High Moisture Accelerated Mechanical Behavior Degradation of Phosphor/Silicone Composites Used in White Light-Emitting Diodes
Abstract
1. Introduction
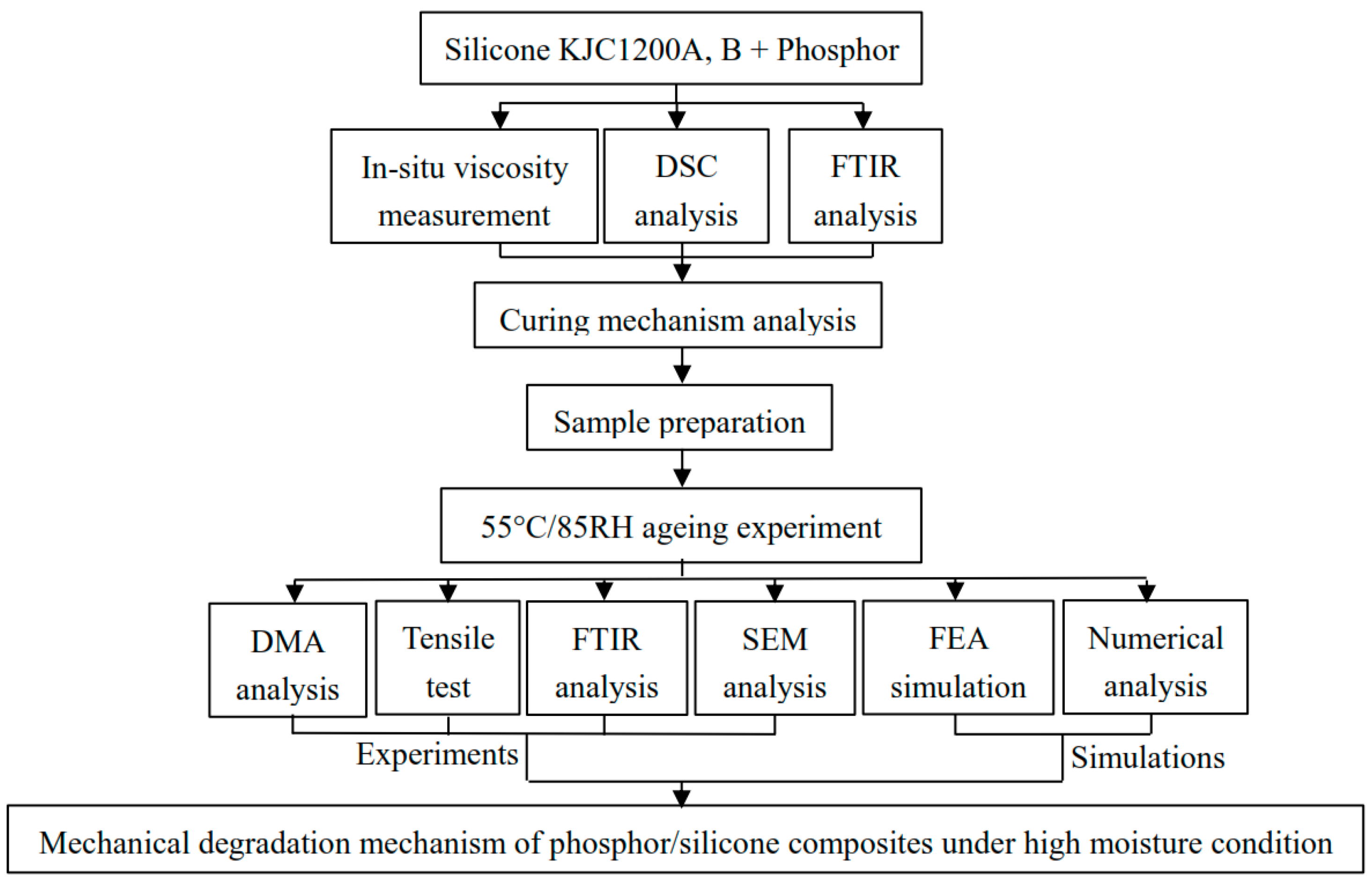
2. Sample Preparation and Experimental Setup
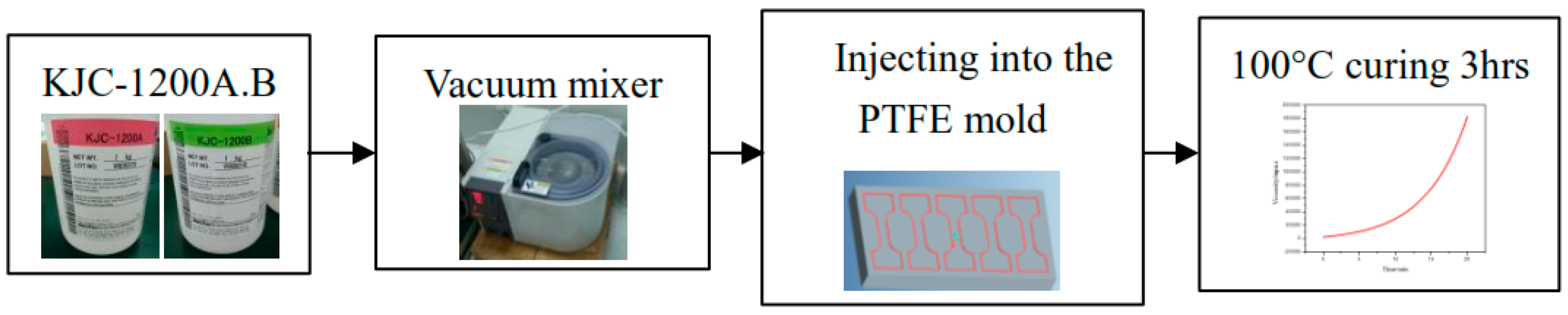
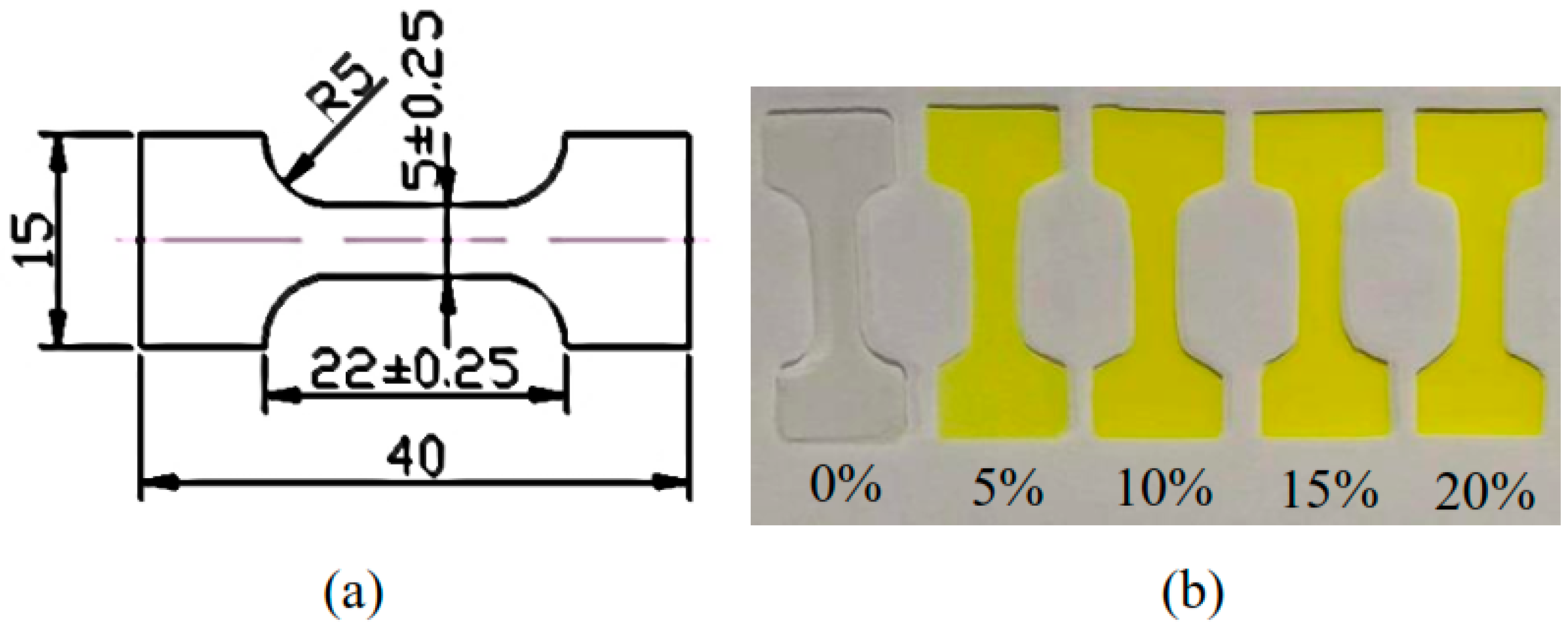
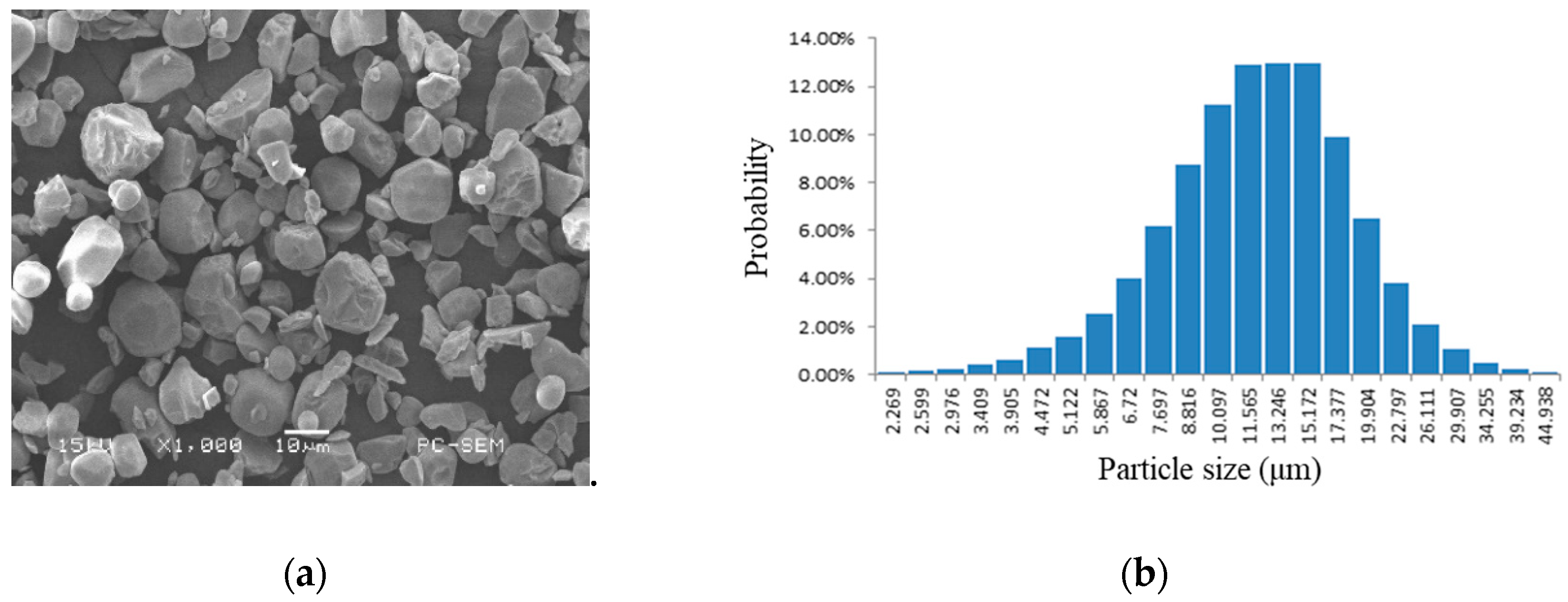
2.1. Sample Preparation
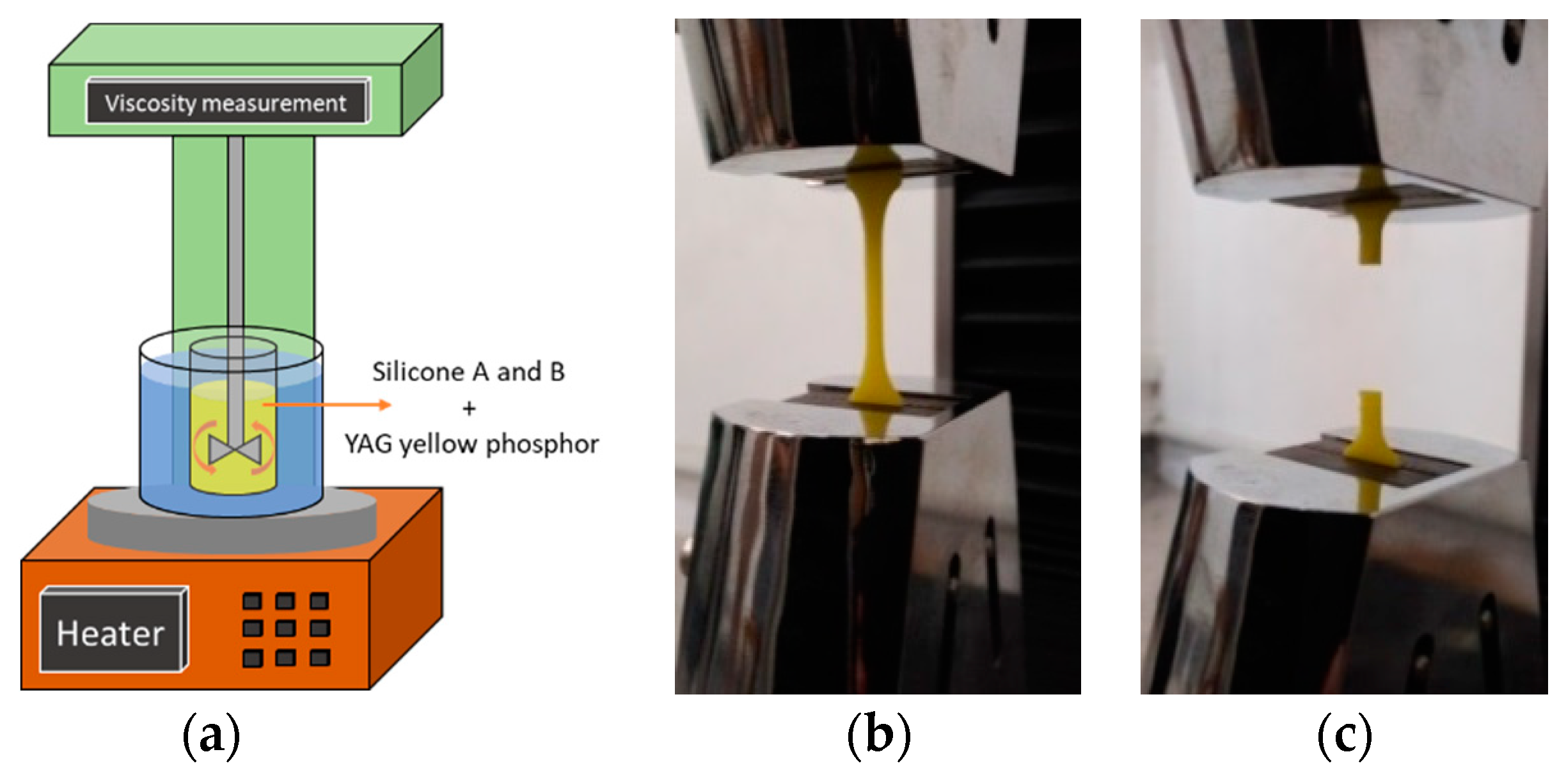
2.2. Experimental Setup
3. Results and Discussion
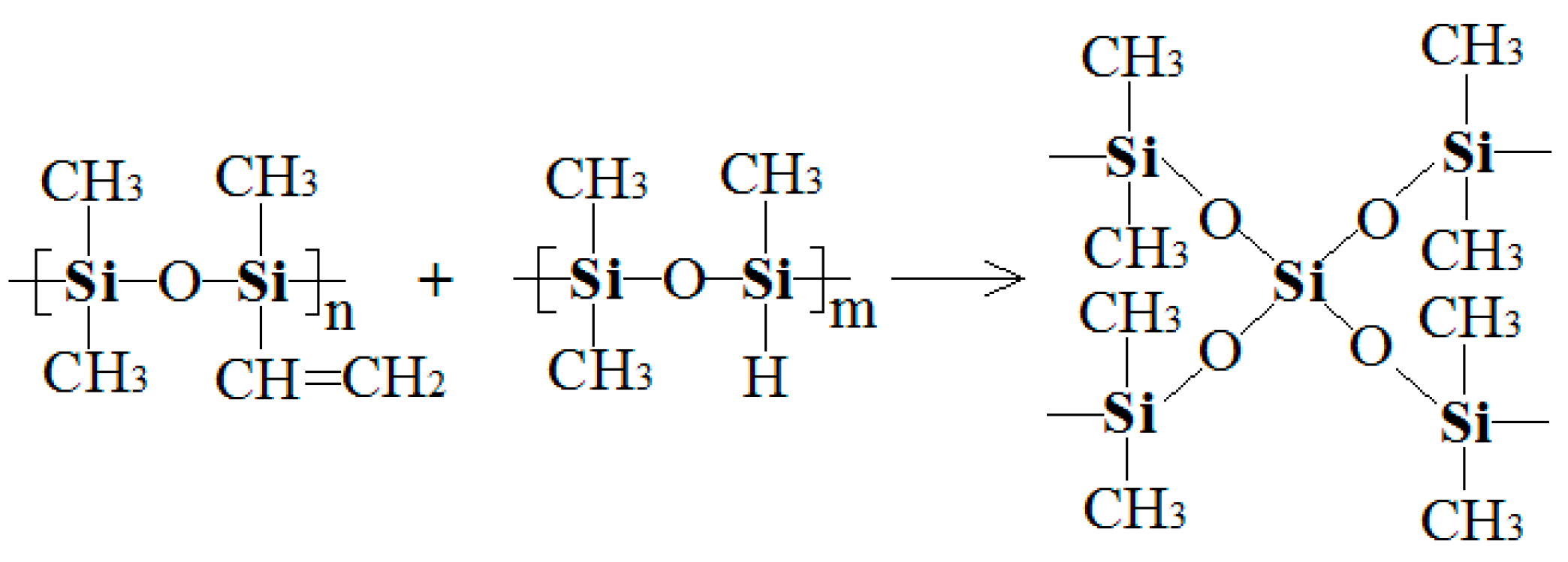
3.1. Curing Mechanism Analysis
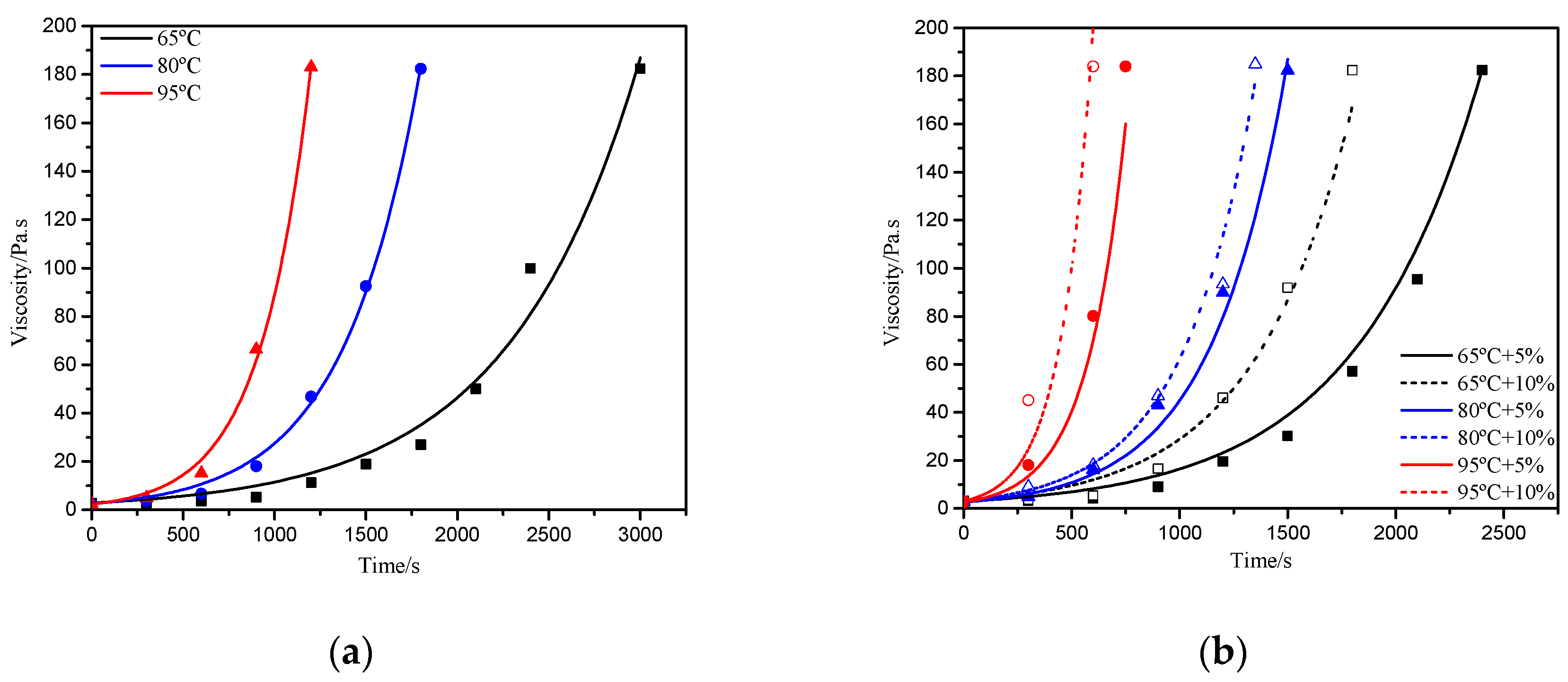
3.1.1. In Situ Viscosity Measurement Results and Discussion
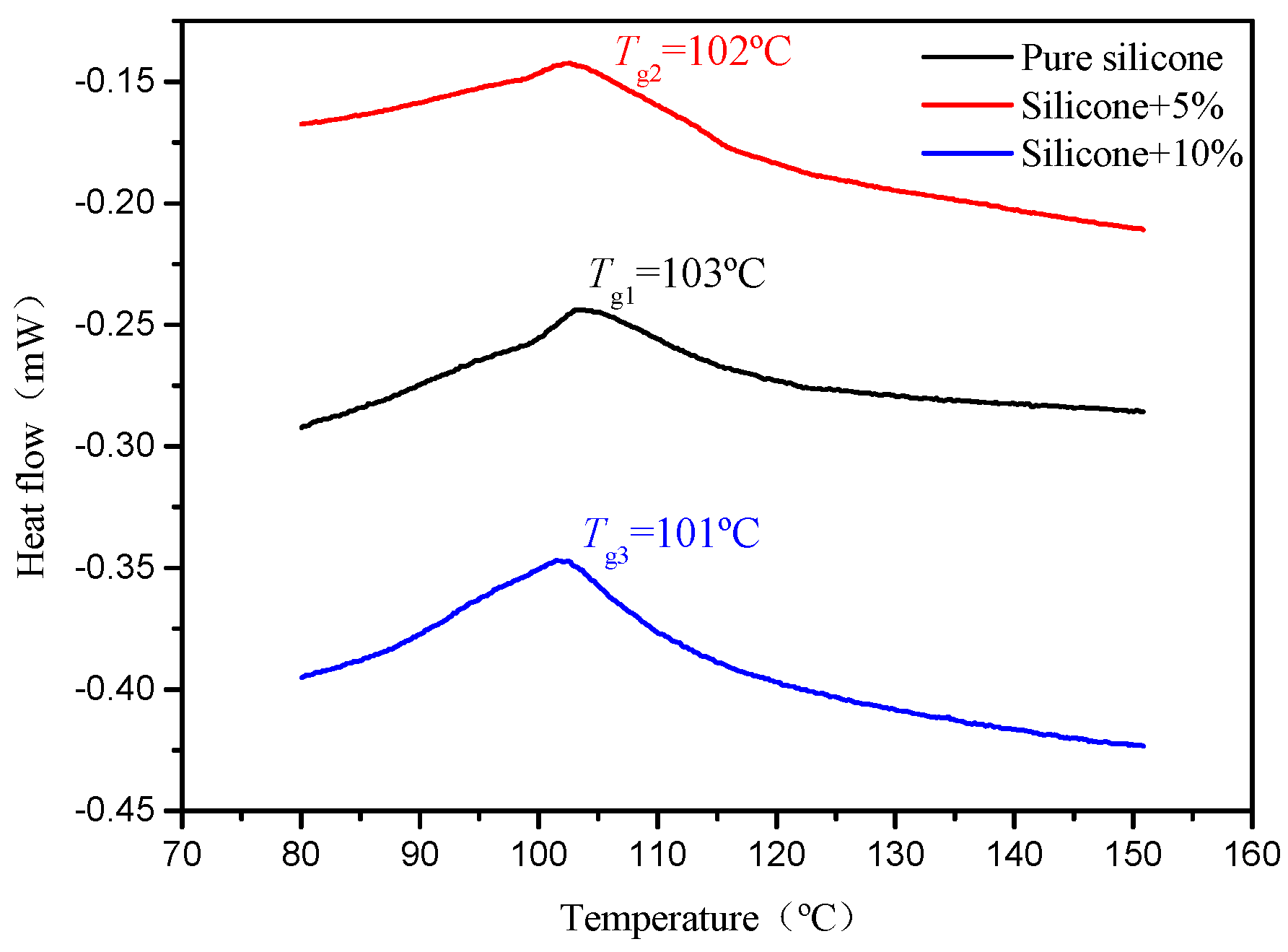
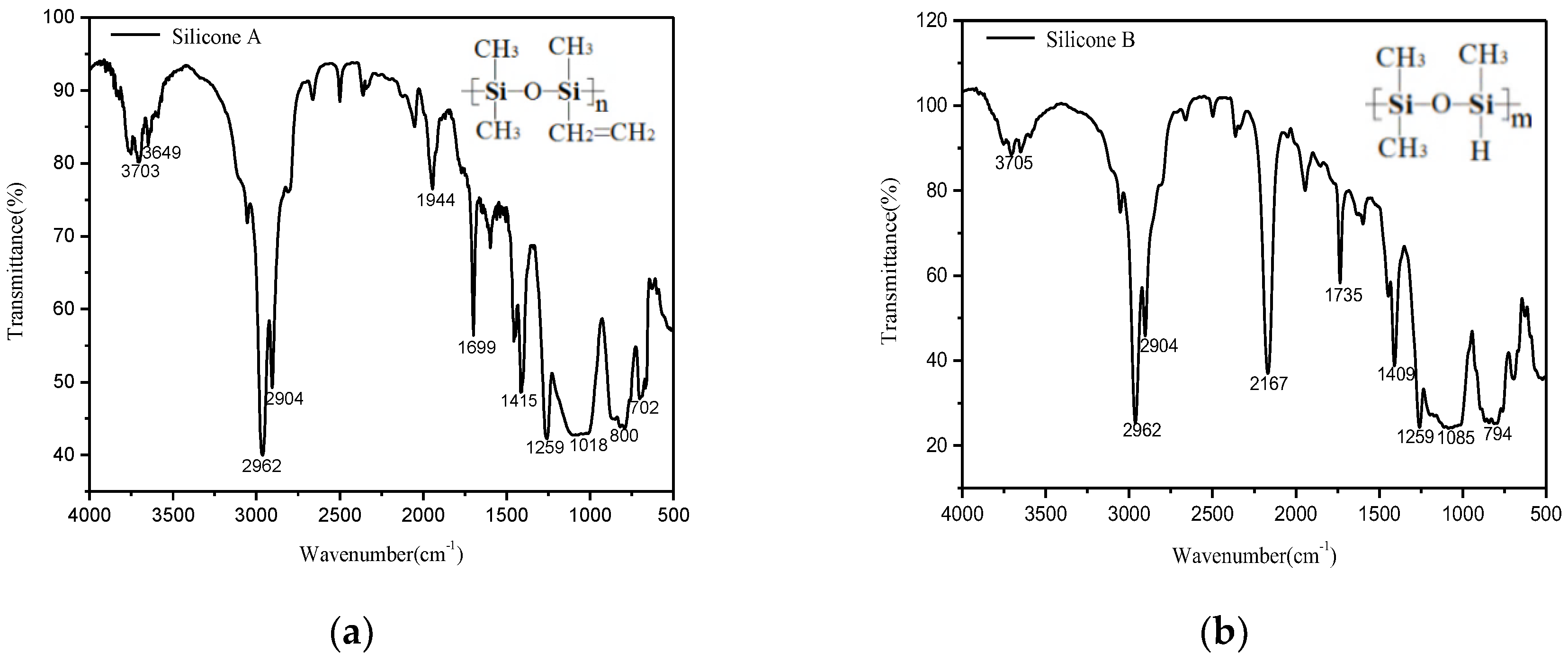
3.1.2. DSC and FTIR Results and Discussion
3.2. Moisture-Accelerated Degradation Mechanism Analysis
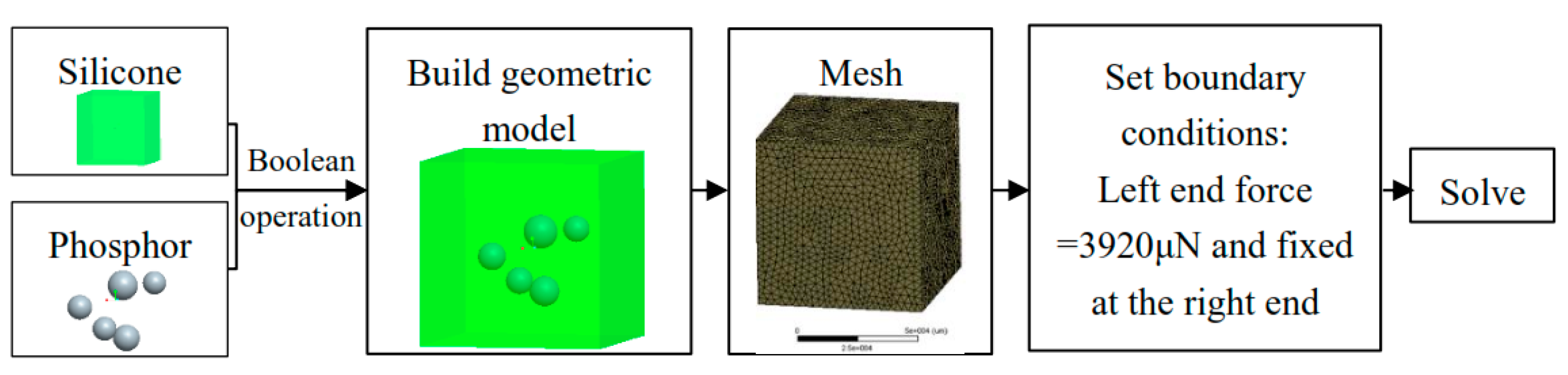
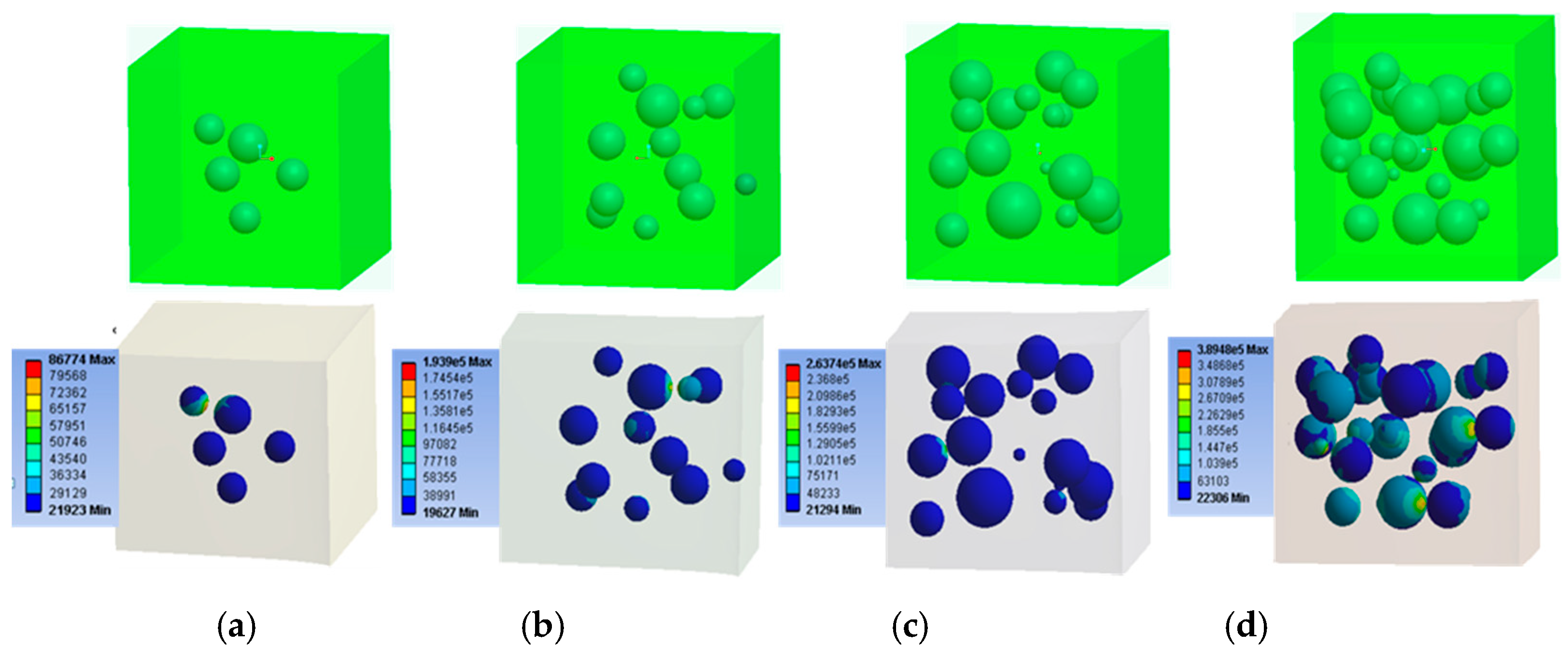
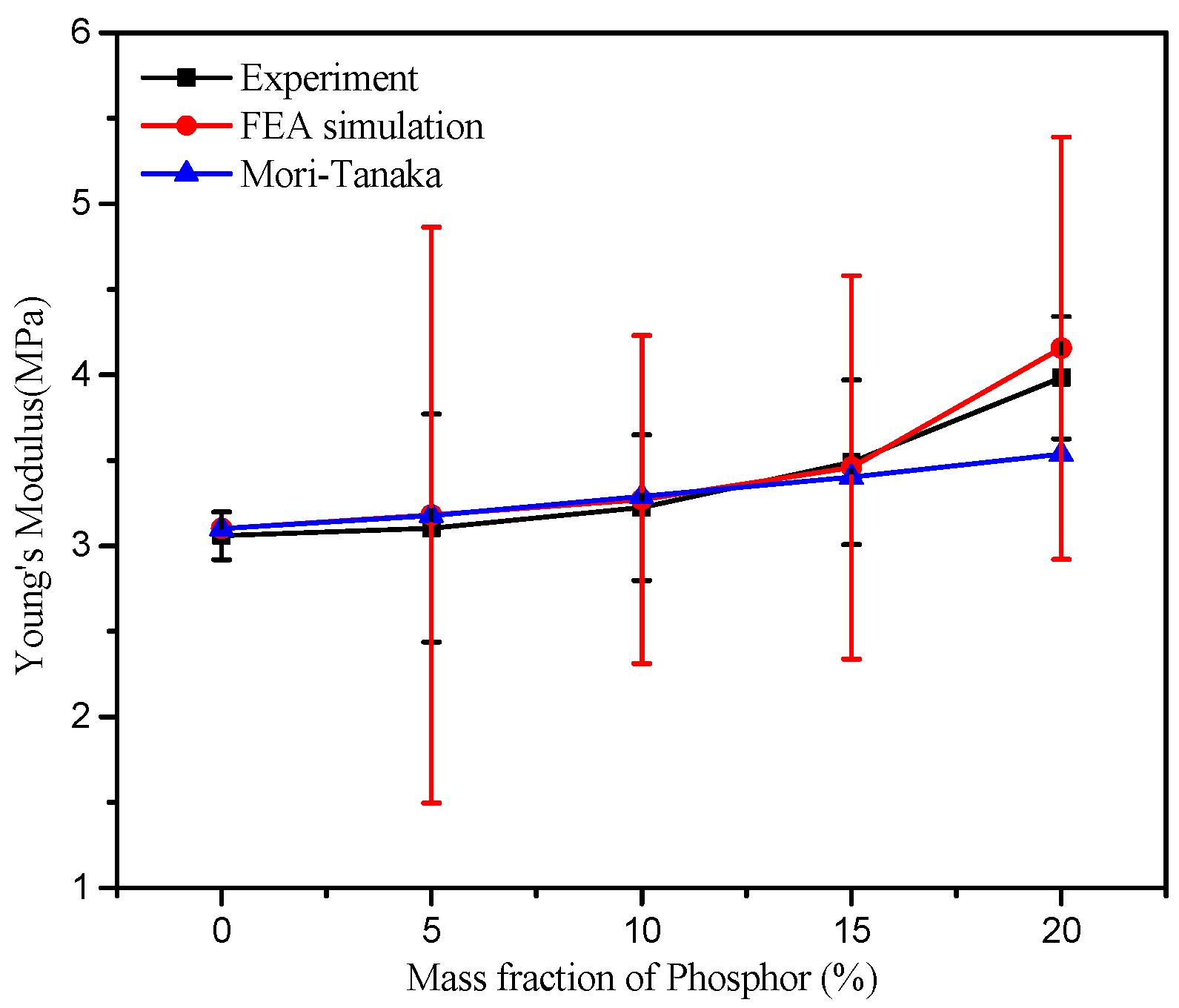
3.2.1. Transient Mechanical Property Prediction with FEA Simulations
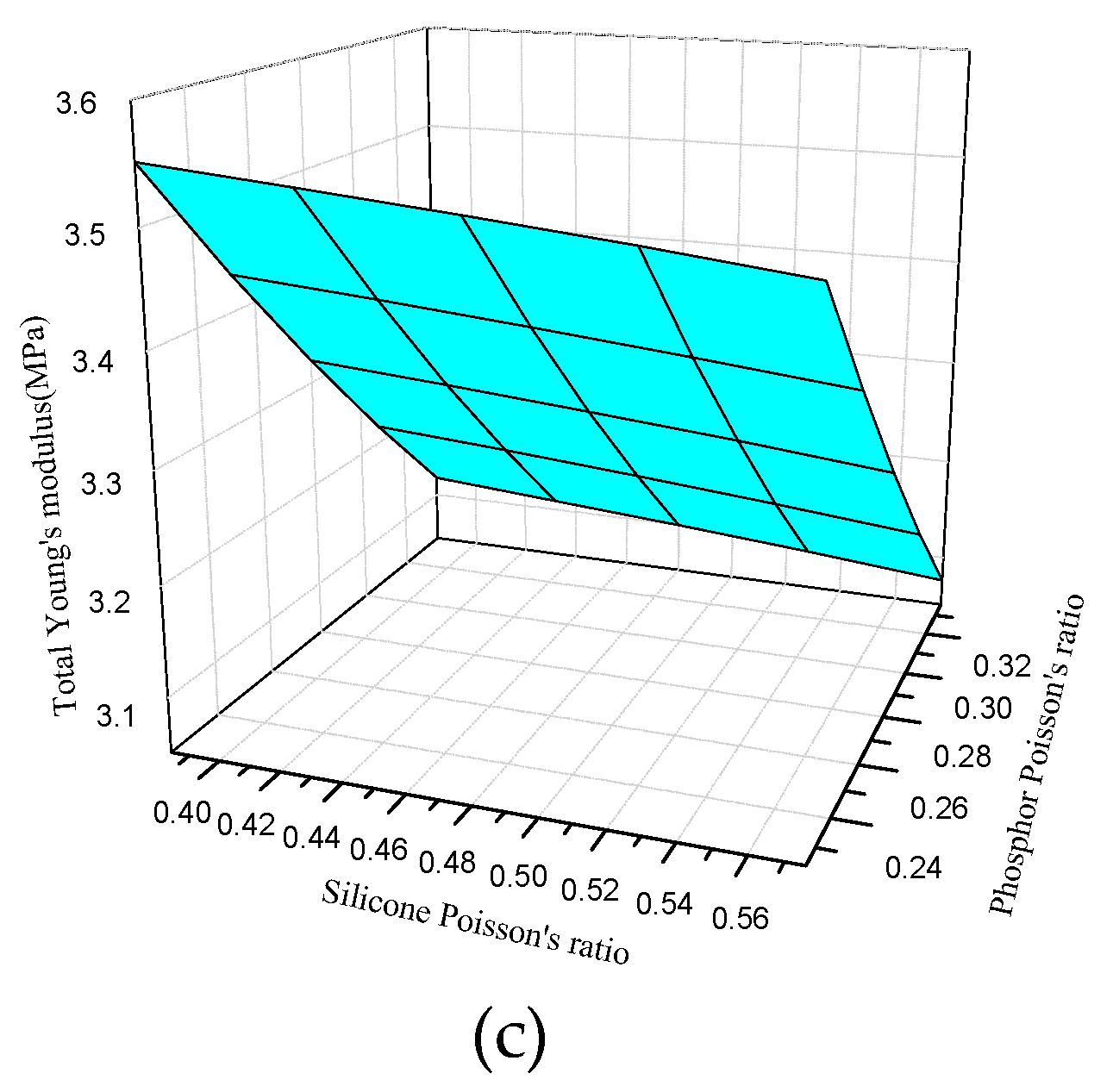
3.2.2. Transient Mechanical Property Prediction with the Mori–Tanaka Method
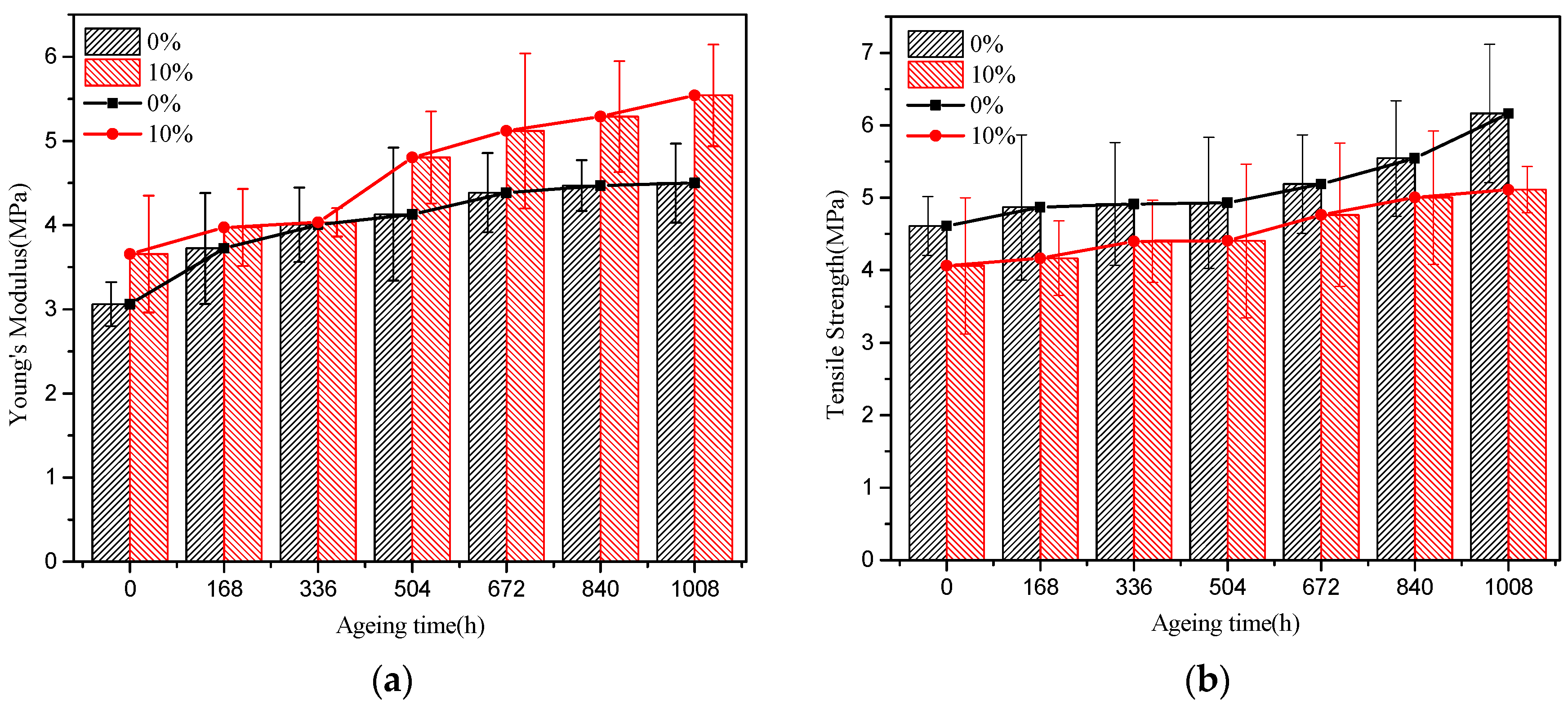
3.2.3. Long-Term Tensile Test Result Analysis
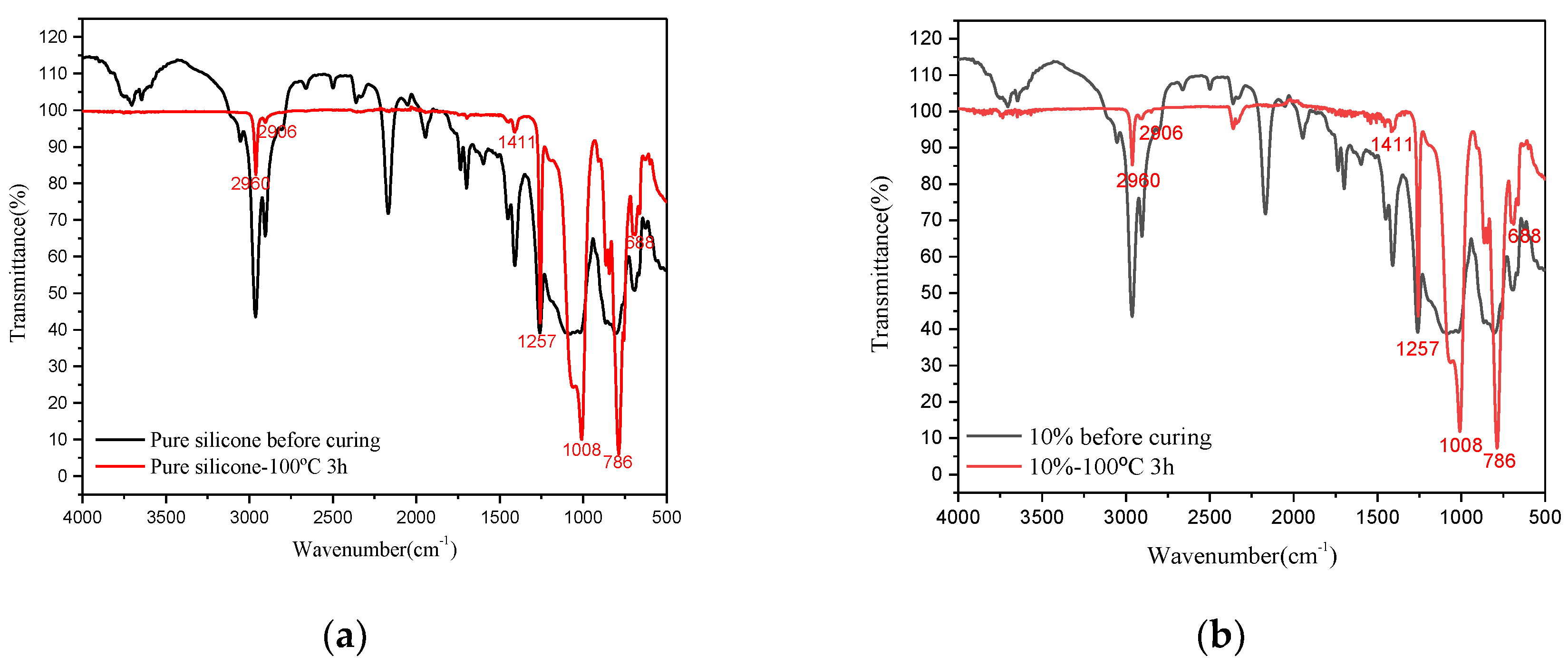
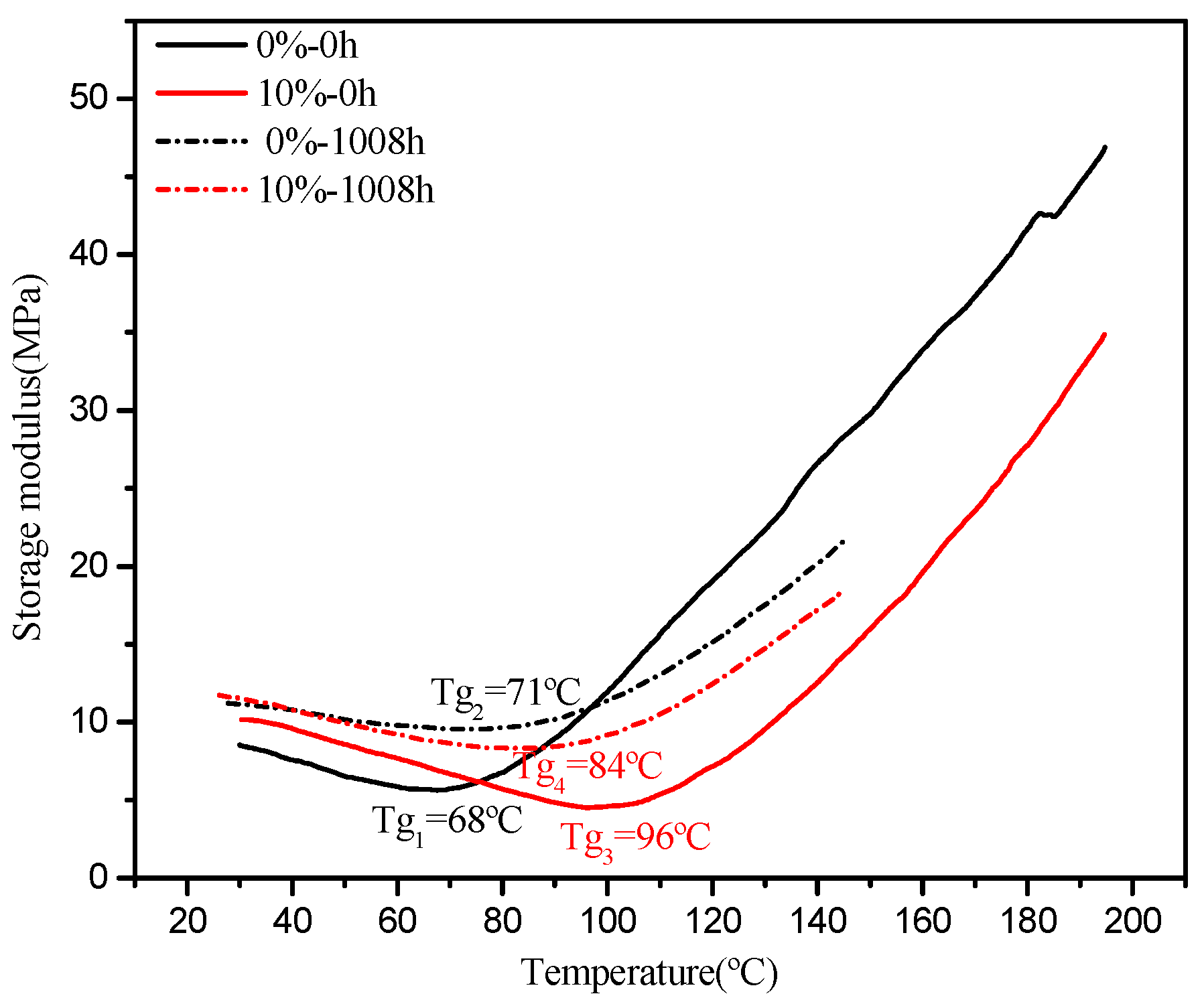
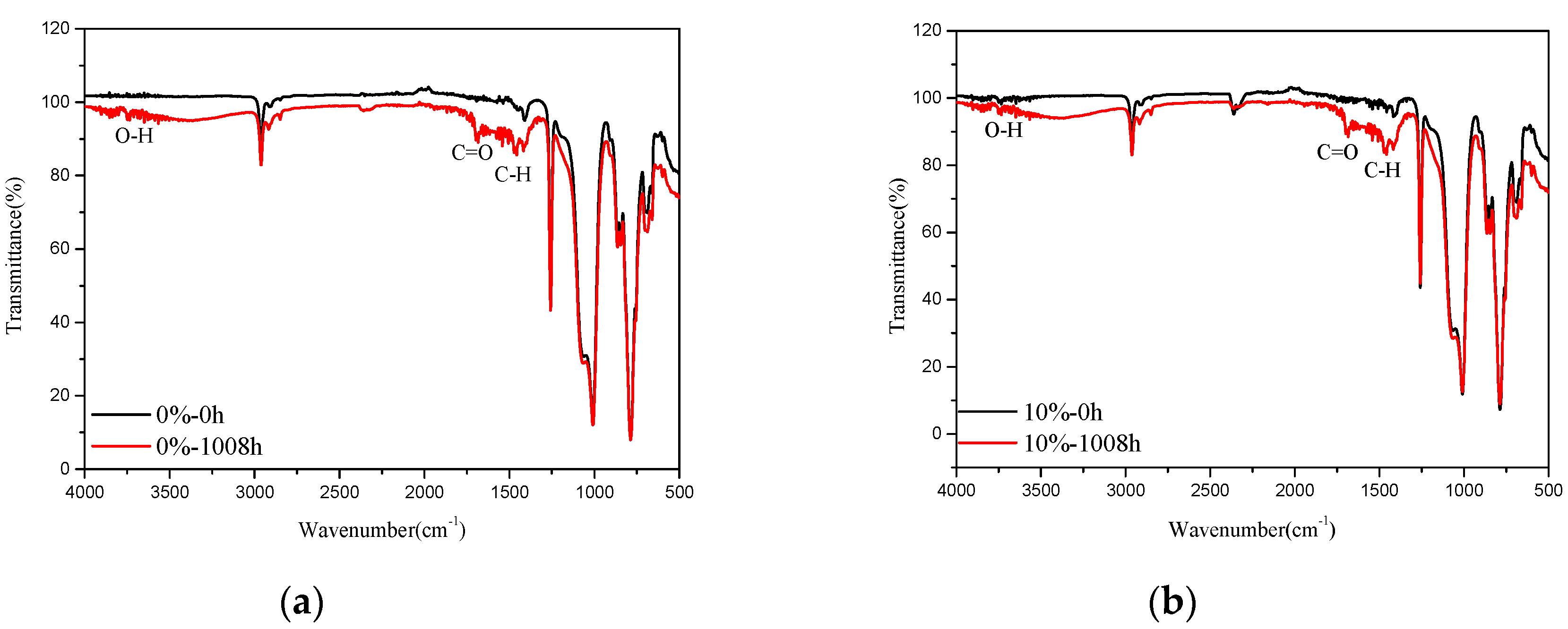
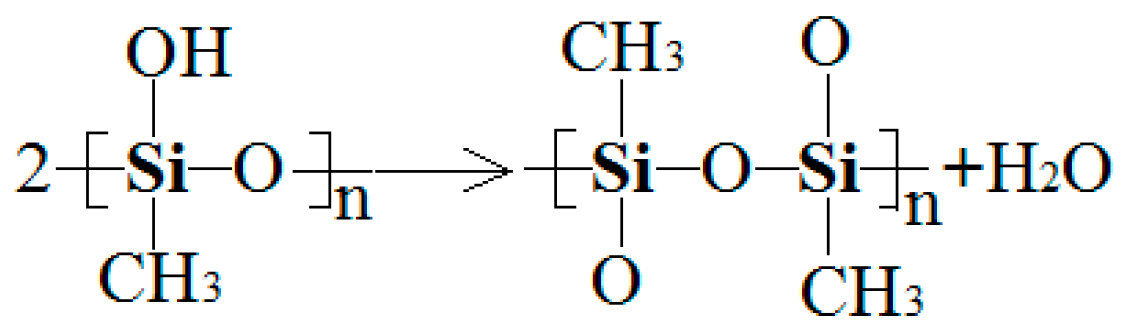
3.2.4. DMA and FTIR Result Analysis
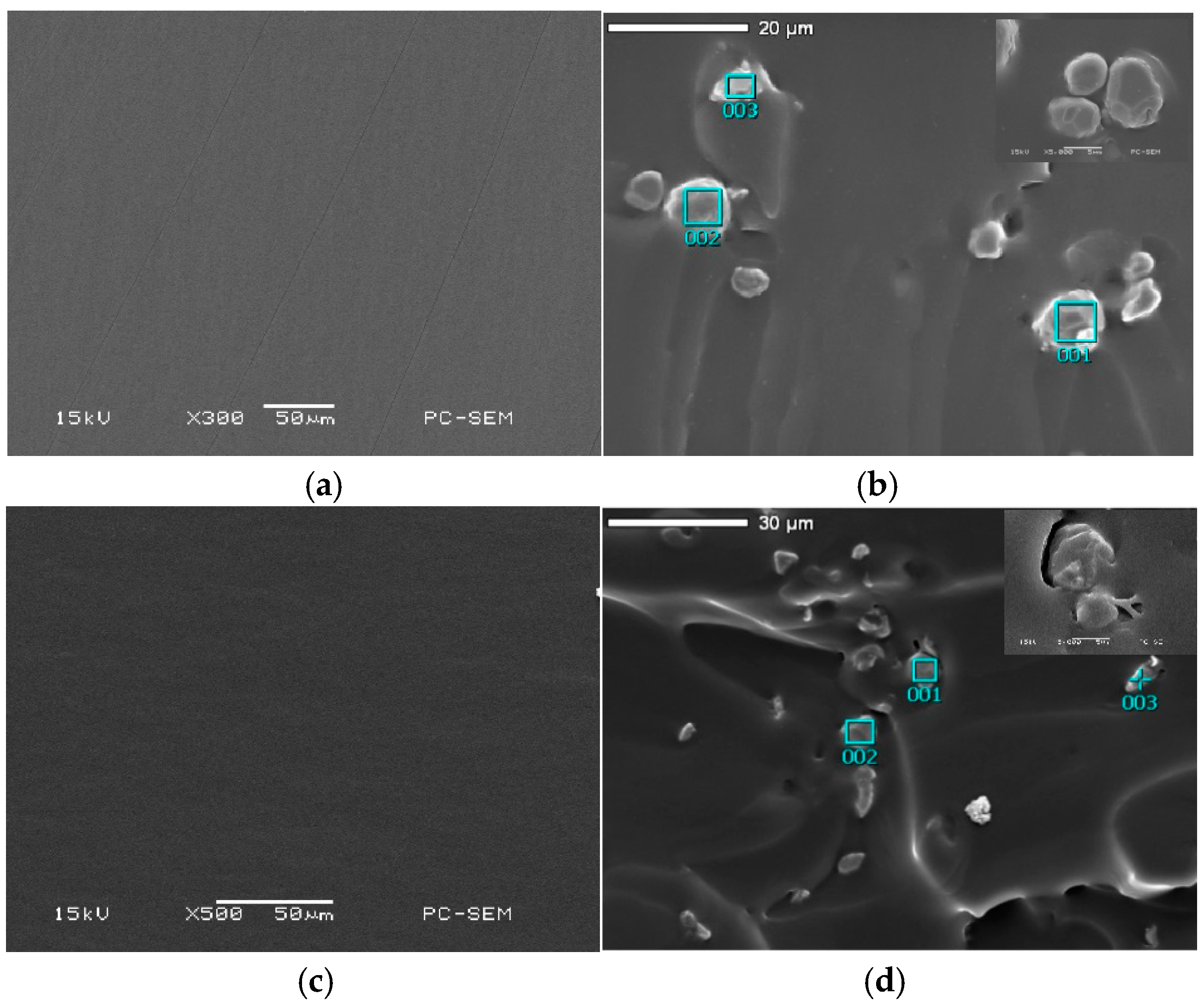
