Preparation of Organo-Montmorillonite Modified Poly(lactic acid) and Properties of Its Blends with Wood Flour
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
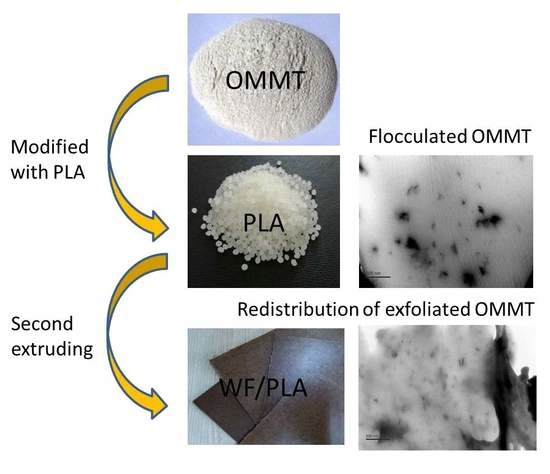
2.2. Preparation of OMMT
2.3. Modification of PLA
2.4. Preparation of PLA/WF Composites
2.5. Characterization and Tests
3. Results and Discussion
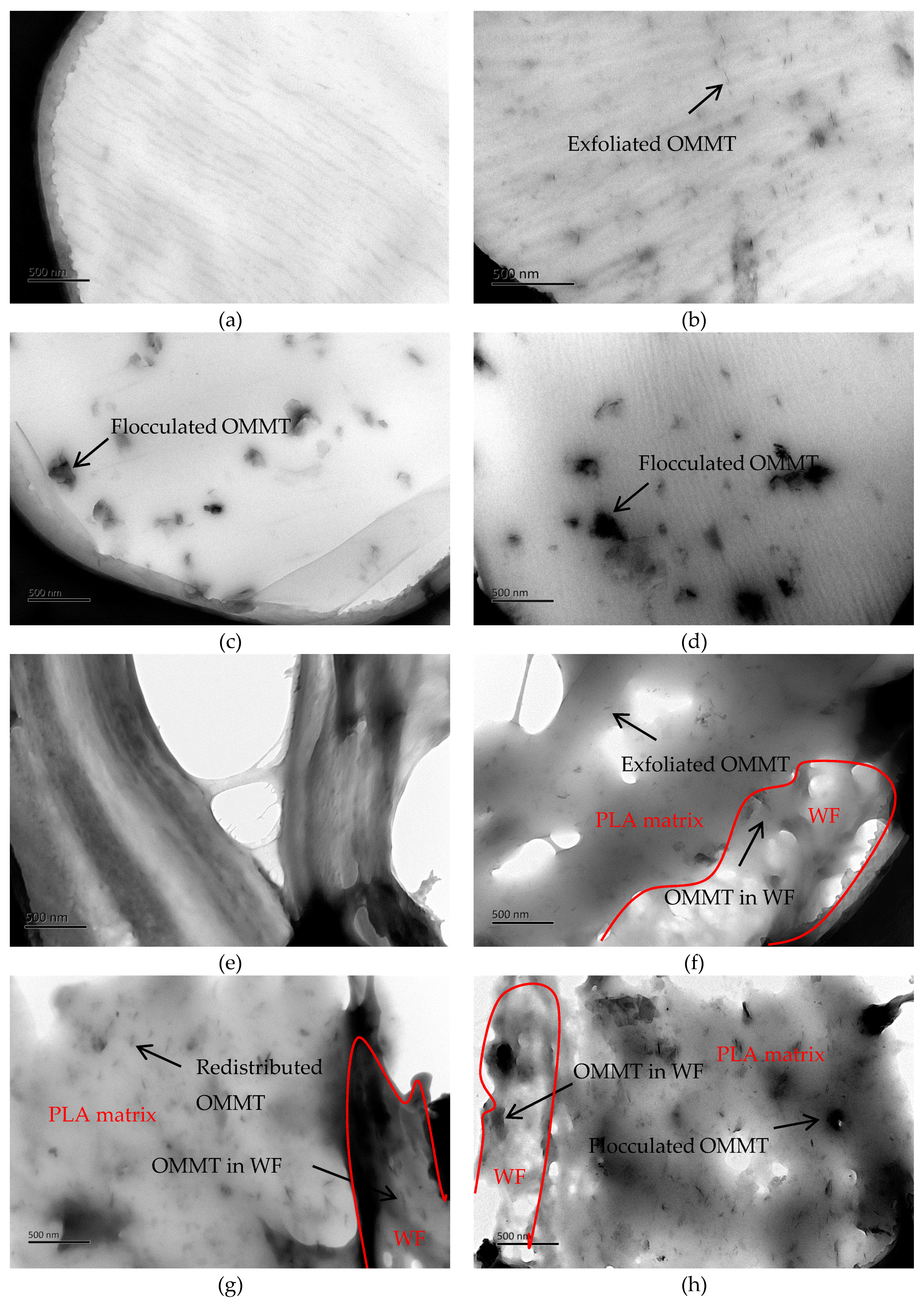
3.1. OMMT Characterization
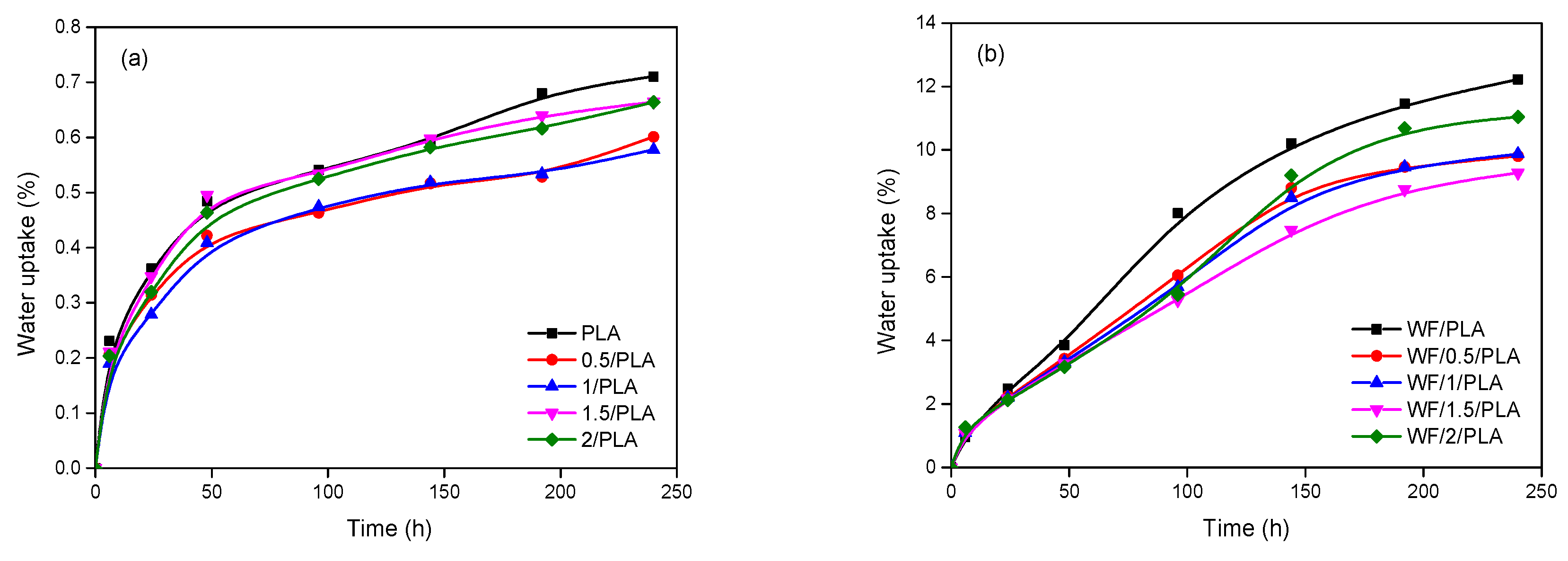
3.2. Water Uptake and Thickness Swelling
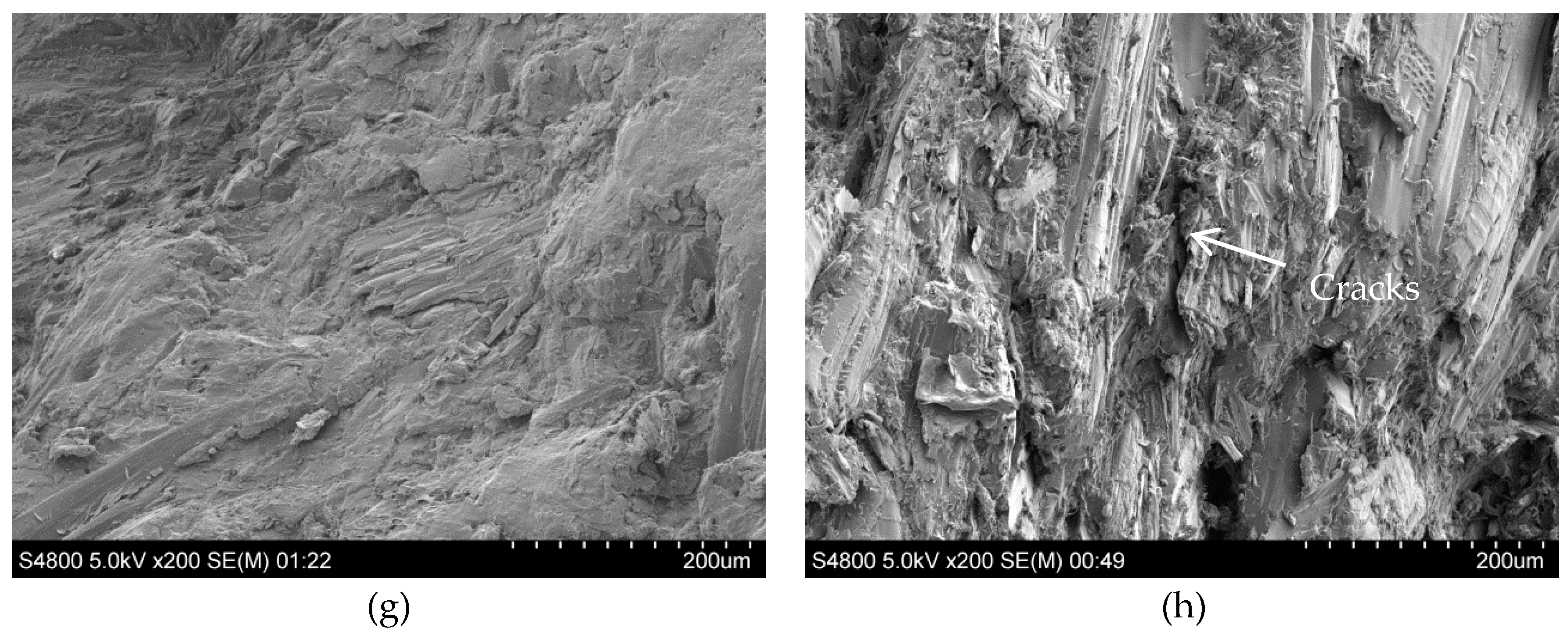
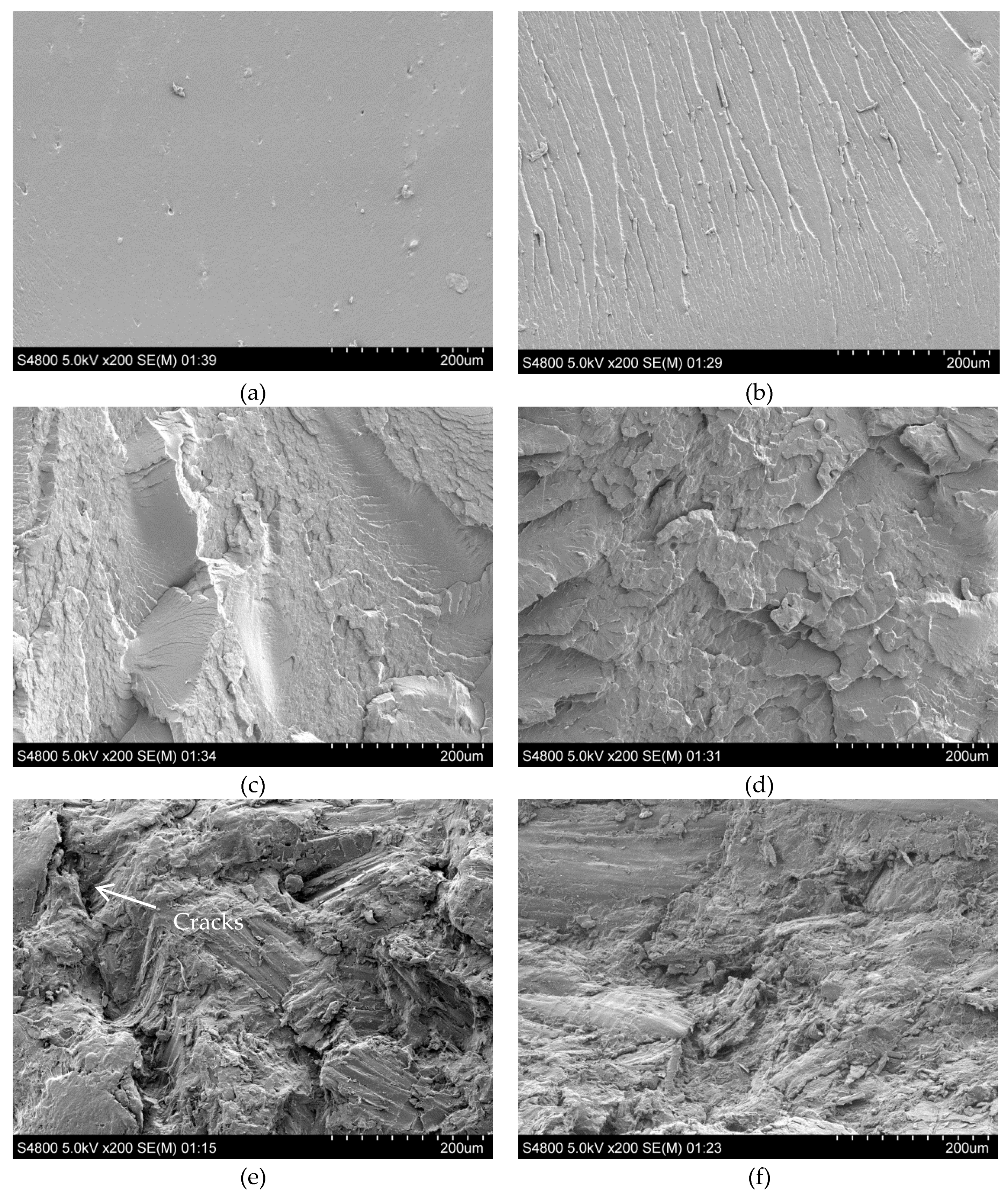
3.3. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zahedi, M.; Tabarsa, T.; Ashori, A.; Madhoushi, M.; Shakeri, A. A comparative study on some properties of wood plastic composites using canola stalk, paulownia, and nanoclay. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, F.; Granda, L.A.; Joffe, R.; Berglund, L.A.; Vilaseca, F. Experimental evaluation of anisotropy in injection molded polypropylene/wood fiber biocomposites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. 2017, 96, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, J.S.; Cha, S.W. Effect of chemical modification on mechanical properties of wood-plastic composite injection-molded parts. Polymers 2018, 10, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, P.; Behravesh, A.H.; Daryabari, S.Y.; Lotfi, M. Experimental investigation on reprocessing of extruded wood flour/HDPE composites. Polym. Compos. 2012, 33, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.M.; Wolcott, M.P. Opportunities for wood/natural fiber-plastic composites in residential and industrial applications. For. Prod. J. 2006, 56, 4–11. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Cao, J.; Peng, Y.; Liu, R. Incorporation of microencapsulated dodecanol into wood flour/high-density polyethylene composite as a phase change material for thermal energy storage. Mater. Des. 2016, 89, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teuber, L.; Militz, H.; Krause, A. Dynamic particle analysis for the evaluation of particle degradation during compounding of wood plastic composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. 