor interface and other topics in the statistical-mechanics of nonuniform, classical fluids. Adv. Phys. 1979, 28, 143–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R. Density functionals in the theory of nonuniform fluids. In Fundamentals of Inhomogeneous Fluids; Henderson, D., Ed.; Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1992; Chapter 3; p. 85. [Google Scholar]
- Egorov, S.A. Effect of repulsive and attractive interactions on depletion forces in colloidal suspensions: A density functional theory treatment. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 70, 031402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chubak, I.; Likos, C.N.; Egorov, S.A. Multiscale Approaches for Confined Ring Polymer Solutions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 4910–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodward, C.E. A density functional theory for polymers: Application to hard chain-hard sphere mixtures in slitlike pores. J. Chem. Phys. 1991, 94, 3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorov, S.A. Interactions between nanoparticles in supercritical fluids: From repulsion to attraction. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 72, 010401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorov, S.A. Interactions between polymer brushes in solvents of variable quality: A density functional theory study. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 129, 064901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wertheim, M.S. Thermodynamic perturbation theory of polymerization. J. Chem. Phys. 1987, 87, 7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, R. Fundamental measure theory for hard-sphere mixtures: A review. J. Phys. Cond. Matt. 2010, 22, 063102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turesson, M.; Forsman, J.; Akesson, T. Simulations and density functional calculations of surface forces in the presence of semiflexible polymers. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 76, 021801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; MacDowell, L.G.; Yethiraj, A. Short chains at surfaces and interfaces: A quantitative comparison between density-functional theories and Monte-Carlo simulations. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 118, 2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Egorov, S.A. Interactions between nanocolloidal particles in polymer solutions: Effect of attractive interactions. J. Chem. Phys. 2005, 123, 144916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, S.; Boda, D.; Henderson, D.; Sokolowski, S. Density functional theory and the capillary evaporation of a liquid in a slit. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 2000, 227, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorov, S.A.; Milchev, A.; Virnau, P.; Binder, K. Semiflexible polymers under good solvent conditions interacting with repulsive walls. J. Chem. Phys. 2016, 144, 174902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Striolo, A.; Egorov, S.A. Interactions between Sterically Stabilized Spherical Colloidal Particles: Implicit and Explicit Solvent. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 126, 014902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egorov, S.A.; Milchev, A.; Nikoubashman, A.; Binder, K. Phase Separation and Nematic Order in Lyotropic Solutions: Two Types of Polymers with Different Stiffnesses in a Common Solvent. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 956–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egorov, S.A.; Binder, K. When does Wenzel’s extension of Young’s equation for the contact angle of droplets apply? A density functional study. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 152, 194707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egorov, S.A.; Stephens, M.D.; Skinner, J.L. Absorption line shapes and solvation dynamics of CH3I in supercritical Ar. J. Chem. Phys. 1997, 107, 10485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.; Nikoubashman, A.; Leibler, L.; Rubinstein, M.; Midya, J.; Kumar, S.K. Gas Transport in Interacting Planar Brushes. ACS Polym. Au 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milchev, A.; Egorov, S.A.; Nikoubashman, A.; Binder, K. Nematic order in solutions of semiflexible polymers: Hairpins, elastic constants, and the nematic-smectic transition. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 149, 174909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milchev, A.; Egorov, S.A.; Binder, K. Absorption/expulsion of oligomers and linear macromolecules in a polymer brush. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 184905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, R.J.; Poling-Skutvik, R.; Howard, M.P.; Nikoubashman, A.; Egorov, S.A.; Conrad, J.C.; Palmer, J.C. Influence of polymer flexibility on nanoparticle dynamics in semidilute solutions. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 1260–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.B.; Huang, W.M. On the origin of the Vogel-Fulcher-Tammann law in the thermo-responsive shape memory effect of amorphous polymers. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 105021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Egorov, S.A. Interactions between Sterically Stabilized Nanoparticles: The Effects of Brush Bidispersity and Chain Stiffness. Polymers 2021, 13, 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13142296
Egorov SA. Interactions between Sterically Stabilized Nanoparticles: The Effects of Brush Bidispersity and Chain Stiffness. Polymers. 2021; 13(14):2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13142296
Chicago/Turabian StyleEgorov, Sergei A. 2021. "Interactions between Sterically Stabilized Nanoparticles: The Effects of Brush Bidispersity and Chain Stiffness" Polymers 13, no. 14: 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13142296
APA StyleEgorov, S. A. (2021). Interactions between Sterically Stabilized Nanoparticles: The Effects of Brush Bidispersity and Chain Stiffness. Polymers, 13(14), 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13142296