3.2.5. SEM/EDS Result Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, J.; Zhang, M.; Luo, X.; Qian, C.; Fan, X.; Ji, A.; Zhang, G.Q. Phosphor–silicone interaction effects in high power white light emitting diode packages. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 17557–17569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Fan, J.; Qian, C.; Li, Y.; Fan, X.; Ji, A.; Zhang, G. Investigation of photoluminescence and thermal effect of phosphor films used in phosphor-converted white LEDs. In Proceedings of the 2015 12th China International Forum on Solid State Lighting, Shenzhen, China, 2–4 November 2015; pp. 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, C.; Luo, L.L.; Fan, J.J.; Li, X.Q.; Fan, X.J.; Zhang, G.Q. Effects of phosphor dispersion on optical characteristics of LED Chip Scale Package LEDs. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Thermal, Mechanical and Multi-Physics Simulation and Experiments in Microelectronics and Microsystems, Dresden, Germany, 3–5 April 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Zibold, A.; Dammann, M.; Schmidt, R.; Konstanzer, H.; Kunzer, M. Influence of air pollutants on the lifetime of LEDs and analysis of degradation effects. Microelectron. Reliab. 2017, 76, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lall, P.; Zhang, H.; Davis, L. A comparison of temperature and humidity effects on phosphor converted LED package and the prediction of remaining useful life with state estimation. In Proceedings of the 2016 15th IEEE Intersociety Conference on Thermal and Thermomechanical Phenomena in Electronic Systems, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 