2016, 84, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teuber, L.; Osburg, V.S.; Toporowski, W.; Militz, H.; Krause, A. Wood polymer composites and their contribution to cascading utilization. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 110, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Agarwal, U.P.; Matuana, L.; Sabo, R.C.; Stark, N.M. Performance of high lignin content cellulose nanocrystals in poly(lactic acid). Polymer 2018, 135, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.C. Effect of extrusion temperature on the physico-mechanical properties of unidirectional wood fiber-reinforced polylactic acid composite (WFRPC) components using fused deposition modeling. Polymers 2018, 10, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlet, K.; Saulnier, F.; Dubois, M.; Béakou, A. Improvement of wood polymer composite mechanical properties by direct fluorination. Mater. Des. 2015, 74, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinihashemi, S.K.; Arwinfar, F.; Najafi, A.; Nemli, G.; Ayrilmis, N. Long-term water absorption behavior of thermoplastic composites produced with thermally treated wood. Measurement 2016, 86, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panaitescu, D.M.; Nicolae, C.A.; Vuluga, Z.; Vitelaru, C.; Sanporean, C.G.; Zaharia, C.; Florea, D.; Vasilievici, G. Influence of hemp fibers with modified surface on polypropylene composites. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 37, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; He, H.; Yu, P.; Zhou, L.; Luo, Y.; Jia, D. Sustainable utilization of waste printed circuit boards powders in HDPE-wood composites: Synergistic effects of multicomponents on structure and properties. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, N.; Md Tahir, P.; Jawaid, M. A review on potentiality of nano filler/natural fiber filled polymer hybrid composites. Polymers 2014, 6, 2247–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosnita, M.; Cazan, C.; Duta, A. The influence of inorganic additive on the water stability and mechanical properties of recycled rubber, polyethyleneterephthalate, high density polyethylene and wood composites. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Hao, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, T.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Q. The reinforcement efficacy of nano- and microscale silica for extruded wood flour/HDPE composites: The effects of dispersion patterns and interfacial modification. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 1899–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thellen, C.; Orroth, C.; Froio, D.; Ziegler, D.; Lucciarini, J. Influence of montmorillonite layered silicate on plasticized poly (L-lactide) blown films. Polymer 2005, 46, 11716–11727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukusima, K.; Abbate, C.; Tabuani, D.; Gennari, M.; Camino, G. Biodegradation of poly(lactic acid) and its nanocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2009, 94, 1646–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wen, N.; Zheng, Y. The preparation of calcium pimelate modified OMMT from natural Ca-montmorillonite and its application as β-nucleating agent for polypropylene. Polym. Test. 2018, 65, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, K.P.; Decker, J.J.; Olson, B.G.; Lin, J.; Jamieson, A.M.; Nazarenko, S. Probing the confining effect of clay particles on an amorphous intercalated dendritic polyester. Polymer 2017, 112, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liao, L.; Xia, Z. Synergistic effect of cationic and anionic surfactants for the modification of Ca-montmorillonite. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 1811–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Poloso, T.; Hetzer, M.; De Kee, D. Enhancement of wood/polyethylene composites via compatibilization and incorporation of organoclay particles. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2007, 47, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabari, H.Z.; Nourbakhsh, A.; Ashori, A. Effects of nanoclay and coupling agent on the physico-mechanical, morphological, and thermal properties of wood flour/polypropylene composites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2011, 51, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhoushi, M.; Chavooshi, A.; Ashori, A.; Ansell, M.; Shakeri, A. Properties of wood plastic composite panels made from waste sanding dusts and nanoclay. J. Compos. Mater. 2014, 48, 1661–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Cao, J.; Luo, S.; Wang, X. Effects of two types of clay on physical and mechanical properties of poly(lactic acid)/wood flour composites at various wood flour contents. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 2566–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.K.; Hetzer, M.; De Kee, D. PLA/clay/wood nanocomposites: Nanoclay effects on mechanical and thermal properties. J. Compos. Mater. 2010, 45, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Chen, Y.; Cao, J. Effects of modifier type on properties of in situ organo-montmorillonite modified wood flour/poly(lactic acid) composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.; Liao, M.; Zhang, W. Surface modification of montmorillonite and application to the preparation of polybutadiene/montmorillonite nanocomposites. Polym. Int. 2007, 56, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikkhah, S.J.; Ramazani, S.A.A.; Baniasadi, H.; Tavakolzadeh, F. Investigation of properties of polyethylene/clay nanocomposites prepared by new in situ Ziegler-Natta catalyst. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 2309–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Harper, D.P.; Taylor, A.M. Effect of extractives on water sorption and durability of wood-plastic composites. Wood Fiber Sci. 2009, 41, 279–290. [Google Scholar]
