Partially Acetylated Cellulose Dissolved in Aqueous Solution: Physical Properties and Enzymatic Hydrolysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Equipment and Characterization Methods
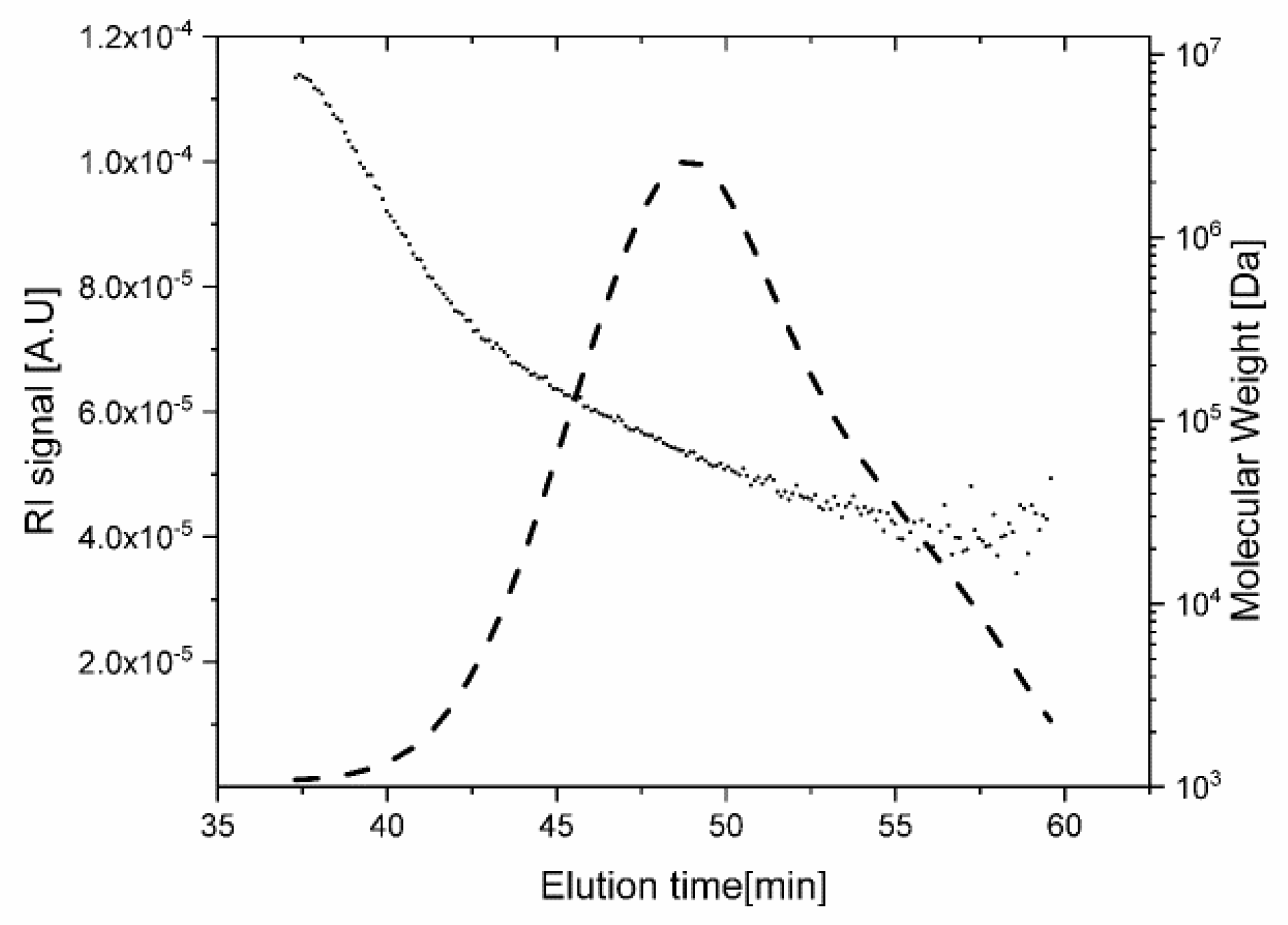
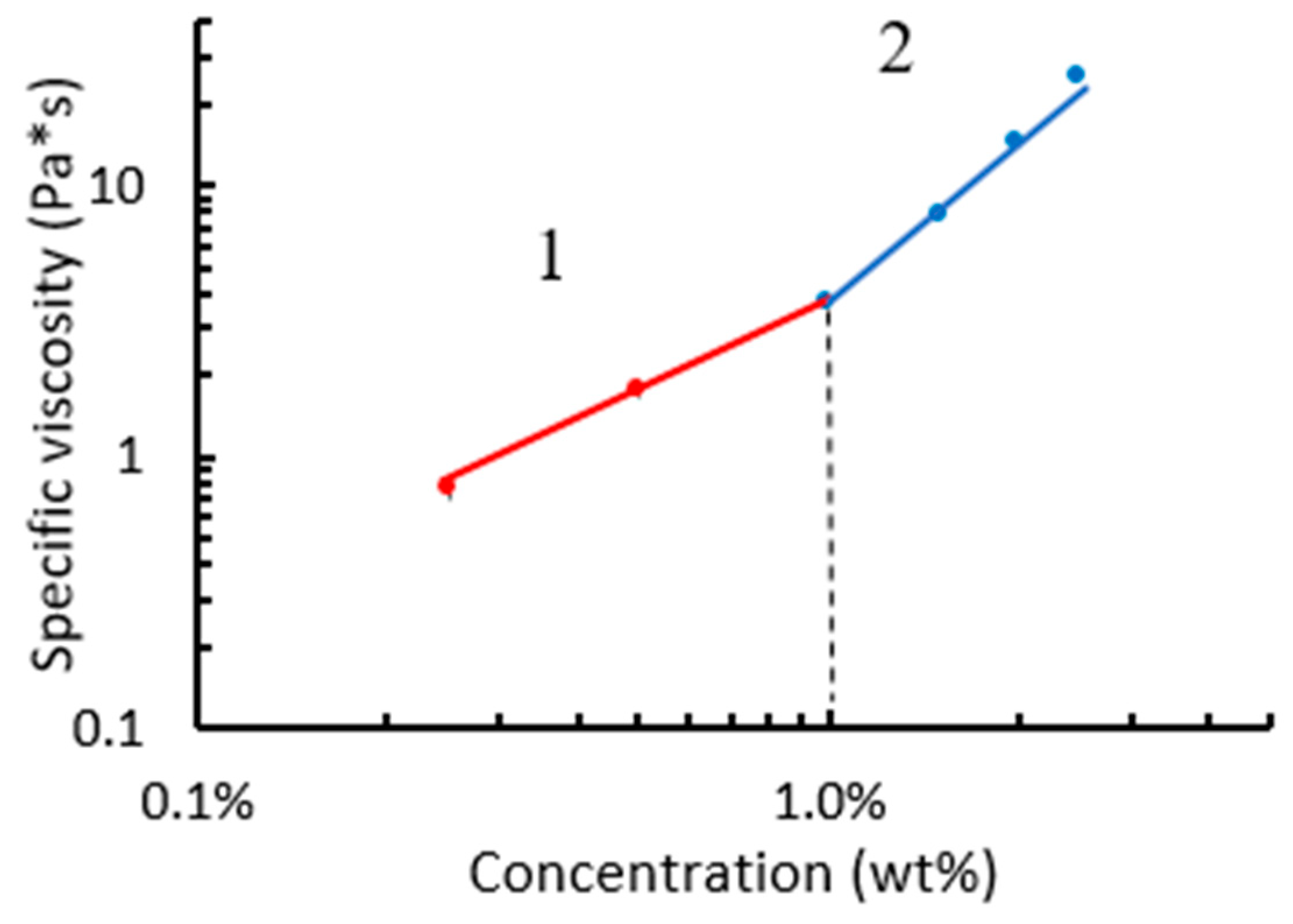
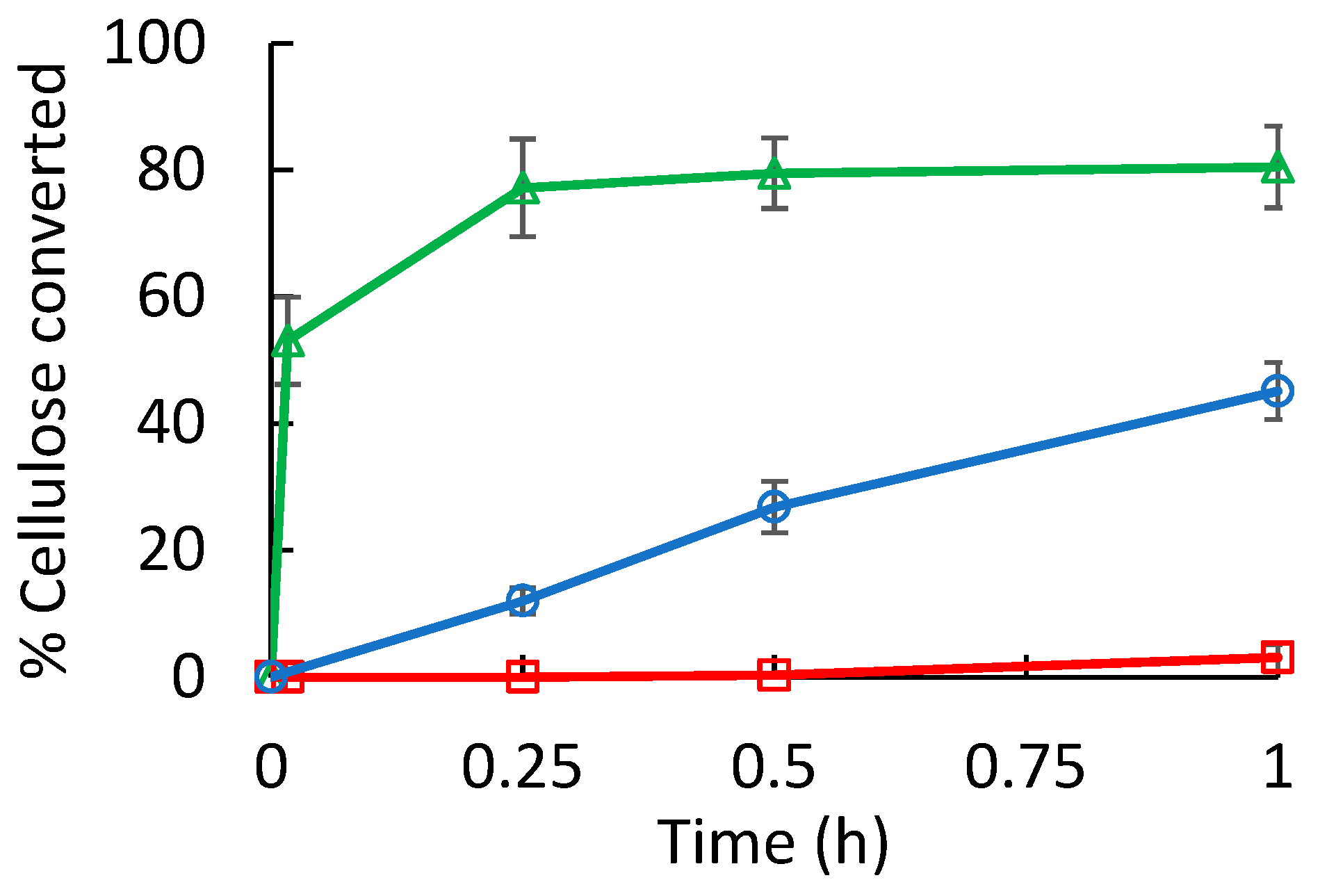
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malm, C.J.; Barkey, K.T.; Salo, M. Far-Hydrolyzed Cellulose Acetates. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1957, 49, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Kamide, K.; Okajima, K.; Kowsaka, K.; Matsui, T. Solubility of cellulose acetate prepared by different methods and its correlationships with average acetyl group distribution on glucopyranose units. Polym. J. 1987, 19, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, T.; Sato, Y.; Shibata, T. 13C-NMR Spectral Studies on the Distribution of Substituents in Water-Soluble Cellulose Acetate. J. Polym. Sci. 1985, 23, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, C.M.; Edgar, K.J.; Wilson, A.K. Preparation and Characterization of Cellulose Monoacetates: The Relationship between Structure and Water Solubility. Macromolecules 1991, 24, 3060–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, J.; He, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y. Homogeneous acetylation of cellulose at relatively high concentrations in an ionic liquid. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 18, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocahut, A.; Delannoy, J.Y.; Vergelati, C.; Mazeau, K. Conformational analysis of cellulose acetate in the dense amorphous state. Cellulose 2014, 21, 3897–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, J.L.; Kadla, J.F. CTA III: A third polymorph of cellulose triacetate. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 2013, 32, 120–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, J.; Lu, F.; Wang, B.; Xu, F.; Ma, M.; Zhang, X. Synthesis of Highly Polymerized Water-soluble Cellulose Acetate by the Side Reaction in Carboxylate Ionic Liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium Acetate. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alfassi, G.; Rein, D.M.; Cohen, Y. Partial cellulose acetylation in 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate induced by dichloromethane. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2018, 56, 2458–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, T.; Takahashi, S.I.; Ito, H.; Inagaki, H.; Noishiki, Y. Tissue biocompatibility of cellulose and its derivatives. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1989, 23, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochek, A.M.; Kalyuzhnaya, L.M. Interaction of water with cellulose and cellulose acetates as influenced by the hydrogen bond system and hydrophilic-hydrophobic balance of the macromolecules. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2002, 75, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swatloski, R.P.; Spear, S.K.; Holbrey, J.D.; Rogers, R.D. Dissolution of cellulose with ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 4974–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rein, D.M.; Khalfin, R.; Szekely, N.; Cohen, Y. True molecular solutions of natural cellulose in the binary ionic liquid-containing solvent mixtures. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 112, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghuwanshi, V.S.; Cohen, Y.; Garnier, G.; Garvey, C.J.; Russell, R.A.; Darwish, T.; Garnier, G. Cellulose Dissolution in Ionic Liquid: Ion Binding Revealed by Neutron Scattering. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 7649–7655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napso, S.; Rein, D.M.; Khalfin, R.; Cohen, Y. Semidilute Solution Structure of Cellulose in an Ionic Liquid and Its Mixture with a Polar Organic Co-solvent Studied by Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering. J. Polym. Sci. PART B Polym. Phys. 2017, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Pang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Sun, R. Regenerated cellulose film with enhanced tensile strength prepared with ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate (EMIMAc). Cellulose 2013, 20, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Niu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J. Liquid crystalline phase and gel-sol transitions for concentrated microcrystalline cellulose (MCC)/1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate (EMIMAc) solutions. