Effects of Three Different Injection-Molding Methods on the Mechanical Properties and Electrical Conductivity of Carbon Nanotube/Polyethylene/Polyamide 6 Nanocomposite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
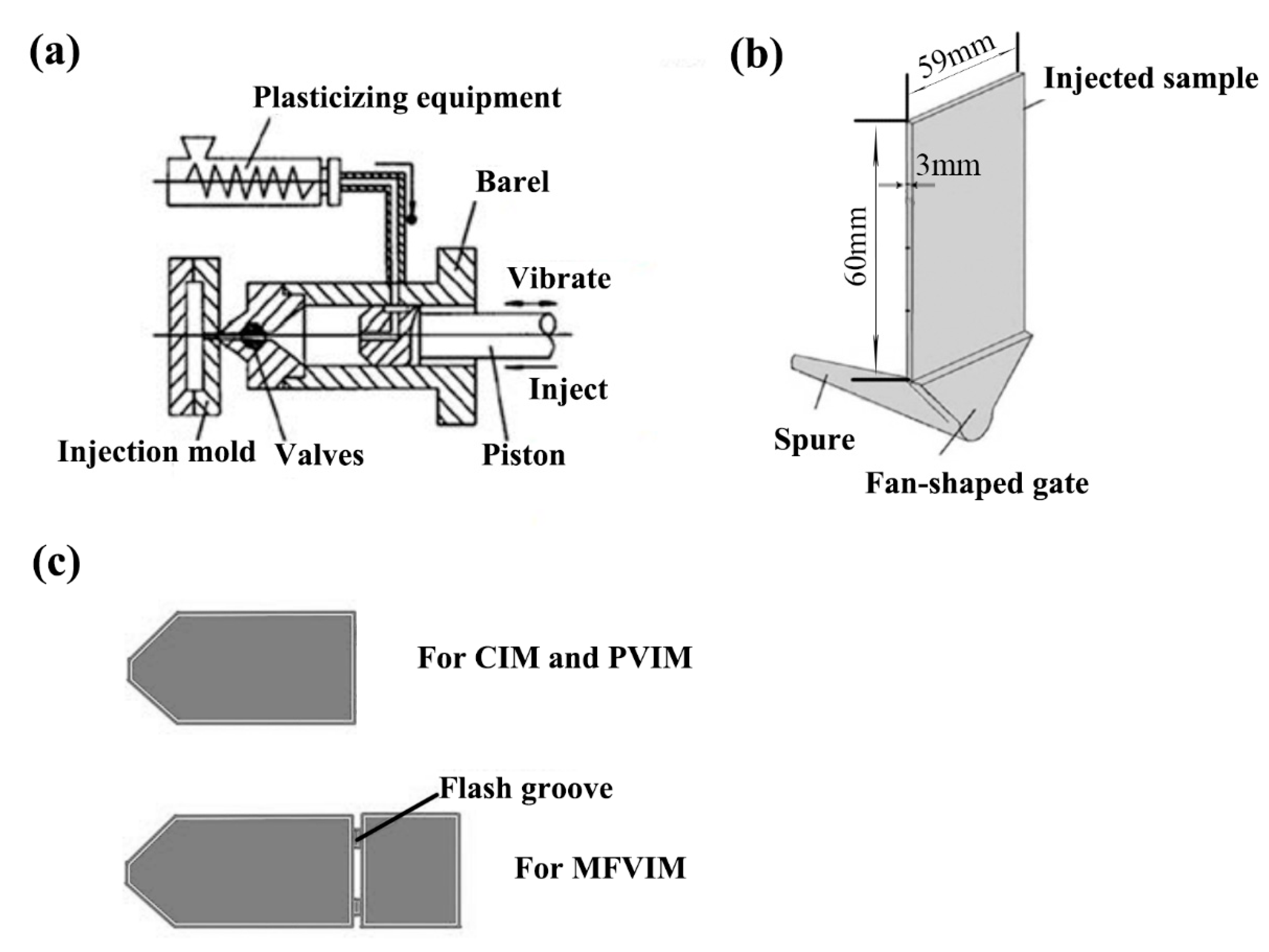
2.1. Materials and Sample Preparation
2.2. Optical Microscope Observations (POM)
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
2.4. Measurement of Mechanical Properties
2.5. Electrical Properties Measurements
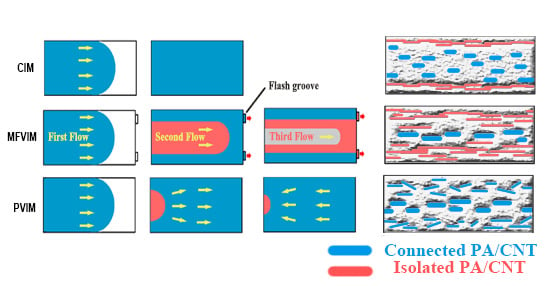
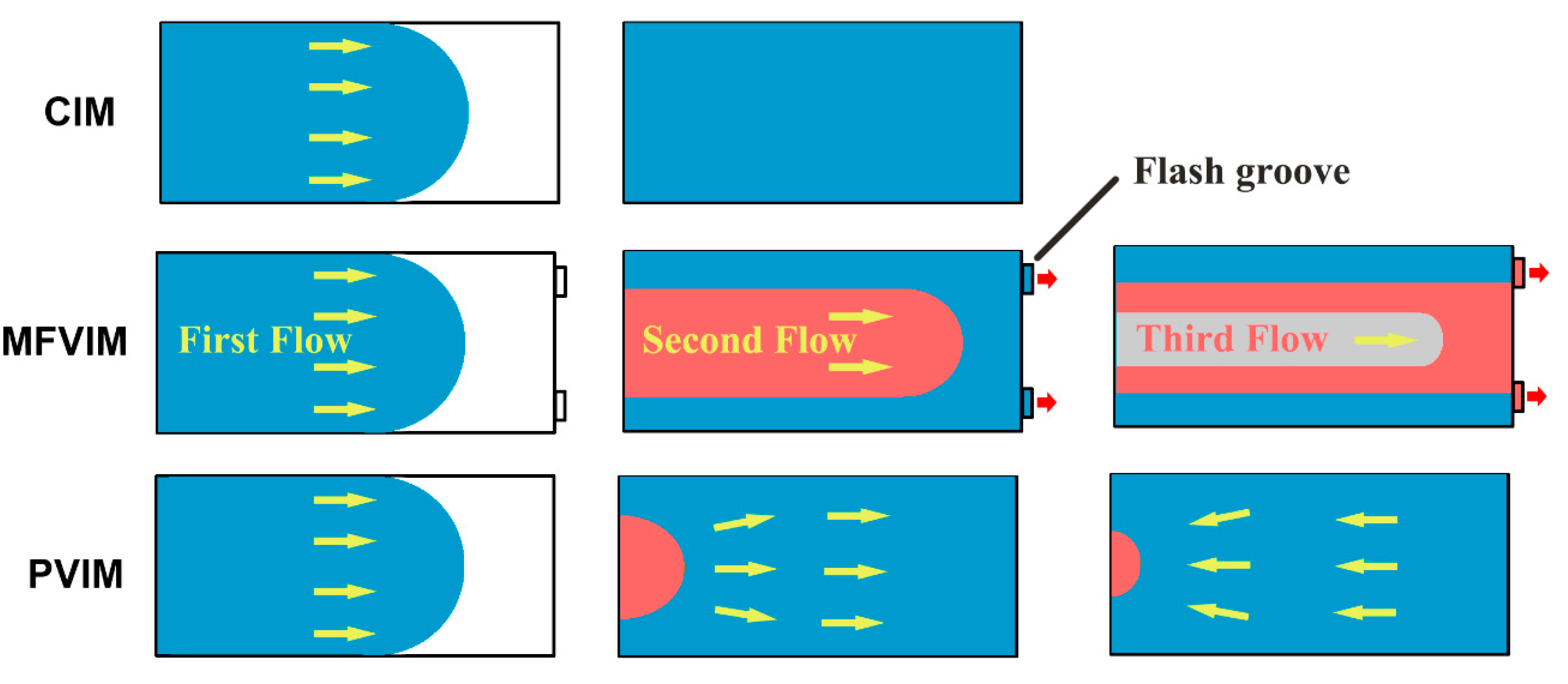
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mechanical and Electrical Conductivity
3.2. Phase Morphology
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dasari, A.; Yu, Z.-Z.; Mai, Y.-W. Electrically conductive and super-tough polyamide-based nanocomposites. Polymer 2009, 50, 4112–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubbels, F.; Jérôme, R.; Vanlathem, E.; Deltour, R.; Blacher, S.; Brouers, F. Kinetic and thermodynamic control of the selective localization of carbon black at the interface of immiscible polymer blends. Chem. Mater. 1998, 10, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skipa, T.; Lellinger, D.; Böhm, W.; Saphiannikova, M.; Alig, I. Influence of shear deformation on carbon nanotube networks in polycarbonate melts: Interplay between build-up and destruction of agglomerates. Polymer 2010, 51, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegel, S.; Pötschke, P.; Petzold, G.; Alig, I.; Dudkin, S.M.; Lellinger, D. Dispersion, agglomeration, and network formation of multiwalled carbon nanotubes in polycarbonate melts. Polymer 2008, 49, 974–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.C.L.; Soares, B.G.; Silva, A.A.; da Silva, J.M.F.; Barra, G.M.; Livi, S. Conductive heterogeneous blend composites of PP/PA12 filled with ionic liquids treated-CNT. Polym. Test. 2019, 74, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, S.; Paiva, M.C.; Covas, J.A. Dispersion and re-agglomeration phenomena during melt mixing of polypropylene with multi-wall carbon nanotubes. Polym. Test. 2013, 32, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonder, L.; Ophir, A.; Kenig, S.; McCarthy, S. The effect of carbon nanotubes on the rheology and electrical resistivity of polyamide 12/high density polyethylene blends. Polymer 2011, 52, 5085–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogales, A.; Broza, G.; Roslaniec, Z.; Schulte, K.; Šics, I.; Hsiao, B.S.; Sanz, A.; García-Gutiérrez, M.C.; Rueda, D.R.; Domingo, C. Low percolation threshold in nanocomposites based on oxidized single wall carbon nanotubes and poly (butylene terephthalate). Macromolecules 2004, 37, 7669–7672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-X.; Wang, W.-Y.; Yang, J.-H.; Zhang, N.; Huang, T.; Wang, Y. Excellent electroactive shape memory performance of EVA/PCL/CNT blend composites with selectively localized CNTs. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 22793–22802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabzadeh, M.; Kamal, M.R. Melt processing of PA-66/clay, HDPE/clay and HDPE/PA-66/clay nanocomposites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2004, 44, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, D.; Liu, K.; Du, H.; Zhang, J. The transfer of carbon nanotubes in an immiscible high density polyethylene and polyamide 6 blend. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2014, 25, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Q. A change of phase morphology in poly (p-phenylene sulfide)/polyamide 66 blends induced by adding multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Polymer 2006, 47, 7821–7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooneie, A.; Nazockdast, H.; Shahsavan, F. Effect of selective localization of carbon nanotubes in PA6 dispersed phase of PP/PA6 blends on the morphology evolution with time, part 1: Droplet deformation under simple shear flows. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2015, 55, 1504–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Liu, X.; Lian, M.; Pan, Y.; Chen, Q.; Liu, H.; Zheng, G.; Guo, Z.; Schubert, D.W.; Shen, C. Self-reinforcing and toughening isotactic polypropylene via melt sequential injection molding. Polym. Test. 2018, 67, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, L.; Zheng, G.; Liu, C.; Qin, Q.; Mi, L. Crystalline structure and remarkably enhanced tensile property of β-isotactic polypropylene via overflow microinjection molding. Polym. Test. 2019, 76, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spina, R.; Spekowius, M.; Hopmann, C. Simulation of crystallization of isotactic polypropylene with different shear regimes. Thermochim. Acta 2018, 659, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanticse, L.J.; Tanabe, Y.; Matsui, K.; Kaburagi, Y.; Suda, K.; Hoteida, M.; Endo, M.; Yasuda, E. Shear-induced preferential alignment of carbon nanotubes resulted in anisotropic electrical conductivity of polymer composites. Carbon 2006, 44, 3078–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alig, I.; Skipa, T.; Engel, M.; Lellinger, D.; Pegel, S.; Pötschke, P. Electrical conductivity recovery in carbon nanotube–polymer composites after transient shear. Phys. Status Solidi (B) 2007, 244, 4223–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalay, G.; Bevis, M.J. Processing and physical property relationships in injection-molded isotactic polypropylene. 1. Mechanical properties. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1997, 35, 241–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R.; Mano, J.; Reis, R.; Cunha, A.; Bevis, M. Mechanical performance of starch based bioactive composite biomaterials molded with preferred orientation. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2002, 42, 1032–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.-J.; Li, Z.-M.; Li, L.-B.; Mendes, E. Crystalline morphology of isotactic polypropylene (IPP) in injection molded poly (ethylene terephthalate)(PET)/IPP microfibrillar blends. Polymer 2007, 48, 1729–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.A.; Viana, J.C.; Cunha, A.M. Novel morphologies produced by active shear rotation during injection molding. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2007, 292, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Silva, C.; Viana, J.; van Hattum, F.; Cunha, A.; Tucker, C., III. Prediction of fiber orientation in a rotating compressing and expanding mold. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2008, 48, 1405–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, D.; Xia, C.; Jin, M.; Wang, F.; Shen, K.; Zhang, J. Quantification of the effect of shish-kebab structure on the mechanical properties of polypropylene samples by controlling shear layer thickness. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 4571–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Qian, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Shen, K. A multi-layer bioinspired design with evolution of shish-kebab structures induced by controlled periodical shear field. Express Polym. Lett. 2013, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Liu, F.; Guo, C.; Fu, Q.; Shen, K.; Zhang, J. Shish–kebab-like cylindrulite structures resulted from periodical shear-induced crystallization of isotactic polypropylene. Polymer 2011, 52, 2970–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.-G.; Leng, Y. Squeezing and stick–slip friction behaviors of lubricants in boundary lubrication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 6560–6565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooneie, A.; Gonzalez-Gutierrez, J.; Holzer, C. Atomistic modelling of confined polypropylene chains between ferric oxide substrates at melt temperature. Polymers 2016, 8, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Wang, K.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Du, R.; Fu, Q. Excellent tensile ductility in highly oriented injection-molded bars of polypropylene/carbon nanotubes composites. Polymer 2007, 48, 5688–5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-J.; Cho, K.-S.; Ryu, S.-K. Filler–elastomer interactions: Influence of oxygen plasma treatment on surface and mechanical properties of carbon black/rubber composites. Carbon 2003, 41, 1437–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Luo, W.; Yang, J.; Duan, X.; Wen, Y.; Zhou, H.; Chen, R.; Shan, B. Simulation of dispersion and alignment of carbon nanotubes in polymer flow using dissipative particle dynamics. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2017, 126, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooneie, A.; Hufenus, R. Hybrid carbon nanoparticles in polymer matrix for efficient connected networks: Self-assembly and continuous pathways. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 3547–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooneie, A.; Holzer, C. Reinforced local heterogeneities in interfacial tension distribution in polymer blends by incorporating carbon nanotubes. Polymer 2017, 125, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wan, C.; Zhang, Y. Investigation on the multiwalled carbon nanotubes reinforced polyamide 6/polypropylene composites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2009, 49, 1909–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.D.; Shen, L.; Phang, I.Y.; Liu, T. Carbon nanotubes reinforced nylon-6 composite prepared by simple melt-compounding. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, A.R.; Sreekumar, T.V.; Liu, T.; Kumar, S.; Ericson, L.M.; Hauge, R.H.; Smalley, R.E. Crystallization and orientation studies in polypropylene/single wall carbon nanotube composite. Polymer 2003, 44, 2373–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xu, C.; Liang, J.; Wei, B.; Wu, D.; Zhu, S. Study on poly (methyl methacrylate)/carbon nanotube composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 271, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, B.B.; Kinloch, A.J.; Mohammed, R.D.; Taylor, A.C.; Sprenger, S. Toughening mechanisms of nanoparticle-modified epoxy polymers. Polymer 2007, 48, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, M.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, J. High impact performance induced by a synergistic effect of heteroepitaxy and oriented layer-unoriented layer alternated structure in IPP/HDPE injection molded part. Polymer 2019, 175, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Mi, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Shen, K.; Zhang, J. Insight into understanding the influence of blending ratio on the structure and properties of high-density polyethylene/polystyrene microfibril composites prepared by vibration injection molding. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 58, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, F.; Xia, H.; Qian, X.; Shen, K.; Zhang, J. Improving the electrical conductivity of a carbon nanotube/polypropylene composite by vibration during injection-moulding. Carbon 2011, 49, 3274–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göldel, A.; Kasaliwal, G.; Pötschke, P. Selective localization and migration of multiwalled carbon nanotubes in blends of polycarbonate and poly (styrene-acrylonitrile). Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2009, 30, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pötschke, P.; Pegel, S.; Claes, M.; Bonduel, D. A novel strategy to incorporate carbon nanotubes into thermoplastic matrices. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2008, 29, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Mao, C.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Yang, X. Control of carbon nanotubes at the interface of a co-continuous immiscible polymer blend to fabricate conductive composites with ultralow percolation thresholds. Carbon 2014, 73, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumita, M.; Sakata, K.; Asai, S.; Miyasaka, K.; Nakagawa, H. Dispersion of fillers and the electrical conductivity of polymer blends filled with carbon black. Polym. Bull. 1991, 25, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.S.; Burbine, S.; Shivaprakash, N.K.; Mead, J. 3D-printable PP/SEBS thermoplastic elastomeric blends: Preparation and properties. Polymers 2019, 11, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S. Polymer Interface and Adhesion; M. Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1982; Volume 188. [Google Scholar]
- Nuriel, S.; Liu, L.; Barber, A.; Wagner, H. Direct measurement of multiwall nanotube surface tension. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2005, 404, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surface-Tension. Available online: http://www.surface-tension.de/solid-surface-energy.htm (accessed on 10 October 2015).
