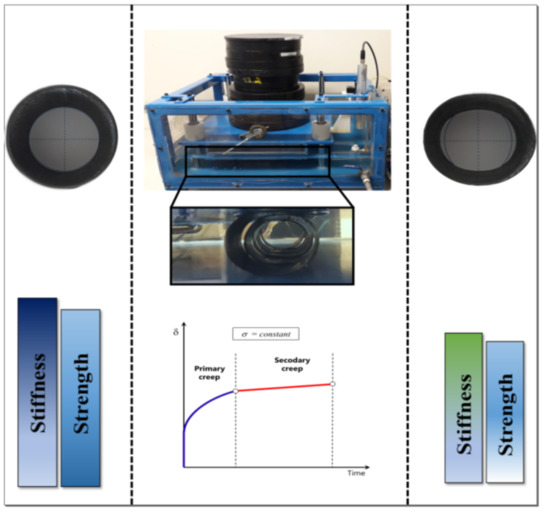
Creep and Residual Properties of Filament-Wound Composite Rings under Radial Compression in Harsh Environments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Manufacturing
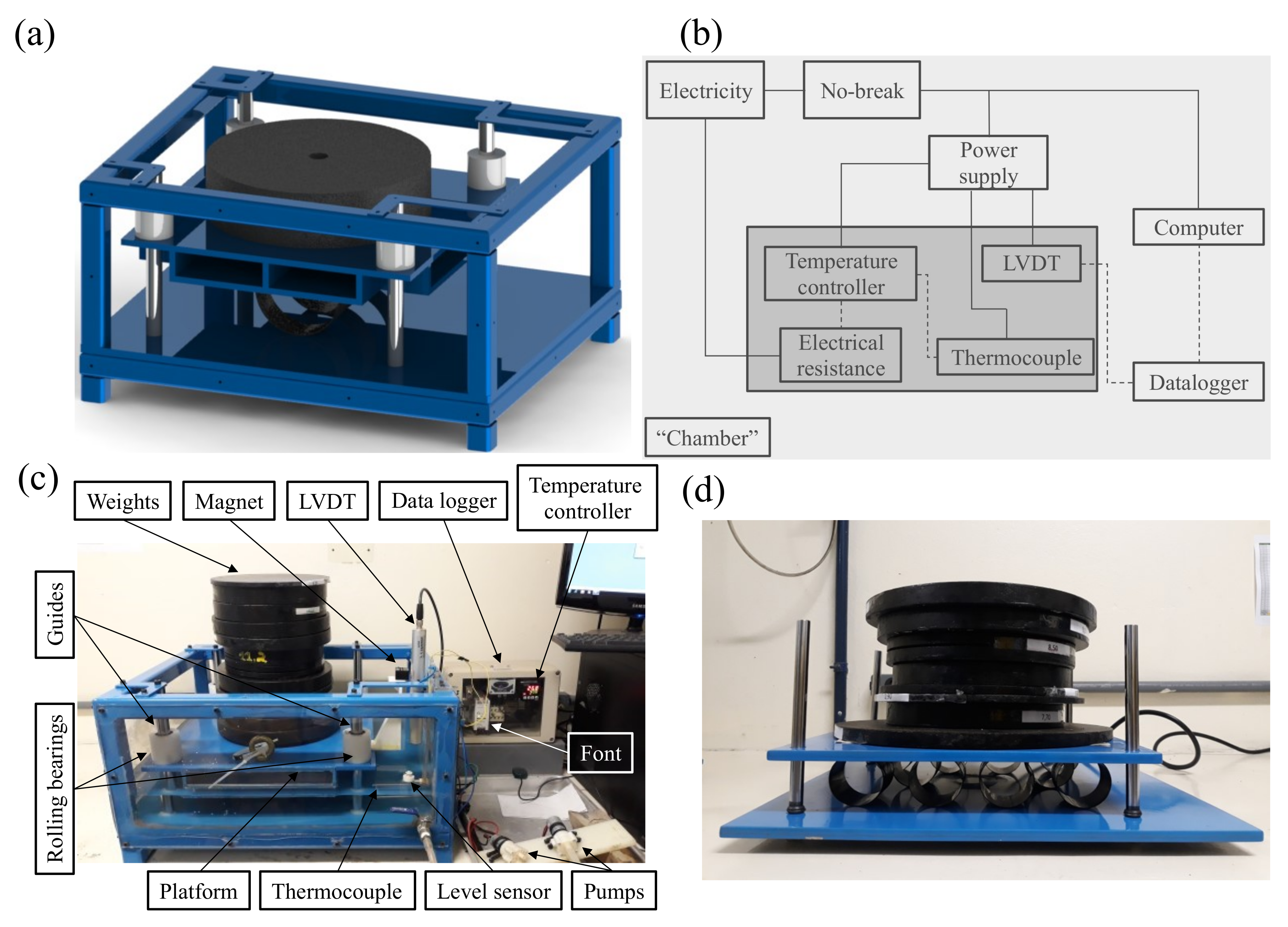
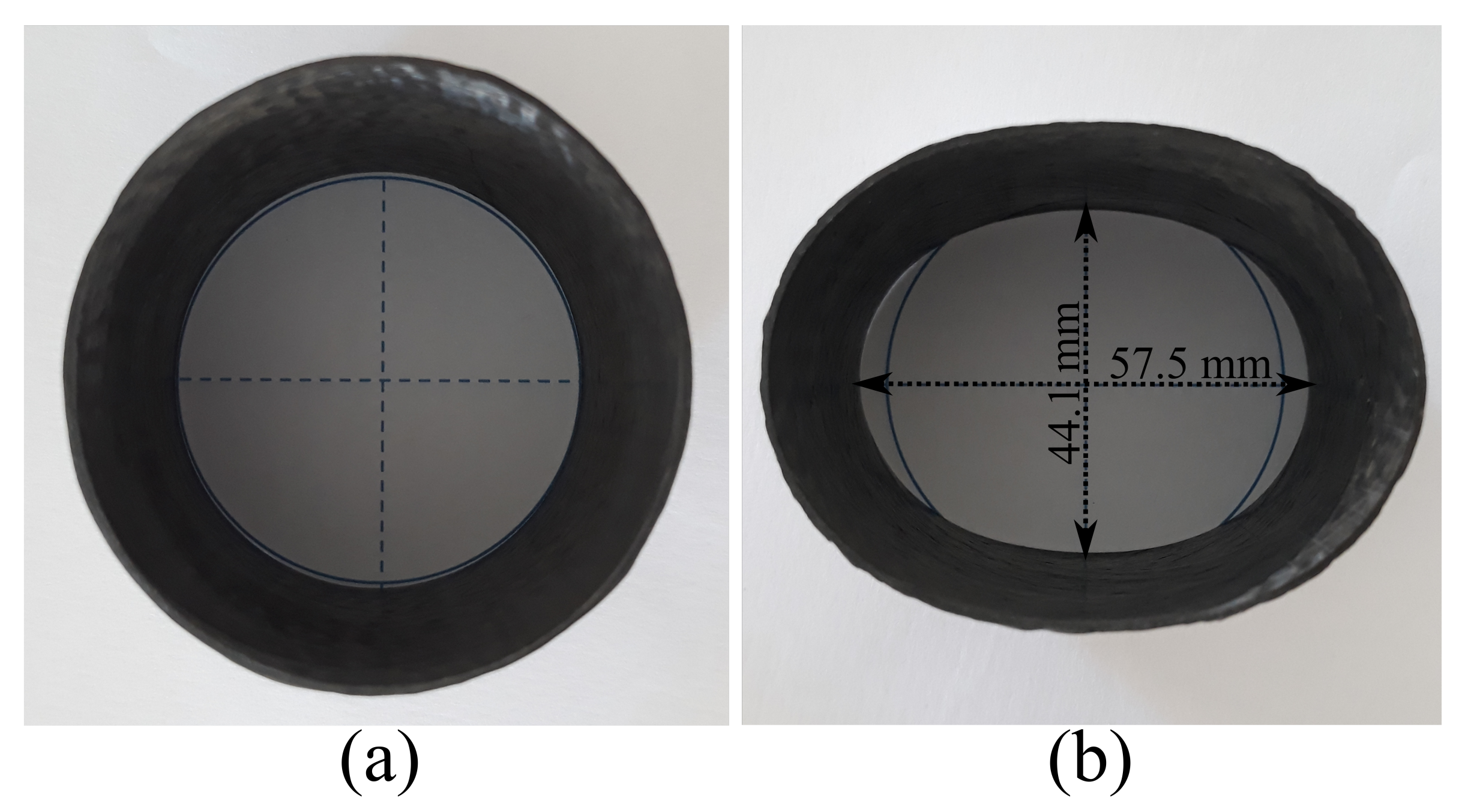
2.2. Design of the Creep Equipment
2.3. Water Uptake Determination
2.4. Thermal and Dynamical-Mechanical Analysis
2.5. Creep: Testing and Modeling
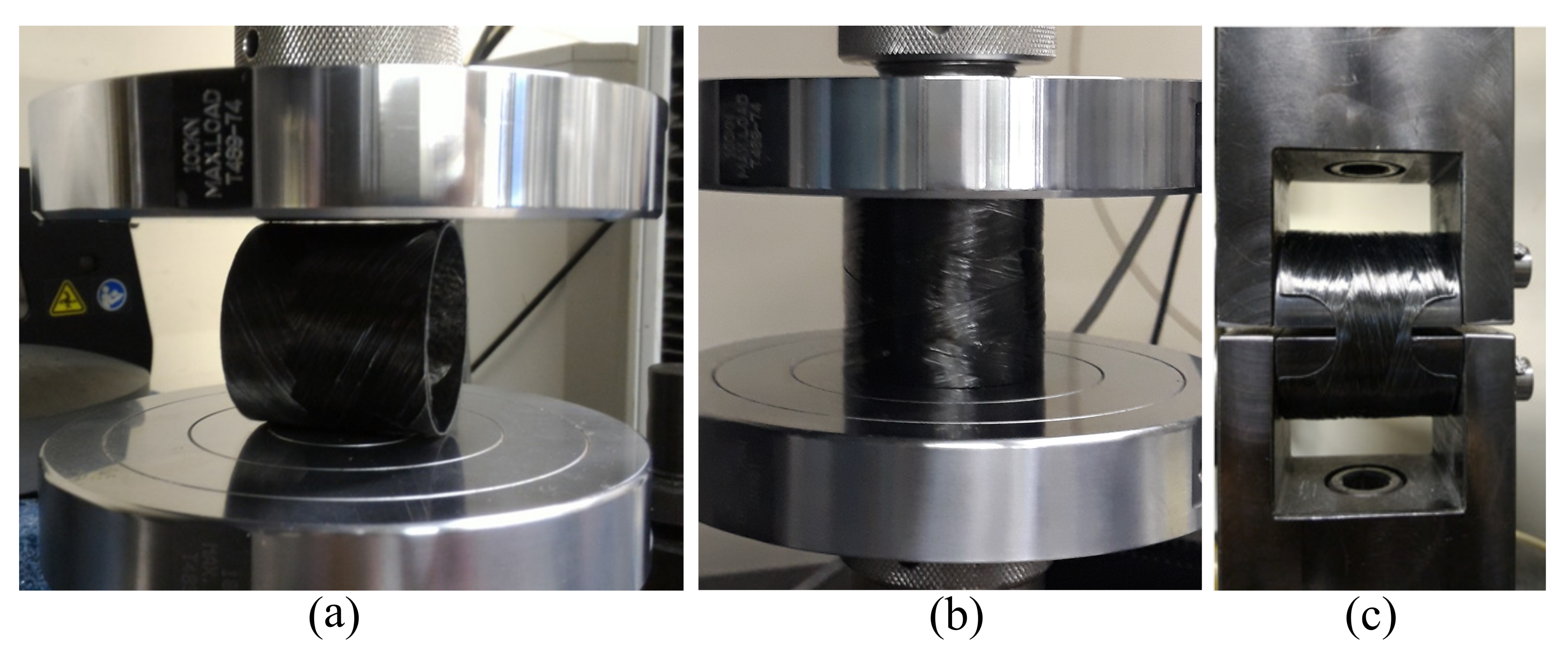
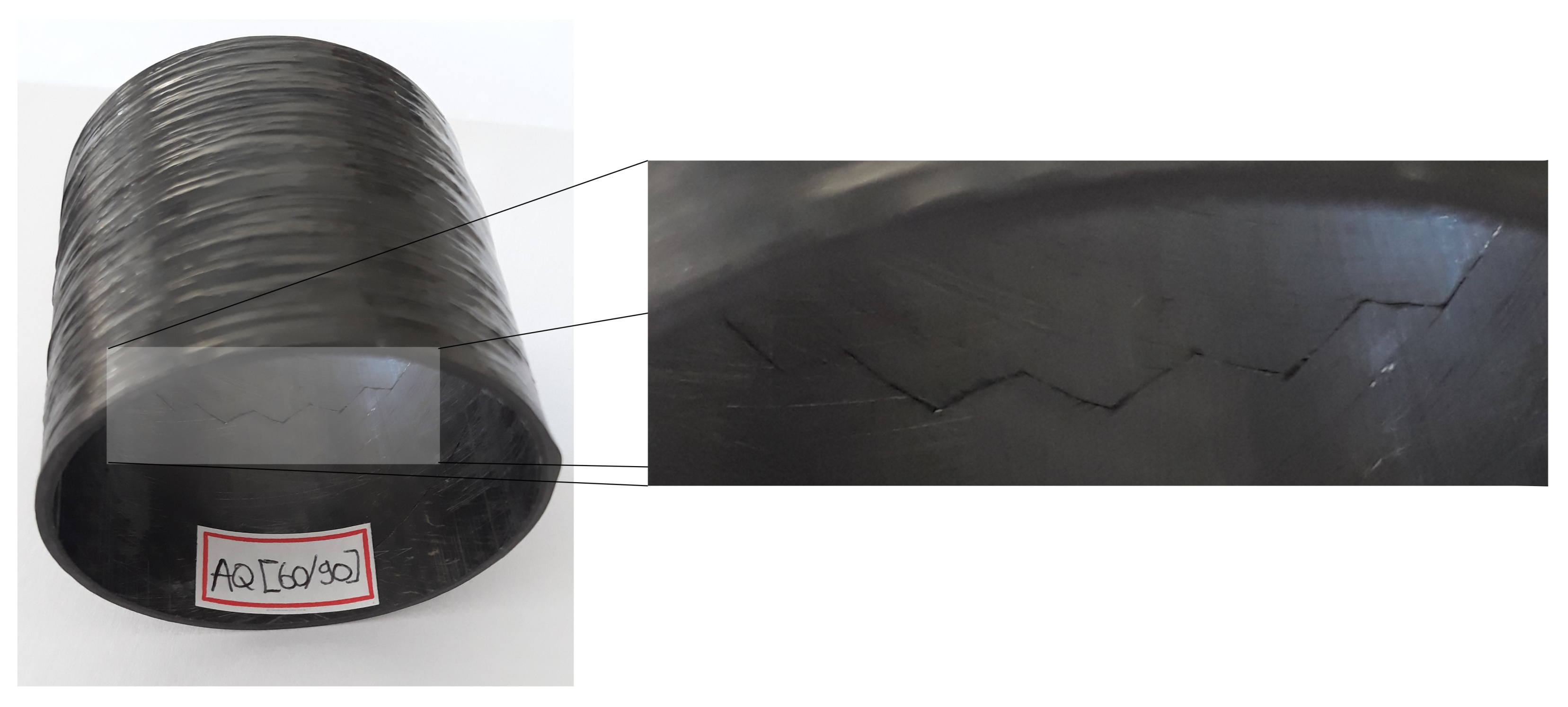
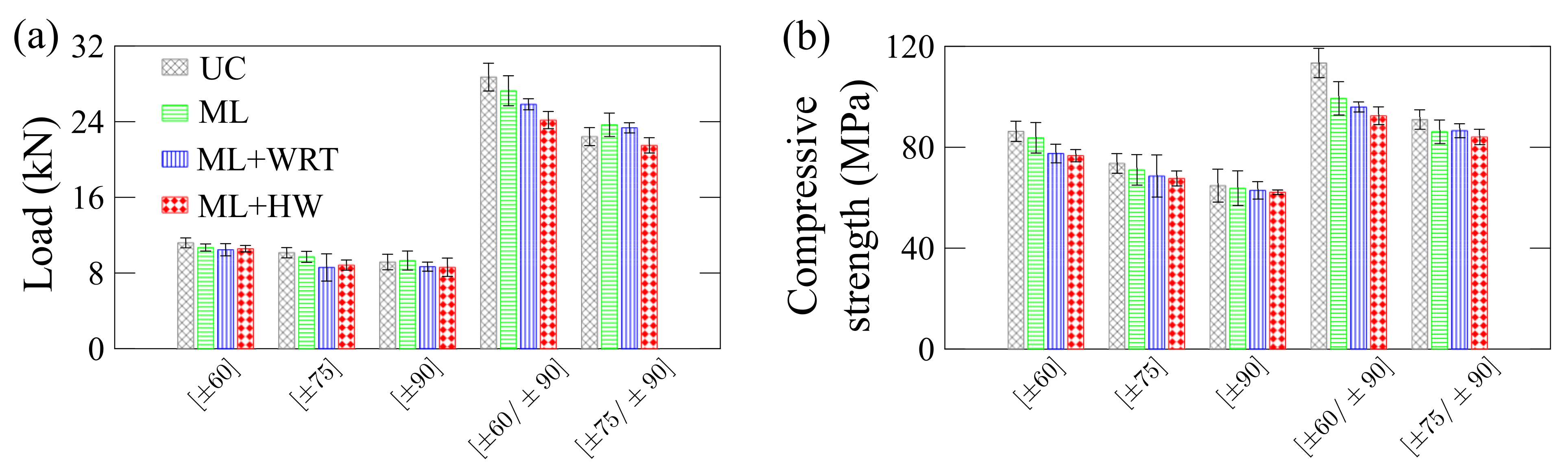
2.6. Post-Creep Residual Properties
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Towpreg Curing Investigation
3.2. Water Uptake
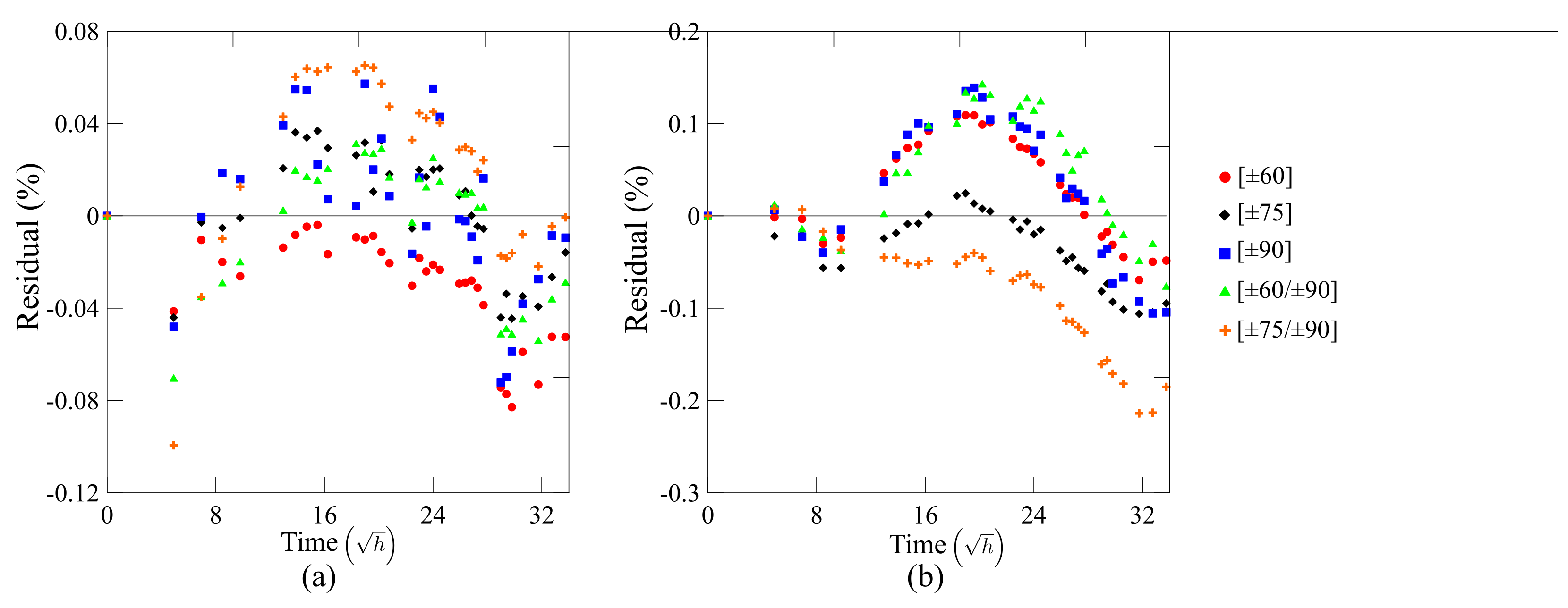
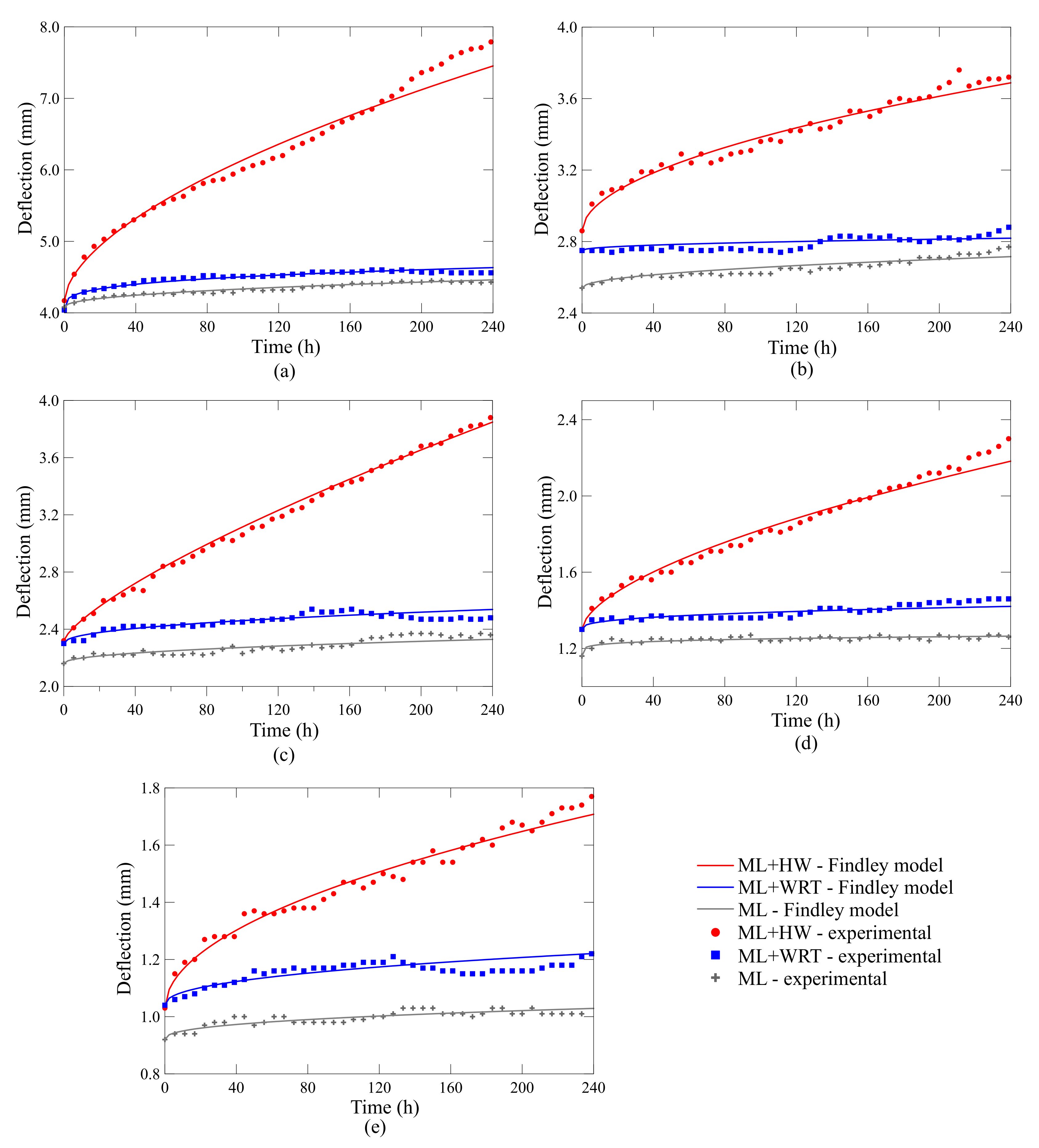
3.3. Creep Performance
3.4. Residual Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lan, X.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Len, J.J. Thermomechanical properties and deformation behavior of a unidirectional carbon-fiber-reinforced shape memory polymer composite laminate. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 222, 1109284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida Jr., J.H.S.; Lorandi, N.P.; Bregolin, B.P.; Ornaghi, H.L., Jr.; Amico, S.C. Creep and interfacial behavior of carbon fiber reinforced epoxy filament wound laminates. Polym. Compos. 