Electrospun Anion-Conducting Ionomer Fibers—Effect of Humidity on Final Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
3. Results and Discussion
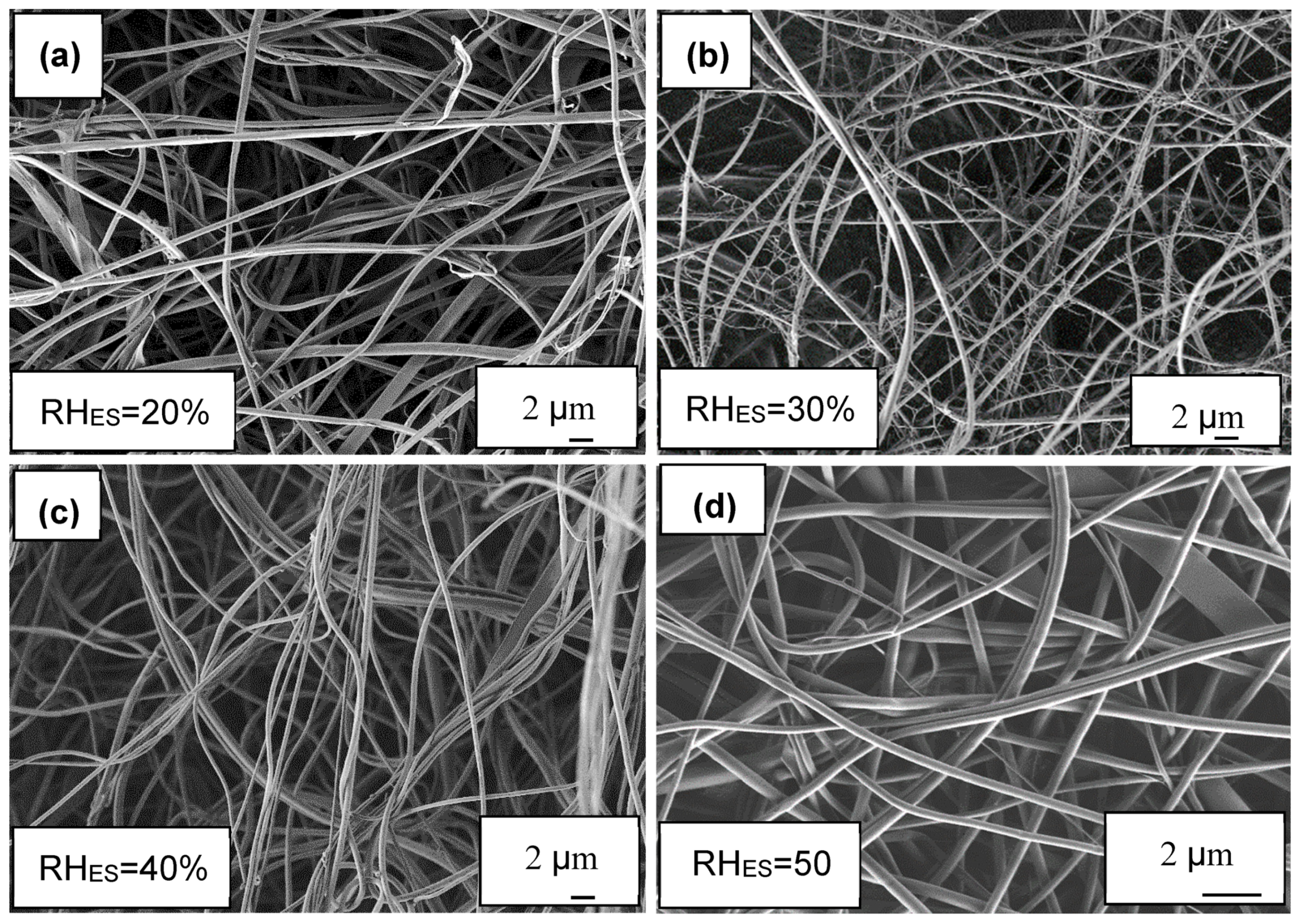
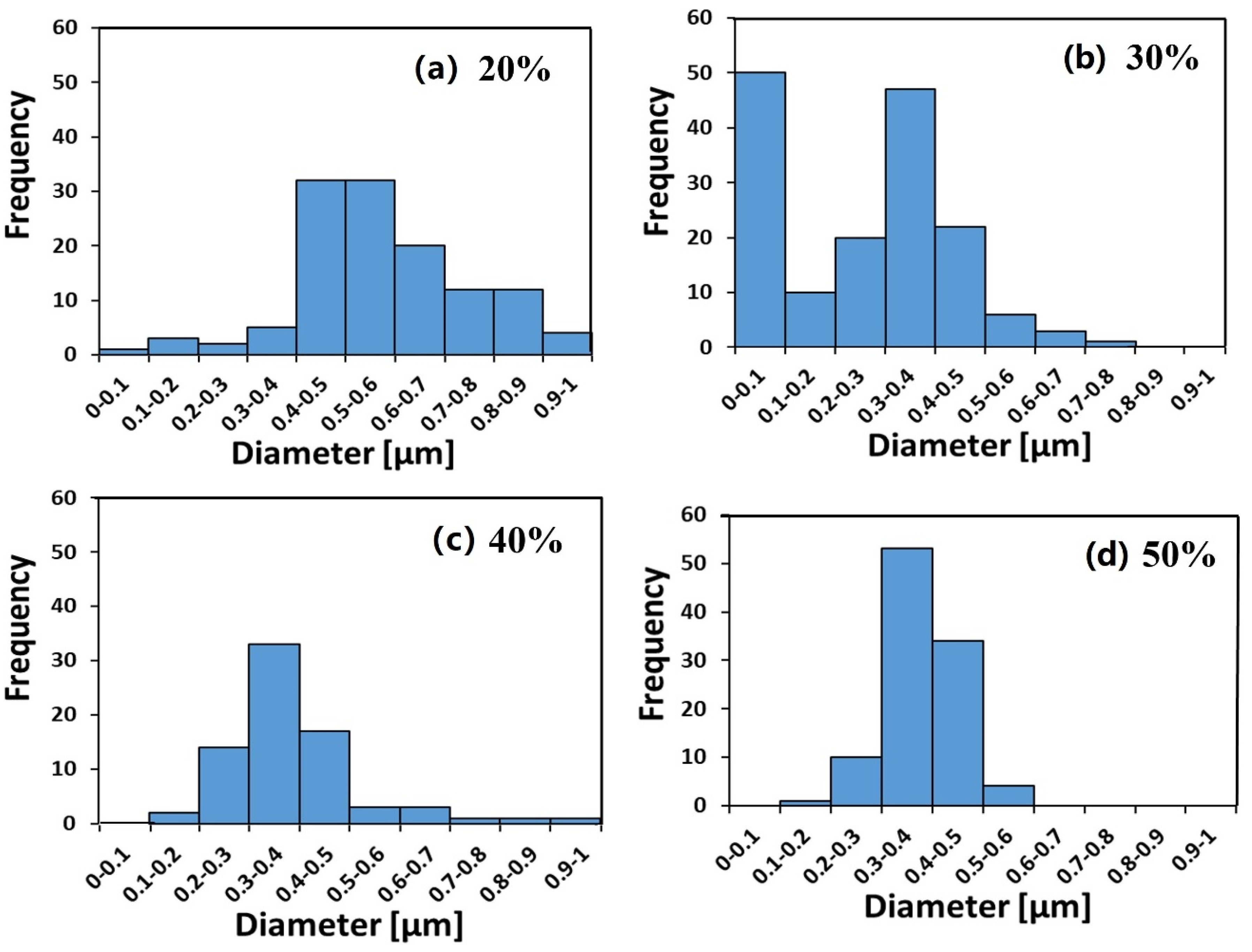
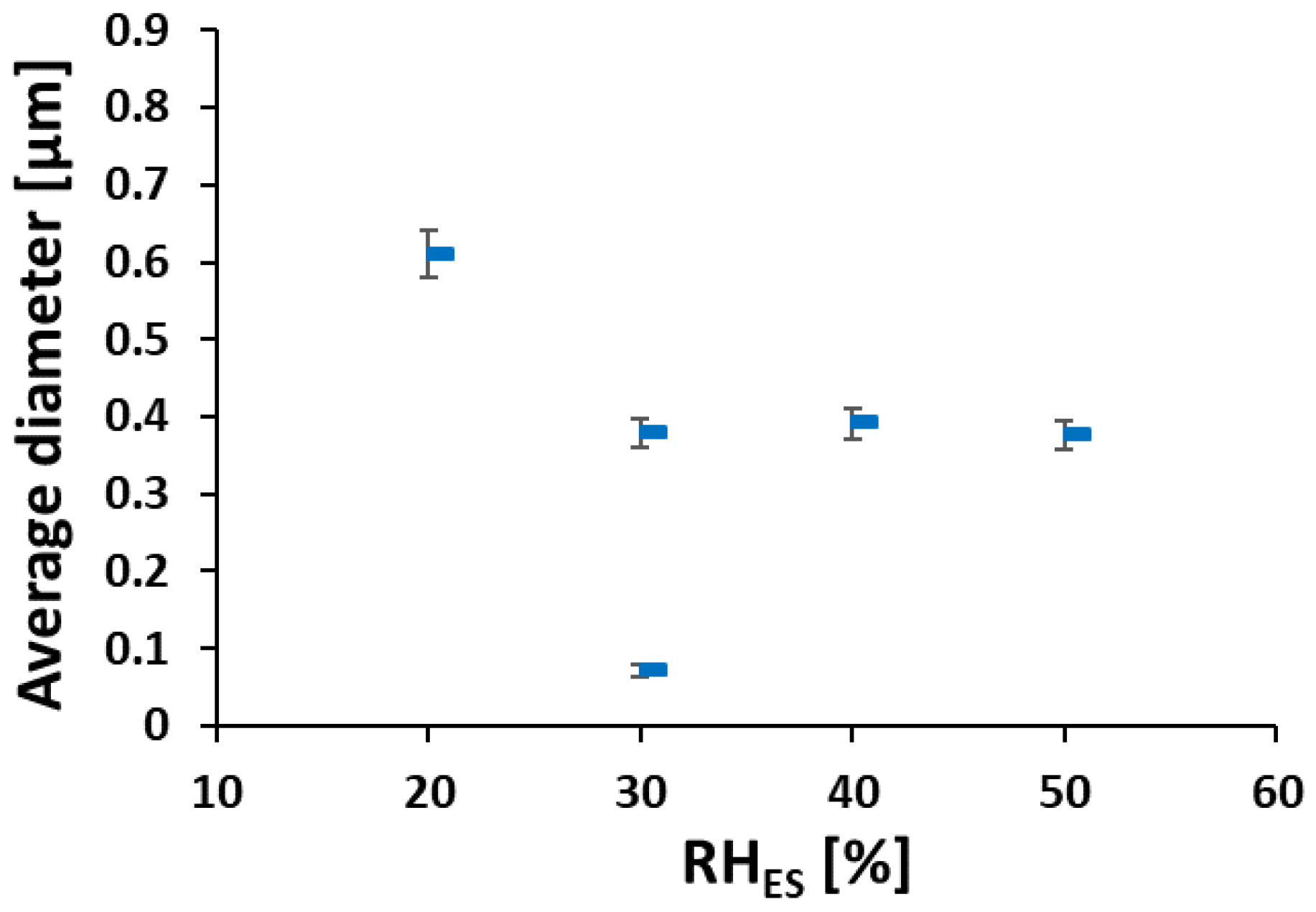
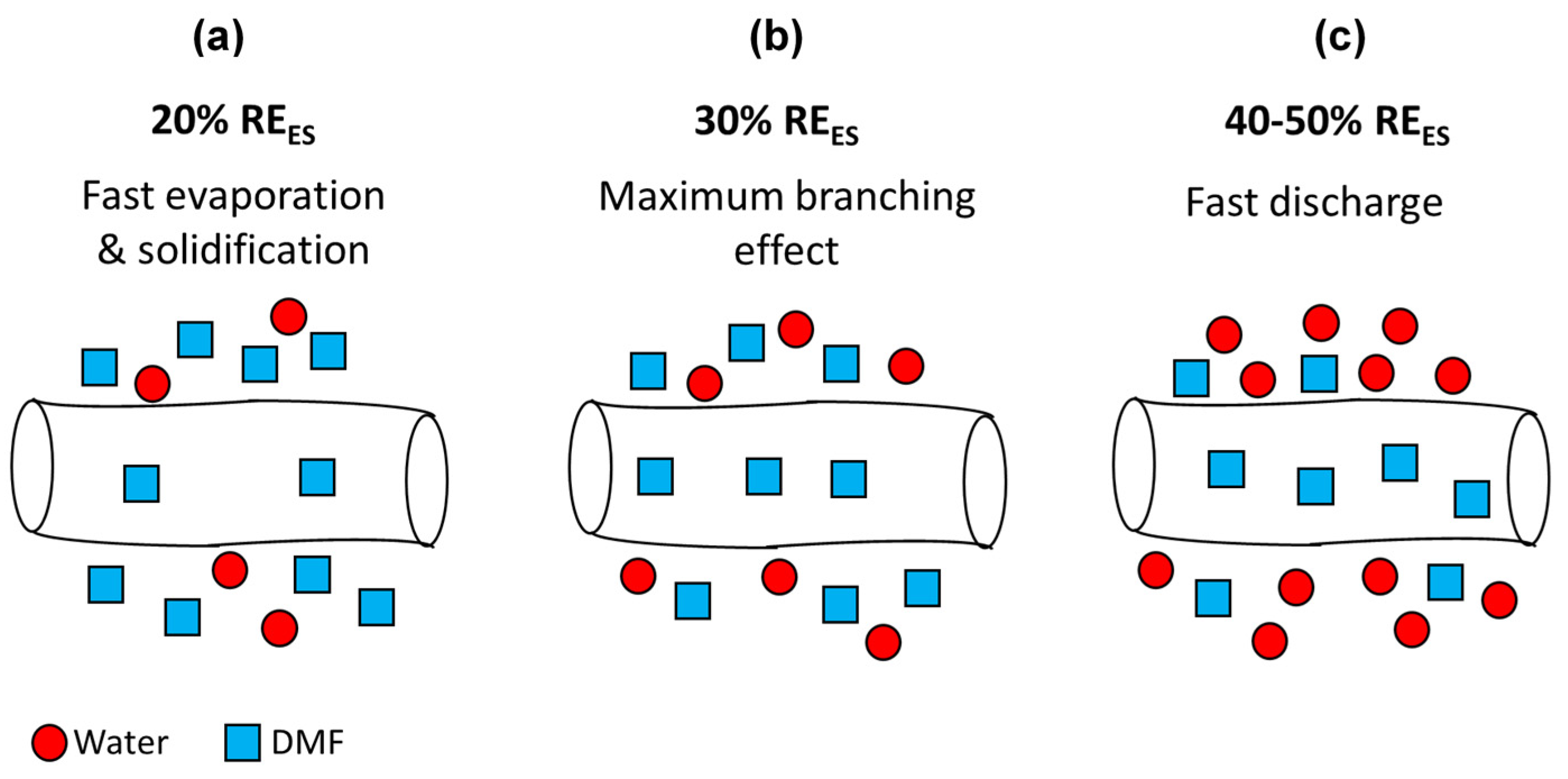
3.1. Ionomer Fibers Morphology
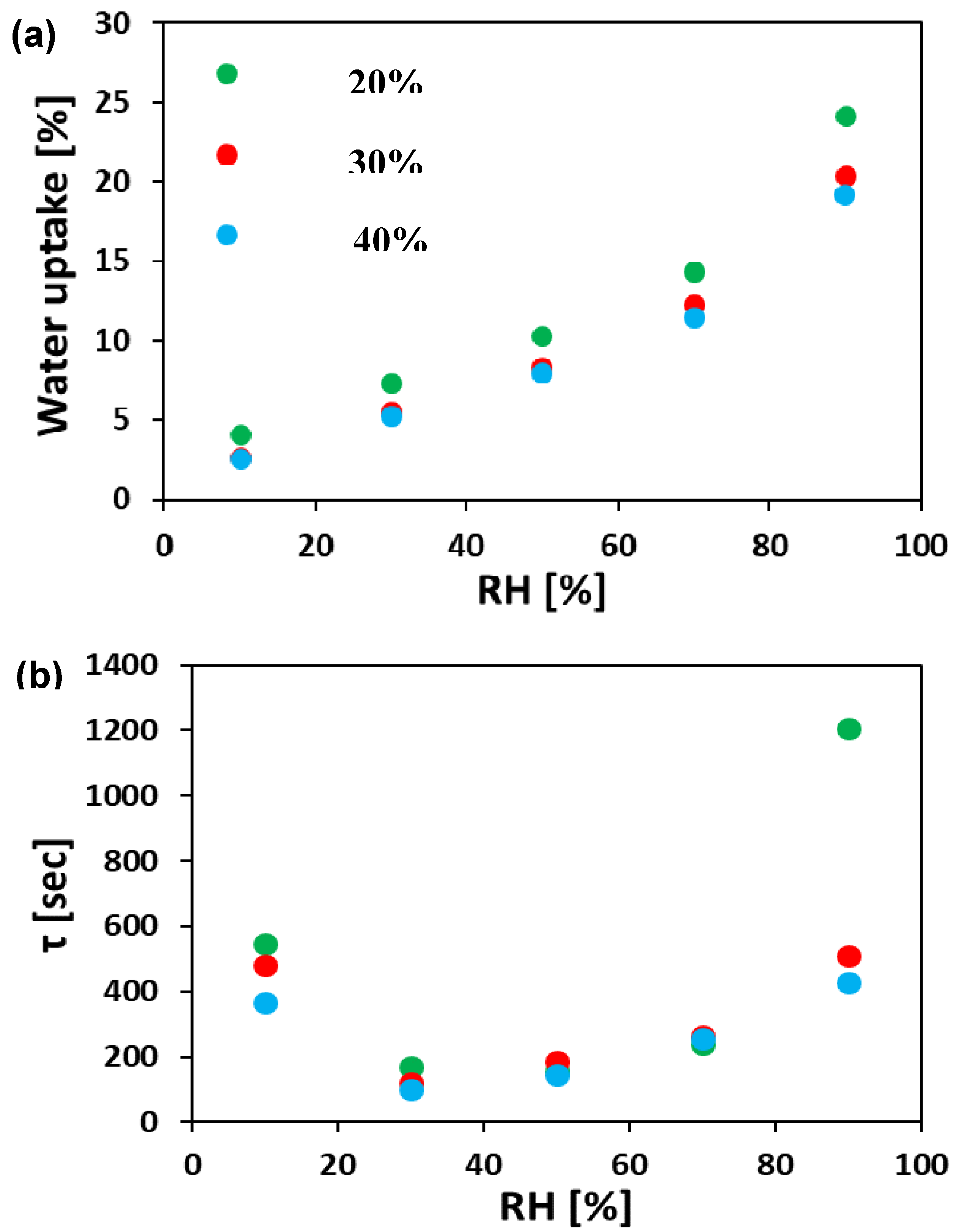
3.2. Water Uptake
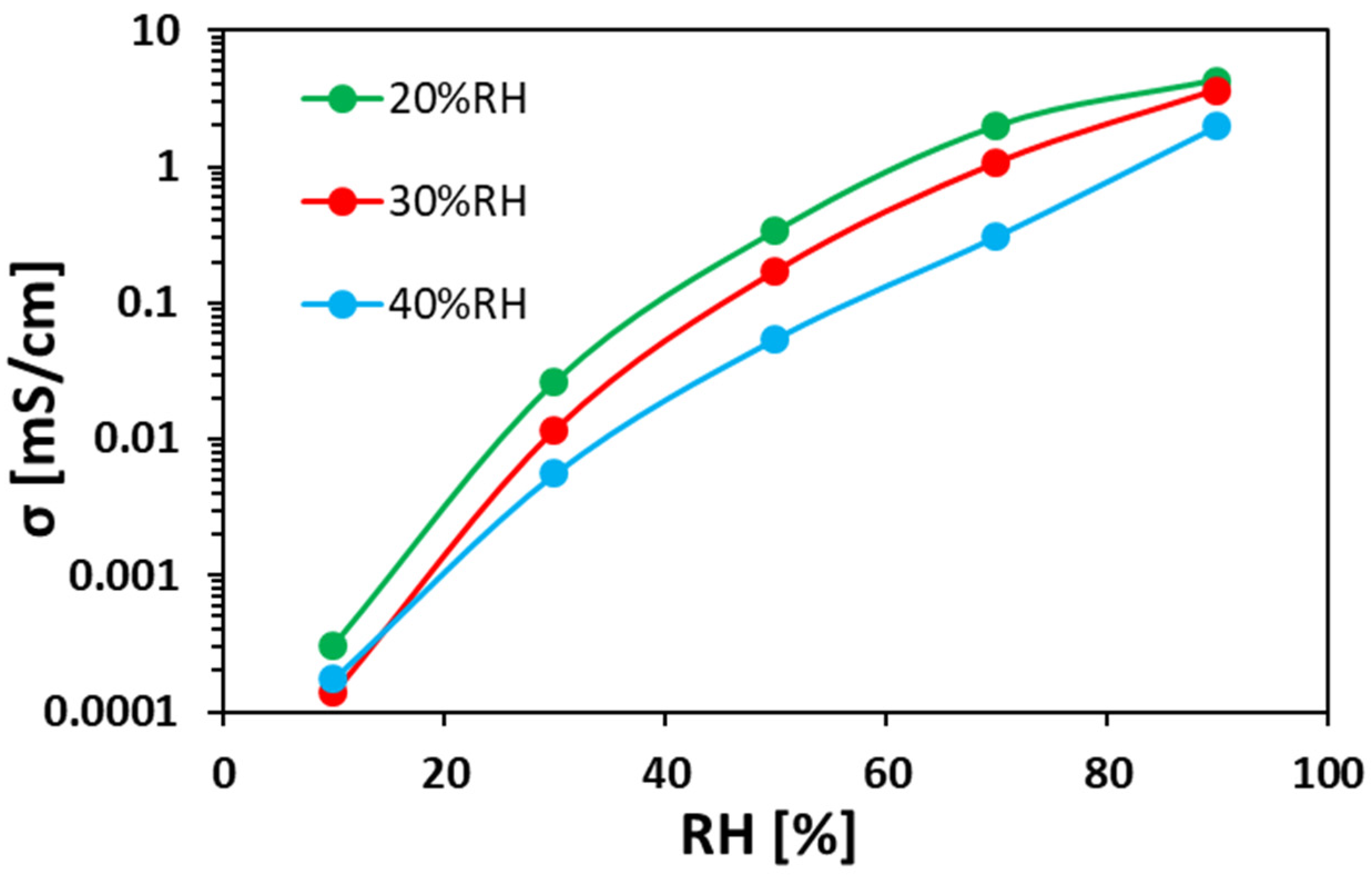
3.3. Anion Conductivity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chronakis, I.S. Novel nanocomposites and nanoceramics based on polymer nanofibers using electrospinning process—A review. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2005, 167, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, W.E.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on electrospinning design and nanofibre assemblies. Nanotechnology 2006, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halperin, V.; Shter, G.E.; Beilin, V.; Grader, G.S. Mesoporous K/Fe–Al–O nanofibers by electrospinning of solution precursors. J. Mater. Res. 2015, 30, 3142–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmueli, Y.; Shter, G.E.; Assad, O.; Haick, H.; Sonntag, P.; Ricoux, P.; Grader, G.S. Structural and electrical properties of single Ga/ZnO nanofibers synthesized by electrospinning. J. Mater. Res. 2012, 27, 1672–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elishav, O.; Beilin, V.; Shter, G.E.; Dinner, O.; Halperin, V.; Grader, G.S. Formation of Core-Shell Mesoporous Ceramic Fibers. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 100, 3370–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, H. Fabrication of conductive polypyrrole nanofibers by electrospinning. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.M. One-Dimensional Nanostructures; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2008; Volume 3, ISBN 0387741321. [Google Scholar]
