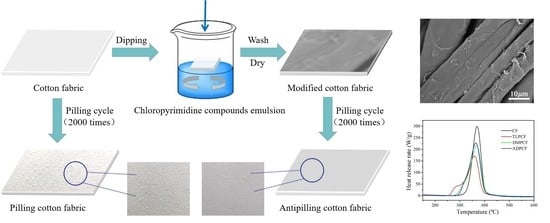
Durable Antipilling Modification of Cotton Fabric with Chloropyrimidine Compounds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
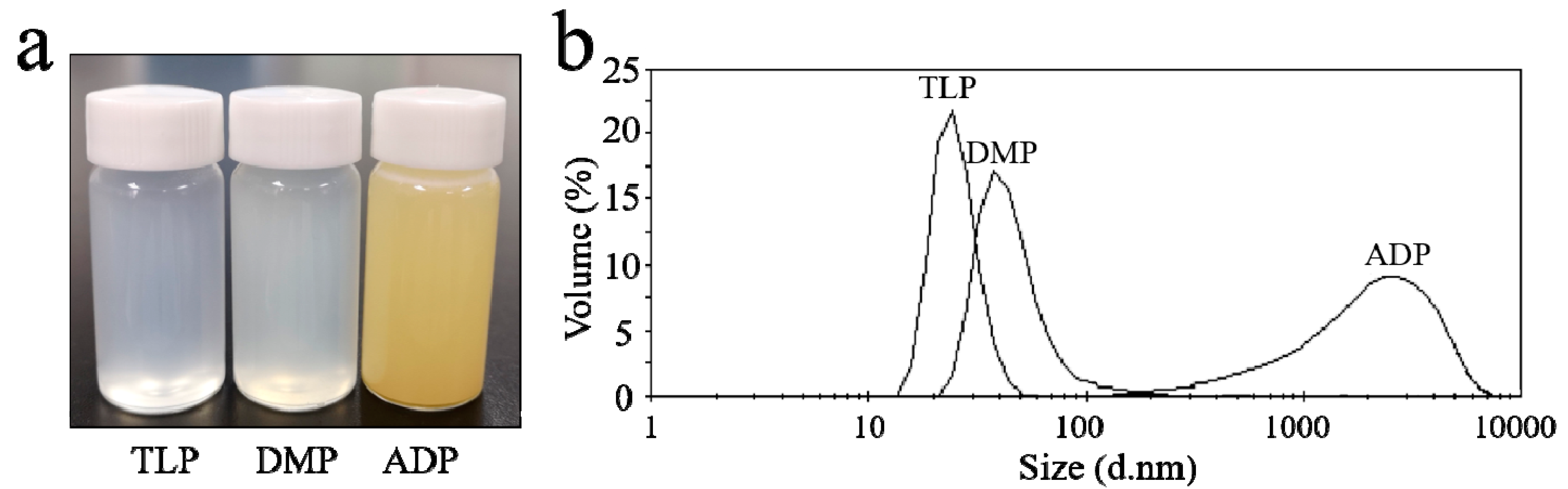
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of Dispersed Emulsions
2.3. Preparation of Chloropyrimidine-Modified Cotton Fabrics
2.4. Dyeing of Cotton Fabrics
2.5. Characterization and Measurements
2.5.1. Pilling Characterization
2.5.2. Surface Morphology and Structure Analysis
2.5.3. Thermal Properties
2.5.4. Durability to Washing
2.5.5. Mechanical Properties
2.5.6. Color Measurements and Colorfastness
3. Results and Discussion
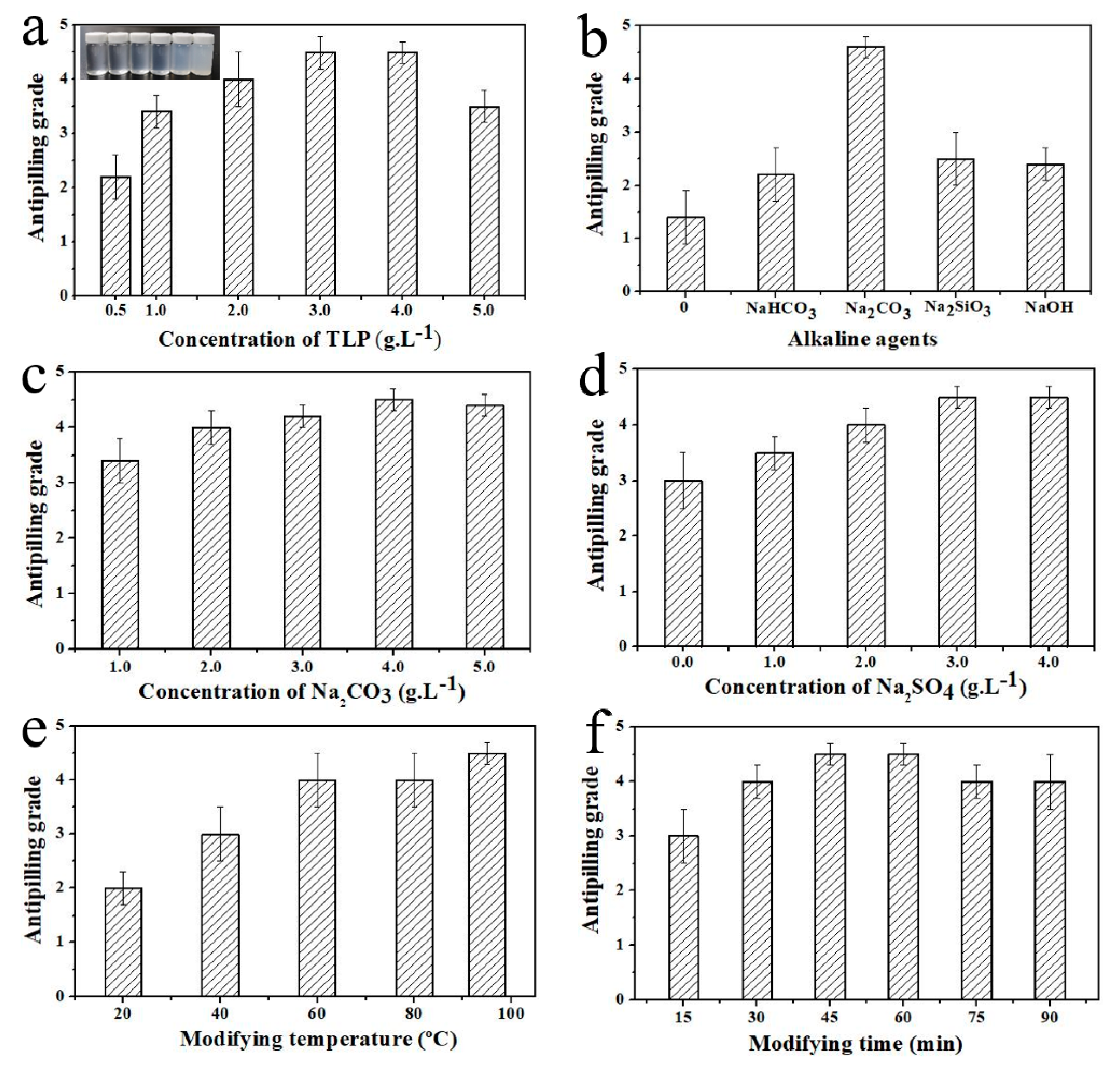
3.1. Effects of Reaction Conditions on Antipilling Grade of TLP-Modified Cotton Fabric
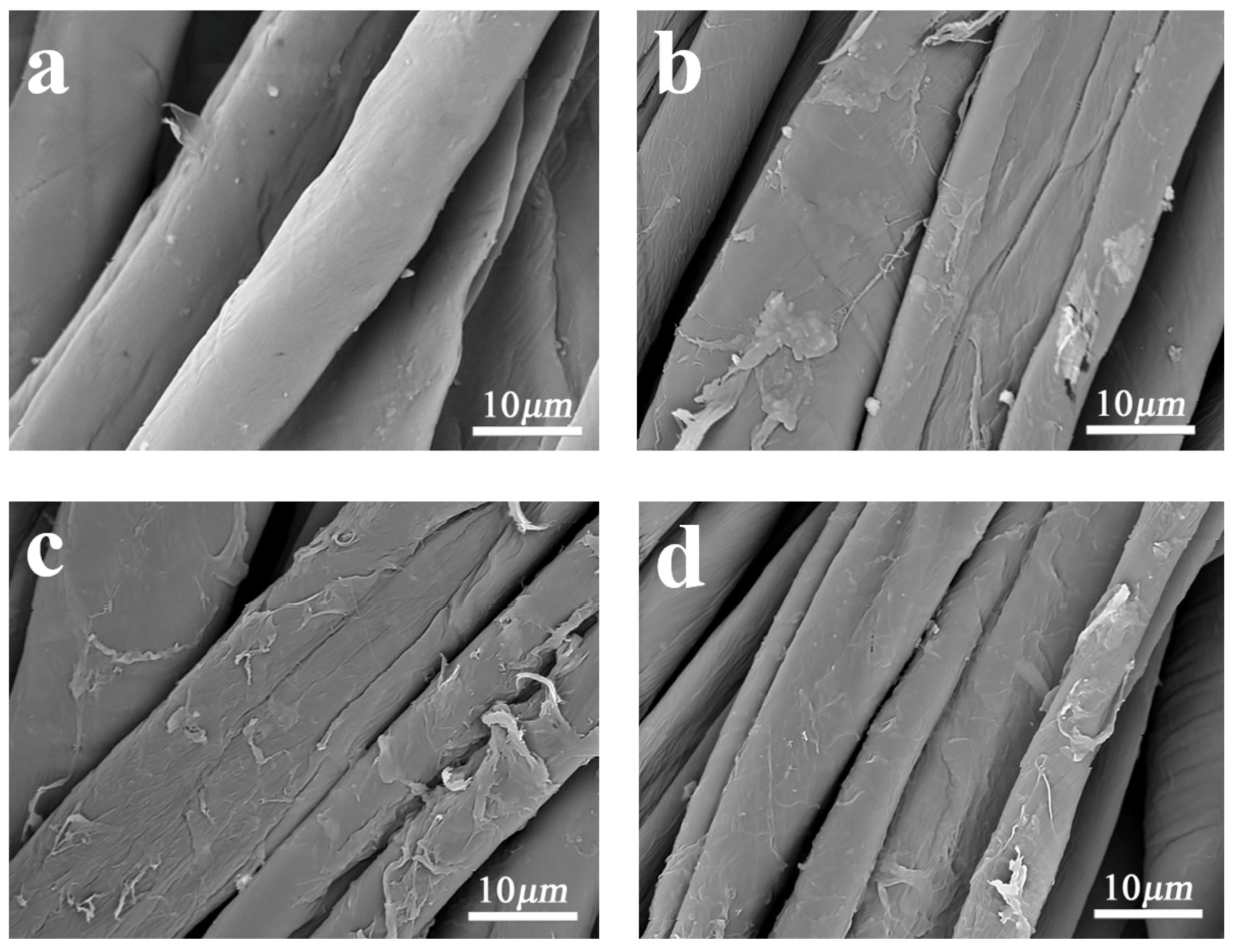
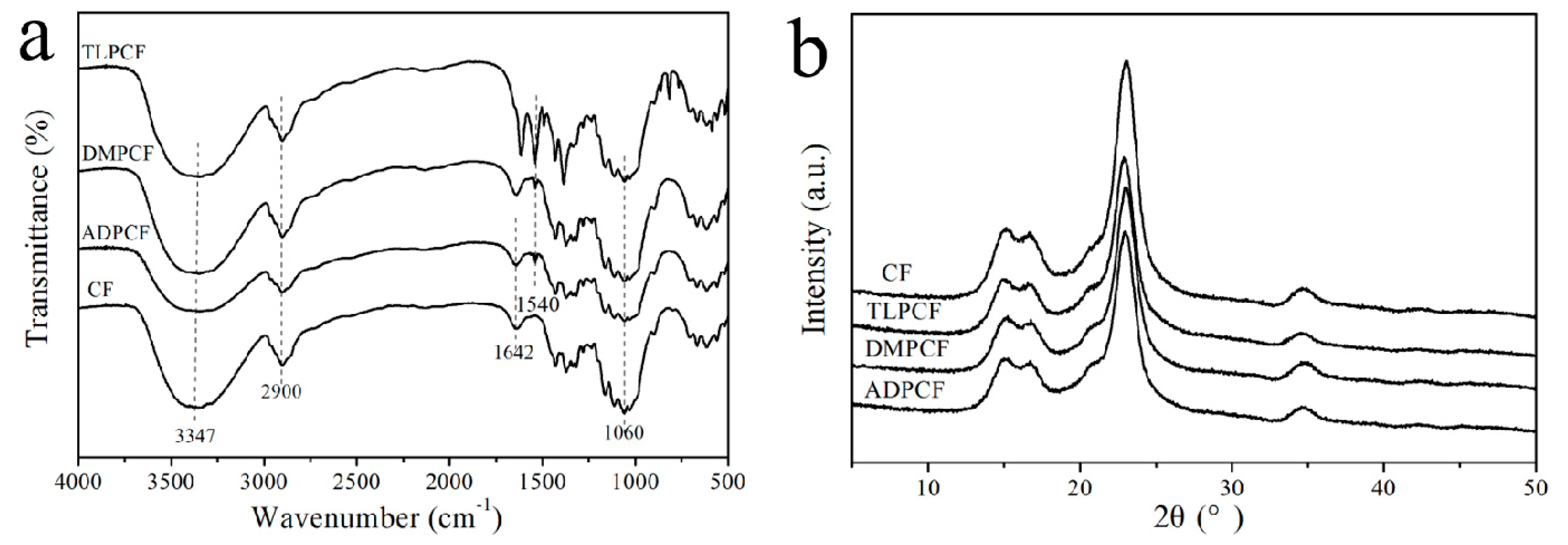
3.2. Surface Morphology and Chemical Structure
3.3. Antipilling Performance and Washing Durability
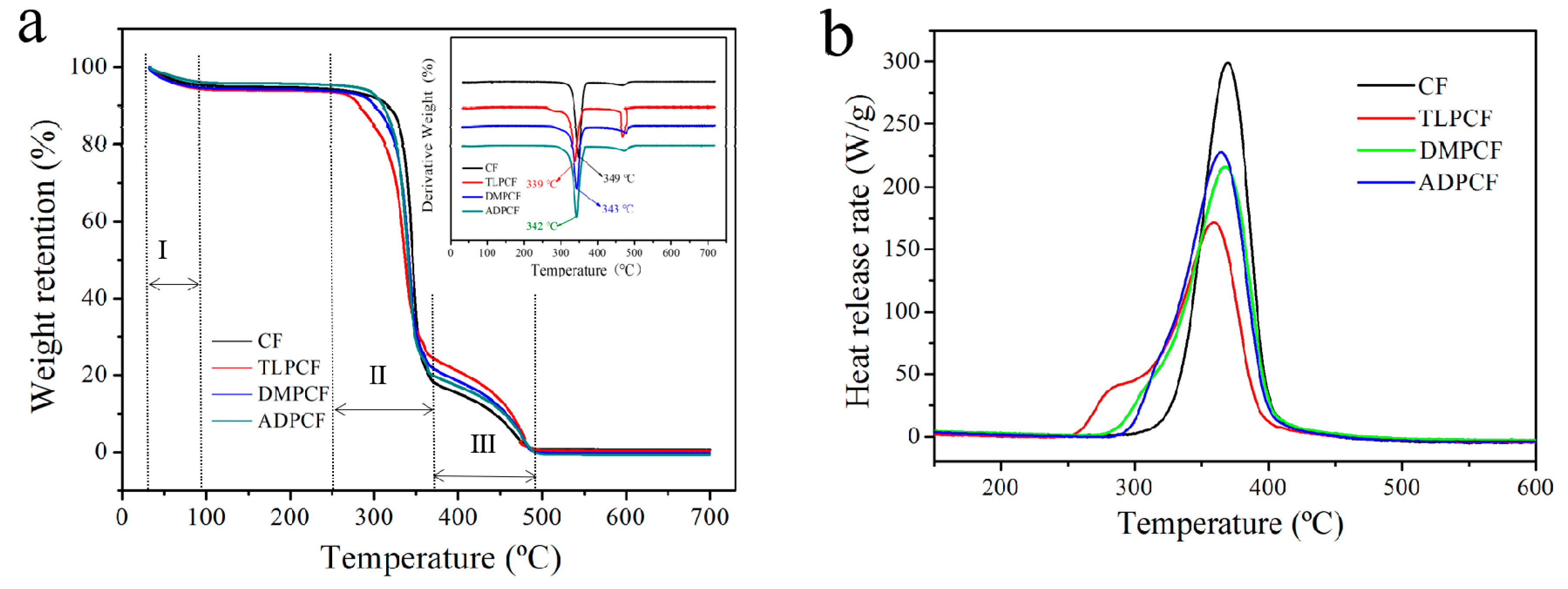
3.4. Thermal Properties
3.5. Mechanical Properties
3.6. Dyeing Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rong, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, B.; Mao, Z.; Xu, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, Y.; Feng, X.; Sui, X. Durable antibacterial and hydrophobic cotton fabrics utilizing enamine bonds. Carbohyd. Polym. 2019, 211, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xia, L.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, H.; Wang, A.; Xu, W.; Wang, Y. Structure and properties of carboxymethyl cotton fabric loaded by reduced graphene oxide. Carbohyd. Polym. 2019, 214, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, D.; Du, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z. Structure and properties of silk fibroin grafted carboxylic cotton fabric via amide covalent modification. Carbohyd. Polym. 2017, 161, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rub, M.A. Effect of additives (TX-114) on micellization and microstructural phenomena of amphiphilic ibuprofen drug (sodium salt): Multi-technique approach. J. Lumin. 