2018, 34, E2199–E2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Almeida Jr., J.H.S.; St-Pierre, L.; Wang, Z.; Castro, S.G.P. Reliability-based buckling optimization with an accelerated Kriging metamodel for filament-wound variable angle tow composite cylinders. Compos. Struct. 2020, 254, 112821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornaghi, H.L., Jr.; Neves, R.M.; Monticeli, F.M.; Almeida Jr., J.H.S. Viscoelastic characteristics of carbon fiber-reinforced epoxy filament wound laminates. Compos. Commun. 2020, 21, 100418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida Jr., J.H.S.; Souza, S.D.B.; Botelho, E.C.; Amico, S.C. Carbon fiber-reinforced epoxy filament-wound composite laminates exposed to hygrothermal conditioning. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 51, 4697–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guedes, R.M. A systematic methodology for creep master curve construction using the stepped isostress method (SSM): A numerical assessment. Mech. Time-Depend. Mater. 2018, 22, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohmyoh, H.; Ito, Y.; Eguchi, K.; Daido, W.; Utsunomiya, J.; Nakano, Y. Creep behavior of glass-fiber-reinforced nylon 6 products. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 4213–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornaghi, H.L., Jr.; Almeida Jr., J.H.S.; Monticeli, F.M.; Neves, R.M.; Cioffi, M.O.H. Time-temperature behavior of carbon/epoxy laminates under creep loading. Mech. Time-Depend. Mater. [CrossRef]
