Coordination Dynamics and Thermal Stability with Aminal Metallogels and Liquids
Abstract
1. Introduction
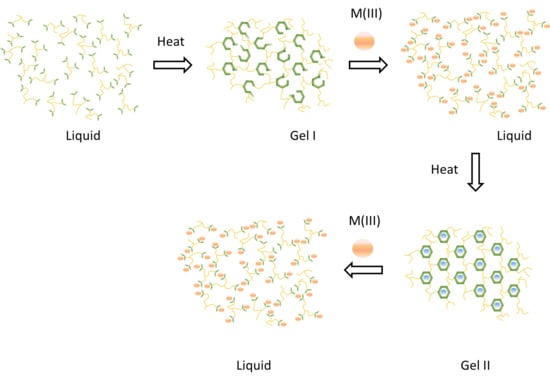
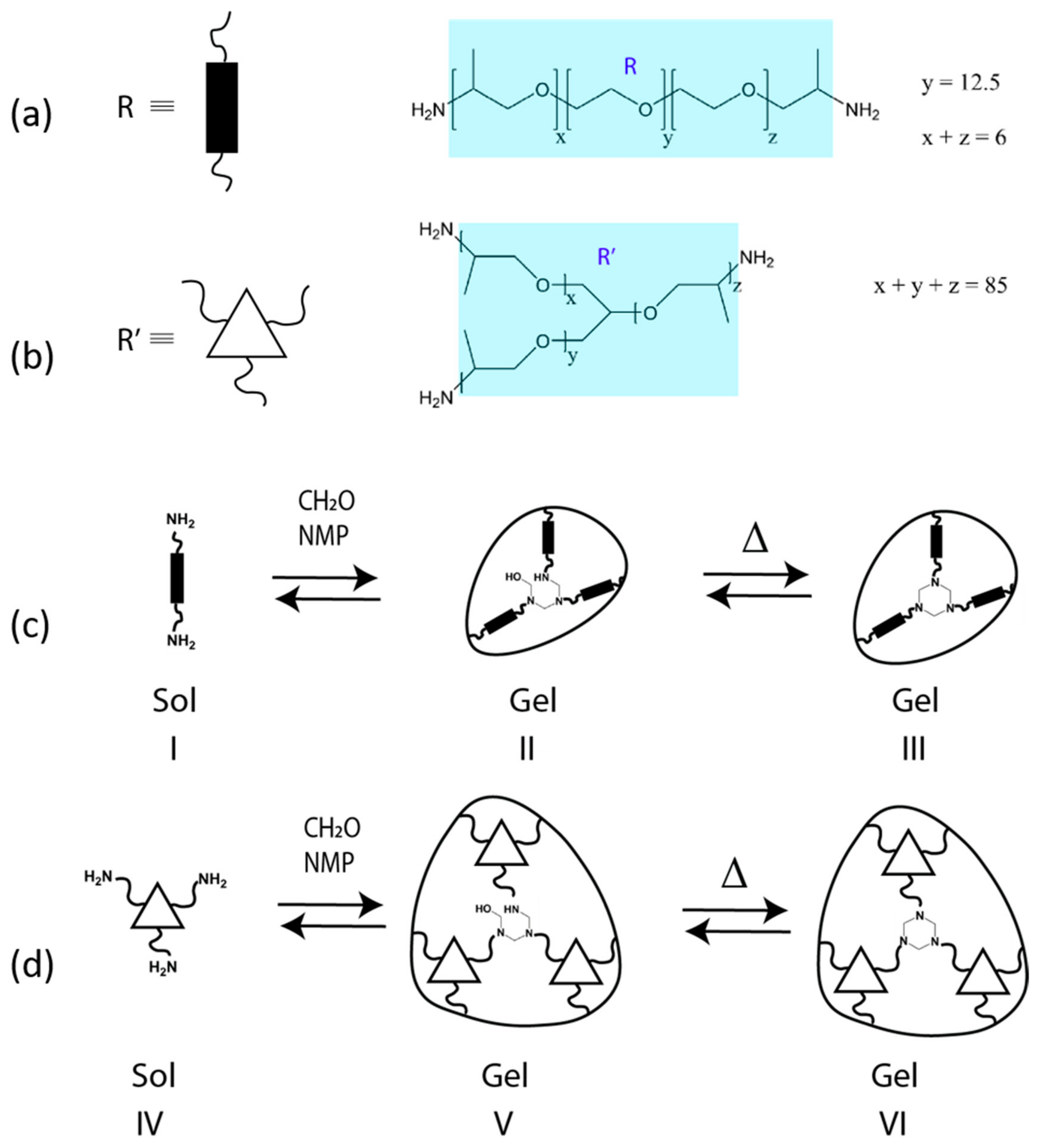
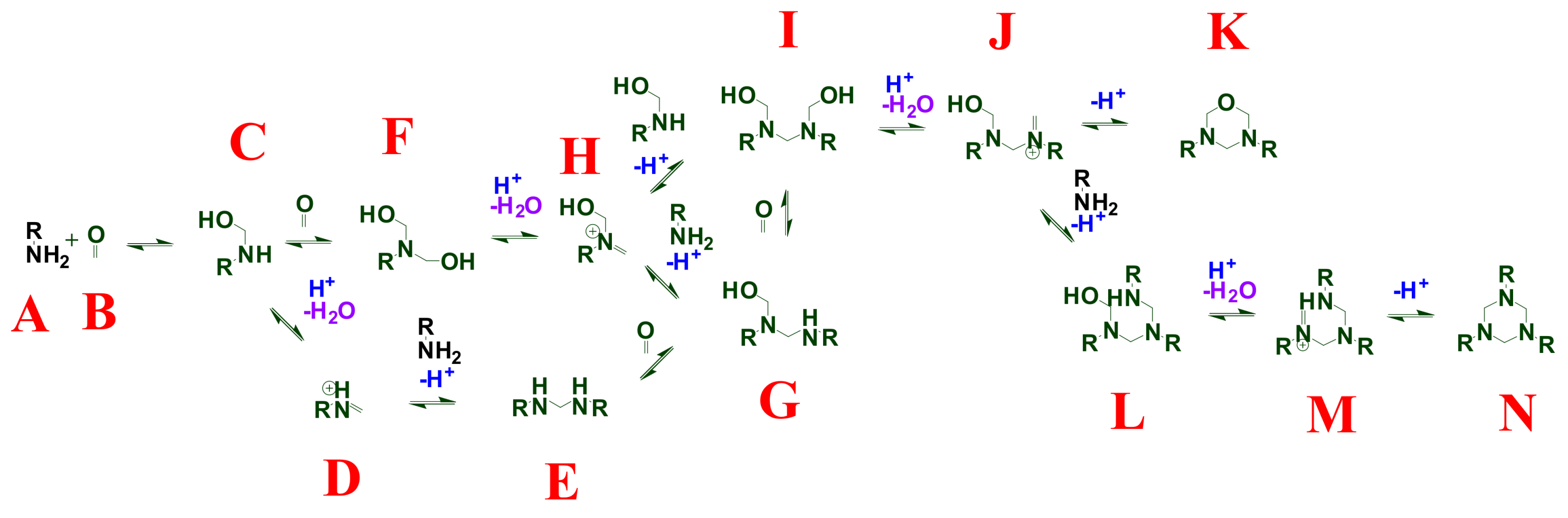
2. Background and Mechanisms for HT Dynamism
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Instrument Descriptions
3.1.1. Pressurized Rheological Instrumentation
3.1.2. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Instrumentation
3.2. Chemicals
3.3. Methods
3.3.1. Hemiaminal (Kinetic) Gel Preparation Procedure
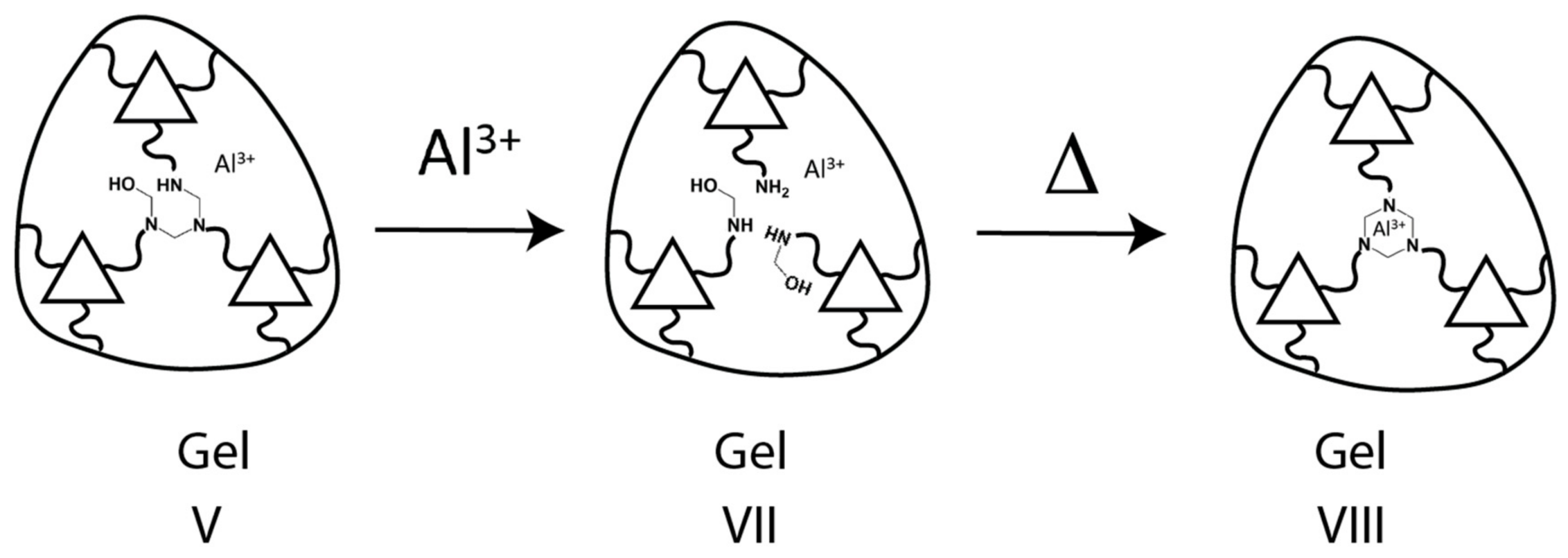
3.3.2. Transformation of the Hemiaminal (kinetic) Gel to Liquid Phase—Method for the Transformation of VII to VIII in Scheme 3
3.3.3. Transformation of the Liquid Phase to the PHT (thermodynamic) Gel—Method for the Transformation of VIII to IX in Scheme 3
3.3.4. Pressurized Rheological Study under Elevated Temperature—Simulation of the Well Environment
3.3.5. Gel Preparation and Gel Breaking for Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) Multiamine versus Polypropylene Glycol (PPG) Multiamine Reactivity Comparison
