Electrospinning and Post-Spun Chain Conformations of Synthetic, Hydrophobic Poly(α-amino acid)s
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
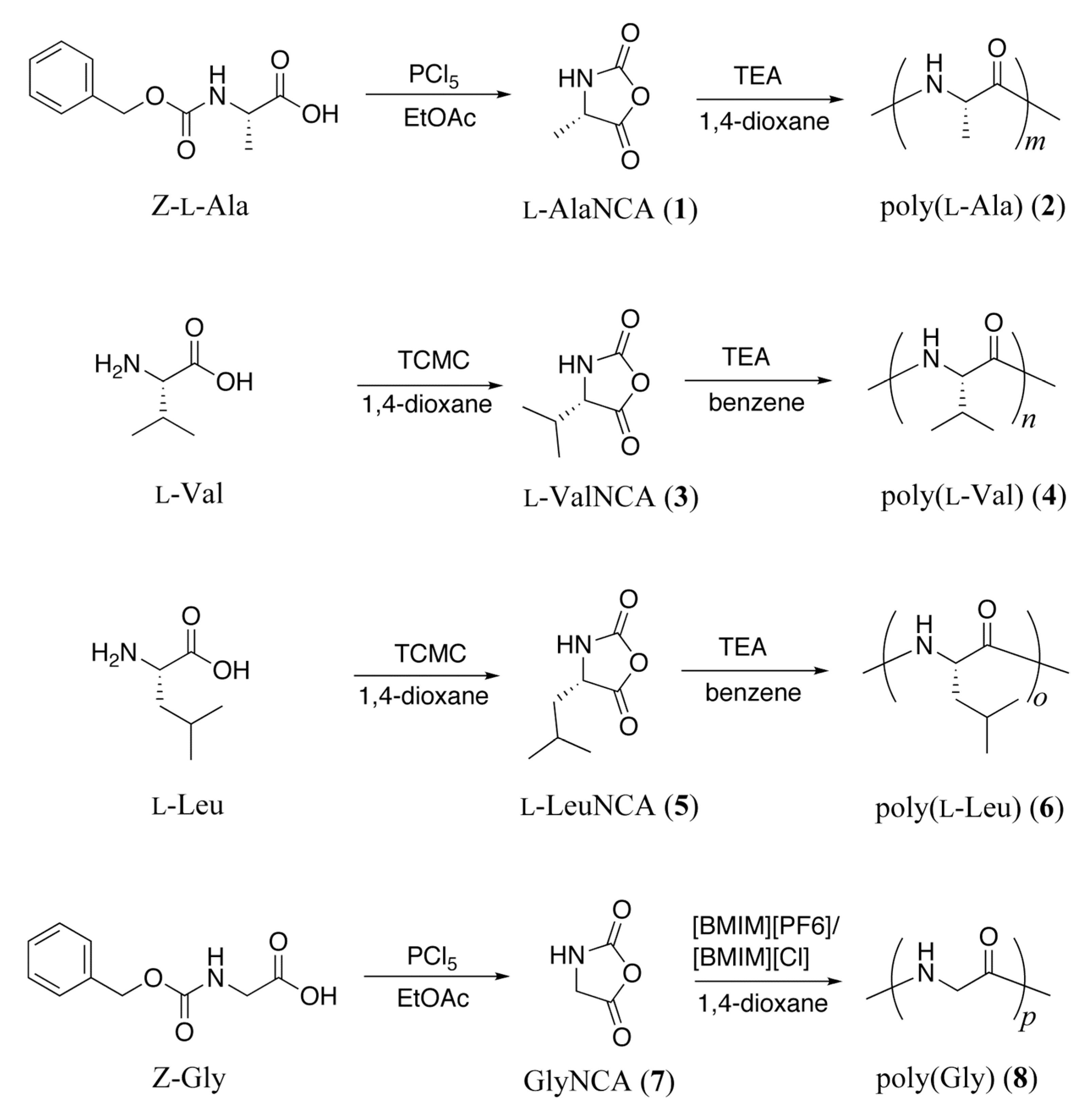
2.2. Synthesis of Poly(α-amino acids)
2.2.1. General Procedure for Synthesis of Poly(α-amino acids)
2.2.2. l-Ala NCA (1)
2.2.3. Poly(l-Ala) (2)
2.2.4. l-Val NCA (3)
2.2.5. Poly(l-Val) (4)
2.2.6. l-Leu NCA (5)
2.2.7. Poly(l-Leu) (6)
2.2.8. Gly NCA (7)
2.2.9. Poly(Gly) (8)
2.3. Electrospinning of Poly(amino acids)
2.4. Preparation of Poly(l-Ala) Film
2.5. Wide-Angle X-ray Diffraction (WAXD)
2.6. FT-IR Spectroscopy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Poly(amino acids)
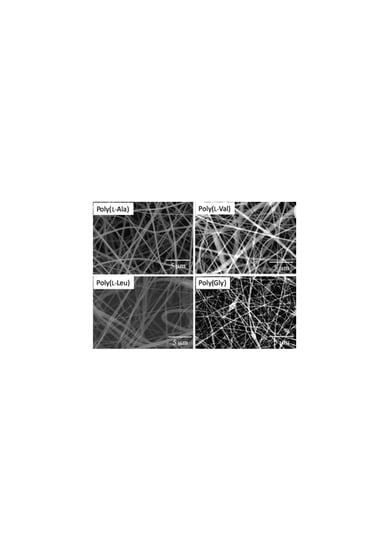
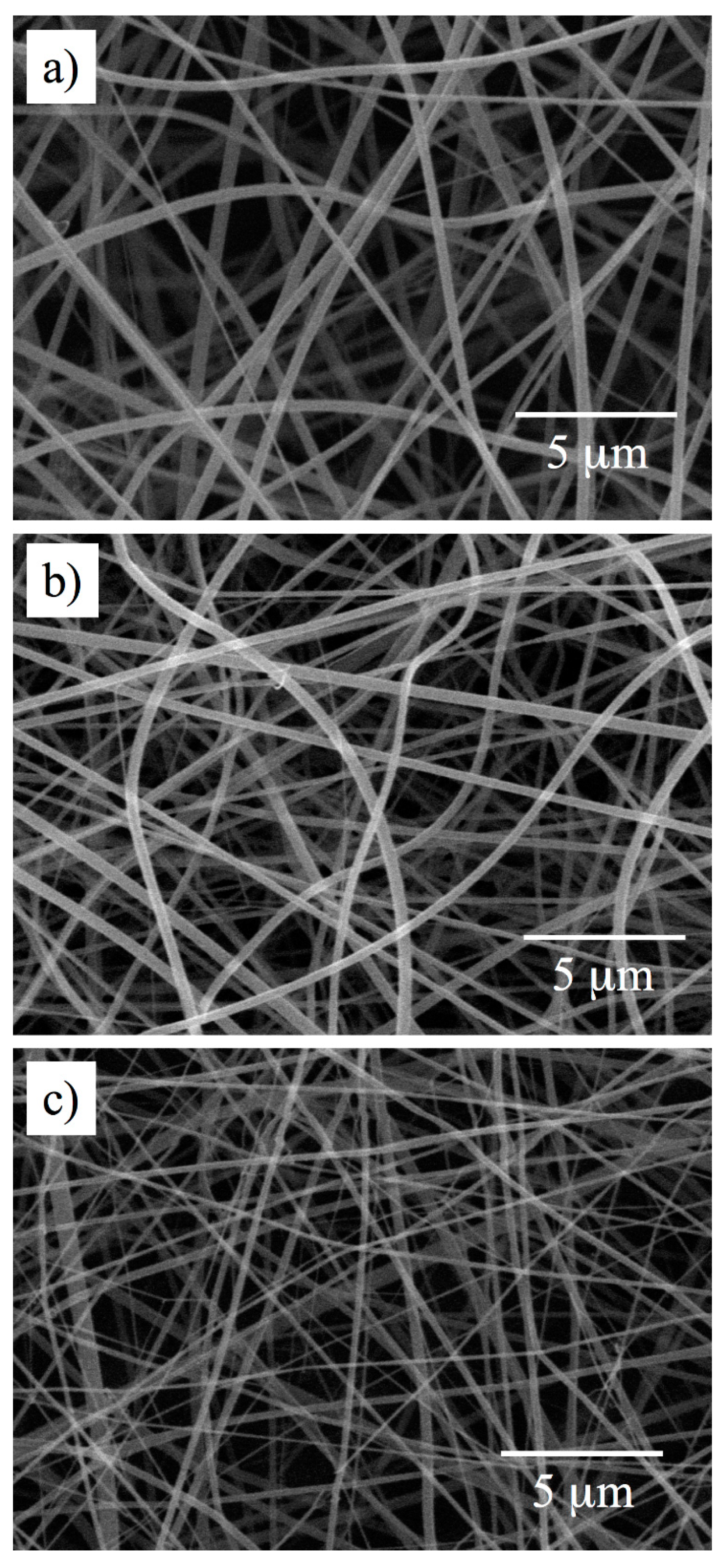
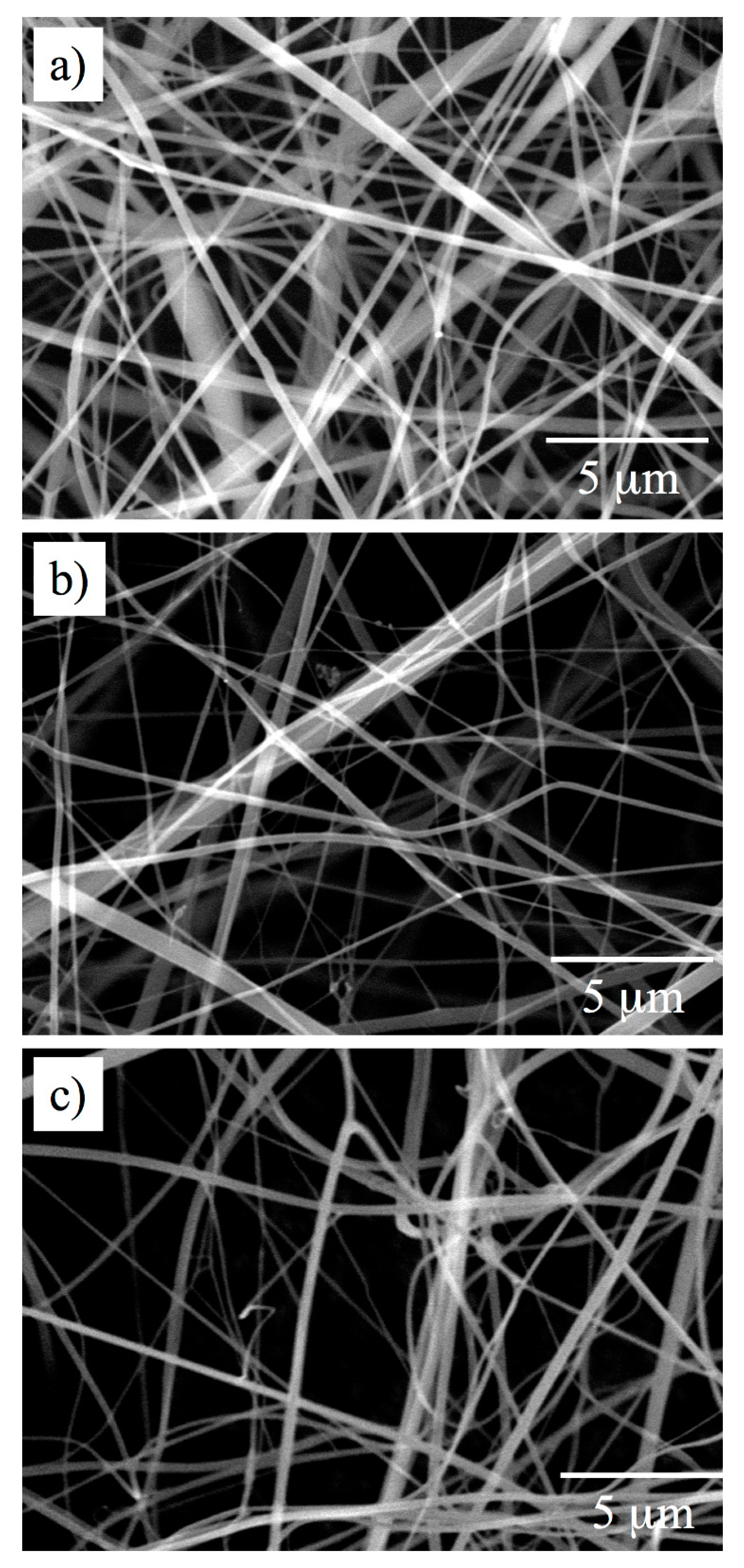
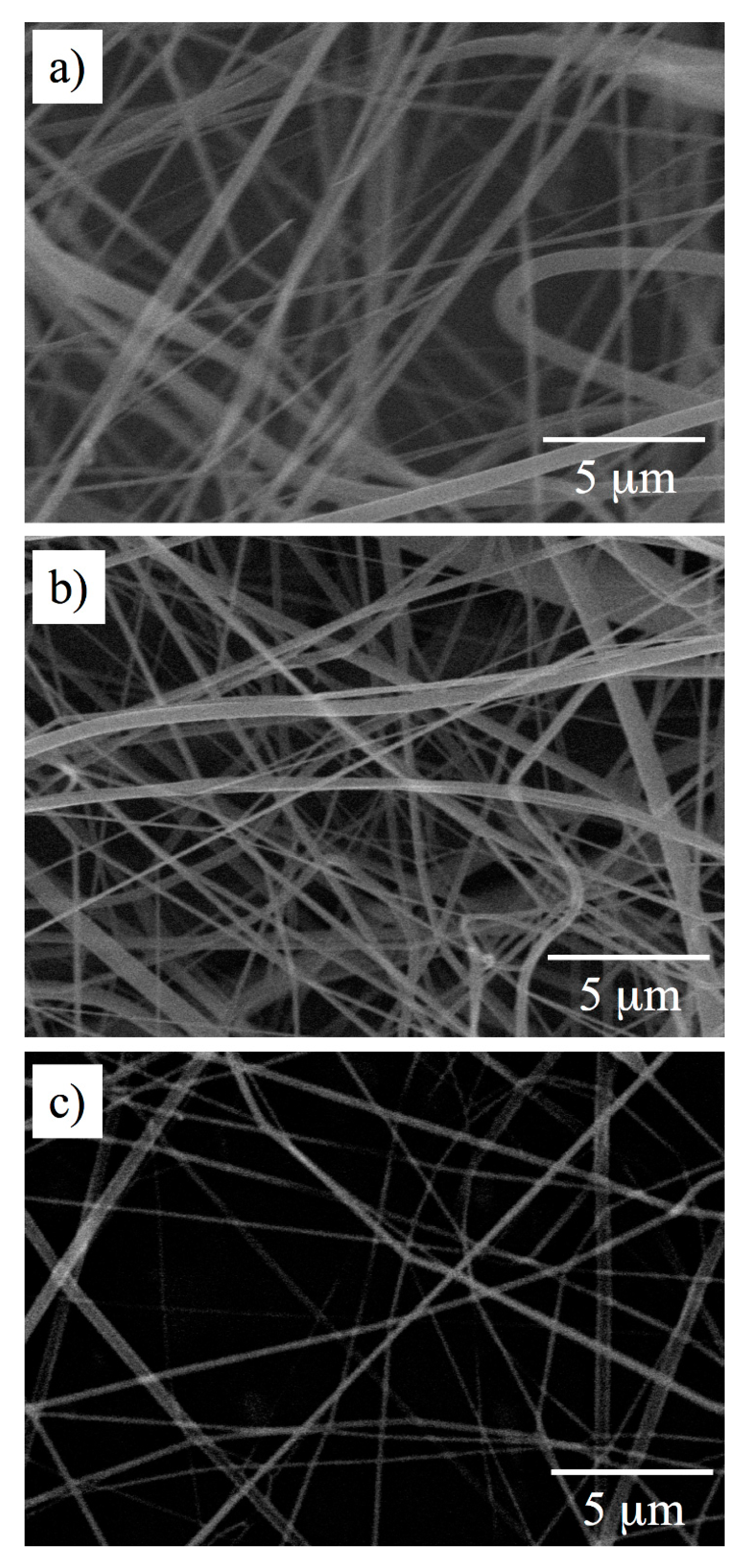
3.2. Electrospinning
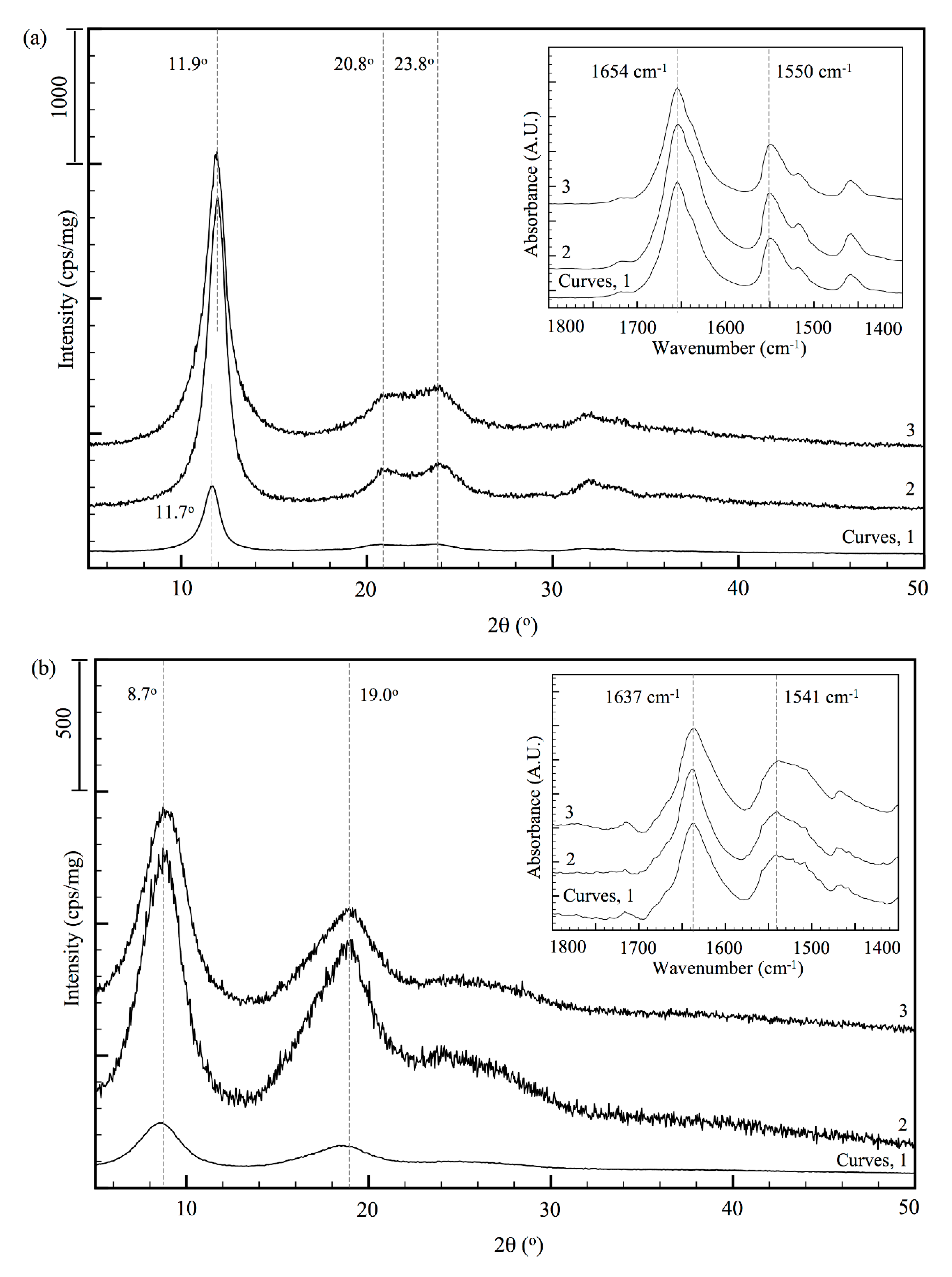
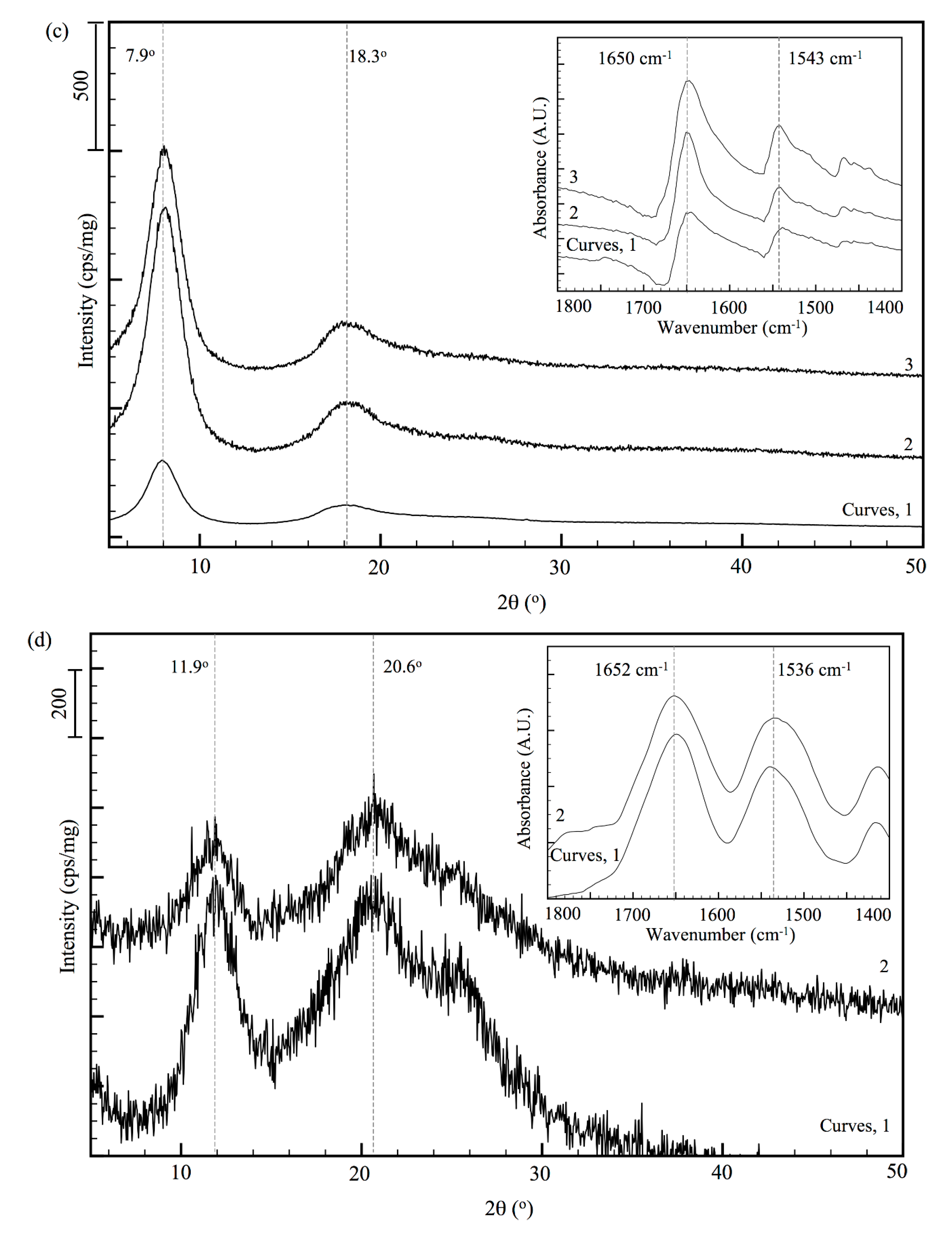
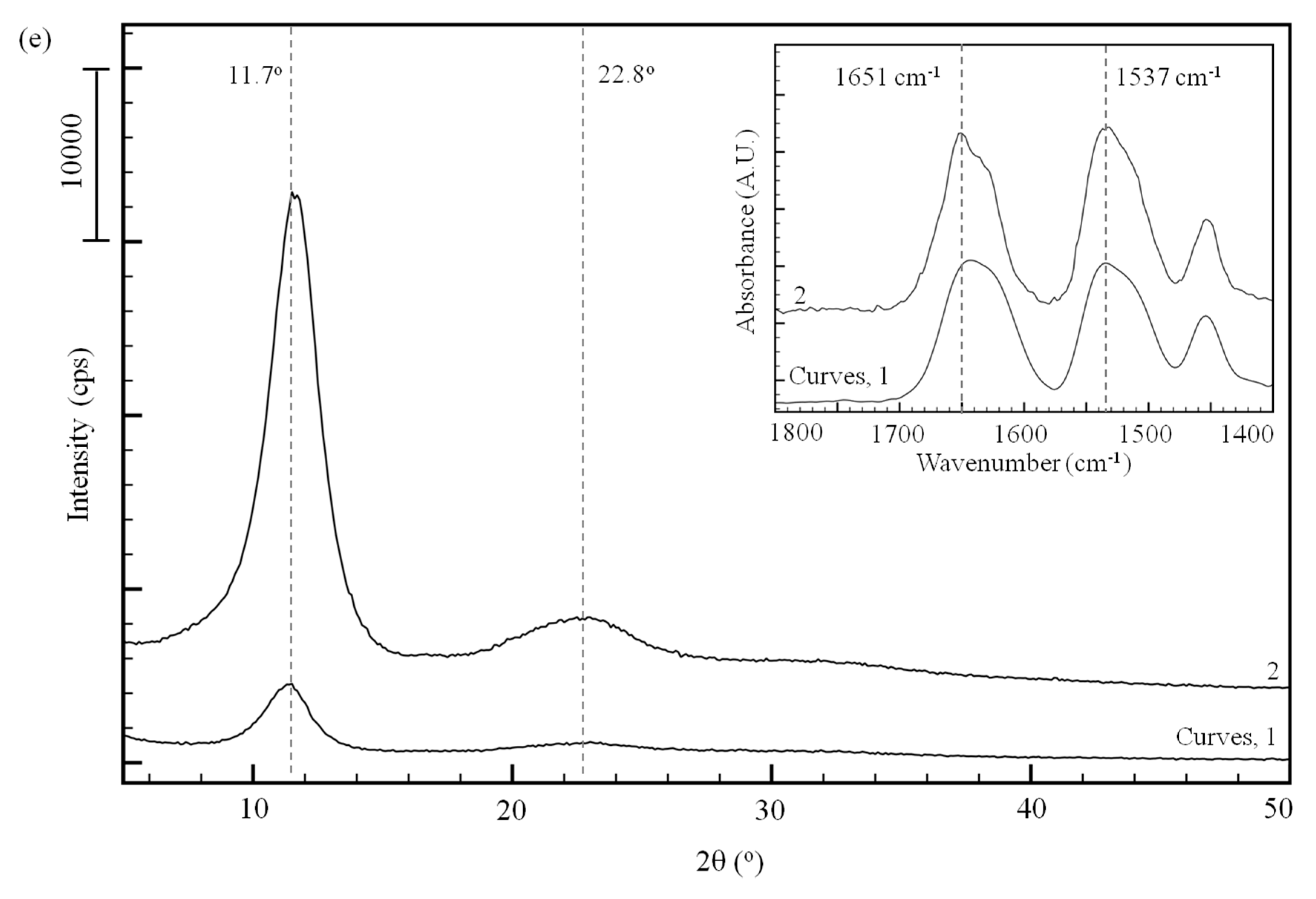
3.3. Analysis of Internal Structures in Poly(amino acid)-ESNWs