- Gregorova, A.; Sedlarik, V.; Pastorek, M.; Jachandra, H.; Stelzer, F. Effect of compatibilizing agent on the properties of highly crystalline composites based on poly(lactic acid) and wood flour and/or mica. J. Polym. Envrion. 2011, 19, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.T.; Wu, C.S. Preparation of poly(ethylene-octene) elastomer/clay/wood flour nanocomposites by a melting method. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2005, 290, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdov, A.D.; deC Christiansen, J.; Gupta, R.K.; Shah, A.P. Model for anomalous moisture diffusion through a polymer-clay nanocomposite. J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Phys. 2003, 41, 476–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yan, N. Crystallization behavior of organo-nanoclay treated and untreated kraft fiber-HDPE composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 54, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Labels | OMMT (wt %) | PLA (wt %) | WF (wt %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| 0.5/PLA | 0.5 | 99.5 | 0 |
| 1/PLA | 1 | 99 | 0 |
| 1.5/PLA | 1.5 | 98.5 | 0 |
| 2/PLA | 2 | 98 | 0 |
| PLA/WF | 0 | 50 | 50 |
| 0.5/PLA/WF | 0.25 | 49.75 | 50 |
| 1/PLA/WF | 0.5 | 49.5 | 50 |
| 1.5/PLA/WF | 0.75 | 49.25 | 50 |
| 2/PLA/WF | 1 | 49 | 50 |
| Labels | Final Water Uptake (%) | Diffusion Coefficient (×10-10) (m2/s) | Thickness Swelling (%) | Crystallinity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | 0.71(0.01) | 1.59(0.04) | 0(0) | 30.0 |
| 0.5/PLA | 0.58(0.02) | 1.38(0.02) | 0(0) | 31.5 |
| 1/PLA | 0.60(0.03) | 1.38(0.07) | 0(0) | 31.9 |
| 1.5/PLA | 0.66(0.03) | 1.46(0.03) | 0(0) | 32.3 |
| 2/PLA | 0.66(0.05) | 1.42(0.02) | 0(0) | 32.7 |
| PLA/WF | 12.22(0.12) | 2.37(0.11) | 12.68(0.58) | 39.6 |
| 0.5/PLA/WF | 9.81(0.08) | 2.12(0.15) | 9.26(0.34) | 40.0 |
| 1/PLA/WF | 9.87(0.20) | 2.00(0.11) | 8.79(0.17) | 39.9 |
| 1.5/PLA/WF | 9.28(0.10) | 1.75(0.09) | 7.36(0.26) | 40.1 |
| 2/PLA/WF | 11.04(0.27) | 2.19(0.13) | 10.68(0.64) | 40.1 |