- Almeida Jr., J.H.S.; Ornaghi, H.L., Jr.; Lorandi, N.P.; Marinucci, G.; Amico, S.C. On creep, recovery, and stress relaxation of carbon fiber-reinforced epoxy filament wound composites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2018, 58, 1837–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, H.; Guedes, R.M. Long-term behaviour of GFRP pipes: Reducing the prediction test duration. Polym. Test. 2010, 29, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merah, N.; Nizamuddin, S.; Khan, Z.; Al-Sulaiman, F.; Mehdi, M. Effects of harsh weather and seawater on glass fiber reinforced epoxy composite. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2010, 29, 3104–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farshad, M.; Necola, A. Effect of aqueous environment on the long-term behavior of glass fiber-reinforced plastic pipes. Polym. Test. 2004, 23, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, R.M.; Sá, A.; Faria, H. On the prediction of long-term creep-failure of GRP pipes in aqueous environment. Polym. Compos. 2010, 31, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, H.; Ma, X.; Shang, F.; Ma, Y.; Shao, Z.; Hou, D. Flexural creep tests and long-term mechanical behavior of fiber-reinforced polymeric composite tubes. Compos. Struct. 2018, 193, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, M.W.; Jellison, B.D.; Ellison, T. Moisture effects on the thermal and creep performance of carbon fiber/epoxy composites for structural pipeline repair. Compos. B Eng. 2013, 45, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CADWIND User Manual—MATERIAL SA, 2007. Available online: https://www.material.be/cadwind/intro/ (accessed on 27 November 2020).
- Almeida Jr., J.H.S.; Ribeiro, M.L.; Tita, V.; Amico, S.C. Damage modeling for carbon fiber/epoxy filament wound composite tubes under radial compression. Compos. Struct. 2017, 160, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, Y.; Sun, L. Effect of temperature and cyclic hygrothermal aging on the interlaminar shear strength of carbon fiber/bismaleimide (BMI) composite. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 4341–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.H.; Springer, G.S. Moisture Absorption and Desorpition of Composite Materials. J. Compos. Mater. 1976, 10, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, R.M.; Sá, A.; Faria, H. Influence of moisture absorption on creep of GRP composite pipes. Polym. Test. 2007, 26, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, P.; Silva, M.; Santos, P.; Parente, J.; Bezazi, A. Viscoelastic behaviour of composites with epoxy matrix filled by cork powder. Compos. Struct. 2020, 234, 111669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.W.; Lai, J.S.; Zureick, A.H. Creep Behavior of Fiber-Reinforced Polymeric Composites: A Review of the Technical Literature. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 1995, 14, 588–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggers, F.; Almeida Jr., J.H.S.; Azevedo, C.B.; Amico, S.C. Mechanical response of filament wound composite rings under tension and compression. Polym. Test. 2019, 78, 105951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De’Nève, B.; Shanahan, M.E.R. Water absorption by an epoxy resin and its effect on the mechanical properties and infra-red spectra. Polymer 1993, 34, 5099–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhieb, H.; Buijnsters, J.G.; Eddoumy, F.; Vázquez, L.; Celis, J.P. Surface and sub-surface degradation of unidirectional carbon fiber reinforced epoxy composites under dry and wet reciprocating sliding. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2013, 55, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Takemura, K. Influence of water absorption on creep behaviour of carbon fiber/epoxy laminates. Proc. Eng. 2011, 10, 2731–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rafiee, R.; Ghorbanhosseini, A. Analyzing the long-term creep behavior of composite pipes: Developing an alternative scenario of short-term multi-stage loading test. Compos. Struct. 2020, 254, 112868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guen-Geffroy, A.L.; Gac, P.Y.L.; Habert, B.; Davies, B. Physical ageing of epoxy in a wet environment: Coupling between plasticization and physical ageing. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2019, 168, 108947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.R.; Yee, A.F. Moisture diffusion and hygrothermal aging in bismaleimide matrix carbon fiber composites—Part I: Uni-weave composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2002, 62, 2099–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.H.M.; Jansen, K.M.B.; Luinge, J.W.; Bersee, H.E.N.; Benedictus, R. Effect of fiber-matrix adhesion on the creep behavior of CF/PPS composites: Temperature and physical aging characterization. Mech. Time-Depend. Mater. 2016, 20, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rafiee, R.; Habibagahi, M.R. Evaluating mechanical performance of GFRP pipes subjected to transverse loading. Thin. Wall. Struct. 2018, 138, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisbôa, T.V.; Almeida Jr., J.H.S.; Dalibor, I.H.; Spickenheuer, A.; Marczak, R.J.; Amico, S.C. The role of winding pattern on filament wound composite cylinders under radial compression. Polym. Compos. 2020, 41, 2446–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Kolstein, H.; Bijlaard, F.; Qiang, X. Effects of hygrothermal aging on glass-fibre reinforced polymer laminates and adhesive of FRP composite bridge: Moisture diffusion characteristics. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2014, 57, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Hong, W.H.; Lee, W.; Park, J.H.; Yoon, S.J. Pipe Stiffness Prediction of Buried GFRP Flexible Pipe. Polym. Compos. 2014, 22, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Nomenclature | Description |