31 May–3 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Zhou, L.; Luo, H.; Xiao, W.; Cao, M.; Hu, Y.; Jing, G.; Liu, Y. Research on failure mechanism of the phosphors and sealants for white light emitting diode package. In Proceedings of the 2016 17th International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology, Wuhan, China, 16–19 August 2016; pp. 1297–1300. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, R.; Luo, X.; Liu, S. Effect of the amount of phosphor silicone gel on optical property of white light-emitting diodes packaging. In Proceedings of the 2011 12th International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology and High Density Packaging, Shanghai, China, 8–11 August 2011; Volume 204, pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Hu, R.; Luo, X. Modeling on phosphor sedimentation phenomenon during curing process of high power LED packaging. J. Solid State Lighting 2014, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Chen, W.; Hao, J.; Wu, D.; Yu, X.; Chen, Y.; Hu, R.; Wang, K.; Luo, X. Structural optimization for remote white light-emitting diodes with quantum dots and phosphor: Packaging sequence matters. Opt. Express 2016, 24, A1560–A1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, S.S.; Chung, Y.P.; Chan, C.K.; Kuo, P.L. Function and performance of silicone copolymer. Part IV. Curing behavior and characterization of epoxy–siloxane copolymers blended with diglycidyl ether of bisphenol-A. Polymer 2000, 41, 