| Labels | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Flexural Modulus (GPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Impact Strength (J/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | 33.5(2.4) | 2.54(0.35) | 29.0(1.8) | 1.21(0.05) | 3.4(0.4) |
| 0.5/PLA | 57.2(3.8) | 3.08(0.40) | 43.9(2.2) | 1.29(0.09) | 10.9(2.2) |
| 1/PLA | 42.2(4.5) | 3.59(0.18) | 37.3(1.0) | 1.36(0.05) | 7.3(0.6) |
| 1.5/PLA | 38.9(4.0) | 4.72(0.17) | 35.2(2.1) | 2.13(0.18) | 6.0(0.7) |
| 2/PLA | 38.1(2.0) | 3.49(0.22) | 29.1(0.9) | 1.54(0.20) | 4.8(0.7) |
| PLA/WF | 38.0(1.2) | 6.99(0.23) | 18.7(2.9) | 1.66(0.22) | 2.2(0.7) |
| 0.5/PLA/WF | 40.9(5.4) | 6.80(0.31) | 20.9(3.9) | 2.03(0.15) | 3.6(0.9) |
| 1/PLA/WF | 48.3(4.3) | 7.19(0.81) | 28.5(1.7) | 2.22(0.15) | 3.9(0.5) |
| 1.5/PLA/WF | 55.4(5.9) | 7.40(0.47) | 32.9(2.1) | 2.26(0.10) | 5.5(0.4) |
| 2/PLA/WF | 38.2(3.3) | 7.33(0.44) | 25.1(3.0) | 2.03(0.19) | 3.6(0.4) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, R.; Yin, X.; Huang, A.; Wang, C.; Ma, E. Preparation of Organo-Montmorillonite Modified Poly(lactic acid) and Properties of Its Blends with Wood Flour. Polymers 2019, 11, 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020204
Liu R, Yin X, Huang A, Wang C, Ma E. Preparation of Organo-Montmorillonite Modified Poly(lactic acid) and Properties of Its Blends with Wood Flour. Polymers. 2019; 11(2):204. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020204
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ru, Xiaoqian Yin, Anmin Huang, Chen Wang, and Erni Ma. 2019. "Preparation of Organo-Montmorillonite Modified Poly(lactic acid) and Properties of Its Blends with Wood Flour" Polymers 11, no. 2: 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020204
APA StyleLiu, R., Yin, X., Huang, A., Wang, C., & Ma, E. (2019). Preparation of Organo-Montmorillonite Modified Poly(lactic acid) and Properties of Its Blends with Wood Flour. Polymers, 11(2), 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020204