- Baji, A.; Mai, Y.W.; Wong, S.C.; Abtahi, M.; Chen, P. Electrospinning of polymer nanofibers: Effects on oriented morphology, structures and tensile properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junoh, H.; Jaafar, J.; Norddin, M.N.A.M.; Ismail, A.F.; Othman, M.H.D.; Rahman, M.A.; Yusof, N.; Salleh, W.N.W.; Ilbeygi, H. A review on the fabrication of electrospun polymer electrolyte membrane for direct methanol fuel cell. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere, S.; Subianto, S.; Savych, I.; Jones, D.J.; Rozière, J. Electrospinning: Designed architectures for energy conversion and storage devices. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megelski, S.; Stephens, J.S.; Chase, D.B.; Rabolt, J.F. Micro-and nanostructured surface morphology on electrospun polymer fibers. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 8456–8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casper, C.L.; Stephens, J.S.; Tassi, N.G.; Chase, D.B.; Rabolt, J.F. Controlling surface morphology of electrospun polystyrene fibers: Effect of humidity and molecular weight in the electrospinning process. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisignano, D. Polymer Nanofibers: Building Blocks for Nanotechnology; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2013; Volume 8, ISBN 1849735743. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishna, S. An Introduction to Electrospinning and Nanofibers; WORLD SCIENTIFIC: Singapore, 2005; ISBN 978-981-256-415-3. [Google Scholar]
- Haider, A.; Haider, S.; Kang, I.-K. A comprehensive review summarizing the effect of electrospinning parameters and potential applications of nanofibers in biomedical and biotechnology. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, Q.P.; Sharma, U.; Mikos, A.G. Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for tissue engineering applications: A review. Tissue Eng. 2006, 12, 1197–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, A.M.; Pintauro, P.N. Alkaline Fuel Cell Membranes from Electrospun Fiber Mats. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2012, 15, B27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajon, R.; Balaji, S.; Guo, S.M. Electrospun Nafion Nanofiber for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Application. J. Fuel Cell Sci. Technol. 