- Bose, S.; Bhattacharyya, A.R.; Bondre, A.P.; Kulkarni, A.R.; Pötschke, P. Rheology, electrical conductivity, and the phase behavior of cocontinuous PA6/ABS blends with MWNT: Correlating the aspect ratio of MWNT with the percolation threshold. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2008, 46, 1619–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Hufenus, R.; Qin, Z.; Chen, L.; Gooneie, A. Tailored gradient morphologies and anisotropic surface patterns in polymer blends. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2019, 304, 1800601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Hufenus, R.; Qin, Z.; Chen, L.; Gooneie, A. Tuning gradient microstructures in immiscible polymer blends by viscosity ratio. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 48165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yu, F.; Deng, H.; Huang, Y.; Li, G.; Fu, Q. Morphology evolution of polymer blends under intense shear during high speed thin-wall injection molding. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 6257–6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayla, A.; Campagne, C.; Rochery, M.; Devaux, E. Electrical, rheological properties and morphologies of biphasic blends filled with carbon nanotubes in one of the two phases. Synth. Met. 2011, 161, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Peng, Y.; Xiang, F.; Zhang, J. Selective distribution, reinforcement, and toughening roles of MWCNTS in immiscible polypropylene/ethylene-co-vinyl acetate blends. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2010, 48, 1882–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooneie, A.; Nazockdast, H.; Shahsavan, F. Effect of selective localization of carbon nanotubes in PA6 dispersed phase of PP/PA6 blends on the morphology evolution with time, part 2: Relaxation of deformed droplets after cessation of flow. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2016, 56, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Sample | HDPE | PA | CNT |
|---|---|---|---|
| A0.5(C/M/P) | 50 wt.% | 50 wt.% | 0.5 Phr |
| A1(C/M/P) | 50 wt.% | 50 wt.% | 1 Phr |
| A2(C/M/P) | 50 wt.% | 50 wt.% | 2 Phr |
| B0.5(C/M/P) | 75 wt.% | 25 wt.% | 0.5 Phr |
| B1(C/M/P) | 75 wt.% | 25 wt.% | 1 Phr |
| B2(C/M/P) | 75 wt.% | 25 wt.% | 2 Phr |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mi, D.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, W. Effects of Three Different Injection-Molding Methods on the Mechanical Properties and Electrical Conductivity of Carbon Nanotube/Polyethylene/Polyamide 6 Nanocomposite. Polymers 2019, 11, 1779. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111779
Mi D, Zhao Z, Zhu W. Effects of Three Different Injection-Molding Methods on the Mechanical Properties and Electrical Conductivity of Carbon Nanotube/Polyethylene/Polyamide 6 Nanocomposite. Polymers. 2019; 11(11):1779. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111779
Chicago/Turabian StyleMi, Dashan, Zhongguo Zhao, and Wenli Zhu. 2019. "Effects of Three Different Injection-Molding Methods on the Mechanical Properties and Electrical Conductivity of Carbon Nanotube/Polyethylene/Polyamide 6 Nanocomposite" Polymers 11, no. 11: 1779. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111779
APA StyleMi, D., Zhao, Z., & Zhu, W. (2019). Effects of Three Different Injection-Molding Methods on the Mechanical Properties and Electrical Conductivity of Carbon Nanotube/Polyethylene/Polyamide 6 Nanocomposite. Polymers, 11(11), 1779. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111779