3.3.6. NMR Model Compound Preparation
3.3.7. High Temperature Stability Gels Procedure
3.3.8. Computational Methods
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Overview of Previously Reported Gel Dynamics
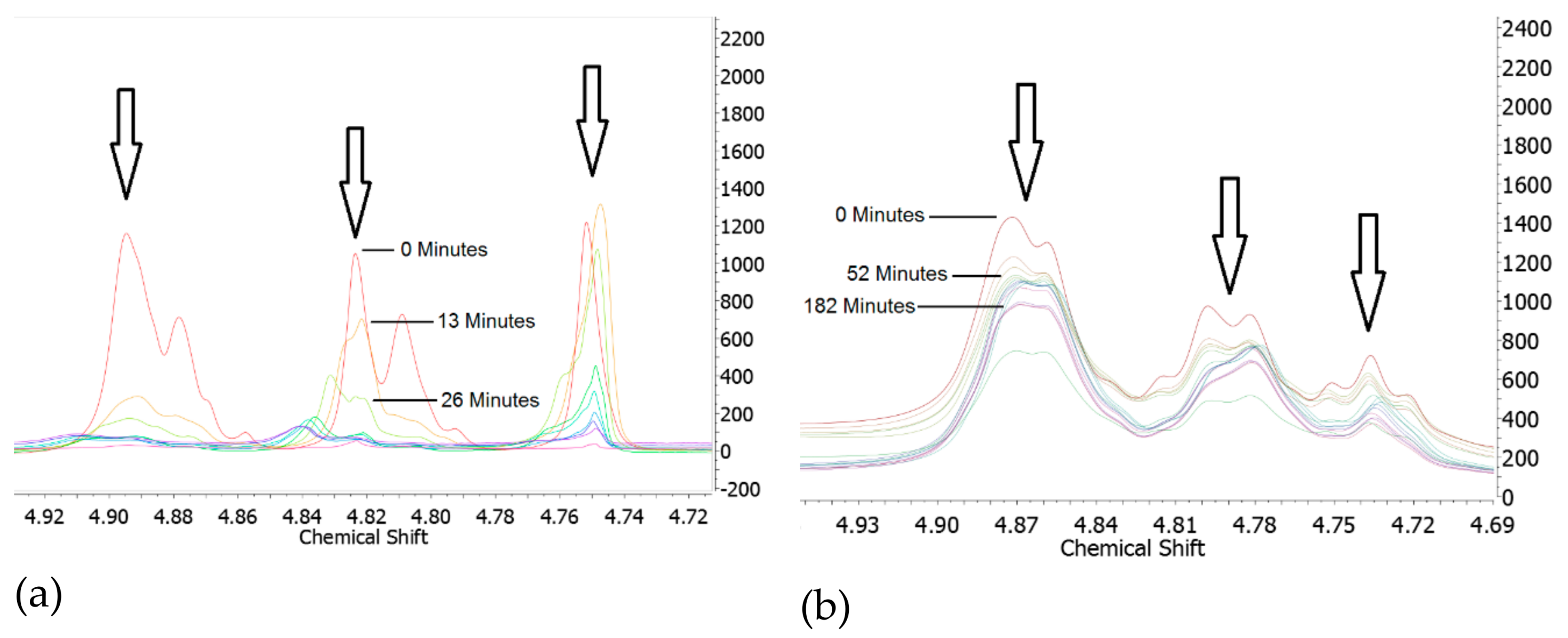
4.2. PHT Breakdown with Water
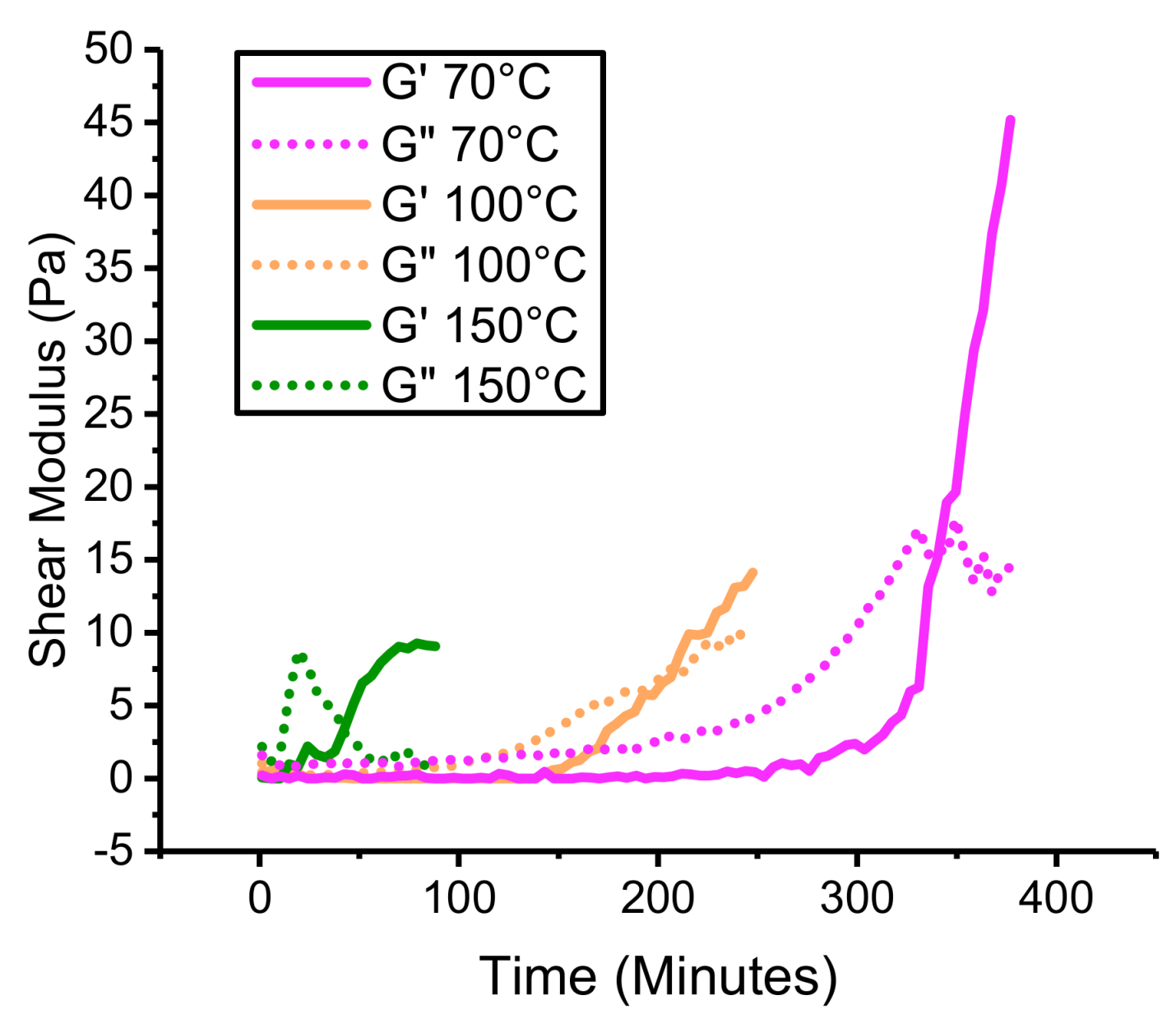
4.3. Thermal Stability of PHT
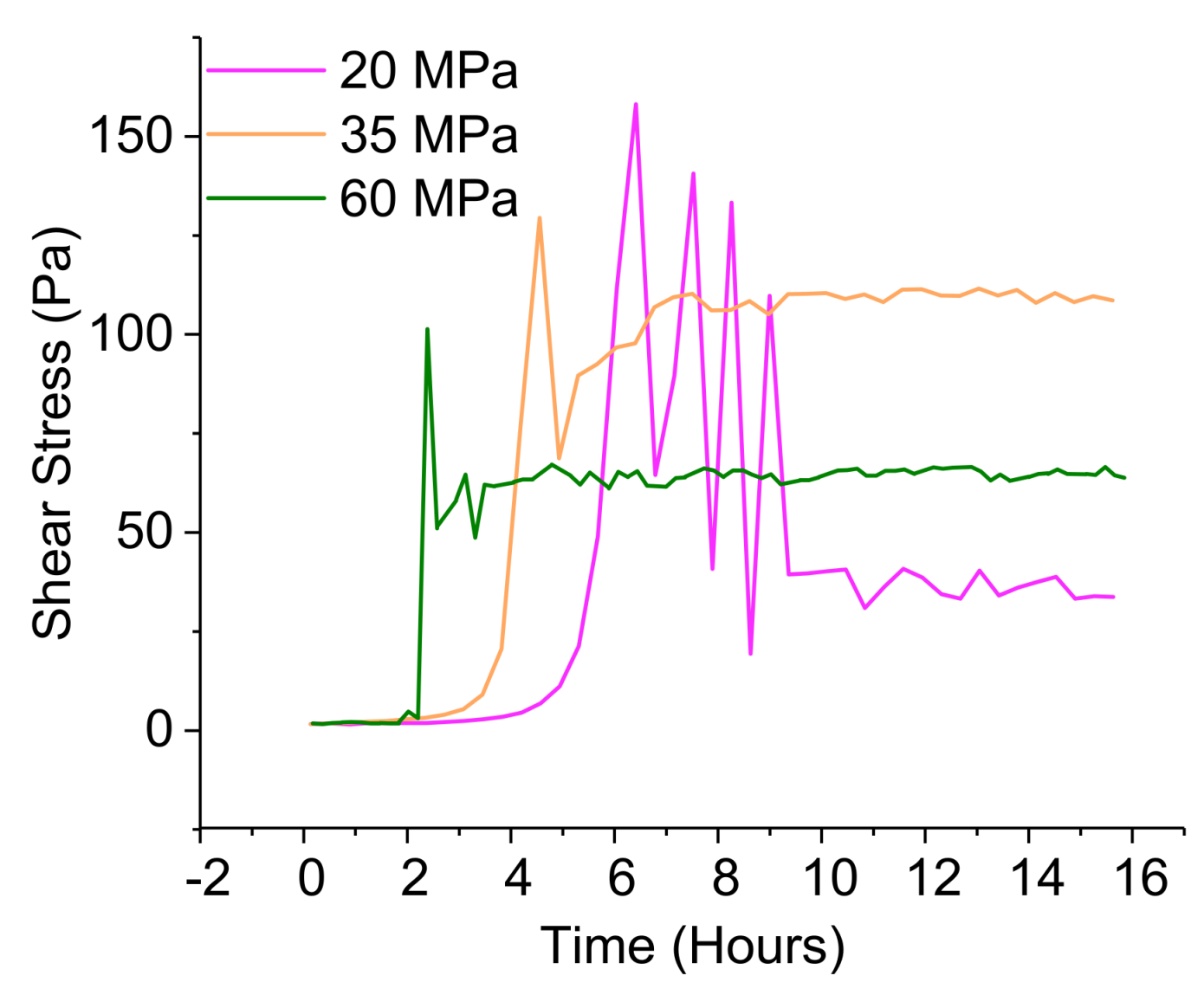
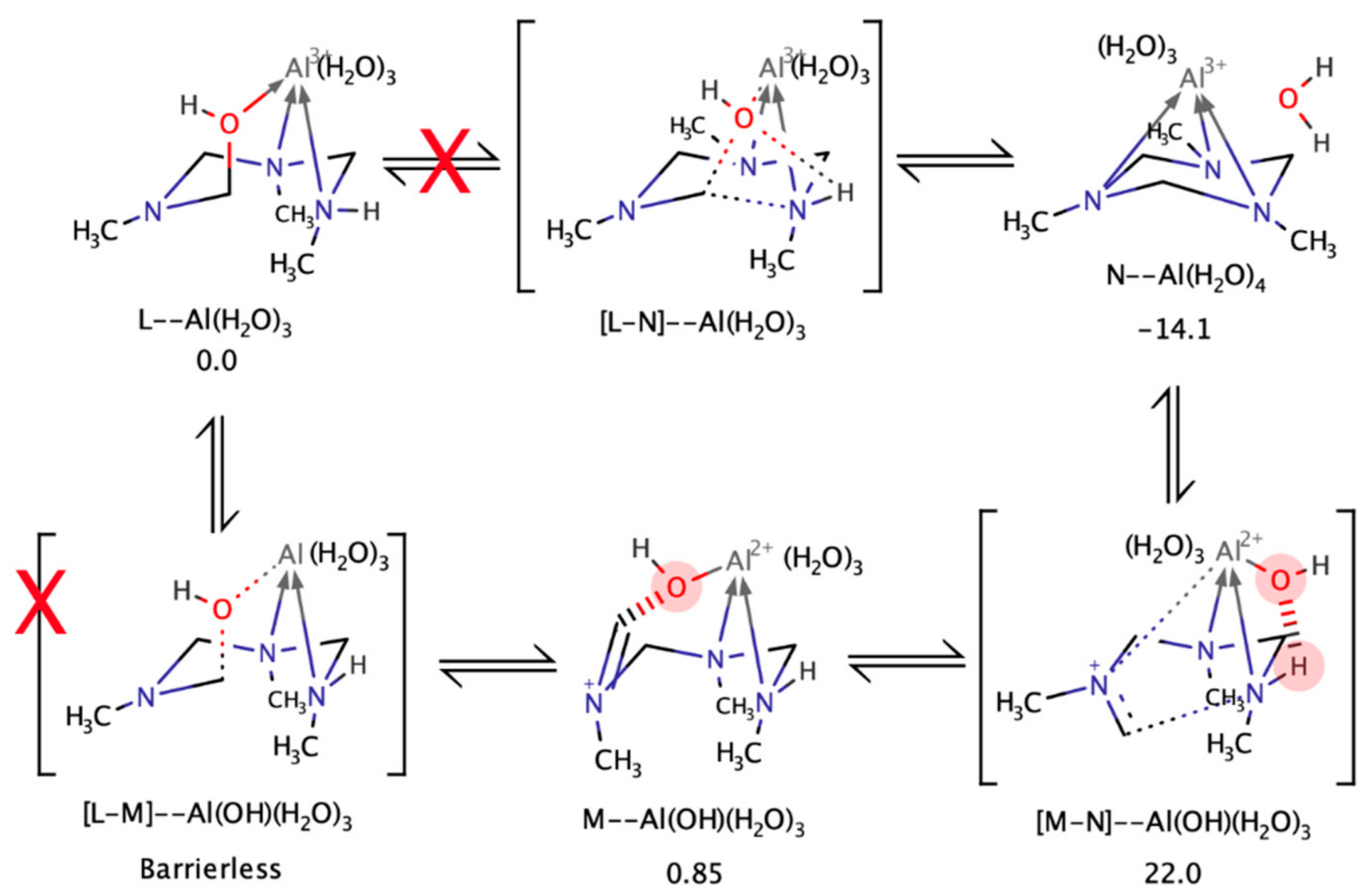
4.4. Kinetics with Al(III)
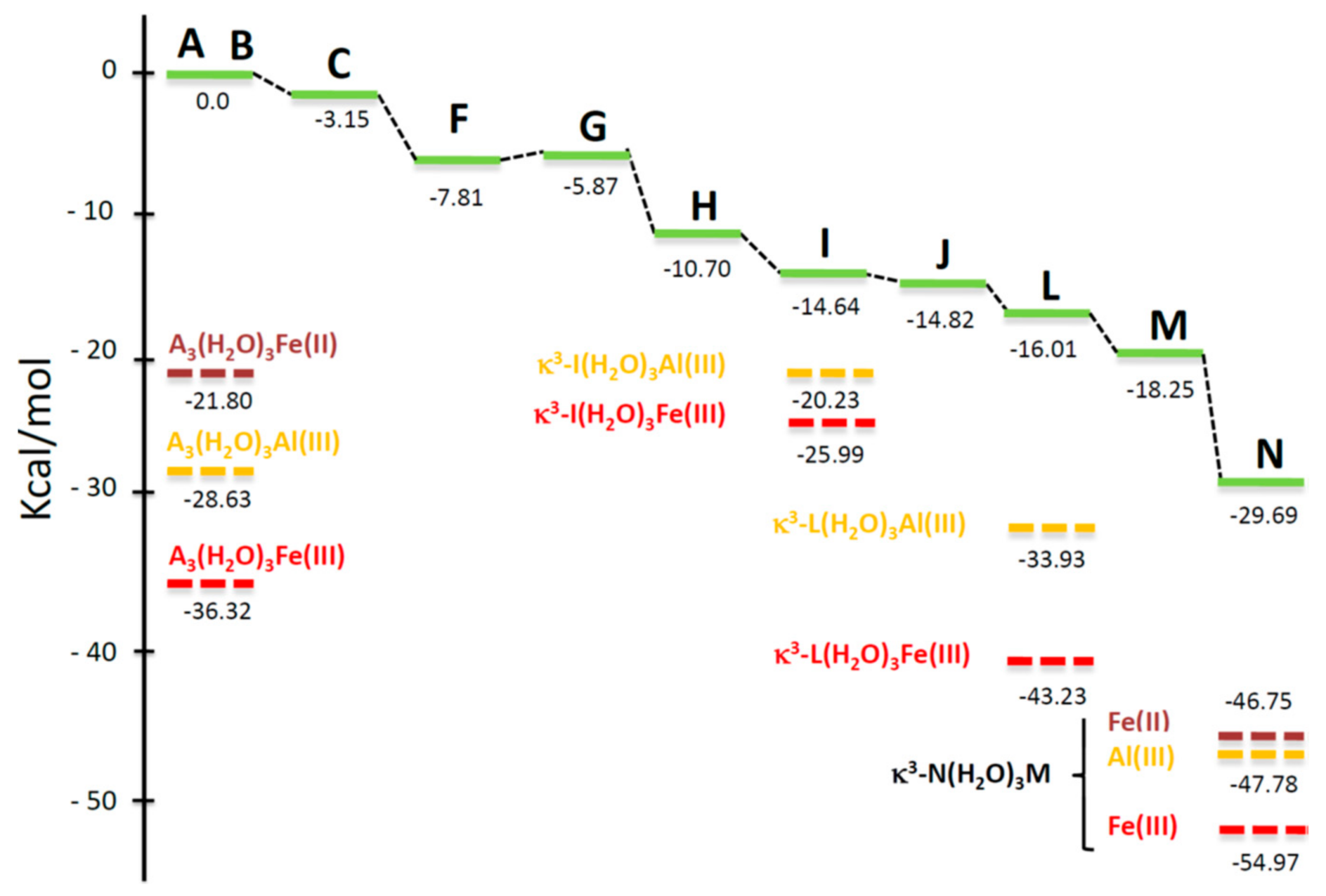
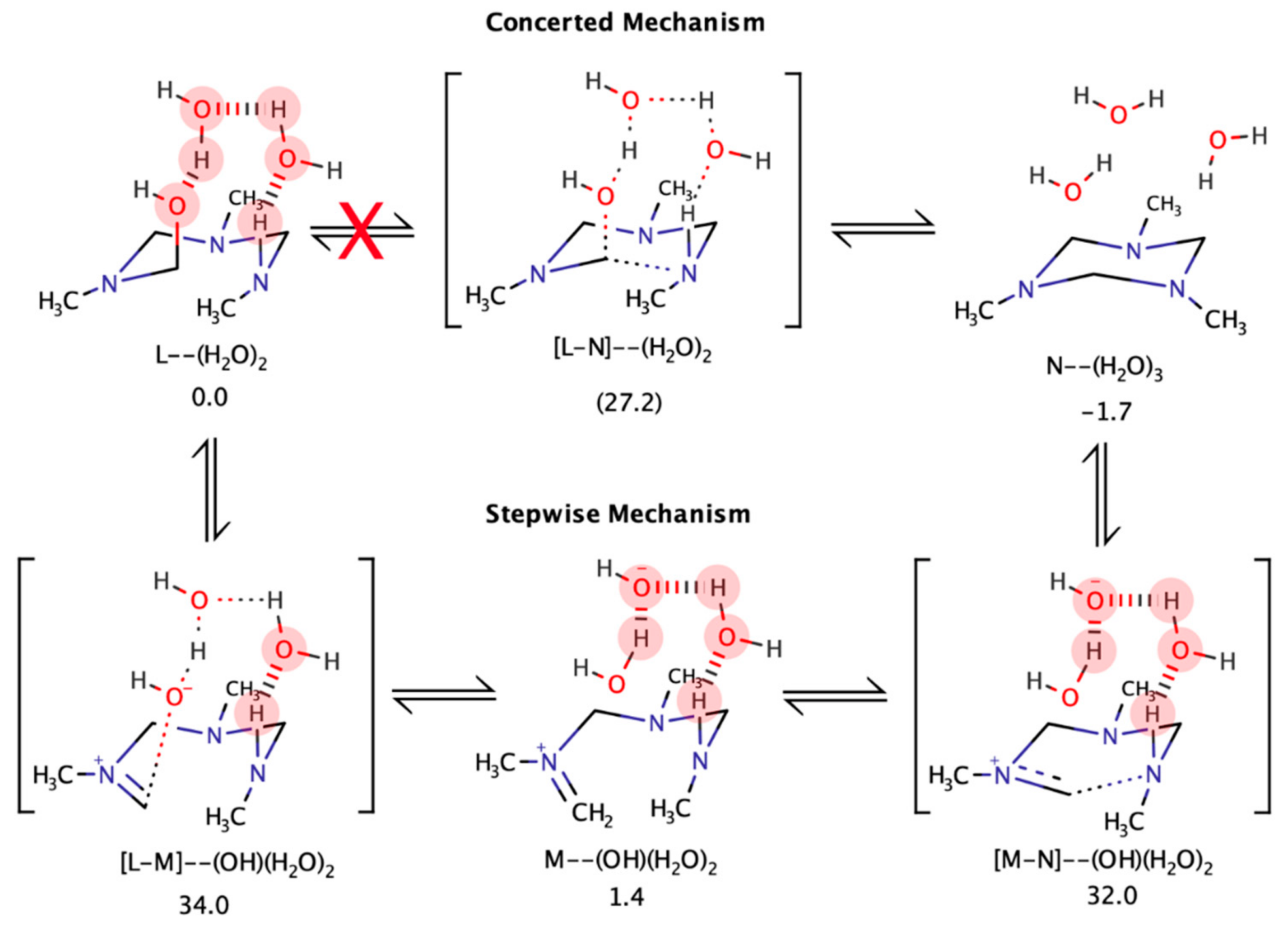
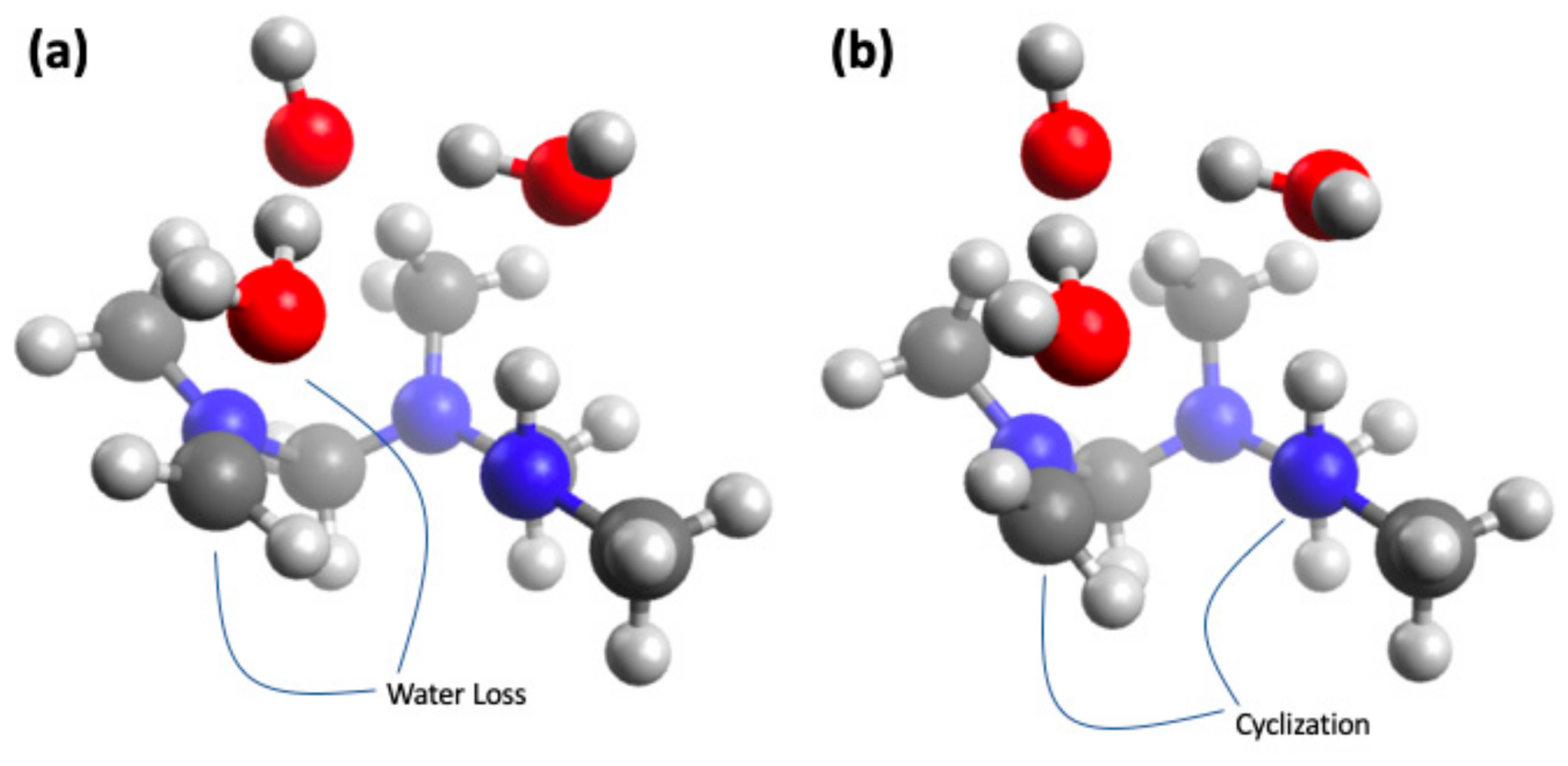
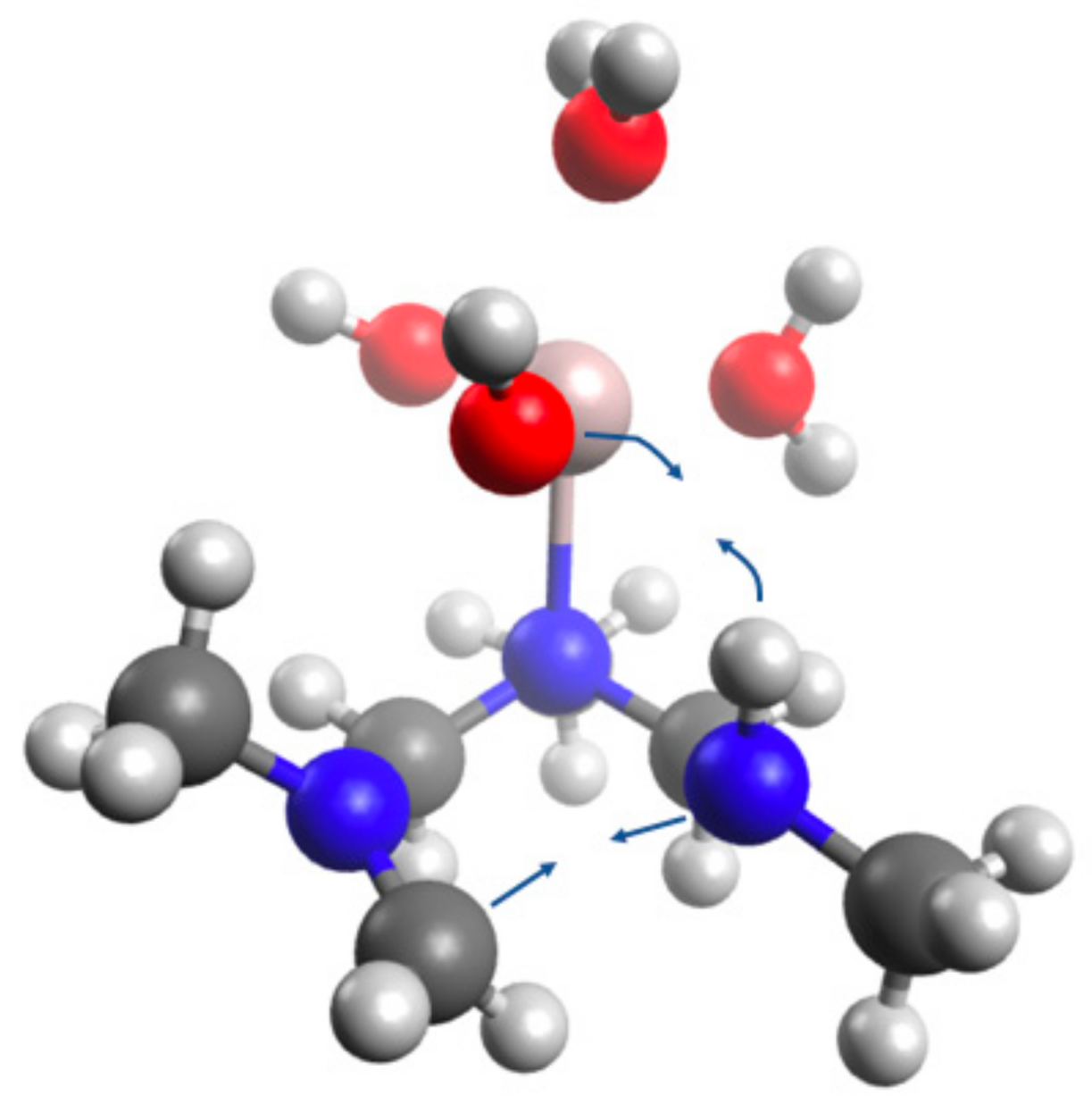
4.5. Computational Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lehn, J.-M. From supramolecular chemistry towards constitutional dynamic chemistry and adaptive chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Barboiu, M. Constitutional Dynamic Materials—Toward Natural Selection of Function. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 809–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-Y.; Zeng, L.