1. Introduction
Among several processes which are applied to increase oil recovery, polymer flooding has been widely implemented as a mobility control technique in tertiary enhanced oil recovery (EOR) [
1]. The most basic method of recovering oil from a reservoir is by pressure depletion [
2]. The pressure difference between the oil reservoir and the surface will lead to production of oil until the reservoir pressure becomes too low for production. Reservoir utilization is poor, typically 95%–80% of the oil remains in the ground, and the energy costs of demobilizing the oil field and remobilizing at a new site is relatively high. The energy recovery is improved by injecting water or gas into the reservoir to maintain pressure. This reduces the remaining oil to 80%–40%. Still, in most cases, there is more oil left in the reservoir than produced at the end of the economic lifetime of the oil field. So-called tertiary methods are used to reduce the remaining oil down to 60%–30% of the initial volume. This includes injection of fluids or gases not naturally present in the reservoir [
2]. The purpose of polymer flooding is to improve the sweep efficiency compared to waterflooding by the addition of water-soluble polymer to viscosify the injected fluid. The increase in fluid viscosity results in improved macroscopic displacement of oil by reducing the mobility ratio between the water and the oil phase (injected fluid mobility vs. displaced fluid mobility), which reduces frontal instability. It may also increase microscopic displacement since the viscous force which mobilizes trapped oil droplet may overcome the capillary forces preventing the oil droplets from being mobilized [
2,
3]. Commonly, two types of polymers have been utilized in EOR applications: synthetic polymers, primarily partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide (HPAM), and biopolymers, mainly xanthan. Both polymers are used as viscosifying agents [
4]. Wang, et al. [
5] reported the success of polymer flooding in increasing oil recovery factor of Daqing oil field in China. Among many other successful field polymer flooding projects reported by Standnes and Skjevrak [
6], HPAM is the most commonly used EOR polymer.
HPAM transported in oil reservoirs will experience different flow velocities due to high flow rates at the injector and also due to local pore size variations. This results in expansion and contraction of polymer flow inside the porous media. It would accordingly exhibit different flow regimes with respect to shear rates. These different flow regimes have been widely discussed previously, e.g., by Chauveteau [
7], Southwick and Manke [
8], Stavland, et al. [
9], Zamani, et al. [
10], and Skauge, et al. [
11]. Due to its viscoelastic nature, its in situ viscosity is a contribution of viscous and elastic properties, e.g., shear and extensional viscosity, respectively [
12].
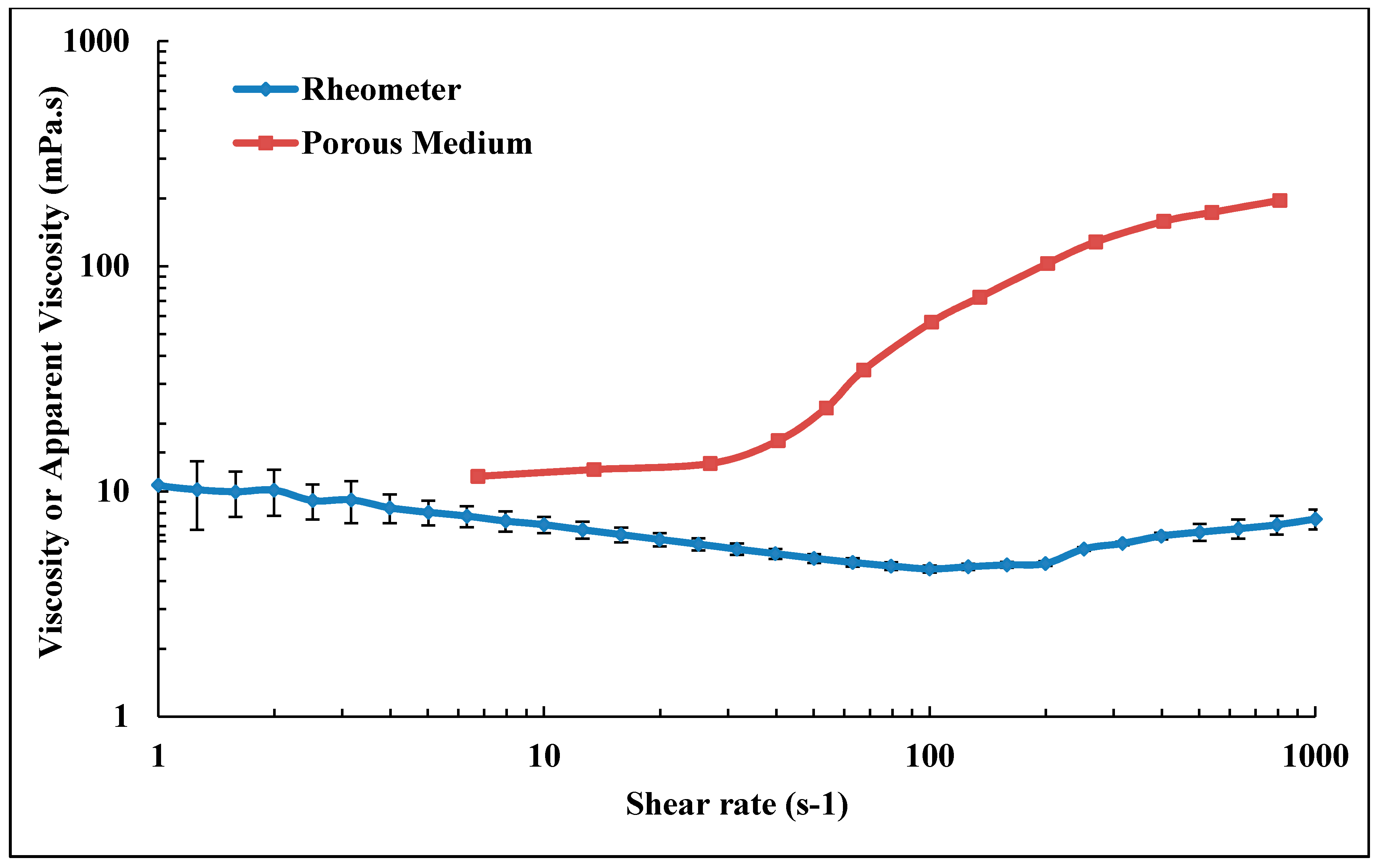
In a pure shear flow such as the flow in viscometer, HPAM exhibits shear thinning behavior that can be described by a power law equation [
13]. Shear thinning behavior is an ideal injectivity characteristic of EOR polymers, where viscosity decreases with the increase in shear rate. High flow velocities are inherent in wellbore areas [
14]. They cause an increase in polymer apparent viscosity in porous medium (shear thickening) in contrast to dominant bulk thinning behavior measured in a viscometer. In a porous medium, at low flow velocities, shear viscosity is dominant while the flow is dominated by extensional viscosity at high velocities [
15]. During the extensional flow, polymer coils experience high extensional stresses that induce flow resistance which gives the substantial rise on apparent viscosity [
16,
17]. This is theoretically interpreted by coil transition theory [
7]; however, this theory has been debated subsequently by transient network theory, which explains the origin of shear thickening regarding disentanglement timescale [
18,
19]. Regardless of the theoretical interpretations of shear thickening, it has been experimentally observed even at very low concentrations of HPAM, see, e.g., [
20,
21,
22,
23]. It increases linearly with the flow velocity after the onset of shear thickening [
24]. The onset of shear thickening has been given high attention in literature; even more than the effect of the magnitude of shear thickening on viscosity [
22]. The onset of shear thickening is a function of many parameters, such as polymer molecular weight, concentration, degree of hydrolysis, salinity, temperature and rock permeability [
9,
15,
23,
25].