2018, 197, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Chen, H.Y.; Wang, W.T.; Liu, Y.Q.; Zhao, P.H. Synthesis of a formaldehyde-free phosphorus-nitrogen flame retardant with multiple reactive groups and its application in cotton fabrics. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2015, 120, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Nagarajana, S.; Shu, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, L.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, J. Green and facile surface modification of cellulose nanocrystal as the route to produce poly (lactic acid) nanocomposites with improved properties. Carbohyd. Polym. 2018, 197, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Kimura, S.; Nishiyama, Y.; Isogai, A. Cellulose nanofibers prepared by TEMPO-mediated oxidation of native cellulose. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2485–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.R.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Sharma, S.K.; Hsiao, B.S. Efficient removal of UO22+ from water using carboxycellulose nanofibers prepared by the nitro-oxidation method. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 13885–13893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.R.; Zheng, B.; Sharma, S.K.; Zhan, C.; Wang, R.; Bhatia, S.R.; Hsiao, B.S. High aspect ratio carboxycellulose nanofibers prepared by nitro-oxidation method and their nanopaper properties. ACS Appl. Namo Mater 2018, 1, 3969–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.; Raj, M.C.; Athira, K.B.; Rubiyah, M.H.; Joy, J.; Moores, A.; Drisko, G.; Sanchez, C. Nanocellulose, a versatile green platform: From biosources to materials and their applications. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 11575–11625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montarsolo, A.; Mossotti, R.; Innocenti, R.; Vassallo, E. A study on washing resistance of pp-HMDSO films deposited on wool fabrics for antipilling purposes. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2013, 224, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.A.; EL-Badry, K.; Eid, B.M.; Hassan, T.M. A new approach for biofinishing of cellulose-containing fabrics using acid cellulases. Carbohyd. Polym. 2011, 83, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, C.W.; Lam, Y.L. Low Stress Mechanical Properties of Plasma-Treated Cotton Fabric Subjected to Zinc Oxide-Anti-Microbial Treatment. Materials 2013, 6, 314–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, M.; K. Zia, M.H.; Bhatti, N.; Jamil, T.; Hussain, R.; Zuber, M. Modification of cellulosic fiber with polyurethane acrylate copolymers. Part, I. Physicochemica properties. Carbohyd. Polym. 2012, 87, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugaa, M.R.; Zaharia, C.; Bălan, M.; Bressyc, C.; Ziarellid, F.; Margaillan, A. Surface modification of silk fibroin fibers with poly (methyl methacrylate) and poly (tributylsilyl methacrylate) via RAFT polymerization for marine antifouling applications. Mater. Sci. 2015, 51, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalczyk, D.; Brzeziński, S.; Kamińska, I. Multifunctional bioactive and improving the performance durability nanocoatings for finishing PET/CO woven fabrics by the sol-gel method. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 649, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabasum, S.; Zuber, M.; Jamil, T.; Shahid, M.; Hussain, R. Antimicrobial and pilling evaluation of modified cellulosic fabrics using polyurethane acrylate copolymers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 56, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Chen, G.; Xing, T. Ration design and preparation of flame retardant silk fabrics coated with reduced graphene oxide. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 474, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Liu, Y.; Wu, D. Synthesis and characterization of polyacrylate modified by polysiloxane latexes and films. Prog. Org. Coat. 2014, 77, 1774–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Molla, M.M. Synthesis of polyurethane acrylate oligomers as aqueous UV-curable binder for inks of ink jet in textile printing and pigment dyeing. Dyes. Pigments. 