|---|---|
| UC | Baseline: UnConditioned |
| ML | Creep in radial compression (Mechanical Loading) |
| ML + WRT | Creep in radial compression (Mechanical Loading) and Water at Room Temperature (23 C) |
| ML + HW | Creep in radial compression (Mechanical Loading) and Hot Water (40 C) |
| Conditioning | (MPa) | (MPa) | (C) | (C) | (C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ML | 5601 | 502 | 79 | 86 | 101 |
| ML + WRT | 4822 | 540 | 75 | 79 | 95 |
| ML + HW | 3303 | 481 | 69 | 79 | 88 |
| Laminate | Conditioning | h [mm] | D [mm2/h] (×10−4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [±60] | WRT | 0.506 | 0.72 | 1.03 |
| HW | 1.784 | 1.92 | ||
| [±75] | WRT | 0.399 | 0.77 | 1.89 |
| HW | 1.601 | 1.59 | ||
| [±90] | WRT | 0.357 | 0.70 | 1.83 |
| HW | 1.716 | 1.29 | ||
| [±60/±90] | WRT | 0.497 | 1.54 | 9.63 |
| HW | 1.861 | 7.47 | ||
| [±75/±90] | WRT | 0.441 | 1.69 | 28.3 |
| HW | 1.731 | 5.58 |
| Laminate | Thickness [mm] | Applied Load [N] |
|---|---|---|
| [±60] | 0.72 ± 0.016 | 135.0 |
| [±75] | 0.77 ± 0.006 | 181.5 |
| [±90] | 0.70 ± 0.010 | 203.0 |
| [±60/±90] | 1.54 ± 0.007 | 446.5 |
| [±75/±90] | 1.69 ± 0.017 | 585.0 |
| [±60] | [±75] | [±90] | ||||||||
| ML | ML + WRT | ML + HW | ML | ML + WRT | ML + HW | ML | ML + WRT | ML + HW | ||
| d0 | 4.08 | 4.04 | 4.17 | 2.54 | 2.75 | 2.86 | 2.16 | 2.30 | 2.32 | |
| A (×10−2) | 3.028 | 12.84 | 13.30 | 1.243 | 0.547 | 4.712 | 1.301 | 1.977 | 2.548 | |