In conjunction with shear thickening at high flow velocities discussed above, HPAM solution is also prone to mechanical degradation [
3,
26]. Mechanical degradation of polymer can be described as an irreversible process that leads to the breakage of polymer molecules due to high mechanical stresses induced by high flow velocities or elongational deformations [
16,
26,
27,
28]. The breakage of polymer chain induces a significant loss on polymer viscosity. Consequently, it reduces its displacement efficiency [
28]. Mechanical degradation is a function of flow velocity, pore geometry, pore tortuosity, polymer-fluid and polymer-rock interactions and physicochemical properties of the polymer. It would be high for high flow rate, high molecular weight polymer, high brine salinity and low formation permeability [
26,
29]. Claims have been made that mechanical degradation occurs at the entry point of the sand face and therefore is independent of path length [
7,
28,
30,
31].
Polymer injectivity is strongly bound with its rheology [
11,
30]. For instance, shear thickening behavior limits polymer injectivity through associative pressure build-up that might cause wellbore fracturing or polymer mechanical degradation. In cases where fracturing or fracture growth occurs due to polymer injection, it might spoil the economy of polymer flooding project due to early breakthrough and loss of polymer sweep efficiency [
32]. However, in cases where mechanical degradation occurs, it can alter polymer rheological properties and cause loss in viscosity. Both fracturing and polymer mechanical degradation make the pre-assessment of polymer injectivity challengeable.
HPAM mechanical degradation could be minimized if the polymer is submitted for a certain amount of mechanical degradation prior injection into reservoir [
2,
3,
16]. This approach is well-known as the polymer pre-shearing process. This was discussed in Seright, et al. [
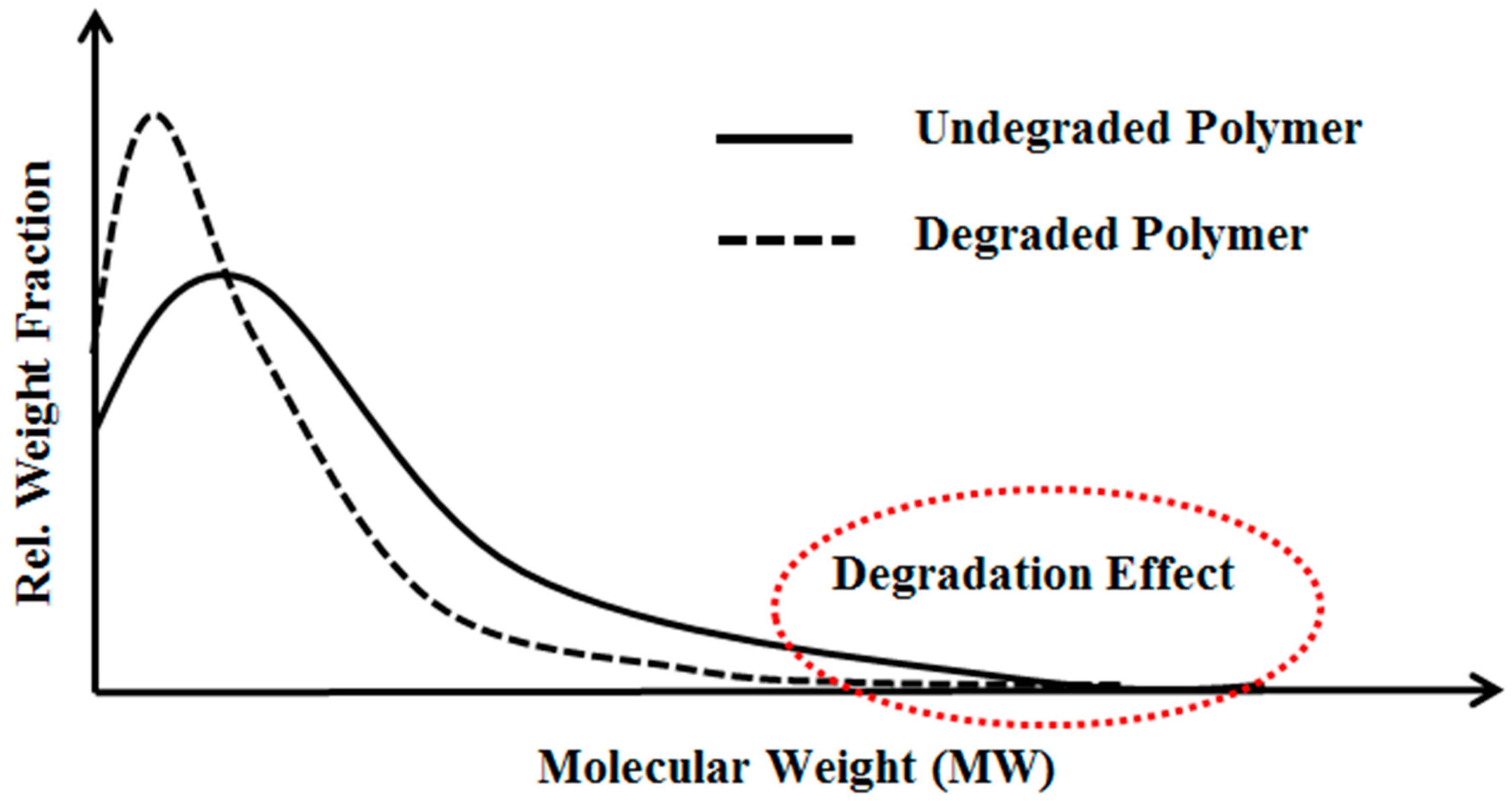