-H.; Feng, J. Dynamic covalent gels assembled from small molecules: From discrete gelators to dynamic covalent polymers. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2017, 28, 168–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandon, E.J.; Vozoff, M.; Kolawa, E.A.; Studor, G.F.; Lyons, F.; Keller, M.W.; Beiermann, B.; White, S.R.; Sottos, N.R.; Curry, M.A.; et al. Structural health management technologies for inflatable/deployable structures: Integrating sensing and self-healing. Acta Astronautica 2011, 68, 883–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Tan, T. Preparation of chitosan/ethylcellulose complex microcapsule and its application in controlled release of Vitamin D2. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4469–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamar, L.; Shimon, E. Methods Compositions and Devices Utilizing Stinging Cells/Capsules for Delivering a Theraputic or a Cosmetic Agent into a Tissue. U.S. Patent 7,338,665, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, S.P.; Mualem, Y. Diffusion of fertilizers from controlled-release sources uniformly distributed in soil. Fert. Res. 1994, 39, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.W. Pushing the Extended-Reach Envelope at Sakhalin: An Operator. In Proceedings of the IADC/SPE Drilling Conference and Exhibition, San Diego, CA, USA, 6–8 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Boul, P.J.; Rasner, D.; Thaemlitz, C.J. Constitutionally Dynamic Oil Well Construction Fluids–Metalloaminal Chemistry. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 17043–17047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boul, P.J.; Rasner, D.K.; Jarowski, P.D.; Thaemlitz, C.J. Dynamic covalent hexahydrotriazine breakdown through nucleophilic attack by phosphine. MRS Commun. 2019, ASAP. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boul, P.J.; Jarowski, P.D.; Thaemlitz, C.J. Phase Change Transformations with Dynamically Addressable Aminal Metallogels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 15385–15391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clegg, J.K.; Harrowfield, J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Lehn, J.