Highly Sensitive Detection of Melamine Based on the Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer between Conjugated Polymer Nanoparticles and Gold Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Chemicals and Apparatus
2.2. Preparation of AuNPs
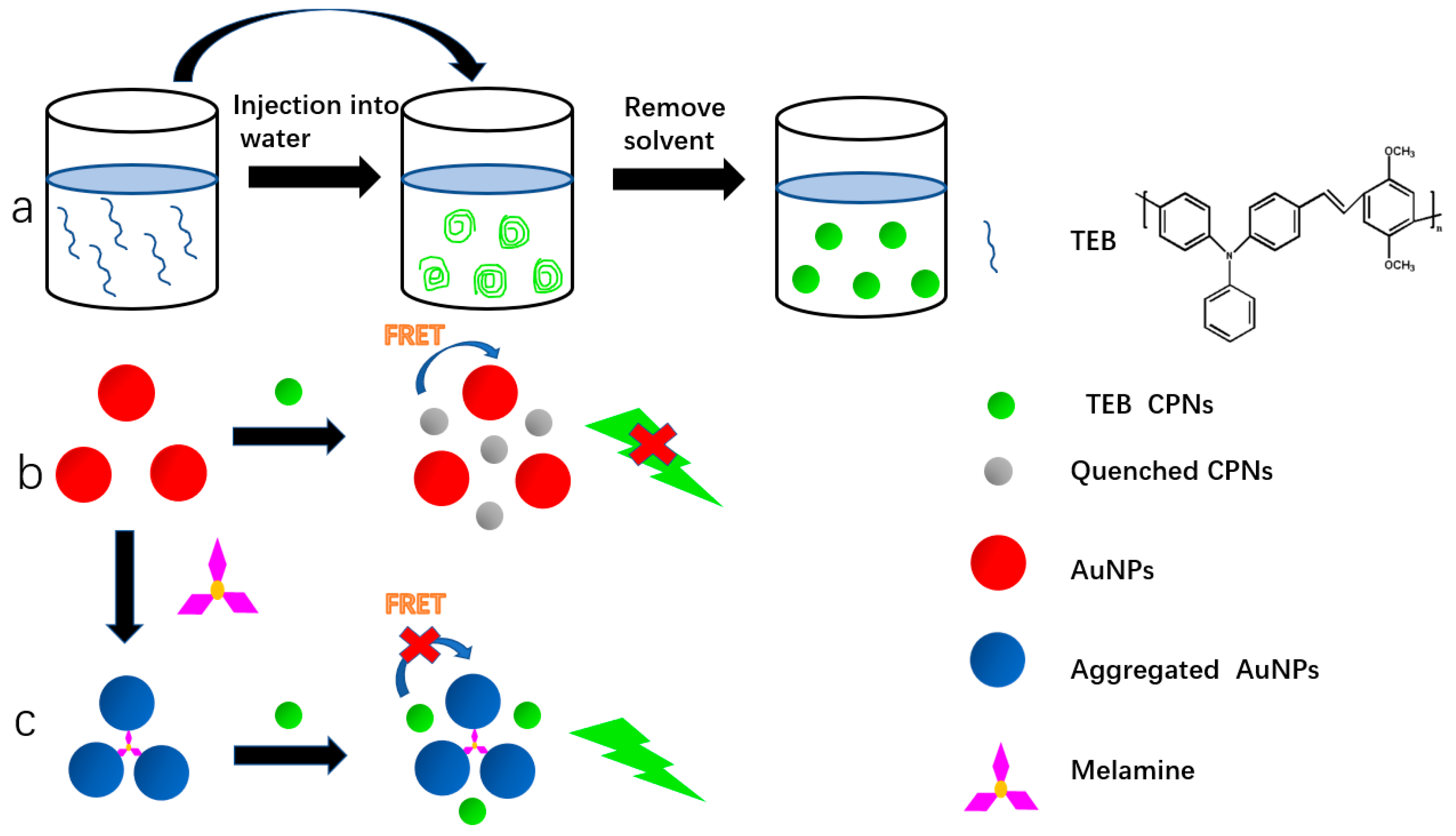
2.3. Preparation of CPNs
2.4. Fluorescence Analysis
2.5. Pretreatment of Real Samples
3. Results and Discussion
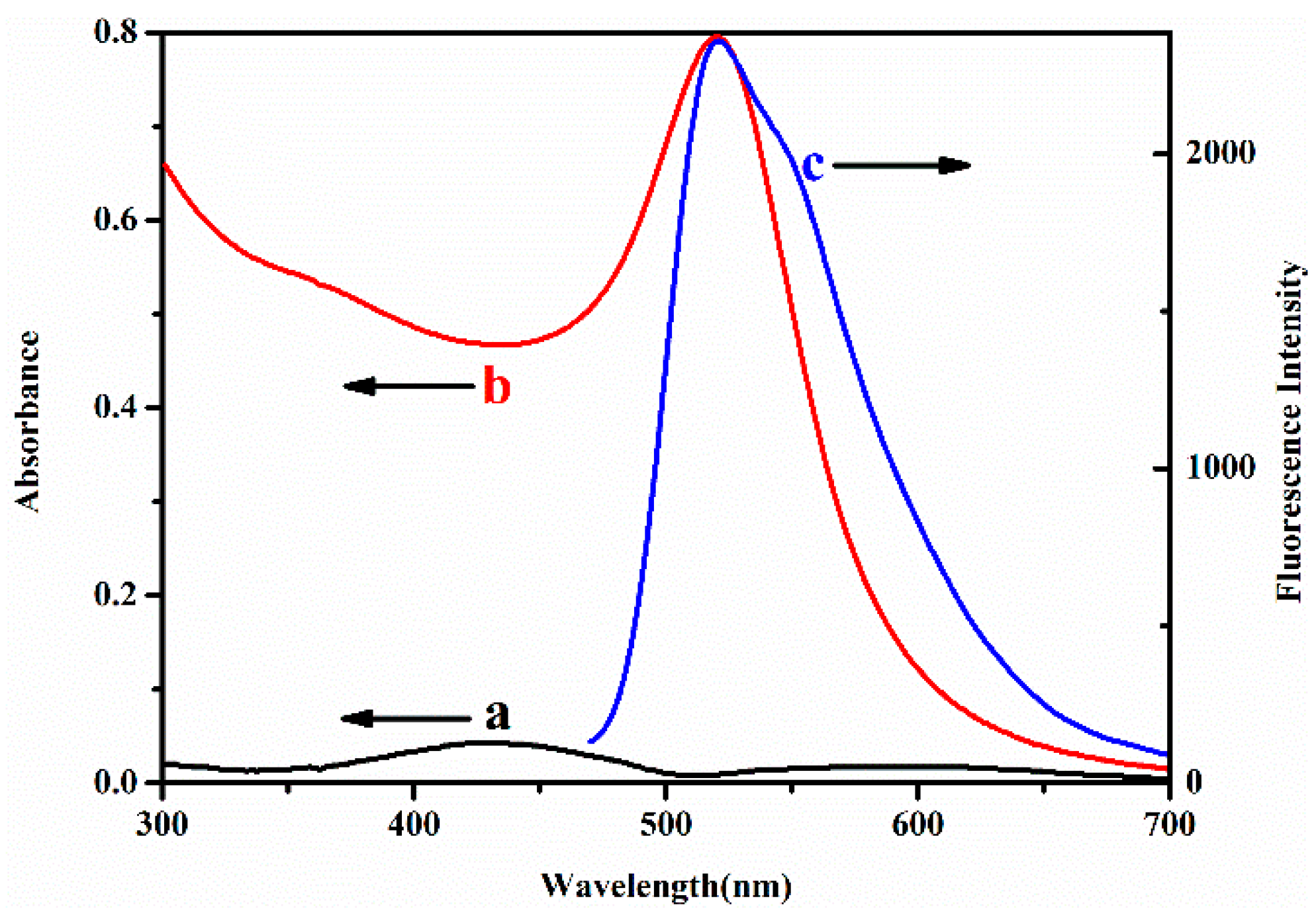
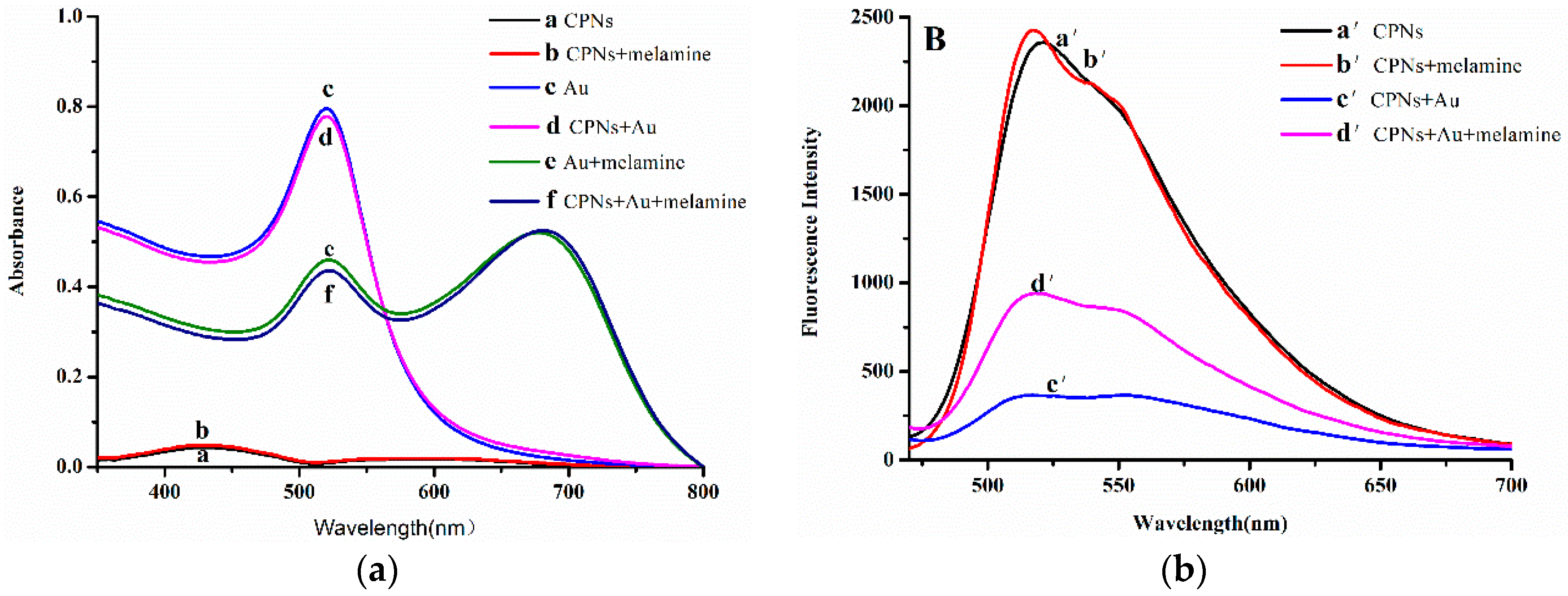
3.1. Optical Characteristics of AuNPs and CPNs
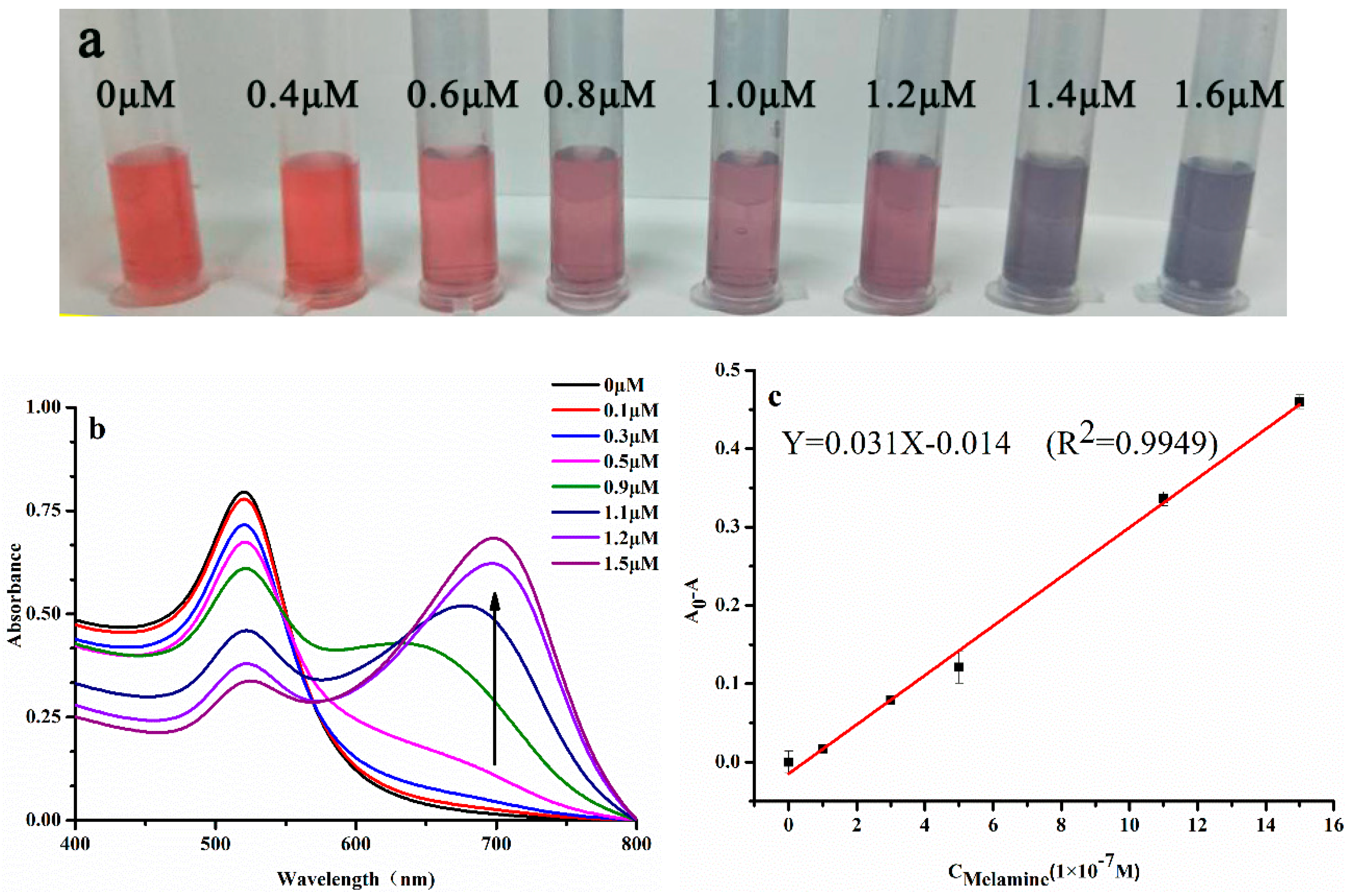
3.2. Interaction of AuNPs-CPNs with Melamine
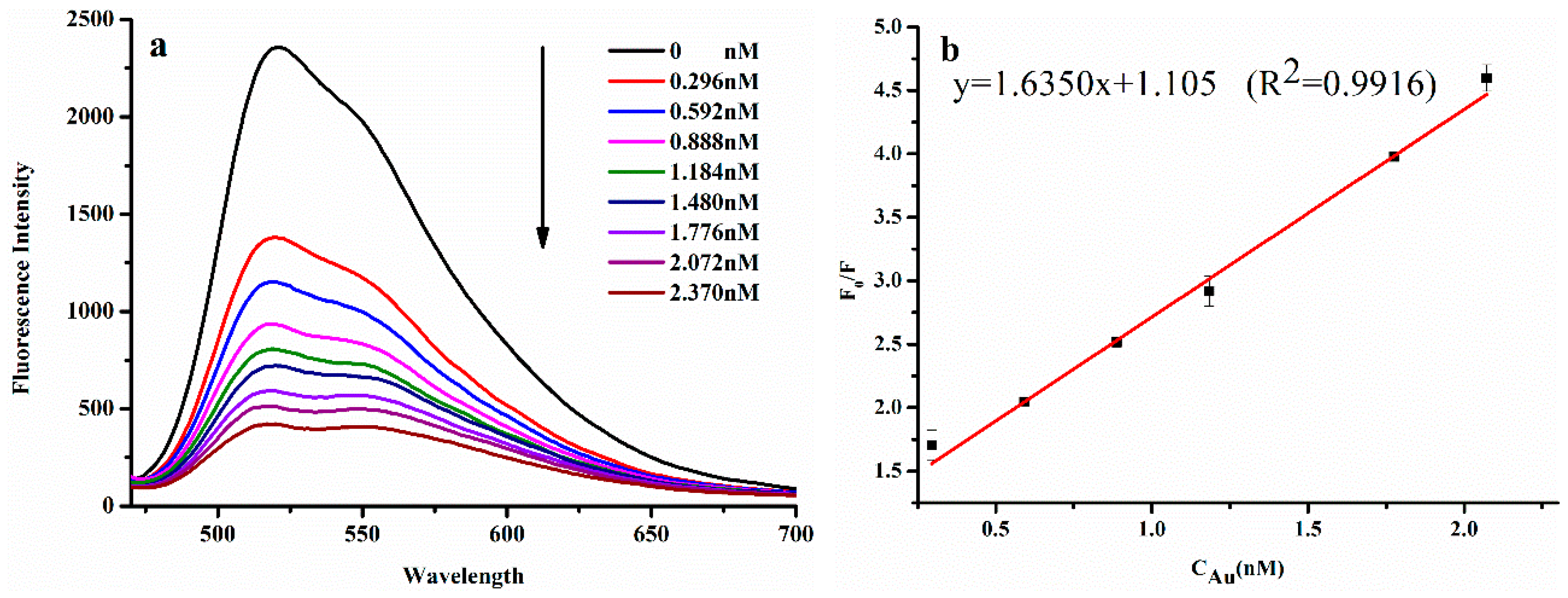
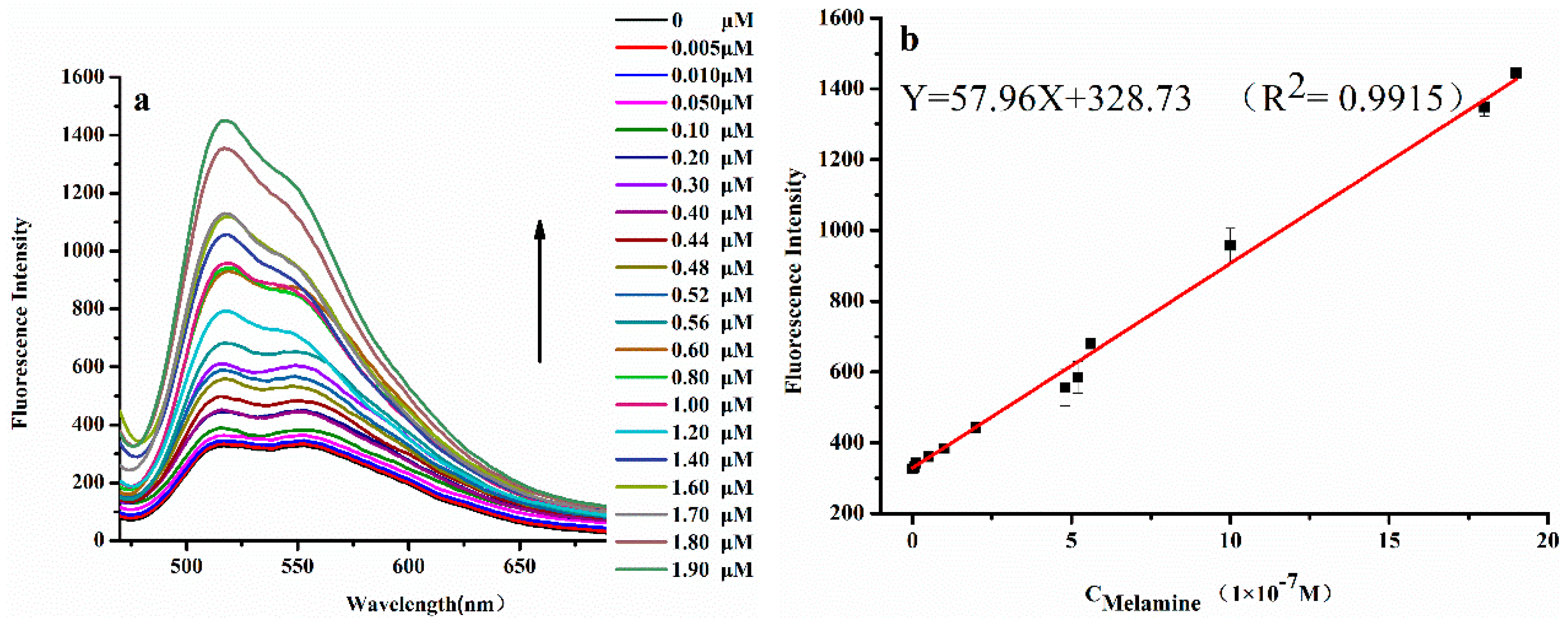
3.3. FRET-Based AuNPs-CPNs Emission Response to Melamine
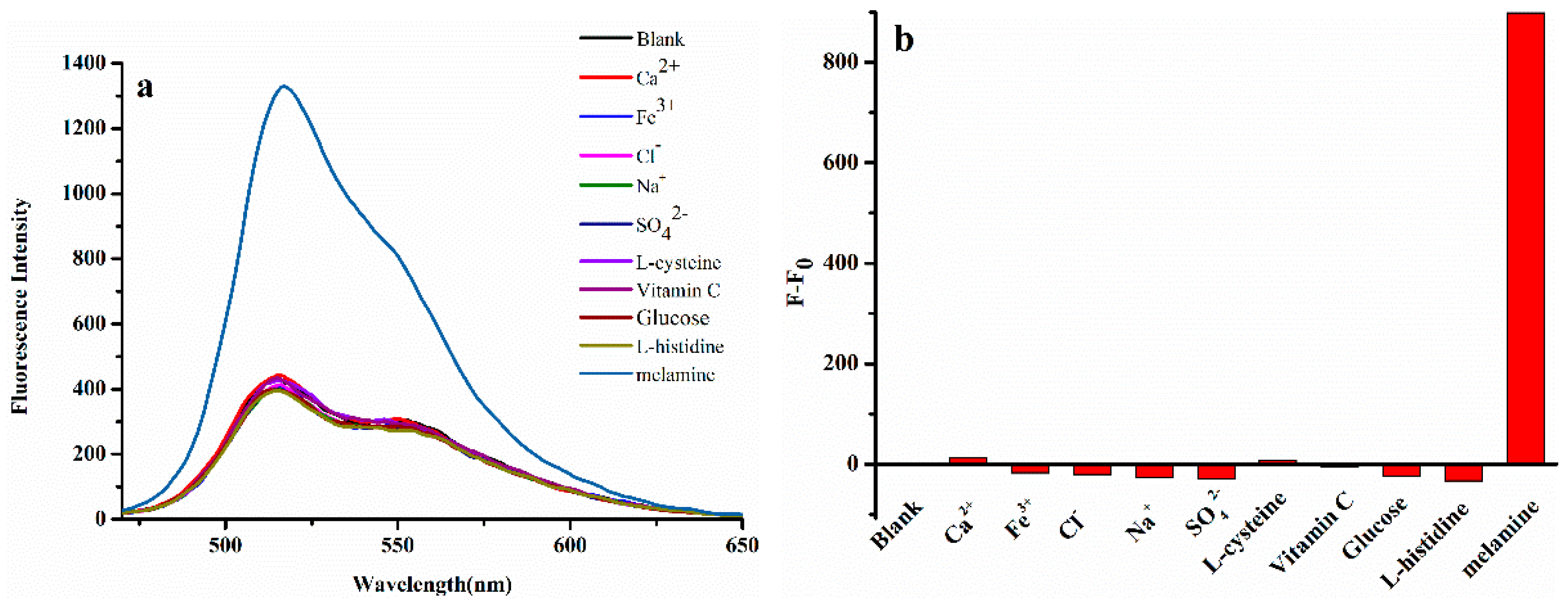
3.4. Selective Studies and the Application to Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W. Gold nanoparticles-based chemiluminescence resonance energy transfer for ultrasensitive detection of melamine. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 149, 698–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wu, H.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, S. Label-free fluorescence turn-on sensing for melamine based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer between CdTe/CdS quantum dots and gold nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 61667–61672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Shen, F.; Zhang, M.; Guo, J.; Luo, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, C. Highly sensitive detection of melamine based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer between rhodamine B and gold nanoparticles. Dyes Pigm. 2014, 111, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Long, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, S. An