33], in which mechanical degradation of HPAM solution occurs at the high end of polymer molecular weight distribution (MWD), as shown in
Figure 1. This is because high molecular weight molecules have large size, which could offer more resistance to flow. Therefore, large elongational stresses causing breakdown of molecules resulting in degradation. During the pre-shearing process, high molecular weight species will break down into some combination of lower molecular weight fragments, leading to a new MWD. The new MWD of degraded polymer translated into lower MWD. Hence, HPAM viscoelastic properties that depend on high molecular weight species are more affected compared to shear viscosity that depends on average molecular weight which relatively less altered by pre-shearing process [
26]. Moreover, the pre-shearing process results in better filterability [
34] by removing polymer aggregates or micro gel that responsible for pore blockage. This eliminates the high apparent resistance factors that may appear at low flow rates cause injectivity issues [
29]. Chain scission mechanisms associated with polymer degradation or shearing were extensively discussed by Odell, et al. [
35] and Muller, et al. [
36]. The amount of pre-shearing should be optimized to avoid the loss of polymer viscosity and improve its injectivity characteristics [
37].
To represent the flow of polymer near wellbore areas and as it advances within the reservoir using linear cores is challenging due to different states of velocity regimes. For example, unsteady state flow conditions are present at wellbore areas, while a steady state condition is applied in the lab for core flood studies. The experimental design of core flood has to consider filtration and degradation effects on polymers, as reported by some earlier studies, e.g., Martin [
38,
39]. The effect of the prefiltering process in which the polymer subjected to low flow rate before injection has an insignificant impact on polymer in situ viscosity [