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Lindbråthen, A.; Sandru, M.; Gutierrez, M.T.G.; Zhang, X.; Hillestad, M.; He, X. Spinning cellulose hollow fibers using 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate-dimethylsulfoxide co-solvent. Polymers 2018, 10, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, E.; Miyafuji, H. Reaction behavior of cellulose in an ionic liquid, 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. J. Wood Sci. 2013, 59, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, S.; Liebert, T.; Schöbitz, M.; Schaller, J.; Meister, F.; Günther, W.; Heinze, T. Interactions of ionic liquids with polysaccharides 1. Unexpected acetylation of cellulose with 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2007, 28, 2311–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadi, A.P.; Schall, C.A.; Varanasi, S. Mitigation of cellulose recalcitrance to enzymatic hydrolysis by ionic liquid pretreatment. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2007, 137–140, 407–421. [Google Scholar]
- Dadi, A.P.; Varanasi, S.; Schall, C.A. Enhancement of Cellulose Saccharification Kinetics Using an Ionic Liquid Pretreatment Step. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2006, 95, 904–910. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Jones, C.L.; Baker, G.A.; Xia, S.; Olubajo, O.; Person, V.N. Regenerating cellulose from ionic liquids for an accelerated enzymatic hydrolysis. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 139, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardo, J.R.; Gírio, F.M.; Łukasik, R.M. The effect of the chemical character of ionic liquids on biomass pre-treatment and posterior enzymatic hydrolysis. Molecules 2019, 24, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Sun, S.; Cao, X.; Sun, R. The role of pretreatment in improving the enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 199, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samayam, I.P.; Hanson, B.L.; Langan, P.; Schall, C.A. Ionic-liquid induced changes in cellulose structure associated with enhanced biomass hydrolysis. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3091–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Takabe, K.; Xu, F. Unraveling variations of crystalline cellulose induced by ionic liquid and their effects on enzymatic hydrolysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfassi, G.; Rein, D.M.; Cohen, Y. Cellulose emulsions and their hydrolysis. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.L. Use of DinitrosaIicyIic Acid Reagent for Determination of Reducing Sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, C.T.; Hourston, D.J. Specific refractive index increments of certain polysaccharide systems. Polymer 1975, 16, 474–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-S. Handbook Of Size Exclusion Chromatography And Related Techniques; Wu, C., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; ISBN 978-0-8247-4710-7. [Google Scholar]
- Ghareeb, H.O.; Radke, W. Separation of cellulose acetates by degree of substitution. Polymer 2013, 54, 2632–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghareeb, H.O.; Malz, F.; Kilz, P.; Radke, W. Molar mass characterization of cellulose acetates over a wide range of high DS by size exclusion chromatography with multi-angle laser light scattering detection. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghareeb, H.O.; Radke, W. Characterization of cellulose acetates according to DS and molar mass using two-dimensional chromatography. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, D.M.; Khalfin, R.; Cohen, Y. Cellulose as a novel amphiphilic coating for oil-in-water and water-in-oil dispersions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 386, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Águila-Hernández, J.; Trejo, A.; García-Flores, B.E. Volumetric and surface tension behavior of aqueous solutions of polyvinylpyrrolidone in the range (288 to 