upconversion fluorescence resonance energy transfer nanosensor for one step detection of melamine in raw milk. Talanta 2015, 136, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Hu, J.; Ni, P.; Li, Z. A carbon dot based biosensor for melamine detection by fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 202, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaclavik, L.; Rosmus, J.; Popping, B.; Hajslova, J. Rapid determination of melamine and cyanuric acid in milk powder using direct analysis in real time-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 4204–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, R.; Zhang, R.; Qin, W. Potentiometric sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer for determination of melamine in milk. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 141, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Ye, Q.; Cui, P.; Zhang, L. Efficient fluorescence energy transfer system between CdTe-doped silica nanoparticles and gold nanoparticles for turn-on fluorescence detection of melamine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 4550–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, T.-H.; Thiagarajan, S.; Chen, S.-M. Detection of melamine in milk powder and human urine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 4537–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.; Wang, X.; Duan, L.; Gao, W.; Ji, L.; Tang, B. A new nanoprobe based on FRET between functional quantum dots and gold nanoparticles for fluoride anion and its applications for biological imaging. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 36, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Cao, X.; Li, H.; Guan, F.; Guo, J.; Shen, F.; Luo, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhang, L. Sensitive fluorescent detection of melamine in raw milk based on the inner filter effect of Au nanoparticles on the fluorescence of CdTe quantum dots. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1894–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.; Nandi, S.; Bhattacharya, S.C. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer from Fluorescein to Safranine T in solutions and in micellar medium. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2005, 173, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zheng, A.; Chen, A.; Gao, Y.; He, C.; Kai, X.; Wu, G.; Chen, Y. A functionalized gold nanoparticles and Rhodamine 6G based fluorescent sensor for high sensitive and selective detection of mercury (II) in environmental water samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 599, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannozzi, A.M.; Rolle, F.; Sega, M.; Abete, M.C.; Marchis, D.; Rossi, A.M. Rapid and sensitive detection of melamine in milk with gold nanoparticles by Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering. Food Chem. 2014, 159, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, H.; Liu, B.; Guan, G.; Zhang, Z.; Han, M.-Y. A simple, reliable and sensitive colorimetric visualization of melamine in milk by unmodified gold nanoparticles. Analyst 2010, 135, 1070–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Brook, M.A.; Li, Y. Design of gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric biosensing assays. Chembiochem 2008, 9, 2363–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Seth, R.; Kumar, H. Colorimetric detection of melamine in milk by citrate-stabilized gold nanoparticles. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 456, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, B.; Cheng, D.; Mao, L. Visual detection of melamine in raw milk using gold nanoparticles as colorimetric probe. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, N.R.; Gearheart, L.; Murphy, C.J. Seeding Growth for Size Control of 5−40 nm Diameter Gold Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2001, 17, 6782–6786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lu, Y. Fast colorimetric sensing of adenosine and cocaine based on a general sensor design involving aptamers and nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 45, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Miao, Q.; Zhen, X.; Ding, D.; Pu, K. Intraparticle Molecular orbital engineering of semiconducting polymer nanoparticles as amplified theranostics for in vivo photoacoustic imaging and photothermal therapy. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4472–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Hansen, S.J.; Hou, Q.; Yu, J.; Zeigler, M.; Jin, Y.; Burnham, D.R.; McNeill, J.D.; Olson, J.M.; Chiu, D.T. Design of highly emissive polymer dot bioconjugates for in vivo tumor targeting. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 123, 3492–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, X.; Zhang, C.; Xie, C.; Miao, Q.; Lim, K.L.; Pu, K. Intraparticle energy level alignment of semiconducting polymer nanoparticles to amplify chemiluminescence for ultrasensitive in vivo imaging of reactive oxygen species. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 6400–6409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Uppuyuri, P.K.; Zhen, X.; Pramanik, M.; Pu, K. Self-quenched semiconducting polymer nanoparticles for amplified in vivo photoacoustic imaging. Biomaterials 2017, 119, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, K.; Shuhendler, A.J.; Valta, M.P.; Cui, L.; Saar, M.; Peehl, D.M.; Rao, J. Phosphorylcholine-coated semiconducting polymer nanoparticles as rapid and efficient labeling agents for in vivo cell tracking. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2014, 3, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, J.; Sun, C.; Liu, J.; Liao, L.-D.; Yuan, Y.; Thakor, N.; Wang, J.; Liu, B. Biocompatible conjugated polymer nanoparticles for efficient photothermal tumor therapy. Small 2015, 11, 1603–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macneill, C.M.; Coffin, R.C.; Carroll, D.L.; Levi-Polyachenko, N.H. Low band gap donor-acceptor conjugated polymer nanoparticles and their NIR-mediated thermal ablation of cancer cells. Macromol. Biosci. 2013, 13, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Ye, Q.; Cui, P.; Chen, X.; Li, M.; Wang, L. Selective “turn-on” fluorescent sensing for biothiols based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer between acridine orange and gold nanoparticles. Anal. Methods 2011, 3, 1180–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, H. Highly Sensitive and Naked Eye Dual-readout Method for ʟ-Cysteine Detection Based on the NSET of Fluorophore Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2014, 35, 1159–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qin, Y.N.; Liu, Z.E. The Preparation and Fluorescence of Conjugated Polymer Nanoparticles with Triphenylamin Derivatives. Int. Conf. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2015, 3, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sun, J.; Mei, H.; Gao, F. Organic semiconductor polymer nanodots as a new kind of off-on fluorescent probe for sulfide. Microchim. Acta 2016, 184, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Jin, Y.; Schneider, T.; Burnham, D.R.; Smith, P.B.; Chiu, D.T. Ultrabright