2009, 6, 031004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundarrajan, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Green Processing of a Cationic Polyelectrolyte Nanofibers in the Presence of Poly (vinyl alcohol). Int. J. Green Nanotechnol. 2011, 3, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, R.; Sundarrajan, S.; Vanangamudi, A.; Singh, G.; Matsuura, T.; Ramakrishna, S. Green processing mediated novel polyelectrolyte nanofibers and their antimicrobial evaluation. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2014, 299, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Bubel, K.; Chen, F.; Kissel, T.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A. Nanofibers by green electrospinning of aqueous suspensions of biodegradable block copolyesters for applications in medicine, pharmacy and agriculture. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 2077–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Bui, N.; Manickam, S.S.; McCutcheon, J.R. Controlling electrospun nanofiber morphology and mechanical properties using humidity. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2011, 49, 1734–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezarati, R.M.; Eifert, M.B.; Cosgriff-Hernandez, E. Effects of humidity and solution viscosity on electrospun fiber morphology. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2013, 19, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Han, C.C. Construction of hierarchical structures by electrospinning or electrospraying. Polymer 2012, 53, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-Y.; Lee, I.-H. Relative humidity effect on the preparation of porous electrospun polystyrene fibers. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 10, 3473–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.-T.; Lee, J.-S.; Shin, J.-H.; Ahn, Y.-C.; Hwang, Y.-J.; Shin, H.-S.; Lee, J.-K.; Sung, C.-M. Investigation of pore formation for polystyrene electrospun fiber: Effect of relative humidity. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2005, 22, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, C.-L.; Boyce, M.C.; Rutledge, G.C. Morphology of porous and wrinkled fibers of polystyrene electrospun from dimethylformamide. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 2102–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, H.; Miyake, J.; Shimada, S.; Uchida, M.; Miyatake, K. Anion exchange membranes composed of perfluoroalkylene chains and ammonium-functionalized oligophenylenes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 21779–21788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, L.D.; Mamizuka, E.M.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Antimicrobial particles from cationic lipid and polyelectrolytes. Langmuir 2010, 26, 12300–12306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; He, G.; Xue, J.; Otoo, O.; He, X.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Yin, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Douglin, J.C. Self-crosslinked blend alkaline anion exchange membranes with bi-continuous phase separated morphology to enhance ion conductivity. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 597, 117769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siroma, Z.; Ioroi, T.; Fujiwara, N.; Yasuda, K. Proton conductivity along interface in thin cast film of Nafion®. Electrochem. Commun. 2002, 4, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willdorf-Cohen, S.; Mondal, A.N.; Dekel, D.R.; Diesendruck, C.E. Chemical stability of poly (phenylene oxide)-based ionomers in an anion exchange-membrane fuel cell environment. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 22234–22239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karan, K. Interesting Facets of Surface, Interfacial, and Bulk Characteristics of Perfluorinated Ionomer Films. Langmuir 2019, 35, 13489–13520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amel, A.; Gavish, N.; Zhu, L.; Dekel, D.R.; Hickner, M.A.; Ein-Eli, Y. Bicarbonate and chloride anion transport in anion exchange membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 514, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, S.; Shin, S.-H.; Kim, Y.; Moon, S.-H. A review on recent developments of anion exchange membranes for fuel cells and redox flow batteries. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 37206–37230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merle, G.; Wessling, M.; Nijmeijer, K. Anion exchange membranes for alkaline fuel cells: A review. J. Memb. Sci. 2011, 377, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amel, A.; Smedley, S.B.; Dekel, D.R.; Hickner, M.A.; Ein-Eli, Y. Characterization and chemical stability of anion exchange membranes cross-linked with polar electron-donating linkers. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, F1047–F1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Wycisk, R.; Pintauro, P.; Yarlagadda, V.; Van Nguyen, T. Electrospun Nafion®/Polyphenylsulfone composite membranes for regenerative Hydrogen bromine fuel cells. Materials. 2016, 9, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Lee, K.M.; Wycisk, R.; Pintauro, P.N.; Mather, P.T. Nanofiber composite membranes with low equivalent weight perfluorosulfonic acid polymers. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 6282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballengee, J.B.; Pintauro, P.N. Preparation of nanofiber composite proton-exchange membranes from dual fiber electrospun mats. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 442, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, R.; Cavaliere, S.; Jones, D.J.; Rozière, J. Electrospun nanofibre composite polymer electrolyte fuel cell and electrolysis membranes. Nano Energy 2016, 26, 729–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subianto, S.; Giancola, S.; Ercolano, G.; Nabil, Y.; Jones, D.; Rozière, J.; Cavaliere, S. Electrospun nanofibers for low-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. In Electrospinning for Advanced Energy and Environmental Applications; Sara, C., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 29–59. ISBN 1482217678. [Google Scholar]
- Subianto, S.; Cavaliere, S.; Jones, D.J.; Rozière, J. Effect of side-chain length on the electrospinning of perfluorosulfonic acid ionomers. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2013, 51, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, A.M.; Turley, F.E.; Wycisk, R.J.; Pintauro, P.N. Electrospun and Cross-Linked Nano fiber Composite Anion Exchange Membranes. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, A.M.; Wycisk, R.J.; Ren, X.; Turley, F.E.; Pintauro, P.N. Crosslinked poly(phenylene oxide)-based nanofiber composite membranes for alkaline fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarin, A.L.; Kataphinan, W.; Reneker, D.H. Branching in electrospinning of nanofibers. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 64501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Huang, X.; Wu, B. Some fascinating phenomena in electrospinning processes and applications of electrospun nanofibers. Polym. Int. 2007, 56, 1330–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Yarin, A.L. Electrospinning jets and polymer nanofibers. Polymer 2008, 49, 2387–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevorkyan, A.; Shter, G.E.; Shmueli, Y.; Buk, A.; Meir, R.; Grader, G.S. Branching effect and morphology control in electrospun PbZr 0.52 Ti 0.48 O 3 nanofibers. J. Mater. Res. 2014, 29, 1721–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottesfeld, S.; Dekel, D.R.; Page, M.; Bae, C.; Yan, Y.; Zelenay, P.; Kim, Y.S. Anion exchange membrane fuel cells: Current status and remaining challenges. J. Power Sources 2018, 375, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekel, D.R.; Rasin, I.G.; Brandon, S. Predicting performance stability in anion exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2019, 420, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omasta, T.J.; Park, A.M.; LaManna, J.M.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, X.; Wang, L.; Jacobson, D.L.; Varcoe, J.R.; Hussey, D.S.; Pivovar, B.S. Beyond catalysis and membranes: Visualizing and solving the challenge of electrode water accumulation and flooding in AEMFCs. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, H.A.; Lavacchi, A.; Vizza, F.; Marelli, M.; Di Benedetto, F.; D’Acapito, F.; Paska, Y.; Page, M.; Dekel, D.R. A Pd/C-CeO 2 Anode Catalyst for High-Performance Platinum-Free Anion Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 6108–6111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekel, D.R. Alkaline membrane fuel cell (AMFC) materials and system improvement-state-of-the-art. ECS Trans. 