2007, 74, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Sun, Y.; Gua, H.; Zhou, X. Synthesis and application of acrylate copolymer as high ink-absorption and fast drying coating agent for polyester fabric. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 136, 105298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wu, J.; Yang, Z.; Pu, M.P. Synthesis and properties of poly (acrylic acid)/Mica superabsorbent nanocomposite. Macromol. Rapid. Commun. 2001, 22, 422–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, M.; Zia, K.M.; Bhatti, H.N.; Jamil, T.; Hussain, H.; Zuber, M. Modification of cellulosic fiber with polyurethane acrylate copolymers. Part I. Physicochemical properties. Carbohyd. Polym. Basel 2012, 87, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, G.; Ma, W.; Huang, Z. Waterborne polyurethane/poly (n-butyl acrylate-styrene) hybrid emulsions: Particle formation, film properties, and application. Prog. Org. Coat. 2012, 74, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, C.W.; Yuen, C.W.M.; Hung, O.N. Improving the pilling property of knitted wool fabric with atmospheric pressure plasma treatment. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2013, 228, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuelela, A.M.; Mohamed, T.A.; Wilson, L.D.; Zoghaib, W.M. Raman and infrared spectra, normal coordinate analysis and ab initio calculations of 4-Amino-2-chloropyrimidine-5-carbonitrile. J. Mol. Struct. 2016, 1115, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzon, G.; Zahid, M.; Heredia-Guerrero, J.A.; Balliana, E.; Zendri, E.; Athanassiou, T.; Bayer, I.S. Hydrophobic treatment of woven cotton fabrics with polyurethane modified aminosilicone emulsions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 490, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuber, M.; Zia, K.M.; Tabassum, S.; Jamil, T.; Barkaat-ul-Hasin, S.; Khosa, M.K. Preparation of rich handles soft cellulosic fabric using amino silicone based softener, partII: Colorfastnessproperties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Zhou, Q.; Zhu, X.; Guo, J.; Mia, M.S.; Yan, X.; Chen, G.; Xing, T. A superhydrophobic bionic coating on silk fabric with flame retardancy and UV shielding ability. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 483, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.; Heredia-Guerrero, J.A.; Athanassiou, A.; Bayer, I.S. Robust water repellent treatment for woven cotton fabrics with eco-friendly polymers. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 319, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.H.; Jia, S.T.; Zhang, J.; Tian, L.Q. Superhydrophobic surfaces on cotton textiles by complex coating of silica nanoparticles and hydrophobization. Thin. Solid. Films 2009, 517, 4593–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bran, J.; Pecastaings, G.; Sèbe, G. A versatile method for the surface tailoring of cellulose nanocrystal building blocks by acylation with functional vinyl esters. Carbohyd. Polym. 2017, 169, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halluin, D.; Rullbarrull, M.; Bretel, J.; Labrugère, G.; Grognec, C.; Felpin, E.L. Chemically modified cellulose filter paper for heavy metal remediation in water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1965–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garside, P.; Wyeth, P. Identification of cellulosic fibers by FTIR spectroscopy-thread and single fiber analysis by attenuated total reflectance. Stud. Conserv. 2003, 48, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.H.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.L.; Tan, J.L.; Zhu, H.L. Influence of HNO3/H3PO4-NaNO2 mediated oxidation on the structure and properties of cellulose fibers. Carbohyd. Polym. 