| n | 0.462 | 0.279 | 0.585 | 0.483 | 0.462 | 0.523 | 0.468 | 0.454 | 0.747 | |
| [±60/±90] | [±75/±90] | |||||||||
| ML | ML + WRT | ML + HW | ML | ML + WRT | ML + HW | |||||
| d0 | 1.16 | 1.30 | 1.30 | 0.92 | 1.04 | 1.03 | ||||
| A (×10−2) | 4.000 | 1.694 | 3.292 | 1.183 | 1.676 | 4.165 | ||||
| n | 0.175 | 0.358 | 0.600 | 0.405 | 0.434 | 0.509 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eggers, F.; Almeida Jr, J.H.S.; Lisbôa, T.V.; Amico, S.C. Creep and Residual Properties of Filament-Wound Composite Rings under Radial Compression in Harsh Environments. Polymers 2021, 13, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010033
Eggers F, Almeida Jr JHS, Lisbôa TV, Amico SC. Creep and Residual Properties of Filament-Wound Composite Rings under Radial Compression in Harsh Environments. Polymers. 2021; 13(1):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010033
Chicago/Turabian StyleEggers, Frederico, José Humberto S. Almeida Jr, Tales V. Lisbôa, and Sandro C. Amico. 2021. "Creep and Residual Properties of Filament-Wound Composite Rings under Radial Compression in Harsh Environments" Polymers 13, no. 1: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010033
APA StyleEggers, F., Almeida Jr, J. H. S., Lisbôa, T. V., & Amico, S. C. (2021). Creep and Residual Properties of Filament-Wound Composite Rings under Radial Compression in Harsh Environments. Polymers, 13(1), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010033