and Bioorthogonal Labeling of Cellular Targets Using Semiconducting Polymer Dots and Click Chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 122, 9626–9630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Shen, F.; Zhang, M.; Guo, J.; Luo, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Sun, C.; Liu, J. Efficient inner filter effect of gold nanoparticles on the fluorescence of CdS quantum dots for sensitive detection of melamine in raw milk. Food Control 2013, 34, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frens, G. Controlled Nucleation for the Regulation of the Particle Size in Monodisperse Gold Suspensions. Nat. Phys. Sci. 1973, 241, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Du, L.; Su, X. Detection of melamine based on the fluorescence resonance energy transfer between CdTe QDs and Rhodamine B. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 4060–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Wang, L.; Huang, C.; Hu, B.; Su, W.; Xiao, Q. Graphene quantum dot coupled with gold nanoparticle based “off-on” fluorescent probe for sensitive and selective detection of l-cysteine. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1855–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhong, J.; Wu, J.; Fu, F.; Chen, G.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, X.; Lin, S. Sensitive turn-on fluorescent detection of melamine based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Analyst 2011, 136, 1659–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zheng, C.; Dong, T.; Liu, K.; Han, H.; Liang, J. Wavelength Dependence of Fluorescence Quenching of CdTe Quantum Dots by Gold Nanoclusters. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 3011–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Mandal, S.; Selvakannan, P.R.; Pasricha, R.; Mandale, A.B.; Sastry, M. Investigation into the Interaction between Surface-Bound Alkylamines and Gold Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2003, 19, 6277–6282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, K.; Liu, Y.; Lu, L. Hydrogen-bonding recognition-induced color change of gold nanoparticles for visual detection of melamine in raw milk and infant formula. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 9496–9497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatasami, G.; Sowa, J.R., Jr. A rapid, acetonitrile-free, HPLC method for determination of melamine in infant formula. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 665, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Liu, Y. Fluorescent detection and imaging of Hg2+ using a novel phenanthroline derivative based single- and two-photon excitation. Mater. Sci. Eng. Carbon 2016, 59, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
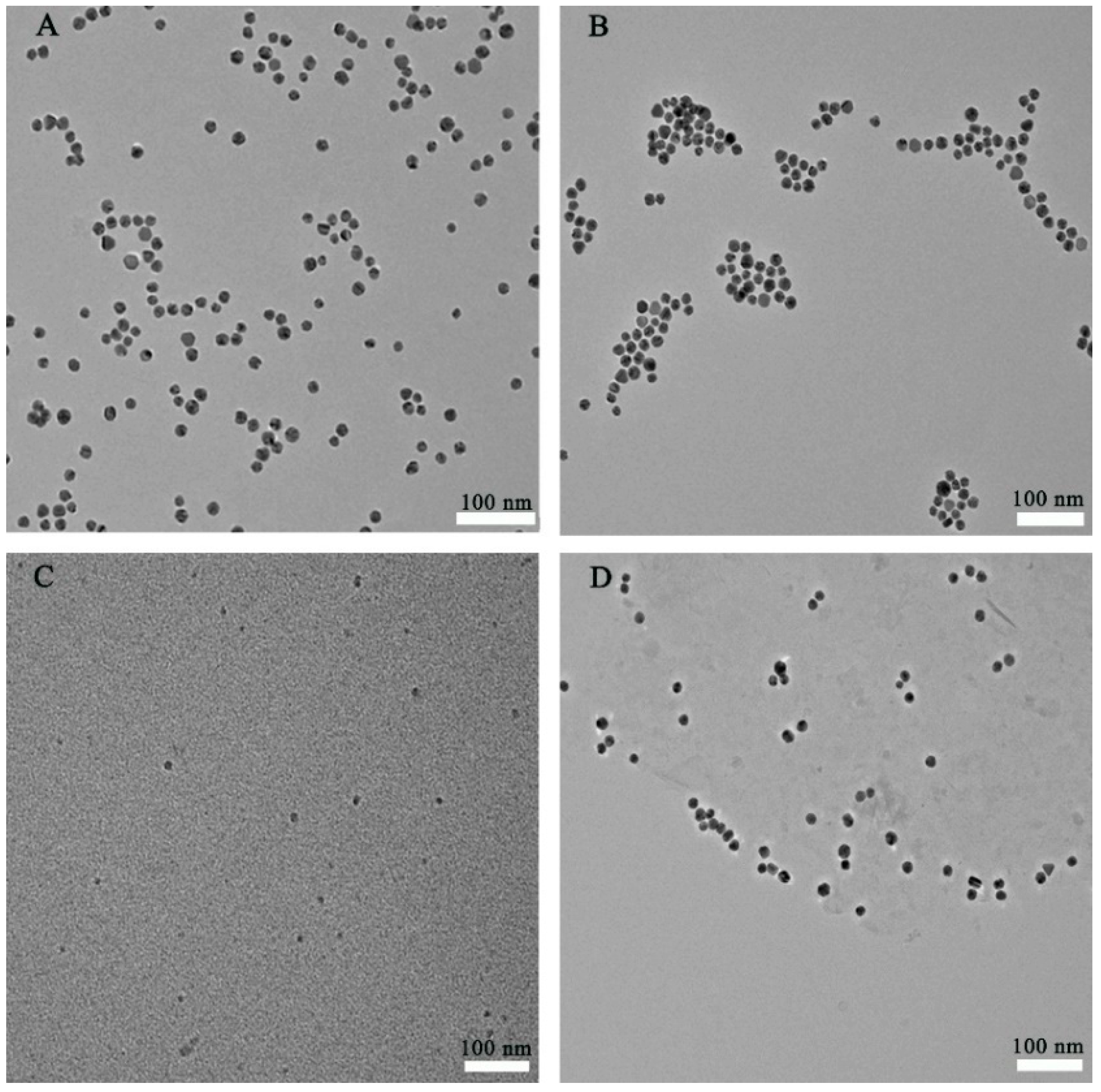
| Method | LOD (μM) | Ref. | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HPLC | 0.79 | [41] | 97.2–101.2 |
| Turn-off fluorescence CdTe quantum dots | 0.31 | [11] | 103–104 |
| CdTe QDs and Rhodamine B | 0.01 | [35] | 99.2–104 |
| FRET/carbon dots and Au nanoparticles | 0.036 | [5] | 90.5–111.4 |
| FRET between CdTe/CdS QDs and AuNPs | 0.03 | [2] | 90.0–101 |
| Au nanoparticles and Melamine | 0.0068 | This work (1) | - |
| FRET/CPNs and Au nanoparticles | 0.0017 | This work (2) | 95.93–100.8 |
| Components | Concentration (nΜ) (CPNs/AuNPs: /Melamine) | Ф |
|---|---|---|
| CPNs | 187/0/0 | 0.22 |
| CPNs +Au NPs (1) | 187/1.184/0 | 0.022 |
| CPNs +Au NPs (2) | 187/2.370/0 | 0.0050 |
| CPNs + AuNPs + melamine (1) | 187/2.370/300 | 0.0086 |