3.4. Ordered Structure Content
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. On polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites—A review. Compos. Sci. Tech. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Ryu, Y.J.; Lee, D.R. Manufacturing the cellulose web by using electro-spinning and in vitro behaviour of oxidized cellulose web. J. Korean Fiber Soc. 2002, 39, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ohkawa, K.; Cha, D.; Kim, H.; Nishida, A.; Yamamoto, H. Electrospinning of chitosan. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2004, 25, 1600–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, K.; Hayashi, S.; Nishida, A.; Yamamoto, H.; Ducreux, J. Preparation of pure cellulose nanofiber via electrospinning. Text. Res. J. 2009, 79, 1396–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Mondrinos, M.J.; Gandhi, M.R.; Ko, F.K.; Weiss, A.S.; Lelkes, P.I. Electrospun protein fibers as matrices for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5999–6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohgo, K.; Zhao, C.; Kobayashi, M.; Asakura, T. Preparation of non-woven nanofibers of Bombyx mori silk, Samia cynthia ricini silk and recombinant hybrid silk with electrospinning method. Polymer 2003, 44, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukigara, S.; Gandhi, M.; Ayutsede, J.; Micklus, M.; Ko, F. Regeneration of Bombyx mori silk by electrospinning, part 1: Processing parameters and geometric properties. Polymer 2003, 44, 5721–5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Reneker, D.H. DNA fibers by electrospinning. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 1997, 36, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, J.; Ko, F.K. Encyclopedia of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology. Nanofibers 2004, 6, 727–738. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Ding, M.; Shi, C.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, P.; Qiao, R.; Wang, X.; Zhong, J. Resorbable polymer electrospun nanofibers: History, shapes and application for tissue engineering. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Han, J.; Wang, F.; Shao, W.; Xiong, R.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, H.; Yang, Y.; Samal, S.K.; Zhang, F.; et al. Electrospun nanofibers membranes for effective air filtration. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1600353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Zhu, M.; Jiang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, R.; Huang, C. Green electrospun nanofibers and their application in air filtration. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 303, 1800336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hadi, B.; Shaohua, J.; Holger, S.; Seema, A. Composite polymeric membranes with directionally embedded fibers for controlled dual actuation. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2018, 39, 1800082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Qiao, R.; Su, J.; Yam, J.; Xie, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhong, J. Recent advances of electrospun nanofibrous membranes in the development of chemosensors for heavy metal detection. Small 2017, 13, 1604293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minato, K.I.; Ohkawa, K.; Yamamoto, H. Chain Conformations of poly (γ-benzyl-L-glutamate) pre and post an electrospinning process. Macromol. Biosci. 2006, 6, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, D.B.; Haynie, D.T. Insoluble synthetic polypeptide mats from aqueous solution by electrospinning. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 2728–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, D.B.; Cross, M.C.; Haynie, D.T. A synthetic polypeptide electrospun biomaterial. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 2994–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynie, D.T.; Khadka, D.B.; Cross, M.C. Physical properties of polypeptide electrospun nanofiber cell culture scaffolds on a wettable substrate. Polymers 2012, 4, 