2014, 111, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Baker, J.O.; Himmel, M.E.; Parilla, P.A.; Johnson, D.K. Cellulose crystallinity index: Measurement techniques and their impact on interpreting cellulase performance. Biotechnol. Biofuels. 2010, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, F.A.; Mercê, A.L.R.; Alguacil, F.J.; López-Delgado, A. A kinetic study on the thermal behaviour of chitosan. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2008, 91, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, O.C.; Dikin, D.A.; Putz, K.W.; Brinson, L.C.; Nguyen, S.T. Electrically conductive “alkylated” graphene paper via chemical reduction of amine functionalized graphene oxide paper. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 892–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.R.; Varma, A.J. Thermal stability of cellulose and their nanoparticles: Effect of incremental increases in carboxyl and aldehyde groups. Carbohyd. Polym. 2014, 114, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastjerdi, R.; Montazer, M.; Shahsavan, S. A new method to stabilize nanoparticles on textile surfaces. Colloid Surface A 2009, 345, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; He, Q. Applications of micro-scale combustion calorimetry to the studies of cotton and nylon fabrics treated with organophosphorus flame retardants. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2011, 91, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xing, T.; Chen, G. Silk flame retardant finish by ternary silica sol containing boron and nitrogen. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 421, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, T.; Saito, M.; Tsutsumi, A.; Matsuo, T. Measurement of fabric hand by sensory method and inspection on its effectiveness for worsted woven fabrics. J. Text. Mach. Soc. Jpn. 1997, 43, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Stylios, G.K. Investigating the plasma modification of natural fiber fabrics-the effect on fabric surface and mechanical properties. Text. Res. J. 2005, 75, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orzada, B.T.; Moore, M.A.; Chen, Y.; Collier, B.J. Effects of laundering on fabric drape, bending and shear. Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Tech. 2009, 21, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prachayawarakorn, J.; Boonsawat, K. Physical, chemical and dyeing properties of bombyx mori silks grafted by 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate and methyl methacrylate. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 106, 1526–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

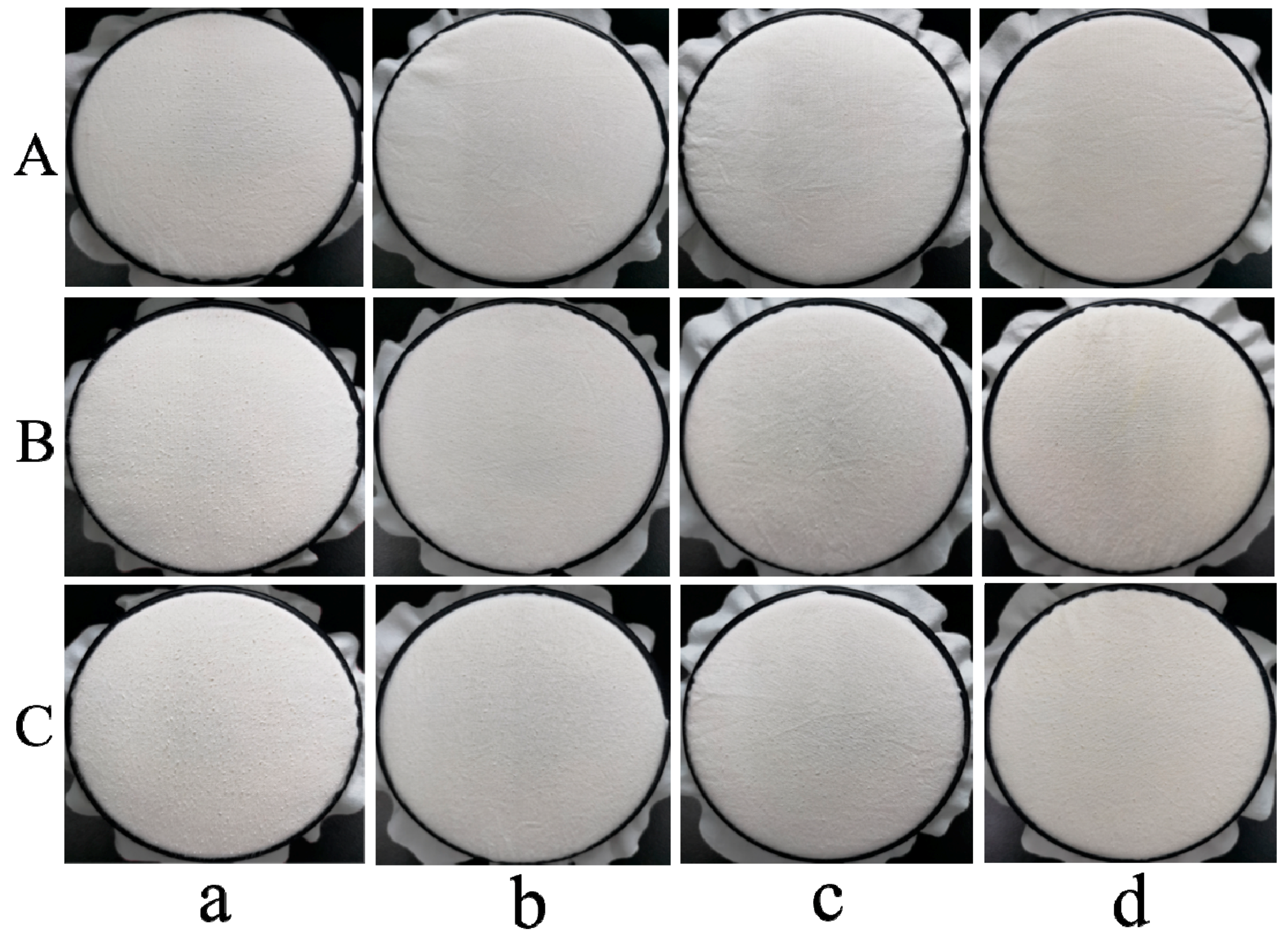
| Pilling Grade | a | b | c | d |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before washing | 2–3 | 5 | 4–5 | 5 |
| 5 times washing | 2 | 4 | 3–4 | 4 |
| 10 times washing | 1–2 | 3–4 | 3 | 3–4 |
| Sample | △m (%) | HRC (J/ (g. K)) | PHRR (W/g) | THR (KJ/g) | T (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CF | 87.0 | 300 | 300.2 | 13.1 | 369.6 |
| TLPCF | 85.8 | 173 | 173.2 | 11.3 | 358.8 |
| DMPCF | 74.5 | 216 | 215.4 | 12.1 | 368.0 |
| ADPCF | 75.2 | 228 | 228.0 | 12.4 | 364.4 |
| Sample | Tensile Strength (N) | Elongation at Break (%) | Whiteness (%) | Permeability (mm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CF | 590.13 | 10.24 | 78.6 | 235.8 |
| TLPCF | 542.33 | 9.65 | 81.2 | 228.9 |
| DMPCF | 552.36 | 10.65 | 78.4 | 187.8 |
| ADPCF | 535.56 | 9.17 | 30.2 | 190.0 |
| Sample | B (gf cm2/cm) | 2HB (gf cm/cm) | MIU | SMD (μm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Warp | Weft | Warp | Weft | Warp | Weft | Warp | Weft | |
| CF | 0.0627 | 0.0348 | 0.0741 | 0.0405 | 0.159 | 0.157 | 4.508 | 2.990 |
| TLPCF | 0.0638 | 0.0352 | 0.0819 | 0.0423 | 0.152 | 0.159 | 4.370 | 2.540 |
| DMPCF | 0.0697 | 0.0377 | 0.0824 | 0.0433 | 0.179 | 0.180 | 3.527 | 3.598 |
| ADPCF | 0.0731 | 0.0354 | 0.1040 | 0.0488 | 0.183 | 0.159 | 3.997 | 3.513 |
| Dyestuff | Sample | K/S | Color Parameter | Rubbing Fastness | Washing Fastness | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | a* | b* | C* | H | Dry | Wet | Staining (Cotton) | Staining (Wool) | Fastness | |||