3263–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalilullah, I.; Reza, T.; Chen, L.; Mazumder, A.K.M.M.H.; Fan, J.; Qian, C.; Zhang, G.; Fan, X. In-situ characterization of moisture absorption and hygroscopic swelling of silicone/phosphor composite film and epoxy mold compound in LED packaging. In Proceedings of the 2017 18th International Conference on Thermal, Mechanical and Multi-Physics Simulation and Experiments in Microelectronics and Microsystems, Dresden, Germany, 3–5 April 2017; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.Z.; Song, C.Y.; Sun, M.M.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X.G.; Wang, L.; Xue, G.; Zhao, M.; Liu, C.Z.; Mei, G.; et al. The Research Progress in Shrinkage of UV-Curing. Chem. Adhes. 2016, 38, 373–377. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.Q.; Cai, J.; Qin, X.F.; Bai, T.; Wang, D.Q.; Li, Y.-P. Study on the rheological properties of liquid-crystalline epoxy resin modified E-51 resin system. Thermoset. Resin 2015, 30, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Fan, J.; Liu, J.; Hu, A.; Qian, C.; Fan, X.; Zhang, G. Study of ultraviolet assisted cure mechanism of the phosphor/silicone composites used in White LEDs. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology (ICEPT 2018), Shanghai, China, 8–11 August 2018; pp. 525–530. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Fan, J.; Zhang, M.; Qian, C.; Fan, X.; Zhang, G. Degradation mechanism analysis for phosphor/silicone composites aged under high temperature and high humidity condition. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology (ICEPT 2017), Harbin, China, 16–19 August 2017; pp. 1331–1336. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Tan, C.M.; Chang, L.B. Early degradation of high power packaged LEDs under humid conditions and its recovery—Myth of reliability rejuvenation. Microelectron. Reliab. 2016, 61, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.J.; Wang, Z.; Luo, X.; Zhou, L.; Fan, X.J.; Zhang, G.Q. Degradation Mechanism Analysis for LED Phosphors under Hygrothermal Environment. Rare Metal. Mater. Eng. 2018. accepted paper. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Mu, X.; Wang, K.; Gan, Z.; Luo, X.; Liu, S. Dynamic Mechanical Properties of the Transparent Silicone Resin for High Power LED Packaging. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology High Density Packaging (2008 ICEPT-HDP), Shanghai, China, 28–31 July 2008; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.H.; Li, H.; Li, Q.Q.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.P. Storage Life Prediction of Silicone Rubber by Laboratory Accelerated Aging Test. Synth. Mater. Aging Appl. 2013, 42, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Gac, P.Y.L.; Saux, V.L.; Paris, M.; Marco, Y. Ageing mechanism and mechanical degradation behaviour of polychloroprene rubber in a marine environment: Comparison of accelerated ageing and long term exposure. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, R.; Jiao, F. Comparison of LED package reliability under thermal cycling and thermal shock conditions by experimental testing and finite element simulation. In Proceedings of the Electronic Components and Technology Conference, Lake Buena Vista, FL, USA, 31 May–3 June 2011; pp. 454–459. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, K.; Chen, M.; Liu, S. Fluid–solid coupling thermo-mechanical analysis of high power LED package during thermal shock testing. Microelectron. Reliab. 2012, 52, 1726–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.G.; Kang, J.H.; Jang, I.H.; Chan, S.I.; Jang, J.S. Conclusion of the accelerated stress conditions affecting phosphor-converted LEDs using the fractional factorial design method. Microelectron. Reliab. 2013, 53, 1519–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, L.; Chagnon, G.; Favier, D.; Orgéas, L.; Vacher, P. Mechanical experimental characterisation and numerical modelling of an unfilled silicone rubber. Polym. Test. 2008, 27, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, F.; Zheng, H. Study on mechanical behavior and interfacial strength of YAG phosphor-filled silicone. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology and High Density Packaging, Guilin, China, 13–16 August 2012; pp. 1443–1446. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Wang, S.; Cao, C.; Liu, S. Influence of phosphor amount on microstructure and damage evolution of silicone/phosphor composite in light-emitting diodes packaging. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 107, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, X.; Liu, S.; Zhu, F.; Liu, X. Estimation of homogenized Youngs modulus of silicone/phosphor composite considering random dispersion and size variation of phosphor particles. J. Compos. Mater. 2015, 50, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Zhu, F.; Fan, J.; Tao, J.; Lin, X.; Wang, F.; Shi, L. Investigation of mechanical properties of silicone/phosphor composite used in light emitting diodes package. Polymers 2018, 10, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM International. ASTM D1708-18, Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics by Use of Microtensile Specimens; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z. Determination of Young’s modulus of the syntactic foam plastics by differential scheme. J. Beijing Univ. Aeronaut. Astronaut. 1996, 6, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Hu, N.; Zheng, H.; Fukunaga, H. Evaluation of mechanical properties of particulate composites with a combined self-consistent and Mori–Tanaka approach. Mech. Mater. 2009, 41, 1288–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

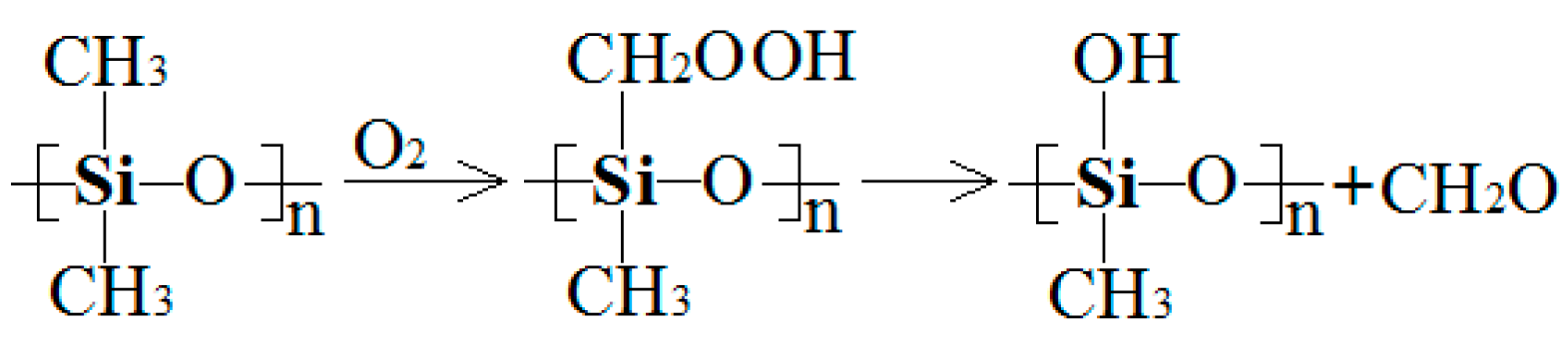
| Silicone A | Silicone B | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Vibration Frequency/cm−1 | Vibration Mode | Vibration Frequency/cm−1 | Vibration Mode |
| 2962, 2904 | CH3 | 2962, 2904 | CH3 |
| 1699 | CH2=CH2 | 2167 | Si–H |
| 1415, 1259 | Si–CH3 | 1415, 1259 | Si–CH3 |
| 1100–1000 | Si–O–Si | 1100–1000 | Si–O–Si |
| 800 | C–Si | 800 | C–Si |
| Components | Density (g/cm3) | Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Poisson’s Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silicone | 1.04 | 3.10 | 0.48 |