1535–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroaki, Y.; Kazuhiro, Y. Creation of superhydrophobic poly(L-phenylalanine) nonwovens by electrospinning. Polymers 2018, 10, 1212. [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann, M.; Zervas, L.; Ross, W.F. Synthesis of peptides of L-lysine and their behavior with papain. J. Biol. Chem. 1935, 111, 245–260. [Google Scholar]
- Bamford, C.H.; Elliot, A.; Hanby, W.E. Synthetic Polypeptides—Preparation, Structure and Properties; Academic Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1956; p. 48. [Google Scholar]
- Ohkawa, K.; Minato, K.I.; Kumagai, G.; Hayashi, S.; Yamamoto, H. Chitosan nanofiber. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 3291–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, H.; Iwata, M.; Ito, S.; Endo, T. Ring-opening polymerization of γ-benzyl-L-glutamate-N-carboxyanhydride in ionic liquids. Polymer 2007, 48, 5867–5877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, F.S. Proteins and Polypeptides, in Applications of Infrared Spectroscopy in Biochemistry, Biology, and Medicine; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1973; pp. 188–231. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuboi, K.; Marcelletti, E.; Matsumoto, H.; Ashizawa, M.; Minagawa, M.; Furuya, H.; Tanioka, A.; Abe, A. Preparation of poly(γ-benzyl-l-glutamate) nanofibers by electrospinning from isotropic and biphasic liquid crystal solutions. Polymer 2012, 44, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]

| Title | TFA:DCM | 2θ (o) | Imax (cps) (a) | W (mg) (b) | C (cps/mg) (c) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poly(l-Ala)-ESNW | 10:0 | 11.5 | 29200 | 56.0 | 521 |
| 8:2 | 11.7 | 44100 | 21.3 | 2070 | |
| 5:5 | 11.7 | 42100 | 19.7 | 2140 | |
| Poly(l-Val)-ESNW | 10:0 | 8.5 | 15200 | 74.0 | 205 |
| 8:2 | 8.5 | 13200 | 11.5 | 1150 | |
| 5:5 | 8.5 | 19200 | 22.3 | 861 | |
| Poly(l-Leu)-ESNW | 10:0 | 7.9 | 34800 | 128 | 272 |
| 8:2 | 7.9 | 36400 | 36.3 | 1000 | |
| 5:5 | 7.9 | 33000 | 36.0 | 917 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Devarayan, K.; Nakagami, S.; Suzuki, S.; Yuki, I.; Ohkawa, K. Electrospinning and Post-Spun Chain Conformations of Synthetic, Hydrophobic Poly(α-amino acid)s. Polymers 2020, 12, 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020327
Devarayan K, Nakagami S, Suzuki S, Yuki I, Ohkawa K. Electrospinning and Post-Spun Chain Conformations of Synthetic, Hydrophobic Poly(α-amino acid)s. Polymers. 2020; 12(2):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020327
Chicago/Turabian StyleDevarayan, Kesavan, Souta Nakagami, Shuichi Suzuki, Ichiro Yuki, and Kousaku Ohkawa. 2020. "Electrospinning and Post-Spun Chain Conformations of Synthetic, Hydrophobic Poly(α-amino acid)s" Polymers 12, no. 2: 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020327
APA StyleDevarayan, K., Nakagami, S., Suzuki, S., Yuki, I., & Ohkawa, K. (2020). Electrospinning and Post-Spun Chain Conformations of Synthetic, Hydrophobic Poly(α-amino acid)s. Polymers, 12(2), 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020327