40]. This is also observed in the experimental study performed by Skauge, et al. [
23]. They investigated the role of polymer phase behavior on in situ viscosity, in which they found the molecular weight of polymer is the key factor dominating in situ rheology of semi-dilute polymers. Jouenne, et al. [
41] performed degradation studies using a blender, capillaries and porous media. The kinetics of degradation fit a master curve as a function of normalized time, regardless of the media in which the degradation occurred. Moreover, the polymer will not be further degraded beyond the point of highest strain which determined the steady state value of degradation. Until the steady state was reached, degradation increased with the number of passes of the point of highest strain. This was reached at less than 6 mm in synthetic porous media.
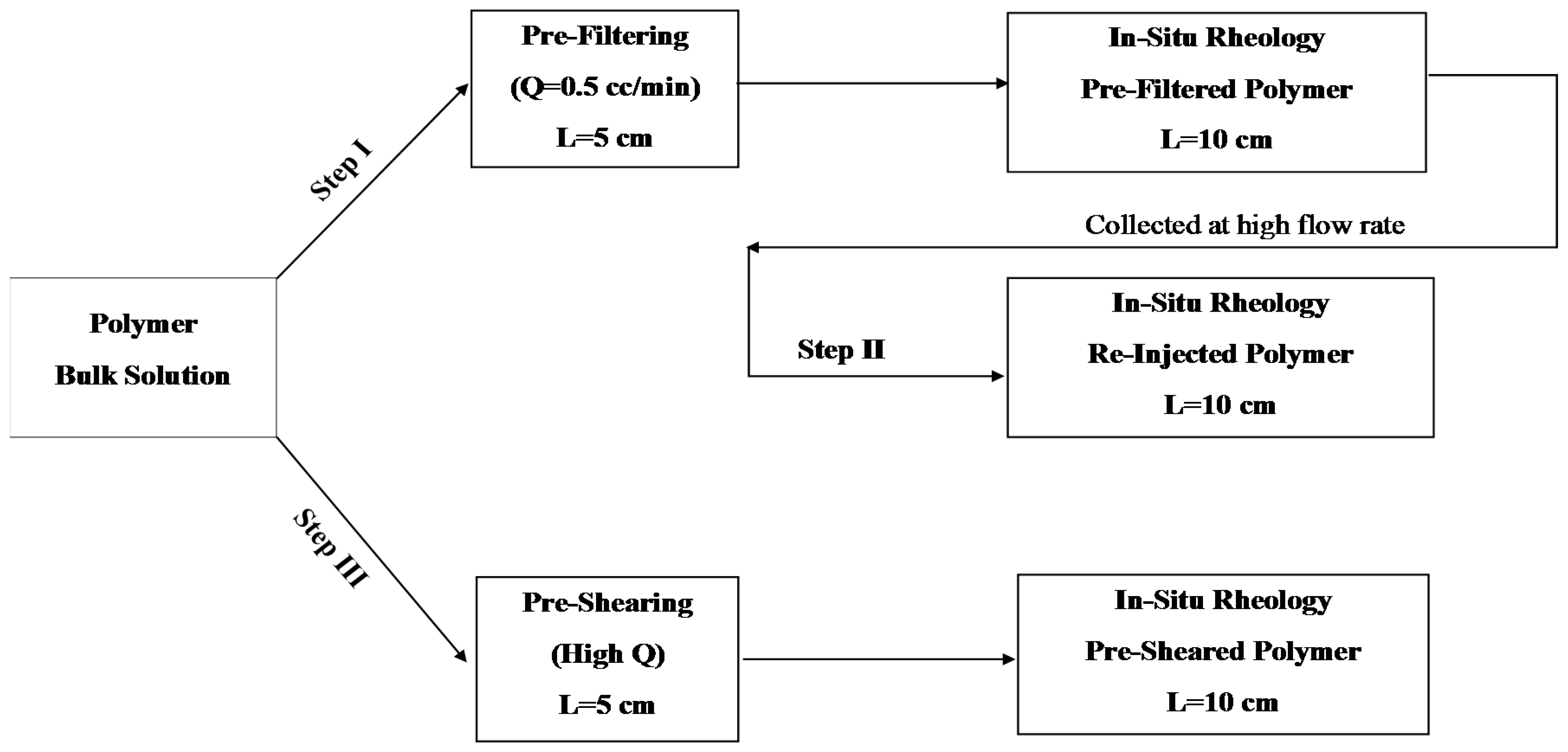
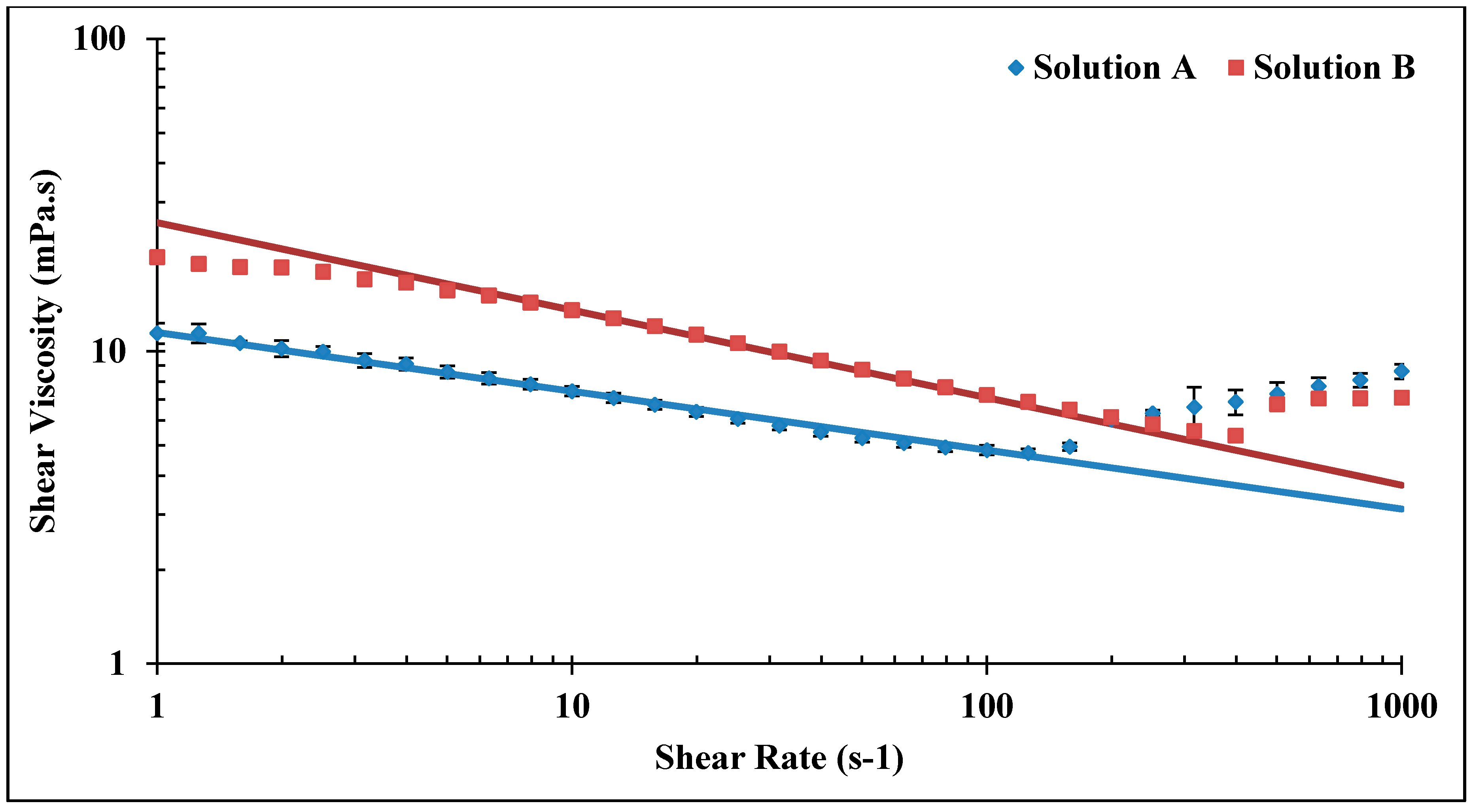
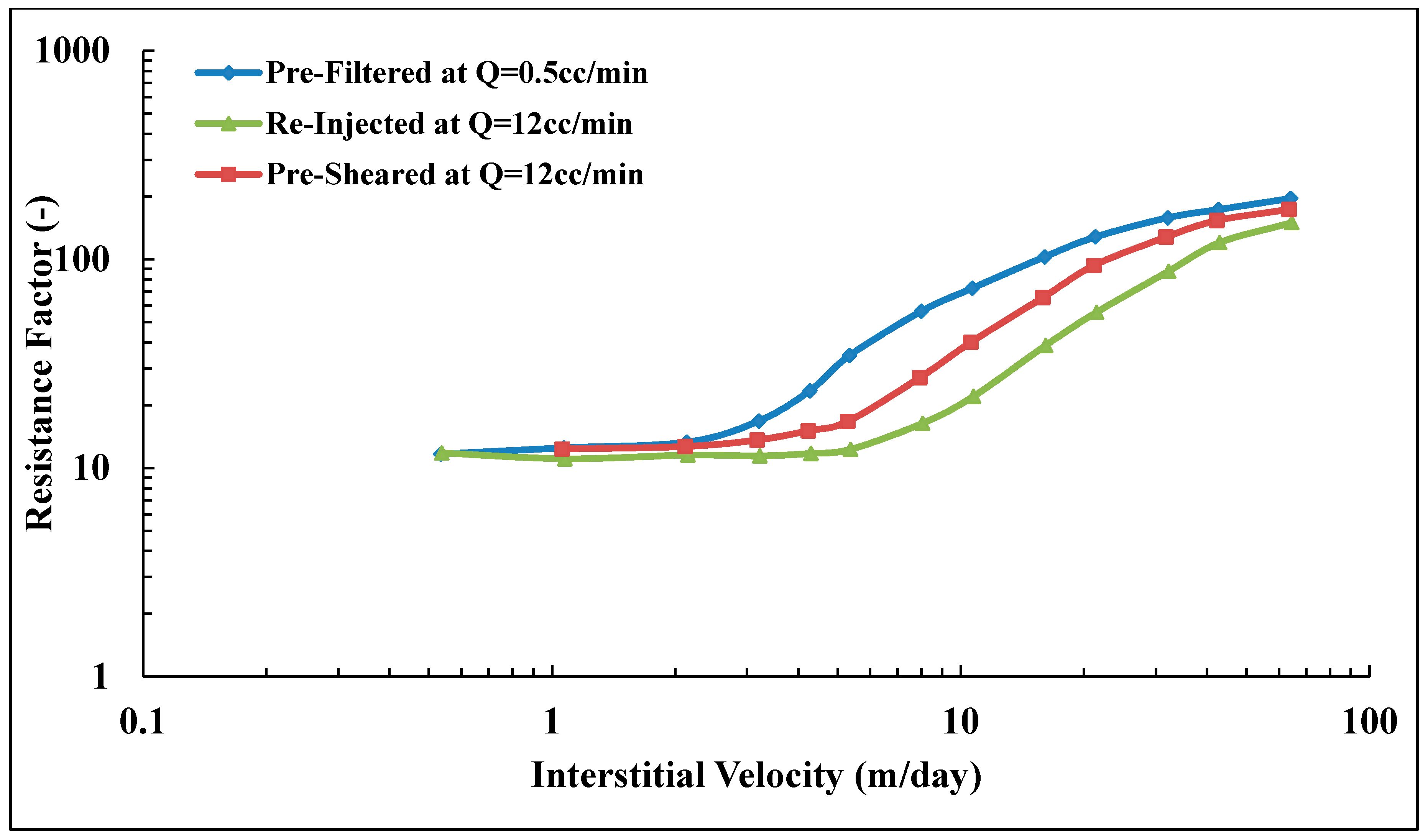
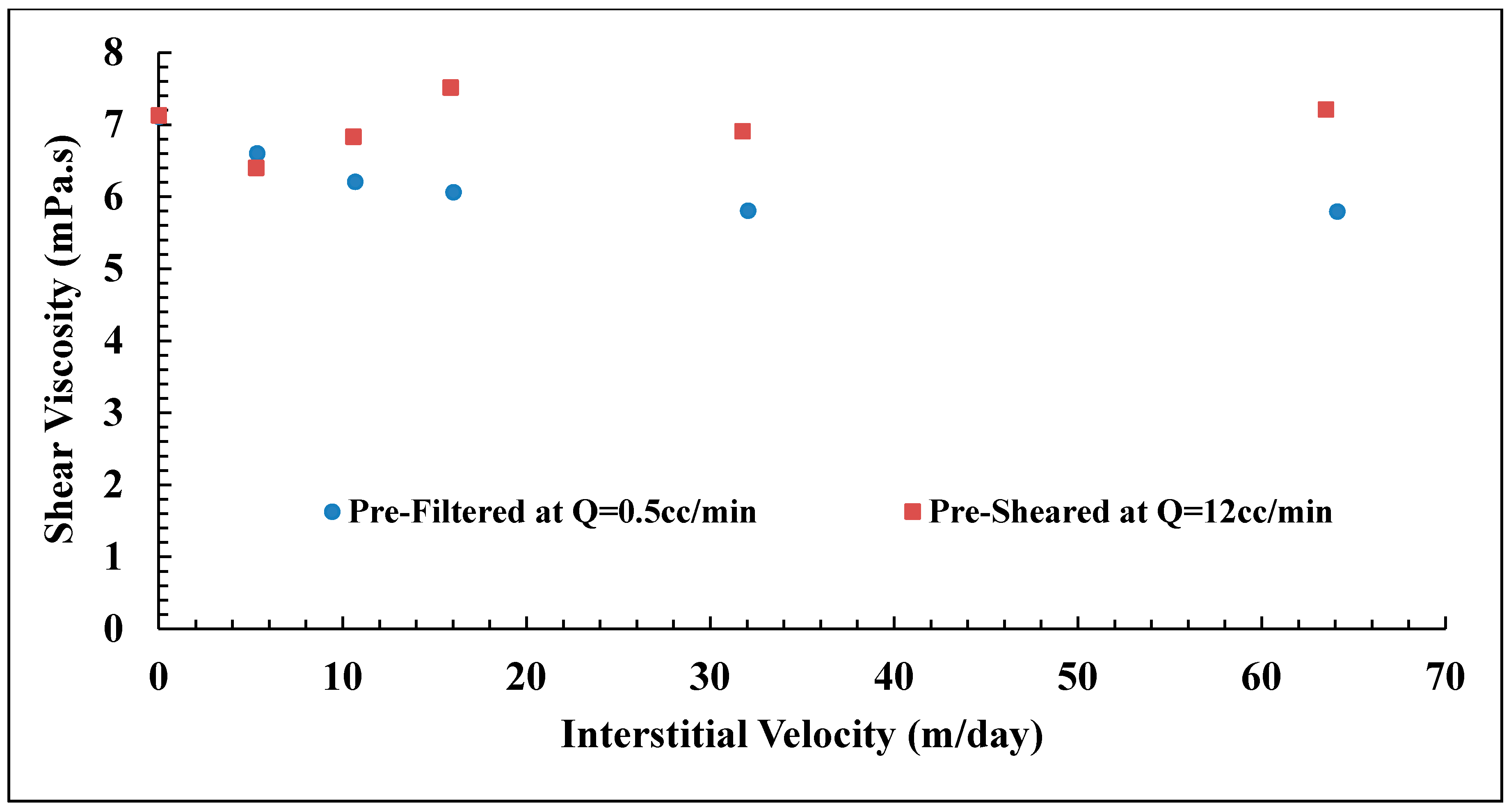
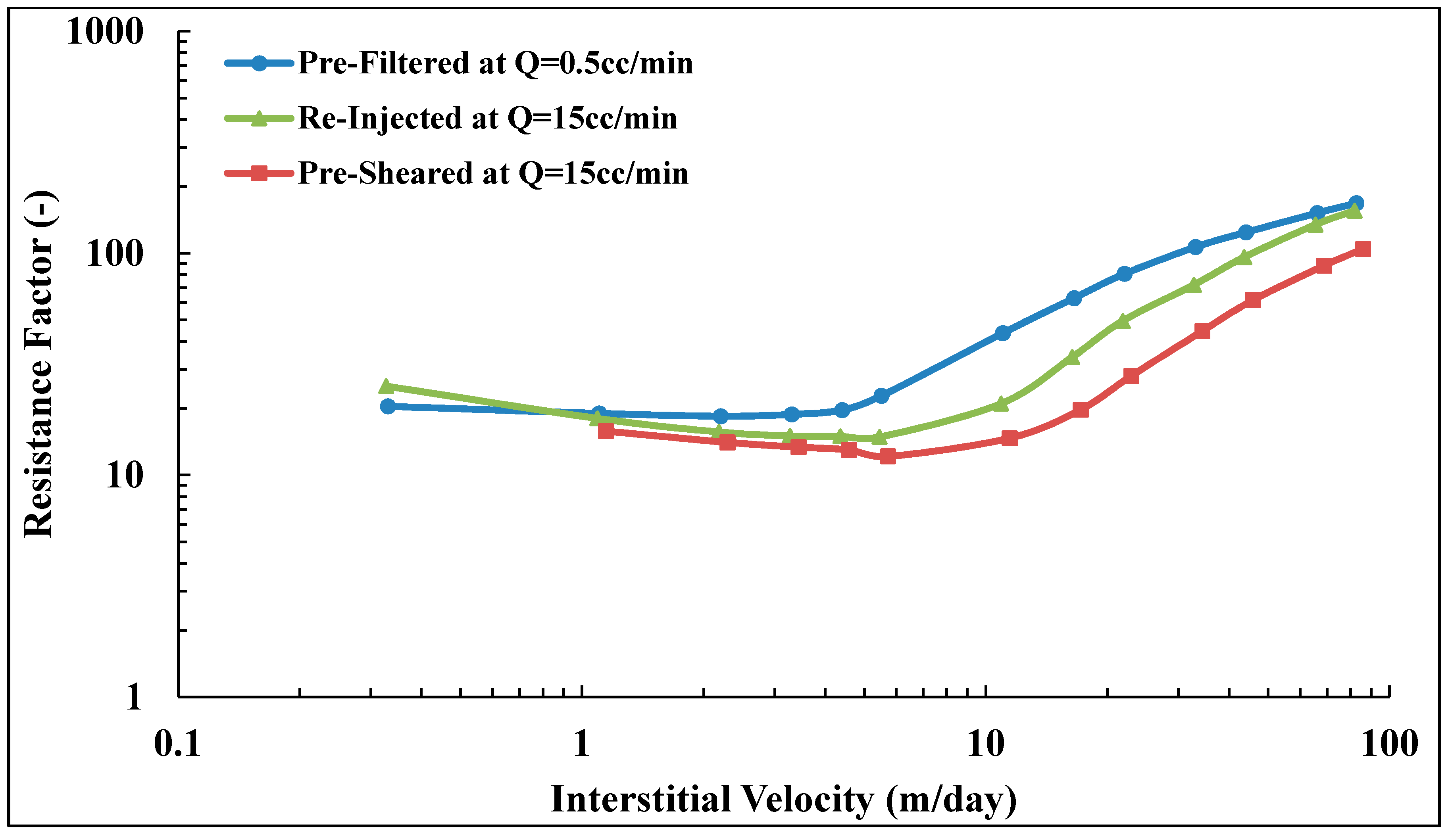