303) K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2011, 56, 2371–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boraston, A.B.; Bolam, D.N.; Gilbert, H.J.; Davies, G.J. Carbohydrate-binding modules: Fine-tuning polysaccharide recognition. Biochem. J. 2004, 382, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimlos, M.R.; Beckham, G.T.; Matthews, J.F.; Bu, L.; Himmel, M.E.; Crowley, M.F. Binding preferences, surface attachment, diffusivity, and orientation of a family 1 carbohydrate-binding module on cellulose. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 20603–20612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfassi, G.; Rein, D.M.; Cohen, Y. Enhanced hydrolysis of cellulose hydrogels by morphological modification. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 40, 1635–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| wt% Experimental | wt% Calculated |
|---|---|
| 2.5 | 2.3 |
| 2.0 | 1.8 |
| 1.5 | 1 |
| 1 | 0.7 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alfassi, G.; Rein, D.M.; Shpigelman, A.; Cohen, Y. Partially Acetylated Cellulose Dissolved in Aqueous Solution: Physical Properties and Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Polymers 2019, 11, 1734. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111734
Alfassi G, Rein DM, Shpigelman A, Cohen Y. Partially Acetylated Cellulose Dissolved in Aqueous Solution: Physical Properties and Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Polymers. 2019; 11(11):1734. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111734
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlfassi, Gilad, Dmitry M. Rein, Avi Shpigelman, and Yachin Cohen. 2019. "Partially Acetylated Cellulose Dissolved in Aqueous Solution: Physical Properties and Enzymatic Hydrolysis" Polymers 11, no. 11: 1734. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111734
APA StyleAlfassi, G., Rein, D. M., Shpigelman, A., & Cohen, Y. (2019). Partially Acetylated Cellulose Dissolved in Aqueous Solution: Physical Properties and Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Polymers, 11(11), 1734. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111734