| Reactive red 3BF | CF | 6.37 | 50.69 | 57.04 | −4.87 | 57.24 | 355.13 | 4 | 3 | 4–5 | 4–5 | 4 |
| TLPCF | 6.42 | 50.87 | 57.18 | −4.76 | 57.38 | 355.24 | 4 | 3–4 | 4–5 | 4–5 | 4 | |
| DMPCF | 6.94 | 50.08 | 57.65 | −4.51 | 57.83 | 355.52 | 4 | 3–4 | 4–5 | 4–5 | 4 | |
| ADPCF | 6.50 | 50.58 | 56.82 | −4.53 | 57.00 | 355.44 | 4 | 3–4 | 4–5 | 4–5 | 4 | |
| Reactive yellow 3RF | CF | 5.73 | 74.29 | 21.43 | 66.07 | 69.46 | 72.03 | 4 | 3–4 | 4–5 | 4–5 | 4 |
| TLPCF | 5.80 | 74.06 | 21.27 | 65.87 | 69.22 | 72.11 | 4–5 | 3–4 | 4–5 | 4–5 | 4 | |
| DMPCF | 5.76 | 76.49 | 25.56 | 69.35 | 73.91 | 69.77 | 4 | 3–4 | 4–5 | 4–5 | 4 | |
| ADPCF | 5.92 | 75.73 | 25.90 | 69.21 | 73.90 | 69.48 | 4 | 3–4 | 4–5 | 4–5 | 4 | |
| Reactive blue KN-R | CF | 4.60 | 48.38 | −2.31 | −37.38 | 37.45 | 266.46 | 4–5 | 3–4 | 4–5 | 4–5 | 4 |
| TLPCF | 5.97 | 45.17 | −1.03 | −39.16 | 39.17 | 268.50 | 4–5 | 3–4 | 4–5 | 4–5 | 4 | |
| DMPCF | 5.76 | 45.95 | −1.82 | −37.81 | 37.86 | 267.25 | 4–5 | 3–4 | 4–5 | 4–5 | 4 | |
| ADPCF | 5.30 | 47.17 | −2.15 | −37.68 | 37.74 | 266.74 | 4–5 | 3–4 | 4–5 | 4–5 | 4 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, X.; Xing, T.; Chen, G. Durable Antipilling Modification of Cotton Fabric with Chloropyrimidine Compounds. Polymers 2019, 11, 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101697
Dong X, Xing T, Chen G. Durable Antipilling Modification of Cotton Fabric with Chloropyrimidine Compounds. Polymers. 2019; 11(10):1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101697
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Xue, Tieling Xing, and Guoqiang Chen. 2019. "Durable Antipilling Modification of Cotton Fabric with Chloropyrimidine Compounds" Polymers 11, no. 10: 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101697
APA StyleDong, X., Xing, T., & Chen, G. (2019). Durable Antipilling Modification of Cotton Fabric with Chloropyrimidine Compounds. Polymers, 11(10), 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101697