2013, 50, 2051–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Ash, U.; Pandey, R.P.; Ozioko, A.G.; Ponce-González, J.; Handl, M.; Weissbach, T.; Varcoe, J.R.; Holdcroft, S.; Liberatore, M.W.; et al. Water Uptake Study of Anion Exchange Membranes. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 3264–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noga, Z.; Mondal, A.N.; Weissbach, T.; Steven, H.; Dekel, D.R. Effect of CO2 on the properties of anion exchange membranes for fuel cell applications. J. Member. Sci. 2019, 586, 140–150. [Google Scholar]
- Ziv, N.; Mustain, W.E.; Dekel, D.R. The Effect of Ambient Carbon Dioxide on Anion-Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. ChemSusChem 2018, 11, 1136–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhegur, A.; Gjineci, N.; Willdorf-Cohen, S.; Mondal, A.N.; Diesendruck, C.E.; Gavish, N.; Dekel, D.R. Changes of Anion Exchange Membrane Properties During Chemical Degradation. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.S.; Zhao, T.S.; Yang, W.W. Measurements of water uptake and transport properties in anion-exchange membranes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 5656–5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusoglu, A.; Kwong, A.; Clark, K.T.; Gunterman, H.P.; Weber, A.Z. Water Uptake of Fuel-Cell Catalyst Layers. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, F530–F535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziv, N.; Dekel, D.R. A practical method for measuring the true hydroxide conductivity of anion exchange membranes. Electrochem. Commun. 2018, 88, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, K. Characterizing through-plane and in-plane ionic conductivity of polymer electrolyte membranes. ECS Trans. 2011, 41, 1371–1380. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, C.; Fang, H.; Duan, G.; Zou, Y.; Chen, S.; Hou, H. Investigating the draw ratio and velocity of an electrically charged liquid jet during electrospinning. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 13608–13613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann-Lahav, M.; Halabi, M.; Shter, G.E.; Beilin, V.; Balaish, M.; Ein-Eli, Y.; Dekel, D.R.; Grader, G.S. Electrospun ionomeric fibers with anion conducting properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 1901733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elishav, O.; Grader, G.S. Electrospun Fe-Al-O Nanobelts for Selective CO2 Hydrogenation to Light Olefins. Unpublished work. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- De Vrieze, S.; Van Camp, T.; Nelvig, A.; Hagström, B.; Westbroek, P.; De Clerck, K. The effect of temperature and humidity on electrospinning. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelipenko, J.; Kristl, J.; Janković, B.; Baumgartner, S.; Kocbek, P. The impact of relative humidity during electrospinning on the morphology and mechanical properties of nanofibers. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 456, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgarten, P.K. Electrostatic spinning of acrylic microfibers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1971, 36, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Halabi, M.; Mann-Lahav, M.; Beilin, V.; Shter, G.E.; Elishav, O.; Grader, G.S.; Dekel, D.R. Electrospun Anion-Conducting Ionomer Fibers—Effect of Humidity on Final Properties. Polymers 2020, 12, 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051020
Halabi M, Mann-Lahav M, Beilin V, Shter GE, Elishav O, Grader GS, Dekel DR. Electrospun Anion-Conducting Ionomer Fibers—Effect of Humidity on Final Properties. Polymers. 2020; 12(5):1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051020
Chicago/Turabian StyleHalabi, Manar, Meirav Mann-Lahav, Vadim Beilin, Gennady E. Shter, Oren Elishav, Gideon S. Grader, and Dario R. Dekel. 2020. "Electrospun Anion-Conducting Ionomer Fibers—Effect of Humidity on Final Properties" Polymers 12, no. 5: 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051020
APA StyleHalabi, M., Mann-Lahav, M., Beilin, V., Shter, G. E., Elishav, O., Grader, G. S., & Dekel, D. R. (2020). Electrospun Anion-Conducting Ionomer Fibers—Effect of Humidity on Final Properties. Polymers, 12(5), 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051020