-M.; Lim, W.T.; Thuéry, P. Chelation-controlled molecular morphology: Aminal to imine rearrangements. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 4335–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, C.H.; ter Hurrne, G.M.; Wojtecki, R.J.; Jones, G.O.; Horn, H.W.; Meijer, E.W.; Frank, C.W.; Hedrick, J.L.; Garcia, J.M. Supramolecular motifs in dynamic covalent PEG-hemiaminal organogels. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, J.M.; Jones, G.O.; Virwani, K.; McCloskey, B.D.; Boday, D.J.; ter Huurne, G.M.; Horn, H.W.; Coady, D.J.; Bintaleb, A.M.; Alabdulrahman, A.M.S.; et al. Recyclable, strong thermosets and organogels via paraformaldehyde condensation with diamines. Science 2014, 344, 732–735. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, G.O.; García, J.M.; Horn, H.W.; Hedrick, J.L. Computational and Experimental Studies on the Mechanism of Formation of Poly(hexahydrotriazine)s and Poly(hemiaminal)s from the Reactions of Amines with Formaldehyde. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 5502–5505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojtecki, R.J.; Jones, G.O.; Yuen, A.Y.; Chin, W.; Boday, D.J.; Nelson, A.; Yang, J.M.G.Y.; Hedrick, J.L. Developments in Dynamic Covalent Chemistries from the Reaction of Thiols with Hexahydrotriazines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 14248–14251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| 65—5 Gel Formulation | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Material | Weight | Molar Ratio | Moles |
| N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) | 41.2 g | 64.9 | 0.416 |
| Paraformaldehyde | 1.04 g | 5.4 | 0.0346 |
| Jeffamine T- 5000 | 32.0 g | 1 | 0.0064 |
| Aluminium Chloride Hexahydrate | 1.85 g | 1.2 | 0.0077 |
| Gel Formulation with Jeffamine ED900 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Material | Weight | Molar Ratio | Moles |
| N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) | 41.2 g | 47.8 | 0.416 |
| Paraformaldehyde | 1.04 g | 3.9 | 0.0346 |
| Jeffamine ED900 | 7.8 g | 1 | 0.0087 |
| Aluminium Chloride Hexahydrate | 0.25 g | 0.012 | 0.0001 |
