Rheology and 3D Printability of Percolated Graphene–Polyamide-6 Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Composite Preparation via Melt-Mixing
2.3. Preparation of Test Specimens
2.4. Dynamic Shear Rheology
2.5. Steady Shear Rheology
3. Theory and Calculations
3.1. Carreau–Yasuda Model
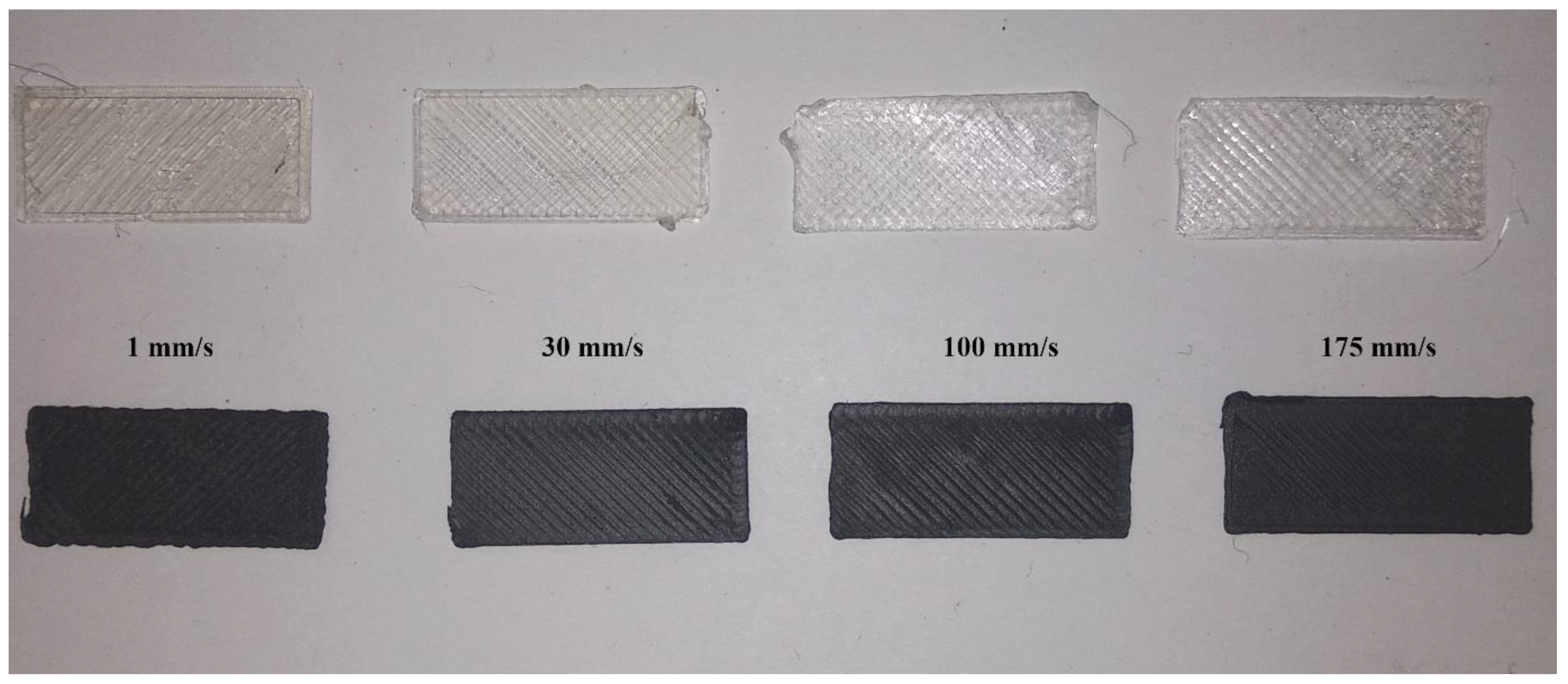
3.2. Printing Envelope
4. Results and Discussion
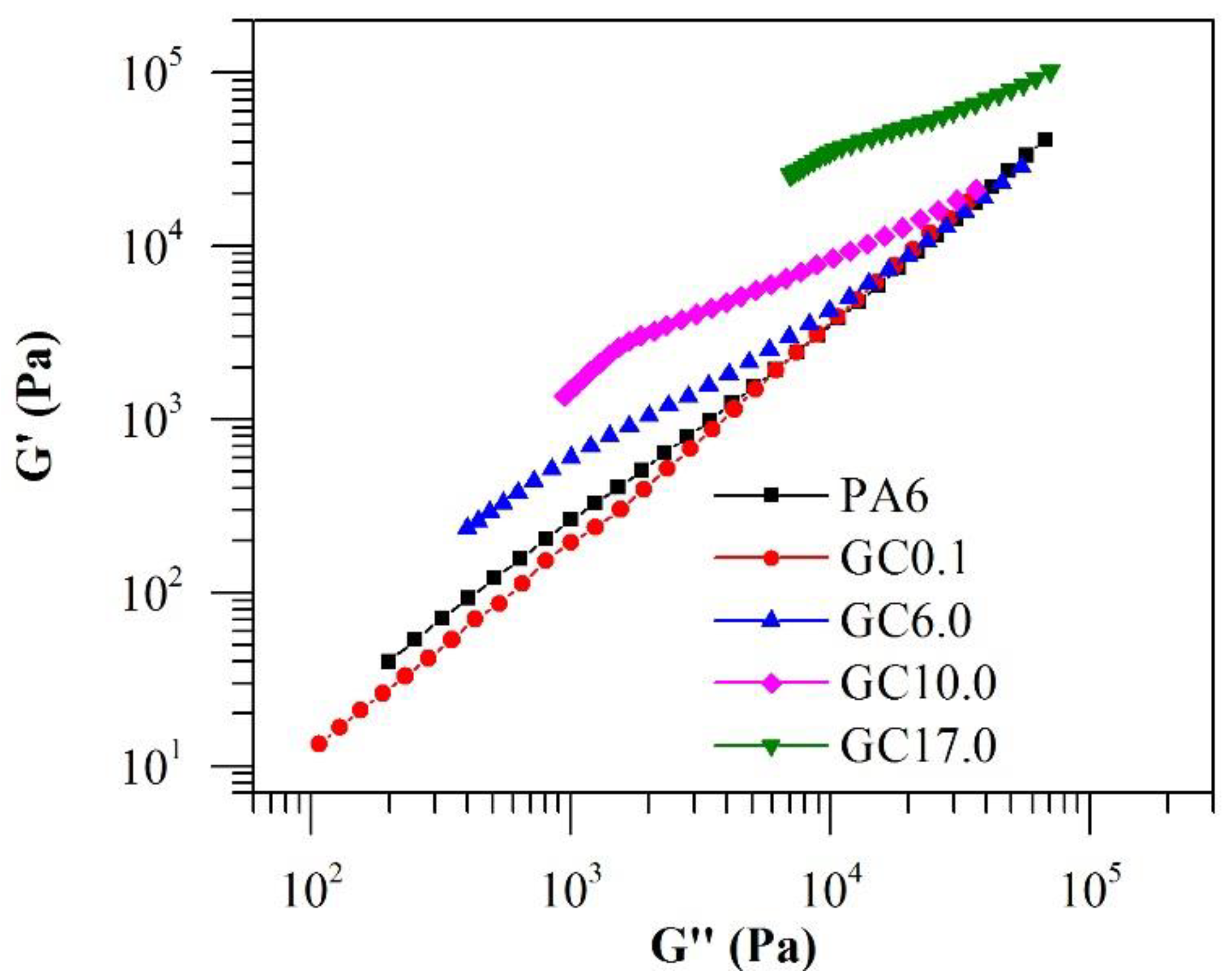
4.1. Dynamic Shear Rheology
4.2. Steady Shear Rheology and Printing Envelope
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ngo, T.D.; Kashani, A.; Imbalzano, G.; Nguyen, K.T.Q.; Hui, D. Additive manufacturing (3d printing): A review of materials, methods, applications and challenges. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 143, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, J.; Schiffres, S.N.; Stevens, A.G.; Hart, A.J. Rate limits of additive manufacturing by fused filament fabrication and guidelines for high-throughput system design. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlegenov, Y.; Wong, Y.S.; Hong, G.S. A dynamic model for nozzle clog monitoring in fused deposition modelling. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2017, 23, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beran, T.; Mulholland, T.; Henning, F.; Rudolph, N.; Osswald, T.A. Nozzle clogging factors during fused filament fabrication of spherical particle filled polymers. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 23, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, P.; Zhao, J.; Wu, W.; Ye, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S. Effects of extrusion speed and printing speed on the 3d printing stability of extruded peek filament. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 37, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Singh, S.; Fraternali, F. Development of in-house composite wire based feed stock filaments of fused deposition modelling for wear-resistant materials and structures. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 98, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, T.N.A.T.; Abdullah, A.M.; Akil, H.M.; Mohamad, D.; Rajion, Z.A. Preparation and characterization of a newly developed polyamide composite utilising an affordable 3d printer. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2015, 34, 1628–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genina, N.; Holländer, J.; Jukarainen, H.; Mäkilä, E.; Salonen, J.; Sandler, N. Ethylene vinyl acetate (eva) as a new drug carrier for 3d printed medical drug delivery devices. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 90, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Ren, Y.; Liao, G.; Jiang, S.; Liu, F.; Guo, J.; Xu, G. Thermal and mechanical properties of polyamide 12/graphene nanoplatelets nanocomposites and parts fabricated by fused deposition modeling. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dul, S.; Fambri, L.; Pegoretti, A. Fused deposition modelling with abs–graphene nanocomposites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 85, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Ramakrishna, S.; Singh, R. Material issues in additive manufacturing: A review. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 25, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayoral, B.; Harkin-Jones, E.; Khanam, P.N.; Almaadeed, M.A.; Ouederni, M.; Hamilton, A.R.; Sun, D. Melt processing and characterisation of polyamide 6/graphene nanoplatelet composites. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 52395–52409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.-M.; Cheong, S.-S.; Chang, T.-H. Rheological properties of graphene/nylon 6 nanocomposites prepared by masterbatch melt mixing. J. Polym. Res. 2016, 23, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canales, J.; Fernández, M.; Peña, J.J.; Muñoz, M.E.; Santamaría, A. Rheological methods to investigate graphene/amorphous polyamide nanocomposites: Aspect ratio, processing, and crystallization. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2014, 55, 1142–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.W.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.R.; Wang, X.Z.; Deng, Y.H. Incorporation of graphitic nano-filler and poly(lactic acid) in fused deposition modeling. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, B.G.; Lewis, J.A. 3d-printing of lightweight cellular composites. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5930–5935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, L.; Han, S.; Peng, X.; Jian, X.; Wang, J. Development of 3d-printed basalt fiber reinforced thermoplastic honeycombs with enhanced compressive mechanical properties. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 125, 105518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xia, X.; Liu, X.; Huang, B.; Xiao, L.; Qian, Q.; Chen, Q. Preparation and rheological and mechanical properties of poly(butylene succinate)/talc composites for material extrusion additive manufacturing. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2019, 304, 1900021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calafel, M.I.; Aguirresarobe, R.H.; Sadaba, N.; Boix, M.; Conde, J.I.; Pascual, B.; Santamaria, A. Tuning the viscoelastic features required for 3d printing of pvc-acrylate copolymers obtained by single electron transfer-degenerative chain transfer living radical polymerization (set-dtlrp). Express Polym. Lett. 2018, 12, 824–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duty, C.; Ajinjeru, C.; Kishore, V.; Compton, B.; Hmeidat, N.; Chen, X.; Liu, P.; Hassen, A.A.; Lindahl, J.; Kunc, V. What makes a material printable? A viscoelastic model for extrusion-based 3d printing of polymers. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 35, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strano, M.; Rane, K.; Vangosa, F.B.; Di Landro, L. Extrusion of metal powder-polymer mixtures: Melt rheology and process stability. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 273, 116250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.P.M.; Baum, T.; Shanks, R.; Daver, F. Graphene–polyamide-6 composite for additive manufacture of multifunctional electromagnetic interference shielding components. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. Article in press. [CrossRef]
- Dealy, J.M.A.; Wissbrun, K.F. Melt Rheology and Its Role in Plastics Processing Theory and Applications; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zare, Y.; Park, S.P.; Rhee, K.Y. Analysis of complex viscosity and shear thinning behavior in poly (lactic acid)/poly (ethylene oxide)/carbon nanotubes biosensor based on carreau–yasuda model. Results Phys. 2019, 13, 102245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.P.M.; Czajka, M.; Shanks, R.; Daver, F. Low-defect graphene–polyamide-6 composites and modeling the filler–matrix interface. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Ronca, S.; Andablo-Reyes, E.; Forte, G.; Rastogi, S. Unique rheological response of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylenes in the presence of reduced graphene oxide. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weir, M.P.; Johnson, D.W.; Boothroyd, S.C.; Savage, R.C.; Thompson, R.L.; King, S.M.; Rogers, S.E.; Coleman, K.S.; Clarke, N. Distortion of chain conformation and reduced entanglement in polymer–graphene oxide nanocomposites. ACS Macro Lett. 2016, 5, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kashi, S.; Gupta, R.K.; Kao, N.; Bhattacharya, S.N. Electrical, thermal, and viscoelastic properties of graphene nanoplatelet/poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) biodegradable nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Achaby, M.; Arrakhiz, F.Z.; Vaudreuil, S.; Essassi, E.M.; Qaiss, A.; Bousmina, M. Preparation and characterization of melt-blended graphene nanosheets-poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanocomposites with enhanced properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 127, 4697–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Muller, R.; Abraham, J. Rheology and Processing of Polymer Nanocomposites; John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Shi, Y.; Miao, J.B.; Xia, R.; Su, L.F.; Qian, J.S.; Chen, P.; Zhang, Q.L.; Liu, J.W. Evaluation of rheological and thermal properties of polyvinylidene fluoride (pvdf)/graphene nanoplatelets (gnp) composites. Polym. Test. 2018, 67, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryamitsyn, V.; Ganesan, V. Mechanisms of steady-shear rheology in polymer-nanoparticle composites. J. Rheol. 2006, 50, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, M.; Edwards, S.F. The Theory of Polymer Dynamics; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Narimissa, E.; Gupta, R.K.; Kao, N.; Choi, H.J.; Jollands, M.; Bhattacharya, S.N. Melt rheological investigation of polylactide-nanographite platelets biopolymer composites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2013, 54, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Specimen | η0* (Pa∙s) | α | λ (s) | n | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA6 | 2013 | 1.9 | 0.49 | 0.77 | 0.99 |
| GC0.1 | 1022 | 0.5 | 0.46 | 0.77 | 0.99 |
| GC6.0 | 4097 | 5.6 | 14.1 | 0.73 | 0.99 |
| GC10.0 | 13550 | 4.8 | 6.2 | 0.37 | 0.99 |
| GC17.0 | 213729 | 8.7 | 7.5 | 0.28 | 0.99 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, K.P.M.; Brandt, M.; Shanks, R.; Daver, F. Rheology and 3D Printability of Percolated Graphene–Polyamide-6 Composites. Polymers 2020, 12, 2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092014
Lee KPM, Brandt M, Shanks R, Daver F. Rheology and 3D Printability of Percolated Graphene–Polyamide-6 Composites. Polymers. 2020; 12(9):2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092014
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Kok Peng Marcian, Milan Brandt, Robert Shanks, and Fugen Daver. 2020. "Rheology and 3D Printability of Percolated Graphene–Polyamide-6 Composites" Polymers 12, no. 9: 2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092014
APA StyleLee, K. P. M., Brandt, M., Shanks, R., & Daver, F. (2020). Rheology and 3D Printability of Percolated Graphene–Polyamide-6 Composites. Polymers, 12(9), 2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092014