| CPNs + AuNPs + melamine (2) | 187/2370/1200 | 0.016 |
| CPNs + melamine | 187/0/1200 | 0.22 |
| Sample | Amount Added (10−7 M) | Amount Founded (10−7 M) | Recovery (%) | R.S.D. (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5.2 | 5.080 | 97.74 | 5.0 |
| 2 | 14 | 13.430 | 95.93 | 4.1 |
| 3 | 18 | 18.144 | 100.8 | 2.7 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.-j.; Gao, Z.-y.; Wang, Q.-b.; Zhang, X.; Yao, J.-s.; Qiao, C.-d.; Liu, Q.-z. Highly Sensitive Detection of Melamine Based on the Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer between Conjugated Polymer Nanoparticles and Gold Nanoparticles. Polymers 2018, 10, 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10080873
Zhang C-j, Gao Z-y, Wang Q-b, Zhang X, Yao J-s, Qiao C-d, Liu Q-z. Highly Sensitive Detection of Melamine Based on the Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer between Conjugated Polymer Nanoparticles and Gold Nanoparticles. Polymers. 2018; 10(8):873. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10080873
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Cui-jiao, Zhi-yan Gao, Qiu-bo Wang, Xian Zhang, Jin-shui Yao, Cong-de Qiao, and Qin-ze Liu. 2018. "Highly Sensitive Detection of Melamine Based on the Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer between Conjugated Polymer Nanoparticles and Gold Nanoparticles" Polymers 10, no. 8: 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10080873
APA StyleZhang, C.-j., Gao, Z.-y., Wang, Q.-b., Zhang, X., Yao, J.-s., Qiao, C.-d., & Liu, Q.-z. (2018). Highly Sensitive Detection of Melamine Based on the Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer between Conjugated Polymer Nanoparticles and Gold Nanoparticles. Polymers, 10(8), 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10080873