| Breakdown of PHT Gel | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amine Used in PHT Gel | Phosphine | Phosphine + NMP | Strong Acid + Heat | DI H2O |
| Polyoxyethlyene Diamine (ED900) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Polyoxyproplyene Triamine (T5000) | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| NMP Salt Solution Table | |
|---|---|
| Salt Used | Density (g/cc) |
| Aluminium Chloride Hexahydrate | 1.11 |
| Calcium Bromide Hydrate | 1.25 |
| Calcium Chloride Dihydrate | 1.17 |
| Calcium Chloride Hexahydrate | 1.22 |
| Cesium Chloride | 1.21 |
| Sodium Bromide | 1.05 |
| Zinc Bromide | 1.35 |
| High Temperature Thermodynamic Gel Stability | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salt Catalyst Used | PHT Gel at 70 °C | Stability at 150 °C | |||
| 1 h | 24 h | 3 Days | 7 Days | ||
| No Salt | Yes | No | - | - | - |
| Aluminium Chloride Hexahydrate | Yes | No | - | - | - |
| Calcium Bromide | Yes | No | - | - | - |
| Cesium Chloride | Yes | No | - | - | - |
| Zinc Bromide | Yes | Yes | No | - | - |
| Calcium Chloride Dihydrate | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | - |
| Calcium Chloride Hexahydrate | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | - |
| Sodium Bromide | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boul, P.J.; Rasner, D.K.; Jarowski, P.D.; Thaemlitz, C.J. Coordination Dynamics and Thermal Stability with Aminal Metallogels and Liquids. Polymers 2019, 11, 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11081237
Boul PJ, Rasner DK, Jarowski PD, Thaemlitz CJ. Coordination Dynamics and Thermal Stability with Aminal Metallogels and Liquids. Polymers. 2019; 11(8):1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11081237
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoul, Peter J., Diana K. Rasner, Peter D. Jarowski, and Carl J. Thaemlitz. 2019. "Coordination Dynamics and Thermal Stability with Aminal Metallogels and Liquids" Polymers 11, no. 8: 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11081237
APA StyleBoul, P. J., Rasner, D. K., Jarowski, P. D., & Thaemlitz, C. J. (2019). Coordination Dynamics and Thermal Stability with Aminal Metallogels and Liquids. Polymers, 11(8), 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11081237