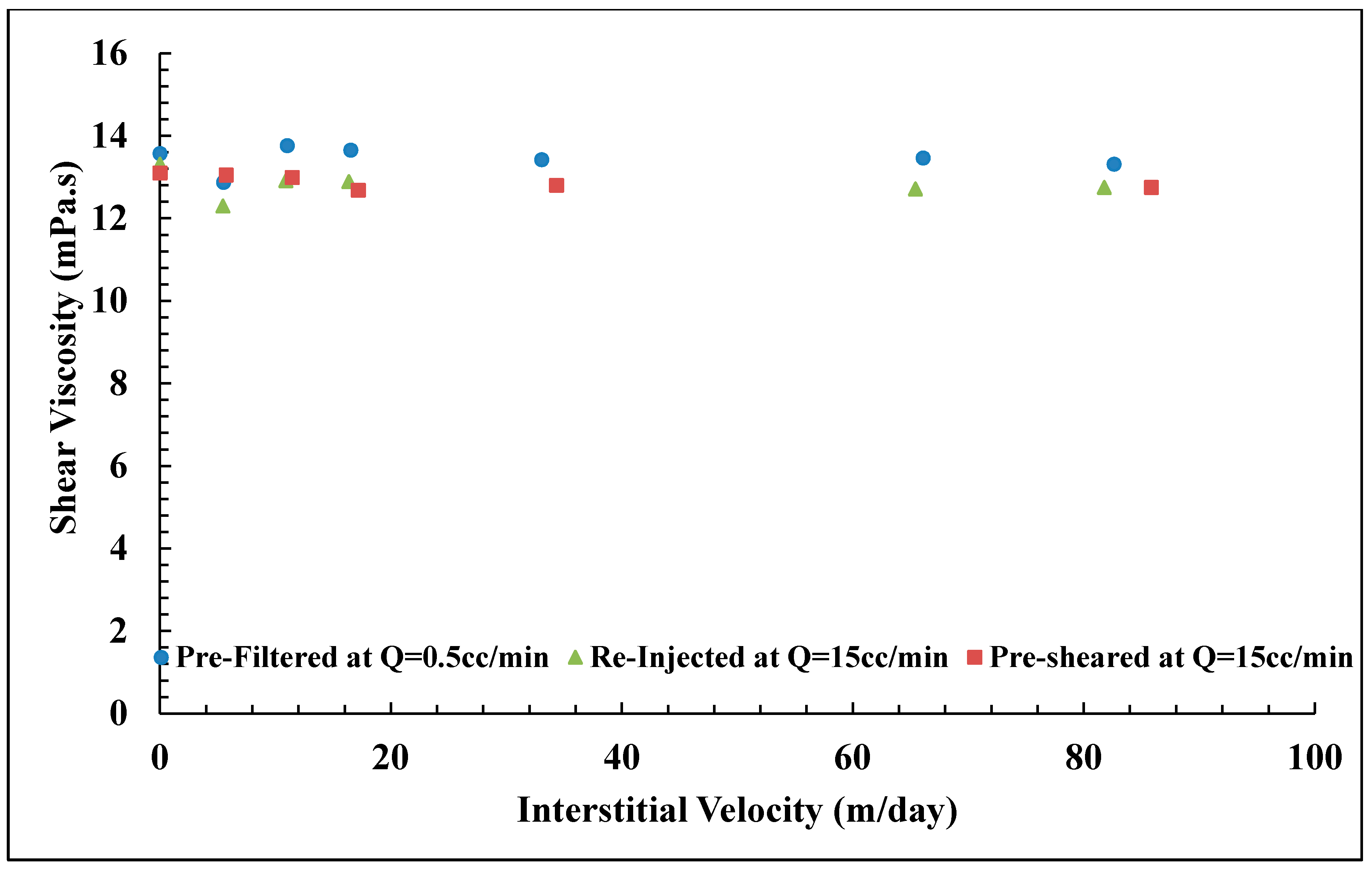
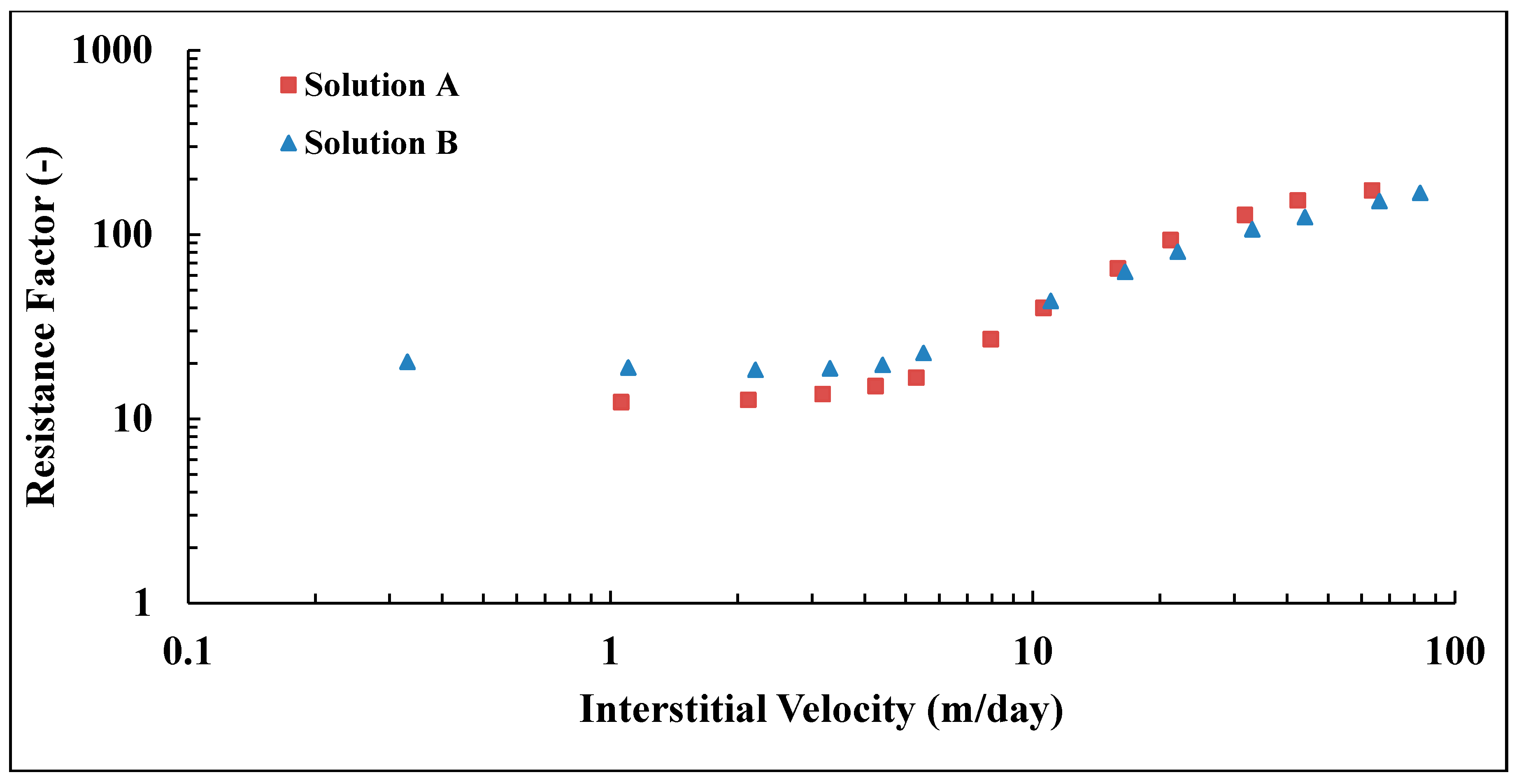
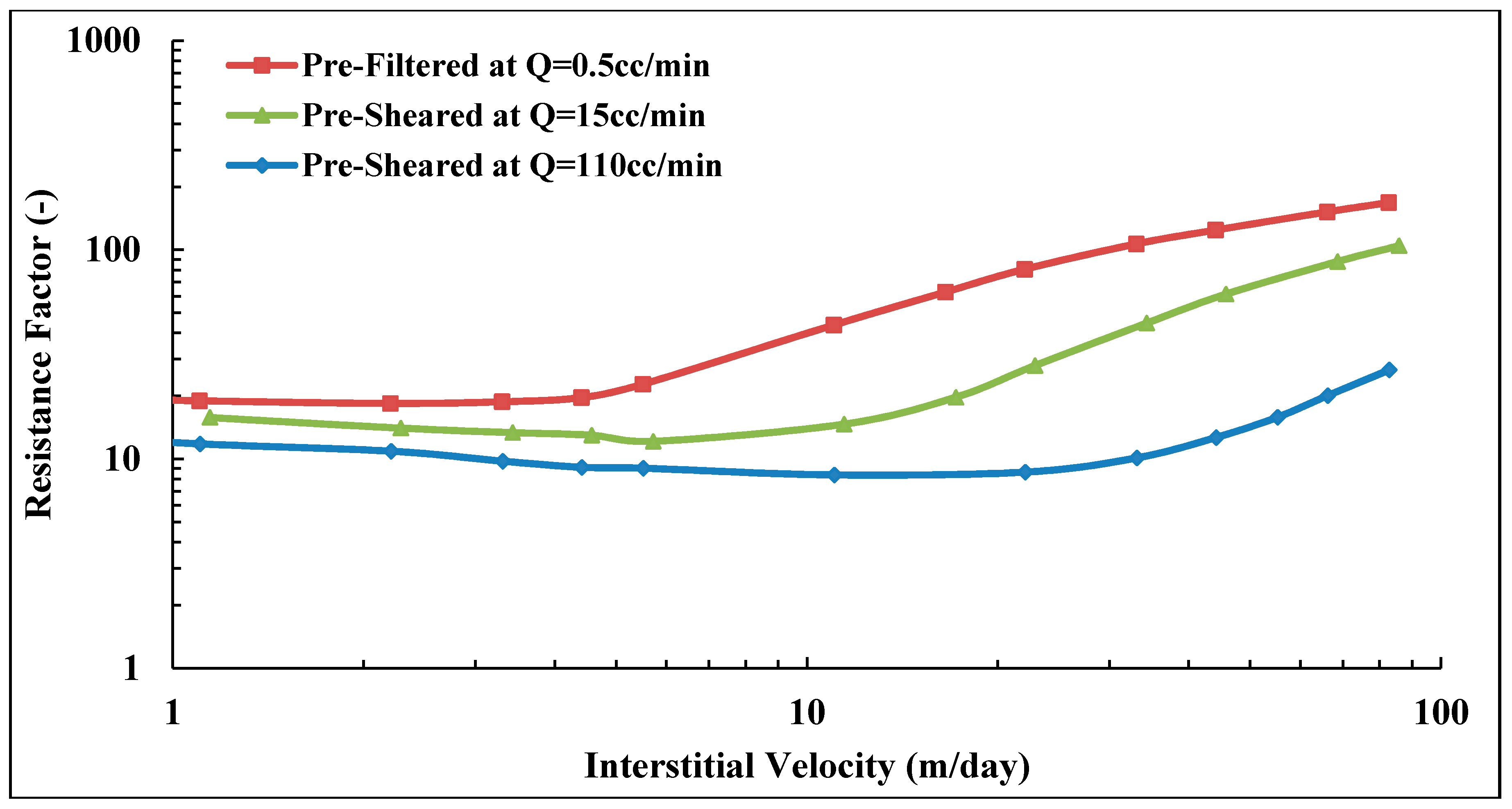
The present work aims to study the influence of mechanical degradation on HPAM rheology at a larger scale, at 5–10 cm of propagation. This was performed by flooding polymer through porous media and analyzing the injected and eluted samples. For this purpose, highly permeable outcrop rock (Bentheimer cores) was used. The experiments were carried out at room temperature using two types of semi-dilute HPAM polymers dissolved in brines with a given salinity. The polymers were pre-treated by prefiltering or pre-shearing through porous media prior to injection in order to represent the filtration and shearing processes induced on the polymer by the porous media in a field case. In such a field case, the polymer might be sheared near the injection well, where high flow velocities are achieved. High molecular weight fractions may be filtered by retention mechanisms as it propagates through the porous media at either high (near-well) or low velocity (deeper in the reservoir). Propagation effects were evaluated by re-injecting polymer that had already experienced high shear to evaluate if further mechanical degradation would occur at the same flow velocities (and thereby same shear rates). Results from this study reveal that pre-shearing at high flow rates (representative of near wellbore areas) has a larger impact than prefiltration. One consequence of this is that mechanical degradation due to high shear may improve injectivity without significantly reducing polymer in situ viscosity at (lower) reservoir flow rates. Another key observation is that polymer degradation occurs successively for high MW polymer. This indicates that it is not only the molecular weight and point of highest strain that determine the degree of degradation but also the exposure time and number of exposures to high strain. These are important aspects to implement in polymer flood design.