| Phosphor | 4.56 | 335,000 | 0.28 |
| Components | Elements | Averaged Element Contents before Ageing (%) | Averaged Element Contents after Ageing (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phosphor | O | 8.91 | 11.32 |
| Al | 28.18 | 27.57 | |
| Y | 57.37 | 52.01 | |
| Silicone | C | 18.58 | 22.72 |
| O | 5.31 | 8.29 | |
| Si | 76.11 | 69.00 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Deng, Z.; Fan, X.; Zhang, G. High Moisture Accelerated Mechanical Behavior Degradation of Phosphor/Silicone Composites Used in White Light-Emitting Diodes. Polymers 2019, 11, 1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11081277
Fan J, Wang Z, Zhang X, Deng Z, Fan X, Zhang G. High Moisture Accelerated Mechanical Behavior Degradation of Phosphor/Silicone Composites Used in White Light-Emitting Diodes. Polymers. 2019; 11(8):1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11081277
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Jiajie, Zhen Wang, Xunwei Zhang, Zhentao Deng, Xuejun Fan, and Guoqi Zhang. 2019. "High Moisture Accelerated Mechanical Behavior Degradation of Phosphor/Silicone Composites Used in White Light-Emitting Diodes" Polymers 11, no. 8: 1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11081277
APA StyleFan, J., Wang, Z., Zhang, X., Deng, Z., Fan, X., & Zhang, G. (2019). High Moisture Accelerated Mechanical Behavior Degradation of Phosphor/Silicone Composites Used in White Light-Emitting Diodes. Polymers, 11(8), 1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11081277





